Role of pAPN and NEU3 in TGEV Infection on Pig
-
摘要:目的
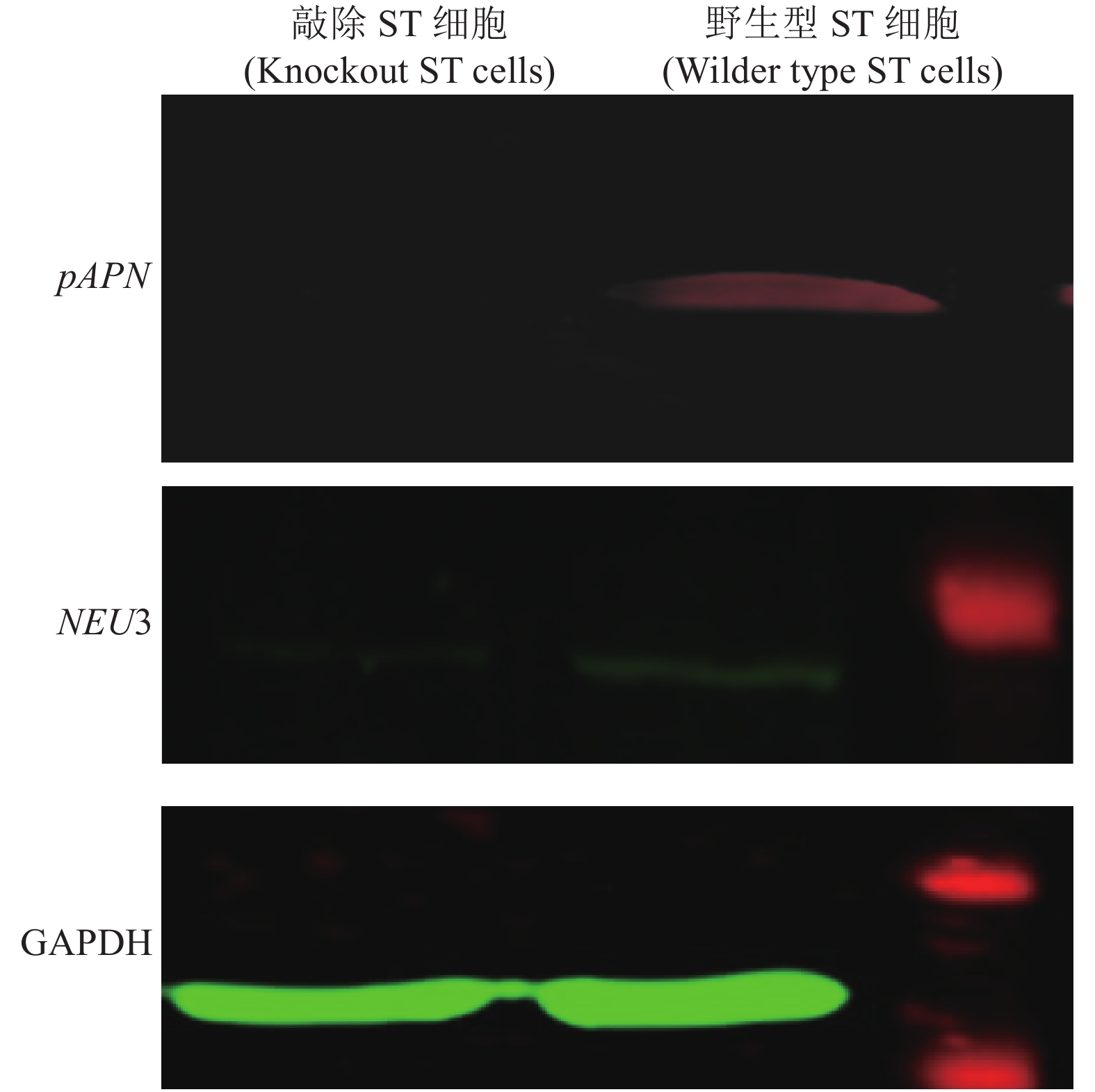
氨基肽酶( pAPN )是猪的传染性胃肠炎病毒(TGEV)侵染的主要受体,验证pAPN和唾液酸神经氨酸酶(NEU3)双基因对猪的传染性胃肠炎病毒(TGEV)入侵机制的影响。 方法 应用CRISPR-Cas9基因编辑技术,敲除猪睾丸细胞(ST)的pAPN和NEU3两个基因。经过病毒感染试验,测定敲除pAPN和NEU3两个目标基因的ST细胞对病毒的侵染变化以及病毒拷贝数的变化、细胞病变改善,同时监测病毒侵染后纤连蛋白的变化。结果 与对照组相比,敲除pAPN和NEU3两个目标基因的ST细胞,明显减轻TGEV侵染引起的细胞病变,TGEV的拷贝数也出现明显下降。此外,同样滴度的TGEV侵染pAPN和NEU3双基因敲除ST细胞后,诱导ST细胞的免疫应答物IFNβ的mRNA水平明显低于野生型ST细胞组。结论 pAPN和NEU3双基因的敲除,明显降低了ST细胞中的TGEV病毒拷贝数,同时也减少病毒引起的细胞病变,这个结果证实细胞中的pAPN和NEU3双基因可作为将来养猪生产中抗病毒治疗及抗病品种选育的靶基因。Abstract:Objective Role of aminopeptidase gene pAPN and sialic acid neuraminidase gene NEU3 in the transmissible gastroenteritis virus (TGEV) infection on pigs was investigated.Methods Being the main receptor of TGEV, pAPN was removed from pAPN and NEU3 in ST cells to verify its supposed key function on the disease. The CRISPR gene editing technique was applied to clip the target gene in ST cells prior to an artificial TGEV infection test. The resulting changes on the infection, virus copy number, cytopathic improvement, and fibronectin were monitored.Results Compared with control, the ST cells free of pAPN and NEU3 significantly attenuated TGEV infection-induced cytopathies and the virus copy number. In addition, at a same TGEV titer the mRNA immune responders induced by the knockdown ST cells were significantly lower than the wild-type counterparts.Conclusion It was confirmed that the removal of pAPN and NEU3 inhibited the TGEV infection in pigs with reduced viral induced cytopathies. Thus, an antiviral therapy and a guideline for breeding resistant pigs could be developed by targeting these two key genes in the ST cells.-
Keywords:
- pAPN /
- NEU3 /
- TGEV /
- Titer of virus
-
0. 引言
【研究意义】随着畜牧业的快速发展,牛繁殖障碍性疾病对牛产业的稳定发展影响显著。其中,赤羽病病毒(akabane virus, AKAV)、牛疱疹病毒1型(bovine herpesvirus 1, BoHV-1)和牛病毒性腹泻病毒(bovine viral diarrhea virus, BVDV)等被认为是牛发生繁殖障碍的主要原因之一[1, 2]。AKAV、BoHV-1和BVDV等病毒性疾病在牛群中广泛传播,给畜牧业带来了严重的经济损失[3−5]。因此,对这些病毒进行快速、准确检测,对于预防和控制疾病的传播具有至关重要的意义。【前人研究进展】目前,针对AKAV、BoHV-1和BVDV的检测方法,如病毒分离、血清学检测等,虽然具有一定的应用价值,但存在操作繁琐、耗时较长、灵敏度不高等问题[6−9]。近年来,分子生物学技术持续迭代发展,反转录聚合酶链式反应(RT-PCR)技术因其高灵敏度、高特异性和快速性等优点,在病毒检测领域得到了广泛应用。单一病毒的RT-PCR检测只能针对一种病毒进行检测,无法满足同时对多种病毒进行检测的需求[10−12],而RT-qPCR对检测技术人员水平要求较高,且容易因气溶胶污染造成假阳性[13, 14]。【本研究切入点】AKAV、BoHV-1和BVDV均可引起牛群发生繁殖障碍,临床症状极为相似,极难区分[1, 2]。因此,建立一种能够一次性测定多种病毒的检测方法,对当前病毒检测的降本增效具有重要意义。【拟解决的关键问题】建立一种可同时检测AKAV、BoHV-1和BVDV病原的多重RT-PCR方法,以了解AKAV、BoHV-1和BVDV等3种牛繁殖障碍相关病原的分布、传播规律及可能的变异情况,以深入了解3种病毒的生物学特性,为制定有效的防控措施提供科学依据。
1. 材料与方法
1.1 病毒阳性核酸和样品
143份牛血液或内脏组织样本采自2023—2024年江西和广西地区疑似或出现繁殖障碍的牛群;AKAV、BoHV-1、BVDV、牛细小病毒(bovine parvovirus, BPV)、牛呼吸道合胞体病毒(bovine respiratory syncytial virus, BRSV)、牛副流感病毒3型(bovine parainfluenza virus 3, BPIV3)、口蹄疫病毒(foot-and-mouth disease virus, FMDV)、牛流行热病毒(bovine ephemeral fever rhabdovirus, BEFV)等阳性核酸样品由江西省农业科学院畜牧兽医研究所实验室保存。
1.2 主要试剂
病毒RNA/DNA快速纯化试剂盒、cDNA合成试剂盒、DNA聚合酶、快速胶回收试剂盒、DH5α化学感受态细胞和质粒快速提取试剂盒均购自南京诺唯赞生物科技股份有限公司;DL2 000 DNA Marker、pMD20-T克隆试剂盒均购自宝日医生物技术有限公司。
1.3 引物设计合成
取GenBank数据库AKAV的S基因、BoHV-1的gH基因、BVDV的3'UTR序列,利用MEGA 6.0软件比对后在其保守区域分别设计3对特异性引物(表1),引物由生工生物工程有限公司合成。
表 1 引物序列Table 1. Sequences of primers病毒
Virus引物序列(5'-3')
The primer sequences for PCR (5'-3')靶基因
Target gene产物大小
Products size/bpAKAV AKAV-F:ACATAAGACGCCACAACCAAGT S 623 AKAV-R:CGAGCAGCTGAACAAAGGTG BoHV-1 BoHV-1-F:TCCTGCCTCTGGAGTTTATGG gH 433 BoHV-1-R:TTGAGGTGGTAGTCAAGGTCG BVDV BVDV-F:CAGCGAAGGCCGAAAAGAGG 3'UTR 308 BVDV-R:CCATGTGCCATGTACAGCAGAG 1.4 病毒DNA/RNA的提取
组织样品以体积比1∶3加入0.01 mol·L−1 PBS(pH 7.3~7.5),放入低温组织研磨仪匀浆后置于冰箱−20 ℃ 3次冻融处理,8 000 r·min−1离心5 min取上清备用;血液样本1 000 r·min−1离心10 min取血清备用。按照病毒RNA/DNA快速纯化试剂盒操作方法提取病毒总DNA/RNA。
1.5 标准质粒的制备
以提取的病毒DNA/RNA为模板进行反转录,分别加入2.0 μL 10 × RT Mix、2.0 μL PureScript II Enzyme Mix、1.0 μL 9N随机引物(50 ng·μL−1)、2.0 μL病毒核酸、13.0 μL DEPC处理水。反应条件:37 ℃孵育20 min,85 ℃灭活5 s。使用反转录得到的cDNA产物进行PCR扩增,分别加入12.5 μL 2 × Multiplex Buffer、1 μL DNA聚合酶 (10 U·μL−1),5 μL 5 × Primer Mix (预先混合所有扩增引物,使每条引物终浓度为1 μmol·μL−1),2.5 μL cDNA/DNA,4.0 μL DEPC处理水。设定反应条件:95 ℃ 3 min 消除模板DNA/cDNA的二级结构;95 ℃ 15 s解开双链DNA,56 ℃ 15 s引物与模板DNA互补配对,72 ℃ 35 s合成新的DNA链,循环重复35次,72 ℃ 5 min确保所有DNA片段完全合成。通过1.5%琼脂糖凝胶电泳对扩增产物进行分离和检测,观察并分析结果。用FastPure Gel DNA Extraction Mini Kit对阳性条带进行高效回收,DNA片段被连接至pMD20-T载体,并转入DH5α后涂布于LB Amp+平板,经初步鉴定确认阳性克隆样品送往生工生物工程(上海)公司进行测序分析。将测序正确的阳性菌液扩大培养后使用FastPure Plasmid Mini Kit提取重组质粒,NanoPhotometer N60测定质粒浓度,并计算质粒拷贝数。
拷贝数/(copies⋅μL−1)=重组质粒浓度(ng⋅μL−1)×6.02×1023(载体碱基数+目的片段碱基数)×660×109 1.6 特异性试验
应用建立的方法对AKAV、BoHV-1、BVDV、BPV、BRSV、BPIV3、FMDV及BEFV阳性样品进行扩增。通过1.5%琼脂糖凝胶电泳对扩增产物进行分离和检测,观察并分析结果。
1.7 敏感性试验
将1.5中获得的重组质粒稀释为1.0×109拷贝·μL−1,按10倍梯度稀释对重组质粒稀释为1.0×101~1.0×108拷贝·μL−1,以此为模板进行PCR扩增,对建立的多重RT-PCR方法进行灵敏度测定。
1.8 重复性试验
应用上述建立的多重PCR检测方法,选取1.5中获得的重组质粒为模板,每隔1周重复1次,检测3次,以确定检测方法的可靠性和重复性。
1.9 临床腹泻样品的检测
应用建立的多重RT-PCR方法,检测2023—2024年从江西和广西地区牛场采集的143份疑似或出现繁殖障碍的牛血液或内脏组织样本中AKAV、BoHV-1和BVDV存在情况;同时与《牛病毒性腹泻/黏膜病病毒荧光RT-PCR检测方法》(DB22/T 1608—2012)、《牛疱疹病毒1型的检测巢式聚合酶链反应法》(DB45/T 2311—2021)及《赤羽病病毒荧光PCR检测方法》(DB21/T 2533—2015)的地方标准检测结果进行对比。
2. 结果与分析
2.1 多重PCR扩增结果
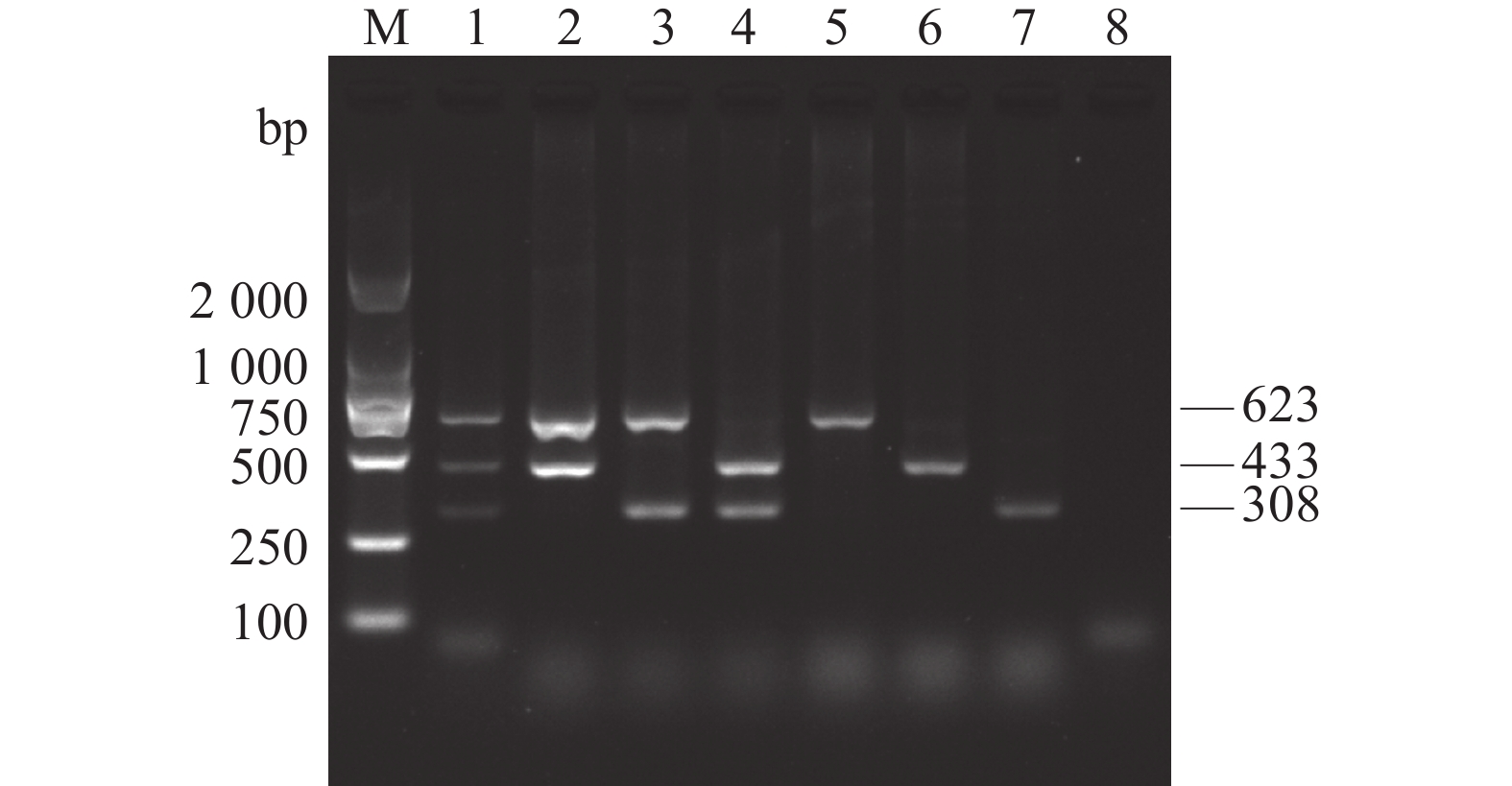
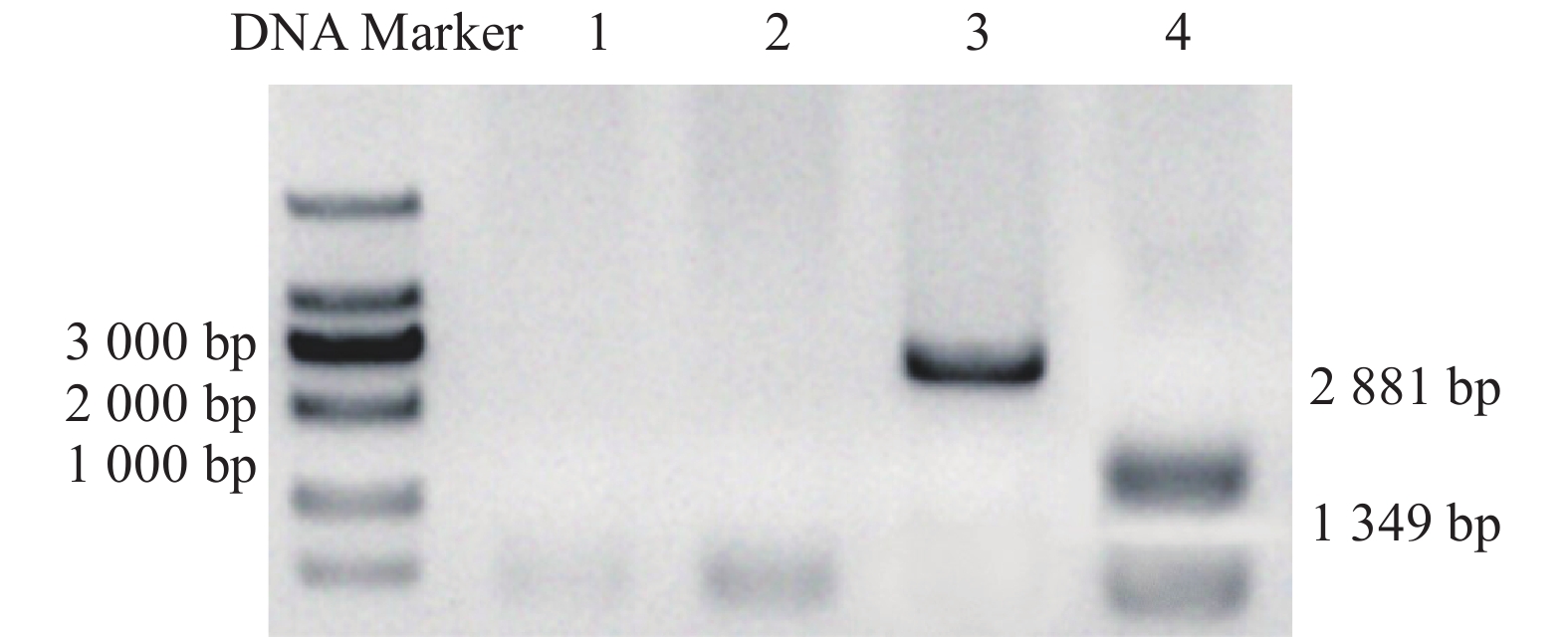
利用AKAV、BoHV-1和BVDV的特异性引物对AKAV、BoHV-1和BVDV标准质粒进行单重、双重和三重PCR扩增,结果(图1)表明,加入AKAV/BoHV-1/BVDV标准质粒均能分别扩增出约623、433、308 bp片段,未见其他条带扩增。
![]() 图 1 AKAV、BoHV-1和BVDV单重和多重PCR扩增M:DL2 000 DNA Marker;1:AKAV、BoHV-1和BVDV;2:AKAV和BoHV-1;3:AKAV和BVDV;4:BoHV-1和BVDV;5:AKAV;6:BoHV-1;7:BVDV;8:阴性对照。Figure 1. Single and multiplex amplified PCR products of AKAV, BoHV-1, and BVDVM: DL2 000 DNA marker; 1: AKAV, BoHV-1, and BVDV; 2: AKAV and BoHV-1; 3: AKAV and BVDV; 4: BoHV-1 and BVDV; 5: AKAV; 6: BoHV-1; 7: BVDV; 8: negative control.
图 1 AKAV、BoHV-1和BVDV单重和多重PCR扩增M:DL2 000 DNA Marker;1:AKAV、BoHV-1和BVDV;2:AKAV和BoHV-1;3:AKAV和BVDV;4:BoHV-1和BVDV;5:AKAV;6:BoHV-1;7:BVDV;8:阴性对照。Figure 1. Single and multiplex amplified PCR products of AKAV, BoHV-1, and BVDVM: DL2 000 DNA marker; 1: AKAV, BoHV-1, and BVDV; 2: AKAV and BoHV-1; 3: AKAV and BVDV; 4: BoHV-1 and BVDV; 5: AKAV; 6: BoHV-1; 7: BVDV; 8: negative control.2.2 PCR产物的克隆与测序分析
将AKAV、BoHV-1和BVDV的阳性PCR产物回收、克隆后进行测序,将测序结果与NCBI数据库公开的序列进行BLAST比对分析。结果表明:扩增得到的疑似AKAV片段序列与KY381273、KY381274、KU375444毒株序列的同源性均高于99%;扩增出的疑似BoHV-1片段序列与MK552112、MH751901、MH751900、MH724208的同源性为100%;扩增出的疑似BVDV片段序列与MT079816、MT002667、ON732849、ON337882的同源性均高于98%;证明所扩增的片段分别为AKAV、BoHV-1和BVDV。
2.3 特异性试验
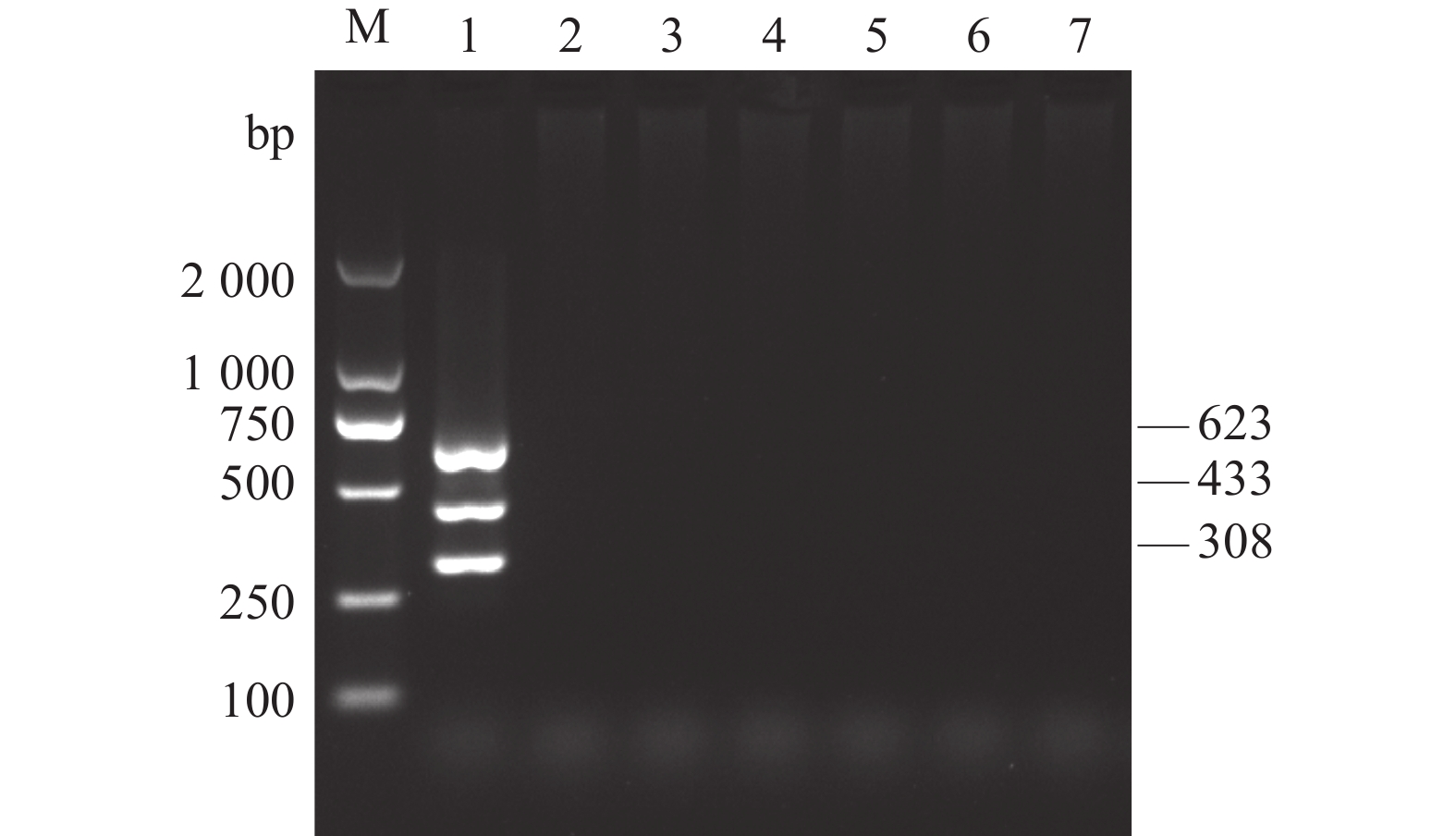
为检验建立的多重PCR方法的特异性,以AKAV、BoHV-1、BVDV、BPV、BRSV、BPIV3、FMDV及BEFV阳性核酸样品为模板,用所设计的引物进行RT-PCR/PCR扩增。结果发现,以BPV、BRSV、BPIV3、FMDV和BEFV为模板的样品均为阴性,只有AKAV、BoHV-1和BVDV阳性核酸样品可分别扩增出约为623、433、308 bp的目的片段,表明该检测方法特异性良好(图2)。
![]() 图 2 AKAV、BoHV-1和BVDV多重PCR特异性试验M:DL2 000 DNA Marker;1:AKAV、BoHV-1和BVDV多重PCR扩增产物; 2~6分别为BPV、BRSV、BPIV3、FMDV和BEFV;7:阴性对照。Figure 2. Validation of assay specificity in detecting BoHV-1, AKAV, and BVDVM: DL2 000 DNA marker; 1: BoHV-1, AKAV, and BVDV; 2–6: BPV, BRSV, BPIV3, FMDV, and BEFV, respectively; 7: negative control.
图 2 AKAV、BoHV-1和BVDV多重PCR特异性试验M:DL2 000 DNA Marker;1:AKAV、BoHV-1和BVDV多重PCR扩增产物; 2~6分别为BPV、BRSV、BPIV3、FMDV和BEFV;7:阴性对照。Figure 2. Validation of assay specificity in detecting BoHV-1, AKAV, and BVDVM: DL2 000 DNA marker; 1: BoHV-1, AKAV, and BVDV; 2–6: BPV, BRSV, BPIV3, FMDV, and BEFV, respectively; 7: negative control.2.4 敏感性试验
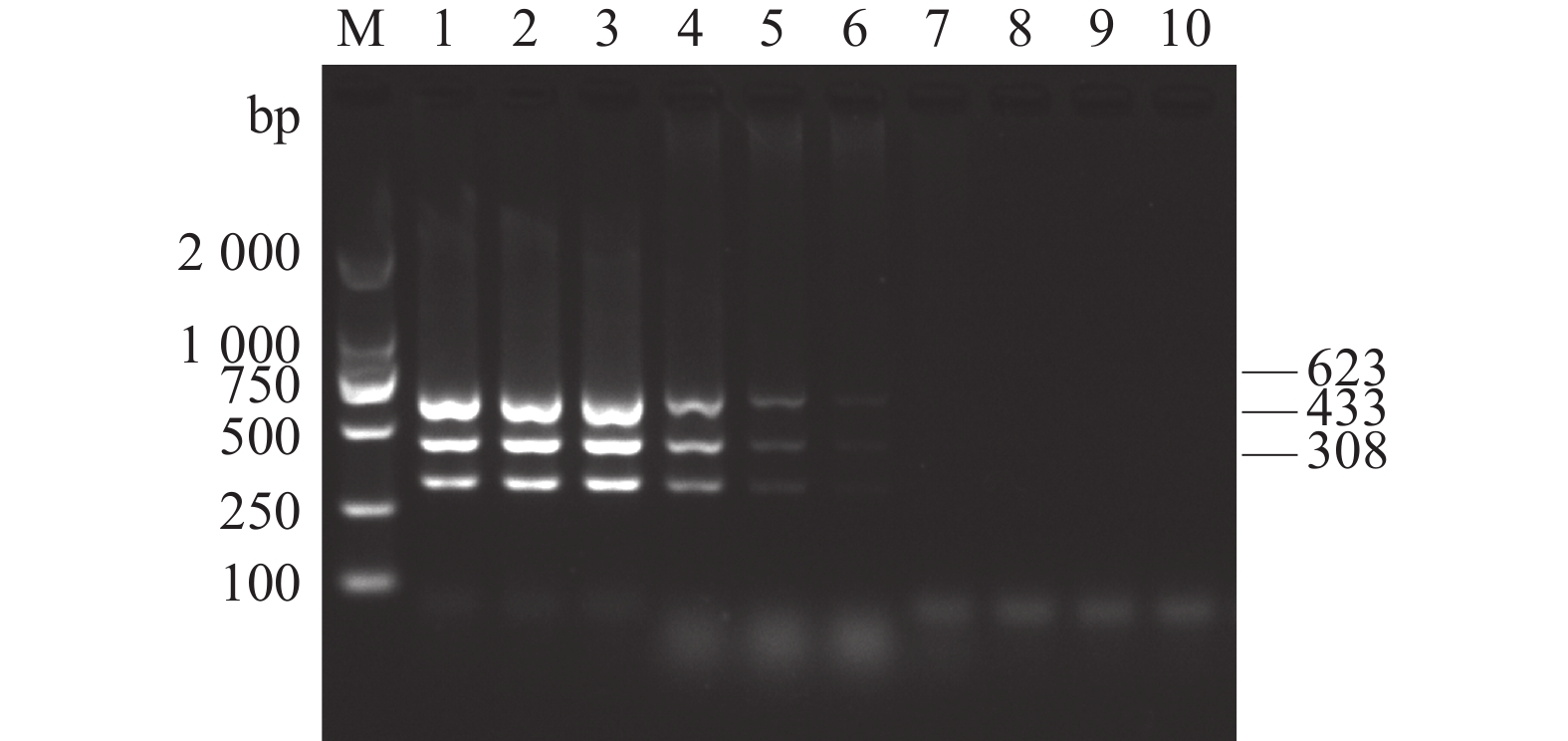
以1.0×108拷贝·μL−1原始浓度的重组质粒进行10倍梯度稀释后作为模板,用本研究建立的多重PCR方法进行最低检测量测定,发现AKAV、BoHV-1和BVDV三者的最低检测量均为1.0×103 拷贝·μL−1(图3)。
2.5 重复性试验
利用建立的AKAV、BoHV-1和BVDV多重PCR检测方法,以不同时间段连续扩增3次,结果(图4)表明,建立的方法具有较好的重复性。
2.6 临床样品检测对比
应用建立的多重PCR方法检测2023—2024年从江西和广西地区牛场采集的143份疑似或出现繁殖障碍的牛血液或内脏组织样品中的AKAV、BoHV-1和BVDV感染情况。结果(表2)显示,AKAV、BoHV-1和BVDV的检出率分别为2.80%(4/143)、21.68%(31/143)和38.46%(55/143)。同时使用地方标准的检测方法进行检验,检出率分别为3.50%(5/143)、23.08%(33/143)和41.26%(59/143)。对比两种检测方法发现,两者的符合率为99.3%、98.6%和97.2%,Kappa系数为0.885、0.960和0.942,说明两种检测方法的结果表现出极高的吻合度。
表 2 临床样本检测结果对比Table 2. Comparison of test results by two methods on clinical specimens病毒
Virus本研究方法
Method in this study地方标准检测方法
Local standardsKappa值
Kappa value阳性样本数
No. of positive samples阳性率
Positivity rate/%阳性样本数
No. of positive samples阳性率
Positivity rate/%赤羽病病毒 AKAV 4 2.80 5 3.50 0.8852 牛疱疹病毒1型 BoHV-1 31 21.68 33 23.08 0.9597 牛病毒性腹泻病毒 BVDV 55 38.46 59 41.26 0.9417 3. 讨论
AKAV、BoHV-1和BVDV是养牛业中引起牛繁殖障碍的主要病原,对牛群健康和生产性能造成了严重影响。近年来,我国活牛和牛产品进口频繁,造成牛肉价格一直萎靡不振,养牛密度加大、防疫松懈、饲养管理不规范等问题日益严重,以致牛疫病呈现出多病原混合感染的复杂局面,这不仅加速了疫病的传播和变异速度,而且显著增加了防疫工作的难度,为养牛业带来了前所未有的重大挑战[15, 16]。针对新现或再现的变异病原,仅凭临床症状对病牛进行快速诊断存在困难,通常需要依赖实验室检测来明确诊断。本研究成功建立了针对AKAV、BoHV-1和BVDV 3种牛繁殖障碍性病原的多重RT-PCR检测方法,其能够同时扩增多个目标序列,实现多种病原体的同步检测,极大地提高了检测效率和准确性。
PCR作为分子生物学领域的最常用的检测方法之一,因其容易操作、灵敏性高、价格低廉等优势,在临床疾病检测中得到了广泛的运用[17, 18]。该技术能够实现对特定DNA片段的精确扩增,为后续的基因分析、疾病诊断以及病原体检测等提供了强有力的技术支持。国内外学者已建立了针对AKAV、BoHV-1和BVDV的单重或多重PCR检测方法[16, 19]。Hwang等[20]根据BVDV 的5'UTR基因建立BVDV CRISPR-Cas13的新型即时核酸检测方法,可即时检测样品中是否含有BVDV病毒核酸,且不需要仪器观察,但是不适合多种病原检测;Kamata等[11]根据AKAV S基因建立AKAV巢式RT-PCR方法,该方法可以从感染AKAV的小鼠各种组织检测到病毒核酸,检测浓度下限为10−5空斑形成单位(plaque forming unit, PFU),其灵敏度比本研究方法高,其主要原因是巢式RT-PCR方法经过两轮扩增,极大地提高了扩增循环数和扩增效率,其缺点是操作复杂、成本高,不适合大规模样品检测;鲍显伟等[21]根据BVDV 5'UTR基因和BoHV-1 UL27基因建立了BVDV和BoHV-1双重PCR方法,本研究与之相比可同时检测3种病原,提高了疾病诊断效率,而且BVDV检测限更低,能够在病毒感染早期阶段提供有效的诊断依据,其原因可能是引物序列不同及PCR反应试剂差异导致。Meng等[22]根据BNoV Rdrp基因、BEV 5'UTR基因、BToV M基因、BCoV N基因、BRV NSP5基因和BVDV 5'UTR基因建立多重实时荧光定量RT-PCR方法,该方法具备高灵敏性、强特异性和定量检测等优点,但此方法因受限于仪器设备和专业的操作技术,易污染产生假阳性等,只适合于专业实验室检测使用。此外,本研究的方法还具有操作简便、结果稳定可靠等特点,适用于大规模样本的筛查和监测。为进一步检验本研究方法的应用效果,对采集的143份疑似或出现繁殖障碍的牛血液或内脏组织样品中的AKAV、BoHV-1和BVDV感染情况进行测定。结果显示,AKAV、BoHV-1、BVDV的检出率分别为3.50%(5/143)、21.68%(31/143)、41.26%(59/143),与地方标准检测结果高度一致,可以在基层养殖场简易实验室进行临床样本的检测,同时满足AKAV、BoHV-1、BVDV的区分诊断。这一结果不仅验证了方法的可靠性,还为我们了解病毒的流行情况、传播规律及可能的变异情况提供了重要依据。
总之,本研究从引起牛只繁殖障碍的角度出发,建立了AKAV、BoHV-1和BVDV多重RT-PCR检测方法,建立的方法特异性高、灵敏性强,在临床样品初步检测效果较好,为我国牛群AKAV、BoHV-1和BVDV的检测和流行病学调查提供了一种快捷简便的分子生物学检测技术。
-
表 1 试剂及来源
Table 1 Names and suppliers of reagents applied
试剂 Reagents 来源 Sources MiniBEST通用DNA提取试剂盒5.0 TaKaRa 9765 TaKaRa小型DNA片段纯化试剂盒Ver.4.0 TaKaRa 9761 无内毒素质粒小提试剂盒 康为-cw2106 MiniBEST通用RNA提取试剂盒 TaKaRa 9767 PrimeScriptTM常温反应试剂 TaKaRa DRR047A SYBR® Premix DimerEraserTM(Perfect Real Time) TaKaRa RR091A SYBR® Premix Ex Taq II(Tli RNaseH Plus),ROX Plus TaKaRa RR82WR 1640 RPMI粉 life technology RPMI 1640培养基 Gibco 1598911 DMEM/F12(高糖) Hyclone 11966-025 DMEM Gibco 11960-044 T4 DNA连接酶 TaKaRa 2011B TaKaRa Ex Taq® TaKaRa RR001C PrimeSTAR® Max DNA聚合酶 TaKaRa R045A Premix TaqTM(Ex TaqTM Version 2.0) TaKaRa RR003A RNA酶 全式基因-j11030 FastDigest Sac I ThermoFD1134 FastDigest Bam HI Thermo FD0055 FastDigest EcoRI Thermo FD0274 兔抗抗磷酸化-STAT6抗体 DZ-23319 兔抗抗-STAT6抗体 CST 9362s IRF3(D614C)XP Rabbit mAb CST 11904 磷酸化-IRF-3(Ser396)(4D4G)兔抗 CST 4947 表 2 sgRNA名称及序列
Table 2 Names and sequences of sgRNA
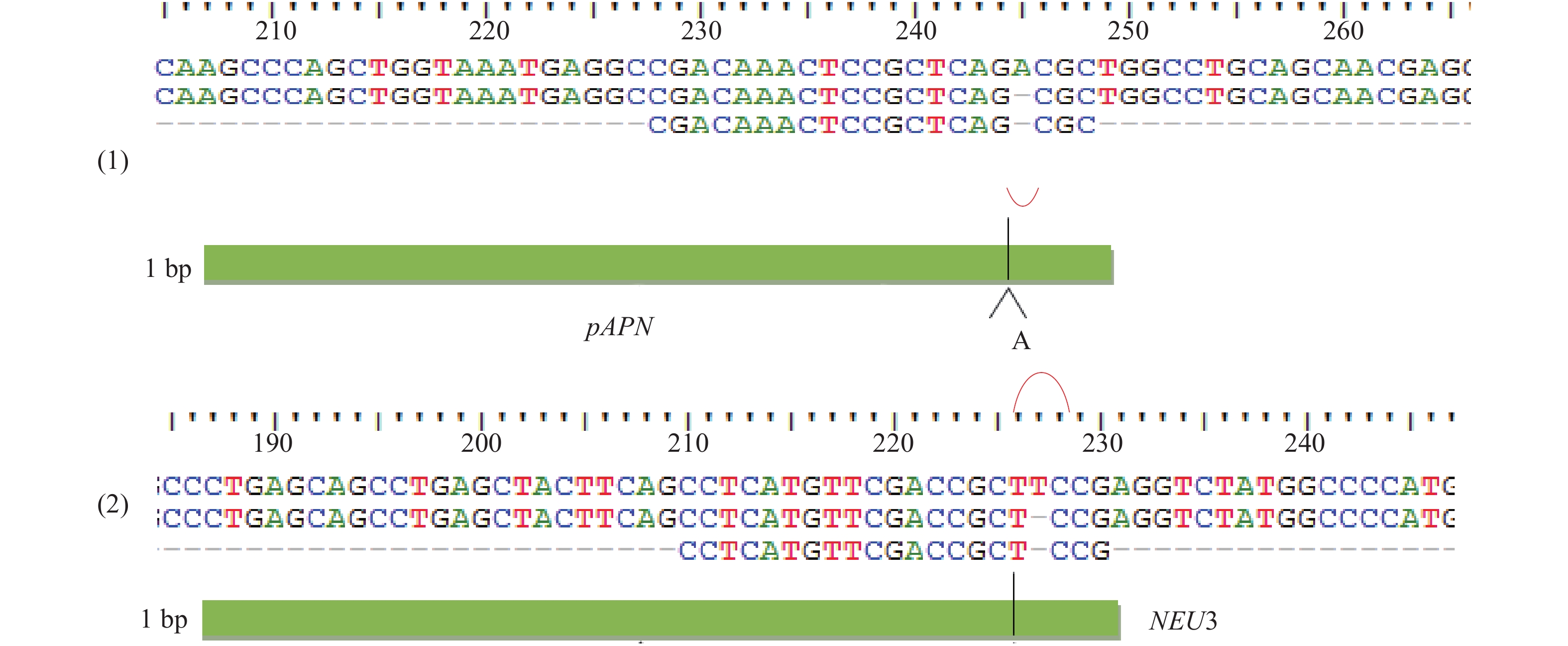
名称 Name 序列 Sequences pAPN sgRNA-1F: 5′CACCGGGGCATCCTCCTCGGCGTGG3′ pAPN sgRNA-1R: 5′AAACCCACGCCGAGGAGGATGCCCC3′ pAPN sgRNA-2F: 5′CACCGCTACCGCAGCGAGTACATGG3′ pAPN sgRNA-2R: 5′AAACCCATGTACTCGCTGCGGTAGC3′ pAPN sgRNA-3F: 5′CACCGCCTCATGTTCGACCGCTCCG3′ pAPN sgRNA-3R: 5′AAACCGGAGCGGTCGAACATGAGGC3′ pAPN sgRNA-4F: 5′CACCGCGACAAACTCCGCTCAGCGC3′ pAPN sgRNA-4R: 5′AAACGCGCTGAGCGGAGTTTGTCG3′ NEU3 sgRNA1-F: 5′CACCGATGCTCAGTCATCGGCGTGA3′ NEU3 sgRNA1-R: 5′AAACTCACGCCGATGACTGAGCATC3′ NEU3 sgRNA2-R: 5′AAACTGGGCAGTACGTATAACTACC3′ NEU3 sgRNA2-F: 5′CACCGGTAGTTATACGTACTGCCCA3′ 表 3 验证引物
Table 3 Primers for verification
名称 Name 序列 Sequences pAPN F:5′ATGGCCAAGG GATTCTACAT3′ pAPN R:5′AACCAAGTATCTCGTGTCGATT3′ NEU3 F:5′ATGGGAAACTCGCCATCAAAAA3′ NEU3 R:5′TTCTTTCTGTTCTTCTACGCAACT3′ 表 4 实时定量PCR引物
Table 4 Primers for RT-PCR reaction system
基因名称 Name of genes 序列 Sequences h-GAPDH-F CCCTGAGCTGAACGGGAAGCTCAC h-GAPDH-R CTTGCTGTAGCCAAATTCGTTGCT h-IFNβ-F AGGACAGGATGAACTTTGAC h-IFNβ-R TGATAGACATTAGCCAGGAG h-Spike protein-F TAATAGCAGT TGTTTCTGCT h-Spike protein-R GCATTGCTGT ACTCTTTGTA 表 5 干扰素mRNA
Table 5 Real time PCR assay for the expression of IFNβ
时间
Time/h双基因敲除细胞
Double knockout/拷贝数野生型细胞
Wild type cells/拷贝数20 1 4 1 1103000 1103900 1102700 40 2 3 3 1290030 1203009 1203007 60 2 2 3 1322000 1322004 1322043 80 3 5 5 1103005 1103008 1103009 100 3 3 3 1140001 1143006 1143003 120 1 2 3 1120000 1102300 1102307 表 6 纤突蛋白的mRNA
Table 6 The T vector containing the TGEV spike protein gene fragment
时间
Time/h双基因敲除细胞
Double knockout/拷贝数野生型细胞
Wild type cells/拷贝数20 41 43 45 1423341 1322356 1421345 40 68 67 60 1367893 1323567 1309876 60 62 69 62 1656431 1665789 1632454 80 43 50 54 1456445 1433421 1432098 100 31 35 32 1432223 1432554 1478909 120 49 35 36 1444009 1422112 1423115 -
[1] 殷相平, 任晓峰, 柳纪省. 猪传染性胃肠炎病毒致病机制的研究进展 [J]. 世界华人消化杂志, 2013, 21(1):39−43. DOI: 10.11569/wcjd.v21.i1.39 YIN X P, REN X F, LIU J X. Progress in understanding pathogenic mechanisms of porcine transmissible gastroenteritis virus [J]. World Chinese Journal of Digestology, 2013, 21(1): 39−43.(in Chinese) DOI: 10.11569/wcjd.v21.i1.39
[2] 吴国平, 尹燕博, 吴时友. 猪传染性胃肠炎病毒(TGEV)研究进展 [J]. 中国兽医杂志, 2003, 39(2):29−32. DOI: 10.3969/j.issn.0529-6005.2003.02.015 WU G P, YIN Y B, WU S Y. Research progress of transmissible gastroenteritis virus [J]. Chinese Journal of Veterinary Medicine, 2003, 39(2): 29−32.(in Chinese) DOI: 10.3969/j.issn.0529-6005.2003.02.015
[3] 柴伟东. 猪传染性胃肠炎基因工程活疫苗的构建与免疫原性测定[D]. 武汉: 华中农业大学, 2010. CHAI W D. Construction and immunogenicity determination of live gene engineering vaccine for infectious gastroenteritis in pigs[D]. Wuhan: Huazhong Agricultural University, 2010. (in Chinese).
[4] 赵珊珊. 猪传染性胃肠炎病毒强弱毒株与猪空肠上皮细胞和猪树突状细胞相互作用的研究[D]. 南京: 南京农业大学, 2014. ZHAO S S. A study on the interaction between porcine jejunal epithelial cells and porcine dendritic cells[D]. Nanjing: Nanjing Agricultural University, 2014. (in Chinese).
[5] JACOBS L, DE GROOT R, VAN DER ZEIJST B A, et al. The nucleotide sequence of the peplomer gene of porcine transmissible gastroenteritis virus (TGEV): Comparison with the sequence of the peplomer protein of feline infectious peritonitis virus (FIPV) [J]. Virus Research, 1987, 8(4): 363−371. DOI: 10.1016/0168-1702(87)90008-6
[6] DELMAS B, GELFI J, L'HARIDON R, et al. Aminopeptidase N is a major receptor for the entero-pathogenic coronavirus TGEV [J]. Nature, 1992, 357(6377): 417−420.
[7] ZHU X, LIU X, WANG X, et al. Contribution of porcine aminopeptidase N to porcine deltacoronavirus iinfcetion [J]. Emerging Microbes infection, 2018, 37(1): 65−70. DOI: 10.1038/357417a0
[8] LI B X, GE ZW, LI YZ, et al. aminopeptidase N is a functional receptor for the PEDV coronavirus [J]. Virology, 2007, 365(1): 166−72.
[9] REN X, LIU B, YIN J, et al. Phage displayed peptides recognizing porcine aminopeptidase N inhibit transmissible gastroenteritis coronavirus infection in vitro [J]. Virology, 2011, 410(2): 299−306. DOI: 10.1016/j.virol.2010.11.014
[10] DELMAS B, KUT E, GELFI J, et al. Overexpression of TGEV Cell Receptor Impairs the Production of Virus Particles [J]. Advances in Experimental Medicine and Biology, 1995, 380: 379−385.
[11] LIU B Q, LI G X, REN X F. Initial identification of the domain of TGEV specific receptor APN [J]. Hlongjiang Animal ence and Veterinary Medicine, 2009(6): 21−26.
[12] SCHWEGMANN-WESSELS C, HERRLER G. Identification of sugar residues involved in the binding of TGEV to porcine brush border membranes [J]. Methods Mol Biol, 2008, 454: 319−329.
[13] TAKAHASHI K, HOSONO M, SATO I, et al. Sialidase NEU3 contributes neoplastic potential on colon cancer cells as a key modulator of gangliosides by regulating Wnt signaling [J]. International Journal of Cancer, 2015, 137(7): 1560−1573. DOI: 10.1002/ijc.29527
[14] SCHULTZE B, ENJUANES L, CAVANAGH D, et al. N-acetylneuraminic acid plays a critical role for the haemagglutinating activity of avian infectious bronchitis virus and porcine transmissible gastroenteritis virus [J]. Oxygen Transport to Tissue XXXIII, 1993, 342: 305.
[15] PARK S, SESTAK K, HODGINS D C, et al. Immune response of sows vaccinated with attenuated transmissible gastroenteritis virus (TGEV) and recombinant TGEV spike protein vaccines and protection of their suckling pigs against virulent TGEV challenge exposure [J]. American Journal of Veterinary Research, 1998, 59(8): 1002−1008.
[16] PENG S Y, LV N, ZHANG Y, et al. Immune response induced by spike protein from transmissible gastroenteritis coronavirus expressed in mouse mammary cells [J]. Virus Research, 2007, 128(1/2): 52−57.
[17] YU T F, LI M, SHAO S L, et al. Genetic Variation Analysis of TGEV Spike Protein Antigenic Sites [J]. Journal of Animal & Veterinary Advances, 2012, 11(3): 361−363.
[18] GELHAUS S, THAA B, ESCHKE K, et al. Palmitoylation of the Alphacoronavirus TGEV spike protein S is essential for incorporation into virus-like particles but dispensable for S-M interaction [J]. Virology, 2014, 464/465: 397−405. DOI: 10.1016/j.virol.2014.07.035
[19] JORDAN L T, DERBYSHIRE J B. Antiviral action of interferon-alpha against porcine transmissible gastroenteritis virus [J]. Veterinary Microbiology, 1995, 45(1): 59−70. DOI: 10.1016/0378-1135(94)00118-G
[20] THANOS D, MANIATIS T. Virus induction of human IFN beta gene expression requires the assembly of an enhanceosome [J]. Cell, 1995, 83(7): 1091−1100. DOI: 10.1016/0092-8674(95)90136-1
[21] WANG Y Y, LIU W N, PING W, et al. Expression of IFN-γ, IL-6and IL-8 in ST cells infected with TGEV and on the intervention of Lactobacillus acidophilus extracellular polysaccharides [J]. Chinese Journal of Veterinary Medicine, 2015(11): 45−48.
[22] LI D, LI J W, LI W H, et al. p53 mediated IFN-β signaling to affect viral replication upon TGEV infection [J]. Veterinary Microbiology, 2018(227): 61−68.




 下载:
下载: