Stem Rot-resistant and Growth-promoting Effects of Trichoderma on Anoectochilus roxburghii
-
摘要:目的
分离具有金线兰茎腐病拮抗作用的木霉菌,为生防菌的开发提供理论基础。
方法以金线兰仿野生种植植株为材料,利用组织分离法分离木霉菌,利用形态特征与ITS和rpb2序列同源性分析鉴定其分类,利用平板对峙法鉴定其抗茎腐病能力,并对不同木霉菌的促生长作用进行评价。
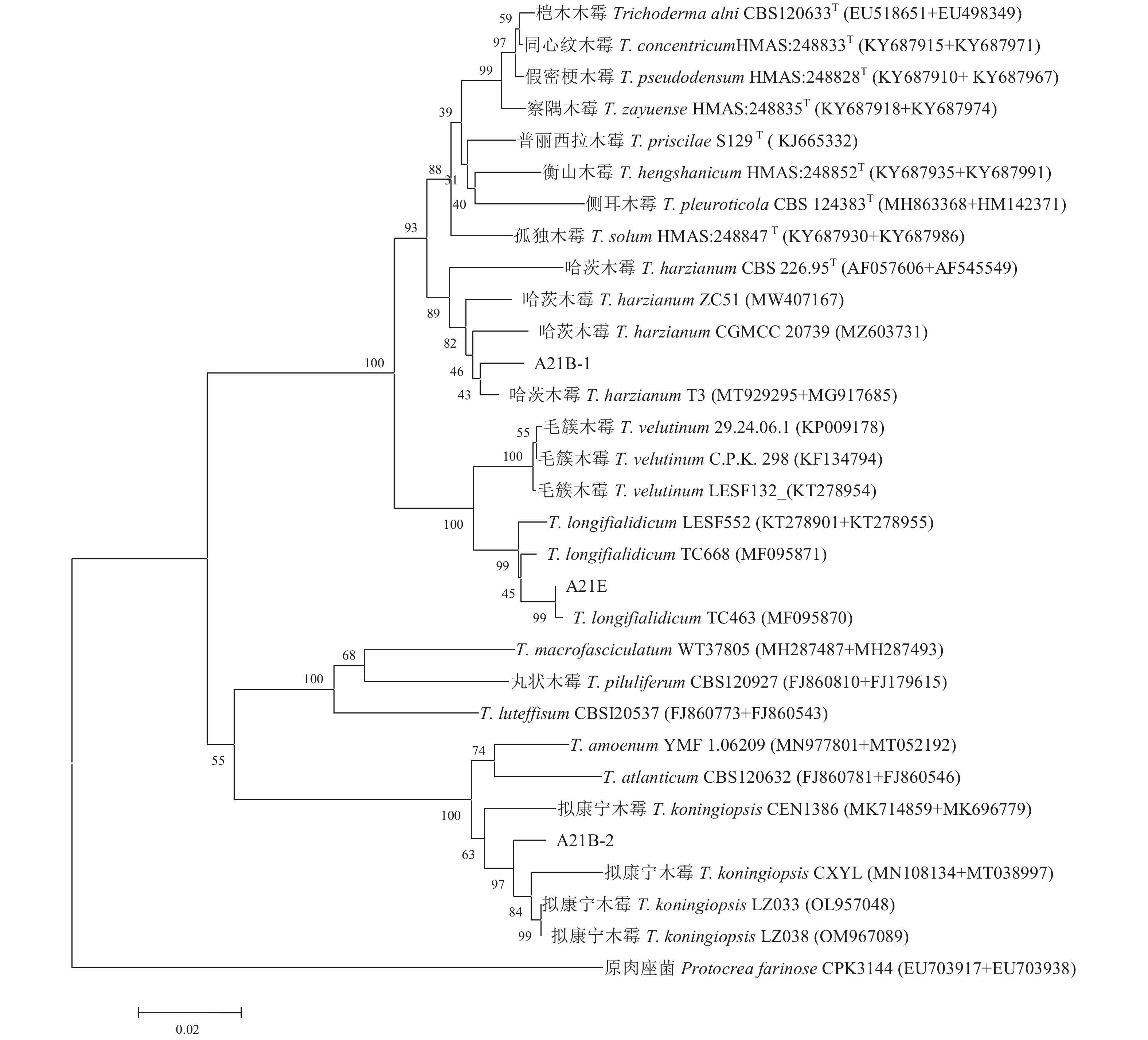
结果利用组织分离法分离3株木霉菌A21B-1、A21B-2和A21E。经鉴定,3株木霉株分别为哈茨木霉、拟康宁木霉和Trichoderma longifialidicum。对峙生长表明,3种木霉菌株均对茎腐病病原菌尖孢镰刀菌ASP01表现较强的抑制作用,其抑制率分别达75.29%、73.55%和 60.02%。室内防效结果表明,A21B-1菌株对茎腐病有较强的抑制作用,接种15 d后病情抑制率达91.9%,可作为该病的生物防治候选菌株。促进生长试验表明,种植6个月后,施用3个木霉菌的金线兰植株的单株重、株高、茎粗、叶面积及SPAD值较对照均显著提高,其中A21B-2与A21E处理的植株单株重比对照分别提高了58.68%与58.99%,叶面积分别提高66.82%与59.73%,可作为金线兰促进生长的候选菌株。同时,施用木霉菌可有效提高金线兰多糖及金线莲苷的含量,其中A21B-2菌株效果最佳,其多糖及金线莲苷含量均较对照提高89.62%与11.83%,可作为促进金线兰药用成分积累的候选菌株。
结论3种不同类型的木霉菌在金线兰对抗茎腐病、促进生长和提高多糖含量方面有显著作用。
Abstract:ObjectiveTrichoderma strains antagonistic to stem rot pathogens were studied to develop a biocontrol agent for the disease on Anoectochilus roxburghii.
MethodFrom the A. roxburghii plants grown under simulated wild conditions, strains of Trichoderma were obtained by tissue isolation and classified by morphological observations and homology analysis with ITS and rpb2 sequences. Ability of the isolates to resist stem rot was evaluated in vitro by the plate confrontation method. Growth of A. roxburghii in the presence of the identified strains was monitored.
ResultsThe resistant A21B-1, A21B-2, and A21E strains were isolated and subsequently identified as T. rugulosum, T. koningiopsis, and T. longifialidicum showing the inhibition rates of 75.29%, 73.55%, and 60.02%, respectively, on Fusarium oxysporum f. sp. opponiarum ASP01. Furthermore, 15 d after a T. rugulosum inoculation in an indoor control evaluation test A. roxburghii exhibited a significant inhibition rate of 91.9% against the stem rot. That suggested a potentially effective means for control on the disease. In addition, the 3 strains displayed a significant growth promoting effect on the A. roxburghii seedlings in a greenhouse with increased plant weight, height, stem diameter, leaf area, and SPAD value in 6 months. Among them, T. koningiopsis and T. longifialidicum not only significantly increased the plant biomass over control by 58.68% and 58.99% and leaf area by 66.82% and 59.73%, respectively, but also elevated the contents of functional polysaccharides and kinsenoside with the greatest increases of 89.62% on polysaccharides and 11.83% on kinsenoside by T. koningiopsis.
ConclusionThree strains of Trichoderma demonstrated in vitro a significant antagonistic effect against the stem rot disease on A. roxburghii. Their presence also significantly promoted the growth and increased the functional polysaccharides and kinsenoside contents in the plant.
-
Keywords:
- Trichoderma /
- Anoectochilus roxburghii /
- Fusarium oxysporum /
- kinsenoside
-
0. 引言
【研究意义】非洲菊(Gerbera jamesonii Bolus)又名扶郞花,为菊科大丁草属多年生宿根花卉,因其具有花色艳丽、花朵硕大、花茎挺拔、连续开花等特点,观赏价值较高,在全球切花贸易中排名第五[1−2]。大丁草属约有80种,主要分布于非洲南部,中国约有20种,主要分布于西南地区[3]。市场上常见的非洲菊是非洲菊的栽培种(Gerbera jamesonii Bolus),由非洲菊野生种(Gerbera jamesonii)与绿叶非洲菊(Gerbera viridifolia)杂交而来,几乎所有的非洲菊商业品种均为这两个种的杂交后代,且几乎都为二倍体(2n=50)[4−5]。荷兰、日本、德国、美国等是主要的育种国家,经过长期的人工培育,已选育出切花、盆栽和庭院等不同用途的品种[6−7],也选育出红、橙、黄、粉、白、紫等不同花色,单瓣、半重瓣和重瓣等不同花序类型,迷你型和细丝状花瓣型等多种不同类型品种[5]。中国不是非洲菊原产地,自20世纪80年代引种进行商业化栽培以来,国内科研机构及花卉企业广泛引进非洲菊种质资源[8−10],主要通过杂交育种方式培育新品种,累计培育非洲菊新品种达100余个 [5]。由于非洲菊种质引进历史较长,种源来源复杂,类型多样,部分种质有同物异名的可能,种内亲缘关系不够明确,严重制约非洲菊种质资源的引进、保护及育种利用。因此,开展非洲菊种质资源遗传多样性及亲缘关系研究十分必要。【前人研究进展】分子标记技术是研究植物遗传多样性的重要手段,能够有效揭示种内和种间的遗传变异[11]。早期非洲菊种质资源遗传多样性的研究主要采用ISSR、RAPD等分子标记技术[12−14]。简单重复序列(simple sequence repeat, SSR)通常由1~6个碱基为单元经过多次重复串联构成的DNA序列,具有共显性、多态性丰富、稳定性高、重复性好、简便易行等优点,目前SSR标记广泛应用于荷花(Nelumbo spp.)、兜兰(Paphiopedilum hirsutissimum)、月季(Rosa hybrida)等多种花卉种质资源遗传多样性研究中[15−17]。根据序列来源,SSR标记可以分为基因组SSR和表达序列标签SSR(expressed sequence tags-SSR, EST-SSR),EST-SSR标记来源于转录区域。2010年Gong等[18]筛选出99个可用EST-SSR标记,并应用于非洲菊种质资源遗传多样性研究中;Benemann等[19]利用17对EST-SSR标记对34份非洲菊种质进行分析,证明EST-SSR标记具有高度多态性;尹茂[20]利用48对EST-SSR标记对123份非洲菊材料遗传多样性和花色性状关联分析,挖掘出5个花色关联SSR标记位点;Yuan等[21]利用14对SSR标记对170份非洲菊种质进行分析,构建出170份非洲菊种质的指纹图谱。【本研究切入点】目前SSR标记应用于非洲菊种质资源遗传多样性的研究还存在可用标记数量仍较稀缺、分析所用标记较少,未能覆盖全部染色体、分析局限于常规舌状花等少数类型种质等的问题,而有关丝状花瓣、卷曲花瓣、盆栽、迷你等非洲菊不同类型及不同来源群体遗传多样性的研究鲜有报道。【拟解决的关键问题】本研究利用筛选出的分布于非洲菊不同染色体上的EST-SSR标记,对不同来源群体、不同类型的170份非洲菊种质资源进行遗传多样性及亲缘关系分析,旨在揭示不同来源群体、不同类型非洲菊种质的遗传多样性及亲缘关系,为非洲菊种质资源的引进、保护及利用等提供依据。
1. 材料与方法
1.1 试验材料
170份非洲菊种质由三明市农业科学研究院提供,种质均保存于国家非洲菊种质资源库,其中1~19号为德国喜乐达公司(Slecta)选育品种,20~27号为荷兰花舞士公司(Florist)选育品种,28~45号为荷兰西露丝公司(Schirus)选育品种,46~59号为来源于日本的盆栽非洲菊种质,60~90号为中国云南省的育种单位选育品种,91~170号种质为市场收集而来(表1)。每份种质剪取嫩叶样品,液氮速冻后置于−80 ℃的超低温冰箱中保存备用。
表 1 供试的非洲菊种质Table 1. Information on 170 G. jamesonii germplasms种质来源
Germplasm sources资源名称
Resource name德国喜乐达
German Slecta莉莉安Liliana(1)、王子Prince(2)、纳坦Natan(3)、阿姆莱特Amlet(4)、茱莉亚Julia(5)、特蕾莎Teresa(6)、里奥内格罗Rionegro(7)、莫蕾莉亚Morelia(8)、黑杰克Black Jack(9)、菲比Febe(10)、福娃Fuwa(11)、艾玛Emma(12)、科蒂奶油Cotti Creme(13)、科蒂奶油变异Cotti Creme(14)、安娜Anacleto(15)、罗德里Rodrigo(16)、米格尔Miguel(17)、红旅Red Trip(18)、希拉里Hillary(19) 荷兰花舞士
Holland Florist菜花黄Aruba(20)、法莱伦斯Fleurance(21)、水粉Ellymay(22)、大臣Testarossa(23)、玲珑Rosalin(24)、热带草原Savannah(25)、阳光露Sunway(26)、阳光海岸Cabana(27) 荷兰西露丝
Holland Schirus伊斯玛拉Esmara(28)、马德里Madeli(29)、佛罗里达Foluolida(30)、卡尔加里Kaerjiali(31)、斐济Feiji(32)、苏黎世Sulishi(33)、维也纳Weiyena(34)芭比娃娃Babiwawa(35)、香格里拉Xianggerila(36)、毛里求斯Maoliqiusi(37)、摩洛哥Moluoge(38)、亚历山大Yalishanda(39)、亚丁Yading(40)、大溪地Daxidi(41)、莫斯科Mosike(42)、巴塞罗那Basailuona(43)、爱丁堡Aidingbao(44)、休斯敦Xiusidun(45) 日本
JapanP01(46)、P02(47)、P03(48)、P04(49)、P05(50)、P06(51)、P07(52)、P08(53)、P09(54)、P10(55)、P11(56)、P12(57)、P13(58)、P14(59) 中国云南
Yunnan, China荣耀Rongyao(60)、秋日Qiuri(61)、醉雪Zuixue(62)、醉红Zuihong(63)、靓粉Liangfen(64)、红韵5号Hongyun No.5(65)、红韵6号Hongyun No.6(66)、红袍Hongpao(67)、紫佳人Zijiaren(68)、金葵花Jinkuihua(69)、温馨Wenxin(70)、醉粉Zuifen(71)、金桂Jingui(72)、国色Guose(73)、粉佳人Fenjiaren(74)、俏佳人Qiaojiaren(75)、曙光Shuguang(76)、宽云1号Kuanyun No.1(77)、紫衣皇后Ziyihuanghou(78)、紫佳人Zijiaren(79)、美阳阳Meiyangyang(80)、紫韵Ziyun(81)、玉镜Yujing(82)、珍爱Zhenai(83)、拉丝1号Spider No.1(84)、拉丝2号Spider No.2(85)、拉丝3号Spider No.3(86)、拉丝4号Spider No.4(87)、拉丝6号Spider No.6(88)、紫拉丝Spider Purple(89)、拉丝8号Spider No.8(90) 混合
Mix开心Kaixin(91)、红星Hongxing(92)、玲珑粉Linglongfen(93)、桑格里厄Sanggelier(94)、F1(95)、冰清玉洁Bingqingyujie(96)、大雪桔Daxuejv(97)、小雪桔Xiaoxuejv(98)、大088 Da088(99)、234(100)、黄色绿心旧Huangselvxinjiu(101)、新大088Xinda 088(102)、路易Luyi(103)、红胜利Hongshengli(104)、红艳Hongyan(105)、云南红Yunnanhong(106)、红黑心Hongheixin(107)、HZ(108)、S29(109)、浅紫Qianzi(110)、紫衣Ziyi(111)、太阳神Taiyangshen(112)、爱神Aishen(113)、卡提Kati(114)、白边紫衣Baibianziyi(115)、紫水晶Zishuijing(116)、紫灵Ziling(117)、绿心靓粉Lvxinliangfen(118)、粉蝶Fendie(119)、大地粉Dadifen(120)、大玲珑Dalinglong(121)、蜜糖Sweet Candy(122)、GU078(123)、薇娅Weiya(124)、LA4(125)、白马王子Dalma(126)、星光Xingguang(127)、彩蝶Caidie(128)、老香槟Laoxiangbin(129)、香槟Xiangbin(130)、新香槟Xinxiangbin(131)、大香槟Daxiangbin(132)、梅罗斯Meiluosi(133)、太阳风暴Taiyangfengbao(134)、纯黄Chunhuang(135)、贵族Guizu(136)、淑女Shunv(137)、紫带白边Zidaibaibian(138)、白色红圈Baisehongquan(139)、橙黄双色Chenghuangshuangse(140)、白粉复色Baifenfuse(141)、晨光Chenguang(142)、双色Shuangse(143)、西瓜红Xiguahong(144)、鲁西亚Luxiya(145)、露西娅Lucia(146)、高山Gaoshan(147)、普罗文斯Puluowensi(148)、多利Fredonzelle(149)、马亚Maya(150)、巴比伦Babilun(151)、上海绿Shanghailv(152)、巴龙Balong(153)、灿烂Canlan(154)、一点红Motezuma(155)、S50(156)、Y5(157)、北极星Beijixing(158)、千禧红Qianxihong(159)、红小花Hongxiaohua(160)、派德Paide(161)、爱心Aixin(162)、B6(163)、火焰Huoyan(164)、CY1804(165)、西瓜红拉丝Spider xiguahong(166)、黄色拉丝Spider yellow(167)、紫色拉丝Spider purple(168)、葵心Kuixin(169)、紫苏Zisu(170) 资源名称后括号内的数字表示种质编号。
Number in parentheses after a germplasm name is sample code.1.2 试验方法
1.2.1 DNA的提取和检测
采用E.Z.N.A.TM HP Plant DNA Kit植物基因组DNA提取试剂盒(美国OMEGA生物技术公司)提取非洲菊叶片基因组DNA,用1%的琼脂糖凝胶电泳和BioDrop超微量蛋白核酸分析仪检测所提取DNA质量及浓度,然后用无菌ddH2O将样品DNA浓度稀释至20 ng·μL−1,−20 ℃保存备用。
1.2.2 SSR引物合成与筛选
从三明市农业科学研究院以非洲菊云南红转录组序列为基础开发的EST-SSR引物中随机选取重复单元为二核苷酸至六核苷酸的引物122对[22],本课题组先前选取65对[23],查阅文献挑选25对[24],共挑选212对引物,交由福州尚亚生物技术有限公司合成。
以6份不同类型非洲菊种质DNA为模板,对照非洲菊云南红全基因组测序结果(另文发表),对挑选出的212对EST-SSR引物进行筛选,以扩增条带清晰、多态性高、重复性好且每对染色体至少选择1对引物的原则,筛选出引物用于后续分析。
1.2.3 PCR反应体系、程序及电泳检测
PCR反应体系、反应程序及电泳检测按照曹奕鸯等[23]的方法实施。
1.2.4 数据处理与分析
在SSR标记位点处,位置相同的条带记为一个标记等位基因,有带记为1,无带为0,缺失为2。利用NTSYS-pc2.10e软件计算遗传距离,基于UPGMA法在MEGA6.06软件中对不同非洲菊种质进行聚类分析;使用Popgen32软件计算位点等位基因数(Na)、有效等位基因数(Ne)、Shannon信息指数(I),群体总等位基因数、总基因型数、平均等位基因数、平均基因型数、平均杂合度、Nei’s遗传距离和遗传一致度;多态信息含量(PIC)则由公式
PICi=1−∑jPij2 计算,其中Pij 表示第i 个位点第j 个等位基因的频率[25]。群体聚类分析则是根据Popgen32软件计算得到的遗传一致度,用UPGMA法进行聚类。2. 结果与分析
2.1 EST-SSR引物的筛选
以6个不同类型的非洲菊种质资源DNA为模板,用212对EST-SSR引物进行PCR扩增、筛选,结果表明,在自主开发的187对EST-SSR引物中,有30对引物扩增条带清晰、多态性高、重复性好,分布于非洲菊1#、3#等21条不同染色体上,部分引物扩增结果见图1;25对参考EST-SSR引物中,9对引物扩增条带清晰,多态性高,重复性好,分布于非洲菊1#、2#等8条不同染色体上。每对染色体匹配1~3对引物(表2),因此选用这39对引物进行遗传多样性分析。
![]() 图 1 部分EST-SSR引物扩增图谱M:100bp DNA marker;1~6:6个不同非洲菊种质样品;A:g131引物扩增结果;B:g139引物扩增结果;C:g145引物扩增结果;红色框部分所示引物在EST-SSR位点处的扩增条带。Figure 1. Map of partial amplified EST-SSR primersM:100bp DNA marker; 1-6: G. jamesonii samples; A: amplified g131 primer; B: amplified g139 primer; C: amplified g145 primer; red box shows different amplification band at EST-SSR location.表 2 39对EST-SSR引物序列Table 2. Sequences of EST-SSR primers
图 1 部分EST-SSR引物扩增图谱M:100bp DNA marker;1~6:6个不同非洲菊种质样品;A:g131引物扩增结果;B:g139引物扩增结果;C:g145引物扩增结果;红色框部分所示引物在EST-SSR位点处的扩增条带。Figure 1. Map of partial amplified EST-SSR primersM:100bp DNA marker; 1-6: G. jamesonii samples; A: amplified g131 primer; B: amplified g139 primer; C: amplified g145 primer; red box shows different amplification band at EST-SSR location.表 2 39对EST-SSR引物序列Table 2. Sequences of EST-SSR primers引物名称
Primer name正向引物
Forward primer反向引物
Reverse primer片段长度
Fragment length/bp染色体位置
Chromosomal locationg23 CATCCCTTACGTTGGCACTT CACCCTTGAAACCCTCTCTG 167 16# g24 AGTGGGAGAAGCTATGCCAA GGGTCGCCATAGCAAATAGA 187 17# g25 GATTGGATGCTAGCTTTGCC GGGCATTTTGGACATTTGAT 162 25# g27 AATCCTCAATGCCACCTTTG GAGGCAGGAATTGACTGGAA 160 16# g28 CGTTTTACATGCAGCCTCAA CTTTGCTTCCTCTGCCTGAC 167 7# g31 ATCGGCTCAAGGTAAGGGAT GCTCAATGGCTTCAGACACA 186 1# g32 ATTTTGAAGGGATTGGTGGG TCATGCCATATTCCCTCGAT 174 25# g36 AGCAAGATCAAAAGACCCGA CCTTTGTCGTCATAGCAATCAA 167 21# g37 CGCCATTAAAGCCTTCTTTC GGAAGGCTTGTGTTGGTTGT 151 3# g39 ACAAAGAATCCGTCCACCAG GACCGTATTGGGCAGGTCTA 164 24# g40 GAGGCGTTATCGGACTTTGA TTCTTCTTGGGACGTAACCG 168 9# g44 TTAGGAGTGGAGTCGCTGCT CGAAAAGCTAGCAAATGGACA 200 21# g47 GAAATCCGTGAAAGGTCGAA TGTACAAACCCACCTCCCTT 193 11# g64 CGCTTCCTCCTACAACAAGC GTGTCCCCACCATTCAAGTT 163 9# g81 CCAAAAGCCGAAATTGCTAC AATCACATTTGCAAGCGACA 149 3# g91 CCGAGCAAATTGTGGATCTT CGACACCTTTCCAAGCATCT 154 5# g93 TGCTGCATCTCATCATTCCT AGGAGAATCCATGTAGCCGA 217 18# g96 TCTGTGTTCCTCCGTCTCCT AATCAGTCGGAATGCGAATC 175 18# g108 AATGGCAGCTACTGCGTCTT TCACCATTAACGGCTGATGA 158 11# g100 AAGAATCAGAGCCTGGAGCA CCCCTCTACGCTTCTTGATG 237 6# g110 ATTCATGTAACCAGTGGCGG AAGTAACGGCGATCAACGAC 145 13# g118 GCTGCCCAACAACTCATGTA TACCAAGCACAACCAGGTCA 237 6# g127 CGACCAACGTTCCAAGAAAT CGACAAACACTTCGGAGGAT 205 24# g129 GGCGTACAACACTAGCAGCA TGATTTGTGGAATGGCTTGA 216 12# g131 GTGGAAAAAGAAAATGGCGA CAACATTTTCGATTGCGATG 130 4# g139 TCATCATGGGTCCTTCACAA ACCCACAAAAAGCTTTGCAC 189 8# g145 AGCTAGTGGTGTTTCAGCCA CATCATGACTGACGGGAGTG 157 10# g155 CTGGCTTTGACGAAAACACA ATCGCCATCCTGTCAATTTC 148 20# g167 GCCTGGTGTCAATCCTTGTT TGAATTGCAAAGGGTTGTGA 139 14# g185 AGGAAGTGTGGGGTCACTTG TTTGAAGTTATGCTGCACCG 203 23# GEM57 GGGTTGATGTAGGCTTTGTT TCCTGGATTATCATTCACCAT 155 1# GEM109 TGCTCCTCCTGCATTATCCT TAAGAGGGAGGCGAGAACAG 135 GEM130 GCGGAGATACATTACGTGATAGG AGAGTTTTGCTCGCCAACAT 146 15# GEM148 CGAAGCTCTCAAAGCAAAGG TTCAGGAGGTGATGGTGTCA 140 2# GEM162 AAAGGTGCATTACTTGTTCTCTCC GCTTTGCTCTTGGCTTTGTC 134 12# GEM187 CCCTTCCTTTTTCTACTCCTCCT GATGTCGATCCAGGTTGCTC 154 22# GEM203 TTCTGCTTCTTGGGATGATTG TAAAAACCGTCTCCGTCGTC 141 21# GEM209 GGGTATCCAAAGTCTACGAT ACTAAGTTTGCATAAAGATTGC 135 19# GEM264 GTTGACATCAAACCGTCGTC TCCATATTTTGTTGCACCGTA 157 13# GEM57~GEM264等9对EST-SSR引物来源于参考文献[24]。
Nine pairs of EST-SSR primers, including GEM57-GEM264, were obtained from references [24].2.2 EST-SSR位点多态性分析
利用筛选出的39对EST-SSR引物对170份非洲菊种质资源进行检测(表3),共检测出168个等位基因(Na),每对引物检测到的等位基因为3~7个,平均等位基因为4.308个;有效等位基因(Ne)为1.354~4.772个,平均为2.734个,有效等位基因数与等位基因数存在一定差异,表明等位基因在非洲菊群体中分布不均匀。Shannon信息指数(I)为0.518~1.656,平均为1.098。多态信息含量(PIC)为0.431~0.920,平均为0.760,PIC值大于0.500的高多态标记有37个,占全部标记的94.87%。说明本研究所选EST-SSR标记具有较高的多态性,可有效反映非洲菊种质资源的遗传多样性信息。
表 3 39对EST-SSR标记的遗传参数Table 3. Genetic parameters from 39 EST-SSR marker pairs位点
Locus等位基因数
Number of alleles (Na)有效等位基因数
Effective number of alleles (Ne)Shannon信息指数
Shannon’s information index (I)多态信息含量
Polymorphic information (PIC)g23 5 2.488 1.052 0.770 g24 3 2.030 0.864 0.695 g25 4 3.241 1.244 0.824 g27 6 3.009 1.303 0.843 g28 3 1.354 0.518 0.431 g30 5 3.346 1.316 0.845 g32 6 4.772 1.623 0.920 g36 4 2.672 1.134 0.786 g37 3 2.654 1.037 0.790 g39 3 2.837 1.071 0.801 g40 5 2.629 1.168 0.791 g44 4 2.892 1.162 0.822 g47 4 2.217 0.972 0.734 g64 3 2.057 0.766 0.655 g81 5 3.936 1.461 0.850 g91 4 2.352 1.066 0.762 g93 6 3.209 1.315 0.849 g96 4 1.393 0.593 0.478 g100 7 4.423 1.656 0.917 g108 4 2.670 1.107 0.790 g110 5 4.043 1.486 0.893 g118 4 2.541 1.040 0.773 g127 3 2.300 0.929 0.731 g129 4 1.701 0.679 0.579 g131 4 2.435 1.062 0.772 g139 5 3.478 1.344 0.856 g145 4 3.154 1.261 0.850 g155 3 2.513 1.005 0.770 g167 3 2.563 1.002 0.746 g185 3 1.570 0.656 0.544 GEM57 3 1.982 0.813 0.650 GEM109 5 1.840 0.858 0.644 GEM130 3 1.837 0.800 0.647 GEM148 4 2.274 1.068 0.766 GEM162 6 4.178 1.550 0.905 GEM187 4 1.804 0.801 0.630 GEM203 7 4.159 1.607 0.903 GEM209 4 2.220 0.939 0.734 GEM264 6 3.858 1.510 0.891 平均值 Mean 4.308 2.734 1.098 0.760 2.3 群体间的遗传多样性分析
利用Popgen32软件分析非洲菊种质资源6个不同群体间的遗传多样性(表4) ,结果表明群体间观测到的总等位基因数为114~167,最低为日本群体,最高为混合群体,总基因型数变化范围为156~335,最低为荷兰花舞士群体,最高为混合群体;平均等位基因数与平均基因型数的最低值与最高值的群体分别与总等位基因数和总基因型数的最低值和最高值群体一致。混合群体、中国云南群体以及荷兰花舞士群体平均杂合度均较高,接近0.600,日本群体最低,仅为0.482。总体而言,6个不同群体间遗传多样性差异较大,混合群体和中国云南群体的总等位基因数、总基因型数、平均等位基因数、平均基因型数、平均杂合度均较高,遗传多样性较丰富。
表 4 6个非洲菊群体间的遗传多样性Table 4. Genetic diversity of 6 G. jamesonii populations群体
Population群体大小
Population size总等位基因数
Total allele number总基因型数
Total gene type number平均等位基因数
Average allele number平均基因型数
Average gene type number平均杂合度
Average heterozygosity德国喜乐达
German Slecta19 153 243 3.923 6.231 0.578 荷兰花舞士
Florist Holland8 132 156 3.385 4.000 0.606 荷兰西露丝
Schirus Holland18 145 228 3.718 5.846 0.513 日本
Japan14 114 165 2.923 4.231 0.482 中国云南
Yunnan China31 159 280 4.077 7.179 0.607 混合群体
Mix80 167 335 4.282 8.590 0.604 2.4 不同群体间遗传相似性及聚类分析
对6个非洲菊群体间进行Nei’s遗传一致度和遗传距离检测(表5) ,结果表明群体间遗传距离的变化范围为0.016~0.158,平均为0.069。遗传一致度变化范围为0.854~0.984,平均为0.935。6个群体间,中国云南群体与混合群体的遗传一致度最高(0.984),遗传距离最小(0.016),说明这两个群体的亲缘关系较近。而日本群体和德国群体的遗传一致度最小(0.854),遗传距离最大(0.158),说明这两个群体的亲缘关系较远。
表 5 非洲菊群体间的遗传一致度和遗传距离Table 5. Genetic similarity and distance between G. jamesonii populations群体
Population德国喜乐达
German Slecta荷兰花舞士
Holland Florist荷兰西露丝
Holland Schirus日本
Japan中国云南
Yunnan, China混合
Mix德国喜乐达 German Slecta 0.950 0.956 0.854 0.973 0.982 荷兰花舞士 Holland Florist 0.052 0.951 0.893 0.955 0.973 荷兰西露丝 Holland Schirus 0.045 0.050 0.861 0.943 0.963 日本 Japan 0.158 0.114 0.149 0.891 0.894 中国云南 Yunnan, China 0.028 0.046 0.059 0.116 0.984 混合 Mix 0.018 0.028 0.038 0.112 0.016 右上角为Nei氏遗传一致度,左下角为遗传距离。
Data on upper right corner are Nei’s genetic consistency; those on lower left corner, genetic distance.根据6个非洲菊群体的Nei’s 遗传一致度利用NTSYS-pc2.10e软件对非洲菊群体进行UPGMA聚类分析(图2),结果表明在相似系数0.965处,可将6个群体分为4个组群,第一个组群包括日本群体;第二个组群为荷兰西露丝群体;第三个组群为荷兰花舞士群体;德国群体和中国云南群体以及混合群体位于同一分支,分在第四组群,说明中国云南群体与混合群体及德国群体间的亲缘关系较近。
2.5 非洲菊种质资源聚类分析
基于UPMGA法对170份非洲菊种质进行聚类(图3),结果显示在遗传相似系数0.550处,170份种质共分为6大组群,组群Ⅰ包括5份种质,均为迷你型种质;组群Ⅱ包括2份种质,均为常规舌状花瓣类型种质;组群Ⅲ包括11份种质,含1份丝状瓣种质、5份卷曲花瓣种质;组群Ⅳ包括4份种质,含2份丝状瓣种质、2份常规类型种质;组群Ⅴ包括49份种质,组群Ⅵ种质数量最多,为99份种质。在遗传相似系数0.558处,组群Ⅴ可分为Ⅴ-1、Ⅴ-2、Ⅴ-3、Ⅴ-4共4个亚群,亚群Ⅴ-1包括28份非洲菊种质,含23份常规类型种质、4份丝状瓣种质、1份迷你型种质;亚群Ⅴ-2含2份迷你型种质;亚群Ⅴ-3包括13份种质,含1份卷曲花瓣种质、1份丝状花瓣种质、1份迷你型种质、3份球型种质;亚群Ⅴ-4包括6份种质,含1份球型种质、1份迷你型种质。在遗传相似系数0.570处,组群Ⅵ可分为Ⅵ-1、Ⅵ-2、Ⅵ-3、Ⅵ-4共4个亚群。亚群Ⅵ-1包括29份种质,含1份迷你种质、1份丝状花瓣种质;亚群Ⅵ-2包括24份种质,含14份盆栽类型种质,均来源于日本群体;亚群Ⅵ-3包括17份种质,含2份丝状花瓣种质;亚群Ⅵ-4包括29份非洲菊种质,含7份丝状花瓣种质、1份迷你型种质。
从种质资源在各组群和亚群的分布可以看出,来源于日本群体的全部14份盆栽类型种质集中分布于Ⅵ-2亚群,来源于荷兰西露丝群体的6份卷曲花瓣类型种质,分布于组群Ⅱ(5份)及亚群Ⅴ-3(1份),4份球型非洲菊种质均位于组群Ⅴ的Ⅴ-3和V-4亚群,表明同一类型且群体来源单一的非洲菊种质间组群分布较为单一,亲缘关系较近。丝状花瓣非洲菊、迷你非洲菊、常规非洲菊种质组群分布较为分散,表明这些类型非洲菊种质多样性较高。
迷你型的科蒂奶油(13)与科蒂奶油变异株(14),迷你型的红小花(160)、派德(161)、B6(163),常规类型的玲珑(24)与玲珑粉(93),红艳(105)与云南红(106),大雪桔(97)、小雪桔(98)、大088(99)、234(100)与阳光露(26)等种质间遗传相似系数为1,说明所用39对EST-SSR引物未扩增出差异条带,未能区分这些种质,种质间亲缘关系最近,部分种质有同物异名的可能。
3. 讨论与结论
与传统基因组SSR引物相比,利用转录组序列设计EST-SSR引物速度更快、成本更低且具备良好的属间通用性,被广泛应用于种质资源遗传多样性研究[26−28]。近年来,EST-SSR标记应用于非洲菊种质资源遗传多样性分析的研究已有不少报道。Gong[24]等采用53个EST-SSR标记,扩增出169个等位基因,平均每个位点3.189个,平均PIC值为0.425;尹茂[20]采用48对EST-SSR标记,扩增出155个等位基因,平均每个位点3.22个,平均PIC值为0.44;Benemann等[19]采用17对EST-SSR标记,扩增出101个等位基因,平均每个位点5.94个,平均PIC值为0.67;本研究利用39对EST-SSR标记,对170份非洲菊种质资源进行遗传多样性分析,扩增出168个等位基因,平均每个位点4.308个,PIC值平均为0.760,平均等位基因数高于尹茂[20]、Gong等[24],低于Benemann等[19]的研究结果,这可能与种质资源的多样性、SSR标记的筛选标准有关,相比尹茂[20]、Gong等[24]的结果,本研究所选非洲菊种质包括丝状花瓣、卷曲花瓣、迷你、盆栽等类型,多样性更丰富,Benemann等[19]要求位点基序的重复次数达12次及以上,引物筛选标准更高。本研究SSR位点平均PIC值高于Gong[24]等、尹茂[20]和Benemann等[19]的研究结果,PIC≥0.5的高多态性标记[29]占94.87%,进一步表明所选引物为高多态性引物,可用于非洲菊遗传多样性和亲缘关系分析等研究。
本研究结果显示中国云南群体的遗传多样性高于德国喜乐达、荷兰西露丝、荷兰花舞士、日本等群体,云南省作为非洲菊的主产区及非洲菊种苗的最大产区(占60%以上市场份额)[30],是荷兰西露丝、荷兰花舞士、德国喜乐达等非洲菊育种公司新品种的主推地区,中国云南群体是由云南省科研单位和企业选育品种组成,其育种亲本的来源更加丰富,可能是云南群体遗传多样性较高的重要原因。此外,中国云南群体与混合群体间遗传距离最小,亲缘关系最近,推测云南群体部分品种的杂交亲本可能直接或间接来源于混合群体。因此,加强非洲菊种质资源的引进的广度有助于提高非洲菊种质资源遗传多样性。
本研究对170份非洲菊种质聚类分析结果显示盆栽和卷曲花瓣等类型非洲菊种质组群分布较集中,这可能与本研究中盆栽非洲菊种质为日本种群独有,卷曲花瓣非洲菊种质为荷兰西露丝群体独有,基因交流主要在群体内部有关。玲珑与玲珑粉,云南红与红艳,大雪桔与小雪桔、大088、234、阳光露等种质间亲缘关系最近,且其花型、花色、叶型等综合性状较为接近,推测是品种改良所致。云南红、玲珑、大088等均为多年前从国外引进的品种,当前仍作为主栽品种种植[31−34],因此通过诱变或杂交等育种方法对非洲菊主栽品种进行改良是培育新品种的重要方式。
综上所述,本研究筛选出39对EST-SSR标记,分析了170份不同来源群体、不同类型种质的遗传多样性和亲缘关系,研究结果可为非洲菊种质资源的引进、保护及利用等提供理论依据及数据支撑。
-
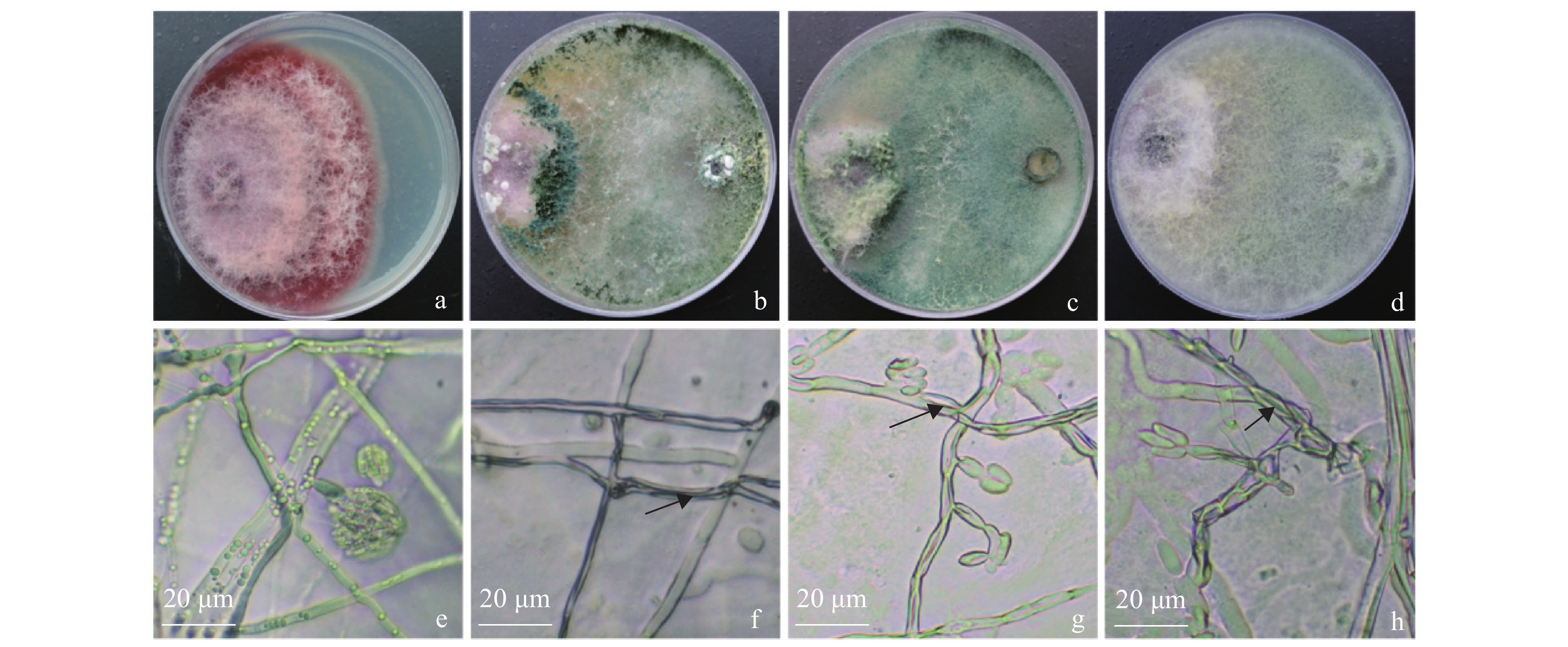
图 1 木霉菌形态特征
a~d、e~h、i~l分别为木霉菌菌株A21B-1、A21B-2与A21E接种于PDA培养7 d后的菌落形态;a、e、i为正面;b、f、 j为背面;c、g、k为分生孢子梗与瓶梗形态,d、h、l为分生孢子形态。
Figure 1. Morphological characteristics of Trichoderma strains
a–d, e–h, and i–l: colony morphology of A21B-1, A21B-2, and A21E, respectively, grown on PDA for 7 d; a, e, and i: front views; b, f, and j: back views; c, g, and k: conidia stem, bottle stem; d, h and l : morphology of conidia, respectively.
图 3 不同木霉菌与尖孢镰刀菌菌株ASP01对峙培养
a,e:尖孢镰刀菌ASP01;b,f:A21B-1与ASP01对峙培养;c,g:A21B-2与ASP01对峙培养;d,h:A21E与ASP01对峙培养;箭头所指为木霉菌菌丝侵入ASP01菌丝并导致尖孢镰刀菌孢子不能正常发育。
Figure 3. Confrontation cultures of Trichoderma strains and F. oxysporum f. sp. opponiarum ASP01
a and e: F. oxysporum f. sp. opponiarum ASP01; b and f: confrontation culture of A21B-1 and ASP01; c and g: confrontation culture of A21B-2 and ASP01; d and h: confrontation culture of A21E and ASP01; arrow points to invasion of Trichoderma hyphae into ASP01 hyphae inhibiting normal development of ASP01 spores.
表 1 木霉菌序列登录号及种名
Table 1 Sequence accession numbers and species of Trichoderma
菌株
Strains登录号
Accession No.种名
SpeciesITS rpb2 A21B-1 ON209377 OR161371 T. harzianum A21B-2 ON209378 OR161372 T. konginggipsis A21E ON209384 OR161373 T. longifialidiucum 表 2 不同木霉菌对尖孢镰刀菌株ASP01抑制效果
Table 2 Inhibition effects of Trichoderma strains on F. oxysporum f. sp. pponiarum ASP01
处理
Treatment病原真菌菌落直径
Colony diameter of pathogens/cm抑制率
Inhibition rates/%CK 5.41±0.08 a 0 c A21B-1 1.33±0.32 c 75.29±6.45 a A21B-2 1.43±0.40 c 73.55±7.38 a A21E 2.17±0.16 b 60.02±2.87 b 数据为平均值±标准误,同列数据后不同小字母表示0.05水平上差异显著。下同。
Data are presented as mean±SD; those with different lowercase letters on same column indicate significant difference at 0.05 level. Same for below.表 3 木霉菌对茎腐病室内防效
Table 3 In vitro stem rot disease control by Trichoderma strains
处理
Treatment接种7 d后 7 d after inoculation 接种15 d 后 15 d after inoculation 感病面积
Infected areas/mm2抑制率
Inhibition rates/%感病面积
Infected areas/mm2抑制率
Inhibition rates/%CK 354.0±90.7 0 c 995.31±55.58 0 d A21B-1 5.33±0.94 98.49±0.26 a 79.93±14.77 91.88±1.47 a A21B-2 23.3±5.73 93.42±1.62 b 242.14±38.53 75.62±3.78 b A21E 11.8±4.09 96.71±1.15 b 334.17±65.76 66.41±6.61 c 表 4 木霉菌对金线兰促生效果
Table 4 A. roxburghii growth promoted by presence of Trichoderma strains
处理
Treatment株高
Plant height/
cm茎粗
Stem diameter/
mm叶数
Number of
leaves叶长
Leaf Length/
mm叶宽
Leaf width/
mm叶面积
Leaf area/
mm2叶厚
Leaf thickness/
mm根长
Root length/
cm根粗
Root diameter/
mm根数
Root numberSPAD 单株重
Single plant
weight/gCK 15.23±1.81 b 2.62±0.30 c 6.67±1.37 b 29.10±3.02 b 26.78±1.84 b 784.69±141.95 b 0.33±0.05 b 7.19±1.08 b 2.02±0.26 b 2.83±0.37 a 46.83±3.84 c 3.17±0.44 c A21B-1 19.15±3.26 a 3.05±0.40 b 7.67±1.37 ab 29.85±2.41 b 28.02±2.99 b 984.27±151.95 b 0.42±0.07 a 6.68±0.68 b 1.95±0.21 b 2.83±0.90 a 56.65±4.18 a 3.25±0.45 b A21B-2 21.02±2.05 a 3.08±0.19 b 8.33±0.47 a 39.55±3.08 a 32.95±2.41 a 1309.01 ±177.04 a0.40±0.00 a 8.93±1.20 a 2.53±0.09 a 2.33±0.47 a 50.53±4.83 b 5.03±0.62 a A21E 19.65±2.00 a 3.65±0.29 a 6.00±2.45 b 38.10±0.73 a 32.85±1.67 a 1253.43 ±87.91 a0.40±0.00 a 9.14±1.36 a 2.10±0.24 b 3.00±0.00 a 56.95±2.16 a 5.04±0.20 a 表 5 木霉菌对金线兰促进次生代谢物积累效果
Table 5 Secondary metabolites accumulated in A. roxburghii promoted by presence of Trichoderma strains
处理
Treatment折干率
Drying rate/%多糖含量
Content of polysaccharide/(mg·g−1)黄酮含量
Content of flavone/(mg·g−1)金线莲苷含量
Content of kinsenoside/(mg·g−1)CK 11.25±0.71d 6.07±0.14 d 8.15±0.43 a 14.29±0.24 b A21B-1 12.88±0.73 cd 7.40±0.68 c 7.20±0.14 c 14.60±0.45 b A21B-2 13.91±0.59 b 11.51±0.35 a 7.43±0.24 bc 15.98±0.97 a A21E 14.58±0.01 a 8.05±0.99 b 7.76±0.78 ab 14.96±1.26 b -
[1] 郑纯, 黄以钟, 季莲芳. 金钱莲文献考证、原植物及商品调查 [J]. 中草药, 1996, 27(3):169−172. ZHENG C, HUANG Y Z, JI L F. Pharmacognostic studies on Jinxianlian Ⅰ. bencaologic review, resource survey and taxonomic identification [J]. Chinese Traditional and Herbal Drugs, 1996, 27(3): 169−172. (in Chinese)
[2] QIU Y, SONG W B, YANG Y, et al. Isolation, structural and bioactivities of polysaccharides from Anoectochilus roxburghii (Wall.) Lindl. : A review [J]. International Journal of Biological Macromolecules, 2023, 236: 123883. DOI: 10.1016/j.ijbiomac.2023.123883
[3] DU X, SUN N, TAMURA T, et al. Higher yielding isolation of kinsenoside in Anoectochilus and its antihyperliposis effect [J]. Biological & Pharmaceutical Bulletin, 2001, 24(1): 65−69.
[4] 叶炜, 颜沛沛, 王培育, 等. 金线兰茎腐病的病原菌鉴定与防治药剂的筛选 [J]. 亚热带农业研究, 2023, 19(1):1−9. YE W, YAN P P, WANG P Y, et al. Pathogen identification of Anoectochium roxborghil stem rot and screening of fungicides [J]. Subtropical Agriculture Research, 2023, 19(1): 1−9. (in Chinese)
[5] 邵清松, 刘洪波, 赵晓芳, 等. 金线莲茎腐病菌的生物学特性及5种杀菌剂对其抑制作用 [J]. 中国中药杂志, 2014, 39(8):1386−1390. SHAO Q S, LIU H B, ZHAO X F, et al. Biological characteristics of Fusarium oxysporum and inhibitory effects of five fungicides [J]. China Journal of Chinese Materia Medica, 2014, 39(8): 1386−1390. (in Chinese)
[6] 路梅, 刘建峰, 郑熊飞, 等. 金线莲茎腐病致病菌的分离及其拮抗菌的筛选 [J]. 浙江农业科学, 2022, 63(10):2354−2358. LU M, LIU J F, ZHENG X F, et al. Isolation of pathogenic bacteria from stem rot of Anoectochilus roxburghii and screening of antagonistic bacteria [J]. Journal of Zhejiang Agricultural Sciences, 2022, 63(10): 2354−2358. (in Chinese)
[7] 赵云青, 陈菁瑛, 林晓军, 等. 金线莲茎腐病病原菌分离及分子鉴定 [J]. 福建农业学报, 2014, 29(10):995−999. DOI: 10.3969/j.issn.1008-0384.2014.10.012 ZHAO Y Q, CHEN J Y, LIN X J, et al. Molecular identification for southern blight pathogen of anoectoch ilusroxburghii(Wall. )Lindl [J]. Fujian Journal of Agricultural Sciences, 2014, 29(10): 995−999. (in Chinese) DOI: 10.3969/j.issn.1008-0384.2014.10.012
[8] 林文珍, 郭迟鸣, 郭莺, 等. 1株海洋草酸青霉HY181-2的分离鉴定及其对金线莲茎腐病病原菌的生防能力 [J]. 西南农业学报, 2021, 34(8):1649−1656. LIN W Z, GUO C M, GUO Y, et al. Isolation and identification of marine Penicillium oxalicum HY181-2 and its biocontrol ability against pathogen of Anoectochilus stem rot [J]. Southwest China Journal of Agricultural Sciences, 2021, 34(8): 1649−1656. (in Chinese)
[9] WOO S L, HERMOSA R, LORITO M, et al. Trichoderma: A multipurpose, plant-beneficial microorganism for eco-sustainable agriculture [J]. Nature Reviews Microbiology, 2023, 21(5): 312−326. DOI: 10.1038/s41579-022-00819-5
[10] SOOD M, KAPOOR D, KUMAR V, et al. Trichoderma: The “secrets” of a multitalented biocontrol agent [J]. Plants, 2020, 9(6): 762. DOI: 10.3390/plants9060762
[11] ZHANG J L, TANG W L, HUANG Q R, et al. Trichoderma: A treasure house of structurally diverse secondary metabolites with medicinal importance [J]. Frontiers in Microbiology, 2021, 12: 723828. DOI: 10.3389/fmicb.2021.723828
[12] 胡卫丛, 黄忠阳, 张宗俊, 等. 化肥减施条件下木霉菌生物有机肥对水果黄瓜生长及品质的影响 [J]. 长江蔬菜, 2023(4):63−66. DOI: 10.3865/j.issn.1001-3547.2023.04.017 HU W C, HUANG Z Y, ZHANG Z J, et al. Effects of Trichoderma bio-organic fertilizer on growth and quality of fruit cucumber under reduced fertilizer application [J]. Journal of Changjiang Vegetables, 2023(4): 63−66. (in Chinese) DOI: 10.3865/j.issn.1001-3547.2023.04.017
[13] 董琼娥, 杨顺安, 罗聪, 等. 微生物菌剂对切花玫瑰白粉病的防效及产质量的影响 [J]. 贵州农业科学, 2022, 50(10):54−59. DOI: 10.3969/j.issn.1001-3601.2022.10.009 DONG Q E, YANG S A, LUO C, et al. Control effect of microbial agent on powdery mildew and yield and quality of cut rose [J]. Guizhou Agricultural Sciences, 2022, 50(10): 54−59. (in Chinese) DOI: 10.3969/j.issn.1001-3601.2022.10.009
[14] 吕亮雨, 段国珍, 苏彩风, 等. 木霉菌微生物菌剂对枸杞生长及土壤性状的影响 [J]. 沈阳农业大学学报, 2022, 53(4):476−482. DOI: 10.3969/j.issn.1000-1700.2022.04.011 LÜ L Y, DUAN G Z, SU C F, et al. Effects of microbial agents on growth and soil properties of Lycium barbarum L [J]. Journal of Shenyang Agricultural University, 2022, 53(4): 476−482. (in Chinese) DOI: 10.3969/j.issn.1000-1700.2022.04.011
[15] 罗庆国, 叶炜, 江金兰, 等. 金线莲组培快繁技术研究 [J]. 南方农业(园林花卉版), 2011, 5(5):43−44. LUO Q G, YE W, JIANG J L, et al. Study on tissue culture and rapid propagation of Anoectochilus roxburghii [J]. South China Agriculture, 2011, 5(5): 43−44. (in Chinese)
[16] WHITE T J, BRUNS T, LEE S, et al. Amplification and direct sequencing of fungal ribosomal RNA genes for phylogenetics[M]//PCR Protocols. Amsterdam: Elsevier, 1990: 315-322.
[17] CHAVERRI P, CASTLEBURY L A, OVERTON B E, et al. Hypocrea/Trichoderma: species with conidiophore elongations and green conidia [J]. Mycologia, 2003, 95(6): 1100−1140. DOI: 10.1080/15572536.2004.11833023
[18] 祁智慧, 庄媛, 张海洋, 等. 粮食上木霉菌的分离鉴定及其生防效果 [J]. 微生物学通报, 2023, 50(7):2860−2875. QI Z H, ZHUANG Y, ZHANG H Y, et al. Isolation, identification, and biocontrol efficacy determination of Trichoderma spp. on grains [J]. Microbiology China, 2023, 50(7): 2860−2875. (in Chinese)
[19] 张静雅, 李欣雨, 张成, 等. 木薯炭疽病拮抗木霉菌筛选与室内防效研究 [J]. 中国生物防治学报, 2022, 38(1):115−124. ZHANG J Y, LI X Y, ZHANG C, et al. Screening of antagonistic Trichoderma against cassava anthracnose and investigation on its control effect in laboratory [J]. Chinese Journal of Biological Control, 2022, 38(1): 115−124. (in Chinese)
[20] 甘林, 代玉立, 杨秀娟, 等. 木霉菌对番茄灰霉病菌的抑制作用 [J]. 福建农业学报, 2016, 31(11):1221−1225. GAN L, DAI Y L, YANG X J, et al. Antagonistic Effect of Trichoderma spp. Strains on Botrytis cinerea [J]. Fujian Journal of Agricultural Sciences, 2016, 31(11): 1221−1225. (in Chinese)
[21] 姚晨虓, 李小杰, 刘畅, 等. 3株拮抗烟草尖孢镰刀菌的木霉菌筛选鉴定及促生防病效果评价 [J]. 中国烟草学报, 2022, 28(4):96−105. YAO C X, LI X J, LIU C, et al. Screening and identification of three strains of Trichoderma spp. antagonizing Fusarium oxysporum and evaluation of their effects on promoting growth and disease control [J]. Acta Tabacaria Sinica, 2022, 28(4): 96−105. (in Chinese)
[22] 曹奕鸯, 李永清, 江金兰, 等. 不同种源金线兰及近缘种多糖和总黄酮含量的研究 [J]. 福建农业学报, 2016, 31(6):604−610. CAO Y Y, LI Y Q, JIANG J L, et al. Polysaccharide and flavonoid contents in Anoectochilus roxburghii and related species [J]. Fujian Journal of Agricultural Sciences, 2016, 31(6): 604−610. (in Chinese)
[23] 陈莹, 王文义, 谌赛男, 等. 不同品系及生长期金线莲的金线莲苷含量变化研究 [J]. 中国现代中药, 2021, 23(8):1423−1429. CHEN Y, WANG W Y, CHEN S N, et al. Changes in kinsenoside content of different strains of Anoectochilus roxburghii at different growth periods [J]. Modern Chinese Medicine, 2021, 23(8): 1423−1429. (in Chinese)
[24] ADEDAYO A A, BABALOLA O O. Fungi that promote plant growth in the rhizosphere boost crop growth [J]. Journal of Fungi, 2023, 9(2): 239. DOI: 10.3390/jof9020239
[25] DUTTA P, MAHANTA M, SINGH S B, et al. Molecular interaction between plants and Trichoderma species against soil-borne plant pathogens [J]. Frontiers in Plant Science, 2023, 14: 1145715. DOI: 10.3389/fpls.2023.1145715
[26] YAO X, GUO H L, ZHANG K X, et al. Trichoderma and its role in biological control of plant fungal and nematode disease [J]. Frontiers in Microbiology, 2023, 14: 1160551. DOI: 10.3389/fmicb.2023.1160551
[27] 黄靖, 陈婵. 接种促生菌对金线莲生物活性成分及土壤细菌群落的影响 [J]. 江苏农业科学, 2022, 50(23):184−191. HUANG J, CHEN C. Influences of inoculation of growth-promoting bacteria on bioactive constituents and soil bacterial communities of Anoectochilus roxburghii [J]. Jiangsu Agricultural Sciences, 2022, 50(23): 184−191. (in Chinese)
[28] VICENTE C S L, SOARES M, FARIA J M S, et al. Insights into the role of fungi in pine wilt disease [J]. Journal of Fungi, 2021, 7(9): 780. DOI: 10.3390/jof7090780
[29] 张祥丽, 曹瑱艳, 杨怡华, 等. 铁皮石斛镰刀菌根腐病病原菌的鉴定及其对链霉菌发酵液的敏感性分析 [J]. 中国生物防治学报, 2022, 38(1):258−266. ZHANG X L, CAO T Y, YANG Y H, et al. Identification of the pathogen causing root rot of Dendrobium officinale and sensitivity to the fermentation broth of Streptomyces [J]. Chinese Journal of Biological Control, 2022, 38(1): 258−266. (in Chinese)
[30] 叶炜, 江金兰, 李永清, 等. 金线兰及近缘种植物遗传多样性ISSR分子标记分析 [J]. 植物遗传资源学报, 2015, 16(5):1045−1054. YE W, JIANG J L, LI Y Q, et al. Analysis of genetic diversity in Anoectochilus roxburghii and it’s relative species using ISSR molecular markers [J]. Journal of Plant Genetic Resources, 2015, 16(5): 1045−1054. (in Chinese)
[31] 赵泽宇. 地生兰与附生兰菌根真菌的差异比较研究[D]. 北京: 北京协和医学院, 2021. ZHAO Z Y. Comparative study on the difference of mycorrhizal fungil between terrestrial and epiphytic orchids[D]. Beijing: Peking Union Medical College, 2021.
[32] 李婷, 王洪旭, 崔广禄, 等. 哈茨木霉在植物应用上的研究进展 [J]. 中国农学通报, 2023, 39(21):57−61. DOI: 10.11924/j.issn.1000-6850.casb2022-0652 LI T, WANG H X, CUI G L, et al. Application of Trichoderma harzianum in plant: Research progress [J]. Chinese Agricultural Science Bulletin, 2023, 39(21): 57−61. (in Chinese) DOI: 10.11924/j.issn.1000-6850.casb2022-0652
[33] XIAO Z Y, ZHAO Q Q, LI W, et al. Strain improvement of Trichoderma harzianum for enhanced biocontrol capacity: Strategies and prospects [J]. Frontiers in Microbiology, 2023, 14: 1146210. DOI: 10.3389/fmicb.2023.1146210
[34] 尤佳琪, 杜然, 顾卫红, 等. 拟康宁木霉T-51菌株生物学特性及其生物防治潜力 [J]. 植物保护学报, 2022, 49(3):946−955. YOU J Q, DU R, GU W H, et al. Biological characteristics and biological control potential of endophytic fungus Trichoderma koningiopsis strain T-51 [J]. Journal of Plant Protection, 2022, 49(3): 946−955.
[35] HUANG L P, WEI M S, LI L Q, et al. Polyketides with Anti-Inflammatory Activity from Trichoderma koningiopsis, a Rhizosphere Fungus from the Medicinal Plant Polygonum paleaceum [J]. Journal of Natural Products, 2023, 86(7): 1643−1653. DOI: 10.1021/acs.jnatprod.2c00842
[36] 董章勇, 罗梅, 陈越, 等. 一株具有生防及诱导抗病作用的拟康宁木霉Tk905菌株及其应用: CN113862160A[P]. 2021-12-31. [37] 罗梅, 罗玉霖, 陈沫冰, 等. 拟康宁木霉Tk1的分离鉴定、拮抗作用及其生物学特性 [J]. 中国生物防治学报, 2020, 36(4):581−586. LUO M, LUO Y L, CHEN M B, et al. Isolation and identification Trichoderma koningiopsis Tk1, and its antagonistic effect and biological characteristics [J]. Chinese Journal of Biological Control, 2020, 36(4): 581−586. (in Chinese)
[38] 涂晶晶, 于存. 拟康宁木霉Hailin菌株对马尾松幼苗的促生和防病作用 [J]. 中国植保导刊, 2020, 40(2):9−16,21. DOI: 10.3969/j.issn.1672-6820.2020.02.002 TU J J, YU C. Effect of Trichoderma koningiopsis on the growth promotion and disease control of Pinus massoniana seedlings [J]. China Plant Protection, 2020, 40(2): 9−16,21. (in Chinese) DOI: 10.3969/j.issn.1672-6820.2020.02.002
[39] 李海云, 宋晓妍, 张秀省, 等. 拟康宁木霉SMF2防治大白菜软腐病机理研究 [J]. 园艺学报, 2012, 39(7):1373−1379. LI H Y, SONG X Y, ZHANG X S, et al. Research on mechanism of Trichoderma pseudokoningii SMF2 controlling soft rot of Chinese cabbage [J]. Acta Horticulturae Sinica, 2012, 39(7): 1373−1379. (in Chinese)
[40] MONTOYA Q V, MEIRELLES L A, CHAVERRI P, et al. Unraveling Trichoderma species in the attine ant environment: Description of three new taxa [J]. Antonie Van Leeuwenhoek, 2016, 109(5): 633−651. DOI: 10.1007/s10482-016-0666-9
[41] 关璟, 王春兰, 郭顺星. 福建产金线莲中黄酮苷成分的研究 [J]. 中草药, 2005, 36(10):1615−1617. GUAN J, WANG C L, GUO S X. Isolation and structural elucidation of flavonoids from Ancecotochilus roxburghii [J]. Chinese Traditional and Herbal Drugs, 2005, 36(10): 1615−1617. (in Chinese)
[42] 何春年, 王春兰, 郭顺星, 等. 兰科开唇兰属植物的化学成分和药理活性研究进展 [J]. 中国药学杂志, 2004, 39(2):81−84. HE C N, WANG C L, GUO S X, et al. Advances in chemistry and pharmacology on plants Orchidaceae Anoectochilus [J]. Chinese Pharmaceutical Journal, 2004, 39(2): 81−84. (in Chinese)
[43] 福建省卫生健康委员会. 福建省食品安全地方标准金线莲: DBS35/ 006—2022 [S]. 福建省卫生健康委员会, 2022. [44] QI C X, ZHOU Q, YUAN Z, et al. Kinsenoside: A promising bioactive compound from Anoectochilus species [J]. Current Medical Science, 2018, 38(1): 11−18. DOI: 10.1007/s11596-018-1841-1
[45] YE S Y, SHAO Q S, ZHANG A L. Anoectochilus roxburghii: A review of its phytochemistry, pharmacology, and clinical applications [J]. Journal of Ethnopharmacology, 2017, 209: 184−202. DOI: 10.1016/j.jep.2017.07.032




 下载:
下载: