Differentiate Transcriptomes of Aerial and Creepy Agaricus bisporus Hyphae
-
摘要:
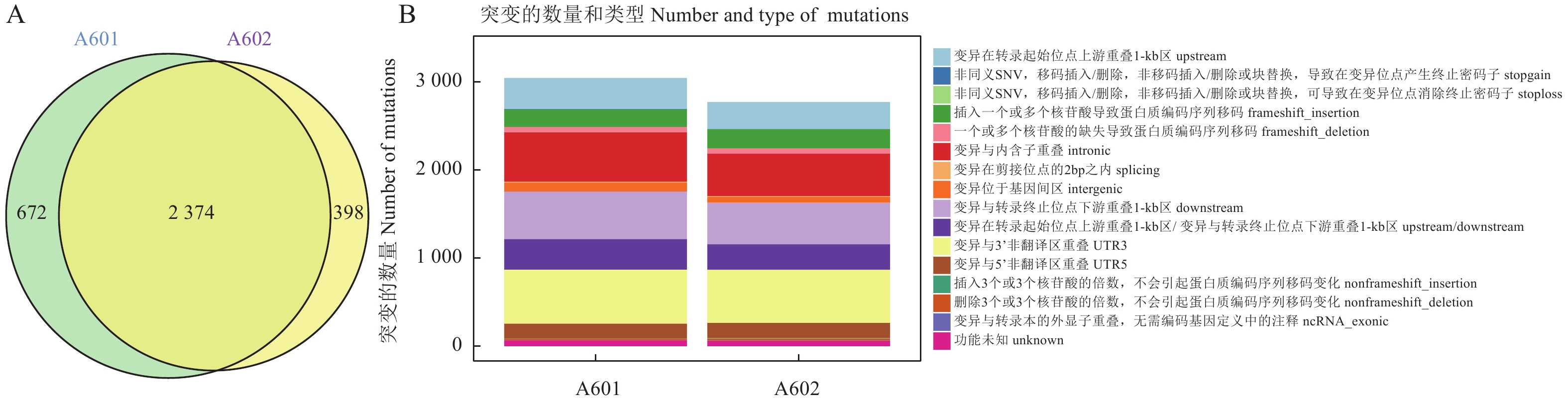
目的 挖掘双孢蘑菌落形态变化可能涉及的重要基因,为双孢蘑菇种质资源评价、新品种选育提供科学依据。 方法 以双孢蘑菇主栽品种As2796为试验菌株,收集同一平板上生长的贴生与气生菌丝,提取样品的RNA进行转录组测序分析。 结果 通过转录组分析,A601(As2796气生组)与A602(As2796贴生组)共鉴定出965个差异表达基因(DEGs)。GO富集分析结果表明,在真菌细胞壁组成方面有疏水蛋白相关的DEGs富集,其中AGABI2DRAFT_13655、AGABI2DRAFT_136569、AGABI2DRAFT_193057属于ABH3蛋白基因家族,在气生菌丝的表达水平显著高于贴生菌丝,可能与气生菌丝的产生有关。研究还发现了疏水表面结合蛋白A(HsbA)相关基因AGABI2DRAFT_194662在气生菌丝中FPKM表达水平为0,在贴生菌丝中为10.24。通过对DEGs进一步分析,富集到8个可能与脂酶同工酶相关的DEGs,气生菌丝中这些基因的表达水平显著高于贴生菌丝。SNP/InDel分析结果表明,As2796气生组SNP数为110 601,贴生组SNP数为111 188,单核苷酸变异中,C:G>T:A的变异次数较多,共筛选出2 374个共同InDel。 结论 成功获得双孢蘑菇不同形态菌丝的转录组数据,并从中挖掘出潜在的相关基因和SNP位点,为双孢蘑菇相关分子标记开发及辅助育种提供参考。 Abstract:Objective Key genes associated with Agaricus bisporus of different mycelial morphology were analyzed. [Methods] As 2796, the main cultivated variety of A. bisporus, with aerial or creepy hyphae grown on same plate were collected for RNA transcriptome sequencing and comparison with reference. Results There were 965 differentially expressed genes (DEGs) between the aerial hyphae-A601 and the creepy hyphae-A602. According to the GO enrichment analysis, the hydrophobic DEGs were enriched in the fungal cell wall, such as AGABI2DRAFT_13655, AGABI2DRAFT_136569, and AGABI2DRAFT_193057 that belonged to the ABH3 protein gene family, with expressions significantly higher in A601 than in A602. Thus, they were postulated to be related to the production of aerial hyphae. In addition, the hydrophobic surface binding protein A (HsbA)-related gene, AGABI2DRAFT_194662, showed a FPKM expression of 0 in A601, but 10.24 in A602. Furthermore, 8 enriched DEGs related to lipase isoenzymes exhibited a FPKM expression significantly higher in A601 than in A602. The SNP/InDel analysis indicated that the SNPs in A601 was 110 601 as opposed to 111 188 in A602, the most frequent mutation in SNPs was C:G>T:A, and that 2 374 common InDels were identified. Conclusion The transcriptomes and possibly associated genes and SNP sites in A. bisporus with different mycelial morphology obtained in this study would be of value for the mushroom germplasm evaluation and breeding. -
Key words:
- Agaricus bisporus /
- As 2796 /
- creepy hypha /
- aerial hypha /
- transcriptome sequencing /
- differentially expressed genes
-
表 1 样品测序数据及与参考基因组的序列比对结果
Table 1. Statistics of experimental data and alignment with reference on genome sequences
编号
ID样品
Sample总Read数
Total clean reads比对到参考基因组的Reads数目
Mapped reads比对到参考基因组的Reads百分比
Mapped reads/%GC含量
GC content/%≥Q30的百分比
≥Q30/%A601 As2796气生 42 155 674 25 410 008 60.28 49.12 92.00 A602 As2796贴生 45 225 288 28 324 702 62.63 49.28 92.37 表 2 新基因功能注释结果统计
Table 2. Number of new genes with functional annotation
用于功能注释的数据库
Annotated Database获得注释的新基因数目
Annotated Gene Number长度在≥300~ 1000 的新基因数目
Gene Number (300≤gene length<1000 )长度≥ 1000 的新基因数目
Gene Number (Gene length≥1000 )COG 15 12 3 GO 21 13 7 KEGG 38 21 14 KOG 20 12 8 Pfam 34 20 12 Swissprot 24 15 8 nr 132 70 57 All 139 76 57 表 3 部分差异表达基因
Table 3. Partial DEGs
编号
NO基因ID
Gene ID相对表达量FPKM
Relative expression FPKMLog2FC Pfam蛋白注释
Pfam protein annotation基因注释
Gene annotationA601 A602 1 AGABI2DRAFT_194497 15.6653 0.0000 −6.78 — — 2 AGABI2DRAFT_177536 20.5777 0.0000 −4.47 — 假设蛋白OH76DRAFT_1359727 3 AGABI2DRAFT_120985 1.0452 0.0000 −3.64 — 假设蛋白AN958_00580 4 AGABI2DRAFT_203489 2.3380 0.0001 −3.85 — 假设蛋白 AN958_02967 5 AGABI2DRAFT_44066 6.2585 0 −3.75 HhH-GPD超家族碱基
切除DNA修复蛋白假设蛋白 AN958_02739 6 AGABI2DRAFT_113583 0.0000 4.2489 4.73 — 假设蛋白 AN958_04089 7 AGABI2DRAFT_117617 0.0008 6.9437 3.30 — 假设蛋白 AN958_03520 8 AGABI2DRAFT_179131 0.0010 2.5569 4.28 — 假设蛋白 AN958_00324 9 AGABI2DRAFT_194662 0 10.2374 4.66 疏水表面结合蛋白A 假设蛋白AN958_09554 10 AGABI2DRAFT_136569 196.301 32.0293 −2.58 真菌疏水蛋白 假定的疏水蛋白 [双孢蘑菇] 11 AGABI2DRAFT_193057 999.26 189.163 −2.38 真菌疏水蛋白 假定的疏水蛋白 [双孢蘑菇] 12 AGABI2DRAFT_136557 19733 3086.17 −2.67 真菌疏水蛋白 假定的疏水蛋白 [双孢蘑菇] 13 AGABI2DRAFT_143464 100.031 896.356 3.21 真菌疏水蛋白 假定的疏水蛋白 [双孢蘑菇] 14 AGABI2DRAFT_178707 31.7555 666.848 4.35 真菌疏水蛋白 假定的疏水蛋白 [双孢蘑菇] 表 5 SNP突变统计表
Table 5. SNP mutation statistics
编号 ID T∶A>G∶C C∶G>G∶C T∶A>A∶T C∶G>T∶A C∶G>A∶T T∶A>C∶G 转化 Ts 颠换 Tv 转换/颠换比 ts/tv A601 6312 5221 7641 42864 6405 42158 85022 25579 3.32 A602 6276 5239 7586 43273 6338 42476 85749 25439 3.37 表 6 全基因组和编码区InDel长度分布表
Table 6. Length distribution of genome-wide and coding region InDel sites
编号
ID区域
Region−10 −9 −8 −7 −6 −5 −4 −3 −2 −1 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 A601 基因组
Genome11 2 0 0 1 2 0 6 106 1235 1559 121 1 0 0 2 0 0 0 0 A601 外显子
Exonic7 1 0 0 1 0 0 3 2 99 221 14 1 0 0 2 0 0 0 0 A602 基因组
Genome14 3 0 0 1 2 0 11 100 1080 1434 121 3 0 0 3 0 0 0 0 A602 外显子
Exonic9 1 0 0 1 0 0 7 2 100 229 15 3 0 0 3 0 0 0 0 -
[1] BERNAŚ E, JAWORSKA G. Vitamins profile as an indicator of the quality of frozen Agaricus bisporus mushrooms [J]. Journal of Food Composition and Analysis, 2016, 49: 1−8. doi: 10.1016/j.jfca.2016.03.002 [2] OWAID M N, BARISH A, ALI SHARIATI M. Cultivation of Agaricus bisporus (button mushroom) and its usages in the biosynthesis of nanoparticles [J]. Open Agriculture, 2017, 2(1): 537−543. doi: 10.1515/opag-2017-0056 [3] MUSZYŃSKA B, KAŁA K, ROJOWSKI J, et al. Composition and biological properties of Agaricus bisporus fruiting bodies- a review [J]. Polish Journal of Food and Nutrition Sciences, 2017, 67(3): 173−181. doi: 10.1515/pjfns-2016-0032 [4] 王翠, 郭仲杰, 尤洁, 等. 双孢蘑菇产、质量性状相关分子标记的初步研究 [J]. 福建农业科技, 2018, 49(7):1−5.WANG C, GUO Z J, YOU J, et al. A preliminary study on molecular markers related to yield and quality traits of Agaricus bisporus [J]. Fujian Agricultural Science and Technology, 2018, 49(7): 1−5. (in Chinese) [5] DAS B, DE B, CHETREE R, et al. Medicinal aspect of mushrooms: A view point[J]. Herbal Medicine in India: Indigenous Knowledge, Practice, Innovation and its Value, 2020: 509-532. [6] ZHANG M, ZHAO L, TANG F, et al. Chemical structures, biological activities, and biosynthetic analysis of secondary metabolites from Agaricus mushrooms: A review [J]. Journal of Agricultural and Food Chemistry, 2024, 72(22): 12387−12397. doi: 10.1021/acs.jafc.4c01861 [7] 柯斌榕, 兰清秀, 卢政辉, 等. 福建省双孢蘑菇栽培技术的变革与发展 [J]. 食药用菌, 2017, 25(1):12−19.KE B R, LAN Q X, LU Z H, et al. Innovation and development of Agaricus bisporus cultivation techniques in Fujian province [J]. Edible and Medicinal Mushrooms, 2017, 25(1): 12−19. (in Chinese) [8] 林杰, 林莫翎. 蘑菇异型菌丝与栽培技术的相关性 [J]. 福建农业, 2007(11):20−21.LIN J, LIN M L. Correlation between heteromorphic hyphae of mushrooms and cultivation techniques [J]. Fujian Agriculture, 2007(11): 20−21. (in Chinese) [9] 詹才新, 凌霞芬. 双孢蘑菇菌落形态和产质量性状间相关性研究 [J]. 食用菌学报, 1997, 4(3):7−12.ZHAN C X, LING X F. Studies on correlation between colonial morphology and characters of productivity and quality of Agaricus bisporus [J]. Acta Edulis Fungi, 1997, 4(3): 7−12. (in Chinese) [10] 李洪荣. 双孢蘑菇不同菌落形态的同工酶分析 [J]. 福建轻纺, 2011(4):43−45.LI H R. Isozyme analysis of different colony morphology of Agaricus bisporus [J]. The Light & Textile Industries of Fujian, 2011(4): 43−45. (in Chinese) [11] CAI Z X, CHEN M Y, LU Y P, et al. Metabolomics and transcriptomics unravel the mechanism of browning resistance in Agaricus bisporus [J]. PLoS One, 2022, 17(3): e0255765. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0255765 [12] LU Y P, GUO Z J, KE B R, et al. Genome-wide association study and transcriptome analysis provide candidate genes for agronomic traits of Agaricus bisporus [J]. Horticulturae, 2024, 10(7): 691. doi: 10.3390/horticulturae10070691 [13] YANG X M, YANG K X, WANG X H, et al. Transcriptomic analysis reveals the mechanism of bacterial disease resistance of postharvest button mushroom (Agaricus bisporus) [J]. Physiological and Molecular Plant Pathology, 2022, 122: 101903. doi: 10.1016/j.pmpp.2022.101903 [14] 秦煜, 郑向丽, 林钟员. 基于转录组测序的红萍SSR和SNP特征分析 [J]. 福建农业科技, 2023, 54(6):44−48.QIN Y, ZHENG X L, LIN Z Y. Characteristic analysis of SSR and SNP in Azolla imbircata based on transcriptome sequencing [J]. Fujian Agricultural Science and Technology, 2023, 54(6): 44−48. (in Chinese) [15] 陈美元. 双孢蘑菇As2796全长cDNA文库的构建及鉴定 [J]. 福建农业学报, 2012, 27(11):1201−1204.CHEN M Y. Construction and identification of full-length cDNA library of Agaricus bisporus As2796 [J]. Fujian Journal of Agricultural Sciences, 2012, 27(11): 1201−1204. (in Chinese) [16] 王泽生. 蘑菇杂交株As2796的种性与栽培技术要点 [J]. 食用菌, 1993, 15(5):9.WANG Z S. Characteristics and cultivation techniques of mushroom hybrid strain As2796 [J]. Edible Fungi, 1993, 15(5): 9. (in Chinese) [17] KIM D, PERTEA G, TRAPNELL C, et al. TopHat2: Accurate alignment of transcriptomes in the presence of insertions, deletions and gene fusions [J]. Genome Biology, 2013, 14(4): R36. doi: 10.1186/gb-2013-14-4-r36 [18] 顾鑫, 杨晓贺, 姚亮亮, 等. 大豆灰斑病菌Race15的全基因组测序分析 [J]. 大豆科学, 2021, 40(4):466−475.GU X, YANG X H, YAO L L, et al. Whole-genome sequencing and analysis of Cercospora sojina race 15 [J]. Soybean Science, 2021, 40(4): 466−475. (in Chinese) [19] JIANG H, WONG W H. Statistical inferences for isoform expression in RNA-Seq [J]. Bioinformatics, 2009, 25(8): 1026−1032. doi: 10.1093/bioinformatics/btp113 [20] ANDERS S, HUBER W. Differential expression analysis for sequence count data[J]. Nature Precedings, 2010. [21] MCKENNA A, HANNA M, BANKS E, et al. The Genome Analysis Toolkit: A MapReduce framework for analyzing next-generation DNA sequencing data [J]. Genome Research, 2010, 20(9): 1297−1303. doi: 10.1101/gr.107524.110 [22] WANG K, LI M, HAKONARSON H. ANNOVAR: Functional annotation of genetic variants from next-generation sequencing data Nucleic Acids Research[J]. ANNOVAR: Functional annotation of genetic variants from next-generation sequencing data Nucleic Acids Research, 2010: 38. [23] 王秉峰. 匍匐型与气生型双孢蘑菇菌株品比试验 [J]. 中国食用菌, 2010, 29(5):19−20.WANG B F. The comparison test of different strains of prostrate and aerial-type Agaricus bisporas [J]. Edible Fungi of China, 2010, 29(5): 19−20. (in Chinese) [24] WANG H C, WANG Z S. The prediction of strain characteristecs of Agaricus bisporus by the application of isozyme electrophoresis [J]. Fujian Mushroom, 1991(1): 38−48. (in Chinese). [25] WANG Z S, WANG H C. Isozyme patterns and characteristics of hybrid strains of Agaricus bisporus [J]. Microl. Neotrop. Apl, 1990(3): 19−29. [26] 金建康, 徐鹤林. 双孢蘑菇气生型与匍匐型的比较研究 [J]. 中国食用菌, 1990, 9(5):3−4.JIN J K, XU H L. Comparative study on aerial type and creeping type of Agaricus bisporus [J]. Edible Fungi of China, 1990, 9(5): 3−4. (in Chinese) [27] 杜炫星, 牛敏敏, 赵清, 等. 李白盾蚧转录组分析及 SSR 位点开发 [J]. 环境昆虫学报, 2023, 45(5):1318−1332.DU X X, NIU M M, ZHAO Q, et al. Analysis of the transcriptome and development of SSR Loci in Pseudaulacaspis prunicola (Maskell) [J]. Journal of Environmental Entomology, 2023, 45(5): 1318−1332. (in Chinese). [28] MORIN E, KOHLER A, BAKER A R, et al. Genome sequence of the button mushroom Agaricus bisporus reveals mechanisms governing adaptation to a humic-rich ecological niche [J]. Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences of the United States of America, 2012, 109(43): 17501−17506. [29] LINDER M B, SZILVAY G R, NAKARI-SETÄLÄ T, et al. Hydrophobins: The protein-amphiphiles of filamentous fungi [J]. FEMS Microbiology Reviews, 2005, 29(5): 877−896. doi: 10.1016/j.femsre.2005.01.004 [30] LUGONES L G, BOSSCHER J S, SCHOLTMEYER K, et al. An abundant hydrophobin (ABH1) forms hydrophobic rodlet layers in Agaricus bisporus fruiting bodies[J]. Microbiology, 1996, 142 ( Pt 5): 1321-1329. [31] LUGONES L G, WÖS H A B, WESSELS J G H. A hydrophobin (ABH3) specifically secreted by vegetatively growing hyphae of Agaricus bisporus (common white button mushroom)[J]. Microbiology, 1998, 144 ( Pt 8): 2345-2353. [32] OHTAKI S, MAEDA H, TAKAHASHI T, et al. Novel hydrophobic surface binding protein, HsbA, produced by Aspergillus oryzae [J]. Applied and Environmental Microbiology, 2006, 72(4): 2407−2413. doi: 10.1128/AEM.72.4.2407-2413.2006 [33] 张烨. 球孢白僵菌疏水表面结合蛋白HsbA的克隆及功能研究[D]. 北京: 中国农业科学院, 2013ZHANG Y. cDNA clone and functional research on hydrophobic surface binding protein HsbA in Beauveria bassiana [D]. Beijing: Chinese Academy of Agricultural Sciences, 2013. (in Chinese) [34] PARK J, LEE S, CHOI J, et al. Fungal cytochrome P450 database [J]. BMC Genomics, 2008, 9: 402. doi: 10.1186/1471-2164-9-402 [35] HLAVICA P. Evaluation of structural features in fungal cytochromes P450 predicted to rule catalytic diversification [J]. Biochimica et Biophysica Acta, 2013, 1834(1): 205−220. doi: 10.1016/j.bbapap.2012.09.012 [36] SMIDA A D, VALDERRAMA X P, AGOSTINI M C, et al. Cadmium stimulates transcription of the cytochrome p450 side chain cleavage gene in genetically modified stable porcine granulosa cells [J]. Biology of Reproduction, 2004, 70(1): 25−31. doi: 10.1095/biolreprod.103.019000 [37] ZHANG M, LIU X C, YUAN L Y, et al. Transcriptional profiling in cadmium-treated rice seedling roots using suppressive subtractive hybridization [J]. Plant Physiology and Biochemistry, 2012, 50: 79−86. doi: 10.1016/j.plaphy.2011.07.015 [38] WANG L L, LI H B, WEI H L, et al. Identification of cadmium-induced Agaricus blazei genes through suppression subtractive hybridization [J]. Food and Chemical Toxicology, 2014, 63: 84−90. doi: 10.1016/j.fct.2013.10.036 [39] 宋媛, 胡秋辉, 苏安祥, 等. 转录组学解析茉莉酸甲酯对双孢蘑菇个体大小的影响机制 [J]. 食品科学, 2021, 42(4):130−137.SONG Y, HU Q H, SU A X, et al. Transcriptomic analysis of the mechanism underlying the effect of methyl jasmonate on the size of Agaricus bisporus [J]. Food Science, 2021, 42(4): 130−137. (in Chinese) [40] 刘俊敏. 镉胁迫对双孢蘑菇抗氧化系统的影响及耐受性相关基因的筛选与鉴定[D]. 厦门: 厦门大学, 2018.LIU J M. Cadmium stress on the effect of antioxidant system in Agaricus bisporus and the identification of differentially expressed genes [D]. Xiamen: Xiamen University, 2018. (in Chinese) [41] XU K H, ZHAO Y, ZHAO Y, et al. Soybean F-box-like protein GmFBL144 interacts with small heat shock protein and negatively regulates plant drought stress tolerance [J]. Frontiers in Plant Science, 2022, 13: 823529. doi: 10.3389/fpls.2022.823529 [42] MÜLLER-STARCK G. Isozymes[M]//Molecular Tools for Screening Biodiversity. Dordrecht: Springer Netherlands, 1998: 75-81. [43] 时如霞, 曾琴, 赵丹. 基于楠木转录组的SSR、SNP、Indel分子标记技术特征分析 [J]. 山地农业生物学报, 2023, 42(4):83−87.SHI R X, ZENG Q, ZHAO D. SSR, SNP and InDel characterization of Phoebe zhennan based on the transcriptome sequence [J]. Journal of Mountain Agriculture and Biology, 2023, 42(4): 83−87. (in Chinese) [44] 贾定洪, 王波, 何晓兰, 等. 基于基因组重测序发掘金针菇 InDel, SV 及丰度 SNP 标记 [J]. 菌物学报, 2024, 43(7):230228.JIA D H, WANG B, HE X L, et al. Exploitation of InDel, SV and abundance SNP markers in Flammulina filiformis based on genome resequencing [J]. Mycosystema, 2024, 43(7): 23022. (in Chinese). [45] 施肖堃, 蔡志欣, 郭仲杰, 等. 18个双孢蘑菇核心种质的重测序初步分析 [J]. 福建农业学报, 2019, 34(10):1167−1172.SHI X K, CAI Z X, GUO Z J, et al. A preliminary report on resequencing 18 representative strains of Agaricus bisporus [J]. Fujian Journal of Agricultural Sciences, 2019, 34(10): 1167−1172. (in Chinese). -








 下载:
下载: