Differentiation in Post-harvest Lipid Metabolism of Oil Palm Fruits
-
摘要:目的
探究薄壳种油棕果实采后阶段脂质合成和积累的机制。
方法选用采后不同处理时间的薄壳型油棕果实[授粉后185 d刚采摘的鲜果(T1)、采收后24 h(T2)、采收后36 h(T3)],结合液相色谱-串联质谱法(Liquid chromatography-tandem mass spectrometry, LC-MS/MS)和RNA测序(RNA sequencing, RNA-seq)技术,对各脂质代谢物和差异表达基因在酸败过程中的动态变化进行测定和分析。
结果在采后不同处理时间的果实脂质中共鉴定出5个脂质大类、23个脂质亚类,520个脂质单体分子。联合分析结果表明,乙醛脱氢酶(aldehyde dehydrogenase 7 family member A1, ALDH7A1; Aldehyde dehydrogenase 2 family, ALDH2)、单酰甘油脂肪酶(Monoacylglycerol lipase, MGL)和磷脂酶A1(Phospholipase A1, PLA1)与二酰基甘油三甲基高丝氨酸(Diacylglycerol trimethylhomoserine, DGTS)、磷脂酸(Phosphatidic acid, PA)、磷脂酰肌醇(Phosphatidylinositol, PI)、磷脂酰胆碱(Phosphatidylcholine, PC)、磷脂酰甘油(Phosphatidylglycerol, PG)、磷脂酰乙醇胺(Phosphatidylethanolamine, PE)等甘油磷脂类物质分别均呈显著负相关,与棕榈酸等游离脂肪酸呈显著正相关;甘油磷酸二酯磷酸二酯酶(Glycerophosphodiester phosphodiesterase domain containing 1, GDPD1)、脂磷酸磷酸酶(Lipid phosphate phosphatase, LPP)和二半乳糖甘油酯合成酶(Digalactosyldiacylglycerolsynthase1, DGD1)与DGTS、PA、PI、PC、PG、PE等甘油磷脂类物质呈显著正相关,与棕榈酸等游离脂肪酸呈显著负相关;MGL与单甘油酯(Monoglyceride, MG)和亚油酸(Linoleic acid, LA)呈极显著正相关,与神经酰胺(Ceramide, Cer)呈显著负相关;DGD1和LPP与MG和LA呈极显著负相关,与Cer呈显著正相关。
结论ALDH7A1、ALDH2、PLA1、MGL可能抑制甘油磷脂类物质的合成,促进棕榈酸等脂肪酸物质的合成;DGD1、LPP和GDP1可能促进甘油磷脂类物质的合成,抑制棕榈酸等脂肪酸物质的合成。
Abstract:ObjectiveMechanism and accumulation of lipid synthesis in thin-shelled oil palm fruits was investigated for breeding of variety resistant to fat rancidity.
MethodFruits of thin-shelled oil palm freshly harvested 185d after pollination (T1), 24h post-harvest (T2), and 36h post-harvest (T3) were collected for LC-MS/MS and RNA-seq determination and analysis on lipid metabolites and differentially expressed genes in mesocarp of oil palm fruits as the lipid oxidation taking place.
ResultIn the fruit development, 5 lipid classes, 23 lipid subclasses, and 520 monomer molecules in mesocarp of the oil palm fruits were identified. It is well known that the hydrolysis of phosphatidylcholine (PC) is a lipid oxidation and the hydrolyzed glycerophosphate choline (GPC) affects PC, lipophosphatase (LPP) promotes synthesis of phosphates and glycerophospholipids, and the expression of chlorophyll relates to chlorophyll content. This study found that the aldehyde dehydrogenase (ALDH7A1 and ALDH2), monoacylglycerol lipase (MGL), phospholipase A1 (PLA1), and glycerophosphodiester phosphodiesterase (GDPD1) significantly negatively correlated with glycerophospholipids, such as diacylglycerol trimethyl homoserine (DGTS), phosphatidic acid (PA), phosphatidylinositol (PI), phosphatidylcholine (PC), phosphatidylglycerol (PG), phosphatidylethanolamine (PE), but significantly positively correlated with palmitic acid, while GDPD1, LPP, and digalactosylglycerol synthase (DGD1) significantly positively correlated with the glycerophospholipids, such as DGTS, PA, PI, PC, PG, PE, but negatively correlated with palmitic acid, whereas MGL monoglyceride (MG) extremely significantly positively correlated with linoleic acid (LA) but significantly negatively correlated with ceramide (Cer), and DGD1 and LPP significantly negatively correlated with MG and LA, but significantly positively correlated with Cer.
ConclusionIt appeared that ALDH7A1, ALDH2, PLA1, and MGL inhibited the glycerophospholipids synthesis but promoted the synthesis of fatty acids such as palmitic acid, while DGD1, LPP, and GDP1 enhanced the synthesis of glycerophospholipids but retarded that of palmitic and other fatty acids.
-
Keywords:
- Oil palm fruit /
- rancidity /
- lipid /
- metabolomics /
- transcriptomics
-
0. 引言
【研究意义】油棕(Elaeis guineensis Jacq.)为多年生的棕榈科油棕属常绿乔木,是全球产油率最高的热区油料经济作物,也是全球食用油供应的重要来源[1],其果皮含油率可达50%以上,被誉为“世界油王”。油棕果是棕榈油的主要生产来源,棕榈油的主要成分是甘油三酯,主要脂肪酸是肉豆蔻酸、棕榈酸、硬脂酸、油酸和亚油酸[2]。因此,棕榈油的品质直接受到了不同脂肪酸含量及其比例的影响[3],而脂质代谢物的合成与降解则动态影响甘油三酯以及脂肪酸组分。然而,目前关于油棕果实采后酸败过程中的脂质合成和代谢调控机制的研究较少。【前人研究进展】脂质作为最重要的生物分子之一,存在于所有植物组织中,是生物膜的主要组成成分,可维持植物体内环境免受外界刺激[4]。它不仅是细胞结构所必需的物质,而且参与调节细胞功能的过程,如运输和调节膜蛋白等。脂类物质主要包括脂肪酸、甘油脂、甘油磷脂、鞘脂、甾醇脂、戊烯醇脂、糖脂和聚酮类八大类[5]。植物中脂质的生物合成和积累是一个复杂的过程,涉及油体的合成、去饱和、组装和形成[6]。棕榈油主要脂类是甘油三酯(Triglyceride, TG)和甘油二脂(Diglyceride, DG),一些组分如磷脂、半乳糖脂等脂质含量较低,但它们是脂质生物合成的关键中间体[7]。Bourgis等[8]和Tranbarger等[9]通过探究脂质组成,以及植物激素水平和脂质生物合成基因转录的关系,揭示了油棕果实中脂质合成和积累的机制。研究表明,磷脂酰胆碱(Phosphatidylcholine, PC)等磷脂类物质是TG生物合成的重要前体[10]。磷脂酸磷酸酶(Phosphatidic acid phosphatase, PAP)催化磷脂酸(Phosphatidic acid, PA)去磷酸化生成DG,DG又可转化为TG[11]。新鲜的油棕果实中含脂肪酶,被采摘后脂肪酶活性增强,导致油脂快速酸败,因此油棕果穗在采后24 h内需快速加工处理,以防止油品变差[12]。【本研究切入点】棕榈油的品质普遍受到油棕果实采后发生的油脂酸败影响。然而,目前关于油棕中果皮脂质合成与代谢过程中的分子机制的研究甚少,且多集中在果实发育阶段,鲜有在果实采后不同时期的相关研究。【拟解决的关键问题】采用转录代谢联合分析方法,对薄壳型油棕果实采后不同处理时间[授粉后185 d刚采摘的鲜果(T1)、采收后24 h(T2)、采收后36 h(T3)]果皮中脂质的含量变化和差异表达基因进行分析,为油棕中果皮采后脂质代谢调控机制研究提供理论基础。
1. 材料与方法
1.1 试验材料
试验于2022年7—8月进行,供试样本取自海南省文昌市中国热带农业研究院椰子研究所基地(110°47′E、19°33′N),试验材料为薄壳油棕样本的中果皮部分。取树势一致且经授粉185 d后的油棕鲜果,采收后均分为3组于28 ℃分别放置0 h(T1)、24 h(T2)和36 h(T3)。经处理样本包裹于锡箔纸中,后置于液氮中速冻1 h并保存于−80 ℃冰箱中以备后续代谢、转录组学检测及相关分析,每个样品进行3次生物学重复。
1.2 试验方法
1.2.1 脂质代谢物的测定及分析
油棕样本经初步处理后委托武汉迈维代谢生物科技股份有限公司进行广靶向的高通量代谢组检测,检测目标代谢物主要为供试样本的脂质代谢物。通过液相色谱-串联质谱法(Liquid chromatography-tandem mass spectrometry, LC-MS/MS)进行脂质代谢物的分离及鉴定,结合倍数变化指标差异倍数(Fold change, FC)和正交偏最小二乘判别分析模型(Orthogonal partial least squares discriminant analysis, OPLS-DA)中的变量投影重要性(Variable importance in projection, VIP)筛选显著差异代谢物。FC用于衡量两组样本之间差异,计算公式为:FC=试验组平均值 / 对照组平均值。OPLS-DA是一种广泛应用于代谢组学数据的模式识别和分类的多变量统计技术。所构建的OPLS-DA模型中,VIP指标被用来衡量各代谢物对分类模型的贡献程度。当VIP > 1 时,表明该代谢物对组间差异具有重要贡献。
在本研究中将浓度倍数变化Fold change ≥ 2或Fold change ≤ 0.5且 VIP ≥1的脂质确认为显著差异脂质代谢物。
1.2.2 RNA提取和高通量测序
油棕样本经初步处理后送至武汉迈维代谢生物科技股份有限公司测序,转录组测序在 Illumina 平台上进行。利用 HISAT2 比对软件将经优化的 Clean Reads 与油棕参考基因组进行准确比对,获得供试样品序列特征信息。利用 FPKM 对转录组数据进行标准化处理以衡量基因表达水平,降低同一片段重复计数导致的计算误差。
本研究将通过筛选条件为 |log2Fold change| ≥1且错误发现率(FDR)< 0.05的差异基因归为表达显著差异基因。
1.2.3 转录组学和代谢组学联合分析
根据转录组学和代谢组学联合分析结果,将同一比较组中的差异表达基因及显著差异代谢物映射至KEGG注释数据库,找到两组学共同富集到的KEGG 通路,并筛选与脂质合成相关的通路。
基于样本中获得的基因及代谢物的定量值进行相关性分析,筛选相关性系数≥ 0.80且P值 ≤ 0.05的关联分析数据用于后续分析。基因表达数据与代谢物数据之间的皮尔逊相关系数由R软件中的cor编程函数计算得到。
1.2.4 数据分析
基于SPSS26.0软件对测序获得的相关组学数据进行单因素方差分析及差异显著性检验,使用Origin2022进行绘图。
2. 结果与分析
2.1 油棕中果皮采后不同处理时间脂质变化分析
2.1.1 油棕中果皮采后不同处理时间脂质含量的动态变化分析
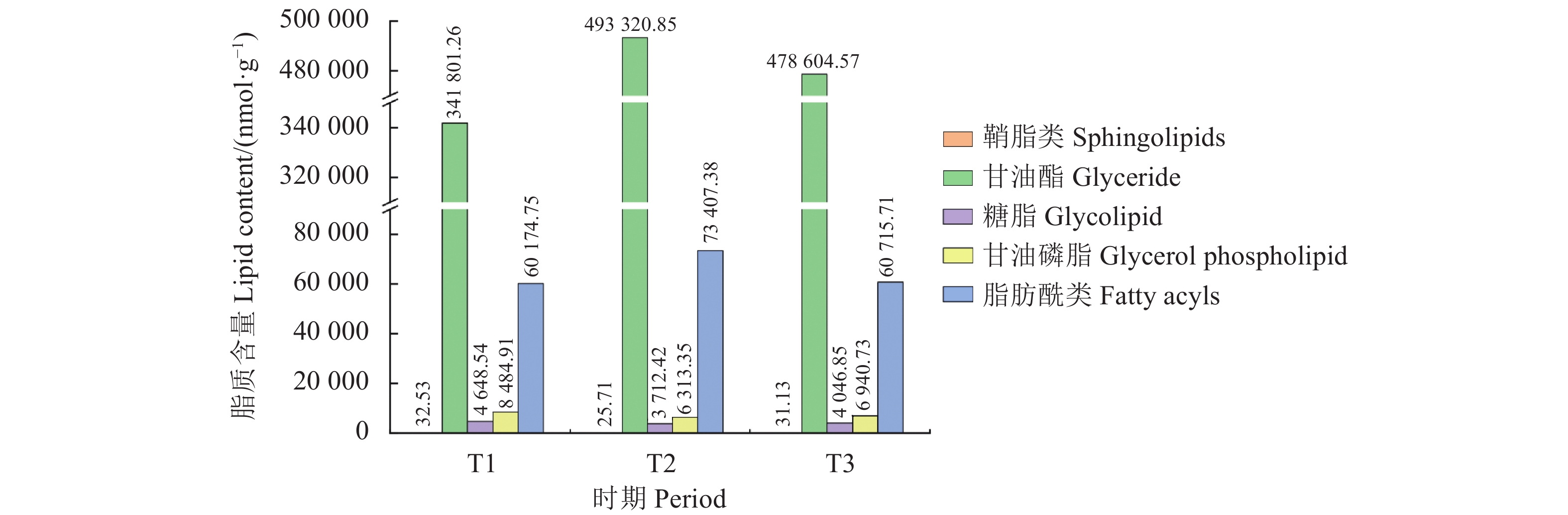
通过LC-MS/MS分析,共检测到鞘脂类(Sphingolipids, SP)、甘油酯(Glyceride, GL)、糖脂(Glycolipid, SL)、甘油磷脂(Glycerol phospholipid, GP)、脂肪酰类(Fatty acyls, FA)等5类脂质(图1),其中含量较高的是GL和FA。
在油棕果实的采后酸败过程中,GL总含量从T1时期的
341801.26 nmol·g−1上升至T2时期的493320.85 nmol·g−1后又下降至T3时期的478604.57 nmol·g−1;FA总含量从T1时期的60174.75 nmol·g−1上升至T2时期的73407.38 nmol·g−1后又下降至T3时期的60715.71 nmol·g−1;SP、SL和GP含量均是从T1时期下降至T2时期后上升至T3时期,在T3时期分别达31.13、4046.8 和6940.73 nmol·g−1。在采后不同处理时间油棕中果皮中共检测到23种脂质亚类,分别为神经酰胺(Ceramide, Cer)、鞘氨醇(Sphingosine, SPH)、甘油二脂(Diglyceride, DG)、单甘油酯(Monoglyceride, MG)、甘油三酯(Triglyceride, TG)、二糖甘油二脂(Disaccharide diglyceride, DGDG)、糖鞘脂(Glycosphingolipids, HexCer)、单糖甘油二脂(Monosaccharide diglyceride, MGDG)、硫代甘油糖脂(Thioglycolipids, SQDG)、二酰基甘油三甲基高丝氨酸(Diacylglycerol trimethylhomoserine, DGTS)、溶血二酰基甘油基三甲基高丝氨酸(Hemolytic diacylglycerol trimethylhomoserine, LDGTS)、溶血磷脂酸(Lysophosphatidic acid, LPA)、溶血磷脂酰胆碱(Lysophosphatidylcholine, LPC)、溶血磷脂酰乙醇胺(Lysophosphatidyl ethanolamine, LPE)、溶血磷脂酰甘油(Lysophosphatidylglycerol, LPG)、溶血磷脂酰肌醇(Lysophosphatidyl inositol, LPI)、磷脂酸(Phosphatidic acid, PA)、磷脂酰胆碱(Phosphatidylcholine, PC)、磷脂酰乙醇胺(Phosphatidylethanolamine, PE)、磷脂酰甘油(Phosphatidylglycerol, PG)、磷脂酰肌醇(Phosphatidylinositol, PI)、磷脂酰甲醇(Phosphatidylcarbinol, PMeOH)和游离脂肪酸(Free fatty acid, FFA)(表1),其中含量较高的是DG、TG和FFA。
表 1 采后不同处理时间油棕中果皮中各亚类脂质含量Table 1. Lipid content of subclasses in rancid oil palm fruit mesocarp(单位:nmol·g−1) 大类
Large category亚类
Subclass采后不同处理时间
Different post harvest processing timesT1 T2 T3 鞘脂类(SP) 神经酰胺(Cer) 28.94±3.85a 21.53±0.51b 25.84±4.13ab 鞘氨醇(SPH) 3.60±0.59b 4.18±0.44ab 5.29±0.59a 甘油酯(GL) 甘油二脂(DG) 315345.99 ±61101.54 460114.66 ±90158.07 450646.11 ±191075.41 单甘油酯(MG) 1946.23 ±288.28b4053.17 ±336.16a2043.03 ±291.06b甘油三酯(TG) 24509.04 ±2703.78 29153.02 ±3638.80 25915.44 ±6506.09 糖脂(SL) 二糖甘油二酯(DGDG) 2743.20 ±435.702248.80 ±555.862299.76 ±1216.49 糖鞘脂(HexCer) 5.00±0.05a 5.29±0.39a 4.19±0.22b 单糖甘油二酯(MGDG) 1058.30 ±200.41745.27±95.96 809.81±378.32 硫代甘油糖脂(SQDG) 842.04±149.80 713.06±124.43 933.09±491.32 甘油磷脂(GP) 二酰基甘油三甲基高丝氨酸(DGTS) 444.84±94.94 328.17±55.95 428.34±229.02 溶血二酰基甘油基三甲基高丝氨酸(LDGTS) 14.77±4.15 15.79±4.04 29.49±14.31 溶血磷脂酸(LPA) 25.35±0.90c 40.73±0.11b 53.25±6.90a 溶血磷脂酰胆碱(LPC) 91.30±2.95c 121.40±4.41b 139.27±10.88a 溶血磷脂酰乙醇胺(LPE) 46.51±1.85c 64.48±1.47b 88.26±9.44a 溶血磷脂酰甘油(LPG) 7.26±0.16b 12.00±0.57a 12.43±1.72a 溶血磷脂酰肌醇(LPI) 2.52±0.05b 9.31±1.31b 49.10±15.01a 磷脂酸(PA) 3706.34 ±225.693320.89 ±586.403715.32 ±506.73磷脂酰胆碱(PC) 1339.82 ±63.09a816.66±32.87b 815.64±42.47b 磷脂酰乙醇胺(PE) 1155.08 ±80.28a604.46±34.88b 582.75±72.54b 磷脂酰甘油(PG) 991.61±56.31a 524.11±4.14b 485.01±4.77b 磷脂酰肌醇(PI) 654.01±32.33ab 453.29±34.92b 540.57±70.70b 磷脂酰甲醇(PMeOH) 5.50±0.17a 2.05±0.08b 1.28±0.10c 脂肪酰类(FA) 游离脂肪酸(FFA) 60174.75 ±4469.14b73407.38 ±2827.63a60715.71 ±476.04b数值为平均值±标准差,不同小写字母表示不同时期之间差异显著(P<0.05)。表2同。
Values are mean ± standard deviation; different lowercase letters indicates significant differences of different treatment times (P<0.05). Same for table 2.在油棕果实的采后酸败过程中,DG总含量从T1时期的
315345.99 nmol·g−1上升至T2时期的460114.66 nmol·g−1后又下降至T3时期的450646.11 nmol·g−1;TG总含量从T1时期的24509.04 nmol·g−1上升至T2时期的29153.02 nmol·g−1后又下降至T3时期的25915.44 nmol·g−1。DGDG和PA等物质含量从T1时期下降至T2时期后上升至T3时期,而PC、PE和PG等物质含量从T1时期一直下降至T3时期。不同脂质亚类在油棕中果皮中的含量随采后不同处理时间的变化趋势存在差异。对脂质中含量较多且具有代表性的22种物质进行统计(表2),其中含量最高的是DG(16:0_18:1),在T1~T3时期其含量不断增加,但增加速率降低,T3时期其含量达
101472.36 nmol·g−1。亚油酸(Linoleic acid, LA)、棕榈酸(Palmitic acid, PiMA)和油酸(Oleic acid, OA)的含量都是从T1时期上升至T2时期后下降至T3时期,T3时期含量分别达11046.89 、16177.21 、26683.76 nmol·g−1。DGDG(16:0_18:1)、SQDG(16:0_18:1)和SQDG(16:0_16:0)属于糖脂类物质,其含量都是从T1时期下降至T2时期后上升至T3时期,T3时期含量分别达656.75、356.16、422.63 nmol·g−1。PA(16:0_18:2)在GP类物质中的占比最高,T3时期其含量达1063.04 nmol·g−1。表 2 采后不同处理时间油棕中果皮中22种脂质单体分子含量Table 2. Molecular contents of 22 lipid monomers in rancid oil palm fruit mesocarp(单位:nmol·g−1) 物质 Substance 采后不同处理时间 Different post harvest processing times T1 T2 T3 神经酰胺 (Cer, 18:2/18:1) 14.52±2.31a 10.66±0.58b 12.41±1.91ab 甘油二酯(DG, 16:0_18:1) 70636.96 ±15009.08 92432.42 ±18944.80 101472.36 ±51725.27 单甘油酯(MG, 18:1) 1403.68 ±224.40b2965.58 ±262.87a1485.12 ±220.97b甘油三酯(TG, 16:0_16:0_18:1) 3516.58 ±764.074308.94 ±930.543231.80 ±1569.97 甘油三酯(TG, 16:0_16:0_18:2) 2629.11 ±346.552608.90 ±543.372440.06 ±446.34二糖甘油二酯(DGDG, 16:0_18:1) 778.55±99.30 612.69±142.67 656.75±368.55 二糖甘油二酯(DGDG, 16:0_18:3) 485.56±86.07 342.74±76.95 333.41±135.86 单糖甘油二酯(MGDG, 18:3_18:3) 324.09±76.51 251.13±55.70 239.09±98.34 硫代甘油糖脂(SQDG, 16:0_18:1) 299.17±43.36 244.37±43.76 356.16±191.01 硫代甘油糖脂(SQDG, 16:0_16:0) 422.55±89.76 335.69±56.08 422.63±217.14 二酰基甘油三甲基高丝氨酸(DGTS, 18:1_18:3) 104.66±17.65 115.37±24.87 133.59±76.09 二酰基甘油三甲基高丝氨酸(DGTS, 18:2_18:3) 124.13±26.63a 48.65±4.42b 62.68±31.21b 磷脂酸(PA, 16:0_18:2) 1354.25 ±101.53a919.47±176.05b 1063.04 ±145.54ab磷脂酰胆碱(PC, 16:0_18:1) 412.13±29.49 390.23±17.30 361.94±27.71 磷脂酰胆碱(PC, 16:0_18:2) 458.78±21.04a 144.72±9.91b 137.97±10.89b 磷脂酰乙醇胺(PE, 18:2_16:0) 505.79±32.61a 225.63±15.30b 207.44±29.24b 磷脂酰甘油(PG, 16:0_16:0) 524.14±36.45a 191.76±5.24b 179.77±9.85b 磷脂酰肌醇(PI, 16:0_18:1) 344.68±14.83a 230.59±17.54b 274.07±44.09b 磷脂酰肌醇(PI, 18:2_16:0) 164.18±10.24a 119.57±10.73b 134.77±13.99b 亚油酸(LA, C18:2) 10188.00 ±782.31b15804.62 ±524.96a11046.89 ±836.18b棕榈酸(PiMA, C16:0) 14345.15 ±1055.52b17834.69 ±819.45a16177.21 ±580.58a油酸(OA, C18:1) 30396.86 ±2655.33a31704.01 ±568.28a26683.76 ±797.90b油棕中果皮 T1~T3脂质代谢物聚类分析(图2)结果表明,第1组中PC(16:0_18:1)和PG(16:0_16:0)等12种脂质在T1时期含量较高,在T2和T3时期含量降低;第2组中DGTS(18:1_18:3)和DG(16:0_18:1)等4种脂质含量在T3时期达到最大值;第3组中LA(C18:2)和TG(16:0_16:0_18:2)等6种脂质含量从T1时期上升至T2时期后下降至T3时期,在T2时期达最大值。
2.1.2 油棕中果皮采后不同处理时间脂质差异代谢物分析
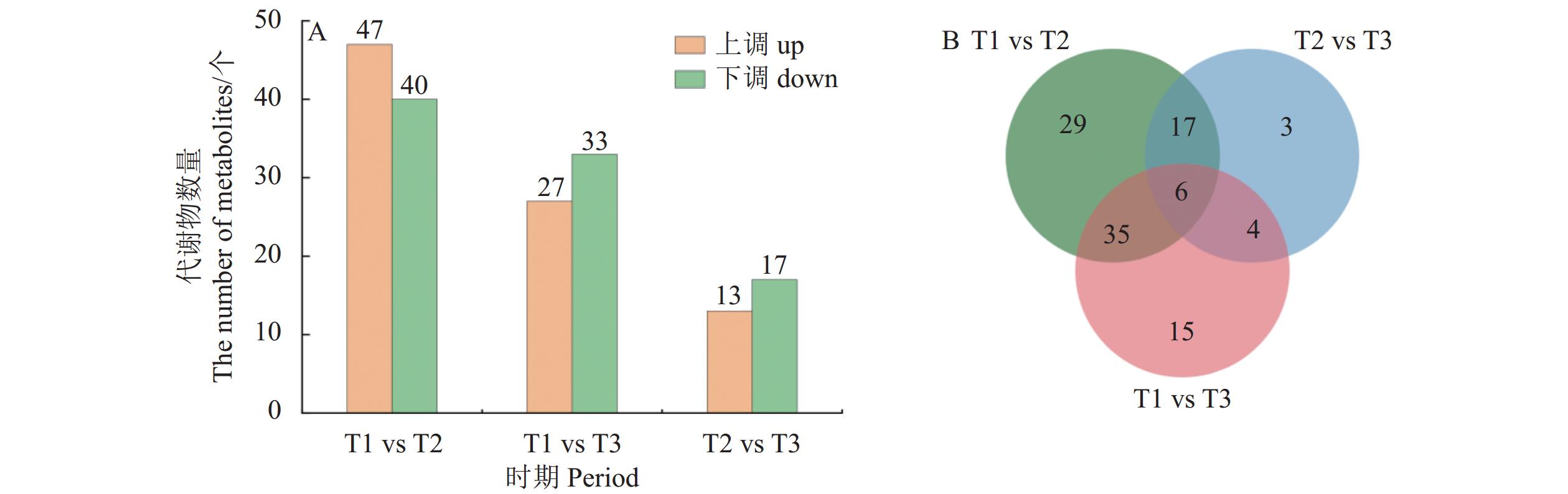
通过对油棕果实T1~T3时期的代谢组数据分析,依据筛选标准选取Fold change≥2或Fold change≤0.5且VIP值≥1的代谢物并对其进行统计(图3A)。对T1和T2进行对比分析发现:相对T1时期而言,T2时期的MG(18:1)、DG(18:1_20:1)、亚麻酸等47个差异代谢物呈现上调,而PE(18:2_16:0)、PC(16:0_18:2)、PG(16:0_16:0)等40个差异代谢物相对下调;而对T1和T3进行对比,则发现LPC(18:1)、DG(14:0_18:3)、DGTS(18:1_20:4)等27个差异代谢物相对上调,PE(18:2_16:0)、PC(16:0_18:2)、PG(16:0_16:0)等33个差异代谢物相对下调;T2和T3的分析对比则发现,LDGTS(18:1)、MGDG(18:1_18:1)等13个差异代谢物上调,MG(18:0)、TG(18:0_18:1_20:0)等17个差异代谢物相对下调。对采后不同处理时间共有差异代谢物的统计结果(图3B)表明,T1和T2、T1和T3共有差异代谢物41个,包括PC(16:0_18:2)、PE(18:2_18:2)、PG(16:0_16:0)等;T1和T2、T2和T3共有差异代谢物23个,包括MG(18:2)、TG(18:0_18:1_20:0)等;T1和T3、T2和T3共有差异代谢物10个,包括LPI(18:1)、LDGTS(18:1)等;T1和T2、T1和T3、T2和T3共有差异代谢物6个,分别为LPI(18:1)、LPI(18:2)、PC(18:2_20:0)、PC(17:0_18:2)、PE(16:3_18:3)和SPH(d18:0)。
2.2 采后不同处理时间油棕中果皮的差异基因表达分析
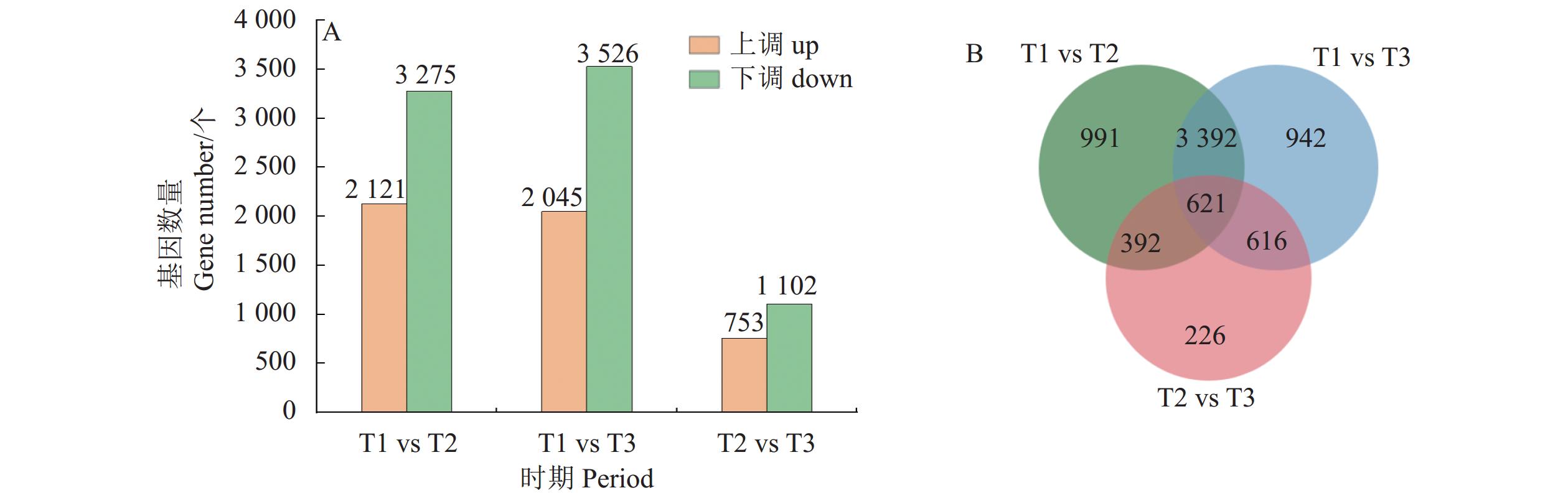
基于T1~T3时期薄壳油棕中果皮转录组数据,参考相关筛选条件( |log2Fold change| ≥ 1且 FDR < 0.05),获得了油棕中果皮采后不同处理时间表达显著上调或下调的差异基因(图4)。T1 vs T2比较组合中发现基因ID为LOC105048762、LOC105059691和LOC105036436等的
2121 个基因显著上调,LOC105060324、LOC105048931和LOC105054906等3275 个基因显著下调;T1 vs T3比较组合中发现基因ID为LOC105036436、LOC105045344和LOC105048762等的2045 个基因显著上调,LOC105039707、LOC105057703和LOC105060324等的3526 个基因显著下调;T2 vs T3比较组合中发现基因ID为LOC105053634、LOC105053635和LOC105053636等的753个基因显著上调,LOC105035265、LOC105039860和LOC105041092等的1102 个基因显著下调。3个比较组合中均存在显著差异表达的基因共621个。2.3 代谢组学和转录组学联合分析
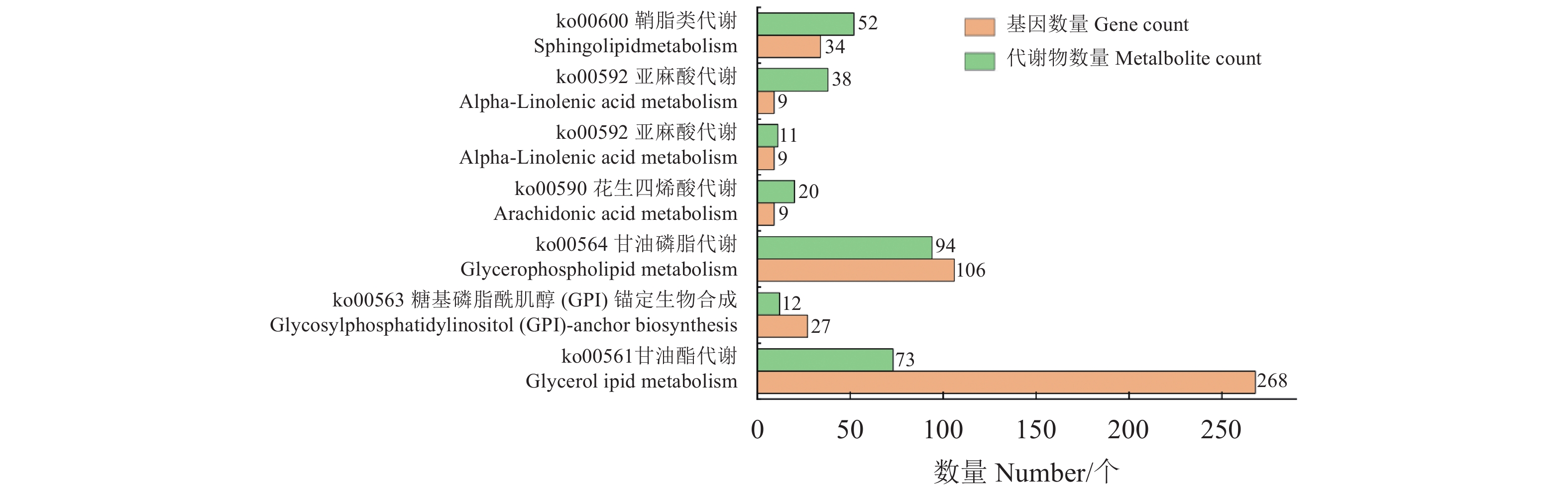
脂质代谢组及转录组数据的关联分析结果表明,差异基因和差异代谢物主要共同富集在鞘脂类代谢(Sphingolipid metabolism)、亚麻酸代谢(Alpha-Linolenic acid metabolism)、亚油酸代谢(Linoleic acid metabolism)、花生四烯酸代谢(Arachidonic acid metabolism)、甘油磷脂代谢(Glycerophospholipid metabolism)、糖基磷脂酰肌醇(GPI)锚定生物合成[Glycosylphosphatidylinositol (GPI)-anchor biosynthesis]和甘油酯代谢(Glycerolipid metabolism)7条与脂质相关的代谢通路上(图5)。在鞘脂类代谢途径中有37个差异表达基因和5种差异代谢物,差异代谢物均属于Cer;在亚麻酸代谢途径中有45个差异表达基因和7种差异代谢物,差异代谢物均属于PC;在亚油酸代谢途径中有14个差异表达基因和7个差异代谢物,差异代谢物均属于PC;在花生四烯酸代谢途径中有12个差异表达基因和7个差异代谢物,差异代谢物均属于PC;在甘油磷脂代谢途径中有67个差异表达基因和39个差异代谢物,差异代谢物中包含了DG、LPA、LPC、PA、PC、PE等6个亚类中的物质;在糖基磷脂酰肌醇(GPI)锚定生物合成途径中有13个差异表达基因和17个差异代谢物,差异代谢物均属于PE;在甘油酯代谢途径中有57个差异表达基因和40个差异代谢物,差异代谢物中包含了MG、DG、TG、LPA、PA5个亚类中的物质,其中甘油酯代谢、甘油磷脂代谢两条途径上的差异代谢物和差异表达基因最多。
甘油酯代谢途径影响着TG等油分主要成分的合成,甘油磷脂代谢途径影响脂质代谢,因此从这两条途径上筛选了22个表达量较高且在采后不同处理时间下存在显著差异表达的基因,以供下一步分析。
在22个显著差异表达基因的Nr蛋白注释分析中发现,油棕中果皮T1~T3过程高表达量的酶有乙醛脱氢酶(ALDH2、ALDH7A1)、二半乳糖甘油酯合成酶(DGD1)、甘油磷酸二酯磷酸二酯酶(GDPD)、脂磷酸磷酸酶(LPP)、单酰甘油脂肪酶(MGL)和磷脂酶A1(PLA1)。其中ALDH7A1、ALDH2、MGL和DGD1属甘油酯代谢途径,PLA1和GDPD1属甘油磷脂代谢途径,LPP同时存在于两条代谢途径上。
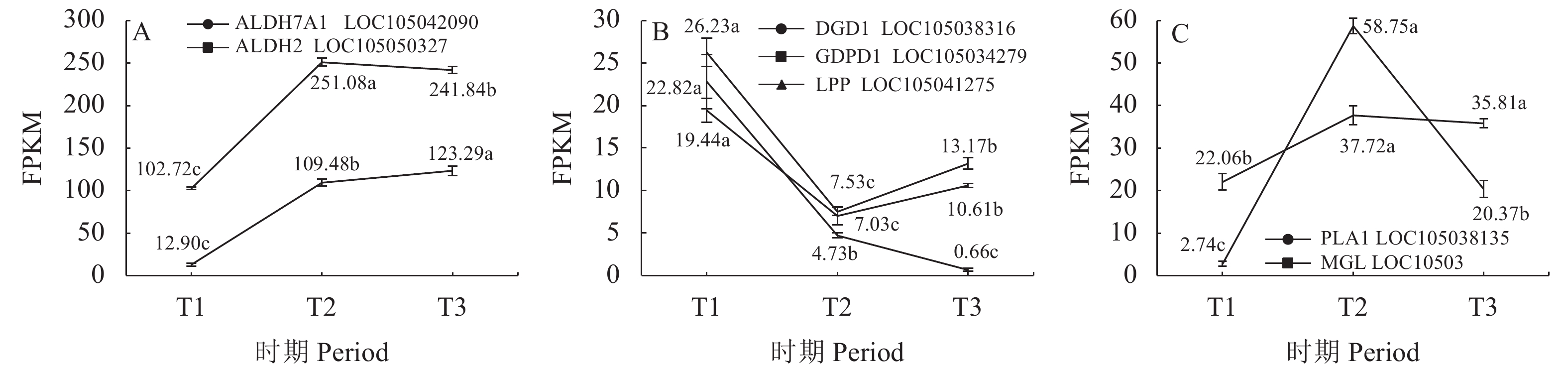
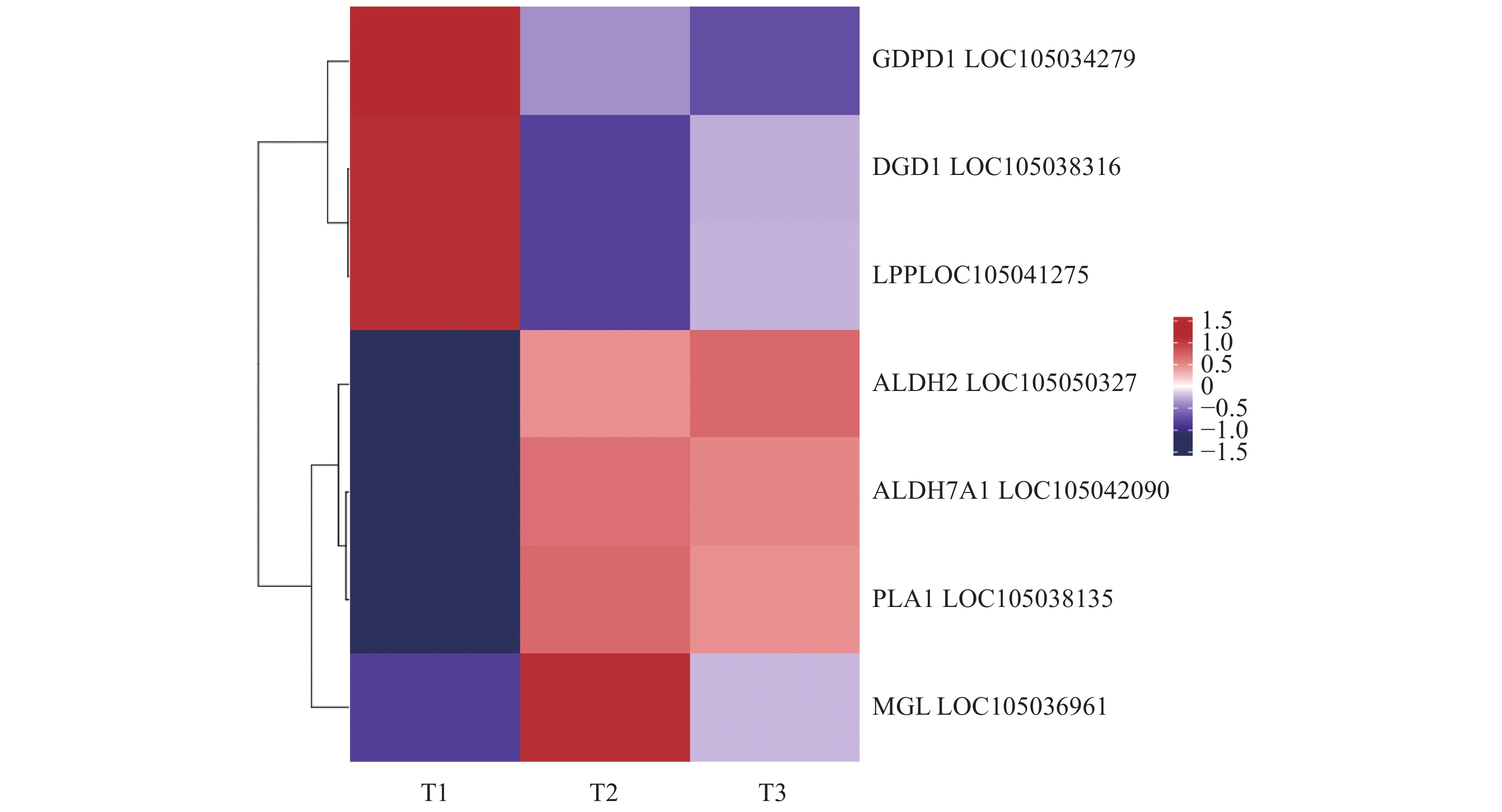
从这7个关键基因表达量动态变化(图6)可知,ALDH7A1、MGL酶合成相关基因表达量均从T1时期迅速上升至T2时期后下降至T3时期,T2时期高表达,3个时期间的基因表达量均存在显著性差异;DGD1、LPP酶合成相关基因表达量均从T1时期迅速下降至T2时期后上升至T3时期,T1时期高表达;GDPD1酶合成相关基因表达量在T1~T3过程中呈下降趋势;ALDH2酶合成相关基因表达量在T1~T3过程中呈上升趋势;PLA1酶合成相关基因表达量从T1时期上升至T2,T2和T3时期其基因表达量无显著差异。
聚类分析结果表明(图7),ALDH2、ALDH7A1、PLA1、MGL在T1时期表达量较低,T2和T3时期表达量上调。DGD1、LPP、GDPD1在T1时期表达量较高,在T2和T3时期表达量下调。
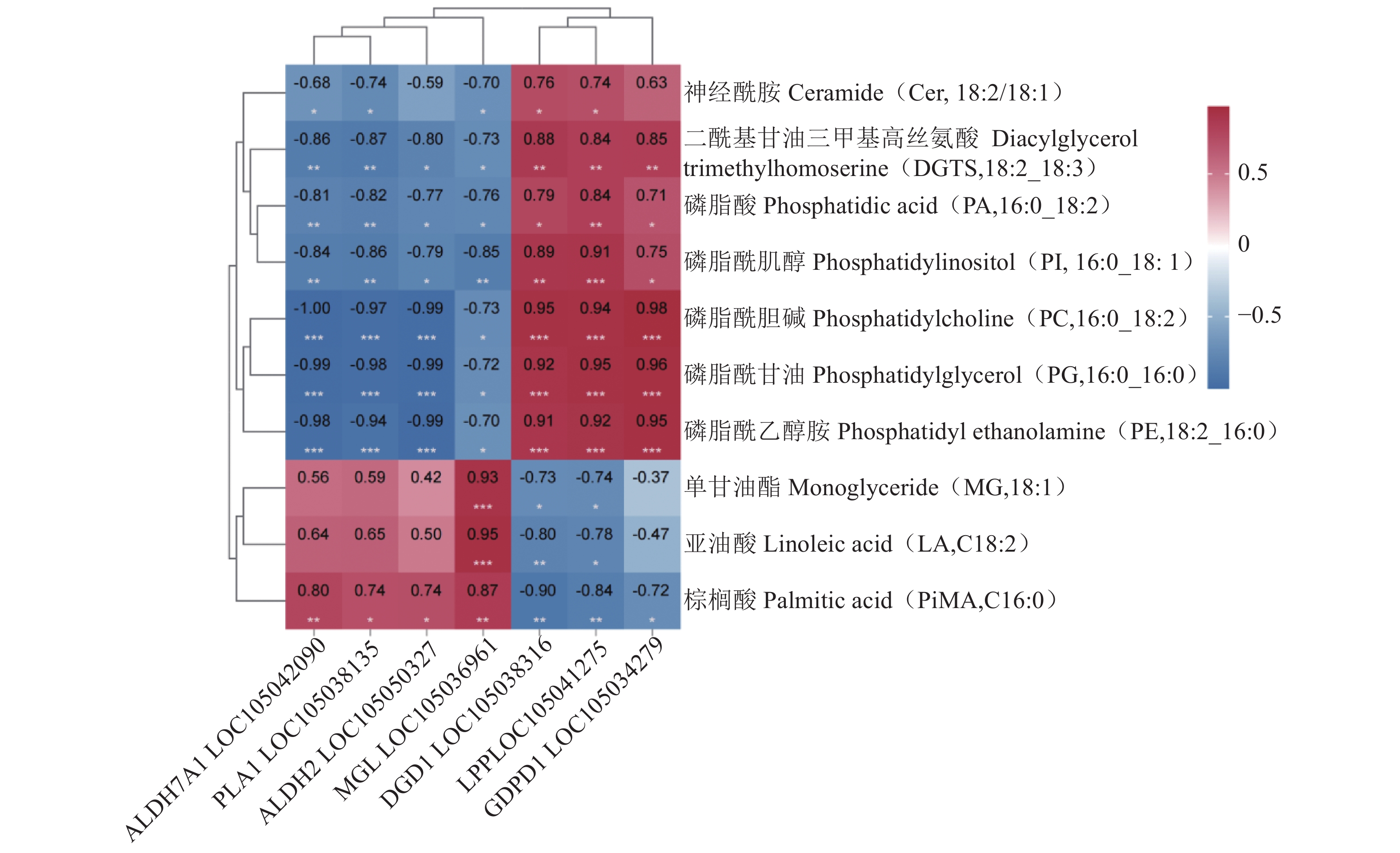
7个关键酶编码基因和10种显著差异代谢物的相关性图谱(图8)显示ALDH7A1、PLA1、ALDH2和MGL脂质合成相关酶基因表达量与DGTS、PA、PI、PC、PG、PE等甘油磷脂类物质含量存在显著负相关关系,与棕榈酸含量显著正相关;DGD1、LPP和GDPD1脂质合成相关酶基因表达量与DGTS、PA、PI、PC、PG、PE等甘油磷脂类物质含量显著正相关,与棕榈酸显著负相关;MGL与MG和LA显著正相关,与Cer显著负相关;DGD1和LPP与MG和LA显著负相关,与Cer显著正相关。ALDH7A1、PLA1、ALDH2和MGL可能抑制甘油磷脂类物质的合成,促进鞘脂类物质和游离脂肪酸物质的合成;而DGD1、LPP和GDPD1可能促进甘油磷脂类物质的合成,抑制鞘脂类物质和游离脂肪酸物质的合成。
3. 讨论与结论
甘油三酯是棕榈油的主要成分,各脂肪酸含量对棕榈油品质存在重要影响。脂质的生物合成和积累是一个复杂的过程,涉及众多物质,影响生物体中甘油三酯和各脂肪酸的含量。代谢组学分析发现,在薄壳种油棕果实采后酸败过程中的脂质共鉴定出5个脂质大类、23个脂质亚类,采后不同处理时间的代谢物含量差异明显。其中GL和FA的含量较高,且在T1~T2时期上升,在T2~T3时期下降;而SP、SL和GP含量在T1~T2时期下降,在T2~T3时期上升。由此推断在采后24~36 h,薄壳种油棕果实中果皮中的GL和FA逐渐转化为SP、SL和GP。转录组学分析发现,薄壳种油棕果实采后3个比较组合中均存在显著差异表达的基因共621个,随着采后中果皮的酸败,差异表达基因数量先增加后减少,且减少的幅度较大,其中下调基因的占比较多。通过KEGG联合分析,发现7条与脂质相关的代谢通路,通过筛选发现ALDH2、ALDH7A1、DGD1、GDPD、LPP、MGL和PLA1等7个关键酶基因在薄壳种油棕果实采后酸败过程中显著差异表达。
脂质过氧化衍生的醛与细胞中的亲核化合物(核酸、蛋白质、膜脂)具有极端的反应性,因此具有潜在的毒性[13]。而醛脱氢酶(ALDHs)是一种进化上保守的酶[14],能够分解细胞中的脂质衍生醛[15,16]。Abdul等[17]发现ALDHs能够减少脂肪酸过氧化产生的醛类物质的累积速度。Li等[18]的研究表明,CoALDH可能在油菜籽脂质合成阶段过量醛的代谢中发挥重要作用。在干旱、高温、盐渍和氧化应激等胁迫作用下会产生大量的有毒醛,进而引起ALDH表达量的增加[19]。研究表明,ALDH的上调是众多应激反应途径激活的共同作用靶点[20]。本研究中ALDH7A1和ALDH2与DGTS、PA、PI、PC、PG、PE等甘油磷脂类物质呈显著负相关,与棕榈酸呈显著正相关,推测ALDH7A1和ALDH2在薄壳种油棕采后对甘油磷脂类物质的合成存在抑制作用,对棕榈酸的合成起促进作用。离体的果实即处于胁迫条件下,在T2和T3时期的表达量上调,其原因可能是对果实中产生的过量醛进行分解,从而一定程度上影响脂质的合成降解,这与杨程等[21]的研究结果一致。
单酰基甘油脂肪酶(MGLs)是脂肪酶的一个亚类,在脂质代谢中发挥作用,影响能量稳态和信号转导过程[22]。在Kim等[23]的研究中发现,AtMGL4对溶血磷脂酰胆碱(LPC)和溶血磷脂酰乙醇胺(LPE)底物表现出水解酶活性,AtMGL1和AtMGL2对溶血磷脂酰乙醇胺(LPE)底物表现出水解酶活性。本研究中发现,MGL的表达量与DGTS、PA、PI、PC、PG、PE等甘油磷脂类物质含量呈显著负相关,这可能是MGL对此类物质表现出水解酶活性而导致的。
磷脂酶(PL)是一组复杂而重要的酶,在植物的生长周期以及对逆境胁迫的响应、应答过程中扮演着重要角色[24],参与了植物广泛的生理过程,如脂质生物合成和代谢、膜稳态、应激反应和细胞信号转导[25,26],根据其水解磷脂的部位不同可分为磷脂酶A(PLA)、磷脂酶C(PLC)和磷脂酶D(PLD)[27]。植物磷脂酶AS(PLAS)是一种广泛存在于生物体中的磷脂酶水解酶[28]。磷脂酶A1(PLA1)能够将PC水解为LPC[29],Zhao等[30]的研究表明PC和PE的浓度影响着花生油氧化速率。本研究中,PLA1表达量与DGTS、PA、PI、PC、PG、PE等甘油磷脂类物质显著负相关,证明在油棕中PLA1也影响着甘油磷脂类物质的水解,进而影响油棕中果皮中脂质的氧化。
GDPD能够将甘油磷酸二酯(GPD)水解为甘油-3-磷酸(G-3-P)。甘油磷酸胆碱(GPC)是GPD中的一个亚类,体外酶活性分析表明,AtGDPD1和AtGDPDL1可水解GPC[31]。GPC是PC的一种衍生物[32],本研究中GDPD1表达量与甘油磷脂类物质呈显著正相关,与单甘油酯和亚油酸等脂肪酸物质呈显著负相关。
Bourgis等发现,LPPβ在油棕果实成熟时期的表达量高,可能参与油脂合成,这与本研究中T1时期LPP高表达的结果一致。脂磷酸磷酸酶(LPP)既可以催化二脂酰甘油焦磷酸(DGPP)转化为磷脂酸(PA),又可催化磷脂酸(PA)转化为甘油二脂(DG)[33,34],这解释了本研究中LPP与PA的极显著正相关关系,同时LPP与其他甘油磷脂类物质也呈显著正相关。
在绿色植物中,70%~80%的脂质参与类囊体膜的形成。研究表明,类囊体膜的形成涉及到叶绿素和光合蛋白的积累,这一过程需要半乳糖脂质单半乳糖甘油二酯(MGDG)及双半乳糖甘油二酯(DGDG)的参与[35−37]。Kelly等[38]的研究发现,拟南芥的叶绿体外包膜中含有两个DGDG合成酶:DGD1和DGD2。Kobayash等[39]的研究发现,MGD1和DGD1的表达都是由光诱导的,且其表达会因叶绿素合成缺陷而受到抑制。本研究中,DGD1在T1时期表达量上调,在T2和T3时期表达量均下调,采后果肉内叶绿素合成受限,这可能抑制了DGD1的表达。结合本研究发现,DGD1与甘油磷脂类物质呈显著正相关,DGD1表达量降低可能抑制甘油磷脂类物质的合成。
综上所述,通过脂质转录代谢组学,发现采后的薄壳种油棕果实含有5个脂质大类、23个脂质亚类、520个脂质单体分子,其中GL和FA的含量较高。ALDH7A1、ALDH2、PLA1、MGL可能抑制甘油磷脂类物质的合成,促进棕榈酸等脂肪酸的合成。DGD1、LPP和GDP1可能促进甘油磷脂类物质的合成,抑制棕榈酸等脂肪酸的合成。本研究探究了薄壳油棕果在采后酸败过程中,各类脂质代谢物及其相关基因表达的变化趋势,为薄壳种油棕的脂质代谢的分子调控机制相关研究奠定理论基础。
-
表 1 采后不同处理时间油棕中果皮中各亚类脂质含量
Table 1 Lipid content of subclasses in rancid oil palm fruit mesocarp
(单位:nmol·g−1) 大类
Large category亚类
Subclass采后不同处理时间
Different post harvest processing timesT1 T2 T3 鞘脂类(SP) 神经酰胺(Cer) 28.94±3.85a 21.53±0.51b 25.84±4.13ab 鞘氨醇(SPH) 3.60±0.59b 4.18±0.44ab 5.29±0.59a 甘油酯(GL) 甘油二脂(DG) 315345.99 ±61101.54 460114.66 ±90158.07 450646.11 ±191075.41 单甘油酯(MG) 1946.23 ±288.28b4053.17 ±336.16a2043.03 ±291.06b甘油三酯(TG) 24509.04 ±2703.78 29153.02 ±3638.80 25915.44 ±6506.09 糖脂(SL) 二糖甘油二酯(DGDG) 2743.20 ±435.702248.80 ±555.862299.76 ±1216.49 糖鞘脂(HexCer) 5.00±0.05a 5.29±0.39a 4.19±0.22b 单糖甘油二酯(MGDG) 1058.30 ±200.41745.27±95.96 809.81±378.32 硫代甘油糖脂(SQDG) 842.04±149.80 713.06±124.43 933.09±491.32 甘油磷脂(GP) 二酰基甘油三甲基高丝氨酸(DGTS) 444.84±94.94 328.17±55.95 428.34±229.02 溶血二酰基甘油基三甲基高丝氨酸(LDGTS) 14.77±4.15 15.79±4.04 29.49±14.31 溶血磷脂酸(LPA) 25.35±0.90c 40.73±0.11b 53.25±6.90a 溶血磷脂酰胆碱(LPC) 91.30±2.95c 121.40±4.41b 139.27±10.88a 溶血磷脂酰乙醇胺(LPE) 46.51±1.85c 64.48±1.47b 88.26±9.44a 溶血磷脂酰甘油(LPG) 7.26±0.16b 12.00±0.57a 12.43±1.72a 溶血磷脂酰肌醇(LPI) 2.52±0.05b 9.31±1.31b 49.10±15.01a 磷脂酸(PA) 3706.34 ±225.693320.89 ±586.403715.32 ±506.73磷脂酰胆碱(PC) 1339.82 ±63.09a816.66±32.87b 815.64±42.47b 磷脂酰乙醇胺(PE) 1155.08 ±80.28a604.46±34.88b 582.75±72.54b 磷脂酰甘油(PG) 991.61±56.31a 524.11±4.14b 485.01±4.77b 磷脂酰肌醇(PI) 654.01±32.33ab 453.29±34.92b 540.57±70.70b 磷脂酰甲醇(PMeOH) 5.50±0.17a 2.05±0.08b 1.28±0.10c 脂肪酰类(FA) 游离脂肪酸(FFA) 60174.75 ±4469.14b73407.38 ±2827.63a60715.71 ±476.04b数值为平均值±标准差,不同小写字母表示不同时期之间差异显著(P<0.05)。表2同。
Values are mean ± standard deviation; different lowercase letters indicates significant differences of different treatment times (P<0.05). Same for table 2.表 2 采后不同处理时间油棕中果皮中22种脂质单体分子含量
Table 2 Molecular contents of 22 lipid monomers in rancid oil palm fruit mesocarp
(单位:nmol·g−1) 物质 Substance 采后不同处理时间 Different post harvest processing times T1 T2 T3 神经酰胺 (Cer, 18:2/18:1) 14.52±2.31a 10.66±0.58b 12.41±1.91ab 甘油二酯(DG, 16:0_18:1) 70636.96 ±15009.08 92432.42 ±18944.80 101472.36 ±51725.27 单甘油酯(MG, 18:1) 1403.68 ±224.40b2965.58 ±262.87a1485.12 ±220.97b甘油三酯(TG, 16:0_16:0_18:1) 3516.58 ±764.074308.94 ±930.543231.80 ±1569.97 甘油三酯(TG, 16:0_16:0_18:2) 2629.11 ±346.552608.90 ±543.372440.06 ±446.34二糖甘油二酯(DGDG, 16:0_18:1) 778.55±99.30 612.69±142.67 656.75±368.55 二糖甘油二酯(DGDG, 16:0_18:3) 485.56±86.07 342.74±76.95 333.41±135.86 单糖甘油二酯(MGDG, 18:3_18:3) 324.09±76.51 251.13±55.70 239.09±98.34 硫代甘油糖脂(SQDG, 16:0_18:1) 299.17±43.36 244.37±43.76 356.16±191.01 硫代甘油糖脂(SQDG, 16:0_16:0) 422.55±89.76 335.69±56.08 422.63±217.14 二酰基甘油三甲基高丝氨酸(DGTS, 18:1_18:3) 104.66±17.65 115.37±24.87 133.59±76.09 二酰基甘油三甲基高丝氨酸(DGTS, 18:2_18:3) 124.13±26.63a 48.65±4.42b 62.68±31.21b 磷脂酸(PA, 16:0_18:2) 1354.25 ±101.53a919.47±176.05b 1063.04 ±145.54ab磷脂酰胆碱(PC, 16:0_18:1) 412.13±29.49 390.23±17.30 361.94±27.71 磷脂酰胆碱(PC, 16:0_18:2) 458.78±21.04a 144.72±9.91b 137.97±10.89b 磷脂酰乙醇胺(PE, 18:2_16:0) 505.79±32.61a 225.63±15.30b 207.44±29.24b 磷脂酰甘油(PG, 16:0_16:0) 524.14±36.45a 191.76±5.24b 179.77±9.85b 磷脂酰肌醇(PI, 16:0_18:1) 344.68±14.83a 230.59±17.54b 274.07±44.09b 磷脂酰肌醇(PI, 18:2_16:0) 164.18±10.24a 119.57±10.73b 134.77±13.99b 亚油酸(LA, C18:2) 10188.00 ±782.31b15804.62 ±524.96a11046.89 ±836.18b棕榈酸(PiMA, C16:0) 14345.15 ±1055.52b17834.69 ±819.45a16177.21 ±580.58a油酸(OA, C18:1) 30396.86 ±2655.33a31704.01 ±568.28a26683.76 ±797.90b -
[1] MURPHY D J. Oil palm: Future prospects for yield and quality improvements [J]. Lipid Technology, 2009, 21(11/12): 257−260.
[2] CORLEY R H V, TINKER P B. The Oil Palm[M]. Oxford, United Kingdom: Blackwell Pub Professional, 2003. CORLEY R H V, TINKER P B. The Oil Palm[M]. Oxford, United Kingdom: Blackwell Pub Professional, 2003.
[3] PARVEEZ G K, RASID O A, MASANI M Y A, et al. Biotechnology of oil palm: Strategies towards manipulation of lipid content and composition [J]. Plant Cell Reports, 2015, 34(4): 533−543. DOI: 10.1007/s00299-014-1722-4
[4] HOU Q C, UFER G, BARTELS D. Lipid signalling in plant responses to abiotic stress[J]. Plant, Cell & Environment, 2016, 39(5): 1029-1048.
[5] GROUP L T. Comprehensive classification system for lipids published[J]. Lipid Technology: the International Magazine of Oils, Fats, Lipids & Waxes, 2005, 17(8): 187.
[6] PATI S, NIE B, ARNOLD R D, et al. Extraction, chromatographic and mass spectrometric methods for lipid analysis [J]. Biomedical Chromatography, 2016, 30(5): 695−709. DOI: 10.1002/bmc.3683
[7] CHEONG W F, WENK M R, SHUI G H. Comprehensive analysis of lipid composition in crude palm oil using multiple lipidomic approaches [J]. Journal of Genetics and Genomics, 2014, 41(5): 293−304. DOI: 10.1016/j.jgg.2014.04.002
[8] FABIENNE B, ARNNA K, XIA C, et al. Comparative transcriptome and metabolite analysis of oil palm and date palm mesocarp that differ dramatically in carbon partitioning[J]. Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences of the United States of America, 2011,108(30):12527–12532.
[9] TRANBARGER T J, DUSSERT S, JOËT T, et al. Regulatory mechanisms underlying oil palm fruit mesocarp maturation, ripening, and functional specialization in lipid and carotenoid metabolism [J]. Plant Physiology, 2011, 156(2): 564−584. DOI: 10.1104/pp.111.175141
[10] LU C F, XIN Z G, REN Z H, et al. An enzyme regulating triacylglycerol composition is encoded by the ROD1 gene of Arabidopsis [J]. Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences of the United States of America, 2009, 106(44): 18837−18842.
[11] NAKAMURA Y, TSUCHIYA M, OHTA H. Plastidic phosphatidic acid phosphatases identified in a distinct subfamily of lipid phosphate phosphatases with prokaryotic origin [J]. Journal of Biological Chemistry, 2007, 282(39): 29013−29021. DOI: 10.1074/jbc.M704385200
[12] 雷新涛, 曹红星. 油棕[M]. 北京: 中国农业出版社, 2013. [13] NAIM S , MISSIHOUN T D , KOTCHONI S O , et al. Aldehyde Dehydrogenases in Arabidopsis thaliana: Biochemical Requirements, Metabolic Pathways, and Functional Analysis[J]. Frontiers in Plant Science, 2011, (2): 65. DOI: 10.3389/fpls.2011.00065.
[14] CHEN Z, CHEN M, XU Z S, et al. Characteristics and expression patterns of the aldehyde dehydrogenase (ALDH) gene superfamily of foxtail millet (Setaria italica L. ) [J]. PLoS One, 2014, 9(7): e101136. DOI: 10.1371/journal.pone.0101136
[15] VASILIOU V, NEBERT D W. Analysis and update of the human aldehyde dehydrogenase (ALDH) gene family [J]. Human Genomics, 2005, 2(2): 138−143. DOI: 10.1186/1479-7364-2-2-138
[16] BROCKER C, VASILIOU M, CARPENTER S, et al. Aldehyde dehydrogenase (ALDH) superfamily in plants: Gene nomenclature and comparative genomics [J]. Planta, 2013, 237(1): 189−210. DOI: 10.1007/s00425-012-1749-0
[17] ABDUL W, ALIYU S R, LIN L L, et al. Family-four aldehyde dehydrogenases play an indispensable role in the pathogenesis of Magnaporthe oryzae [J]. Frontiers in Plant Science, 2018, 9: 980. DOI: 10.3389/fpls.2018.00980
[18] LI Z, WANG J Y, LONG H X, et al. Cloning and expression analysis of an aldehyde dehydrogenase gene from Camellia oleifera [J]. Nanoscience and Nanotechnology Letters, 2017, 9(3): 364−373. DOI: 10.1166/nnl.2017.2340
[19] TAGNON M D, SIMEON K O. Aldehyde dehydrogenases may modulate signaling by lipid peroxidation-derived bioactive aldehydes [J]. Plant Signaling & Behavior, 2017, 12(11): e1387707.
[20] BARTELS D, SUNKAR R. Drought and salt tolerance in plants [J]. Critical Reviews in Plant Sciences, 2005, 24(1): 23−58. DOI: 10.1080/07352680590910410
[21] 杨程, 张淑岩, 韦露, 等. 薄壳种油棕果实发育和采后脂肪酸合成转录代谢差异分析[J/OL]. 分子植物育种, 2023 (2023-06-13). https://kns.cnki.net/kcms/detail/46.1068.S.20230612.1612.020.html. YANG C, ZHANG S Y, WEI L, et al. Differential Analysis of Fatty Acid Synthesis, Transcriptional Metabolism during Fruit Development and Postharvest in Tenera Oil palm[J/OL]. Molecular Plant Breeding, 2023 (2023-06-13). https://kns.cnki.net/kcms/detail/46.1068.S.20230612.1612.020.html.(in Chinese)
[22] RIEGLER-BERKET L, LEITMEIER A, ASCHAUER P, et al. Identification of lipases with activity towards monoacylglycerol by criterion of conserved cap architectures [J]. Biochimica et Biophysica Acta (BBA) - Molecular and Cell Biology of Lipids, 2018, 1863(7): 679−687. DOI: 10.1016/j.bbalip.2018.03.009
[23] KIM R J, KIM H J, SHIM D, et al. Molecular and biochemical characterizations of the monoacylglycerol lipase gene family of Arabidopsis thaliana [J]. The Plant Journal, 2016, 85(6): 758−771. DOI: 10.1111/tpj.13146
[24] MARIANI M E, FIDELIO G D. Secretory phospholipases A2 in plants [J]. Frontiers in Plant Science, 2019, 10: 861. DOI: 10.3389/fpls.2019.00861
[25] RYU S B. Phospholipid-derived signaling mediated by phospholipase A in plants [J]. Trends in Plant Science, 2004, 9(5): 229−235. DOI: 10.1016/j.tplants.2004.03.004
[26] WANG X M. Plant phospholipases [J]. Annual Review of Plant Physiology and Plant Molecular Biology, 2001, 52: 211−231. DOI: 10.1146/annurev.arplant.52.1.211
[27] 史敬芳, 张琪, 宋松泉, 等. 磷脂酶及其调控种子活力研究进展 [J]. 南方农业学报, 2022, 53(9):2612−2623. DOI: 10.3969/j.issn.2095-1191.2022.09.024 SHI J F, ZHANG Q, SONG S Q, et al. Phospholipases and their seed vigor regulation: A review [J]. Journal of Southern Agriculture, 2022, 53(9): 2612−2623. (in Chinese) DOI: 10.3969/j.issn.2095-1191.2022.09.024
[28] MUKHERJEE A B. Biochemistry, molecular biology, and physiology of phospholipase A2 and its regulatory factors [J]. Advances in Experimental Medicine and Biology, 1990, 279: 1−251.
[29] LIM C W, KIM B H, KIM I H, et al. Modeling and optimization of phospholipase A1-catalyzed hydrolysis of phosphatidylcholine using response surface methodology for lysophosphatidylcholine production [J]. Biotechnology Progress, 2015, 31(1): 35−41. DOI: 10.1002/btpr.2009
[30] ZHAO Q Y, WANG M M, ZHANG W B, et al. Impact of phosphatidylcholine and phosphatidylethanolamine on the oxidative stability of stripped peanut oil and bulk peanut oil [J]. Food Chemistry, 2020, 311: 125962. DOI: 10.1016/j.foodchem.2019.125962
[31] CHENG Y X, ZHOU W B, EL SHEERY N I, et al. Characterization of the Arabidopsis glycerophosphodiester phosphodiesterase (GDPD) family reveals a role of the plastid-localized AtGDPD1 in maintaining cellular phosphate homeostasis under phosphate starvation [J]. The Plant Journal, 2011, 66(5): 781−795. DOI: 10.1111/j.1365-313X.2011.04538.x
[32] BANG H J, KIM I H, KIM B H. Phospholipase A1-catalyzed hydrolysis of soy phosphatidylcholine to prepare l-α-glycerylphosphorylcholine in organic-aqueous media [J]. Food Chemistry, 2016, 190: 201−206. DOI: 10.1016/j.foodchem.2015.05.093
[33] CARMAN G M. Phosphatidate phosphatases and diacylglycerol pyrophosphate phosphatases in Saccharomyces cerevisiae and Escherichia coli [J]. Biochimica et Biophysica Acta, 1997, 1348(1/2): 45−55.
[34] MUNNIK T , LIGTERINK W , MESKIENE I ,et al. Distinct osmo-sensing protein kinase pathways are involved in signalling moderate and severe hyper-osmotic stress [J]. The Plant Journal, 1999, 20(4): 381−388. DOI: 10.1046/j.1365-313x.1999.00610.x
[35] LIU Z F, YAN H C, WANG K B, et al. Crystal structure of spinach major light-harvesting complex at 2.72 A resolution [J]. Nature, 2004, 428(6980): 287−292. DOI: 10.1038/nature02373
[36] JORDAN P, FROMME P, WITT H T, et al. Three-dimensional structure of cyanobacterial photosystem I at 2.5 Å resolution [J]. Nature, 2001, 411: 909−917. DOI: 10.1038/35082000
[37] UMENA Y, KAWAKAMI K, SHEN J R, et al. Crystal structure of oxygen-evolving photosystem II at a resolution of 1.9 Å [J]. Nature, 2011, 473: 55−60. DOI: 10.1038/nature09913
[38] KELLY A A, FROEHLICH J E, DÖRMANN P. Disruption of the two digalactosyldiacylglycerol synthase genes DGD1 and DGD2 in Arabidopsis reveals the existence of an additional enzyme of galactolipid synthesis [J]. The Plant Cell, 2003, 15(11): 2694−2706. DOI: 10.1105/tpc.016675
[39] KOBAYASHI K, FUJII S, SASAKI D, et al. Transcriptional regulation of thylakoid galactolipid biosynthesis coordinated with chlorophyll biosynthesis during the development of chloroplasts in Arabidopsis [J]. Frontiers in Plant Science, 2014, 5: 272.




 下载:
下载: