Effects of Selenium and Arbuscular Mycorrhizal Fungi Applications on Growth, Photosynthesis, and Selenium Accumulation of Amaranthus tricolor L.
-
摘要:目的 探明丛枝菌根真菌(Arbuscular mycorrhizal fungi, AMF)在苋菜富硒栽培中的生物效应,综合评价AMF对不同硒形态处理下苋菜生长和硒积累的影响。方法 采用盆栽试验,分析了土施外源硒和接种AMF对苋菜光合作用、生长状况、苋菜红素以及硒积累的影响。结果 硒酸钠、亚硒酸钠和L-硒代半胱氨酸处理均降低了苋菜红素含量,但对菌根侵染率和菌根依赖性均无显著影响,同时显著提高了苋菜叶片叶绿素a、b含量、蒸腾速率(Tr)、气孔导度(Gs)、净光合速率(Pn)和胞间CO2浓度(Ci),其中L-硒代半胱氨酸处理效果最佳,说明外源硒处理对苋菜的生长有一定的正效应。另外,接种AMF对不同硒处理下苋菜的生长也有促进作用,且提高了叶片苋菜红素含量,同时增强了光合能力和根茎叶硒含量的积累。结论 接种AMF和外源硒处理均能提高苋菜的光合能力和硒积累能力,从而促进苋菜生长和提高苋菜营养品质,两者交互处理可作为提高蔬菜富硒栽培的有效措施。Abstract:Objective Amaranth cultivation enriched by applications of selenium and arbuscular mycorrhizal fungi (AMF) was investigated.Methods In a pot experiment, selenium and AMF were added to the soil in cultivating Amaranthus tricolor L. seedlings. Effects on the photosynthesis, growth, and selenium accumulation of the plants were monitored.Results The selenium treatment significantly increased the contents of chlorophyll a and b, transpiration rate (Tr), stomatal conductance (Gs), net photosynthetic rate (Pn), and intercellular CO2 concentration (Ci) but reduced the amaranthine and not significantly affected the infection rate of or dependence on the mycorrhizae of the seedlings. On the other hand, AMF along with the application of various selenium compounds promoted the amaranth growth and increased the leaf amaranthine content, photosynthetic capacity, and selenium accumulation in the roots, stems and leaves.Conclusion Combined AMF and selenium applications benefited the photosynthesis and nutritional quality of A. tricolor.
-
0. 引言
【研究意义】硒(Se)是人体必不可少的微量元素,适量摄入硒能帮助人体增强免疫力、抗癌和抗衰老,还能有效预防多种疾病[1]。我国大约有51%的人缺硒,缺硒省份高达22个,其中30%的县市严重缺硒[2]。通过外源施加硒肥,利用植物的生物强化作用提高农产品硒含量,进而提高食物链的硒水平,是调控硒营养与健康的有效措施之一[3−5]。外源硒施用方式包括土施、叶面喷施、浸种和拌种等,其中土施硒肥和叶面喷施硒肥是目前最主要的施硒方法[6]。唐玉霞等[7]研究发现土壤施用和叶面喷施亚硒酸钠均使河北地区小麦籽粒硒含量显著提高;Kaur和Sharma[8]对小麦分别施加硒酸钠和亚硒酸钠研究发现,硒酸钠处理小麦叶片中的硒积累高于亚硒酸钠处理;黄太庆等[9]在水稻富硒栽培研究中表明,在抽穗期喷施含硒叶面肥效果明显高于在孕穗时施用。由此说明,植物对硒的吸收和积累与土壤条件、硒肥种类及施用时期等多种因素有关。另外,研究还发现,不同植物对硒的耐受能力及吸收能力有很大差异,其中大部分蔬菜属于非富硒植物,虽然能吸收并积累硒,但其富集能力有限且不能在过高硒浓度条件下正常生长[10]。因此,通过农艺措施提高蔬菜对硒的富集量很有必要。【前人研究进展】丛枝菌根真菌(arbuscular mycorrhizal fungi, AMF)能与大多数植物根系形成共生体,并在土壤中形成大量菌丝,增大根际吸收范围,增强宿主植物对养分的吸收,促进宿主植物的生长[11]。苗秀妍[12]认为大豆接种摩西管柄囊霉(Funneliformis mosseae)后增加了土壤中有效硒含量,从而有利于大豆硒吸收;Chen 等[13]研究表明,在0.5 mg·kg−1 硒酸盐和亚硒酸盐处理下,接种F. mosseae或地表球囊霉(Glomus versiforme)均可显著增加水稻硒含量;Luo 等[14]在AMF调控冬小麦对硒酸盐的吸收研究中发现,AMF主要通过上调冬小麦根系硫酸盐转运蛋白基因TaSultr1:1 的相对表达来增加提高硒转运与积累;另外,在莴苣上的研究却发现接种AMF 显著降低了莴苣叶片硒含量,不利于莴苣硒的生物强化[15],在黑麦草上的研究也发现了类似的现象[16]。【本研究切入点】苋菜(Amaranthus tricolor L.)营养丰富,有良好的抗氧化活性,既可以作为蔬菜食用,也可以药用,有“菜中维生素丸”“补血菜”“长寿菜”之称。AMF可以与苋菜形成互惠共生体,增强苋菜对养分的吸收。国内外对硒、AMF以及苋菜均进行了大量的研究,但关于富硒土壤下接种AMF对苋菜的生长效应、光合生理以及硒积累等方面影响的研究鲜有报道。【拟解决的关键问题】通过探讨土施不同形态硒模拟富硒土壤后接种AMF对苋菜生长效应、光合能力及硒积累代谢转化的影响,综合评价接种AMF对不同硒形态处理下苋菜生长和硒积累的影响,为合理种植优质的富硒苋菜提供参考。
1. 材料与方法
1.1 供试材料
供试植物为苋菜(Amaranthus tricolor L.),品种为市场上常见的花红苋菜,种子购自四川省绵阳农资批发市场;供试AMF为摩西球囊霉(Glomus mosseae),菌沙为经苜蓿扩繁所得到的含孢子、菌丝以及侵染根段的根际土。
1.2 试验地概况
采集自西南科技大学龙山教学科研实践基地菜园的黄壤土,土壤风干后磨碎、混匀、过5 mm筛,掺入干净的河砂(黄壤土和河砂的体积比为 7∶1),拌入营养土(黄壤土和营养土的质量比为 3∶1),混匀,再用高压蒸汽灭菌锅于121 ℃下高温湿热灭菌120 min,灭菌完成后黑暗中静置1周,以消除土壤中原本的菌根对AMF的影响。土壤基本理化性质:pH 5.68,有机质16.88 g·kg−1,有效磷12.65 mg·kg−1,有效钾81.21 mg·kg−1,碱解氮118.66 mg·kg−1,总硒含量0.24 mg·kg−1。
1.3 试验方法
1.3.1 试验设计
采用盆栽法,每盆装土1.0 kg并加入菌沙50 g。设置接种AMF、硒形态和硒浓度3个因素,其中硒形态设置了3种,分别为亚硒酸钠、硒酸钠、有机硒(L-硒代半胱氨酸);设置2种硒浓度,分别为0.5 mg·kg−1和2.5 mg·kg−1(该浓度根据供试土壤的总硒含量0.24 mg·kg−1且富硒土壤规定硒含量范围为0.4~3.0 mg·kg−1确定),设置不加硒的清水处理为对照组(CK)。同一硒形态和硒浓度处理下设置接种AMF和不接种AMF(Non-AMF)两种处理,AMF处理组采用二层接种法,先向盆中装入450 g土,然后铺上25 g菌沙,再装入450 g土并铺上25 g菌沙,播入3~5粒苋菜种子,最后用100 g土壤均匀覆盖种子;Non-AMF处理组则采用同样的方式添加50 g灭菌菌沙。共14种处理,每个处理设置5次重复,共计70盆,待苋菜长至5 cm左右进行间苗,每盆保留1株,40 d后收获。
1.3.2 测定项目及方法
苋菜的株高和茎粗在收获前分别采用皮尺和游标卡尺测量,叶干重、茎干重和地下部干重采用烘干称重法,苋菜的根系菌根侵染率采用墨水醋染色法测定[17],并根据以下公式计算侵染率和依赖性。侵染率/%=(菌根侵染的根段数/ 被检根段总数)×100。菌根依赖性/%=(接种AMF的苋菜干重/未接种AMF的苋菜干重)×100
叶绿素含量采用丙酮-乙醇混合液提取法用分光光度计测定[18]。
待苋菜生长30 d后,选择在晴朗的上午使用GFS-3000光合仪测定光合指标。
苋菜根茎叶总硒含量和叶片有机硒含量测定采用荧光光度法进行[21]。
1.4 数据处理
采用Excel 2019进行数据整理,并利用SPSS 26.0进行统计分析,数据图采用Origin 2021进行绘制。
2. 结果与分析
2.1 不同硒处理下苋菜接种AMF后的侵染率和菌根依赖性
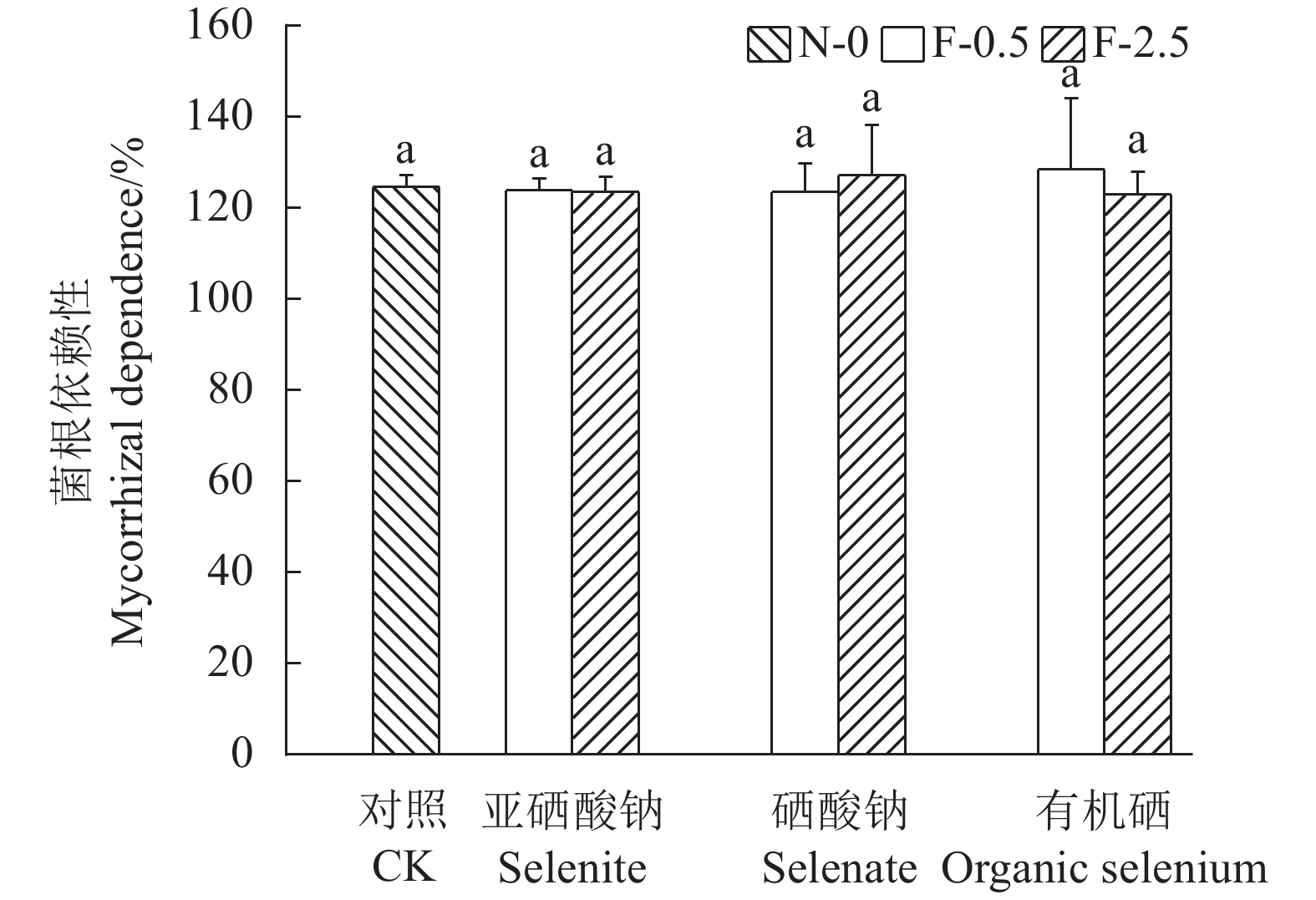
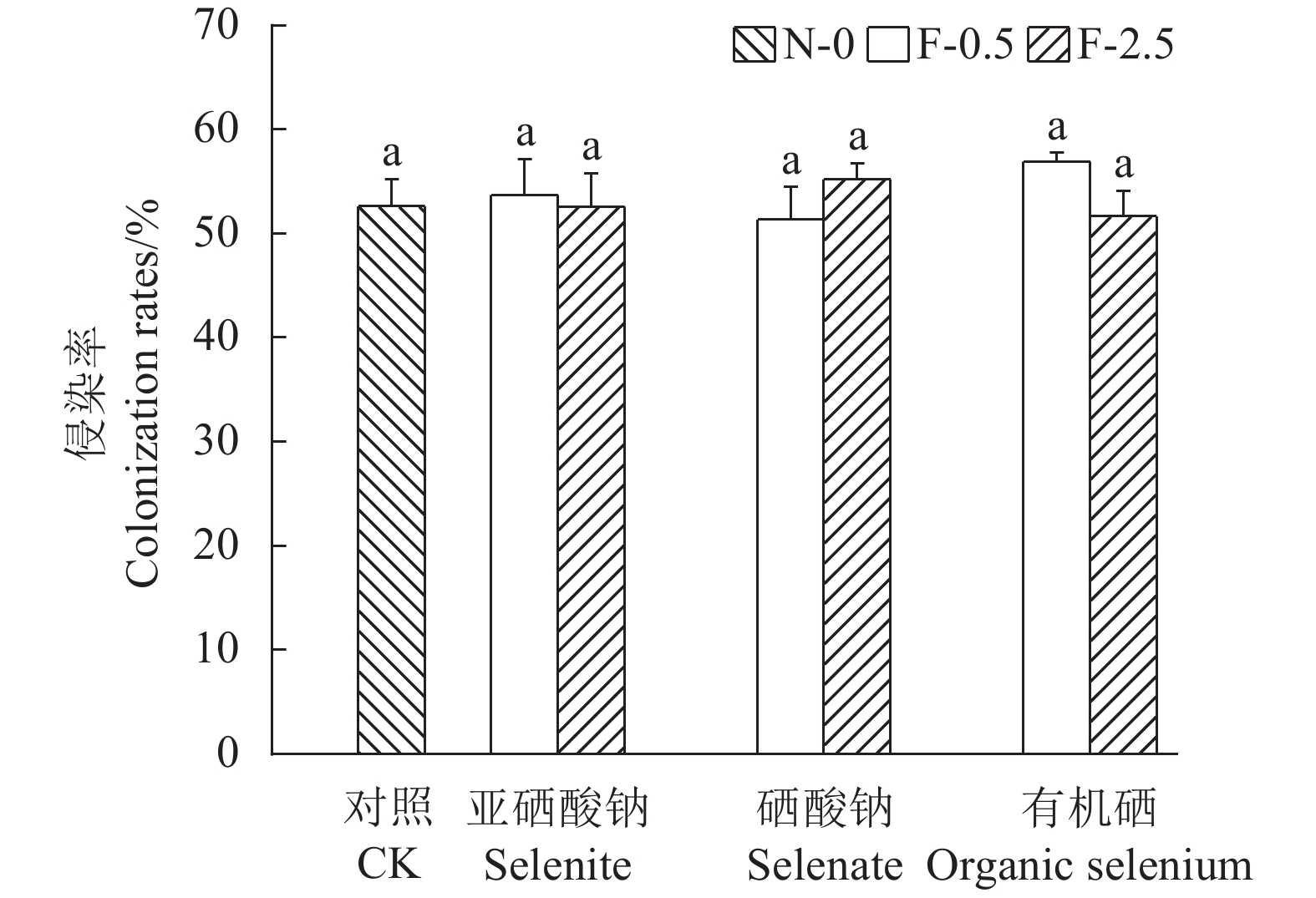
由图1可知,不同硒处理形态,AMF对苋菜根系的侵染率呈现出一定的差异,其中硒酸钠处理降低了苋菜AMF侵染率,亚硒酸钠和有机硒处理增加了苋菜AMF侵染率,但均未达显著水平,即添加不同浓度和不同形态的硒对AMF侵染苋菜根系无显著影响;而从图2可看出,不同外源硒处理之间苋菜对AMF依赖性无显著差别。
![]() 图 1 不同硒处理对苋菜的菌根侵染率的影响①不同小写字母表示P < 0.05水平差异显著;②N-0为土壤中未接种AMF且硒含量为0 mg·kg−1、F-0.5为土壤中接种AMF且硒含量为0.5 mg·kg−1、F-2.5为土壤中接种AMF且硒含量为2.5 mg·kg−1。图2同。Figure 1. Effect of selenium treatments on mycorrhizal infection rate of amaranth①Data with different lowercase letters indicate significant differences at P<0.05; ②N-0: soil without AMF and selenium applications; F-0.5: soil inoculated with AMF and added selenium at concentration of 0.5 mg·kg−1; F-2.5: soil inoculated with AMF and added selenium at concentration of 2.5 mg·kg−1. Same for Fig. 2.
图 1 不同硒处理对苋菜的菌根侵染率的影响①不同小写字母表示P < 0.05水平差异显著;②N-0为土壤中未接种AMF且硒含量为0 mg·kg−1、F-0.5为土壤中接种AMF且硒含量为0.5 mg·kg−1、F-2.5为土壤中接种AMF且硒含量为2.5 mg·kg−1。图2同。Figure 1. Effect of selenium treatments on mycorrhizal infection rate of amaranth①Data with different lowercase letters indicate significant differences at P<0.05; ②N-0: soil without AMF and selenium applications; F-0.5: soil inoculated with AMF and added selenium at concentration of 0.5 mg·kg−1; F-2.5: soil inoculated with AMF and added selenium at concentration of 2.5 mg·kg−1. Same for Fig. 2.2.2 外源硒处理下接种AMF对苋菜生物量的影响
如表1所示,硒酸钠和有机硒处理后苋菜的株高、茎粗、茎干重、叶干重和总生物量均随硒浓度的增加而显著增加(P < 0.05),而亚硒酸钠处理对苋菜的株高、茎粗和茎干重的影响基本不受浓度的影响;与Non-AMF相比,接种AMF显著增加了苋菜的株高、茎粗、总生物量、叶干重和茎干重(P < 0.05),但对于地下部干重而言,AMF只对CK以及0.5 mg·kg−1、2.5 mg·kg−1有机硒处理组存在显著增加作用,分别提高了16.05%、14.13%和8.77%。
表 1 接种AMF对不同硒处理苋菜生物量及生长指标的影响Table 1. Effects of AMF inoculation on biomass and growth indicators of amaranth under different selenium treatments硒处理
Selenium addition/
(mg·kg−1)株高
Plant height/
cm茎粗
Stem diameter/
mm总生物量
Total biomass/
(g·盆−1)叶干重
Leaf dry weight/
(g·盆−1)茎干重
Stem dry weight/
(g·盆−1)地下部干重
Subterranean
part dry weight/
(g·盆−1)Non-AMF AMF Non-AMF AMF Non-AMF AMF Non-AMF AMF Non-AMF AMF Non-AMF AMF 对照CK 14.49±0.08dB 17.97±0.97dA 4.76±0.29dB 5.70±0.20cA 1.89±0.05dB 2.35±0.02dA 0.67±0.03cB 0.86±0.03eA 0.41±0.04cB 0.55±0.07cA 0.81±0.03cB 0.94±0.06cA 亚硒
酸钠
Selenite0.5 16.26±1.11cdB 19.17±1.19cdA 5.24±0.26cdB 6.14±0.49cA 2.11±0.07cB 2.61±0.03cA 0.78±0.10cB 0.99±0.05eA 0.46±0.04cB 0.62±0.04cA 0.87±0.08cA 1.01±0.09bcA 2.5 17.12±1.34cB 20.21±1.35cA 5.30±0.28cB 6.23±0.33cA 2.53±0.06bB 3.12±0.06bA 1.03±0.05bB 1.36±0.07cA 0.51±0.06cB 0.65±0.06cA 0.99±0.08bA 1.11±0.04bA 硒酸钠
Selenate0.5 15.00±0.85cdB 18.74±0.82cdA 5.16±0.05cdB 5.81±0.16cA 1.70±0.08dB 2.1±0.01eA 0.71±0.05cB 0.92±0.10eA 0.44±0.08cB 0.58±0.04cA 0.56±0.04dA 0.60±0.07eA 2.5 23.32±0.73aB 25.25±0.82aA 7.11±0.12aB 7.89±0.25aA 2.63±0.02bB 3.34±0.27bA 1.09±0.09bB 1.52±0.10bA 0.86±0.06aB 1.07±0.11aA 0.68±0.07dA 0.76±0.06dA 有机硒
Organic
selenium0.5 17.14±1.42cB 20.01±0.30cA 5.27±0.40cdB 6.06±0.44cA 2.23±0.21cB 2.84±0.07cA 0.82±0.12cB 1.14±0.10dA 0.50±0.02cB 0.65±0.00cA 0.92±0.07bcB 1.05±0.03bcA 2.5 20.03±1.16bB 22.68±0.98bA 6.27±0.17bB 7.01±0.04bA 3.12±0.03aB 3.83±0.12aA 1.32±0.04aB 1.75±0.07aA 0.66±0.06bB 0.83±0.06bA 1.14±0.03aB 1.24±0.03aA 小写字母表示相同AMF接种下不同形态硒处理间的显著差异(P < 0.05);大写字母表示相同硒处理下Non-AMF和AMF之间的显著差异(P < 0.05)。下同。
Data with lowercase letters on same column indicate significant differences between different selenium treatments with same AMF inoculation at P<0.05; those with different uppercase letters on same row indicate significant differences between treatments with and without inoculated AMF under same selenium treatment at P<0.05. Same for below.2.3 外源硒处理下接种AMF对苋菜叶绿素含量的影响
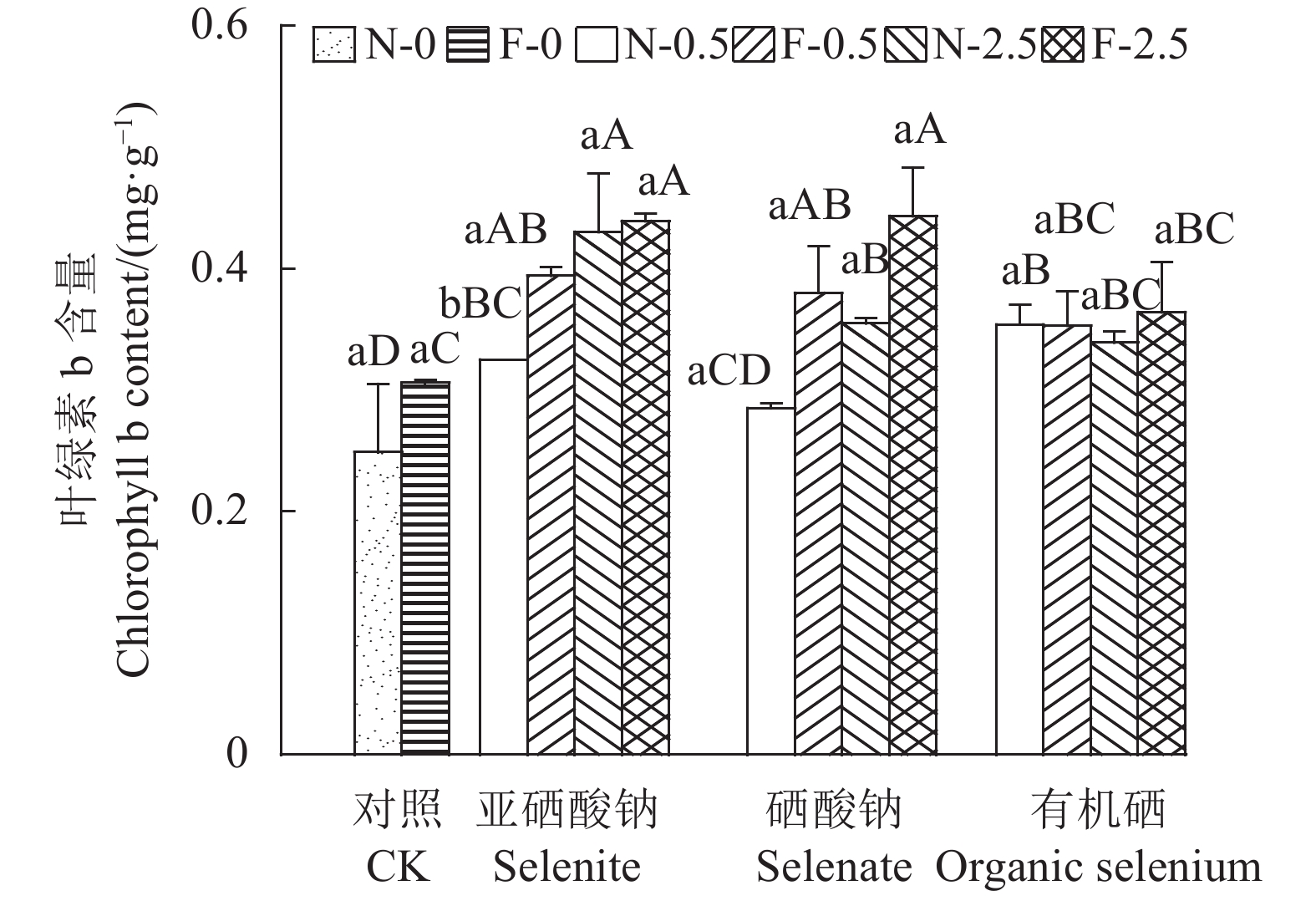
接种AMF和硒处理对苋菜叶绿素含量的影响如图3和图4所示。除0.5 mg·kg−1硒酸钠处理外,相同形态同种浓度硒处理下,接种AMF提高了苋菜叶绿素a和b的含量;在不接种AMF的情况下,0.5 mg·kg−1亚硒酸钠、2.5 mg·kg−1亚硒酸钠、2.5 mg·kg−1硒酸钠以及0.5 mg·kg−1有机硒处理苋菜叶绿素a的含量显著高于CK处理(P < 0.05),其含量分别是CK的1.27倍、1.49倍、1.40倍和1.26倍,但这4种处理之间无显著差异,同时,除有机硒处理外,叶绿素b含量随着硒浓度的增加而增加;接种AMF后,2.5 mg·kg−1亚硒酸钠处理对叶绿素a含量的影响最显著,但3种形态的硒不同浓度处理间的叶绿素b含量均无显著差异。
![]() 图 3 接种 AMF 和硒处理对苋菜叶绿素 a 含量的影响①不同小写字母表示相同硒处理下未接种AMF和接种AMF之间的显著差异(P < 0.05);不同大写字母表示相同AMF接种下不同形态硒处理之间的显著差异(P < 0.05);②N-0为土壤中未接种AMF且硒含量为0 mg·kg−1、F-0为土壤中接种AMF且硒含量为0 mg·kg−1、N-0.5为土壤中未接种AMF且硒含量为0.5 mg·kg−1、F-0.5为土壤中接种AMF且硒含量为0.5 mg·kg−1、N-2.5为土壤中未接种AMF且硒含量为2.5 mg·kg−1、F-2.5为土壤中接种AMF且硒含量为2.5 mg·kg−1。下同。Figure 3. Effect of AMF and selenium applications on chlorophyll a content in amaranth①Data with different lowercase letters indicate significant differences between treatments with and without inoculated AMF under same selenium treatment at P<0.05;those with different capital letters indicate significant differences between different selenium treatments under same AMF treatment at P<0.05;②N-0: soil without AMF and selenium applications; F-0: soil inoculated with AMF but no selenium addition; N-0.5: soil without AMF inoculation but was added with selenium at concentration of 0.5 mg·kg−1; F-0.5: soil inoculated with AMF and added selenium at concentration of 0.5 mg·kg−1; N-2.5: soil without AMF inoculation but was added with selenium at concentration of 2.5 mg·kg−1; F-2.5: soil inoculated with AMF and added selenium at concentration of 2.5 mg·kg−1. Same for below.
图 3 接种 AMF 和硒处理对苋菜叶绿素 a 含量的影响①不同小写字母表示相同硒处理下未接种AMF和接种AMF之间的显著差异(P < 0.05);不同大写字母表示相同AMF接种下不同形态硒处理之间的显著差异(P < 0.05);②N-0为土壤中未接种AMF且硒含量为0 mg·kg−1、F-0为土壤中接种AMF且硒含量为0 mg·kg−1、N-0.5为土壤中未接种AMF且硒含量为0.5 mg·kg−1、F-0.5为土壤中接种AMF且硒含量为0.5 mg·kg−1、N-2.5为土壤中未接种AMF且硒含量为2.5 mg·kg−1、F-2.5为土壤中接种AMF且硒含量为2.5 mg·kg−1。下同。Figure 3. Effect of AMF and selenium applications on chlorophyll a content in amaranth①Data with different lowercase letters indicate significant differences between treatments with and without inoculated AMF under same selenium treatment at P<0.05;those with different capital letters indicate significant differences between different selenium treatments under same AMF treatment at P<0.05;②N-0: soil without AMF and selenium applications; F-0: soil inoculated with AMF but no selenium addition; N-0.5: soil without AMF inoculation but was added with selenium at concentration of 0.5 mg·kg−1; F-0.5: soil inoculated with AMF and added selenium at concentration of 0.5 mg·kg−1; N-2.5: soil without AMF inoculation but was added with selenium at concentration of 2.5 mg·kg−1; F-2.5: soil inoculated with AMF and added selenium at concentration of 2.5 mg·kg−1. Same for below.2.4 外源硒处理下接种AMF对苋菜红素含量的影响
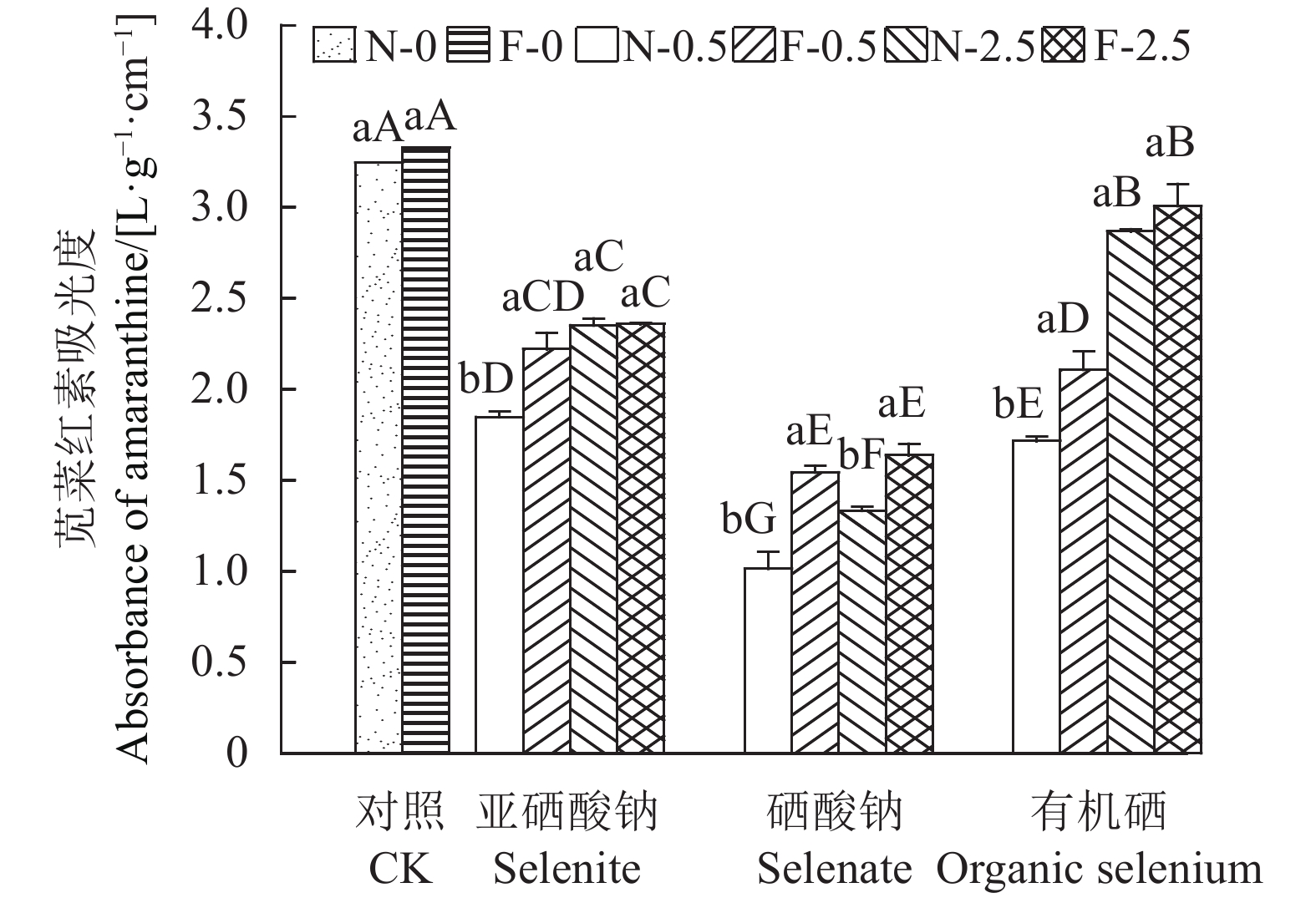
从图5可以发现,硒处理会降低苋菜红素的含量,硒酸钠处理降幅最大,与CK相比,未接种AMF情况下外施0.5 mg·kg−1硒酸钠苋菜红素含量降低了68.78%;另一方面,3种形态硒采用0.5 mg·kg−1处理后,接种AMF均能显著增加苋菜红素含量(P < 0.05),其中硒酸钠处理下接种AMF后使苋菜红素含量增加了52.31%。
2.5 外源硒处理下接种AMF对苋菜光合指标的影响
如表2所示,无论是否接种AMF,硒处理均能显著提高苋菜的光合参数(P < 0.05)。相同的硒形态处理下,苋菜的蒸腾速率(Tr)、气孔导度(Gs)、净光合速率(Pn)和胞间CO2浓度(Ci)均随着硒浓度的增加而显著提高。同时,AMF也能显著提高苋菜的光合参数(P < 0.05), 0.5 mg·kg−1硒酸钠施入后接种AMF处理的苋菜叶片Tr增幅最大,为Non-AMF时的1.70倍;0.5 mg·kg−1亚硒酸钠处理后接种AMF 苋菜叶片Gs增幅最大,为Non-AMF时的1.66倍;0.5 mg·kg−1有机硒处理后接种AMF苋菜叶片 Ci增幅最大,为Non-AMF时的1.42倍。
表 2 接种AMF和不同硒处理对苋菜光合指标的影响Table 2. Effect of AMF inoculation on photosynthetic indexes of amaranth under different selenium treatments硒处理
Selenium addition/ (mg·kg−1)蒸腾速率Tr/
(mmol·m−2·s−1)气孔导度Gs/
(mmol·m−2·s−1)净光合速率Pn/
(µmol·m−2·s−1)胞间CO2浓度Ci/
(μmol·mol−1)Non-AMF AMF Non-AMF AMF Non-AMF AMF Non-AMF AMF 对照CK 0.79±0.03fB 1.08±0.10eA 17.84±0.42dB 29.15±1.48eA 2.25±0.04dB 4.53±0.12dA 114.2±1.74fB 144.6±0.10fA 亚硒酸钠
Selenite0.5 1.19±0.14eB 1.97±0.19dA 33.67±1.06bcB 55.74±3.35abA 3.94±0.53cB 5.63±0.10cA 161.4±2.02eB 199.6±0.95eA 2.5 1.72±0.03aB 2.59±0.05abA 38.94±1.14aB 57.91±1.10aA 6.63±0.72bB 9.33±0.38abA 202.1±1.32bB 226.7±1.25dA 硒酸钠
Selenate0.5 1.35±0.05dB 2.29±0.01cA 31.36±1.87cB 45.20±1.35dA 3.62±0.25cB 5.26±0.24cA 169.1±3.24dB 225.8±1.19dA 2.5 1.61±0.04bB 2.32±0.03cA 34.61±0.62bB 56.96±0.37abA 8.50±0.01aB 9.42±0.43abA 201.5±2.75bB 249.5±3.93cA 有机硒
Organic selenium0.5 1.48±0.01cB 2.44±0.24bcA 33.81±1.08bB 54.49±0.15bA 6.99±0.64bB 9.08±0.40bA 189.8±1.21cB 269.7±3.58bA 2.5 1.68±0.03abB 2.80±0.03aA 37.71±0.96aB 50.26±1.32cA 8.37±0.48aB 9.85±0.24aA 237.4±2.66aB 306.0±5.34aA 2.6 外源硒处理下接种AMF对苋菜硒积累的影响
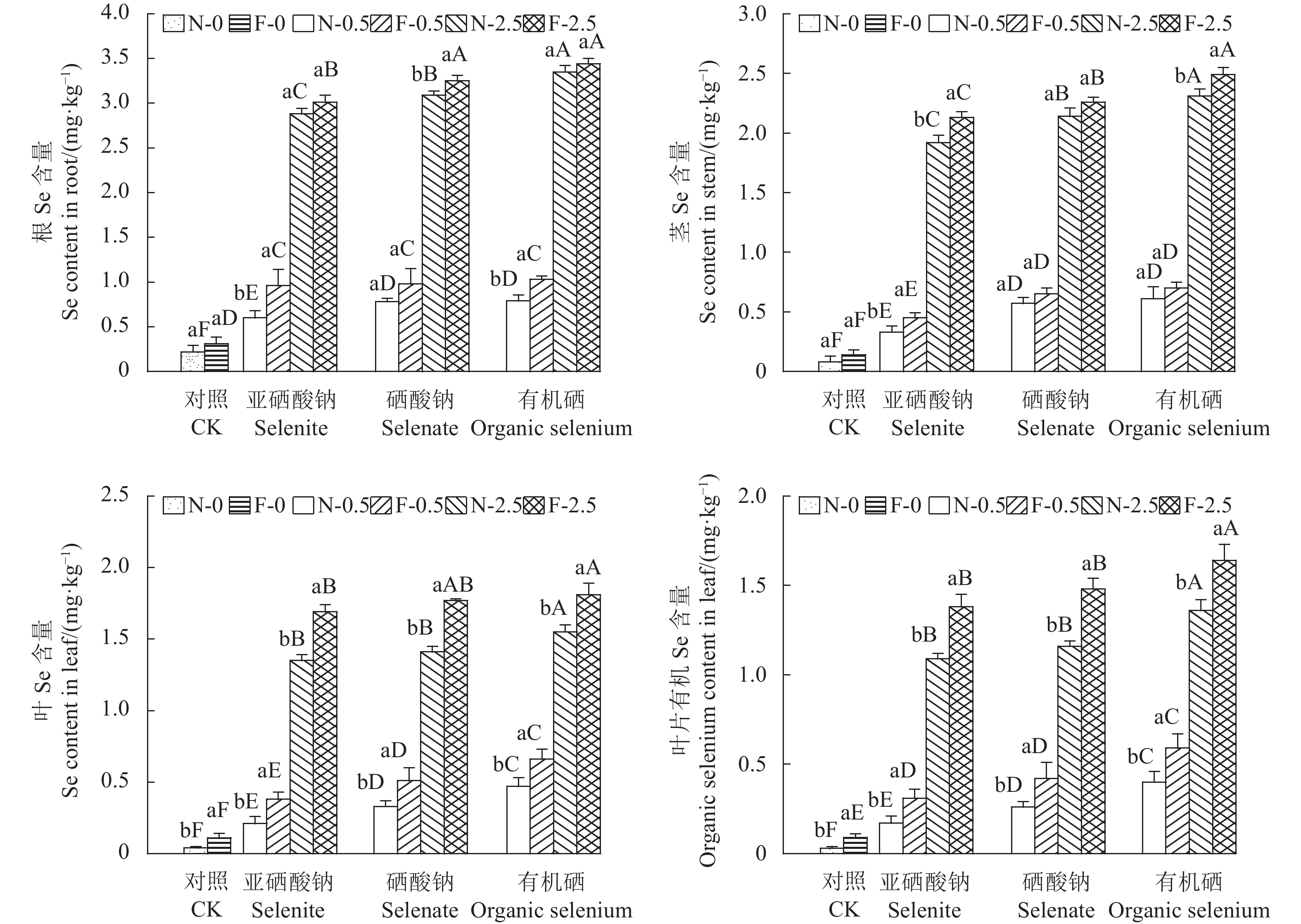
如图6a-c所示,硒处理显著增加了苋菜根茎叶总硒含量(P < 0.05),且总硒含量随着外源硒浓度的增加而增加,接种AMF亦能提高苋菜根茎叶总硒含量。图6d为外源硒处理和接种AMF后苋菜叶片有机硒含量,接种AMF显著增加了苋菜叶片的有机硒含量(P < 0.05),有机硒处理后苋菜叶片有机硒含量显著高于其他几种处理,且叶片有机硒含量随硒处理浓度的增大而增加。
3. 讨论
植物的AMF侵染率会受到土壤pH值、有机质、矿质元素、植物种类等多种因素的影响[22]。前人研究发现施用无机硒肥对水稻[23]、大豆[12]和小麦[24]的侵染率无显著影响,本试验结果也表明,硒处理对AMF在苋菜上的侵染率无显著影响。另外,本试验中显示所有处理下苋菜的AMF依赖性均大于100%,但3种硒处理的AMF依赖性与CK相比均未达到显著水平,说明AMF对苋菜的生长产生了一定的正效应,也进一步验证了硒处理对AMF在苋菜上的侵染影响较小。
本研究的结果表明,接种AMF能显著增加苋菜的株高、茎粗、总生物量、叶干重和茎干重,与刘铭铭等[25]研究指出的接种AMF显著提高了玉米株高、茎粗和干鲜重结果一致,造成这一现象的原因可能是AMF与苋菜形成了共生关系,增强了苋菜根系吸收养分的能力,从而促进其生长。在萝卜[26]、胡萝卜[27]和大白菜[28]等植物上的研究表明,土施硒肥对植物的生物量无显著影响,但本研究发现3种硒处理不同程度地增加了苋菜的株高、茎粗、叶干重和茎干重,尤其在接种AMF后,总生物量较对照显著提高了6.32%、32.56%、18.18%,差异的出现一方面可能是硒对不同植物材料的影响存在不同,另一方面可能是外源硒的施入与AMF存在互作效应。
硒能保护植物叶绿体中的酶,并影响叶片的氧化还原状态,从而增强叶片中光合色素的合成能力,提高叶绿素含量[29]。此外,适宜的硒浓度能增加叶片光合色素含量、提高叶片抗氧化能力,从而延缓叶片衰老[30]。研究表明,施用硒肥能增加草莓[31]、大头菜[32]以及苦荞麦[33]的叶绿素a、b和类胡萝卜素含量。钟松臻等[34] 研究还发现,施硒能提高水稻的光合速率、蒸腾速率和胞间CO2浓度,增强光合能力,从而促进水稻的生长发育。本试验的研究结果表明苋菜经过3种硒处理后的Tr、Gs、Pn和Ci浓度得到了显著的提高,说明外源硒处理在一定程度上可以提高植物的光合效率,促进植物的生长;另一方面,接种AMF处理也显著增加了苋菜Tr、Pn和Ci,且在有机硒处理下增加效应高于无机硒(亚硒酸钠和硒酸钠)处理,说明AMF对苋菜光合能力的作用受到外源硒形态的影响,即有机硒施入后AMF对苋菜的光合能力的提升作用优于无机硒。
苋菜红素是存在于苋菜红色茎、叶中的一种水溶性色素,是反映红花苋菜营养品质的重要参数之一,其颜色鲜艳,稳定性好,具有一定的抗氧化活性[13]。柴明艳[35]对红苋菜的各部位提取物进行了抗氧化活性的探究,发现红苋菜具有良好的抗氧化活性,且叶片的抗氧化活性强于茎部和根部。本研究发现,接种AMF可以不同程度地增加苋菜红素含量,且硒酸钠处理组的增幅最大,为52.31%;加硒处理会降低苋菜红素含量,且硒酸钠处理组的苋菜红素含量显著低于其他3种处理,说明AMF可以促进苋菜红素的合成,但硒会抑制其合成,且AMF的促进作用小于硒的抑制作用。
土施硒处理能显著提高苋菜根、茎、叶的硒含量,且相同处理下,硒含量为根>茎>叶,其原因可能是由于通过向土壤中添加外源硒,苋菜的根部首先从土壤中吸收硒元素,然后再向地上部转运,而向地上部的转运较难。陈雪等[36] 研究也发现植物根、茎、叶各部位的硒含量会随土施硒浓度的增加而显著增加,且根部的硒含量一般大于茎部和叶部的硒含量。黄思思等[37]研究结果显示,喷施有机硒显著增多了茶叶的总硒含量,且茶叶的有机硒含量与总硒含量呈显著正相关。本试验中有机硒处理后的苋菜各部位硒含量显著大于硒酸钠和亚硒酸钠处理后的硒含量,可能是由于硒酸钠和亚硒酸钠属于无机硒,被植物根系吸收后需要先在植物体内转化为有机硒后才能被吸收利用,而土壤中的有机硒不用经过复杂的转化,就能直接被植物吸收利用,从而加快了硒元素从植物根部向地上部转运的速率。
另外,饮食补硒被认为是相对安全、有效的补硒途径,但是无机硒生物有效性低,毒性大且吸收和利用不理想,而有机硒是经过生物转换得到的,生物活性强,利于人体吸收且安全无副作用,只有经过生物转化所形成的有机硒才被认为是对人类安全有效的硒形态[13]。接种AMF能显著增加了苋菜叶片的有机硒含量和有机硒的相对含量,且有机硒处理组的效果明显优于亚硒酸钠处理组和硒酸钠处理组,说明土施有机硒后接种AMF更有利于苋菜积累有机硒,提高农产品安全有效的硒形态含量。此外,外源硒浓度与叶片有机硒含量呈正相关,但对叶片有机硒相对含量影响不显著。
4. 结论
AMF和硒处理增加了苋菜的生物量,增强了苋菜的光合能力和抗氧化能力,促进了苋菜的生长。亚硒酸钠、硒酸钠和有机硒处理对苋菜的影响有一定的差异性,有机硒处理对苋菜生物量、叶绿素含量、光合指标、苋菜红素含量和硒积累转化的影响均优于亚硒酸钠和硒酸钠等无机硒处理。在植物富硒栽培生产中,AMF和硒肥交互处理可作为提高蔬菜富硒栽培的有效措施。
-
图 1 不同硒处理对苋菜的菌根侵染率的影响
①不同小写字母表示P < 0.05水平差异显著;②N-0为土壤中未接种AMF且硒含量为0 mg·kg−1、F-0.5为土壤中接种AMF且硒含量为0.5 mg·kg−1、F-2.5为土壤中接种AMF且硒含量为2.5 mg·kg−1。图2同。
Figure 1. Effect of selenium treatments on mycorrhizal infection rate of amaranth
①Data with different lowercase letters indicate significant differences at P<0.05; ②N-0: soil without AMF and selenium applications; F-0.5: soil inoculated with AMF and added selenium at concentration of 0.5 mg·kg−1; F-2.5: soil inoculated with AMF and added selenium at concentration of 2.5 mg·kg−1. Same for Fig. 2.
图 3 接种 AMF 和硒处理对苋菜叶绿素 a 含量的影响
①不同小写字母表示相同硒处理下未接种AMF和接种AMF之间的显著差异(P < 0.05);不同大写字母表示相同AMF接种下不同形态硒处理之间的显著差异(P < 0.05);②N-0为土壤中未接种AMF且硒含量为0 mg·kg−1、F-0为土壤中接种AMF且硒含量为0 mg·kg−1、N-0.5为土壤中未接种AMF且硒含量为0.5 mg·kg−1、F-0.5为土壤中接种AMF且硒含量为0.5 mg·kg−1、N-2.5为土壤中未接种AMF且硒含量为2.5 mg·kg−1、F-2.5为土壤中接种AMF且硒含量为2.5 mg·kg−1。下同。
Figure 3. Effect of AMF and selenium applications on chlorophyll a content in amaranth
①Data with different lowercase letters indicate significant differences between treatments with and without inoculated AMF under same selenium treatment at P<0.05;those with different capital letters indicate significant differences between different selenium treatments under same AMF treatment at P<0.05;②N-0: soil without AMF and selenium applications; F-0: soil inoculated with AMF but no selenium addition; N-0.5: soil without AMF inoculation but was added with selenium at concentration of 0.5 mg·kg−1; F-0.5: soil inoculated with AMF and added selenium at concentration of 0.5 mg·kg−1; N-2.5: soil without AMF inoculation but was added with selenium at concentration of 2.5 mg·kg−1; F-2.5: soil inoculated with AMF and added selenium at concentration of 2.5 mg·kg−1. Same for below.
表 1 接种AMF对不同硒处理苋菜生物量及生长指标的影响
Table 1 Effects of AMF inoculation on biomass and growth indicators of amaranth under different selenium treatments
硒处理
Selenium addition/
(mg·kg−1)株高
Plant height/
cm茎粗
Stem diameter/
mm总生物量
Total biomass/
(g·盆−1)叶干重
Leaf dry weight/
(g·盆−1)茎干重
Stem dry weight/
(g·盆−1)地下部干重
Subterranean
part dry weight/
(g·盆−1)Non-AMF AMF Non-AMF AMF Non-AMF AMF Non-AMF AMF Non-AMF AMF Non-AMF AMF 对照CK 14.49±0.08dB 17.97±0.97dA 4.76±0.29dB 5.70±0.20cA 1.89±0.05dB 2.35±0.02dA 0.67±0.03cB 0.86±0.03eA 0.41±0.04cB 0.55±0.07cA 0.81±0.03cB 0.94±0.06cA 亚硒
酸钠
Selenite0.5 16.26±1.11cdB 19.17±1.19cdA 5.24±0.26cdB 6.14±0.49cA 2.11±0.07cB 2.61±0.03cA 0.78±0.10cB 0.99±0.05eA 0.46±0.04cB 0.62±0.04cA 0.87±0.08cA 1.01±0.09bcA 2.5 17.12±1.34cB 20.21±1.35cA 5.30±0.28cB 6.23±0.33cA 2.53±0.06bB 3.12±0.06bA 1.03±0.05bB 1.36±0.07cA 0.51±0.06cB 0.65±0.06cA 0.99±0.08bA 1.11±0.04bA 硒酸钠
Selenate0.5 15.00±0.85cdB 18.74±0.82cdA 5.16±0.05cdB 5.81±0.16cA 1.70±0.08dB 2.1±0.01eA 0.71±0.05cB 0.92±0.10eA 0.44±0.08cB 0.58±0.04cA 0.56±0.04dA 0.60±0.07eA 2.5 23.32±0.73aB 25.25±0.82aA 7.11±0.12aB 7.89±0.25aA 2.63±0.02bB 3.34±0.27bA 1.09±0.09bB 1.52±0.10bA 0.86±0.06aB 1.07±0.11aA 0.68±0.07dA 0.76±0.06dA 有机硒
Organic
selenium0.5 17.14±1.42cB 20.01±0.30cA 5.27±0.40cdB 6.06±0.44cA 2.23±0.21cB 2.84±0.07cA 0.82±0.12cB 1.14±0.10dA 0.50±0.02cB 0.65±0.00cA 0.92±0.07bcB 1.05±0.03bcA 2.5 20.03±1.16bB 22.68±0.98bA 6.27±0.17bB 7.01±0.04bA 3.12±0.03aB 3.83±0.12aA 1.32±0.04aB 1.75±0.07aA 0.66±0.06bB 0.83±0.06bA 1.14±0.03aB 1.24±0.03aA 小写字母表示相同AMF接种下不同形态硒处理间的显著差异(P < 0.05);大写字母表示相同硒处理下Non-AMF和AMF之间的显著差异(P < 0.05)。下同。
Data with lowercase letters on same column indicate significant differences between different selenium treatments with same AMF inoculation at P<0.05; those with different uppercase letters on same row indicate significant differences between treatments with and without inoculated AMF under same selenium treatment at P<0.05. Same for below.表 2 接种AMF和不同硒处理对苋菜光合指标的影响
Table 2 Effect of AMF inoculation on photosynthetic indexes of amaranth under different selenium treatments
硒处理
Selenium addition/ (mg·kg−1)蒸腾速率Tr/
(mmol·m−2·s−1)气孔导度Gs/
(mmol·m−2·s−1)净光合速率Pn/
(µmol·m−2·s−1)胞间CO2浓度Ci/
(μmol·mol−1)Non-AMF AMF Non-AMF AMF Non-AMF AMF Non-AMF AMF 对照CK 0.79±0.03fB 1.08±0.10eA 17.84±0.42dB 29.15±1.48eA 2.25±0.04dB 4.53±0.12dA 114.2±1.74fB 144.6±0.10fA 亚硒酸钠
Selenite0.5 1.19±0.14eB 1.97±0.19dA 33.67±1.06bcB 55.74±3.35abA 3.94±0.53cB 5.63±0.10cA 161.4±2.02eB 199.6±0.95eA 2.5 1.72±0.03aB 2.59±0.05abA 38.94±1.14aB 57.91±1.10aA 6.63±0.72bB 9.33±0.38abA 202.1±1.32bB 226.7±1.25dA 硒酸钠
Selenate0.5 1.35±0.05dB 2.29±0.01cA 31.36±1.87cB 45.20±1.35dA 3.62±0.25cB 5.26±0.24cA 169.1±3.24dB 225.8±1.19dA 2.5 1.61±0.04bB 2.32±0.03cA 34.61±0.62bB 56.96±0.37abA 8.50±0.01aB 9.42±0.43abA 201.5±2.75bB 249.5±3.93cA 有机硒
Organic selenium0.5 1.48±0.01cB 2.44±0.24bcA 33.81±1.08bB 54.49±0.15bA 6.99±0.64bB 9.08±0.40bA 189.8±1.21cB 269.7±3.58bA 2.5 1.68±0.03abB 2.80±0.03aA 37.71±0.96aB 50.26±1.32cA 8.37±0.48aB 9.85±0.24aA 237.4±2.66aB 306.0±5.34aA -
[1] HADRUP N, RAVN-HAREN G. Absorption, distribution, metabolism and excretion (ADME) of oral selenium from organic and inorganic sources: A review [J]. Journal of Trace Elements in Medicine and Biology: Organ of the Society for Minerals and Trace Elements (GMS), 2021, 67: 126801. DOI: 10.1016/j.jtemb.2021.126801
[2] 谢邦廷. 典型地球化学景观区硒地球化学特征及生态效应[D]. 北京: 中国地质大学(北京), 2017. XIE B T. Geochemical characteristics and ecological effects of selenium in typical geochemical landscapes[D]. Beijing: China University of Geosciences, 2017. (in Chinese)
[3] CHEN S C, ZHAO H J, ZOU C C, et al. Combined inoculation with multiple arbuscular mycorrhizal fungi improves growth, nutrient uptake and photosynthesis in cucumber seedlings [J]. Frontiers in Microbiology, 2017, 8: 2516. DOI: 10.3389/fmicb.2017.02516
[4] LI X, CHEN A Y, YU L Y, et al. Effects of β-cyclodextrin on phytoremediation of soil co-contaminated with Cd and BDE-209 by arbuscular mycorrhizal amaranth [J]. Chemosphere, 2019, 220: 910−920. DOI: 10.1016/j.chemosphere.2018.12.211
[5] SANMARTÍN C, GARMENDIA I, ROMANO B, et al. Mycorrhizal inoculation affected growth, mineral composition, proteins and sugars in lettuces biofortified with organic or inorganic selenocompounds [J]. Scientia Horticulturae, 2014, 180: 40−51. DOI: 10.1016/j.scienta.2014.09.049
[6] ORLOVSKAYA O A, YATSEVICH K K, VAKULA S I, et al. Characterization of high molecular weight glutenin subunits in wild emmer wheat (Triticum dicoccoides) [J]. Cytology and Genetics, 2020, 54(3): 199−205. DOI: 10.3103/S009545272003010X
[7] 唐玉霞, 王慧敏, 刘巧玲, 等. 河北省麦田土壤硒的含量、形态及其有效性研究 [J]. 华北农学报, 2010, 25(S1):194−197. TANG Y X, WANG H M, LIU Q L, et al. Study on the content, speciation and availability of selenium in wheat field soil of Hebei Province [J]. Acta Agriculturae Boreali-Sinica, 2010, 25(S1): 194−197. (in Chinese)
[8] KAUR M, SHARMA S. Influence of selenite and selenate on growth, leaf physiology and antioxidant defense system in wheat (Triticum aestivum L. ) [J]. Journal of the Science of Food and Agriculture, 2018, 98(15): 5700−5710. DOI: 10.1002/jsfa.9117
[9] 黄太庆, 江泽普, 邢颖, 等. 亚硒酸钠不同施用方法对水稻硒富集及转化的影响 [J]. 西南农业学报, 2021, 34(2):311−319. HUANG T Q, JIANG Z P, XING Y, et al. Effects of different sodium selenite application methods on Se accumulation and transformation in rice [J]. Southwest China Journal of Agricultural Sciences, 2021, 34(2): 311−319. (in Chinese)
[10] YU Y, LUO L, YANG K, et al. Influence of mycorrhizal inoculation on the accumulation and speciation of selenium in maize growing in selenite and selenate spiked soils [J]. Pedobiologia, 2011, 54(5/6): 267−272.
[11] LI J, LIU R F, WU B Y, et al. Influence of arbuscular mycorrhizal fungi on selenium uptake by winter wheat depends on the level of selenate spiked in soil[J]. Chemosphere, 2022, 291(Pt 2): 132813.
[12] 苗秀妍. 丛枝菌根真菌和微肥施用对大豆生长及锌、硒积累的影响[D]. 南宁: 广西大学, 2019. MIAO X Y. Effects of arbuscular mycorrhizal fungi inoculation and trace element fertilization on growth and accumulation of zinc and selenium in soybean[D]. Nanning: Guangxi University, 2019. (in Chinese)
[13] CHEN X, ZHANG Z Y, GU M H, et al. Combined use of arbuscular mycorrhizal fungus and selenium fertilizer shapes microbial community structure and enhances organic selenium accumulation in rice grain [J]. The Science of the Total Environment, 2020, 748: 141166. DOI: 10.1016/j.scitotenv.2020.141166
[14] LUO W Q, LI J, MA X N, et al. Effect of arbuscular mycorrhizal fungi on uptake of selenate, selenite, and selenomethionine by roots of winter wheat [J]. Plant and Soil, 2019, 438(1): 71−83.
[15] DURÁN P, ACUÑA J J, ARMADA E, et al. Inoculation with selenobacteria and arbuscular mycorrhizal fungi to enhance selenium content in lettuce plants and improve tolerance against drought stress [J]. Journal of Soil Science and Plant Nutrition, 2016, 16(1): 201−225.
[16] MUNIER-LAMY C, DENEUX-MUSTIN S, MUSTIN C, et al. Selenium bioavailability and uptake as affected by four different plants in a loamy clay soil with particular attention to mycorrhizae inoculated ryegrass [J]. Journal of Environmental Radioactivity, 2007, 97(2/3): 148−158.
[17] 黄仁华, 陆云梅, 黄炜. 丛枝菌根真菌(AMF)对137Cs污染土壤下宿根高粱生长、根际磷酸酶和富集核素的影响 [J]. 农业环境科学学报, 2013, 32(5):953−959. HUANG R H, LU Y M, HUANG W. Influences of arbuscular mycorrhizal fungi(AMF)on the growth, phosphatase activities and radioactive nuclide bioconcentration of sorghum haipense at soil contaminated with 137 Cs [J]. Journal of Agro-Environment Science, 2013, 32(5): 953−959. (in Chinese)
[18] 吴鹏, 吕剑, 郁继华, 等. 褪黑素对盐碱复合胁迫下黄瓜幼苗光合特性和渗透调节物质含量的影响 [J]. 应用生态学报, 2022, 33(7):1901−1910. WU P, LYU J, YU J H, et al. Effects of melatonin on photosynthetic properties and osmoregulatory substance contents of cucumber seedlings under salt-alkali stress [J]. Chinese Journal of Applied Ecology, 2022, 33(7): 1901−1910. (in Chinese)
[19] 黄丽华, 李芸瑛, 穆晓琨, 等. 苋菜红素的提取纯化及抗氧化活性分析 [J]. 湖北农业科学, 2016, 55(13):3411−3415. HUANG L H, LI Y Y, MU X K, et al. Extraction and purification of red pigment from Amaranthus tricolor L. and analysis of its antioxidant activity [J]. Hubei Agricultural Sciences, 2016, 55(13): 3411−3415. (in Chinese)
[20] SARKER U, OBA S. Leaf pigmentation, its profiles and radical scavenging activity in selected Amaranthus tricolor leafy vegetables [J]. Scientific Reports, 2020, 10: 18617. DOI: 10.1038/s41598-020-66376-0
[21] 黄仁华, 杨会玲, 陆云梅. 贮藏温度对富硒栽培猕猴桃品质和硒组分的影响 [J]. 核农学报, 2015, 29(8):1525−1531. HUANG R H, YANG H L, LU Y M. Effects of storage temperature on quality and selenium component of kiwifruit with Se-enriched cultivation [J]. Journal of Nuclear Agricultural Sciences, 2015, 29(8): 1525−1531. (in Chinese)
[22] WEI Q Y, GOULART B L, DEMCHAK K, et al. Interactive effects of mycorrhizal inoculation and organic soil amendments on nitrogen acquisition and growth of highbush blueberry [J]. Journal of the American Society for Horticultural Science, 2002, 127(5): 742−748. DOI: 10.21273/JASHS.127.5.742
[23] 陈雪. 丛枝菌根真菌对水稻硒吸收、积累的机理研究[D]. 南宁: 广西大学, 2019. CHEN X. The mechanism of arbuscular mycorrhizal fungi inoculation on selenium uptake andaccumulation in rice[D]. Nanning: Guangxi University, 2019. (in Chinese)
[24] LI J, AWASTHI M K, XING W J, et al. Arbuscular mycorrhizal fungi increase the bioavailability and wheat (Triticum aestivum L. ) uptake of selenium in soil [J]. Industrial Crops and Products, 2020, 150: 112383. DOI: 10.1016/j.indcrop.2020.112383
[25] 刘铭铭, 李衍素, 孙锦, 等. 两种丛枝菌根真菌扩繁比较及其对玉米促生的研究 [J]. 农业科技通讯, 2018, (4):63−67. LIU M M, LI Y S, SUN J, et al. Comparison of propagation of two arbuscular mycorrhizal fungi and their effects on maize growth [J]. Bulletin of Agricultural Science and Technology, 2018(4): 63−67. (in Chinese)
[26] DA SILVA D F, CIPRIANO P E, DE SOUZA R R, et al. Biofortification with selenium and implications in the absorption of macronutrients in Raphanus sativus L [J]. Journal of Food Composition and Analysis, 2020, 86: 103382. DOI: 10.1016/j.jfca.2019.103382
[27] SMOLEŃ S, BARANSKI R, LEDWOŻYW-SMOLEŃ I, et al. Combined biofortification of carrot with iodine and selenium [J]. Food Chemistry, 2019, 300: 125202. DOI: 10.1016/j.foodchem.2019.125202
[28] WU Z C, XU S J, SHI H Z, et al. Comparison of foliar silicon and selenium on cadmium absorption, compartmentation, translocation and the antioxidant system in Chinese flowering cabbage [J]. Ecotoxicology and Environmental Safety, 2018, 166: 157−164. DOI: 10.1016/j.ecoenv.2018.09.085
[29] 黄思杰, 刘丹丹, 杨育文, 等. 外源硒对紫色生菜生理指标及营养品质的影响 [J]. 分子植物育种, 2023, 21(18):6126−6133. HUANG S J, LIU D D, YANG Y W, et al. Effect of exogenous selenium on physiological indicators and nutritional quality of purple lettuce [J]. Molecular Plant Breeding, 2023, 21(18): 6126−6133. (in Chinese)
[30] ZAHEDI S M, HOSSEINI M S, MEYBODI N D H, et al. Foliar application of selenium and nano-selenium affects pomegranate (Punica granatum cv. Malase Saveh) fruit yield and quality [J]. South African Journal of Botany, 2019, 124: 350−358. DOI: 10.1016/j.sajb.2019.05.019
[31] ZAHEDI S M, ABDELRAHMAN M, HOSSEINI M S, et al. Alleviation of the effect of salinity on growth and yield of strawberry by foliar spray of selenium-nanoparticles [J]. Environmental Pollution, 2019, 253: 246−258. DOI: 10.1016/j.envpol.2019.04.078
[32] GOLOB A, NOVAK T, MARŠIĆ N K, et al. Biofortification with selenium and iodine changes morphological properties of Brassica oleracea L. var. gongylodes) and increases their contents in tubers [J]. Plant Physiology and Biochemistry: PPB, 2020, 150: 234−243. DOI: 10.1016/j.plaphy.2020.02.044
[33] GOLOB A, STIBILJ V, NEČEMER M, et al. Calcium oxalate druses affect leaf optical properties in selenium-treated Fagopyrum tataricum [J]. Journal of Photochemistry and Photobiology B, Biology, 2018, 180: 51−55. DOI: 10.1016/j.jphotobiol.2018.01.018
[34] 钟松臻, 张宝军, 张木, 等. 硒对水稻光合作用及抗氧化作用的影响 [J]. 中国土壤与肥料, 2017, (4):134−139. ZHONG S Z, ZHANG B J, ZHANG M, et al. Effects of selenium on photosynthesis and antioxidation of rice [J]. Soil and Fertilizer Sciences in China, 2017(4): 134−139. (in Chinese)
[35] 柴明艳. 红苋菜提取物抗氧化活性的研究 [J]. 食品研究与开发, 2016, 37(12):19−23. CHAI M Y. Antioxidant activity of extracts from Amaranthus tricolor L [J]. Food Research and Development, 2016, 37(12): 19−23. (in Chinese)
[36] 陈雪, 沈方科, 张增裕, 等. 硒肥和土壤类型对水稻硒吸收的影响 [J]. 西南农业学报, 2017, 30(9):2010−2016. CHEN X, SHEN F K, ZHANG Z Y, et al. Effects of soil type and selenium application on assimilation of selenium in rice [J]. Southwest China Journal of Agricultural Sciences, 2017, 30(9): 2010−2016. (in Chinese)
[37] 黄思思, 余侃, 唐一龙, 等. 生物有机硒对绿茶产量、品质及硒含量的影响 [J]. 茶叶通讯, 2020, 47(4):610−616. HUANG S S, YU K, TANG Y L, et al. Effect of bioorganic selenium on yield, quality and selenium content of green tea [J]. Journal of Tea Communication, 2020, 47(4): 610−616. (in Chinese)
-
期刊类型引用(1)
1. 贾风勤,黄敏桃,邓利,李金玲,梁梅华,伊洪伟,宋希娟. 干旱、盐分和酸胁迫对药用植物马利筋和苋菜种子萌发的影响. 干旱区研究. 2025(02): 312-320 .  百度学术
百度学术
其他类型引用(0)




 下载:
下载: