Identification and VP1 Sequencing of Duck Hepatitis A Virus Type 3
-
摘要:
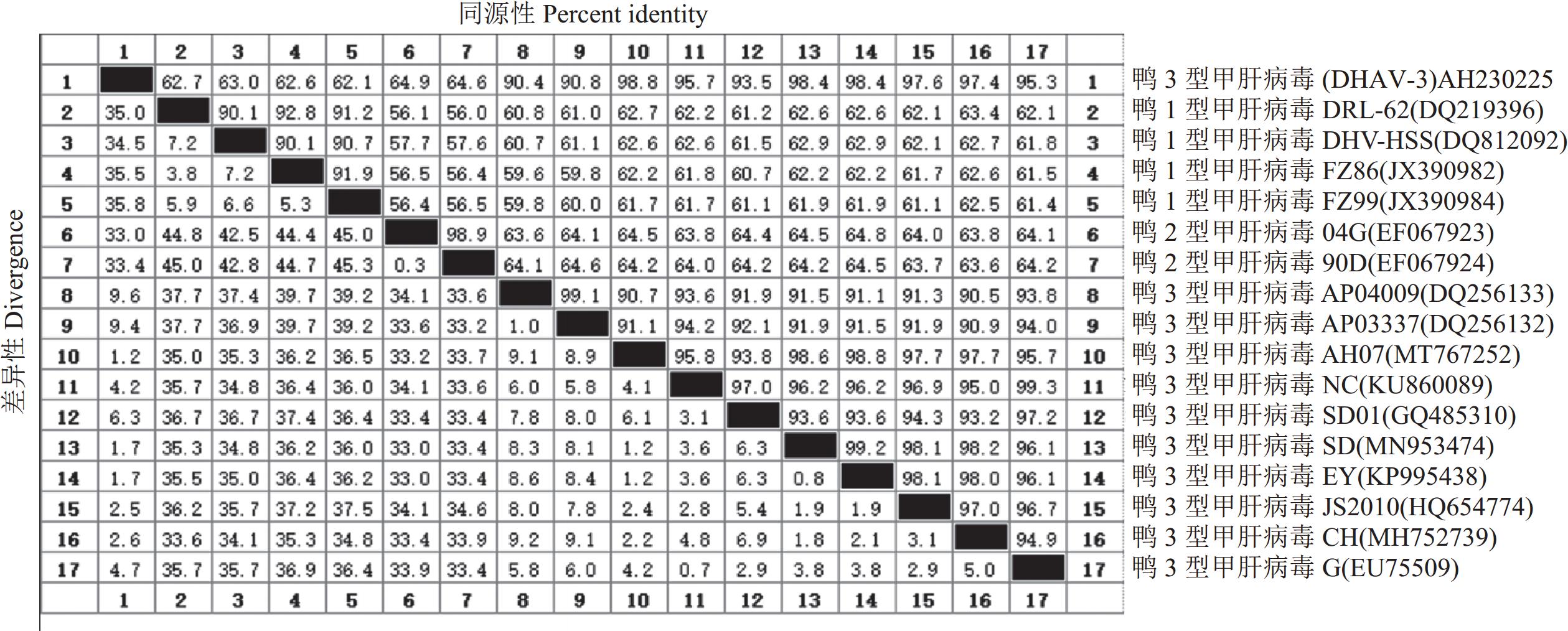
目的 探明引起安徽某鸭场雏鸭肝脏出血和大量死亡的病原及其遗传进化特征。 方法 对安徽省某鸭场的病死雏鸭中采集的出血肝脏开展鸭已知病原核酸检测、病原分离鉴定和动物回归试验,在明确其病原为鸭3型甲肝病毒(Duck hepatitis A virus type 3, DHAV-3)的基础上分析其VP1基因序列分子特征。 结果 细菌分离结果显示,未分离到细菌;经病毒核酸(RT-)PCR检测结果显示,鸭3型甲肝病毒(DHAV-3)核酸阳性,未检测出其他已知引起鸭肝出血的病毒核酸。将该阳性样品经鸭胚进行病毒分离与传代,发现接种后鸭胚发生死亡,胚体全身出血,对第5代尿囊液经RT-PCR检测为DHAV-3,将其命名为AH230225。经测定,该分离株的鸭胚半数致死量(Effective lethal dose 50, ELD50)为10−4.17/0.1 mL。动物回归试验表明,该毒株对樱桃谷雏鸭的致死率为80%,且攻毒死亡鸭肝脏和肾脏的剖检病变与临床典型病变相近。对该分离毒的VP1基因核苷酸序列进行同源性分析,显示AH230225株的VP1基因核苷酸序列与AH07株DHAV-3(安徽分离株)的同源性最高,为98.8%,与GenBank登录的10株DHAV-3分离株VP1基因核苷酸序列同源性为90.4%~98.8%,而与DHAV-1和DHAV-2的VP1基因核苷酸序列同源性分别为62.1%~63.0%、64.6%~64.9%;基于VP1蛋白氨基酸序列的遗传进化显示,该分离株与AH07株DHAV-3处于同一小进化分支上,亲缘关系最近;而与SD01株、G株和韩国株(AP-04009、AP-03337)等亲缘关系较远,即远离DHAV-1和DHAV-2进化分支。 结论 引起安徽某鸭场雏鸭肝脏出血和大量死亡的病原为鸭3型甲肝病毒DHAV-3,同时明确了该毒株VP1基因的分子特征及遗传进化规律,为深入研究DHAV-3的致病机制和制定防控措施提供科学依据。 Abstract:Objective Pathogen that caused duck liver hemorrhage in Anhui Province was identified and its genetics studied. Method A suspected virus strain was isolated from the ducks suffered from liver hemorrhage at a poultry farm in Anhui Province. Pathogenic nucleic acid and an animal regression test were employed to identify the culprit. VP1 of the confirmed duck hepatitis A virus type 3 (DHAV-3) were sequenced and analyzed using biological software. Results No bacterial pathogens were isolated from the culture of the diseased duck liver tissue. However, the specimens were tested positive for DHAV-3 but free of other viruses commonly known for duck liver hemorrhages by RT-PCR. The duck embryos inoculated with the isolate died with massive hemorrhages, and the 5th generation allantoic fluid detected presence of DHAV-3 by RT-PCR. The isolate was subsequently code-named AH230225 and determined to have the effective lethal dose 50 (ELD50) of 10−4.17/0.1 mL. In an animal regression test, the Cherry Valley ducklings had a mortality rate of 80%. The dissected lesions in the liver and kidneys of the dead ducks were similar to the typical clinical specimen. The sequenced VP1 nucleotides of AH230225 showed the greatest homology of 98.8% with the DHAV-3 of Anhui isolate, AH07. Its homologies with the 10 strains of DHAV-3 listed in GenBank were 90.4%~98.8%, with DHAV-1, 62.1%–63.0%, and with DHAV-2, 64.6%–64.9%. It appeared that the VP1 of AH230225 was genetically most closely related to that of AH07 but farther from those of SD01, G, or Korean AP-04009 and AP-03337. In other words, it was distant from DHAV-1 and DHAV-2 on the evolutionary branch. Conclusion The virus that caused the liver hemorrhage on ducks at the farm in Anhui was identified to be DHAV-3 with VP1 closely related genetically to that of AH07. -
Key words:
- Duck hepatitis A virus type 3 /
- isolation and identification /
- VP1
-
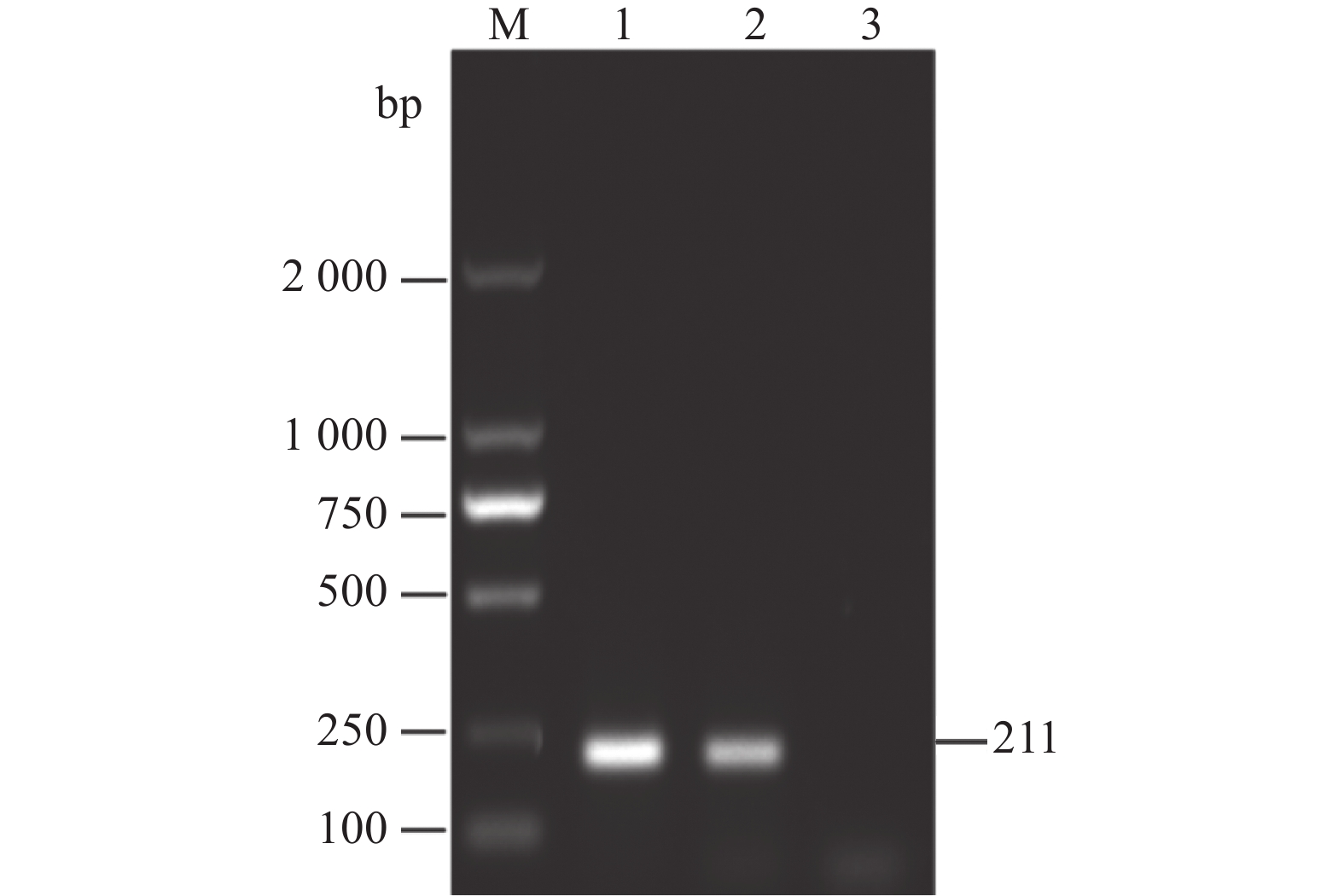
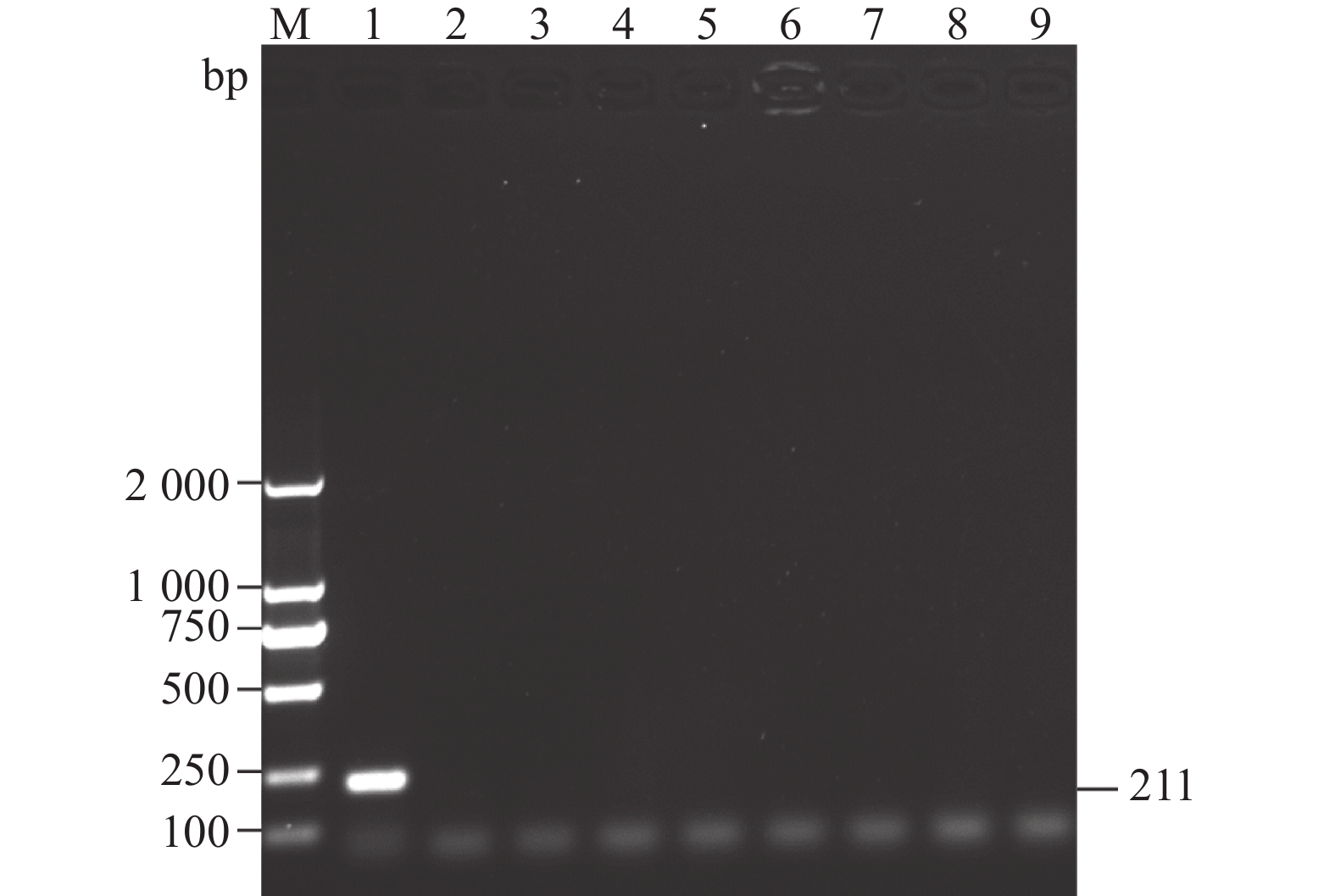
图 1 临床样品RT-PCR检测
M为2000 DNA Maker,1为鸭3型甲肝病毒,2为鸭3型腺病毒,3为禽流感病毒,4为番鸭细小病毒,5为鹅细小病毒,6为番鸭呼肠孤病毒,7为鸭1型甲肝病毒,8为鸭星状病毒,9为阴性对照。
Figure 1. RT-PCR detection on clinical samples
M: 2000 DNA marker; 1: DHAV-3; 2: duck adenovirus type 3 (DAdV-3); 3: avian influenza virus (AIV); 4: Muscovy duck parvovirus (MDPV); 5: goose parvovirus (GPV); 6: Muscovy duck reovirus (MDRV); 7: DHAV-1; 8: duck astrovirus (DAstV); 9: control.
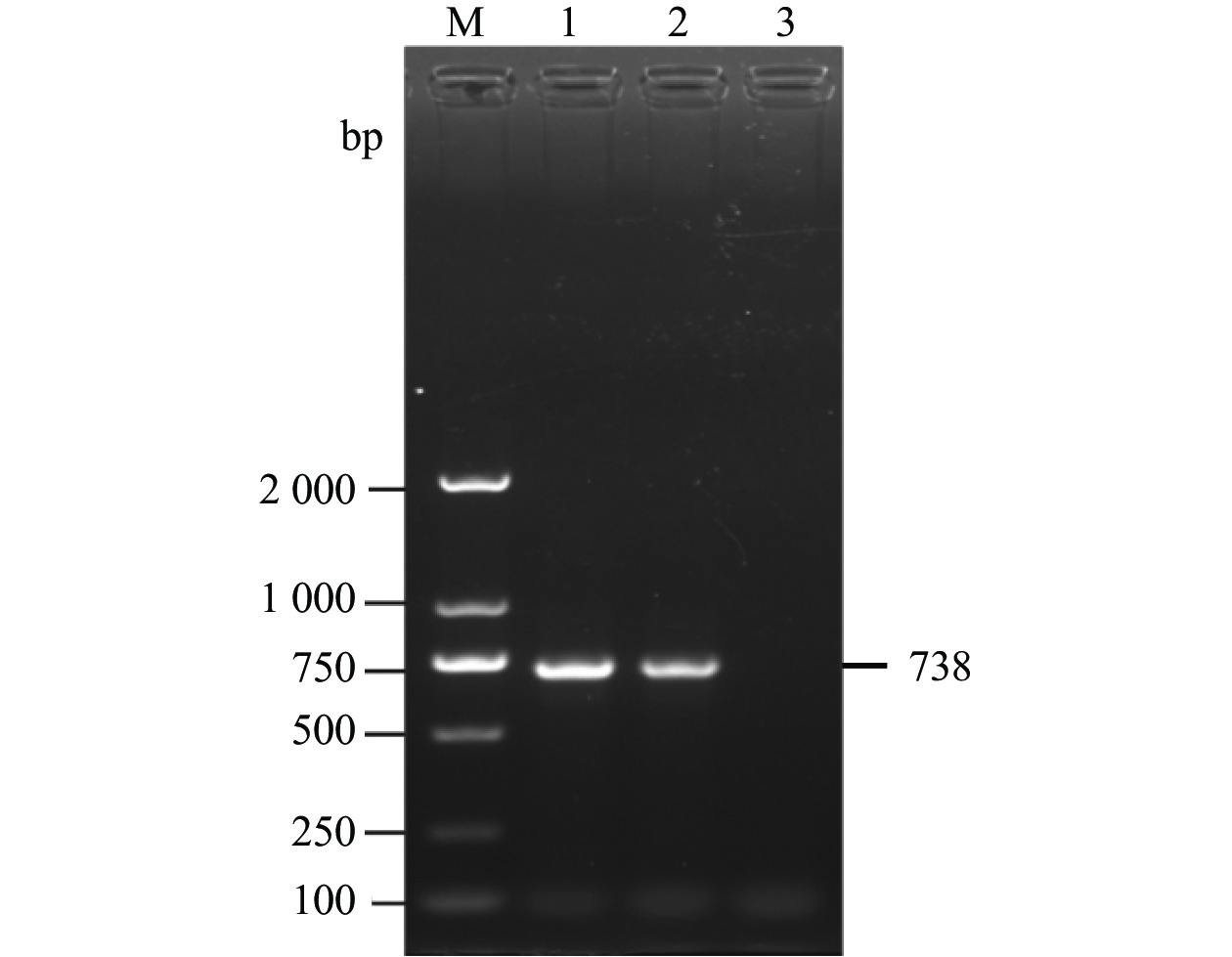
表 1 RT-PCR扩增引物
Table 1. Primers for RT-PCR amplification
引物名称
Primers引物序列
Sequences(5′-3′)退火温度
Annealing temperature/ ℃片段长度
Product size/bpDHAV-3 VP1 F:ATGGCCGCCAATAACCAGGGTGATTC 55 738 R:TTCAATTTCCAAATGGAGCTCAAAGGCAAGTG DHAV-3 F:CACAAACAGCGTAAACGCCA 52 211 R:GCAAGCCTTGGGGATTTTGG 表 2 DHAV参考毒株
Table 2. Reference DHAV strains
登录号
Locus毒株
Virus血清型
Serotype分离时间
Time分离地
IsolateJX390982 FZ86 DHAV-1 1986年 中国福建
Fujian, ChinaDQ219396 DRL-62 DHAV-1 1962年 美国
USAJX390984 FZ99 DHAV-1 1999年 中国福建
Fujian, ChinaDQ812092 DHV-HSS DHAV-1 1995年 韩国
KoreaEF067924 90D DHAV-2 1990年 中国台湾
Taiwan, ChinaEF067923 04G DHAV-2 2004年 中国台湾
Taiwan, ChinaDQ256133 AP-04009 DHAV-3 2004年 韩国
KoreaDQ256132 AP-03337 DHAV-3 2003年 韩国
KoreaEU75509 G DHAV-3 2002年 中国广西
Guangxi, ChinaKU860089 NC DHAV-3 - - GQ485310 SD01 DHAV-3 2008年 中国山东
Shandong, ChinaHQ654774 JS2010 DHAV-3 2010年 中国江苏
Jiangsu, ChinaMH752739 CH DHAV-3 2015年 中国四川
Sichuan, ChinaKP995438 EY DHAV-3 2014年 中国山东
Shandong, ChinaMN953474 SD DHAV-3 2011年 中国山东
Shandong, ChinaMT767252 AH07 DHAV-3 2018年 中国安徽
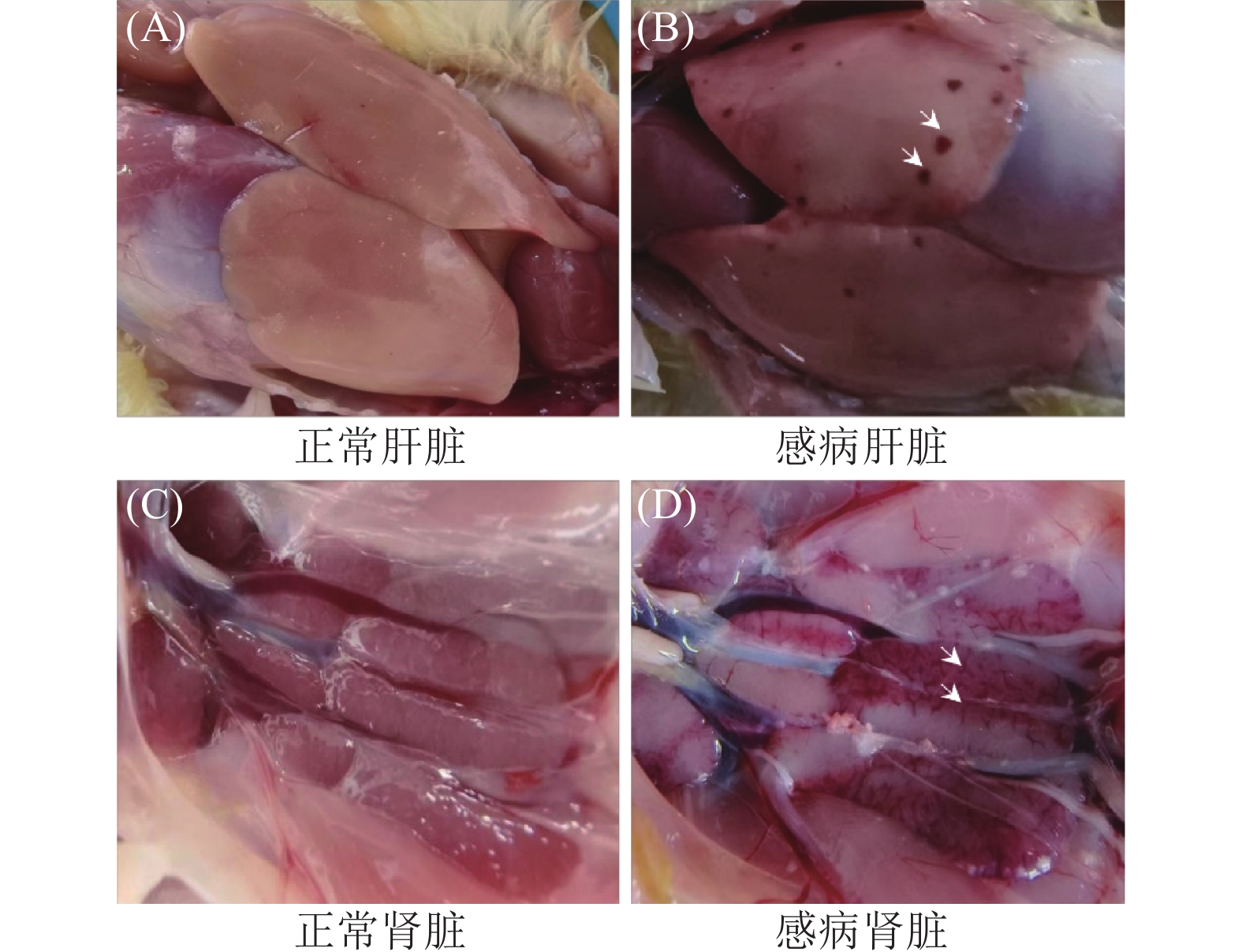
Anhui, China表 3 樱桃谷鸭动物回归试验结果
Table 3. Animal regression test results on Cherry Valley ducks
组别
Groups数量
Number/
羽攻毒后7 d内的死亡鸭数量
Number of dead ducklings during
7 days post infectious/羽死亡率
Mortality/%1 2 3 4 5 6 7 AH230225 5 0 0 2 1 1 0 0 80 (4/5) 对照组CK 5 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0(0/5) -
[1] 苏敬良, 张国中, 黄瑜, 等. 血清3型鸭甲型肝炎病毒弱毒疫苗株培育及免疫原性研究 [J]. 中国兽医杂志, 2009, 45(12):11−14. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.0529-6005.2009.12.003SU J L, ZHANG G Z, HUANG Y, et al. Development of attenuated duck hepatitis A virus serotype 3 strain and evaluation of its antigencity [J]. Chinese Journal of Veterinary Medicine, 2009, 45(12): 11−14. (in Chinese) doi: 10.3969/j.issn.0529-6005.2009.12.003 [2] ZHANG Y Y, WU S, LIU W B, et al. Current status and future direction of duck hepatitis A virus vaccines [J]. Avian Pathology, 2023, 52(2): 89−99. doi: 10.1080/03079457.2022.2162367 [3] FEHÉR E, JAKAB S, BALI K, et al. Genomic epidemiology and evolution of duck hepatitis A virus [J]. Viruses, 2021, 13(8): 1592. doi: 10.3390/v13081592 [4] TSENG C H, TSAI H J. Molecular characterization of a new serotype of duck hepatitis virus [J]. Virus Research, 2007, 126(1/2): 19−31. [5] RAJENDRAN R, SRINIVASAN J, NATARAJAN J, et al. First report of Duck Hepatitis A virus genotype 2 in India [J]. Veterinary Research Communications, 2023, 47(3): 1231−1241. doi: 10.1007/s11259-022-10063-0 [6] 苏敬良, 黄瑜, 贺荣莲, 等. 新型鸭肝炎病毒的分离及初步鉴定 [J]. 中国兽医科技, 2002, 32(1):15−16. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1673-4696.2002.01.005SU J L, HUANG Y, HE R L, et al. Isolation and preliminary identification of a new duck hepatitis virus [J]. Chinese Journal of Veterinary Science and Technology, 2002, 32(1): 15−16. (in Chinese) doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1673-4696.2002.01.005 [7] 胡薛英, 蔡双双, 谷长勤, 等. 新型鸭肝炎病毒感染雏鸭血液生化指标的动态变化 [J]. 中国兽医学报, 2005, 25(6):628−631. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1005-4545.2005.06.021HU X Y, CAI S S, GU C Q, et al. Dynamic changes of biochemical indexes of ducklings infected with new type duck hepatitis virus [J]. Chinese Journal of Veterinary, 2005, 25(6): 628−631. (in Chinese) doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1005-4545.2005.06.021 [8] 施少华, 程龙飞, 傅光华, 等. 鸭肝炎病毒新血清型基因组序列分析 [J]. 微生物学报, 2009, 49(3):309−315. doi: 10.3321/j.issn:0001-6209.2009.03.005SHI S H, CHENG L F, FU G H, et al. Genomic sequence of a new serotype duck hepatitis virus [J]. Acta Microbiologica Sinica, 2009, 49(3): 309−315. (in Chinese) doi: 10.3321/j.issn:0001-6209.2009.03.005 [9] KIM M C, KWON Y K, JOH S J, et al. Recent Korean isolates of duck hepatitis virus reveal the presence of a new geno- and serotype when compared to duck hepatitis virus type 1 type strains [J]. Archives of Virology, 2007, 152(11): 2059−2072. doi: 10.1007/s00705-007-1023-0 [10] DING C Y, ZHANG D B. Molecular analysis of duck hepatitis virus type 1 [J]. Virology, 2007, 361(1): 9−17. doi: 10.1016/j.virol.2007.01.007 [11] KIM M C, KWON Y K, JOH S J, et al. Molecular analysis of duck hepatitis virus type 1 reveals a novel lineage close to the genus Parechovirus in the family Picornaviridae[J]. Journal of General Virology, 2006, 87(Pt 11): 3307-3316. [12] LIU G Q, WANG F, NI Z, et al. Genetic diversity of the VP1 gene of duck hepatitis virus type I (DHV-I) isolates from Southeast China is related to isolate attenuation [J]. Virus Research, 2008, 137(1): 137−141. doi: 10.1016/j.virusres.2008.04.030 [13] FU Y, PAN M, WANG X Y, et al. Complete sequence of a duck astrovirus associated with fatal hepatitis in ducklings[J]. Journal of General Virology, 2009, 90(Pt 5): 1104-1108. [14] LI X J, ZHAO R, LIN W, et al. Evidence of VP1 of duck hepatitis A type 1 virus as a target of neutralizing antibodies and involving receptor-binding activity [J]. Virus Research, 2017, 227: 240−244. doi: 10.1016/j.virusres.2016.10.018 [15] 傅秋玲, 傅光华, 陈红梅, 等. 胰腺炎型鸭1型甲肝病毒结构蛋白VP1基因的克隆和表达 [J]. 福建农业学报, 2014, 29(5):409−412.FU Q L, FU G H, CHEN H M, et al. Cloning and prokaryotic expression of the VP1 gene of pancreotropic duck hepatitis type 1 virus [J]. Fujian Journal of Agricultural Sciences, 2014, 29(5): 409−412. (in Chinese) [16] 傅秋玲, 傅光华, 陈翠腾, 等. 半番鸭源鸭1型甲肝病毒亚型的分离鉴定及其VP1基因分析 [J]. 福建农业学报, 2017, 32(8):813−817.FU Q L, FU G H, CHEN C T, et al. Identification and sequencing of duck hepatitis A virus 1 subtype a isolated from mule ducklings [J]. Fujian Journal of Agricultural Sciences, 2017, 32(8): 813−817. (in Chinese) [17] LIU R C, CHEN C T, HUANG Y, et al. Microbiological identification and analysis of waterfowl livers collected from backyard farms in Southern China [J]. Journal of Veterinary Medical Science, 2018, 80(4): 667−671. doi: 10.1292/jvms.17-0452 [18] 程龙飞, 刘荣昌, 傅光华, 等. 鸭3型腺病毒的分离鉴定及其fiber基因分析 [J]. 中国家禽, 2019, 41(11):47−50.CHENG L F, LIU R C, FU G H, et al. Isolation and identification of duck adenovirus 3 and sequence analysis of fiber gene [J]. China Poultry, 2019, 41(11): 47−50. (in Chinese) [19] 刘家森, 姜骞, 司昌德, 等. 番鸭细小病毒与鹅细小病毒PCR鉴别诊断方法的建立 [J]. 中国兽医科学, 2007, 37(6):469−472.LIU J S, JIANG Q, SI C D, et al. Establishment of PCR assay for differentiation of Muscovy duck parvovirus from goose parvovirus [J]. Veterinary Science in China, 2007, 37(6): 469−472. (in Chinese) [20] 胡奇林, 林锋强, 陈少莺, 等. 应用RT-PCR技术检测番鸭呼肠孤病毒 [J]. 中国兽医学报, 2004, 24(3):231−232.HU Q L, LIN F Q, CHEN S Y, et al. Detection of Muscovy duck reovirus by RT-PCR [J]. Chinese Journal of Veterinary, 2004, 24(3): 231−232. (in Chinese) [21] LIN Y, YANG J, HE D L, et al. Differently expression analysis and function prediction of long non-coding RNAs in duck embryo fibroblast cells infected by duck tembusu virus [J]. Frontiers in Immunology, 2020, 11: 1729. doi: 10.3389/fimmu.2020.01729 [22] DOAN H T T, LE X T K, DO R T, et al. Molecular genotyping of duck hepatitis A viruses (DHAV) in Vietnam [J]. Journal of Infection in Developing Countries, 2016, 10(9): 988−995. doi: 10.3855/jidc.7239 [23] HASSAN T I R, EID A A M, GHANEM I A I, et al. First report of duck hepatitis A virus 3 from duckling flocks of Egypt [J]. Avian Diseases, 2020, 64(3): 269−276. [24] ROHAIM M A, NAGGAR R F E, ABDELSABOUR M A, et al. Insights into the genetic evolution of duck hepatitis A virus in Egypt [J]. Animals, 2021, 11(9): 2741. doi: 10.3390/ani11092741 [25] YEHIA N, ERFAN A M, OMAR S E, et al. Dual circulation of duck hepatitis A virus genotypes 1 and 3 in Egypt [J]. Avian Diseases, 2021, 65(1): 1−9. [26] WEN X, ZHU D, CHENG A, et al. Molecular epidemiology of duck hepatitis a virus types 1 and 3 in China, 2010-2015 [J]. Transboundary and Emerging Diseases, 2018, 65(1): 10−15. doi: 10.1111/tbed.12741 [27] 徐倩, 陈琳琳, 张瑞华, 等. 鸭甲肝病毒3型2012年山东分离株VP1基因的序列分析 [J]. 病毒学报, 2013, 29(5):522−528.XU Q, CHEN L L, ZHANG R H, et al. Sequence analysis of VP1 gene of the duck hepatitis A virus type 3 strains isolated from Shandong Province of China in 2012 [J]. Chinese Journal of Virology, 2013, 29(5): 522−528. (in Chinese) [28] ZHANG R, XIA L, CHEN J, et al. Molecular epidemiology and genetic diversity of duck hepatitis A virus type 3 in Shandong province of China, 2012–2014 [J]. Acta Virologica, 2017, 61(4): 463−472. doi: 10.4149/av_2017_409 [29] YANG C T, SHAH P T, BAHOUSSI A N, et al. Duck hepatitis a virus: Full-length genome-based phylogenetic and phylogeographic view during 1986–2020 [J]. Virus Research, 2023, 336: 199216. doi: 10.1016/j.virusres.2023.199216 [30] NIU Y J, MA H Y, DING Y H, et al. The pathogenicity of duck hepatitis A virus types 1 and 3 on ducklings [J]. Poultry Science, 2019, 98(12): 6333−6339. doi: 10.3382/ps/pez455 [31] LIU R C, SHI S H, HUANG Y, et al. Comparative pathogenicity of different subtypes of duck hepatitis A virus in Pekin ducklings [J]. Veterinary Microbiology, 2019, 228: 181−187. doi: 10.1016/j.vetmic.2018.11.030 [32] 管飘萍, Enkhbayar Munkhbayar, 黄紫贝, 等. 22株鸭甲型肝炎病毒的分离鉴定及其VP1基因的序列分析 [J]. 中国家禽, 2021, 43(1):105−109.GUAN P P, MUNKHBAYAR E, HUANG Z B, et al. Isolation, identification and sequening of VP1 gene of 22 isolates of duck hepatitis A virus [J]. China Poultry, 2021, 43(1): 105−109. (in Chinese) [33] GAO J M, CHEN J H, SI X K, et al. Genetic variation of the VP1 gene of the virulent duck hepatitis A virus type 1 (DHAV-1) isolates in Shandong province of China [J]. Virologica Sinica, 2012, 27(4): 248−253. doi: 10.1007/s12250-012-3255-8 -







 下载:
下载: