Somatic incompatibility and genetic difference of Ganoderma sinense
-
摘要:
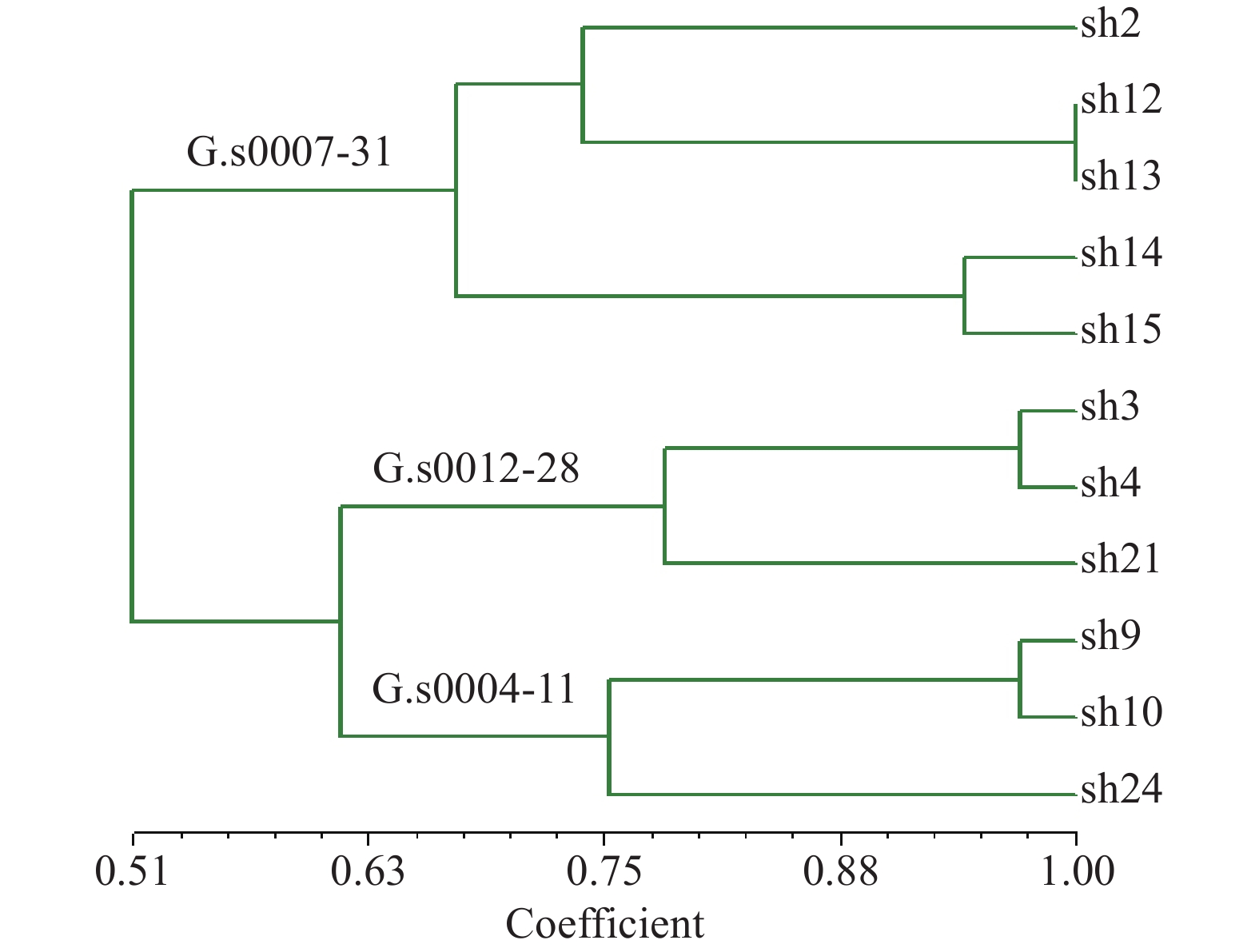
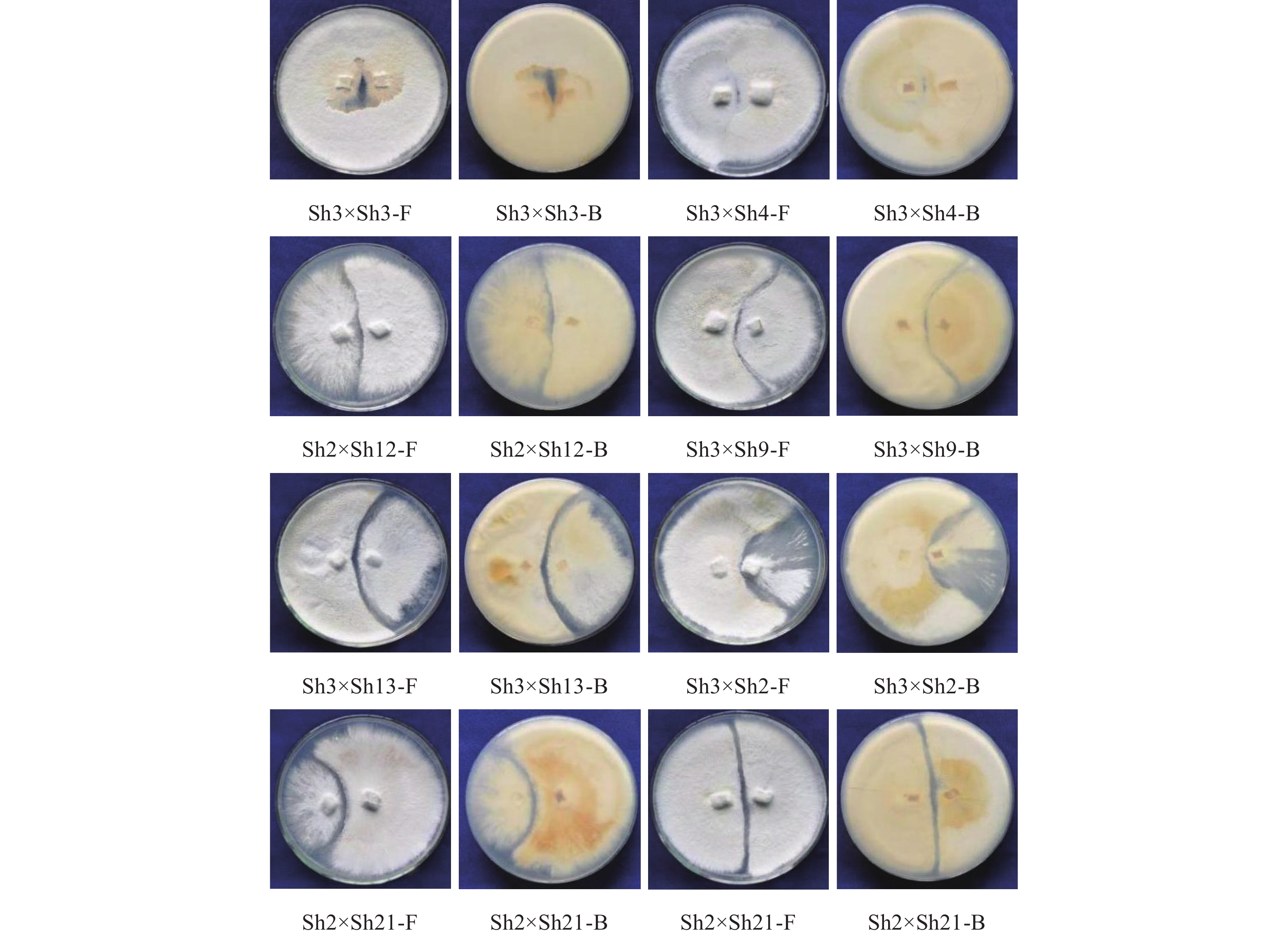
目的 评价紫芝菌株间体细胞不亲和反应与遗传差异的关系,为应用体细胞不亲和性评价紫芝菌株间的遗传差异提供依据。 方法 以7个不同交配基因型的紫芝单核体为亲本,应用单向或者双向核迁移技术构建双核体菌株;通过在PDA培养基配对检测双核体菌株间的体细胞不亲和性,并采用ISSR、RAPD和SRAP 3种分子标记综合分析双核体菌株间的遗传差异。 结果 构建了5类遗传背景清晰的不同双核体菌株11个,它们之间的体细胞不亲性反应分为亲和、不亲和,其中不亲和反应出现隔离区、隔离区带线状和类似墙式结构的3种类型;3种分子标记综合分析显示,11个菌株间的遗传相似系数0.29~0.97,UPMGA聚类树状图能很好的展示11个双核体菌株间的遗传差异,并与亲本来源相一致。 结论 紫芝菌株间的体细胞不亲性反应主要受细胞核的影响,而细胞质的影响极小,并且紫芝菌株间的体细胞不亲性反应类型与菌株间的遗传差异相对应,在以后的紫芝种质资源遗传差异评价中,可应用操作简便的体细胞不亲和性进行初步分析。 Abstract:Objective The relation between somatic incompatibility (SI) and genetic difference of Ganoderma sinense was investigated. This will provide the basis for evaluating genetic differences of G.sinense strains by SI test. Method Construction of dikaryon strains using unidirectional or bidirectional nuclear migration test with seven monokaryon of G.sinense as parents. Then SI reaction was tested on the PDA medium, and the genetic differences between them were analyzed by ISSR, RAPD and SRAP molecular markers. Result Eleven dikaron strains of five types with clear genetic relationship were obtained. The SI reactions were result in compatibility and incompatibility. And the incompatibility emerged three types of gap, gap with line and wall-like structure. The combined analysis of ISSR, RAPD and SRAP molecular markers genetic similarity coefficients ranging from 0.29 to 0.97 among the eleven strains.The UPMGA clustering diagram was able to demonstrate the genetic relationship of eleven trains, and these genetic relationships correspond to those of the parental sources. Conclusion The nucleus has a large effect on the SI response of G.sinense, whereas the cytoplasm has a minimal effect on it. The type of SI reaction of G. sinense strains corresponds to their genetic differences. So in the future evaluation of genetic differences in G. sinense germplasm resources, a simple and convenient method of SI could be applied for preliminary analysis. -
Key words:
- antagonism /
- genetic relationship /
- molecular marker
-
表 1 引物序列
Table 1. sequences of primers used for molecular markers
分子标记
Molecular marker引物
primer序列(5′-3′)
sequences分子标记
Molecular marker引物
primer序列(5′-3′)
sequencesISSR ISSR6 DHB (CGA)5 SRAP ME4 TGAGTCCAAACCGGACC ISSR ISSR17 (TG)8RC SRAP ME5 TGAGTCCAAACCGGAAG ISSR ISSR18 VHV (GT)8 SRAP ME6 TGAGTCCAAACCGGTAG RAPD S17 AGGGAACGAG SRAP EM8 GACTGCGTACGAATTAGC RAPD S18 CCACAGCAGT SRAP EM13 GACTGCGTACGAATTGGT RAPD S367 AGCGAGCAAG SRAP EM14 GACTGCGTACGAATTCAG SRAP ME3 TGAGTCCAAACCGGAAT SRAP EM17 GACTGCGTACGAATTCCA ISSR引物中的单字母简写代表多碱基混合位点。位置: D= (A, G, T), H= (A, C, T), B= (C, G, T), R= (A, G), V= (A, C, G).
Single letter abbreviations of ISSR primers for mixed base. Positions: D= (A, G, T), H= (A, C, T), B= (C, G, T), R= (A, G), V= (A, C, G).表 2 测试菌株信息
Table 2. Information of tested strains
菌株
strain亲本和交配型
Parents and mating types菌株
strain亲本和交配型
Parent and mating typeSh2 G.s0007-31FP A1B7、G.s0011-16 A3B3 Sh13 G.s0007-31 A1B7、G.s0011-3 FP A2B2 Sh3 G.s0011-16 FP A3B3、G.s0012-28 A5B5 Sh14 G.s0007-31 FP A1B7、G.s0012-26 A4B4 Sh4 G.s0011-16 A3B3、G.s0012-28 FP A5B5 Sh15 G.s0007-31 A1B7、G.s0012-26 FP A4B4 Sh9 G.s0004-11 A1B1、G.s0011-16 FP A3B3 Sh21 G.s0011-3 A2B2、G.s0012-28 FP A5B5 Sh10 G.s0004-11 FP A1B1、G.s0011-16 A3B3 Sh24 G.s0004-11 A1B1、G.s0014-36 FP A7B7 Sh12 G.s0007-31 FP A1B7、G.s0011-3 A2B2 FP代表母本。
Female parent (FP).表 3 测试菌株的体细胞不和性与遗传关系
Table 3. Somatic incompatibility and genetic relationship between strains
异核体类别
Type of heterokaryon配对
pairing拮抗信息
Information of antagonism遗传相似系数
Genetic similarity coefficientⅠ 同核异质体
Same dikaryon in different FPSh3×Sh4 - 0.97 Sh12×Sh13 - 0.97 Sh14×Sh15 - 0.95 Ⅱ 细胞质和一个核相同,另一个核不同
one same monokaryon with one different monokaryon in the same FPSh2×Sh14 G+ 0.66 Sh2×Sh12 G+ 0.74 Sh3×Sh9 GL++ 0.66 Ⅲ 细胞质相同,细胞核不同
Different dikaryon in the same FPSh4×Sh15 G+++ 0.46 Sh3×Sh13 G+++ 0.63 Sh9×Sh13 G++ 0.57 Ⅳ 一个核相同,另一个核与细胞质都不同
one same monokaryon with one different monokaryon in different FPSh3×Sh10 GL++ 0.69 Sh2×Sh15 G+ 0.66 Sh3×Sh2 W-l S 0.54 Ⅴ 细胞质和细胞核均不同
Different dikaryon in different FPSh2×Sh21 G++ 0.66 Sh3×Sh14 G+++ 0.49 Sh14×Sh24 G++++ 0.29 FP代表母本;SI反应分为(1)无拮抗-,(2)隔离型G,和(3)隔离型带线状GL和(4)菌丝墙式结构W-l S;“+”表示弱拮抗,“++”中等拮抗,“+++”强拮抗,“++++”非常强拮抗。
Female parent (FP), Three types of SI reaction, (1) no antagonism -, (2) [G] gap, (3) [GL] gap with line (4) hyphal wall-like structure (W-l S). + slight reaction, ++ moderate reaction, +++ strong reaction, ++++ more strong reaction. -
[1] 黄年来, 林志彬, 陈国梁. 中国食药用菌学[M]. 上海: 上海科技文献出版社, 2010: 1623-1673. [1] 黄年来, 林志彬, 陈国良, 等. 中国食药用菌学[M]. 上海: 上海科学技术文献出版社, 2010: 1623-1673. [2] 刘新锐, 王圣铕, 谢宝贵, 等. 紫芝不亲和性因子分析 [J]. 菌物学报, 2014, 33(2):464−468. [2] 刘新锐, 王圣铕, 谢宝贵, 等. 紫芝不亲和性因子分析[J]. 菌物学报, 2014, 33(2): 464-468. Liu X R, Wang S Y, Xie B G, , et al. Incompatibility factors of Ganoderma sinense[J]. Mycosystema, 2014, 33(2): 464-468. (in Chinese)[知网中文][知网英文]Liu X R, Wang S Y, Xie B G, et al. Incompatibility factors of Ganoderma sinense [J]. Mycosystema, 2014, 33(2): 464−468. (in Chinese) [3] Liming T, Chan W , Baokai C , et al. Lanostane triterpenoids from mycelia-associated Ganoderma sinense and their anti-inflammatory activity. [J]. Phytochemistry, 2023, 215: 113870-113870. [3] TENG L M, WANG C, CUI B K, et al. Lanostane triterpenoids from mycelia-associated Ganoderma sinense and their anti-inflammatory activity[J]. Phytochemistry, 2023, 215: 113870. [PubMed] [4] Gao S Y, Zhang P, Zhang C Y, et al. Meroterpenoids from Ganoderma sinense protect hepatocytes and cardiomyocytes from oxidative stress induced injuries[J]. Fitoterapia, 2018, 131: 73-79. [4] GAO S Y, ZHANG P, ZHANG C Y, et al. Meroterpenoids from Ganoderma sinense protect hepatocytes and cardiomyocytes from oxidative stress induced injuries[J]. Fitoterapia, 2018, 131: 73-79. [PubMed] [5] WU N, PENG B, LI T, et al. Rapid Simultaneous Determination of Four Ganoderic Acids in Ganoderma (Chinese Name: Lingzhi) by Direct Infusion–Multiple Reaction Monitoring Cubed[J]. Journal of Analysis and Testing, 2024, 8(1): 52-62. [5] WU N, PENG B, LI T, et al. Rapid simultaneous determination of four ganoderic acids in Ganoderma (chinese Name: Lingzhi) by direct infusion–multiple reaction monitoring cubed[J]. Journal of Analysis and Testing, 2024, 8(1): 52-62. [LinkOut] [6] Mei R Q, Zuo F J, Duan X Y, et al. Ergosterols from Ganoderma sinense and their anti-inflammatory activities by inhibiting NO production[J]. Phytochemistry Letters, 2019, 32: 177-180. [6] MEI R Q, ZUO F J, DUAN X Y, et al. Ergosterols from Ganoderma sinense and their anti-inflammatory activities by inhibiting NO production[J]. Phytochemistry Letters, 2019, 32: 177-180. [LinkOut] [7] Jiang Y F, Chang Y J, Liu Y, et al. Overview of Ganoderma sinense polysaccharide-an adjunctive drug used during concurrent Chemo/Radiation therapy for cancer treatment in China[J]. Biomedicine & Pharmacotherapy, 2017, 96: 865-870. [7] JIANG Y F, CHANG Y J, LIU Y, et al. Overview of Ganoderma sinense polysaccharide-an adjunctive drug used during concurrent Chemo/Radiation therapy for cancer treatment in China[J]. Biomedicine & Pharmacotherapy = Biomedecine & Pharmacotherapie, 2017, 96: 865-870. [PubMed] [8] HAN W, CHEN H, ZHOU L, et al. Polysaccharides form Ganoderma Sinense-rice bran fermentation products and their anti-tumor activities on non-small-cell lung cancer [J]. BMC Complement Medicine Therap1es, 2021, 21(1): 169. [8] HAN W, CHEN H J, ZHOU L, et al. Polysaccharides from Ganoderma Sinense - rice bran fermentation products and their anti-tumor activities on non-small-cell lung cancer[J]. BMC Complementary Medicine and Therapies, 2021, 21(1): 169. [PubMed] [9] Lind M, Stenlid J, Olson A. Genetics and QTL mapping of somatic incompatibility and intraspecific interactions in the basidiomycete Heterobasidion annosum s. l[J]. Fungal Genetics and Biology, 2007, 44 (12): 1242-1251. [9] LIND M, STENLID J, OLSON A. Genetics and QTL mapping of somatic incompatibility and intraspecific interactions in the basidiomycete Heterobasidion annosum s. l[J]. Fungal Genetics and Biology: FG & B, 2007, 44(12): 1242-1251. [PubMed] [10] Marcais B, Caël O, Delatour C. Genetics of somatic incompatibility in Collybia fusipes[J]. Mycological Research, 2000, 104 (3): 304-310. [10] MARCAIS B, CAËL O, DELATOUR C. Genetics of somatic incompatibility in Collybia fusipes[J]. Mycological Research, 2000, 104(3): 304-310. [LinkOut] [11] 唐传红, 张劲松, 陈明杰, 等. 利用拮抗试验和RAPD对灵芝属菌株进行分类研究 [J]. 微生物学通报, 2005, 32(5):72−76. [11] 唐传红, 张劲松, 陈明杰, 等. 利用拮抗试验和RAPD对灵芝属菌株进行分类研究[J]. 微生物学通报, 2005, 32(5): 72-76. TANG C H, ZHANG J S, CHEN M J, et al. Study on classification of strains of Ganoderma by anatagonistic effect and rapd[J]. Microbiology, 2005, 32(5): 72-76. (in Chinese)[知网中文][知网英文] doi: 10.3969/j.issn.0253-2654.2005.05.015Tang C H, Zhang J S, Chen M J, et al. Study on classification of strains of Ganoderma by anatagonistic effect and Rapd [J]. Microbiology China, 2005, 32(5): 72−76. (in Chinese) doi: 10.3969/j.issn.0253-2654.2005.05.015 [12] 李黎. 中国木耳栽培种质资源的遗传多样性研究[D]. 武汉: 华中农业大学, 2016[12] 李黎. 中国木耳栽培种质资源的遗传多样性研究[D]. 武汉: 华中农业大学, 2011. LI L. Studies on Genetic Diversity of Auricularia Auricula-judae Cultivated Germplasm Resources in China[D]. Wuhan: Huazhong Agricultural University, 2011. (in Chinese)[知网博士中文][知网博士英文] [13] 张瑞颖. 香菇菌株多相鉴定鉴别技术研究[D]. 北京: 中国农业大学, 2004[13] 张瑞颖. 香菇菌株多相鉴定鉴别技术研究[D]. 北京: 中国农业大学, 2004. ZHANG R Y. Study on Polyphasic Strain-typing Technique of Lentinula Edodes[D]. Beijing: China Agricultural University, 2004. (in Chinese)[知网硕士中文][知网硕士英文] [14] 刘靖宇, 宋秀高, 叶夏, 等. 香菇菌株遗传多样性ISSR、RAPD和SRAP综合分析 [J]. 食用菌学报, 2011, 18(3):1−8. [14] 刘靖宇, 宋秀高, 叶夏, 等. 香菇菌株遗传多样性ISSR、RAPD和SRAP综合分析[J]. 食用菌学报, 2011, 18(3): 1-8. LIU J Y, SONG X G, YE X, et al. Differentiation of Lentinula edodes Strains Using ISSR, RAPD and SRAP markers[J]. Acta Edulis Fungi, 2011, 18(3): 1-8. (in Chinese)[知网中文][知网英文] doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1005-9873.2011.03.001Liu J Y, Song X G, Ye X, et al. Differentiation of Lentinula edodes strains using ISSR, RAPD, SRAP markers [J]. Acta Edulis Fungi, 2011, 18(3): 1−8. (in Chinese) doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1005-9873.2011.03.001 [15] 徐珍, 章炉军, 尚晓冬, 等. 金针菇品种 DUS 测试性状的分级与评价[J]. 菌物学报, 2019, 38(5): 658-668[15] 徐珍, 章炉军, 尚晓冬, 等. 金针菇品种DUS测试性状的分级与评价[J]. 菌物学报, 2019, 38(5): 658-668. XU Z, ZHANG L J, SHANG X D, et al. Gradation and evaluation for Flammulina filiformis DUS testing traits[J]. Mycosystema, 2019, 38(5): 658-668. (in Chinese)[知网中文][知网英文]Xu Z, Zhang L J, Shang X D, et al. Gradation and evaluation for Flammulina filiformis DUS testing traits[J]. Mycosystema, 2019, 38 (5): 658-668. (in Chinese) [16] 刘靖宇, 刘新锐, 邓优锦, 等. 双向核迁移在香菇遗传和育种中的应用研究[J]. 菌物学报, 2011, 30(5): 774-781. [16] 刘靖宇, 刘新锐, 邓优锦, 等. 双向核迁移在香菇遗传和育种中的应用研究[J]. 菌物学报, 2011, 30(5): 774-781. LIU J Y, LIU X R, DENG Y J, et al. The application of the ‘bidirectional haploid nuclei migration’ in breeding and genetics of Lentinula edodes[J]. Mycosystema, 2011, 30(5): 774-781. (in Chinese)[知网中文][知网英文]Liu J Y, Liu X R, Deng Y J, et al. The application of the ‘bidirectional haploid nuclei migration’ in breeding and genetics of Lentinula edodes. [J] Mycosystema, , 2011, 30(5): 774-781. (in Chinese) [17] Caten C. Vegetative incompatibility and cytoplasmic infection in fungi[J]. Microbiology, 1972, 72(2): 221-229. [17] CATEN C E. Vegetative incompatibility and cytoplasmic infection in fungi[J]. Journal of General Microbiology, 1972, 72(2): 221-229. [PubMed] [18] Worrall JJ. Somatic incompatibility in basidionycetes[J]. Mycologia, 1997, 89 (1): 24-36. [18] WORRALL J J. Somatic incompatibility in basidiomycetes[J]. Mycologia, 1997, 89(1): 24-36. [LinkOut] [19] Giovannetti M, Sbrana C, Strani P, et al. Genetic diversity of isolates of Glomus mosseae from different geographic areas detected by vegetative compatibility testing and biochemical and molecular analysis[J]. Apply Environment Microbiology, 2003, 69: 616-624. [19] GIOVANNETTI M, SBRANA C, STRANI P, et al. Genetic diversity of isolates of Glomus mosseae from different geographic areas detected by vegetative compatibility testing and biochemical and molecular analysis[J]. Applied and Environmental Microbiology, 2003, 69(1): 616-624. [PubMed] [20] May G. Somatic incompatibility and individualism in the coprophilous basidiomycete[J], Coprinus cinereus. Transactions of the British Mycological Society, 1988, 91 (3): 443-451. [20] MAY G. Somatic incompatibility and individualism in the coprophilous Basidiomycete, Coprinus cinereus[J]. Transactions of the British Mycological Society, 1988, 91(3): 443-451. [LinkOut] [21] Hansen EM, Stenlid J, Johansson M. Genetic control of somatic incompatibility in the root-rotting basidiomycete Heterobasidion annosum[J]. Mycological Research , 1993, 97 (10): 1229-1233. [21] HANSEN E M, STENLID J, JOHANSSON M. Genetic control of somatic incompatibility in the root-rotting basidiomycete Heterobasidion annosum[J]. Mycological Research, 1993, 97(10): 1229-1233. [LinkOut] -







 下载:
下载: