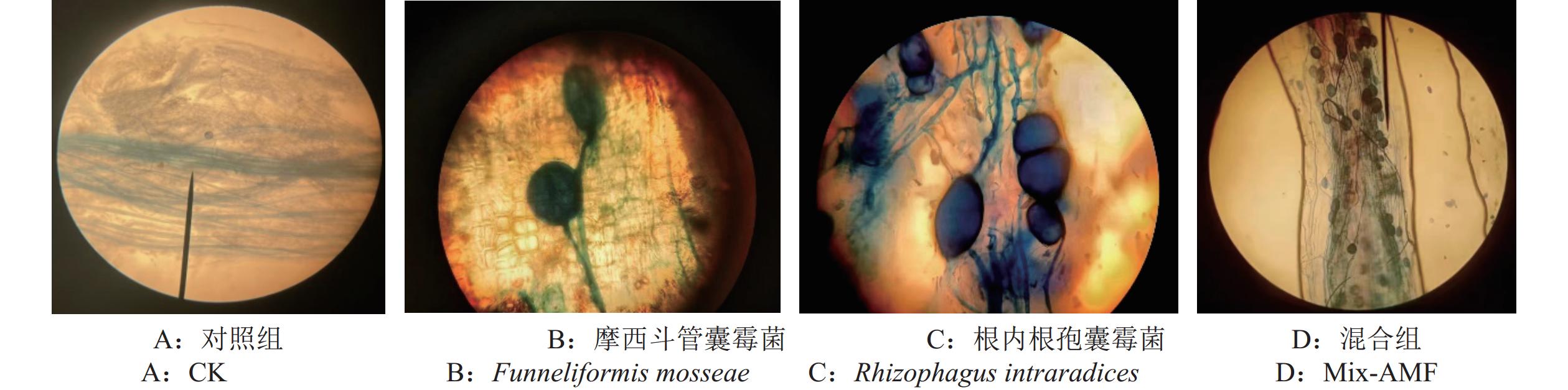
Seedling Growth and Secondary Metabolism of Taxus chinensis as Affected by Arbuscular Mycorrhizal Fungi
-
摘要:目的
研究丛枝菌根真菌(arbuscular mycorrhizal fungi, AMF)对南方红豆杉苗期生长及次生代谢的影响,揭示南方红豆杉与AMF的共生关系,为南方红豆杉的种植和利用提供科学依据。
方法以南方红豆杉幼苗(Taxus wallichiana var. Mairei)为材料,盆栽试验条件下,在其根部接种根内根孢囊霉菌(Rhizophagus intraradices)和摩西斗管囊霉菌(Funneliformis mosseae)以及两菌种的混合菌剂,本试验接种与种植同步进行。研究AMF对南方红豆杉苗期的苗高、主根长、地径等植物生长指标、土壤理化性质以及次生代谢物紫杉醇含量的影响。
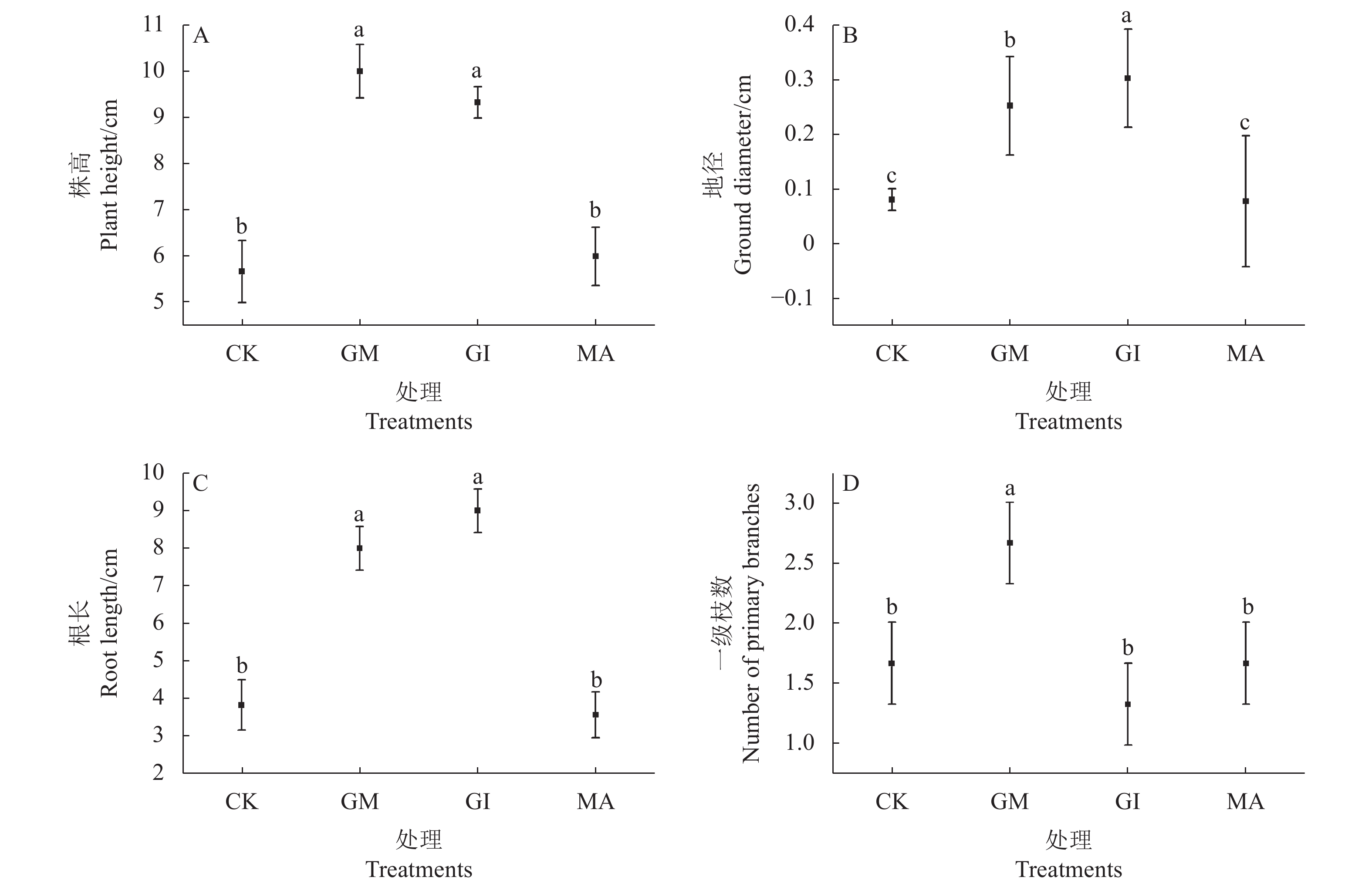
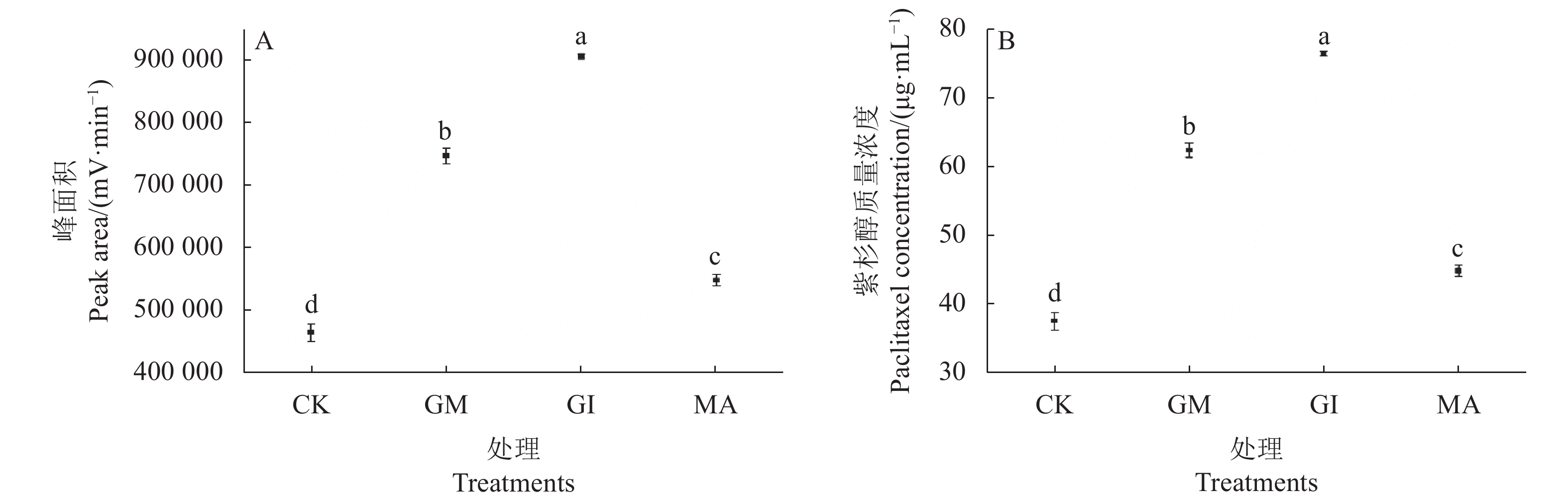
结果(1)接种AMF能显著促进南方红豆杉苗木株高、地径、根长和一级枝数的增长,其中接种R. intraradices和F. mosseae对株高和根长的增长达到显著水平,接种R. intraradices对地径的增长效果最显著,接种F. mosseae对一级枝数的增加效果最好;(2)AMF的生长指标与土壤速效磷含量、土壤碱解氮和土壤速效钾含量等土壤理化性质显著相关,其中侵染率与速效磷呈现显著负相关性(P<0.05),而其他指标例如碱解氮、速效钾等与生长指标均呈显著相关(P<0.05);(3)接种AMF均能显著提高紫杉醇的含量,其中接种R. intraradices 效果最好。
结论根内根孢囊霉菌与南方红豆杉的共生模式更能促进其生长和次生代谢产物的积累。
Abstract:ObjectiveThe symbiotic effects of the arbuscular mycorrhizal fungi (AMF) on the growth and secondary metabolism of Taxus chinensis seedlings were investigated.
MethodRhizosphere soil of T. chinensis seedlings were artificially inoculated with the AMF, Rhizophagus intraradices and/or Funneliformis mosseae, as the plants were growing in a pot experiment. Seedling growth measured by the plant height, primary root length, and underground girth as well as plant secondary metabolite paclitaxel and physicochemical qualities of the soil were monitored.
Result(1) The AMF inoculation significantly raised the height, underground stem diameter, root length, and number of primary branches of the seedlings. Simultaneously applying R. intraradices and F. mosseae significantly increased the height and root length of the seedlings. Individually, R. intraradices rendered the most significant effect on the growth of underground plant parts, while F. mosseae on the number of top-graded branches. (2) AMF proliferation was affected by the chemical composition of the soil with the infecting rate significantly correlated negatively with the quick-acting phosphorus (P<0.05) and positively with the alkali soluble nitrogen and quick-acting potassium (P<0.05). And (3) the presence of AMF, especially R. intraradices, in the rhizosphere soil significantly heightened the paclitaxel secretion.
ConclusionThe symbiosis between T. chinensisand R. intraradices, more than that between T. chinensis and F. mosseae, significantly enhanced the growth and secondary metabolism of the seedlings.
-
Keywords:
- Arbuscular mycorrhizal fungi /
- Taxus chinensis /
- secondary metabolism /
- paclitaxel /
- interactions
-
0. 引言
【研究意义】猪流行性腹泻(porcine epidemic diarrhea, PED)是由猪流行性腹泻病毒(porcine epidemic diarrhea virus, PEDV)引起的一种接触性传染性病,临床表现和猪传染性胃肠炎极其相似,表现为以水样便腹泻、呕吐和脱水为主要表征的肠道疾病。该病可以感染所有日龄阶段的猪,尤其是新生仔猪,一旦发病,其死亡率高达100%[1]。1971年PED在欧洲首次被报道,随后蔓延到世界许多地区;2010年我国多个省份突然爆发了PED,美国、加拿大和墨西哥也大规模爆发,仅2014年就导致美国近千万头仔猪死亡,占美国所有仔猪的近十分之一[2],给全球生猪养殖业带来了巨大的经济损失。PEDV是一种单股、正链RNA病毒,具有冠状结构特征。全基因组约长28 kb,包括5′端帽、5′和3′非翻译区、3′poly-A 尾部以及7个开放阅读框[3]。ORF2和ORF4~6编码4种结构蛋白,包括S、E、M和N蛋白。其中,S蛋白是PEDV主要的免疫蛋白,在PEDV存活和逃避宿主免疫中起着至关重要的作用,为机体产生中和抗体的主要蛋白,在免疫监测中处于优先地位[4]。利用S蛋白建立PEDV快速检测方法具有较高的可行性。【前人研究进展】PEDV的检测方法主要包括病毒分离鉴定、中和试验、酶联免疫吸附试验等[5]。这些方法虽然灵敏性和特异性均较高,但在现实操作中过程繁琐、时间长、仪器价格昂贵、需要专业人员才能操作,而且ELISA试剂盒多为进口,成本高[6]。重组酶介导核酸等温扩增(RAA)是一种新型检测技术,具有快速、简单、低成本等优点,不需要复杂的热环境,在恒温条件下就能快速检测,相对于其他检测方法,优势显著[7]。近年来,该方法在病毒、细菌的研究中得到成功应用。Mao等[8]研究报道,猴痘病毒(monkeypox virus, MPXV)在RAA中对于其他痘病毒,如牛痘病毒(vaccinia virus, VACV)具有特异性和非交叉反应性。Nie等[9]报道采用乙脑病毒(japanese encephalitis virus, JEV)的RT-RAA方法对母猪流产胎儿和公猪的肿胀睾丸样本进行检测,检出率仅为6.49%。此外,RAA还被应用于人类疾病检测。Zhao等[10]采用RAA方法对人泌尿生殖系统中的血吸虫进行检测,与尿液显微镜检查具有100%的一致性。【本研究切入点】对于利用PEDV的S蛋白建立RT-RAA检测方法目前尚未见报道。【拟解决的关键问题】本研究根据PEDV S基因的高度保守区,设计多对引物和探针,建立针对PEDV 的S基因荧光RT-RAA检测方法,测定其敏感性、特异性和重复性,并进行临床初步应用,为研究PED的诊断与防控提供技术支撑。
1. 材料与方法
1.1 病毒及临床样品
PEDV以及猪传染性胃肠炎病毒(porcine transmissible gastroenteritis virus, TGEV)、猪瘟病毒(classical swine fever virus, CSFV)、伪狂犬病病毒(porcine pseudorabies virus, PRV)、猪繁殖与呼吸综合征病毒(porcine reproductive and respiratory syndrome virus, PRRSV)、猪轮状病毒(porcine rotavirus, PoRV)等猪源病毒由福建省农业科学院畜牧兽医研究所收集保存;40份疑似PEDV感染临床样品为2020–2024年采自福建省19个家庭农场(表1)。
表 1 疑似猪流行性腹泻病料收集的来源信息Table 1. Information source and collection of suspected porcine epidemic diarrhea specimens地区
Region样本数(份)/来源猪场(个)
Samples/Farms宁德 Ningde 5/2 三明 Sanming 6/2 龙岩 Longyan 10/6 漳州 Zhangzhou 8/3 莆田 Putian 11/6 合计 Total 40/19 1.2 主要试剂
pMD19-T购自TaKaRa公司;Trelief5α感受态细胞购自擎科公司;引物和探针均由亚尚生物工程有限公司合成;RT-RAA核酸扩增试剂盒(荧光型)购自杭州众测生物科技有限公司;高保真聚合酶购自诺唯赞生物公司;质粒提取试剂盒及胶回收试剂盒购自艾科瑞公司。
1.3 引物及探针的设计与筛选
从GenBank基因数据库中下载25株PEDV的S基因序列,通过DNAMAN生物信息学软件分析PEDV的S基因的高度保守区域(图1),利用Primer 5.0软件对PEDV的S基因设计多对引物、探针。引物、探针信息见表2。
表 2 引物和探针Table 2. Primers and probes名称
Name序列(5′-3′)
SequencePEDV S-DF AAATCTGGCAGTATTGGCTAC PEDV S-DR ATCGGCTGAAAGAATGTCC PEDV S-F1 TATTCCCACCAACTTTAGTATGAGTATTAG PEDV S-F2 GTATTCCCACCAACTTTAGTATGAGTATTA PEDV S-F3 AGTATTCCCACCAACTTTAGTATGAGTATT PEDV S-R1 TAATGCTGACTCTATGGTCTTACATGCTGC PEDV S-R2 GTTGTAATGCTGACTCTATGGTCTTACATG PEDV S-R3 TGTAATGCTGACTCTATGGTCTTACATGCT PEDV S-P GACAGAATATTTACAGCTTTACAACACGCC(i6FAMdT)(THF)(iBHQ1dT)TAGTGTTGATTGTGC-C3spacer 1.4 核酸的提取
按照核酸提试剂盒说明书, 提取PEDV、TGEV、CSFV、PRV、PCV、PRRSV、PoRV核酸,并保存于–80 ℃备用。
1.5 重组质粒标准品的构建
根据PEDV S基因序列设计引物(PEDV-DF/DR),以逆转录cDNA为模板进行PCR扩增,预期扩增产物大小为969 bp。将胶回收的产物与pMD19-T载体连接,经PCR检测后,送至生工生物工程(上海)股份有限公司测序鉴定,重组质粒经测序正确后作为标准质粒。通过分光光度计测定浓度,计算拷贝数。
1.6 RT-RAA反应体系
根据荧光型RT-RAA核酸扩增试剂盒说明书,配置50.0 μL反应体系,包括buffer A缓冲液25.0 μL、引物F(10 μmol·L−1)2.0 μL、引物R(10 μmol·L−1)2.0 μL、探针(10 μmol·L−1)0.6 μL、buffer B缓冲液2.5 μL、样本5.0 μL,最后加ddH2O至50.0 μL。混匀后10 s低速离心,荧光定量PCR仪测定吸光值。
1.7 引物筛选及反应条件优化
将构建好的标准质粒作为模板,设置不同上、下游引物组合处理,筛选出起峰时间最早、荧光信号最强的最佳引物对;确定最佳引物后,以标准质粒作为模板,在37、39、42 ℃下反应20 min,确定最佳反应温度;采用确定的最佳试验条件,将反应时间设定为17、20、25 min进行RT-RAA反应,确定最佳反应时间。
1.8 特异性试验
通过建立的RT-RAA检测方法对TGEV、CSFV、PRV、PCV、PRRSV、PoRV病毒核酸进行检测,评价方法的特异性。
1.9 重复性试验
以102 、103、105拷贝·μL−1的3种标准质粒浓度作为模板进行荧光RT-RAA反应,重复3次,以评估检测方法的重复性。
1.10 灵敏度试验
将标准质粒用无核酸酶水进行10倍倍比稀释,选用100~106标准质粒作为模板进行RT-RAA反应,评价方法的敏感性。
1.11 临床检测
利用本研究所建立的荧光RT-RAA检测方法和Ren等[11]建立的实时荧光定量PCR检测方法,对2020–2024年采集的40份猪组织样品进行检测,比较两者检测结果。
2. 结果与分析
2.1 重组标准质粒的鉴定
以引物PEDV-DF/DR进行PCR扩增,结果(图2)显示在969 bp左右有目的条带,和预期结果一致。测序结果显示重组标准质粒构建成功,经测定其质量浓度为47.1 ng·μL−1,拷贝数为4.43×1010。
2.2 最佳引物对及反应条件优化
通过上、下游引物不同组合,进行实时荧光RT-RAA检测,结果(图3)显示,F3/R3引物对的扩增效果最好。通过比较不同温度条件下的起峰时间、荧光信号,结果(图4)显示,当反应温度为42 ℃时,扩增曲线效果最好。通过比较不同时间下的反应强度,结果(图5)显示,当反应时间为20 min时,扩增曲线效果最好。因此,选择42 ℃下作用20 min为最适反应条件。

2.3 特异性试验
以PEDV及TGEV、CSFV、PRV、PCV、PRRSV、PoRV的核酸为模板,进行RT-RAA荧光扩增,结果(图6)显示,PEDV产生明显荧光信号,判定为阳性,而其他均无扩增曲线,判为阴性,表明该方法具有很好的特异性。
2.4 重复性试验
以102、103和105拷贝·μL−1的标准质粒为模板。通过建立的荧光RT-RAA进行的重复性试验,结果(图7)显示,相同浓度标准质粒的差异很小,说明本试验所建立的荧光RT-RAA具有良好的重复性。
2.5 灵敏度试验
将标准质粒进行10倍倍比稀释,以100~106为模板进行RT-RAA 扩增,结果(图8)显示,随着标准质粒拷贝数的降低,出峰时间逐渐延长,荧光强度逐渐减弱,最低检出拷贝数为102拷贝数,与常规RT-PCR[12]相比较,PEDV荧光RT-RAA检测方法的最低检出拷贝数是常规RT-PCR检测方法的
1000 倍。表明该RT-RAA检测方法具有较高的灵敏度。2.6 临床样品检测
利用本试验所建立的PEDV RT-RAA检测方法对40份临床样本进行检测,结果(表3)显示,3份样品为阳性,阳性率7.5%,与RT-qPCR方法结果相同,说明本试验建立的荧光RT-RAA检测方法,适用于对PEDV的临床检测。
表 3 临床样本的检测Table 3. Detection on clinical samples方法
Method阳性样品
Number of
positives/份阴性样品
Number of
negatives/份总数
Total/份阳性率
Positivity
rate/%RT-RAA 3 37 40 7.5 RT-qPCR 3 37 40 7.5 3. 讨论与结论
PED具有很强的传染性,在全球许多地区的感染率和死亡率均较高,给生猪养殖业造成重大经济损失[13]。目前,虽然有许多上市的PED疫苗,包括灭活疫苗、减毒活疫苗和亚单位疫苗等,但PEDV在长期的流行期间,会适应不同的地区环境[14]。PEDV研究的最新进展指出,目前尚无特有效的疫苗来防控该病[15],PEDV仍然对养猪业的健康造成严重威胁。
近年来,许多学者建立了多种PEDV检测方法,主要包括RT-PCR、RT-qPCR和LAMP等。俞正玉等[16]建立的PRDV的RT-PCR检测方法,最低可检测出103 ng·μL−1的PEDV样品,对华东地区采集的318份样品进行检测,PEDV阳性率为34.3%。Song等[17]建立了可同时检测包含PEDV在内的4种常见猪病的TaqMan多重荧光定量RT-PCR方法,最低检测下限为101拷贝·μL−1。Li等[18]建立并优化了一种PEDV RT-LAMP检测法,通过加入SYBR Green I荧光染料对PEDV进行检测,在61.9 ℃、59 min或80 ℃、3 min即可完成检测,灵敏度要比传统的RT-PCR高100倍。这些方法特异性和灵敏度虽然较高,但由于其操作繁琐、检测时间长、专业性强、不适合快速临床检测。RT-RAA检测方法是近年来兴起的一种检测方法,能够克服以上检测方法检测时间长、操作繁琐等局限性,并已应用于多种病毒检测,如猪轮状病毒(PoRV)[19]、猪繁殖与呼吸综合征病毒(PRRSV)[20]、禽流感病毒(avian influenza virus, AIV)[21]等。在建立RT-RAA检测方法的过程中,引物和探针的选择与设计十分重要,但目前尚无专门的设计程序。因此,建立RT-RAA检测方法重中之重在于引物、探针的筛选。本研究对多株PEDV S蛋白序列进行比对,选择较为保守的区域设计了3对引物和1个探针,通过自由组合筛选出最佳引物对。此外,在RT-RAA反应体系化中,对反应温度的优化也十分重要,本研究将最佳引物温度逐渐提高至42 ℃后,起峰速度、荧光信号均明显增强,因此选择42 ℃为最佳反应温度,这样大大地提高了检测效率。
综上所述,本研究所建立的PEDV RT-RAA检测方法具有灵敏度强、特异性高和重复性好的特点,极大压缩了检测时间和成本,很适合基层对PEDV的快速检测,具有广泛的应用前景。
-
表 1 不同 AM 真菌的土壤理化性质(平均值+标准误)
Table 1 Soil physicochemical properties under AMF treatments (mean+SE)
处理
Treatment酸碱度
pH含水量
Moisture
content/%速效钾
Rapidly available
potassium/
(μg·mL−1)碱解氮
Alkali hydrolyzable
nitrogen/
(mg·kg−1)速效磷
Rapidly available
phosphorus/
(mg·L−1)侵染率
Colonization
rate/%CK 6.57±0.52b 41.02±3.61a 1.46±0.56c 1.58±0.76b 6.13±0.12a 2.03±0.10c GM 6.01±0.29d 41.12±5.33a 1.76±0.25b 2.85±1.16a 4.67±0.05b 18.56±5.81b GI 6.31±0.92c 42.09±1.94a 2.14±0.38a 3.11±3.16a 4.48±0.50b 28.34±3.35a MA 6.99±0.32a 41.27±3.47a 1.81±1.20b 1.93±1.91b 6.88±0.13a 17.82±9.07b 同一列数据后字母不同者表示差异显著(P < 0.05)。
Date with different letters are significantly different (P < 0.05) in the same column.表 2 土壤理化性质与生长指标相关性分析
Table 2 Correlation between soil physicochemical property and seedling growth
项目
Item速效钾
Rapidly
available
potassium碱解氮
Alkali
hydrolyzable
nitrogen速效磷
Rapidly
available
phosphorus酸碱度
pH侵染率
Colonization
rate根长
Root
length地径
Ground diameter株高
Plant
height速效钾 Rapidly available potassium 1 碱解氮 Alkali hydrolyzable nitrogen 0.618* 1 速效磷 Rapidly available phosphorus −0.493 −0.818** 1 酸碱度 pH −0.230 −0.559 0.814** 1 侵染率 Colonization rate 0.855** 0.789** −0.618* −0.336 1 根长 Root length 0.683* 0.812** −0.868** −0.795** 0.747** 1 地径 Ground diameter 0.709** 0.868** −0.883** −0.781** 0.821** 0.917** 1 株高 Plant height 0.534 0.782** −0.837** −0.795** 0.621* 0.845** 0.878** 1 *表示显著相关(P < 0.05),**表示极显著相关P < 0.01。
* Indicates significant correlation at P<0.05; **Indicates extremely significant correlation at P<0.01. -
[1] 张淑彬, 王幼珊, 殷晓芳, 等. 不同施磷水平下AM真菌发育及其对玉米氮磷吸收的影响 [J]. 植物营养与肥料学报, 2017, 23(3):649−657. DOI: 10.11674/zwyf.16406 ZHANG S B, WANG Y S, YIN X F, et al. Development of arbuscular mycorrhizal(AM) fungi and their influences on the absorption of N and P of maize at different soil phosphorus application levels [J]. Journal of Plant Nutrition and Fertilizer, 2017, 23(3): 649−657. (in Chinese) DOI: 10.11674/zwyf.16406
[2] 索炎炎, 张翔, 司贤宗, 等. 丛枝菌根真菌和根瘤菌对连作花生养分吸收及土壤微生物特性的影响[J]. 中国土壤与肥料, 2023,(2): 106-112. SUO Y Y, ZHANG X, SI X Z , et al. Effects of mycorrhizal fungi and rhizobacteria on nutrient uptake and soil microbial properties of continuous peanut[J]. Soil and Fertilizer Sciences in China, 2023,(2): 106-112. (in Chinese)
[3] 徐玲霞, 柳巧, 王景仪, 等. 南方红豆杉内生真菌多样性及内生真菌对紫杉醇和中间产物含量的影响 [J]. 植物资源与环境学报, 2022, 31(4):50−56. DOI: 10.3969/j.issn.1674-7895.2022.04.06 XU L X, LIU Q, WANG J Y, et al. Diversity of endophytic fungi in Taxus wallichiana var. mairei and effects of endophytic fungi on contents of taxol and intermediates [J]. Journal of Plant Resources and Environment, 2022, 31(4): 50−56. (in Chinese) DOI: 10.3969/j.issn.1674-7895.2022.04.06
[4] 时光黎. 天目山地区南方红豆杉种子命运的研究[D]. 南京: 南京林业大学, 2010. SHI G L. Study on the seed fate of Taxus mairei in Tianmu Mountain area[D]. Nanjing: Nanjing Forestry University, 2010. (in Chinese)
[5] LUN B S, SHAO L W, WANG Y, et al. Taxanes from Taxus wallichiana var. mairei cultivated in the southern area of the Yangtze River in China [J]. Natural Product Research, 2017, 31(20): 2341−2347. DOI: 10.1080/14786419.2017.1305381
[6] 王海娟. 菌剂与肥料配施对露天矿排土场土壤养分含量及紫花苜蓿生长的影响[D]. 呼和浩特: 内蒙古大学, 2014 WANG H J. Effects of combined application of microbial inoculum and fertilizer on soil nutrient content and alfalfa growth in open pit dump[D]. Hohhot: Inner Mongolia University, 2014. (in Chinese)
[7] 马放, 苏蒙, 王立, 等. 丛枝菌根真菌对小麦生长的影响 [J]. 生态学报, 2014, 34(21):6107−6114. MA F, SU M, WANG L, et al. Effects of Arbuscular mycorrhizal fungi(AMF) on the growth of wheat [J]. Acta Ecologica Sinica, 2014, 34(21): 6107−6114. (in Chinese)
[8] 耿云芬, 邱琼, 卯吉华, 等. 铁力木幼苗接种丛枝菌根菌剂的效应[J]. 林业科技开发, 2015.29(5): 64-66. GENG Y F, QIU Q, MAO J H, et al. Effects of inoculation of Tilikum seedlings with mycorrhizal fungicides[J]. China Forestry Science and Technology, 2015.29(5): 64-66. (in Chinese)
[9] 徐志荣, 赵英杰, 王婷, 等. 真菌诱导子对南方红豆杉细胞生长及紫杉醇合成的影响 [J]. 湖北农业科学, 2017, 56(17):3283−3286. XU Z R, ZHAO Y J, WANG T, et al. Effects of fungus elicitor on the cells growth and paclitaxel accumulation of Taxus chinensis var. mairer [J]. Hubei Agricultural Sciences, 2017, 56(17): 3283−3286. (in Chinese)
[10] 陈易展, 刘蔚漪, 张玉薇, 等. 南方红豆杉濒危现状分析与保护对策 [J]. 林业勘察设计, 2018(3):66−69. CHEN Y Z, LIU W Y, ZHANG Y W, et al. The endangered status analysis and protection countermeasures of Taxus chinensis var. mairei [J]. Forestry Prospect and Design, 2018(3): 66−69. (in Chinese)
[11] 付晓峰, 张桂萍, 张小伟, 等. 溶磷细菌和丛枝菌根真菌接种对南方红豆杉生长及根际微生物和土壤酶活性的影响 [J]. 西北植物学报, 2016, 36(2):353−360. FU X F, ZHANG G P, ZHANG X W, et al. Effects of PSB and amf on growth, microorganisms and soil enzyme activities in the rhizosphere of Taxus chinensis var. mairei seedlings [J]. Acta Botanica Boreali-Occidentalia Sinica, 2016, 36(2): 353−360. (in Chinese)
[12] PHILLIPS J M, HAYMAN D S. Improved procedures for clearing roots and staining parasitic and vesicular-arbuscular mycorrhizal fungi for rapid assessment of infection [J]. Transactions of the British Mycological Society, 1970, 55(1): 158−IN18. DOI: 10.1016/S0007-1536(70)80110-3
[13] 许伊蕾, 张静雪, 李合义, 等. 土壤分析新、旧标准方法对水分定义的区别与应用 [J]. 农家参谋, 2018(6):17. XU Y L, ZHANG J X, LI H Y, et al. Difference and application of new and old standard methods for soil analysis on the definition of moisture [J]. The Farmers Consultant, 2018(6): 17. (in Chinese)
[14] 任奕蒙. 弱酸性土壤有效磷测定中两种检测方法的对比 [J]. 山西化工, 2023, 43(4): 79−80, 93. REN Y M. Comparison of two detection methods for the determination of effective phosphorus in weakly acidic soil [J]. Shanxi Chemical Industry, 2023, 43(4): 79−80, 93. (in Chinese)
[15] 宋惠洁, 胡丹丹, 邬磊, 等. 长期有机无机肥配施下玉米氮素利用率和红壤碱解氮含量的阶段性变化 [J]. 植物营养与肥料学报, 2022, 28(11):2030−2040. SONG H J, HU D D, WU L, et al. Stage changes of nitrogen utilization and alkaline nitrogen content of red soil in maize under long-term organic and inorganic fertilization [J]. Journal of Plant Nutrition and Fertilizers, 2022, 28(11): 2030−2040. (in Chinese)
[16] 王筱滢, 刘青丽, 李志宏, 等. 不同施肥位点对烤烟钾积累及土壤有效钾含量的影响 [J]. 中国土壤与肥料, 2019(1):49−54. WANG X Y, LIU Q L, LI Z H, et al. Effects of different fertilization sites on potassium accumulation and soil effective potassium content in roasted tobacco [J]. Soil and Fertilizer Sciences in China, 2019(1): 49−54. (in Chinese)
[17] 许凌峰, 李卓蔚, 郭冬琴, 等. 不同丛枝菌根真菌组合对滇重楼根系生理特性的影响 [J]. 华西药学杂志, 2023, 38(1):65−69. XU L F, LI Z W , GUO D Q, et al. Effects of different Arbuscular mycorrhiza fungi combinations on root physiological characteristics of Paris Polyphylla var. Yunnanensis [J]. West China Journal of Pharmaceutical Sciences, 2023, 38(1): 65−69. (in Chinese)
[18] 曹明奡, 张菲, 黄光明, 等. 丛枝菌根真菌对低磷胁迫下核桃幼苗根系磷吸收的影响及机制 [J]. 林业科学, 2023, 59(12):117−124. DOI: 10.11707/j.1001-7488.LYKX20220253 CAO M A, ZHANG F, HUANG G M, et al. Effects of arbuscular mycorrhizal fungi on phosphorus uptake of walnut seedling roots under low phosphorus stress and the potential mechanisms [J]. Scientia Silvae Sinicae, 2023, 59(12): 117−124. (in Chinese) DOI: 10.11707/j.1001-7488.LYKX20220253
[19] 陈美兰, 郭兰萍, 杨光, 等. 药用植物AM共生体系评价方法和关键技术的探讨 [J]. 中国中药杂志, 2011, 36(21):3051−3056. CHEN M L, GUO L P, YANG G, et al. Discussion on appraisal methods and key technologies of arbuscular mycorrhizal fungi and medicinal plant symbiosis system [J]. China Journal of Chinese Materia Medica, 2011, 36(21): 3051−3056. (in Chinese)
[20] LIU R J , ChEN Y L . Mycorrhizology[M]. Beijing:Science Press,2007. LIU R J , ChEN Y L . Mycorrhizology[M]. Beijing:Science Press,2007.
[21] 陶冬雪, 高英志. 土壤解磷微生物促进植物磷素吸收策略研究进展 [J]. 生态学报, 2023, 43(11):4390−4399. TAO D X, GAO Y Z. Advances on the strategies of soil phosphate solubilizing microorganisms to promote plant phosphorus uptake [J]. Acta Ecologica Sinica, 2023, 43(11): 4390−4399. (in Chinese)
[22] QIU L, BI Y L, JIANG B, et al. Arbuscular mycorrhizal fungi ameliorate the chemical properties and enzyme activities of rhizosphere soil in reclaimed mining subsidence in Northwestern China [J]. Journal of Arid Land, 2019, 11(1): 135−147. DOI: 10.1007/s40333-018-0019-9
[23] 李佳齐, 王晓慧, 何鑫, 等. 丛枝菌根真菌提高植物耐酸碱能力及改善土壤pH应用潜力 [J]. 中国农学通报, 2023, 39(34):123−129. DOI: 10.11924/j.issn.1000-6850.casb2023-0503 LI J Q, WANG X H, HE X, et al. Improvement of plant acid and alkali resistance and soil pH application potential by arbuscular mycorrhizal fungi [J]. Chinese Agricultural Science Bulletin, 2023, 39(34): 123−129. (in Chinese) DOI: 10.11924/j.issn.1000-6850.casb2023-0503
[24] 潘龙. 丛植菌根真菌与解磷细菌互作促进土壤有机磷矿化的研究[D]. 新乡: 河南科技学院. 2022 PAN L. Study on the interactions between clumping mycorrhizal fungi and phosphorus-solubilizing bacteria to promote soil organic phosphorus mineralization[D]. Xin Xiang, Henan Institute of Science and Technology. 2022. (in Chinese)
[25] 赵祥, 曾广萍, 杨盼, 等. AM真菌对红花生长及其有效成分的影响 [J]. 干旱区研究, 2019, 36(4):935−942. ZHAO X, ZENG G P, YANG P, et al. Effects of arbuscular mycorrhizal fungi on growth and active constituents of Carthamus tinctorius [J]. Arid Zone Research, 2019, 36(4): 935−942. (in Chinese)
[26] 彭凤珍, 杜亚填, 周春长, 等. 南方红豆杉菌根紫杉醇含量及其菌根菌组分离纯化和种属鉴定 [J]. 天然产物研究与开发, 2022, 34(5):800−809. PENG F Z, DU Y T, ZHOU C C, et al. Paclitaxel content in mycorrhizal of Taxus chinensis var. mairei and isolation purification and species identification of its fungal [J]. Natural Product Research and Development, 2022, 34(5): 800−809. (in Chinese)




 下载:
下载: