Functions of MeUGT25 in Resistance of Cassava to Bacterial Wilt Disease
-
摘要:目的 克隆木薯中UDP依赖型糖基转移酶(UDP-glycosyltransferases, UGTs)基因MeUGT25,并进行抗枯萎病功能研究,为木薯抗病分子育种提供新的基因资源。方法 通过RT-PCR技术从木薯叶片(SC124)中克隆MeUGT25基因。随后,利用病毒诱导的基因沉默(virus induced gene silencing, VIGS)和地毯草黄单胞菌(Xamthomonas axonopodis pv. Manihotis, Xam)侵染试验研究MeUGT25基因在木薯中的抗病功能。结果 病菌Xam能显著诱导MeUGT25基因的表达。在3株阳性干扰植株中,qRT-PCR检测显示它们的MeUGT25基因表达量分别降低71%、70%和69%。Xam侵染试验结果表明,叶片接种Xam 6 d后,MeUGT25V-2和MeUGT25V-3植株叶片上的细菌数量相比对照明显增多,但MeUGT25V-1阳性植株的细菌统计数量和对照叶片相比没有显著差异。然而,从叶片的发病情况来看,3个干扰植株叶片上的菌斑均比对照明显。结论 降低木薯叶片中MeUGT25基因的表达量会影响叶片抵抗Xam病菌侵染的能力,推测MeUGT25基因在木薯抗枯萎病中发挥正调控作用。Abstract:Objective Disease resistance to Xamthomonas axonopodis pv. Manihotis (Xam) of cassava related to MeUGT25, a UDP-glycosyltransferases (UGT) gene, was studied for breeding purposes.Method MeUGT25 was cloned from cassava leaves (SC124) by RT-PCR. Subsequently, virus-induced gene silencing (VIGS) andXam infection challenge experiment were conducted to confirm the disease resistance of the plant.Result The expression of MeUGT25 was significantly induced by the presence of Xam. In 3 transgenic plants, qRT-PCR showed reductions in MeUGT25 expression by 71%, 70%, and 69%. In 6 d after an Xam−inoculation, the bacterial counts on the leaves of MeUGT25V-2 and MeUGT25V-3 plants increased significantly, but not of MeUGT25V-1. On the other hand, apparent plaques appeared on the leaves of the MeUGT25 gene silencing plants indicating the lowered MeUGT25 expression had significantly reduced the resistance of cassava to Xam infection.Conclusion Reduction of MeUGT25 expression in cassava mitigated the ability of the leaves to resist invasion by Xam suggesting a positive regulatory role of the gene played in the disease resistance.
-
Keywords:
- Cassava /
- MeUGT /
- biotic stress /
- VIGS /
- Xamthomonas axonopodis pv. Manihotis
-
0. 引言
【研究意义】木薯(Manihot esculenta Crantz)作为世界三大薯类之一,具有极强的适应性,能够抗旱和耐贫瘠,已被广泛种植于全球近百个国家和地区,为全球十分之一以上人口提供主粮[1]。在我国,木薯是广西、广东和海南地区的一种重要的经济作物,不仅是当地重要的经济作物,而且还具有巨大的发展潜力,其淀粉可以用来生产燃料乙醇和工业淀粉,是一种重要的绿色能源作物 [1]。糖基化修饰是一种普遍存在的植物修饰反应,其中催化该反应的酶是糖基转移酶(glycosyl transferases, GTs)。GTs可以将糖基,如葡萄糖、半乳糖和木糖等,添加到不同的天然化合物中,从而形成更稳定的糖酯或糖苷 [2-4]。其中一类使用UDP作为糖基供体的GTs被称为UDP依赖型糖基转移酶(UDP-glycosyltransferases,UGTs) [5],它们在植物生长发育和逆境胁迫响应过程中发挥着重要作用,主要参与对植物激素和重要次生代谢物的修饰 [6]。地毯草黄单胞菌(Xamthomonas axonopodis pv. Manihotis, Xam)引起的木薯细菌性枯萎病是木薯的主要病害之一 [7- 8]。因此,研究木薯UDP依赖型糖基转移酶基因的功能,对揭示其在木薯应答生物胁迫中的作用机制具有重要意义。【前人研究进展】目前,已经发现的植物GTs家族数量超过100个,几乎所有植物中都发现了这类酶 [9]。在拟南芥中,UGT84B1基因的过表达会导致糖基化生长素的含量升高[10]。过表达UGT73C6和UGT73C5基因会导致转基因植株中糖基化油菜素类固醇的含量增加 [11-12]。ABA在植物应对非生物胁迫,如干旱和高盐中发挥着重要作用,UGTs家族基因也可以通过糖基化修饰来影响ABA在植物体内的稳态 [13]。在拟南芥中,UGT71B6,UGT71B7和UGT71B8等基因可以通过调节ABA的含量来调控植株在非生物逆境中的耐受性 [13-14]。UGT71C5基因的过表达会导致转基因植株对干旱的敏感性增加,这主要是因为ABA的糖酯化使得植株中ABA的含量减少 [15]。植物对生物胁迫的响应主要是通过水杨酸和茉莉酸介导的两条信号通路,这两条通路往往以拮抗的形式起作用 [16-18]。对UGT76B1基因的研究表明,糖基化的小分子参与了连接水杨酸和茉莉酸途径的植物防御信号的转导。缺失UGT76B1基因会提高植株对丁香假单胞菌的抗性,从而降低对坏死性铜斑病链球菌的抗性;而在无病原菌侵染的情况下,过表达UGT76B1基因会使植物利用水杨酸信号通路抵御病菌的能力降低,但同时会提高植物利用茉莉酸信号通路抵御病菌的能力 [19-21]。【本研究切入点】分析木薯UGTs基因家族的转录组数据发现,MeUGT25基因的表达显著受到Xam菌株的诱导。MeUGT25基因与MeUGT85K4/MeUGT85K5具有很高的同源性,但MeUGT85K4/MeUGT85K5基因主要参与木薯生氰糖苷的合成 [22],而MeUGT25基因的功能仍有待深入研究。【拟解决的关键问题】本研究构建MeUGT25基因的VIGS载体,并采用农杆菌侵染的方式对木薯叶片中的MeUGT25基因进行沉默,评估该基因在木薯抵抗细菌性枯萎病中的作用,以期为进一步研究该基因参与木薯抗细菌性枯萎病的机理奠定基础。
1. 材料与方法
1.1 试验材料
供试木薯品种:华南124(SC124),由中国热带农业科学院提供。
供试试剂:DNA回收纯化试剂盒、质粒提取试剂盒、pMD18-T载体、荧光定量PCR反应试剂、Nimble Cloning克隆试剂盒、反转录试剂盒,均购自天根生化科技(北京)有限公司;限制性核酸内切酶购自Thermo Fisher Scientific公司,PCR引物由生工生物工程(上海)股份有限公司合成,pTRV载体由海南大学施海涛老师实验室惠赠。
主要仪器设备:超微量紫外分光光度计(Thermo,美国),PCR仪(耶拿,德国),EPS300电泳仪(Tanon,上海),CT15RT高速冷冻离心机(TECHCOMP,中国),4100凝胶成像仪(Tanon,上海),MX3000荧光定量PCR仪(安捷伦,美国)。
1.2 试验方法
1.2.1 转录组数据分析
从GEO数据库中下载木薯叶片在Xam处理下的表达数据 [23],并从中挑选MeUGTs基因家族的表达数据进行分析 [7]。
1.2.2 Xam侵染木薯叶片和MeUGT25基因表达分析
首先提前将Xam母液进行复苏,吸取1 mL复苏的菌液至刚配置的LB液体培养基,培养至OD600=0.6左右。用MgCl2溶液稀释重悬菌液至OD600=0.2(MgCl2终浓度10 mmol·L−1,加入万分之五的表面活性剂silwet L-77)。采用种植45 d后的木薯,使用注射器将稀释的菌液从倒数第二片叶片开始接种,接种至少6片木薯叶片。然后置于温室中继续培养(注意保湿) [24],处理5 d和7 d后,选择倒数第2~3片完全展开叶提取总RNA,进行反转录。使用设计好的MeUGT25基因的定量引物进行荧光定量PCR,内参基因使用木薯MeEF1a基因,根据2−ΔΔCT方法计算基因的相对表达量。
1.2.3 构建MeUGT25基因的干扰载体
根据MeUGT25基因(Manes.04G015600.1)的核苷酸序列挑选干扰片段,干扰片段序列的挑选原则为:插入病毒载体的基因片段长度在200~350 bp;避免UGT基因家族高度保守的序列;挑选MeUGT25基因自身特异的序列;根据以上原则设计干扰载体引物(表1),并通过扩增获得291 bp的片段 [25]。扩增程序:95 ℃ 5 min;35个循环:95 ℃ 10 s,57 ℃ 30 s,72 ℃ 30 s;72 ℃ 10 min;16 ℃ 保存。反应体系:ddH2O 8.0 μL;2×PrimeStar Max 10.0;上游引物/下游引物 0.5 μL;模板 1.0 μL。PCR产物用1%琼脂糖凝胶电泳进行检测,回收目的片段连接至T载体,然后转化大肠杆菌TOP10感受态细胞。测序正确后通过双酶切连接至pTRV载体,进行菌液PCR和双酶切验证,全部正确后保留菌液和质粒。
表 1 引物序列Table 1. Sequences of primers applied引物名称
Primer上游引物
Forward Primer(5′-3′)下游引物
Reverse Primer(5′-3′)用途
UsageMeUGT25 gtgagtaaggttaccgaattcTTTGATTGCCCAGATCGTCG gagacgcgtgagctcggtaccCAGGCTGGTGGCTACAACGG 载体构建 qMeUGT25 CCGGAATTCTTTGATTGCCCAGATCGTCG CGGGGTACCCAGGCTGGTGGCTACAACG 荧光定量 MeEF1a TGAACCACCCTGGTCAGATTGGAA AACTTGGGCTCCTTCTCAAGCTCT 荧光定量 划线部分为上游同源臂/下游同源臂+酶切位点 。
Underline shows upstream homology arm/downstream homologous arm with restriction enzyme digestion sites.1.2.4 病毒诱导MeUGT25基因的沉默
将干扰载体pTRV2-MeUGT25和空白载体pTRV2分别转入农杆菌(GV3010菌株),然后将农杆菌分别注射到木薯叶片中,共注射10个植株,在最下面一片叶片的基部进行注射,注射后的植株置于温室中并注意保湿。侵染14 d后从每株倒数第二片开始取样,取2~3片叶片提取RNA并进行反转录,采用实时荧光定量PCR检测MeUGT25基因的表达量(表1)。反应体系:ddH2O 8.0 μL;2×SYBR qPCR Master Mix 10.0 μL;上游引物/下游引物 0.5 μL;模板 1.0 μL。内参基因使用木薯MeEF1a基因。反应程序:95 ℃预变性30 s;95 ℃10 s,57 ℃ 30 s,40个循环;然后通过熔解曲线(95 ℃ 15 s,57 ℃ 1 min,95 ℃ 15 s)分析检测引物的特异性。使用2−△△Ct法计算MeUGT25基因的相对表达量(3次生物学重复)。
1.2.5 Xam细菌数量和叶片抗病表型分析
待侵染14 d后检测基因沉默效果,随后选择成功干扰的植株,从靠近基部的叶片开始接种Xam,接种6片;对照叶片也从靠近基部的的叶片开始接种Xam。在接种Xam菌液的0 d和6 d时,分别使用打孔器取侵染后的木薯叶片,每个处理收集10个叶圆盘,叶片样品用无菌水漂洗2 min(重复3次),洗干净后将叶片碾碎。然后将样品进行梯度稀释(103、104、105、106、107、108),取10 μL不同浓度梯度(6个浓度梯度)的菌液接种至LB平板,每个浓度梯度重复3次。平板密封恒温培养箱培养(28 ℃, 16 h),最后统计细菌数量。分别在0 d和6 d时,观察表型变化并拍照记录。
2. 结果与分析
2.1 Xam诱导下MeUGT25基因的表达情况分析
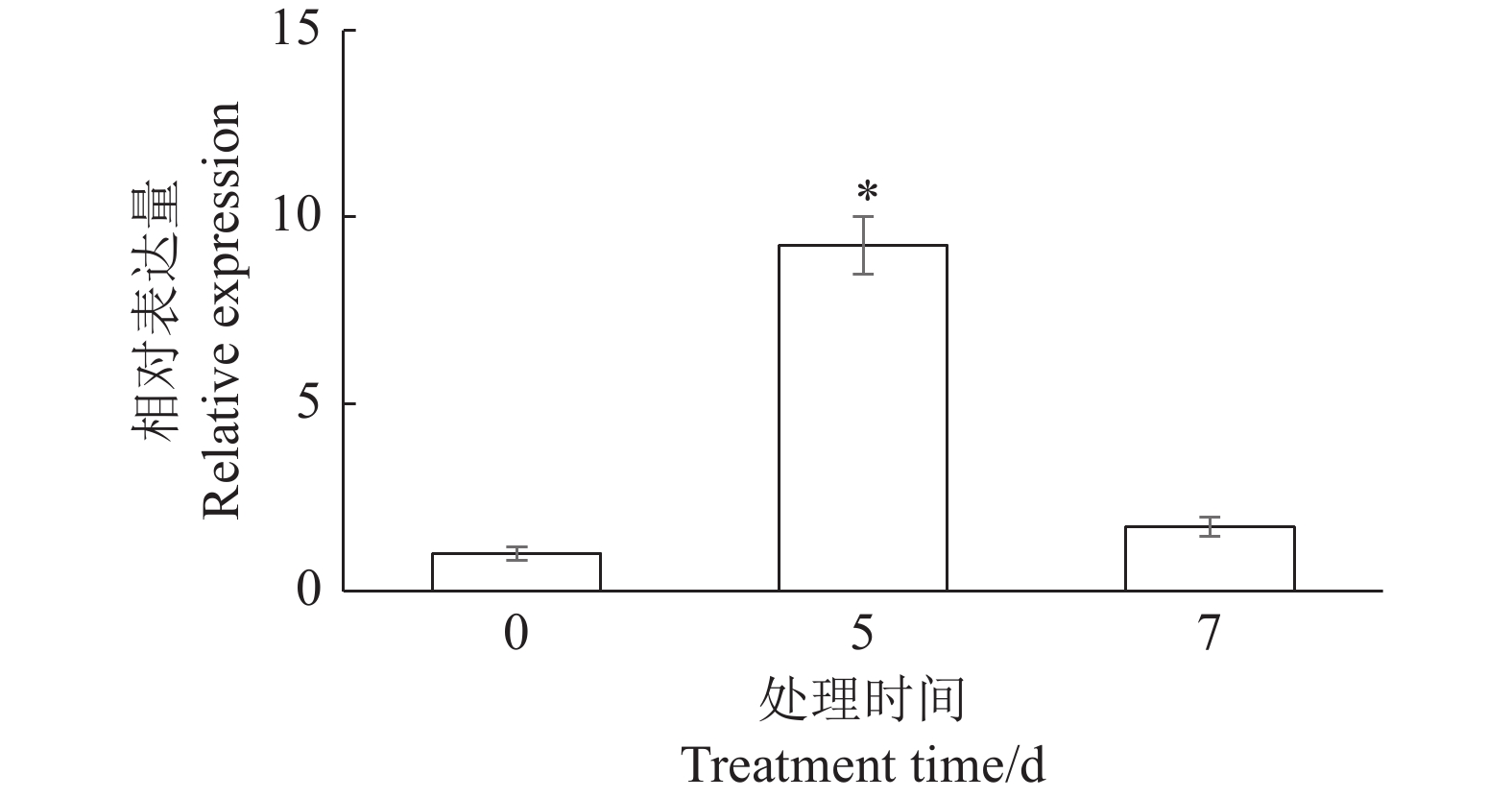
对从GEO数据库中下载的转录组数据进行分析 [23],发现Xam菌株能够诱导MeUGT25基因的表达上调。进一步使用Xam菌株处理木薯叶片,定量PCR分析显示MeUGT25基因确实受到Xam病菌处理的诱导。在侵染5 d后,MeUGT25基因的表达量达到最高,随后在7 d时表达量下降到正常水平,MeUGT25基因的表达量相比对照0 d最高提高9.2倍(图1)。以上结果表明,MeUGT25基因的表达会受到Xam病菌的诱导。
2.2 干扰载体pTRV2-MeUGT25的构建
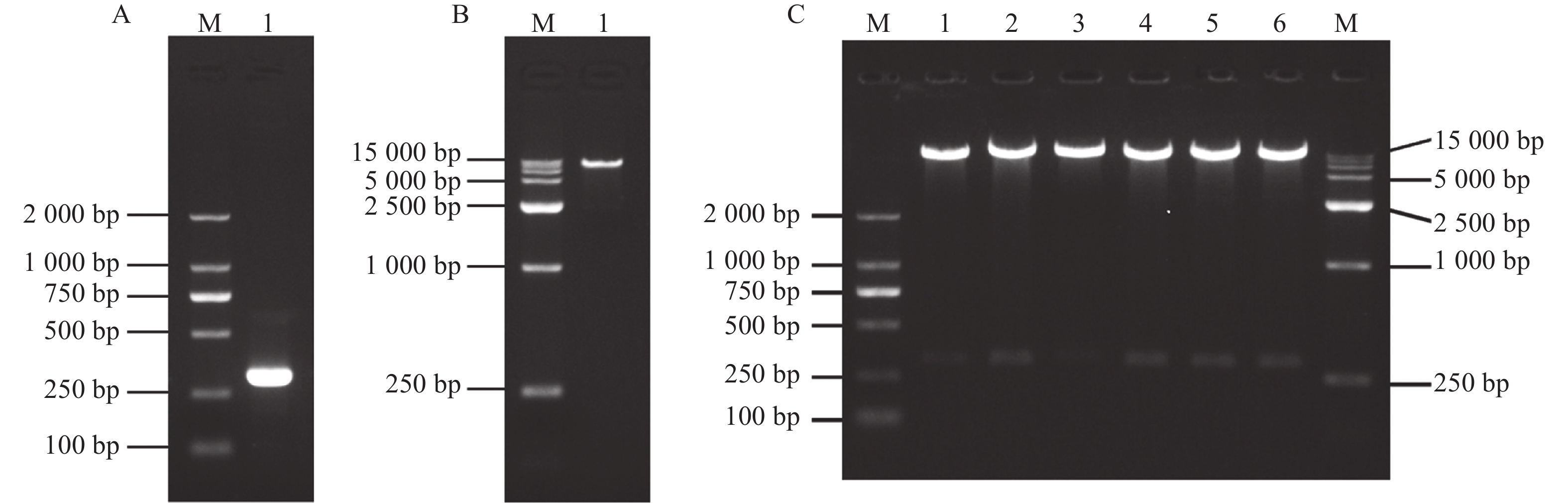
根据MeUGT25基因的序列,本研究挑选1个291 bp的片段作为干扰片段,其两端添加的酶切位点分别为EcoRⅠ和KpnⅠ。得到扩增片段后进行测序,待测序正确后,将其连接到pTRV2载体,从而得到干扰载体pTRV2-MeUGT25。本研究采用菌液PCR和双酶切方法对构建的载体进行验证。如图2所示,图2A为成功克隆的干扰片段,图2B为酶切后的干扰载体框架,图2C为干扰载体pTRV2-MeUGT25经双酶切后的琼脂凝胶电泳图。这些验证结果表明,干扰载体pTRV2-MeUGT25构建成功。
2.3 沉默植株中MeUGT25基因的表达量分析
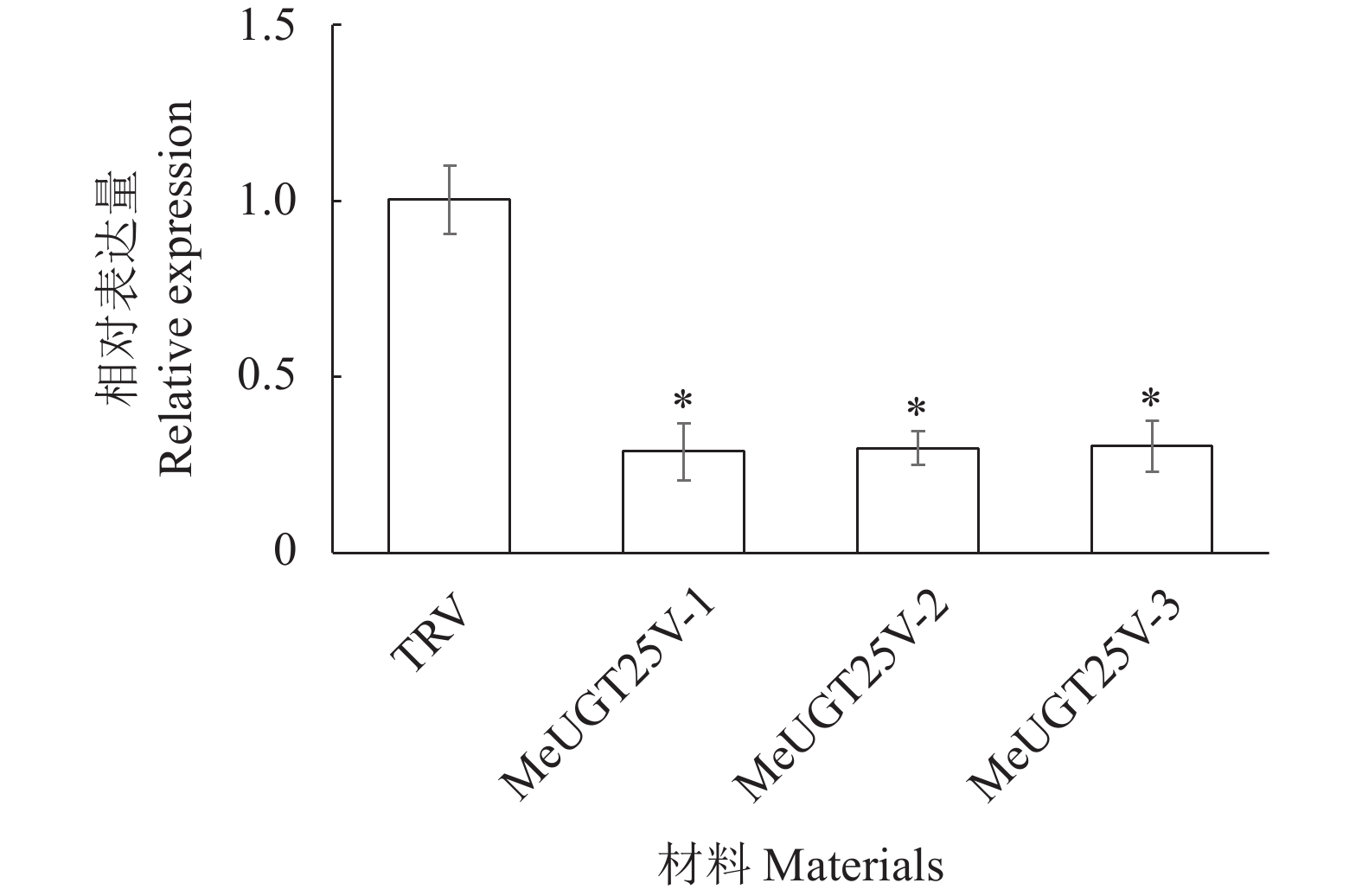
VIGS作为快速表征感兴趣基因表型的筛选技术,与传统的基因功能分析方法相比,VIGS能够在侵染植物当代对目标基因进行沉默和功能分析。本研究通过VIGS方法抑制MeUGT25基因的表达,获得3株MeUGT25基因部分沉默的阳性植株,分别命名为MeUGT25V-1、MeUGT25V-2和MeUGT25V-3。荧光定量结果显示,MeUGT25基因的表达量分别降低71%、70%和69%(图3),表明MeUGT25基因在木薯叶片中的表达量受到显著的抑制。
2.4 MeUGT25基因沉默表达对木薯抗病性的影响
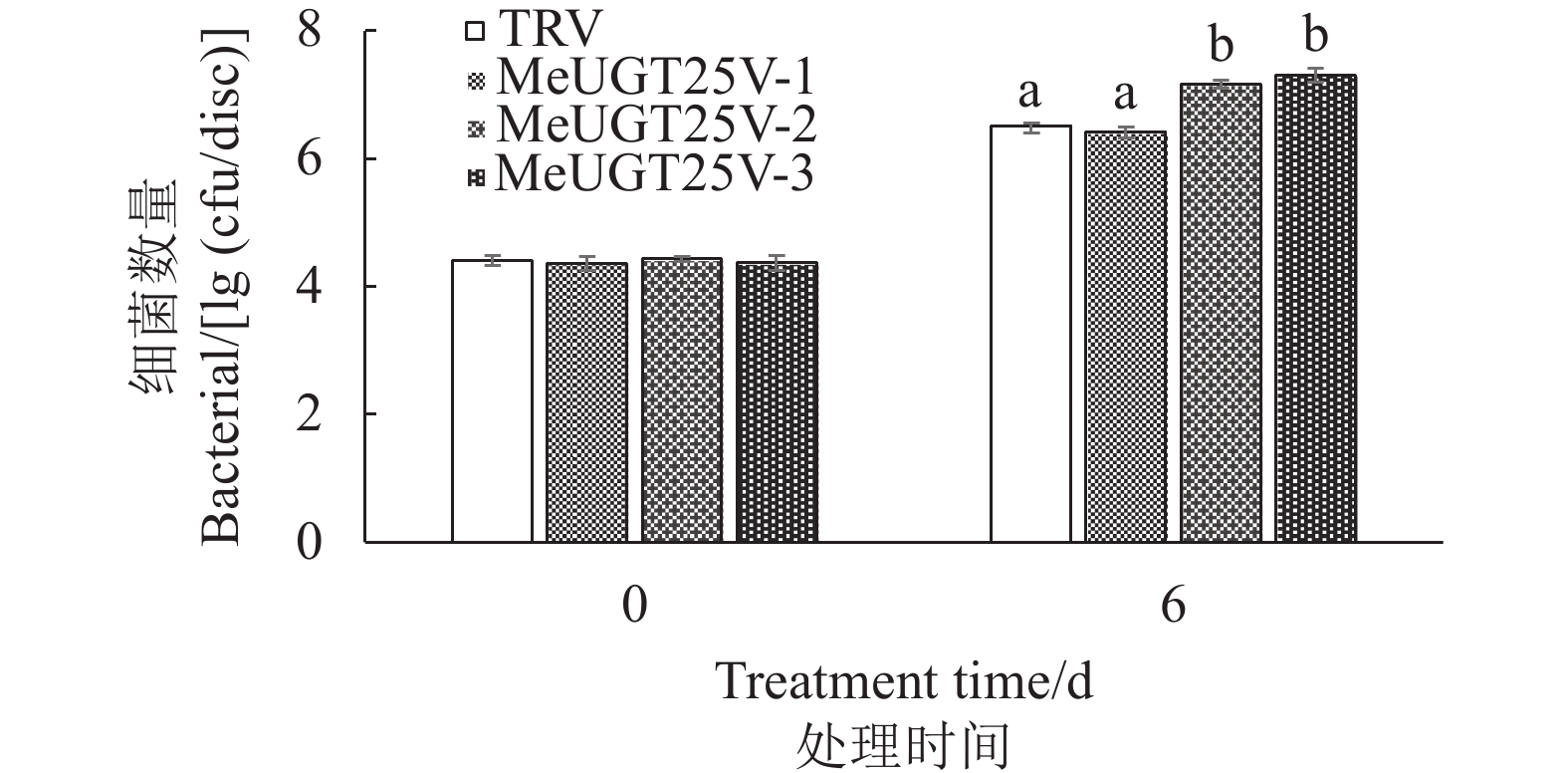
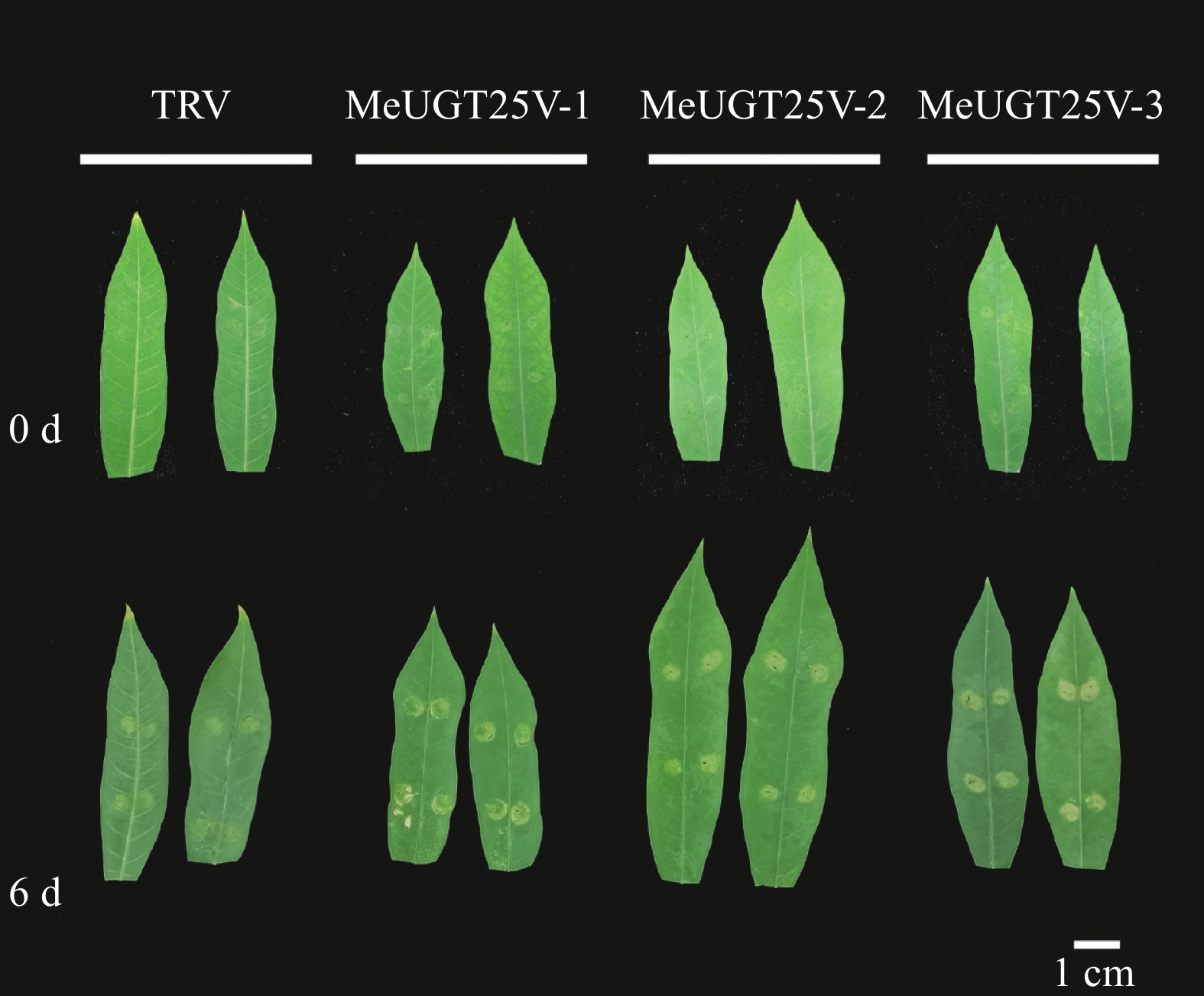
为探究MeUGT25基因在木薯抗病中的功能,分别在对照叶片和阳性干扰植株叶片上接种Xam菌株。如图4所示,对照叶片和阳性干扰植株叶片在接种0 d时,细菌数量没有显著差异;而接种6 d后,MeUGT25V-2和MeUGT25V-3植株叶片上的细菌数量相比对照显著增加,而MeUGT25V-1阳性植株叶片上的细菌数与对照无显著差异。值得注意的是,从叶片的表型图(图5)可以看出,3个干扰植株叶片上的菌斑均比对照叶片明显(图5)。这些结果表明,降低木薯叶片中MeUGT25基因的表达量会显著影响叶片抵抗Xam病菌侵染的能力。
3. 讨论与结论
木薯作为重要的粮食和经济作物,也是未来绿色能源的重要原料之一 [1],然而细菌性枯萎病对木薯产业造成严重威胁。该病最早在拉丁美洲被发现,并逐渐传播到世界各地。它曾经毁灭性地影响多个国家的木薯产业,也对我国的木薯产业造成严重威胁 [1, 8]。因此,解析木薯抵抗细菌性枯萎病的机制对于木薯产业具有重要意义。
UGTs家族基因在植物的生长发育过程中起着重要作用,其功能是通过对植物激素和重要次生代谢物进行不同程度的糖基化修饰来实现的 [4]。例如,通过调节植物激素如ABA、油菜素类固醇和生长素等物质的含量,UGTs参与植物的发育过程,同时也影响植株对非生物逆境的耐受性 [10-12, 14]。此外,研究表明,UGTs也参与生物胁迫的响应 [21]。例如,缺失UGT74F1基因功能会导致植株中水杨酸水平的降低,从而使植株对病菌变得更加敏感 [26]。此外,ugt76b1突变体中UGT76B1基因的缺失可能导致茉莉酸水平的降低,使植株对特定病菌更加敏感 [21]。此外,研究还发现,通过干扰MeUGT41基因的表达会导致木薯叶片抵抗病菌侵染的能力降低 [27]。在本研究中,MeUGT25基因在叶片中的表达量降低会明显降低叶片对Xam病菌的抵抗力,说明MeUGT25基因具有正调控木薯叶片抵抗细菌性枯萎病的能力。通过序列比对分析发现,MeUGT25基因与UGT76B1/UGT74F1基因有较近的进化关系,推测MeUGT25基因可能通过调节水杨酸和茉莉酸的合成来应对Xam病菌的侵染。然而,在干扰植株MeUGT25V-1中,叶片上的细菌数量与对照叶片相比没有显著差异。类似的现象在其他研究中也有出现,例如抑制小麦中TaLCYB基因的表达,有时会观察到个别转基因阳性植株的表型与对照组相似,这可能是由于其他同源基因的补偿效应所致 [28]。本研究结果为进一步揭示MeUGT25基因在木薯抵抗细菌性枯萎病中的机制提供了基础和线索。下一步的研究可以探究过表达MeUGT25基因是否能提高木薯叶片对细菌性枯萎病的抵抗能力,并探讨水杨酸和茉莉酸的含量是否和MeUGT25基因的表达量相关。
MeUGT25基因可以被枯萎病菌诱导表达上调,而降低木薯叶片中MeUGT25基因的表达量会降低叶片抵抗Xam病菌侵染的能力,因此推测MeUGT25基因在木薯抗枯萎病中发挥着正向调控作用。
-
表 1 引物序列
Table 1 Sequences of primers applied
引物名称
Primer上游引物
Forward Primer(5′-3′)下游引物
Reverse Primer(5′-3′)用途
UsageMeUGT25 gtgagtaaggttaccgaattcTTTGATTGCCCAGATCGTCG gagacgcgtgagctcggtaccCAGGCTGGTGGCTACAACGG 载体构建 qMeUGT25 CCGGAATTCTTTGATTGCCCAGATCGTCG CGGGGTACCCAGGCTGGTGGCTACAACG 荧光定量 MeEF1a TGAACCACCCTGGTCAGATTGGAA AACTTGGGCTCCTTCTCAAGCTCT 荧光定量 划线部分为上游同源臂/下游同源臂+酶切位点 。
Underline shows upstream homology arm/downstream homologous arm with restriction enzyme digestion sites. -
[1] 张鹏, 杨俊, 周文智, 等. 能源木薯高淀粉抗逆分子育种研究进展与展望 [J]. 生命科学, 2014, 26(5):465−473. DOI: 10.13376/j.cbls/2014069 ZHANG P, YANG J, ZHOU W Z, et al. Progress and perspective of cassava molecular breeding for bioenergy development [J]. Chinese Bulletin of Life Sciences, 2014, 26(5): 465−473.(in Chinese) DOI: 10.13376/j.cbls/2014069
[2] BOURNE Y, HENRISSAT B. Glycoside hydrolases and glycosyltransferases: Families and functional modules [J]. Current Opinion in Structural Biology, 2001, 11(5): 593−600. DOI: 10.1016/S0959-440X(00)00253-0
[3] PAQUETTE S, MØLLER B L, BAK S. On the origin of family 1 plant glycosyltransferases [J]. Phytochemistry, 2003, 62(3): 399−413. DOI: 10.1016/S0031-9422(02)00558-7
[4] CAI J H, JOZWIAK A, HOLOIDOVSKY L, et al. Glycosylation of N-hydroxy-pipecolic acid equilibrates between systemic acquired resistance response and plant growth [J]. Molecular Plant, 2021, 14(3): 440−455. DOI: 10.1016/j.molp.2020.12.018
[5] LIU Y Q, WANG Q, LIU X N, et al. pUGTdb: A comprehensive database of plant UDP-dependent glycosyltransferases [J]. Molecular Plant, 2023, 16(4): 643−646. DOI: 10.1016/j.molp.2023.01.003
[6] LI Q, YU H M, MENG X F, et al. Ectopic expression of glycosyltransferase UGT76E11 increases flavonoid accumulation and enhances abiotic stress tolerance in Arabidopsis [J]. Plant Biology, 2018, 20(1): 10−19. DOI: 10.1111/plb.12627
[7] WU C L, DAI J, CHEN Z S, et al. Comprehensive analysis and expression profiles of cassava UDP-glycosyltransferases (UGT) family reveal their involvement in development and stress responses in cassava [J]. Genomics, 2021, 113(5): 3415−3429. DOI: 10.1016/j.ygeno.2021.08.004
[8] 黄洁, 李开绵, 叶剑秋, 等. 我国的木薯优势区域概述 [J]. 广西农业科学, 2008, 39(1):104−108. HUANG J, LI K M, YE J Q, et al. A summary review of dominant regions of cassava growing in China [J]. Guangxi Agricultural Sciences, 2008, 39(1): 104−108.(in Chinese)
[9] CAMPBELL J, DAVIES G, et al. A classification of nucleotide-diphospho-sugar glycosyltransferases based on amino acid sequence similarities[J]. The Biochemical Journal, 1998, 329 (Pt 3): 719.
[10] JACKSON R G, KOWALCZYK M, LI Y, et al. Over-expression of an Arabidopsis gene encoding a glucosyltransferase of indole-3-acetic acid: Phenotypic characterisation of transgenic lines [J]. The Plant Journal, 2002, 32(4): 573−583. DOI: 10.1046/j.1365-313X.2002.01445.x
[11] HAYASHI K I. The interaction and integration of auxin signaling components [J]. Plant and Cell Physiology, 2012, 53(6): 965−975. DOI: 10.1093/pcp/pcs035
[12] POPPENBERGER B, FUJIOKA S, SOENO K, et al. The UGT73C5 of Arabidopsis thaliana glucosylates brassinosteroids [J]. Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences of the United States of America, 2005, 102(42): 15253−15258.
[13] CHEN T T, LIU F F, XIAO D W, et al. The Arabidopsis UDP-glycosyltransferase75B1, conjugates abscisic acid and affects plant response to abiotic stresses [J]. Plant Molecular Biology, 2020, 102(4): 389−401.
[14] DONG T, XU Z Y, PARK Y, et al. Abscisic acid uridine diphosphate glucosyltransferases play a crucial role in abscisic acid homeostasis in Arabidopsis [J]. Plant Physiology, 2014, 165(1): 277−289. DOI: 10.1104/pp.114.239210
[15] LIU Z, YAN J P, LI D K, et al. UDP-Glucosyltransferase71C5, a major glucosyltransferase, mediates abscisic acid homeostasis in Arabidopsis [J]. Plant Physiology, 2015, 167(4): 1659−1670. DOI: 10.1104/pp.15.00053
[16] JONES J D G, DANGL J L. The plant immune system [J]. Nature, 2006, 444(7117): 323−329. DOI: 10.1038/nature05286
[17] VLOT A C, DEMPSEY D A, KLESSIG D F. Salicylic Acid, a multifaceted hormone to combat disease [J]. Annual Review of Phytopathology, 2009, 47: 177−206. DOI: 10.1146/annurev.phyto.050908.135202
[18] CHEN L, WANG W S, WANG T, et al. Methyl salicylate glucosylation regulates plant defense signaling and systemic acquired resistance [J]. Plant Physiology, 2019, 180(4): 2167−2181. DOI: 10.1104/pp.19.00091
[19] CHAE E, TRAN D T N, WEIGEL D. Cooperation and conflict in the plant immune system [J]. PLoS Pathogens, 2016, 12(3): e1005452. DOI: 10.1371/journal.ppat.1005452
[20] PASTORCZYK-SZLENKIER M, BEDNAREK P. UGT76B1 controls the growth-immunity trade-off during systemic acquired resistance [J]. Molecular Plant, 2021, 14(4): 544−546. DOI: 10.1016/j.molp.2021.03.012
[21] VON SAINT PAUL V, ZHANG W, KANAWATI B, et al. The Arabidopsis glucosyltransferase UGT76B1 conjugates isoleucic acid and modulates plant defense and senescence [J]. The Plant Cell, 2011, 23(11): 4124−4145. DOI: 10.1105/tpc.111.088443
[22] KANNANGARA R, MOTAWIA M S, HANSEN N K K, et al. Characterization and expression profile of two UDP-glucosyltransferases, UGT85K4 and UGT85K5, catalyzing the last step in cyanogenic glucoside biosynthesis in cassava [J]. The Plant Journal, 2011, 68(2): 287−301. DOI: 10.1111/j.1365-313X.2011.04695.x
[23] MUÑOZ-BODNAR A, PEREZ-QUINTERO A L, GOMEZ-CANO F, et al. RNAseq analysis of cassava reveals similar plant responses upon infection with pathogenic and non-pathogenic strains of Xanthomonas axonopodis pv. manihotis [J]. Plant Cell Reports, 2014, 33(11): 1901−1912. DOI: 10.1007/s00299-014-1667-7
[24] YAN Y, HE X Y, HU W, et al. Functional analysis of MeCIPK23 and MeCBL1/9 in cassava defense response against Xanthomonas axonopodis pv. manihotis [J]. Plant Cell Reports, 2018, 37(6): 887−900. DOI: 10.1007/s00299-018-2276-7
[25] 宋震, 李中安, 周常勇. 病毒诱导的基因沉默(VIGS)研究进展 [J]. 园艺学报, 2014, 41(9):1885−1894. DOI: 10.16420/j.issn.0513-353x.2014.09.004 SONG Z, LI Z A, ZHOU C Y. Research advances of virus-induced gene silencing(VIGS) [J]. Acta Horticulturae Sinica, 2014, 41(9): 1885−1894.(in Chinese) DOI: 10.16420/j.issn.0513-353x.2014.09.004
[26] GEORGE THOMPSON A M, IANCU C V, NEET K E, et al. Differences in salicylic acid glucose conjugations by UGT74F1 and UGT74F2 from Arabidopsis thaliana [J]. Scientific Reports, 2017, 7: 46629. DOI: 10.1038/srep46629
[27] 叶威, 骆秋娴, 蔡美琪, 等. 木薯UDP依赖型糖基转移酶14基因在木薯抗病性中的功能研究 [J]. 热带作物学报, 2022, 43(7):1322−1327. DOI: 10.3969/j.issn.1000-2561.2022.07.002 YE W, LUO Q X, CAI M Q, et al. Function of MeUGT14 gene in cassava under biotic stress [J]. Chinese Journal of Tropical Crops, 2022, 43(7): 1322−1327.(in Chinese) DOI: 10.3969/j.issn.1000-2561.2022.07.002
[28] ZENG J, WANG C, CHEN X, et al. The lycopene β-cyclase plays a significant role in provitamin A biosynthesis in wheat endosperm [J]. BMC Plant Biology, 2015, 15: 112. DOI: 10.1186/s12870-015-0514-5
-
期刊类型引用(0)
其他类型引用(1)




 下载:
下载: