Agronomic Traits and Genetic Characteristics of a New Auricularia auricula-judae Variety, Nan'er No.1
-
摘要: 采用菌丝拮抗试验、菌丝生长速度测定、主要农艺性状对比、分子标记等分析方法,比较黑木耳新品种南耳1号与当地主栽品种新科1号、新科5号和Au139的主要性状和遗传特性。结果表明:南耳1号与当地主栽品种的菌丝间均存在明显拮抗现象;南耳1号菌丝生长速度较慢,但产量分别比新科1号、新科5号和Au139高12.7%、13.3%和19.6%;南耳1号鲜耳及干耳的背面颜色分别为红褐色和青褐色,明显区别于3个当地主栽品种(黑褐色和灰黑色);南耳1号与新科1号、新科5号和Au139的遗传相似系数分别为0.303、0.409和0.197。Abstract: Major agronomic traits and genetic characteristics of the new Auricularia auricula-judae variety, Nan'er No. 1, were compared with those of Xinke No. 1, Xinke No. 5 and Au 139. The mycelial antagonistic property and growth rate as well as the morphology and molecular markers of the mushrooms were studied. The results showed that there was significant antagonism in mycelium between Nan'er No.1 and the local varieties. The mycelial growth rate of Nan'er No. 1 was slower with a yield 12.7%, 13.3% and 19.6% greater than Xinke No. 1, Xinke No. 5 and Au 139, respectively. The reddish-brown color on the back of the fresh pileus and the blueish-brown tint on that of the dried pileus of Nan'er No. 1 distinctively differed from the dark-brown and grayish-black of the other varieties. The genetic similarity coefficients of Nan'er No. 1 with Xinke No. 1, Xinke No. 5 and Au 139 were determined to be 0.303, 0.409 and 0.197, respectively.
-
Keywords:
- Auricularia auricula-judae /
- antagonism /
- agronomic trait /
- molecular marker
-
黑木耳Auricularia auricula-judae又称黑耳子、云耳、光木耳、细木耳[1],隶属木耳目Auriculariales木耳科Auricu1ariaceae木耳属Auricularia,是一种味道鲜美的胶质真菌,有“菌中瑰宝”、“素中之王”等美誉,在国际上称其为“中餐中的黑色瑰宝”[2-3],具有降血脂[4]、抗炎[5]、抗病毒[6]、抗肿瘤[7]、抗氧化和延缓衰老[8]等多种功效。黑木耳已成为我国第二大食用菌栽培品种。据统计,2016年全国黑木耳鲜耳产量679.54万t,占全年全国食用菌总产量的18.9%。黑木耳主产地在我国东北地区,随着“北耳南扩”产业的发展,浙江、福建等南方地区袋栽黑木耳“全日光间歇喷雾栽培模式”得到了快速发展,形成了一定的产业基础[9]。南方市场上黑木耳菌株很多都是由东北引进,如雪梅黑碗、雪梅1号、吉黑3号、黑威单片、黑威15和丰收2号等[10-11],但由于南北气候差异大,并不一定都能很好地适应南方栽培环境条件,具体表现在产量降低、抗性变差、易发生“流耳”现象。因此,选育适合南方栽培的黑木耳菌株,直接关系到南方黑木耳产业的快速、健康、持续发展。南耳1号是在福建省南平市野外采集、分离、驯化、筛选出的优良黑木耳菌株,是经福建省农作物品种审定委员会认定的新品种(闽认菌2013004)。由于生产上黑木耳栽培菌株来源广泛、数量众多,加上各地相互引种频繁,容易出现“同种异名”或“同名异种”的现象。因此,简便、快速、稳定、准确地鉴别菌株,已成为科研工作者的一项重要研究内容。本研究在前期研究的基础上[12],采用菌丝拮抗试验、菌丝生长速度测定、主要农艺性状对比、分子标记等分析方法,研究南耳1号的主要性状和遗传特性,为黑木耳种质资源评价分析提供理论依据。
1. 材料与方法
1.1 供试菌株
南耳1号由南平市农业科学研究所选育。新科1号、新科5号和Au139为当地主栽品种,来源于福建省三明市真菌研究所。
1.2 试剂与仪器
1.2.1 培养基与试剂
试管斜面PDA培养基:马铃薯(去皮)200 g、葡萄糖20 g、琼脂条20 g、水1 000 mL,自然pH值;PDA液体培养基:马铃薯(去皮)200 g、葡萄糖20 g、水1 000 mL,自然pH值;栽培料培养基:杂木屑78.5%、麸皮12%、棉籽壳8%、轻质碳酸钙1%、石灰0.5%,含水量52%,自然pH值。RAPD、ISSR和SRAP引物由上海生工生物工程有限公司合成。
1.2.2 仪器
冷冻离心机(Sigma 3K30)、PCR扩增仪(Eppendorf AG22331 Hamburg)、凝胶成像系统(TANON-2008)、掌型离心机(江苏海门市麒麟医用仪器厂Lx-100手掌型离心机)、灭菌锅(上海三申YX600W)、超净工作台(苏州净化设备有限公司SW-CJ-1FB型)。
1.3 拮抗试验
取连续活化转接2次的菌株,接种到直径9 cm、含PDA培养基的培养皿上,每个培养皿接2个菌株,相距约2 cm,两两一组,共6组,每组3个重复。置于25℃下培养,观察记录培养皿内2个株菌丝间是否产生拮抗现象。
1.4 菌丝生长速度测定
采用规格17.5 cm×40.0 cm×0.005 cm的聚乙烯塑料袋,装料高度约15 cm,料面平整(未打孔),上下松紧一致,塞上棉花塞,及时高压灭菌(0.14 MPa)2.5 h后,冷却备用。在接种箱内,采用“两点”接种法接种,每支试管母种接两袋,每个菌株接10袋,放置于25℃培养室发菌。当菌丝吃料2~3 cm时,用记号笔沿菌丝端统一画一条初始线。然后20 d划一次线,40 d划一次线,60 d再划一次线,每个菌株5个重复。量取相邻两条线的距离,计算每隔20 d菌丝生长速度。
1.5 DNA提取
采用CTAB (十六烷基三乙基溴化铵)沉淀法提取DNA[13]。
1.6 RAPD、ISSR和SRAP扩增及扩增产物检测
1.6.1 RAPD扩增
扩增体系:1 μL模板(含30 ng DNA),2.5 μL10×buffer缓冲液(含Mg2+),2.5 μL dNTP(2.5 mmol·L-1),1 μL Primer(10 μmol·L-1),0.25 μL TaqDNA聚合酶(5 U·μL-1), 最后用ddH2O将总体积补至25 μL。扩增程序:94℃预变性7 min;94℃变性1 min、34℃退火1 min、72℃延伸1 min, 35个循环;最后72℃延伸10 min。
1.6.2 ISSR扩增
体系:参照RAPD扩增体系。扩增程序:94℃预变性5 min;94℃变性1 min、48℃退火1 min、72℃延伸1 min, 35个循环,最后72℃延伸10 min。
1.6.3 SRAP扩增
体系:参照RAPD扩增体系,其中引物为1 μL Primer me(10 μmol·L-1)和1 μL Primer em(10 μmol·L-1)。扩增程序:94℃预变性5 min;94℃变性1 min、34℃退火1 min、72℃延伸1 min, 5个循环;94℃变性1 min、50℃退火1 min、72℃延伸1 min, 35个循环;最后72℃延伸10 min。
1.6.4 扩增产物检测
取6 μL PCR扩增产物,加上1 μL 6×溴酚蓝上样缓冲液,混匀。混合液在1.0%琼脂糖凝胶(含GoldviewTMDNA染料)上进行电泳,160 V电压电泳55 min后于紫外凝胶成像系统上观察、拍照。
1.7 供试菌株出耳
栽培试验点设在南平市农业科学研究所南山路口食用菌试验基地。2016年8月开始制袋,其菌袋规格为15 cm×55 cm×0.004 5 cm聚乙烯塑料袋,每袋湿料重1.4 kg,装料长度约40 cm。采用常压灭菌,冷却后在接种箱内接种,每个菌株接300袋、3次重复,共接3 600袋。接种后立即套袋,套袋规格为17 cm×55 cm×0.001 cm聚乙烯塑料袋,“井”字形摆放,勿压住接种口,每层3袋,摆5层,培菌温度控制在24~26℃。菌丝满袋后5 d,脱去套袋,选用黑木耳专用刺孔机刺孔,孔形为三角形,其孔宽(三角形底边)约8 mm,孔深(三角形高)约10 mm,每袋孔数约180个。刺孔后,“井”字形堆放,每层2袋,层高不超过8层。刺孔后养菌恢复5~7 d后下地排场。出菇管理按黑木耳“干干湿湿”交替管理的常规方法进行[14]。
1.7.1 主要农艺性状测定
观察记录出耳时鲜耳背面与腹面的颜色、绒毛、皱褶,以及晒干后耳片背面与腹面的颜色。然后以第1潮采收的干耳为对象,称取各个菌株干耳15 g,放入水中常温浸泡8 h,取出后沥干称重,计算其泡发率(泡发率用1:x表示,x = 泡发后重量/干耳重);并随机抽取各个菌株12朵,测定耳片中心厚度[15]。
1.7.2 产量测定
测定记录各个菌株每潮次的干耳重量。
1.8 统计分析
利用DPS-6.5软件的多重比较LSD法分析菌丝生长速度和干耳产量的数据。利用NTSYSpc 2.1软件,采用Jaccard聚类平均法(UPGMA)对3种分子标记综合进行聚类分析,构建各菌株的遗传聚类分析图谱和遗传相似系数表。
2. 结果与分析
2.1 拮抗试验
接种6 d后,不同菌株的菌丝开始接触,15 d后观察拮抗情况。从表 1可以看出,南耳1号与其他菌株间都产生了明显的拮抗线(拮抗反应强),其拮抗类型为隔离型,菌丝交接处后期可见黄色分泌物,说明体细胞不亲和,亲缘关系较远;新科1号与新科5号两个菌株间未出现拮抗线(无拮抗反应),表明两者间亲缘关系较近。
表 1 不同菌株间拮抗试验结果Table 1. Antagonism among different strains菌株 南耳1号 新科1号 新科5号 新科1号 ++ 新科5号 ++ - Au139 ++ ++ ++ 注:++表示拮抗反应强;-表示无拮抗反应。 2.2 菌丝生长速度测定
从表 2中可以看出,4个供试菌株菌丝萌发快,菌丝都表现洁白、粗壮、浓密。在菌丝培养的前两个时段(1~40 d)4个菌株中除新科1号外的菌株菌丝生长速度有缓慢增加的趋势,菌株间无显著性差异;在菌丝培养的第三个时段(41~60 d)4个菌株中除Au139外的菌株菌丝生长速度开始下降,其中南耳1号下降速度最快。从菌丝的这三个时段(1~60 d)的平均生长速度来看,南耳1号菌丝生长速度较慢,为0.176 cm·d-1,与其他3个菌株有显著性差异;新科5号、Au139和新科1号菌丝生长速度较快,分别为0.191、0.186、0.186 cm·d-1,这3个菌株间的生长速度没有显著性差异。
表 2 不同菌株的菌丝生长速度Table 2. Mycelial growth rates of different strains菌株 1~20 d生长速度/(cm·d-1) 21~40 d生长速度/(cm·d-1) 41~60 d生长速度/(cm·d-1) 1~60 d生长速度/(cm·d-1) 菌丝长势 新科5号 0.187±0.012 a 0.200±0.010 a 0.185±0.006 a 0.191±0.004 a +++ Au139 0.175±0.013 a 0.192±0.011 a 0.192±0.012 a 0.186±0.003 a +++ 新科1号 0.190±0.015 a 0.190±0.008 a 0.178±0.004 a 0.186±0.005 a +++ 南耳1号 0.180±0.017 a 0.190±0.006 a 0.157±0.011 b 0.176±0.008 b +++ 注:+++表示菌丝洁白、浓密、粗壮。同列数据后面小写字母不同表示品种间差异达0.05显著水平。表 3同。 表 3 产量及主要农艺性状Table 3. Average yield and major agronomic traits菌株 干耳产量/(g·袋-1) 鲜耳耳片厚度/mm 干耳背面颜色 干耳腹面颜色 鲜耳背面性状 鲜耳腹面性状 泡发率 南耳1号 108.5±3.3 a 0.91 青褐色 黑色 红褐色、短绒毛、皱褶深 黑褐色、光亮 1:16.8 新科1号 96.3±2.4 b 0.95 灰黑色 黑色 黑褐色、短绒毛、皱褶深 黑褐色、光亮 1:16.2 新科5号 95.8±1.9 b 0.94 灰黑色 黑色 黑褐色、短绒毛、皱褶深 黑褐色、光亮 1:16.3 Au139 90.7 ±2.2c 1.12 灰黑色 黑色 黑褐色、短绒毛、皱褶深 黑褐色、光亮 1:15.3 2.3 主要农艺性状比较
4个供试菌株的产量及主要农艺性状见表 3,从表中可看出,南耳1号产量最高,平均单袋干耳产量108.5 g,与其他3个菌株存在显著性差异,比新科1号增产12.7%、比新科5号增产13.3%、比Au139增产19.6%。从子实体的主要农艺性状来看,南耳1号鲜耳耳片较薄、泡发率较高、鲜耳背面颜色红褐色、干耳背面颜色青褐色,与其他3个菌株有明显区别;新科1号和新科5号的耳片形态特征一致,其鲜耳耳片厚度中等,鲜耳背面黑褐色、短绒毛、皱褶深,干耳背面颜色灰黑色;Au139鲜耳耳片较厚,鲜耳颜色比新科1号和新科5号略黑。
2.4 3种分子标记综合分析
经引物筛选,得到扩增条带清晰,稳定性、重复性和多态性较好的3种分子标记引物,其中RAPD引物有5条,即S33、S42、S118、S361和S1006;ISSR引物有6条,即ISSR1、ISSR2、ISSR3、ISSR4、ISSR5和ISSR8;SRAP有4对引物,即me5-em10、me6-em6、me1-em10和me4-em9。引物序列见表 4。
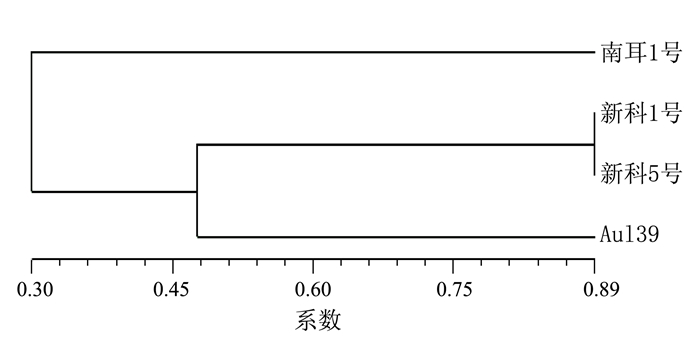
表 4 RAPD、ISSR和SRAP扩增所使用引物Table 4. Primers of RAPD, ISSR and SRAP分子标记 引物 序列 RAPD S33 CAGCACCCAC S42 GGACCCAACC S118 GAATCGGCCA S361 CATTCGAGCC S1006 GTAAGCCCCT ISSR ISSR1 CTCCTCCTCCTCSC ISSR2 BDBACAACAACAACAACA ISSR3 CACACACACACACACAWG ISSR4 CACCACCACCACSC ISSR5 VDHTCGTCGTCGTCGTCG ISSR8 CATACATACATACATAG SRAP me1 TGAGTCCAAACCGGATA me4 TGAGTCCAAACCGGACC me5 TGAGTCCAAACCGGAAG me6 TGAGTCCAAACCGGTAG em6 GACTGCGTACGAATTGCA em9 GACTGCGTACGAATTACG em10 GACTGCGTACGAATTTAG 利用筛选出的5条RAPD、6条ISSR和4对SRAP多态性引物对供试菌株扩增,分别得到26、23、17条多态性条带,其中多态性比例分别为90.5%、82.1%和86.7%。综合RAPD、ISSR和SRAP图谱获得的多态性条带,构建遗传聚类分析图谱(图 2)和遗传相似系数表(表 5),结果显示,南耳1号与新科1号、新科5号和Au139的遗传差异较大,其遗传相似系数分别为0.303、0.409和0.197。新科1号和新科5号亲缘关系较近,遗传相似系数为0.894。
表 5 黑木耳3种分子标记综合分析遗传相似系数Table 5. Similarity coefficients of 4 A. auricula-judae varieties based on 3 molecular markers菌株 南耳1号 新科1号 新科5号 Au139 南耳1号 1.000 新科1号 0.303 1.000 新科5号 0.409 0.894 1.000 Au139 0.197 0.500 0.455 1.000 3. 讨论与结论
优良菌株是食用菌生产快速、稳定发展的重要前提。随着国家对食用菌新品种重视程度的不断提高,借助传统的选择育种、诱变育种、杂交育种、原生质体融合育种等方法[16],加上20世纪80年代开始兴起的基因工程育种,食用菌新菌株不断被选育出来。食用菌菌株间的差异可体现在菌丝的体细胞不亲和性、子实体的形态学特征及DNA的序列分析等[17-19]。体细胞不亲和性的直观反映是拮抗试验,这是传统鉴定食用菌菌株间遗传差异的方法,可从拮抗反应类型、拮抗反应程度、菌丝间交接处色素3个方面区分[20]。王玉玲对4个香菇菌株和2个金针菇菌株之间的拮抗反应进行试验后认为,亲缘关系较近的菌株,其拮抗较弱或无拮抗现象,而亲缘关系较远的菌株则有明显拮抗现象[21]。本研究中南耳1号与其他3个对照菌株间都有明显拮抗现象,说明它与这3个菌株亲缘关系较远;新科1号和新科5号菌丝间没有产生拮抗线,说明这2个菌株间亲缘关系较近。
黑木耳的子实体形态学特征,包括子实体朵形(簇生型或菊花型)、耳片背面及腹面的颜色、耳片的厚度、耳片背面的皱褶程度、耳片大小、泡发率等。本研究中南耳1号鲜耳背面颜色红褐色、干耳背面颜色青褐色,与其他3个菌株有明显的区别。在实践上,子实体形态特征很容易受环境因素、栽培条件和观察者的辨别经验等因素影响,具有一定的局限性。
分子标记技术是从DNA序列水平上反映其遗传关系,与形态学和生理生化指标相比更客观、更准确,在黑木耳种质资源研究上有着广泛的应用前景。张介驰利用筛选的10个RAPD引物对8个黑木耳生产菌株进行鉴别分类,相似系数在0.70时,将其分为3个组群,其中一个组群的2个菌株的遗传相似系数为0.97,说明其亲缘关系较近[22];利用筛选的10个ISSR引物对东北地区27个黑木耳生产菌株进行鉴别分类,相似系数在0.75时,将其分为3个组群,其中一个组群的9个菌株的遗传相似系数高于0.97,可确认这些菌株间的亲缘关系较近或者是同一菌株[23]。本研究中从RAPD、ISSR和SRAP等3种分子标记中共选出66条多态性较明显的条带进行综合聚类分析,4个供试菌株的遗传相似系数在0.197~0.894,表明这些菌株间的遗传差异较大,其中新科1号和新科5号遗传相似系数为0.894,遗传差异小,跟拮抗试验中这2个菌株的亲缘关系较近的结果相吻合。
-
表 1 不同菌株间拮抗试验结果
Table 1 Antagonism among different strains
菌株 南耳1号 新科1号 新科5号 新科1号 ++ 新科5号 ++ - Au139 ++ ++ ++ 注:++表示拮抗反应强;-表示无拮抗反应。 表 2 不同菌株的菌丝生长速度
Table 2 Mycelial growth rates of different strains
菌株 1~20 d生长速度/(cm·d-1) 21~40 d生长速度/(cm·d-1) 41~60 d生长速度/(cm·d-1) 1~60 d生长速度/(cm·d-1) 菌丝长势 新科5号 0.187±0.012 a 0.200±0.010 a 0.185±0.006 a 0.191±0.004 a +++ Au139 0.175±0.013 a 0.192±0.011 a 0.192±0.012 a 0.186±0.003 a +++ 新科1号 0.190±0.015 a 0.190±0.008 a 0.178±0.004 a 0.186±0.005 a +++ 南耳1号 0.180±0.017 a 0.190±0.006 a 0.157±0.011 b 0.176±0.008 b +++ 注:+++表示菌丝洁白、浓密、粗壮。同列数据后面小写字母不同表示品种间差异达0.05显著水平。表 3同。 表 3 产量及主要农艺性状
Table 3 Average yield and major agronomic traits
菌株 干耳产量/(g·袋-1) 鲜耳耳片厚度/mm 干耳背面颜色 干耳腹面颜色 鲜耳背面性状 鲜耳腹面性状 泡发率 南耳1号 108.5±3.3 a 0.91 青褐色 黑色 红褐色、短绒毛、皱褶深 黑褐色、光亮 1:16.8 新科1号 96.3±2.4 b 0.95 灰黑色 黑色 黑褐色、短绒毛、皱褶深 黑褐色、光亮 1:16.2 新科5号 95.8±1.9 b 0.94 灰黑色 黑色 黑褐色、短绒毛、皱褶深 黑褐色、光亮 1:16.3 Au139 90.7 ±2.2c 1.12 灰黑色 黑色 黑褐色、短绒毛、皱褶深 黑褐色、光亮 1:15.3 表 4 RAPD、ISSR和SRAP扩增所使用引物
Table 4 Primers of RAPD, ISSR and SRAP
分子标记 引物 序列 RAPD S33 CAGCACCCAC S42 GGACCCAACC S118 GAATCGGCCA S361 CATTCGAGCC S1006 GTAAGCCCCT ISSR ISSR1 CTCCTCCTCCTCSC ISSR2 BDBACAACAACAACAACA ISSR3 CACACACACACACACAWG ISSR4 CACCACCACCACSC ISSR5 VDHTCGTCGTCGTCGTCG ISSR8 CATACATACATACATAG SRAP me1 TGAGTCCAAACCGGATA me4 TGAGTCCAAACCGGACC me5 TGAGTCCAAACCGGAAG me6 TGAGTCCAAACCGGTAG em6 GACTGCGTACGAATTGCA em9 GACTGCGTACGAATTACG em10 GACTGCGTACGAATTTAG 表 5 黑木耳3种分子标记综合分析遗传相似系数
Table 5 Similarity coefficients of 4 A. auricula-judae varieties based on 3 molecular markers
菌株 南耳1号 新科1号 新科5号 Au139 南耳1号 1.000 新科1号 0.303 1.000 新科5号 0.409 0.894 1.000 Au139 0.197 0.500 0.455 1.000 -
[1] 黄毅.食用菌工厂化栽培实践[M].福州:福建科学技术出版社, 2014:262-272. [2] 刘福阳, 王怡暄, 王爱仙, 等."雪梅1号"黑木耳在福建省区试及应用评价[J].北方园艺, 2017(14):160-165. http://d.old.wanfangdata.com.cn/Periodical/bfyany201714032 [3] 杨新美.中国食用菌栽培学[M].北京:农业出版社, 1988:355-376. [4] CHEN G, LUO Y C, JI B P, et al. Hypocholesterolemic effects of Auricularia auricula ethanol extract in ICR mice fed a cholesterol-enriched diet[J].Journal of Food Science and Technology, 2011, 48(6):692-698. DOI: 10.1007/s13197-010-0196-9
[5] DAMTE D, REZA M A, LEE S J, et al.Anti-inflammatory activity of dichloromethane extract of Auricularia auricular in RAW264.7 cells[J].Toxicological Research, 2011, 27(1):11-14. DOI: 10.5487/TR.2011.27.1.011
[6] NGUYEN T L, CHEN J, HU Y L, et al.In vitro antiviral activity of sulfated Auricularia auricula polysaccharides[J].Carbohydrate Polymers, 2012, 90(3):1254-1258. DOI: 10.1016/j.carbpol.2012.06.060
[7] REZA A, CHOI M J, DAMTE D, et al.Comparative antitumor activity of different solvent fractions from an Auricularia auricular-judae ethanol extract in P388D1 and sarcoma 180 cells[J].Toxicological Research, 2011, 27(2):77-83. DOI: 10.5487/TR.2011.27.2.077
[8] ZHANG H, WANG Z Y, ZHANG Z, et al.Purified Auricularia auricular-judae polysaccharide(AAP I-a)prevents oxidative stress in an ageing mouse model[J].Carbohydrate Polymers, 201l, 84(1):638-648. DOI: 10.1016/j.carbpol.2010.12.044
[9] 姚方杰."北耳南扩"的喜与忧[J].中国食用菌, 2012, 31(1):61-62. DOI: 10.3969/j.issn.1003-8310.2012.01.022 [10] 王爱仙, 巫仁高, 刘福阳, 等.福建省木耳新品种引进与筛选[J].福建农业学报, 2014, 29(9):874-878. DOI: 10.3969/j.issn.1008-0384.2014.09.011 [11] 王爱仙, 肖淑霞, 巫仁高, 等.袋栽黑木耳新品种引进对比试验[J].中国食用菌, 2018, 37(4):17-21. http://d.old.wanfangdata.com.cn/Periodical/zgsyj201804005 [12] 巫仁高, 王爱仙, 刘福阳, 等.黑木耳新品种Au053的选育与应用[J].食药用菌, 2013, 21(4):227-229. http://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-ZSYC201304015.htm [13] 刘新锐, 邓优锦, 谢宝贵, 等.鲍鱼菇的ITS-RFLP分析[J].菌物学报, 2007, 26(S1):185-191. http://d.old.wanfangdata.com.cn/Conference/6498412 [14] 巫仁高.福建黑木耳栽培关键技术[J].食用菌, 2014(5):52-53. DOI: 10.3969/j.issn.1000-8357.2014.05.038 [15] 陈影, 姚方杰, 张友民, 等.黑木耳种质资源的农艺性状测试方法[J].食药用菌, 2014, 22(3):153-154. http://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-ZSYC201403020.htm [16] 吕作舟.食用菌栽培学[M].北京:高等教育出版社, 2006:80-90. [17] 熊芳.分子标记鉴别侧耳属10种食用菌种质资源的研究[D].福州: 福建农林大学, 2008. http://cdmd.cnki.com.cn/Article/CDMD-10389-2009058457.htm [18] 李玉.中国黑木耳[M].长春:长春出版社, 2001. [19] 李黎, 范秀芝, 肖扬, 等.中国木耳栽培种质生物学特性及遗传多样性分析[J].菌物学报, 2010, 29(5):644-652. http://d.old.wanfangdata.com.cn/Periodical/jwxt201005004 [20] 李黎.中国木耳栽培种质资源的遗传多样性研究[D].武汉: 华中农业大学, 2011. http://cdmd.cnki.com.cn/article/cdmd-10504-1011405145.htm [21] 王玉玲.几种香菇、金针菇菌丝体的氨基酸组成及相互之间的拮抗现象[J].河南师范大学学报(自然科学版), 1999, 27(3):106-109. DOI: 10.3969/j.issn.1000-2367.1999.03.031 [22] 张介驰, 马庆芳, 张丕奇, 等.用RAPD分子标记鉴别黑木耳菌种的研究[J].菌物研究, 2006, 4(4):54-56. DOI: 10.3969/j.issn.1672-3538.2006.04.010 [23] 张介驰, 马庆芳, 张丕奇, 等.用ISSR分子标记鉴别东北地区黑木耳生产菌株的研究[J].菌物学报, 2007, 26(4):534-538. http://d.old.wanfangdata.com.cn/Periodical/jwxt200704008 -
期刊类型引用(4)
1. 宋吉玲,陆娜,闫静,亢学平,黄小苏,周小华. 黑木耳菌株农艺性状评价与遗传差异分析. 西北农林科技大学学报(自然科学版). 2021(03): 147-154 .  百度学术
百度学术
2. 王爱仙,王怡暄,刘福阳,刘金仙,巫仁高. 茶枝屑代料栽培黑木耳配方. 北方园艺. 2021(12): 121-126 .  百度学术
百度学术
3. 刘昆昂,马宏,刘萌,张根伟,尹淑丽,李书生. 采用r DNA-ITS和SRAP综合分析黑木耳栽培种的遗传多样性. 分子植物育种. 2021(24): 8223-8232 .  百度学术
百度学术
4. 姚远,王晖,孙达锋,陈晓艳,孙跃明,罗瑞,王英会,田果廷. 黑木耳“高原云耳1号”选育报告. 中国食用菌. 2019(06): 8-12 .  百度学术
百度学术
其他类型引用(3)




 下载:
下载: