Microbe-mediated Phytoremediation on Low Concentration Oil Sludge
-
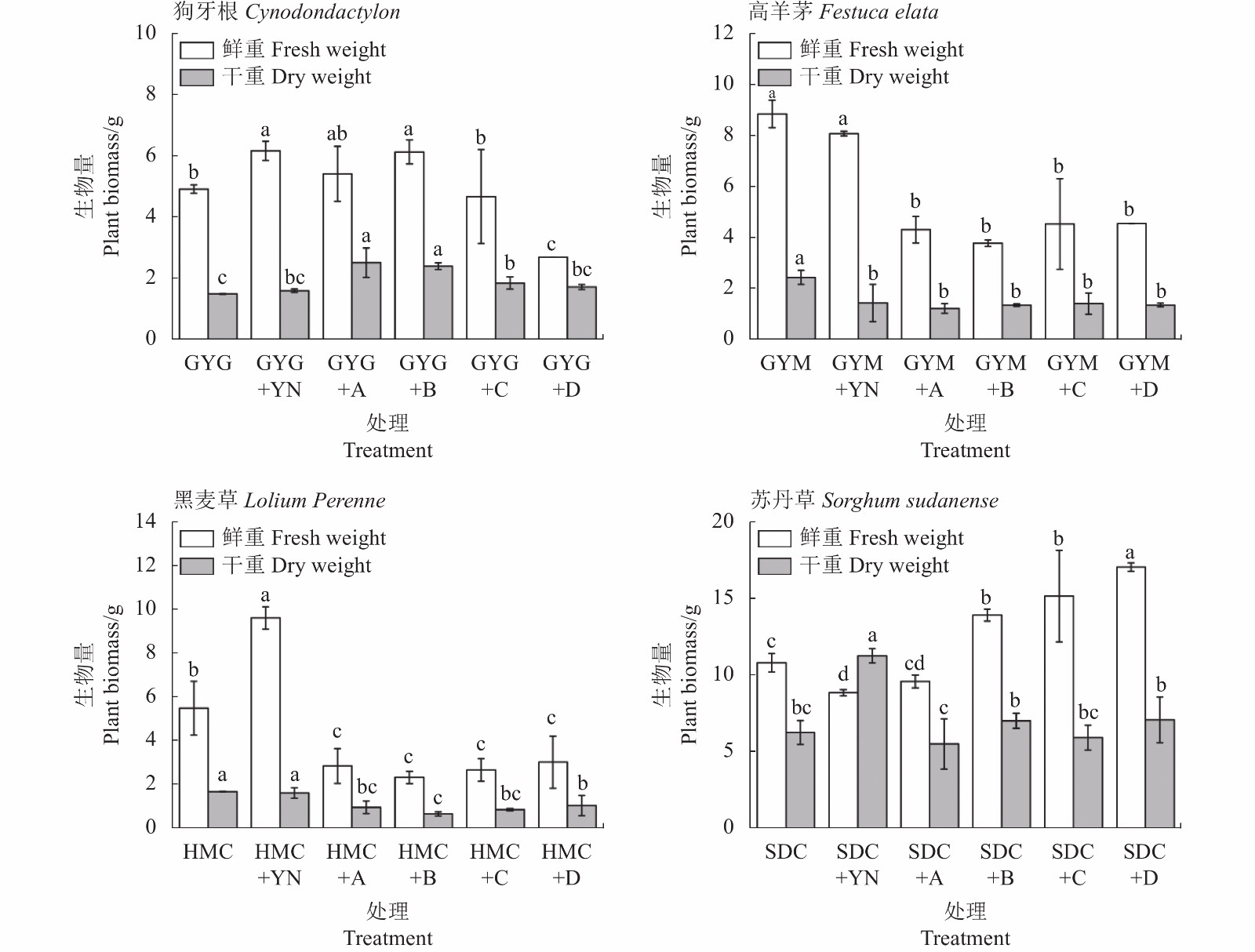
摘要:目的 探究4种新疆本土草本植物生物修复含油污泥的潜力,及其与微生物联合修复对低浓度含油污泥处理效果。方法 以狗牙根(Cynodondactylon)、高羊茅(Festuca elata)、黑麦草(Lolium Perenne)和苏丹草(Sorghum sudanense)与解脂假丝酵母(Candida lipolytica,菌A)、2株枯草芽孢杆菌[菌B( Bacillus subtilis PL-2)和菌C( Bacillus subtilis XJ-16)]、混菌D(A+B+C)为研究对象,采用盆栽试验,分别设置微生物组、植物组、植物-微生物组及对照4组处理,分析不同处理对石油烃残留量、微生物数量、草种生物量和叶绿素含量的影响。结果 120 d盆栽试验结表明,单独种植狗牙根、单独种植苏丹草、菌B、菌C处理对石油烃的降解效果较为相近,降解率分别为31.39%、34.19%、 33.71%与33.39%,显著高于对照组(P<0.05);草本植物与微生物联合修复中,狗牙根中添加菌A、菌B和菌C效果显著,石油烃的降解率可达43.02%、40.20%和42.54%,且在联合修复后土壤中可培养细菌与真菌数量显著增加,分别为1.50×105~2.59×105 cfu·g−1和4.32×104~5.53×104 cfu·g−1;此外,在添加降解菌后,狗牙根干重和叶绿素总含量均显著提高(P<0.05)。结论 综合石油烃残留量、微生物数量、生物量以及叶绿素含量指标得出,新疆本地植物狗牙根与菌A(解脂菌假丝酵母)、菌B和菌C(均为枯草芽孢杆菌)的联合,可为当地低浓度含油污泥处理提供可行的技术方案。
-
关键词:
- 植物-微生物联合修复 /
- 石油污染 /
- 降解率 /
- 微生物数量 /
- 生理特性
Abstract:Objective Potential of applying native Xinjiang plants in combination with microbes as a bioagent to treat low concentration oil sludge pollution was explored.Method Three treatments of microbes, plants, and plant-microbe combination that used plant including Cynodon dactylon, Festuca elata, Lolium Perenne, or Sorghum sudanense and the microbes including Candida lipolytica (Microbe A), Bacillus subtilis PL-2 (Bacterium B), and/or B. subtilis XJ-16 (Bacterium C) were conducted along with control in a pot experiment for 120 d. Effects of the treatments on petroleum hydrocarbon residues, and microbial population, as well as biomass and chlorophyll content of the plants, were determined.Result Under the single-factor treatments, C. dactylon, S. sudanense, Bacterium B, or Bacterium C provided relatively similar effect in degrading petroleum hydrocarbons with 31.39%, 34.19%, 33.71%, and 33.39% reductions, respectively, which were significantly higher than control (P<0.05). The plant-microbe combinations, on the other hand, showed significantly greater pollution remedying effect, such as achieved by incorporating C. dactylon with Bacterium A, B, and C that delivered the hydrocarbon removal rates of 43.02%, 40.20%, and 42.54%, respectively. Meanwhile, the culturable bacteria count increased significantly from 1.50×105 cfu·g−1 to 2.59×105 cfu·g−1 and fungi count from 4.32×104 cfu·g−1 to 5.53×104 cfu·g−1. In addition, the dry weight and total chlorophyll content of C. dactylon rose significantly in the presence of the microbes (P<0.05).Conclusion In view of petroleum hydrocarbon residue, microbial population, plant biomass, and leaf chlorophyll content, it appeared that the combined applications of Xinjiang native plant C. dactylon with yeast C. lipolytica and bacterium B. subtilis PL-2 or XJ-16 could be feasible for cleaning the environmental pollution caused by low concentration oil sludge in the area. -
0. 引言
【研究意义】随着全球气候的变化,涝渍胁迫已成为威胁农业生产的主要非生物胁迫之一。全球约有12%的土地受涝渍胁迫的影响,造成农作物产量损失高达20%[1-2]。我国受涝最为严重的地区是黄淮平原和长江中下游,约占全国总受灾面积的3/4[3]。当地面积水淹没部分或全部玉米根部时,引起根部缺氧,植物上部叶片气孔关闭、蒸腾效率和光合作用降低,限制光合同化物运输,造成籽粒灌浆能力下降,影响玉米产量和品质[4-5]。广西雨量充沛,全年降雨大部分集中在5~8月,而5~6月份正值春玉米籽粒灌浆期,该时期遭受涝渍胁迫,会造成玉米减产及品质下降。因此,探究淹水胁迫对灌浆期玉米籽粒品质的影响,对耐涝品种选育、耐涝机制及栽培技术研究等具有理论价值和实践意义。【前人研究进展】玉米整个生育期对水分的需求量较大,但却不耐涝。淹水胁迫对玉米产量影响较大的时期为苗期、拔节期、抽雄期和灌浆期[2, 4, 6]。已有研究发现,玉米拔节期遭遇淹水胁迫对其产量的影响最大,其次是苗期、抽雄期和灌浆期[5]。但也有研究表明,淹水对三叶期影响最大,拔节期次之[4, 6-9]。淹水胁迫影响玉米籽粒的灌浆过程,环境与基因型共同调节粒重和灌浆速率。胁迫持续时间越短,籽粒的库容越大,灌浆速度越快,灌浆期越长,粒重越高,品质越好[10-11]。淹水胁迫严重影响玉米籽粒的品质,其降低幅度与生育期、品种特性、持续时间及强度密切相关[5, 7, 12-14]。三叶期和拔节期胁迫后玉米籽粒淀粉、可溶性总糖、蔗糖、粗蛋白质含量显著下降,粗脂肪含量显著增加[7]。花期遭遇淹水胁迫普通玉米叶片中淀粉升高,蛋白含量降低[14]。灌浆期淹水胁迫后糯玉米叶片中可溶性糖、可溶性蛋白和脯氨酸含量下降,籽粒中可溶性糖和可溶性蛋白含量增加,淀粉和赖氨酸含量下降[5, 15],糯玉米和普通玉米之间差异可能由糯玉米基因差异表达引起[16]。籽粒灌浆过程主要是蔗糖的运输与转化、淀粉的合成与积累[17-18]。蔗糖合成酶(分解方向,SS-I)催化蔗糖分解、促进淀粉合成,其活性高低反映降解蔗糖的能力[17];结合态淀粉合成酶(GBSS)调控淀粉合成的关键酶,与直链淀粉延长有关[18],SS-I和GBSS参与植物对干旱、涝渍等多种胁迫的响应[17, 19-20]。脱落酸(ABA)是一种重要的应激反应激素,在抵御涝渍胁迫中发挥重要作用[21-23]。淹水引起根中ABA含量降低[21],叶片和籽粒中ABA含量增加[22-23],籽粒中积累的ABA可提高弱势粒中蔗糖向淀粉转化过程中相关酶(如GBSS、SS、SSS等)的活性,提升籽粒的库活力,增加弱势粒的灌浆效率,提高植物的抗逆性[22-23]。【本研究切入点】灌浆期是决定玉米籽粒产量和品质的关键时期,但目前关于灌浆期淹水胁迫对玉米品质影响的研究鲜见报道。【拟解决的关键问题】在玉米灌浆期人工模拟淹水胁迫,探究不同耐涝性玉米自交系籽粒的品质变化,分析灌浆期玉米品质响应淹水胁迫的规律,为耐涝品种的选育提供参考。
1. 材料与方法
1.1 试验地概况及试验材料
试验在广西壮族自治区农业科学院玉米研究所明阳基地(22°36'43″E,108°13'59″N)网棚中开展。在春玉米生育期内(2~6月),试验地所在区域多年降水量为703.3 mm,平均气温23.5 ℃,雨热同期,降雨和30 ℃以上气温主要集中在5~6月。供试材料为88M-1-8(桂单242父本)和先21A(桂单162父本),为广西玉米骨干自交系。试验盆高30 cm,上口径33 cm,下口径26 cm,将耕层土壤过筛,混匀后装盆,每盆装15 kg潮土,土壤有机质含量39.4 g·kg−1、速效氮116 mg·kg−1、速效磷210.1 mg·kg−1、速效钾224 mg·kg−1。
1.2 试验方法
1.2.1 试验设计
采用盆栽试验,设置2个处理,分别为正常水分处理(CK)和淹水处理(W),每个处理设14和18 d两个持续时间,即CK-14、CK-18、W-14和W-18,随机排列,重复3次。先21A和88M-1-8分别于2022年2月15日和18日播种,每个试验盆(底部有孔)种植4粒玉米种子,出苗后定苗2株,拔节期挑选长势一致的玉米定苗1株,前期正常水肥管理,2022年5月9日,88M-1-8和先21A分别进行自交授粉。胁迫采用双套盆法,在试验盆外再套一个相同大小的试验盆(底部无孔),以防水分从盆底排出。授粉后立刻进行淹水处理,每天灌水使土壤含水量过饱和,始终保持水面高出盆中土壤表面2~3 cm,使玉米根部处于淹水状态。对照为正常水分处理,整个生育期供水充足,维持土壤相对含水量为75%~80%。分别在胁迫处理的第14 天和第18天采集果穗,每个处理和持续时间设3次重复,每次重复15个果穗,样品短暂保存于−80 ℃超低温冰箱,用于测定相关生理生化指标。
1.2.2 测定指标与方法
可溶性蛋白质、可溶性糖、淀粉、蔗糖含量均参照李小芳和张志良[24]的测定方法。SS-I和GBSS均采用重庆博诺恒生物科技有限公司提供的酶活性试剂盒测定。ABA含量的测定采用高效液相色谱法[25]。
1.3 统计分析
采用Excel 2010进行数据处理,运用SPSS 25.0进行方差分析和相关性分析,采用Excel 2010和Photoshop CC 2020作图。利用主成分分析和隶属函数法综合评价不同处理后各自交系的耐涝性,主要步骤及公式如下[26-27]:
(1)耐涝系数(Waterlogging resistance coefficient,WRC)
耐涝系数=淹水条件下的测定值/正常水分条件下的测定值 (1) (2)变异系数
变异系数 C⋅V= (标准偏差 SD/ 平均值 Mean )×100% (2) (3)隶属函数值
隶属函数值 U(Xj)=(Xj−Xmin)/(Xmax−Xmin) (3) 式中,U(Xj)为各指标的隶属函数值,Xj表示第j个综合指标,Xmax为第j个综合指标的最大值,Xmin为第j个综合指标的最小值。
(4)综合评价
耐涝性综合评价值 D=∑jn=1[U(Xj)×Wj] (4) 式中,D值为胁迫下各试材采用隶属函数分析所得的耐涝性综合评价值。
2. 结果与分析
2.1 淹水胁迫对玉米籽粒可溶性蛋白含量的影响
可溶性蛋白含量可反映植物体内代谢作用的强弱,是衡量玉米籽粒品质的重要指标。由图1可知,2种处理下,W-14和CK-18籽粒中可溶性蛋白含量均随着处理持续天数的增加而显著增加,表明逆境下籽粒中的代谢活动加剧。88M-1-8在W-14和CK-18时的可溶性蛋白含量显著高于先21A(P<0.05,下同),在CK-14和W-18时的蛋白含量与先21A无显著差异。88M-1-8和先21A的可溶性蛋白含量在W-14处理下较CK-14处理分别上升了14.22%和3.48%,在W-18处理下较CK-18分别下降1.51%和上升10.99%。说明淹水胁迫诱导88M-1-8和先21A籽粒中可溶性蛋白含量的增加,2个自交系间差异不显著。
2.2 淹水胁迫对玉米籽粒糖类物质含量的影响
2.2.1 淹水胁迫对玉米籽粒可溶性糖含量的影响
逆境下,植物通过调节可溶性糖等渗透物质含量维持细胞内部稳定,降低对植物的伤害。如图2A所示,淹水胁迫进程中,玉米自交系籽粒中可溶性糖含量变化有所不同,88M-1-8和先21A在正常水分处理时可溶性糖含量分别下降18.24%和上升25.98%,淹水处理分别下降12.00%和27.61%。将淹水处理不同持续天数分别与正常水分处理相比,先21A在W-14上升幅度最大,W-18上升幅度最小。结果表明,淹水胁迫诱导88M-1-8和先21A籽粒中可溶性糖含量的积累,其中W-14的先21A可溶性糖含量最高。
2.2.2 淹水胁迫对玉米籽粒淀粉含量的影响
淀粉是玉米籽粒中碳水化合物的主要储藏形式,也是衡量玉米籽粒品质的重要指标。由图2B可知,随着处理天数的增加,2个自交系籽粒中淀粉含量均显著增加。其中,88M-1-8和先21A在正常水分处理时淀粉含量分别上升7.62倍和5.65倍,在淹水处理时分别上升6.00倍和8.00倍,表明授粉后14-18 d,是淀粉合成的重要时间段。88M-1-8和先21A的淀粉含量在W-14处理下较CK-14处理分别上升了52.65%和9.60%,同时,在W-18下较CK-18分别上升20.24%和55.08%,先21A在W-18上升幅度最大,W-14上升幅度最小。总体来看,淹水胁迫诱导88M-1-8和先21A籽粒中淀粉含量的积累,其中88M-1-8淀粉含量显著高于先21A。
2.2.3 淹水胁迫对玉米籽粒蔗糖含量的影响
蔗糖是光合同化物从“源”到“库”运输的主要形式。逆境下,“源”叶中蔗糖含量降低将影响玉米籽粒中蔗糖含量变化,进而影响籽粒产量和品质[10-11]。如图2C可见,88M-1-8在CK-14和CK-18时的蔗糖含量均显著高于先21A,在W-14和W-18时与先21A无显著差异。88M-1-8和先21A随着2种处理天数的增加,籽粒中蔗糖含量均显著增加。在W-14处理下较CK-14处理时,88M-1-8和先21A的蔗糖含量分别下降1.45%和上升57.48%;在W-18下较CK-18时,2个自交系分别上升1.33%和10.65%。综上所述,淹水胁迫下88M-1-8和先21A籽粒中蔗糖含量没有显著差别,但是与正常水分处理相比,先21A籽粒中蔗糖含量的增幅大于88M-1-8。
2.3 淹水胁迫对玉米淀粉合成相关酶活性的影响
2.3.1 淹水胁迫对玉米籽粒蔗糖合成酶活性的影响
SS-Ⅰ可以催化蔗糖分解成葡萄糖和果糖,进而促进淀粉的合成[17]。由图3A可知,在正常水分和淹水时,2个自交系均随着处理天数的增加,籽粒中SS-Ⅰ活性显著增加。其中,88M-1-8和先21A在正常水分处理时SS-Ⅰ活性分别上升2.40倍和2.86倍,胁迫下分别上升2.20倍和2.58倍。将淹水处理不同持续天数与分别正常水分处理相比,先21A在W-14上升幅度最大,W-18上升幅度最小。总之,淹水处理诱导88M-1-8和先21A中SS-Ⅰ活性持续增加,且88M-1-8增幅小于先21A。
2.3.2 淹水胁迫对玉米籽粒结合态淀粉合成酶活性的影响
GBSS参与籽粒直链淀粉的延长,是调控淀粉合成的关键酶[18]。88M-1-8在CK-14、W-14、CK-18和W-18时的GBSS活性均显著高于先21A(图3B)。88M-1-8和先21A在正常水分处理和淹水处理时GBSS活性均显著增加。88M-1-8和先21A的GBSS活性在W-14处理下较CK-14处理分别下降9.50%和上升54.38%,同时,在W-18下较CK-18分别上升5.44%和19.63%。可见,淹水处理诱导88M-1-8和先21A籽粒中GBSS活性持续增加,虽然88M-1-8增幅小于先21A,但88M-1-8中GBSS活性仍显著高于先21A。
2.4 淹水胁迫对玉米籽粒脱落酸含量的影响
ABA作为逆境激素,通过调节蔗糖分解和淀粉合成酶的活性,参与涝渍胁迫响应[22-23]。88M-1-8在CK-14、CK-18、W-14和W-18处理时的ABA含量均显著高于先21A(图4)。淹水后88M-1-8籽粒的脱落酸含量均显著上升。88M-1-8和先21A在正常水分处理和淹水处理时ABA含量的变化趋势相反,正常水分处理时均显著下降,而淹水处理均有所增加。88M-1-8和先21A的ABA含量在W-14处理下较CK-14处理分别上升17.94%和下降11.97%,同时,在W-18下较CK-18分别上升50.67%和3.09%。以上结果表明,淹水胁迫下88M-1-8和先21A籽粒中ABA含量持续增加,但88M-1-8中ABA含量变化幅度显著高于先21A。
2.5 各项指标的耐涝性分析
2.5.1 各项指标的耐涝系数
根据公式(1)和公式(2)计算各项指标的耐涝系数和变异系数(表1),可溶性糖、蔗糖、GBSS和ABA的变异系数较大,分别为27.22%、23.48%、23.25%和23.29%,其次是淀粉,为17.05%,说明淹水胁迫对可溶性糖、淀粉、蔗糖、GBSS和ABA的影响较大。淹水处理后,可溶性糖、淀粉含量、SS-I活性与正常水分处理相比均有所上升(WRC>1),其余单项指标变化幅度不一致,既有上升又有下降。
表 1 各项指标的耐涝系数Table 1. Waterlogging resistance coefficients on indicators自交系
Inbred line处理天数
Treatment day可溶性蛋白
Soluble protein可溶性糖
Soluble sugar淀粉
Starch蔗糖
Sucrose蔗糖合成酶(分解方向)
SS-I结合态淀粉合成酶
GBSS脱落酸
ABA88M-1-8 14 d 1.14 1.11 1.53 0.99 1.19 0.91 1.18 18 d 0.98 1.19 1.20 1.01 1.09 1.05 1.51 先21A 14 d 1.03 1.79 1.10 1.57 1.20 1.54 0.88 18 d 1.11 1.03 1.55 1.11 1.08 1.20 1.03 平均值 Mean 1.07 1.28 1.34 1.17 1.14 1.17 1.15 标准偏差 STDEV 0.07 0.35 0.23 0.27 0.06 0.27 0.27 变异系数
Variable coefficient/%6.68 27.22 17.05 23.48 5.66 23.25 23.29 2.5.2 主成分分析
根据主成分分析结果(表2、表3和图5),PC1和PC2的贡献率分别为60.27%和28.66%,两者累积贡献率高达88.93%,可用PC1和PC2作为主成分对不同处理的自交系进行耐涝性评价。决定PC1大小的主要是可溶性糖、蔗糖、淀粉、GBSS和ABA,决定PC2大小的主要是可溶性蛋白、淀粉和ABA。在PC1中可溶性糖、蔗糖和GBSS有较高的正向载荷,淀粉和ABA有较高的负向载荷,说明PC1会随着可溶性糖、蔗糖和GBSS增加而升高,随着淀粉和ABA的增加而降低。而在PC2中可溶性蛋白和淀粉有较高的正向载荷,ABA有负向载荷,说明PC2会随着可溶性蛋白和淀粉增加而升高,随着ABA的增加而降低。
表 2 各指标的主成分分析的载荷矩阵Table 2. Load matrix of principle component analysis on indicators指标
Index因子载荷 Factor loading PC1 PC2 可溶性蛋白 Soluble protein −0.42 0.91 可溶性糖 Soluble sugar 0.98 −0.05 淀粉 Starch −0.77 0.61 蔗糖 Sucrose 0.98 0.15 蔗糖合成酶(分解方向) SS-I 0.54 0.48 结合态淀粉合成酶 GBSS 0.92 0.05 脱落酸 ABA −0.61 −0.74 表 3 主成分分析的特征值和贡献率Table 3. Eigenvalue and contribution rate of principle components项目
Item因子载荷 Factor loading PC1 PC2 特征值 Eigen Value 4.22 2.01 贡献率 Contribution rate/% 60.27 28.66 累积贡献率 Cumulative contribution rate/% 60.27 88.93 2.5.3 隶属函数分析
以耐涝系数为原始数据,根据公式(3)计算各综合指标的隶属函数值(表4)。其中,在综合指标PC1中,W-14的88M-1-8隶属函数值U(X1)最小,为0.000;W-14的先21A值最大,为1.000。基于表3中PC1和PC2主成分贡献率,计算获得综合指标值F1、F2,隶属函数值U(X1)、U(X2),综合耐涝评价D值,D值越大,说明耐涝性越强。结果表明,W-14的88M-1-8耐涝性最强,W-18的88M-1-8和W-14的先21A耐涝性次之,W-18的先21A耐涝性最差。
表 4 玉米自交系不同处理的隶属函数分析及耐涝性排序Table 4. Membership function analysis on waterlogging tolerance of maize inbred lines under treatments自交系
Inbred line处理天数
Treatment day综合指标 Comprehensive index 隶属函数值 Subordinate function value D值
D Value排序
RankingF1 F2 U(X1) U(X2) 88M-1-8
88M-1-814 d −0.646 0.798 0.000 1.000 0.539 1 18 d −0.363 −1.447 0.133 0.000 0.291 2 先21A
Xian 21A14 d 1.490 0.154 1.000 0.713 0.286 3 18 d −0.481 0.495 0.077 0.865 0.124 4 3. 讨论
3.1 淹水胁迫对玉米籽粒品质的影响
土壤水分是制约作物籽粒品质的重要因素,它通过改变作物籽粒组分含量进而影响其品质[28]。对不同作物、不同生育期、不同种质进行涝或渍胁迫处理,其籽粒组分含量均发生明显变化[5, 14-15, 29-31]。本研究发现,淹水胁迫导致灌浆期耐涝自交系88M-1-8和不耐涝自交系先21A籽粒的可溶性蛋白、可溶性糖、淀粉和蔗糖含量发生显著变化,与前人研究结果一致[5, 14-15]。
籽粒灌浆过程主要是蔗糖向淀粉转化,受SS-I、GBSS等多种酶的共同调控,参与多种植物逆境适应[17-18, 20]。本研究发现,淹水胁迫诱导88M-1-8中GBSS含量的先降低后增加,先21A籽粒中GBSS含量的持续增加,与小麦受涝后GBSS含量增加一致[20]。随着淹水处理天数增加,2个自交系的SS-I活性和淀粉含量均显著增加,说明淹水胁迫促使SS-Ⅰ和GBSS活性增加,加速蔗糖分解与淀粉合成[17, 19-20]。
淹水时ABA通过调节蔗糖向淀粉转化过程中相关酶(如GBSS、SS、SSS等)的活性,提升籽粒的库活力和灌浆速率,参与涝渍胁迫响应[21-23]。本研究发现淹水胁迫引起耐涝自交系88M-1-8籽粒中ABA含量持续显著增加,而不耐涝自交系先21A中ABA含量降低。淹水胁迫下耐涝自交系籽粒积累大量的ABA,促使GBSS和SS-I活性的增加,加速蔗糖转化成淀粉,增加弱势粒灌浆效率,促进籽粒完成灌浆,提高植株的耐涝性[22-23]。而不耐涝自交系由于ABA含量的下降,籽粒由蔗糖向淀粉转化的速度放缓,灌浆速率降低,造成秃尖、瘪粒等现象[4, 7, 32]。
3.2 玉米自交系耐涝性综合评价
植物耐涝性是受多因素影响的复杂性状,单一指标和统一标准难以作出全面、准确评价。本研究88M-1-8和先21A在单项指标上表现出的耐涝性并不一致,例如在W-14处理下较CK-14相比,先21A的蛋白含量上升幅度最小,88M-1-8上升幅度最大;88M-1-8的可溶性糖含量上升幅度最小,先21A上升幅度最大。耐涝系数可以消除材料间的固有差异,采用主成分分析和隶属函数法对耐涝系数展开综合分析,对其耐涝性作出准确评价,已被广泛用于多种植物中[26-27]。本研究测定不同处理和持续时间下88M-1-8和先21A的可溶性蛋白、可溶性糖、淀粉和蔗糖含量、SS-Ⅰ和GBSS活性等7项生理生化指标,将其转换为耐涝系数,作为评价单项耐涝能力的指标。由于单项指标间存在相互作用,部分信息发生重叠,且指标的权重各不相同,若直接采用隶属函数法进行综合评价,其结果可能与实际结果存在偏差[33]。因此,仅采用隶属函数法评价不同玉米自交系耐涝性具有一定局限性。主成分分析可对多个单项指标进行降维、建模和线性分类,选取较少的综合变量反映尽可能多地原始变量信息,可有效避免多个指标间相关性、信息重叠和人为主观地判断指标权重等情况[34-35]。因此,采用隶属函数法和主成分分析综合评价不同材料的耐涝性是一种科学、有效的评价方法[26, 33]。本研究对7项耐涝系数进行主成分分析,获得2个相互独立的综合指标PC1和PC2,它们累积贡献率为88.93%。再根据综合指标PC1和PC2贡献率确定各自权重,结合隶属函数分析,对不同材料的耐涝性作出综合评价。其中,淀粉和ABA含量是决定PC1和PC2大小的主要指标,也是变异系数较大的重要指标。因此,本研究认为玉米灌浆期籽粒中淀粉和ABA含量的变化情况能在较大程度上反映玉米耐涝性综合评价的结果,如果在玉米耐涝性评价过程中遇到人员、经费和时间不充足,或待评价材料过多的情况,可考虑测定淀粉和ABA含量这2个指标对玉米灌浆期耐涝性进行初步评价。
4. 结论
淹水胁迫显著影响灌浆期玉米籽粒品质。淹水胁迫提高籽粒可溶性蛋白、可溶性糖、淀粉和蔗糖含量、SS-I和GBSS活性。耐涝自交系88M-1-8的GBSS活性、淀粉和ABA含量显著高于不耐涝自交系先21A。随着处理时间的增加,88M-1-8和先21A籽粒品质的耐涝性均有所降低,但88M-1-8耐涝性仍高于先21A。在玉米灌浆期涝害频发区域应选择耐涝自交系,确保自交系优良品质,提高育种效率。
-
表 1 试验处理组
Table 1 Experimental treatments
处理 Treatment 处理代号 Code 备注 Notes 空白对照 Control CK 自然条件下含油污泥降解情况 微生物组 Microbial 解脂假丝酵母菌(A)、枯草芽孢杆菌(B)、枯草芽孢杆菌(C)、混菌D(A+B+C) 添加微生物对含油污泥的降解情况 植物组 Plant 狗牙根(GYG、GYG+YN)、高羊茅(GYM、GYM+YN)、黑麦草(HMC、HMC+YN)、苏丹草(SDC、SDC+YN) GYG、GYN、HMC、SDC为正常土壤条件下生长,GYG+YN、GYN+YN、HMC+YN、SDC+YN为污染土壤中生长。不同草本植物对含油污泥的降解情况。 植物-微生物组 Microbial and Plant GYG+A、GYG+B、GYG+C、GYG+D;GYM+A、GYM+B、GYM+C、GYM+D;HMC+A、HMC+B、HMC+C、HMC+D;SDC+A、SDC+B、SDC+C、SDC+D 植物微生物联合修复对石油烃降解效率 表 2 处理组中石油烃的残留量与降解率
Table 2 Residues and degradation of petroleum hydrocarbons by each treatment
处理组
Group处理
Treatment30 d 60 d 120 d 残留量
Residual amount/g降解率
Degradation rate/%残留量
Residual amount/g降解率
Degradation rate/%残留量
Residual amount/g降解率
Degradation rate/%对照组
Control groupCK 5.71±0.09 ab 8.13±1.62 h 5.20±0.15 a 16.53±2.41 f 4.85±0.05 a 22.15±0.80 k 植物组
Plant groupGYG+YN 5.38±0.23 bcdef 13.72±3.62 efgh 4.33±0.30 efj 30.57±6.02 ab 4.27±0.13 bcdefgh 31.39±2.01 defghi GYM+YN 5.35±0.45 bcdef 13.86±3.62 efgh 4.52±0.13 defg 27.37±2.01 abc 4.45±0.15 bcde 28.57±2.41 ghij HMC+YN 5.30±0.10 bcdefg 14.93±1.61 defgh 4.50±0.05 defg 27.77±0.80 abc 4.35±0.15 cdefg 30.18±2.41 e SDC+YN 4.70±0.05 ghij 24.56±0.80 abc 4.20±0.18 fg 32.58±1.61 a 4.10±0.05 ghi 34.19±0.80 cde 微生物
Microbial groupA 5.25±0.30 bcdefgh 15.73±4.82 defgh 4.63±0.03 cdef 25.75±0.40 abcd 4.27±0.03 ghi 31.39±0.40 defghi B 5.15±0.20 bcdefghi 17.34±3.21 cedfg 4.53±0.03 defg 25.38±3.08 abc 4.10±0.05 ghi 33.71±1.05 cdef C 4.67±0.48 hij 24.97±7.62 abc 4.87±0.28 abcd 21.76±4.41 cdef 4.15±0.20 efghi 33.39±3.21 cdefg D 5.65±0.45 abc 9.31±7.22 gh 4.97±0.08 abc 20.15±0.41 def 4.67±0.28 ab 25.01±5.67 jk 植物—微生物
Microbial and PlantGYG+A 5.40±0.10 bcde 13.32±1.61 efgh 4.22±0.08 fg 32.19±1.21 a 3.55±0.05 k 43.02±0.80 a GYG+B 4.90±0.25 efghij 21.62±4.42 bcde 4.33±0.03 efg 30.57±0.40 ab 3.73±0.08 jk 40.20±1.21 ab GYG+C 5.00±0.30 defghi 19.74±4.82 bcdef 4.35±0.10 efg 30.18±1.61 ab 3.58±0.35 k 42.54±5.22 a GYG+D 4.92±0.28 defghij 20.96±4.42 bcde 5.10±0.15 ab 18.41±2.02 ef 3.95±0.35 ij 36.60±5.62 bc GYM+A 4.75±0.39 defghi 19.32±4.42 bcdef 4.60±0.18 cdef 26.16±3.21 abcd 4.25±0.10 defghi 32.05±2.02 cdefgh GYM+B 4.33±0.13 j 30.57±2.01 a 4.37±0.03 efg 29.78±0.41 ab 4.45±0.10 bcde 28.57±1.61 ghij GYM+C 4.59±0.53 fghij 23.15±3.27 abcd 4.40±0.10 efg 29.78±13.65 ab 4.43±0.16 cdefg 28.96±2.81 fghig GYM+D 5.52±0.10 abcd 11.33±5.70 fgh 5.12±0.08 ab 17.74±1.21ef 4.43±0.08 cdefg 28.97±1.21 fghig HMC+A 5.40±0.33 a 13.37±5.70 efgh 4.33±0.08 efg 30.57±1.21ab 4.20±0.10 defghi 32.58±1.61 cdefgh HMC+B 4.88±0.03 efghij 21.74±0.400 bcde 4.33±0.08 g 29.89±0.54 ab 3.77±0.35 efghi 32.99±0.40 cdefgh HMC+C 4.80±0.15 fghij 23.33±0.41 abcd 4.72±0.28 bcde 24.16±4.42 bcde 4.55±0.10 bc 26.97±1.61 ij HMC+D 5.26±0.73 bcdef 15.69±12.04 defgh 4.52±0.13 defg 27.37±2.01 abc 4.48±0.03 bcd 28.16±0.40 hij SDC +A 5.35±0.50 bcdef 14.13±0.81 edfgh 4.52±0.18 defg 27.38±2.81 abc 3.97±0.03 hij 36.20±0.41 bcd SDC +B 4.33±0.08 j 30.57±1.21 a 4.27±0.03 fg 31.39±0.40 a 4.13±0.08 fghi 33.94±0.98 cde SDC +C 5.10±0.05 cdefghi 18.14±0.80 cedf 4.98±0.18 abc 20.14±2.81 def 4.03±0.18 hi 35.38±2.81 cd SDC +D 4.55±0.15 ig 26.97±2.41 ab 4.55±0.05 defg 26.97±0.81 abcd 4.18±0.03 defghi 32.98±0.41 cdefgh 不同小写字母表示不同处理间差异显著(P<0.05)。表3同。
Different lowercase letters represent significant difference among groups (P<0.05). Same for Table 3.表 3 不同处理土壤中微生物数量
Table 3 Microbial loads in sludge by treatments
处理组
Group处理
Treatment细菌
Bacteria/
(×105 cfu·g−1)真菌
Fungus
(×104 cfu·g−1)对照组 Control group CK 0.08±0.01 i 0.67±0.06 i 植物组 Plant group GYG+YN 1.33±0.10 ef 3.58±0.38 efg GYM+YN 1.09±0.02 g 0.33±0.39 fgh HMC+YN 1.12±0.13 g 0.35±0.20 efg SDC+YN 0.48±0.04 h 2.02±0.28 k 微生物 Microbial group A 1.19±0.04 fg 4.78±0.39 b B 0.96±0.07 g 3.43±0.21 efgh C 1.02±0.07 g 4.13±0.24 bcde D 0.65±0.06 g 2.95±0.38 ghi 植物-微生物
Microbial and plantGYG+A 1.79±0.06 b 5.53±0.58 a GYG+B 1.50±0.07 cde 4.32±0.55 bcd GYG+C 2.59±0.12 a 4.40±0.36 bc GYG+D 1.91±0.08 b 2.00±0.41 k GYM+A 1.45±0.09 cde 4.03±0.43 cde GYM+B 1.39±0.20 de 3.53±0.43 efg GYM+C 1.33±0.09 ef 3.07±0.49 fgh GYM+D 1.32±0.11 ef 3.25±0.03 fgh HMC+A 1.47±0.13 cde 3.67±0.33 def HMC+B 1.61±0.09 c 4.08±0.19 cde HMC+C 1.12±0.27 g 2.75±0.48 hig HMC+D 1.56±0.13 cd 2.30±0.33 igk SDC+A 1.51±0.09 cde 3.15±0.40 fgh SDC+B 1.32±0.10 ef 2.80±0.35 hig SDC+C 1.37±0.07 def 3.50±0.23 efg SDC+D 1.12±0.08 g 2.15±0.26 jk -
[1] 包清华, 黄立信, 修建龙, 等. 油气田含油污泥生物处理技术研究进展 [J]. 化工进展, 2021, 40(5):2762−2773. DOI: 10.16085/j.issn.1000-6613.2020-1299 BAO Q H, HUANG L X, XIU J L, et al. Development in the biological treatment of oily sludge in oil and gas fields [J]. Chemical Industry and Engineering Progress, 2021, 40(5): 2762−2773.(in Chinese) DOI: 10.16085/j.issn.1000-6613.2020-1299
[2] 郭盼, 刘正宁, 李阳, 等. 浅析含油污泥处理技术 [J]. 东方电气评论, 2019, 33(3):6−9. DOI: 10.3969/j.issn.1001-9006.2019.03.002 GUO P, LIU Z N, LI Y, et al. Analysis on oily sludge treatment technology [J]. Dongfang Electric Review, 2019, 33(3): 6−9.(in Chinese) DOI: 10.3969/j.issn.1001-9006.2019.03.002
[3] 梁宏宝, 张全娟, 陈洪涛, 等. 含油污泥联合处理技术的应用现状与展望 [J]. 环境工程技术学报, 2020, 10(1):118−125. DOI: 10.12153/j.issn.1674-991X.20190065 LIANG H B, ZHANG Q J, CHEN H T, et al. Application status and prospect of combined treatment technology for oily sludge [J]. Journal of Environmental Engineering Technology, 2020, 10(1): 118−125.(in Chinese) DOI: 10.12153/j.issn.1674-991X.20190065
[4] 新疆维吾尔自治区质量监督局. 新疆油气田含油污泥及钻井固体废物处理处置技术规范: DB 65/T 3999 -2017[S]. 新疆: 2017. [5] HU G J, LI J B, ZENG G M. Recent development in the treatment of oily sludge from petroleum industry: A review [J]. Journal of Hazardous Materials, 2013, 261: 470−490. DOI: 10.1016/j.jhazmat.2013.07.069
[6] 李俊生, 肖能文. 陆地石油开采生态风险评估的技术研究[M]. 北京: 中国环境出版社, 2013. [7] 马强, 张旭红, 林爱军, 等. 土壤石油烃污染的植物毒性及植物-微生物联合降解 [J]. 环境工程学报, 2009, 3(3):544−548. MA Q, ZHANG X H, LIN A J, et al. Phytoxicity and biodegradation of petroleum hydrocarbon contamination in soil [J]. Chinese Journal of Environmental Engineering, 2009, 3(3): 544−548.(in Chinese)
[8] 王丽萍, 朱新萍, 董双快, 等. 苏丹草与紫花苜蓿对新疆原油污染土壤的响应 [J]. 环境工程, 2016, 34(11):145−149. WANG L P, ZHU X P, DONG S K, et al. Response of sorghum sudanense and Medicago sativa growing on soil contaminated with crude oil in Xinjiang [J]. Environmental Engineering, 2016, 34(11): 145−149.(in Chinese)
[9] 郭鹏, 李汉周, 刘松林, 等. 油田含油污泥土壤降解与修复试验研究 [J]. 石油与天然气化工, 2019, 48(6):105−110. DOI: 10.3969/j.issn.1007-3426.2019.06.021 GUO P, LI H Z, LIU S L, et al. Study on degradation and rehabilitation of oily sludge soil in oil field [J]. Chemical Engineering of Oil & Gas, 2019, 48(6): 105−110.(in Chinese) DOI: 10.3969/j.issn.1007-3426.2019.06.021
[10] 史德青, 张建, 祝威, 等. 胜利油田含油污泥的植物修复研究 [J]. 环境污染与防治, 2008, 30(8):52−55. DOI: 10.3969/j.issn.1001-3865.2008.08.014 SHI D Q, ZHANG J, ZHU W, et al. Phytoremediation of oily sludge of shengli oilfield [J]. Environmental Pollution & Control, 2008, 30(8): 52−55.(in Chinese) DOI: 10.3969/j.issn.1001-3865.2008.08.014
[11] 李文娆, 李小利, 张晓, 等. 甜高粱/紫花苜蓿对石油污染土壤的光合适应性研究 [J]. 河南大学学报(自然科学版), 2015, 45(3):327−333. LI W R, LI X L, ZHANG X, et al. Photosynthetic adaptability of sweet Sorghum and alfalfa to crude oil-polluted soils [J]. Journal of Henan University (Natural Science), 2015, 45(3): 327−333.(in Chinese)
[12] ALI M H, KHAN M I, BASHIR S, et al. Biochar and Bacillus sp. MN54 assisted phytoremediation of diesel and plant growth promotion of maize in hydrocarbons contaminated soil [J]. Agronomy, 2021, 11(9): 1795. DOI: 10.3390/agronomy11091795
[13] ZHOU Q X, CAI Z, ZHANG Z N, et al. Ecological remediation of hydrocarbon contaminated soils with weed plant [J]. Journal of Resources and Ecology, 2011, 2(2): 97−105.
[14] 李合生. 植物生理生化实验原理和技术[M]. 北京: 高等教育出版社, 2000. [15] 沈萍, 陈向东. 微生物学实验[M]. 4版. 北京: 高等教育出版社, 2007. [16] 王如刚, 王敏, 牛晓伟, 等. 超声-索氏萃取-重量法测定土壤中总石油烃含量 [J]. 分析化学, 2010, 38(3):417−420. WANG R G, WANG M, NIU X W, et al. Determination of total petroleum hydrocarbons content in soil by ultrasonic-soxhlet extraction-gravimetric analysis [J]. Chinese Journal of Analytical Chemistry, 2010, 38(3): 417−420.(in Chinese)
[17] 赵媛媛, 张万坤, 马慧, 等. 降解菌ZQ5与紫茉莉对芘污染土壤的联合修复 [J]. 环境工程学报, 2013, 7(7):2752−2756. ZHAO Y Y, ZHANG W K, MA H, et al. Microbial-phytoremediation of pyrene contaminated soil using pyrene-degrading strain ZQ5 with Mirabilis Jalapa [J]. Chinese Journal of Environmental Engineering, 2013, 7(7): 2752−2756.(in Chinese)
[18] 刘永军, 曹中利, 贾海燕, 等. 黑麦草-不动杆菌组合体系对石油污染土壤的生物强化修复 [J]. 化工环保, 2018, 38(1):101−105. DOI: 10.3969/j.issn.1006-1878.2018.01.018 LIU Y J, CAO Z L, JIA H Y, et al. Enhanced bioremediation of petroleum-contaminated soil using ryegrass-acinetobacter combination system [J]. Environmental Protection of Chemical Industry, 2018, 38(1): 101−105.(in Chinese) DOI: 10.3969/j.issn.1006-1878.2018.01.018
[19] 欧阳威, 刘红, 于勇勇, 等. 高羊茅对微生物强化修复石油污染土壤影响的研究 [J]. 环境污染治理技术与设备, 2006(1):94−97. OUYANG W, LIU H, YU Y Y, et al. The combined effects of tall fescue(Festuca arundinace) phyto-remediation and bio-augmentation on treatment of oil-contaminated soil [J]. Techniques and Equipment for Environmental Pollution Control, 2006(1): 94−97.(in Chinese)
[20] HOU J Y, LIU W X, WANG B B, et al. PGPR enhanced phytoremediation of petroleum contaminated soil and rhizosphere microbial community response [J]. Chemosphere, 2015, 138: 592−598. DOI: 10.1016/j.chemosphere.2015.07.025
[21] GLICK B R. Using soil bacteria to facilitate phytoremediation [J]. Biotechnology Advances, 2010, 28(3): 367−374. DOI: 10.1016/j.biotechadv.2010.02.001
[22] 胥九兵, 迟建国, 邱维忠, 等. 石油降解菌剂的研制及其在石油污染土壤修复中的应用 [J]. 生物加工过程, 2009, 7(6):21−24. DOI: 10.3969/j.issn.1762-3678.2009.06.004 XU J B, CHI J G, QIU W Z, et al. Application of bacterial agent capable of degrading petroleum for remediation of oil-contaminated soil [J]. Chinese Journal of Bioprocess Engineering, 2009, 7(6): 21−24.(in Chinese) DOI: 10.3969/j.issn.1762-3678.2009.06.004
[23] 王京秀, 张志勇, 万云洋, 等. 植物-微生物联合修复石油污染土壤的实验研究 [J]. 环境工程学报, 2014, 8(8):3454−3460. WANG J X, ZHANG Z Y, WAN Y Y, et al. Experimental study on plant-microbial remediation of oil-contaminated soil [J]. Chinese Journal of Environmental Engineering, 2014, 8(8): 3454−3460.(in Chinese)
[24] 王洪. 多环芳烃污染农田土壤原位生物修复技术研究[D]. 沈阳: 东北大学, 2011. WANG H. Research on In-situ bioremediation for farm soil contaminated with polycyclic aromatic hydrocarbons[D]. Shenyang: Northeastern University, 2011. (in Chinese)
[25] 刘魏魏, 尹睿, 林先贵, 等. 生物表面活性剂-微生物强化紫花苜蓿修复多环芳烃污染土壤 [J]. 环境科学, 2010, 31(4):1079−1084. LIU W W, YIN R, LIN X G, et al. Interaction of biosurfactant-microorganism to enhance phytoremediation of aged polycyclic aromatic hydrocarbons (PAHs) contaminated soils with alfalfa (Medicago sativa L. ) [J]. Environmental Science, 2010, 31(4): 1079−1084.(in Chinese)
[26] 旷远文, 温达志, 钟传文, 等. 根系分泌物及其在植物修复中的作用 [J]. 植物生态学报, 2003, 27(5):709−717. DOI: 10.3321/j.issn:1005-264X.2003.05.020 KUANG Y W, WEN D Z, ZHONG C W, et al. Root exudates and their roles in phytoremediation [J]. Acta Phytoecologica Sinica, 2003, 27(5): 709−717.(in Chinese) DOI: 10.3321/j.issn:1005-264X.2003.05.020
[27] JONES D L, DARRAH P R. Role of root derived organic acids in the mobilization of nutrients from the rhizosphere [J]. Plant and Soil, 1994, 166(2): 247−257. DOI: 10.1007/BF00008338
[28] MARSCHNER H, ROMHELD V, CAKMAK I. Root-induced changes of nutrient availability in the rhizosphere [J]. Journal of Plant Nutrition, 1987, 10(9): 1175−1184. DOI: 10.1080/01904168709363645
[29] LYNCH J M, WHIPPS J M. Substrate flow in the rhizosphere [J]. Plant and Soil, 1990, 129(1): 1−10. DOI: 10.1007/BF00011685
[30] YANG C H, CROWLEY D E. Rhizosphere microbial community structure in relation to root location and plant iron nutritional status [J]. Applied and Environmental Microbiology, 2000, 66(1): 345−351. DOI: 10.1128/AEM.66.1.345-351.2000
[31] 王丽丽, 杨谦. 接种枯草芽孢杆菌和丛枝菌根真菌促进红三叶修复石油污染土壤 [J]. 江苏农业科学, 2016, 44(5):526−529. WANG L L, YANG Q. Inoculating Bacillus subtilis and arbuscular mycorrhizal fungi to promote remediation of oil contaminated soil by Trifolium repens [J]. Jiangsu Agricultural Sciences, 2016, 44(5): 526−529.(in Chinese)
[32] 高乃媛, 刘宪斌, 赵兴茹. 石油烃对翅碱蓬生理特性的影响及植物-微生物联合降解 [J]. 环境工程学报, 2013, 7(4):1578−1582. GAO N Y, LIU X B, ZHAO X R. Influence of oil in soil on growth and physiological indexes of Suaeda heteroptera and plant-microbial remediation [J]. Chinese Journal of Environmental Engineering, 2013, 7(4): 1578−1582.(in Chinese)
[33] 豆胜才. 红平红球菌KB1协同苜蓿降解石油烃的生态学效应[D]. 兰州: 兰州理工大学, 2020. DOU S C. Ecological effect of Rhodococcus erythropolis Kb1 on alfalfa degradation of petroleum hydrocarbons[D]. Lanzhou: Lanzhou University of Technology, 2020. (in Chinese)
[34] 雒晓芳, 陈丽华, 王冬梅, 等. 不同石油浓度对两种作物生理生化的影响 [J]. 生物技术通报, 2016, 32(10):135−140. LUO X F, CHEN L H, WANG D M, et al. The influence for two corps physiological index by the different petroleum density [J]. Biotechnology Bulletin, 2016, 32(10): 135−140.(in Chinese)
[35] 岳冰冰, 李鑫, 任芳菲, 等. 石油污染对紫花苜蓿部分生理指标的影响 [J]. 草业科学, 2011, 28(2):236−240. DOI: 10.3969/j.issn.1001-0629.2011.02.013 YUE B B, LI X, REN F F, et al. Effects of petroleum contamination on some of physiological indexes of alfalfa [J]. Pratacultural Science, 2011, 28(2): 236−240.(in Chinese) DOI: 10.3969/j.issn.1001-0629.2011.02.013
[36] HO C H, BANKS M K. Degradation of polycyclic aromatic hydrocarbons in the rhizosphere of Festuca arundinacea and associated microbial community changes [J]. Bioremediation Journal, 2006, 10(3): 93−104. DOI: 10.1080/10889860600939609
[37] BINET P, PORTAL J M, LEYVAL C. Dissipation of 3-6-ring polycyclic aromatic hydrocarbons in the rhizosphere of ryegrass [J]. Soil Biology and Biochemistry, 2000, 32(14): 2011−2017. DOI: 10.1016/S0038-0717(00)00100-0
[38] ASLANTAŞ R, ÇAKMAKÇI R, ŞAHIN F. Effect of plant growth promoting rhizobacteria on young apple tree growth and fruit yield under orchard conditions [J]. Scientia Horticulturae, 2007, 111(4): 371−377. DOI: 10.1016/j.scienta.2006.12.016
[39] RYU C M, HU C H, LOCY R D, et al. Study of mechanisms for plant growth promotion elicited by rhizobacteria in Arabidopsis thaliana [J]. Plant and Soil, 2005, 268(1): 285−292. DOI: 10.1007/s11104-004-0301-9
[40] BELIMOV A A, DODD I C, HONTZEAS N, et al. Rhizosphere bacteria containing 1-aminocyclopropane-1-carboxylate deaminase increase yield of plants grown in drying soil via both local and systemic hormone signalling [J]. New Phytologist, 2009, 181(2): 413−423. DOI: 10.1111/j.1469-8137.2008.02657.x
-
期刊类型引用(0)
其他类型引用(2)









 下载:
下载: