Effect of Silage Time on Nutrient Contents of Cymbopogon citratus
-
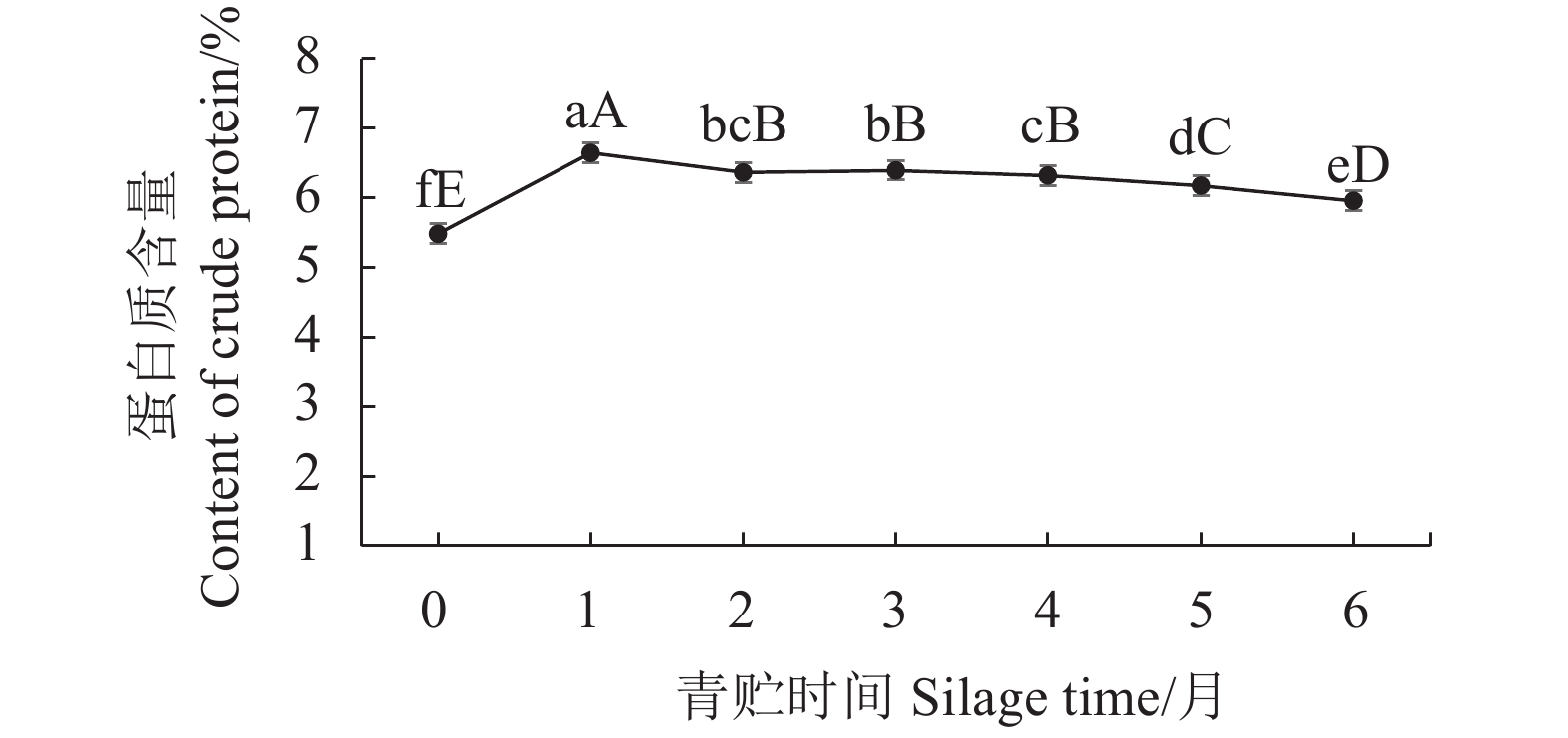
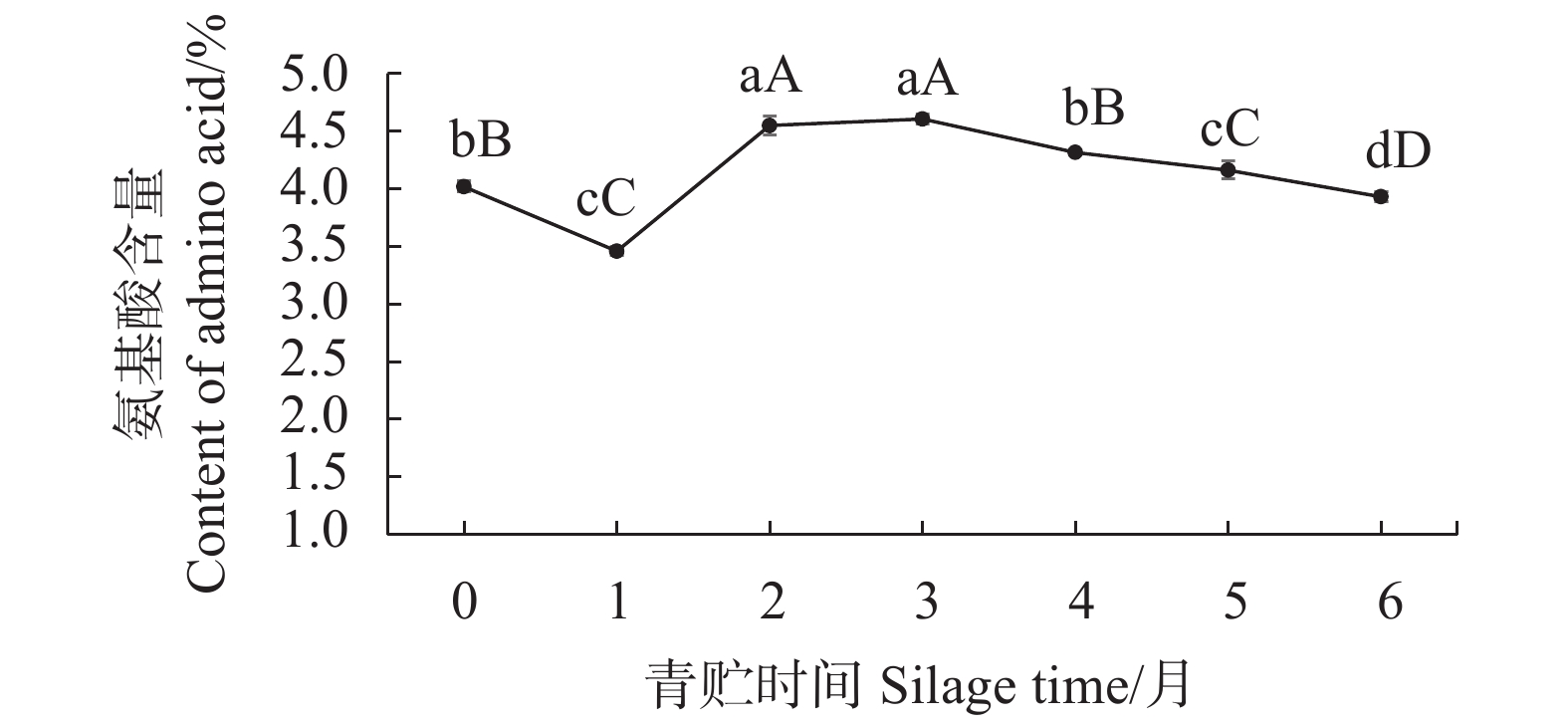
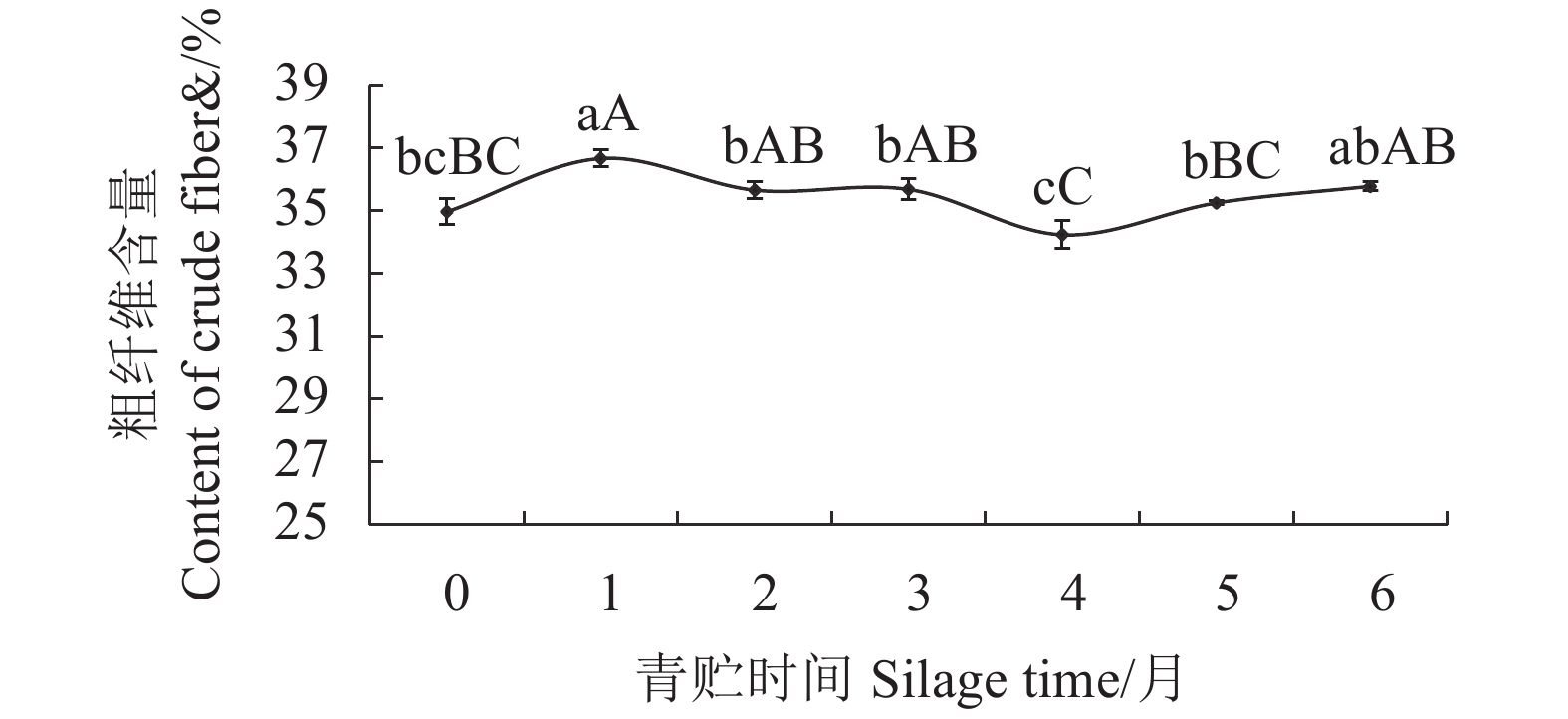
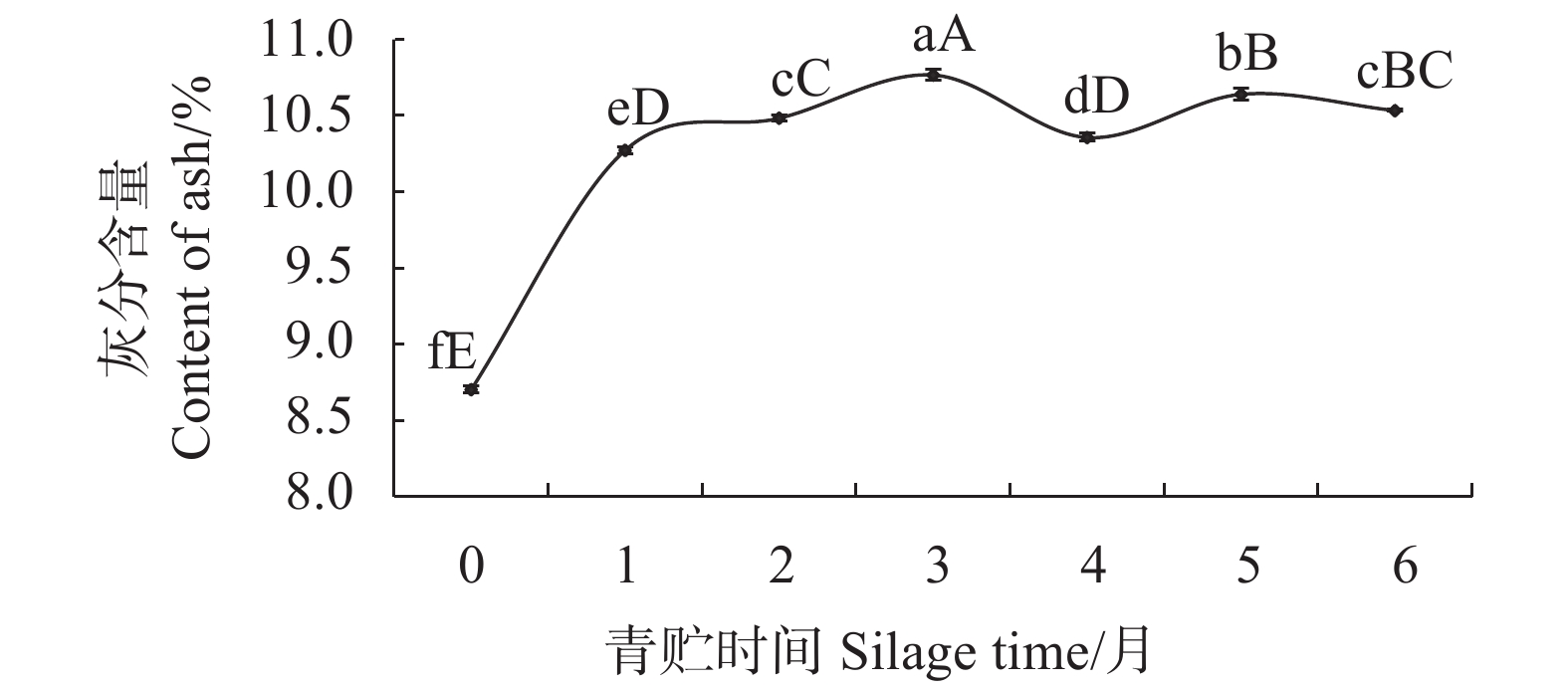
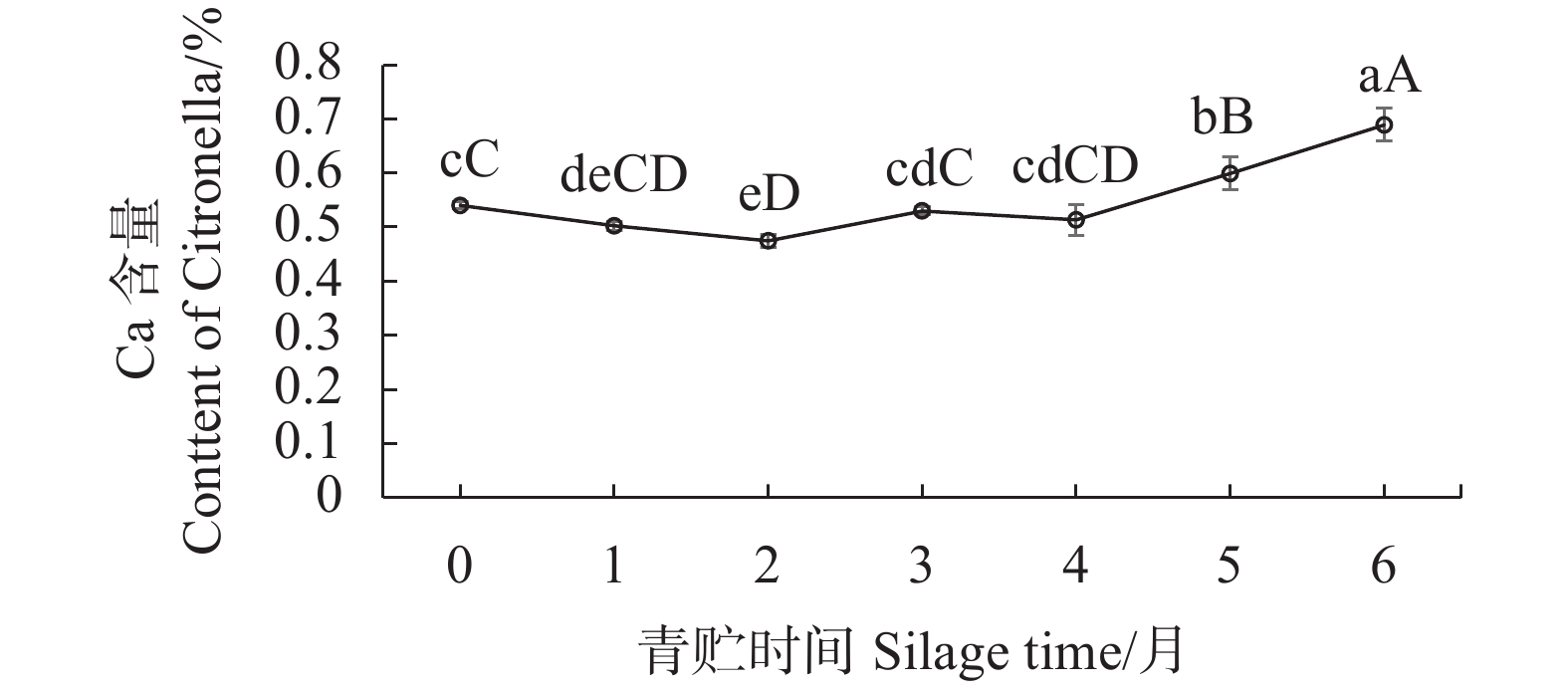
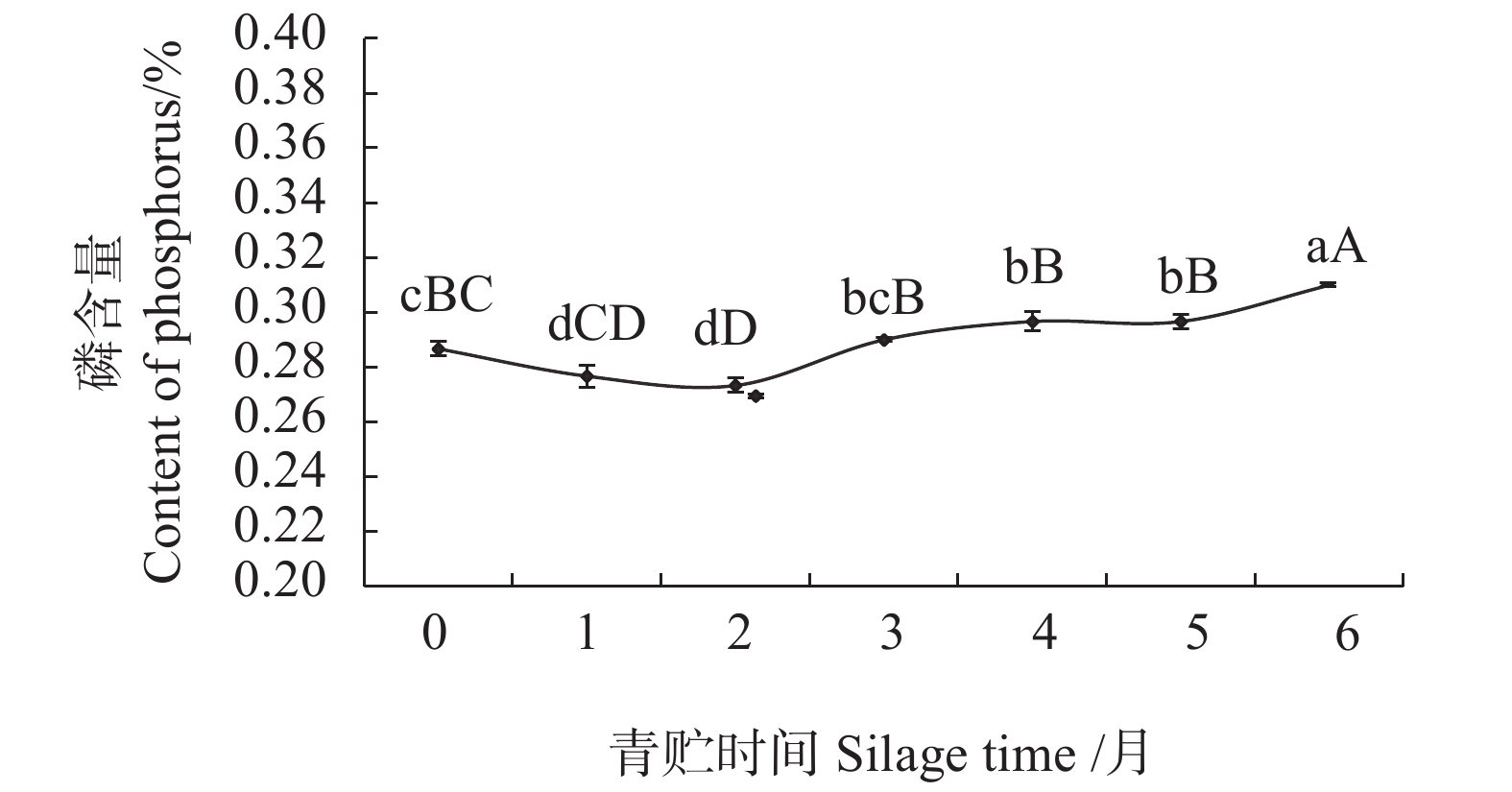
摘要:目的 探究青贮时间对香茅草营养成分的影响,旨在确定适宜的青贮发酵时间,为合理青贮及充分提高香茅饲用价值提供科学依据。方法 采用感官评价和国家标准方法,对不同青贮时间香茅样品的感官品质和营养成分进行评价和测定。结果 香茅青贮1月后,其蛋白质、粗纤维含量显著上升,达到峰值,蛋白质从青贮前的5.48%提高至6.64%,粗纤维从青贮前的34.96%上升至36.65%,青贮2~4月蛋白质较稳定,为6.32%~6.39%,随后明显下降,粗纤维在随后的2~6月较稳定,含量为34.23%~35.77%;钙含量在青贮前4个月变化不明显,第5、6月时有显著提高;磷含量在青贮前5月,先下降后缓慢上升,第6月时达到最高。香茅青贮至3个月时,感官评分等级为1级,氨基酸、粗脂肪和灰分含量均达到最大值,粗蛋白含量保持在较高水平。3月后青贮草料的感官评分等级为2级,其中粗蛋白、氨基酸、粗灰分和粗脂肪等营养成分逐渐降低,草料品质变差。结论 香茅青贮的时间以1~3月为宜,青贮至3月时其营养成分达到最佳值。Abstract:Objective Effect of silage time on nutrient contents of Cymbopogon citratus was studied.Method Changes on the nutrients in C. citratus during silage was monitored periodically to determine the optimal fermentation period for cattle feeding.Result After one month of silage, the protein and crude fiber in citronella increased significantly and peaked with the protein content rose from 5.48% to 6.64% and the crude fiber from 34.96% to 36.65%. In 2-4 months, the protein content became stable ranging from 6.32% to 6.39% before a significant decline, while the crude fiber remained at 34.23%-35.77% for 2-6 months. During the initial 4 months there was no significant changes on the calcium in citronella, but the content increased significantly in 5-6 month. For the first 5 months, the phosphorus content decreased initially followed by a slow incline to reach a peak in the 6th month. Up till 3 months of silage, the fermented citronella was judged to have a Level 1 sensory score with maximized contents on amino acids, crude fat, and ash as well as a constantly high crude protein content. Afterward, however, the sensory score dropped to Level 2 with decreasing crude protein, amino acid, crude ash, and crude fat contents with a deteriorated quality.Conclusion It appeared that 1-3 month of silage would allow citronella to reach the highest nutrient level and prolonged storage could considerably ill-affect the forage quality.
-
Keywords:
- Cymbopogon citratus /
- nutrient content /
- silage time
-
0. 引言
【研究意义】杂交兰Cymbidium hybrid是由国兰和大花蕙兰作为亲本杂交培育而成的一类兰花的特称,其集国兰和大花蕙兰的开花特征于一身[1],花期长,有花观花、无花观叶,观赏和经济价值高,是目前市场上颇具发展潜力的兰花品种[2]。【前人研究进展】近年来,不同学者对杂交兰组织培养技术[3-6]、栽培技术[7-8]、四倍体诱导[9-10]、分子鉴定[11-13]、花期调控[14-15]等方面进行了研究。但杂交兰花期调控的研究局限于高山处理、激素处理、喷施次数等措施对杂交兰开花的影响,因为花期调控技术的不成熟,往往使杂交兰的花期与最佳销售期擦肩而过[16],为此制约杂交兰产业化发展的进程。花芽分化特性的研究是进行花期调控的基础[17]。植物花芽分化是一个复杂的形态建成过程,在花芽分化的过程中,除了形态的改变,更伴随着复杂的生理生化变化[18-19]。【本研究切入点】目前,兰科植物花芽分化方面的研究多集中于大花蕙兰[20-21]、蝴蝶兰[22-23]和卡特兰[24]等,而对杂交兰花芽分化过程中的形态变化及其相关生理指标的变化规律的研究还未见相关报道。【拟解决的关键问题】本研究以杂交兰品种‘黄金小神童’为材料,对杂交兰花芽分化过程的不同阶段进行形态解剖观测、植株外部形态特征观察,对花芽分化过程中可溶性糖、可溶性蛋白、淀粉含量和POD活性及CAT活性等生理生化指标变化进行测定,以期为后期杂交兰花期调控和成花机理研究提供科学依据。
1. 材料与方法
1.1 试验材料
供试材料为成熟期基本一致的杂交兰品种‘黄金小神童’(Cymbidium Golden Elf‘Sun-dust’),由福建省农业科学院作物研究所花卉研究中心种质资源圃提供。
1.2 花芽分化过程的形态观测
采取的花芽用去离子水冲洗后,剥去苞片,并记录下芽的长、宽、高。用于石蜡切片的芽,取样后迅速投入FAA固定液中,抽气固定,后经乙醇脱水、松节油透明、石蜡浸泡、石蜡包埋、切片机切片、明胶液贴片、番红固绿染色、树胶封片等步骤,完成石蜡切片的制作,最后显微镜观察并拍照。试验于2017年7月初至9月初进行,间隔5~7 d取样1次。
1.3 花芽分化过程中的生理指标测定
以发育进程基本一致的带花芽杂交兰植株的叶片为材料,根据花芽分化进程,在各个不同分化期取样进行生理指标的测定,每次取样约1 g,磨碎,根据不同生理指标加入相应试剂进行试验。可溶性糖和淀粉含量的测定采用蒽酮比色法,620 nm处测定吸光值;可溶性蛋白含量的测定采用考马斯亮蓝法,595 nm处测定吸光值;POD活性的测定采用愈创木酚法,计算公式中以每毫克组织蛋白每分钟内能转化1 μg底物所需要的酶量为1个酶活性单位(U);CAT活性的测定采取可见光法,计算公式中以每毫克组织蛋白每秒钟内分解1 μmol H2O2所需要的酶量为1个酶活性单位(U)。
1.4 数据分析
数据采用Excel和SPSS统计软件进行分析。
2. 结果与分析
2.1 杂交兰花芽分化时期及主要特征
根据杂交兰‘黄金小神童’花芽发生和发育的特点,其分化时期可划分为6个阶段(图 1)。在未分化期,芽点从假鳞茎基部叶腋处发出,生长锥顶端呈半圆状凸起,表面平滑整齐(图 1-A),此时,芽高度为0.622~0.638 cm;随后,生长锥进一步伸长增大,呈半球形,有明显凸出状(图 1-B),也标志着芽体进入到花序原基分化期,此时,芽高度为0.678~0.683 cm;随着植株不断生长,不断膨大的生长锥的顶部和侧方分化出的多个凸起,为小花原基(图 1-C),说明此时进入小花原基分化期,芽高度为0.710~0.784 cm;小花原基继续增大变宽,继而从边缘分化出3个凸起,即为萼片原基(图 1-D),但纵切面上只能看到2个萼片原基凸起,此时,芽高度约为0.928~0.984 cm;萼片原基不断伸长弯曲,在其内侧继续分化出花瓣原基凸起(图 1-E);花瓣原基不断伸长,其内侧又分化出新的凸起,为合蕊柱原基;合蕊柱继续生长,其顶端分化出2个花粉块,象征着花芽进入合蕊柱及花粉块分化期(图 1-F~I)。
![]() 图 1 杂交兰‘黄金小神童’花芽分化形态解剖注:A~E依次为:未分化期、花序原基分化期、小花原基分化期、萼片原基分化期、花瓣原基分化期;F~I:合蕊柱及花粉块分化期;1:生长锥;2:花序原基;3:小花原基;4:萼片原基;5:花瓣原基;6:合蕊柱原基;7:唇瓣;8:花瓣;9:花粉块;10:蕊喙。Figure 1. Anatomy of flower bud differentiation of Golden Elf 'Sun-dust'Note:A-E represent stages of undifferentiation, inflorescence primordium differentiation, floret primordium differentiation, sepal primordium differentiation, and petal primordium differentiation, respectively; F-I represents serial column and pollinia differentiation stages. 1: growth corn; 2: inflorescence primorium; 3: flower bud primordium; 4: sepal primordium; 5: petal primordium; 6: column primodium; 7: labellum 8: petal; 9: pollinium; 10: rostellum.
图 1 杂交兰‘黄金小神童’花芽分化形态解剖注:A~E依次为:未分化期、花序原基分化期、小花原基分化期、萼片原基分化期、花瓣原基分化期;F~I:合蕊柱及花粉块分化期;1:生长锥;2:花序原基;3:小花原基;4:萼片原基;5:花瓣原基;6:合蕊柱原基;7:唇瓣;8:花瓣;9:花粉块;10:蕊喙。Figure 1. Anatomy of flower bud differentiation of Golden Elf 'Sun-dust'Note:A-E represent stages of undifferentiation, inflorescence primordium differentiation, floret primordium differentiation, sepal primordium differentiation, and petal primordium differentiation, respectively; F-I represents serial column and pollinia differentiation stages. 1: growth corn; 2: inflorescence primorium; 3: flower bud primordium; 4: sepal primordium; 5: petal primordium; 6: column primodium; 7: labellum 8: petal; 9: pollinium; 10: rostellum.2.2 杂交兰花芽分化过程中可溶性糖和淀粉含量的变化
由图 2可知,随着花芽分化进程,杂交兰叶片中的可溶性糖含量的变化趋势为上升-下降-上升-下降,可溶性糖含量在分化前期不断升高,在小花原基分化期时达到峰值,在进入萼片原基分化期后,可溶性糖含量开始下降,随后进入花瓣原基分化期,又出现上升的趋势,紧接着进入合蕊柱及花粉块分化期,含量又开始下降。运用SPSS软件分析发现,不同分化时期可溶性糖含量之间具有显著性差异。杂交兰叶片中的淀粉含量的具体变化趋势与可溶性糖含量的变化趋势一致,且在小花原基分化期时含量最高。经显著性差异分析发现,淀粉含量除了在小花原基分化期与其他分化期间具有显著性差异外,其他5个分化期间不存在显著性差异,总体上呈现出先上升后下降的变化趋势。
![]() 图 2 杂交兰‘黄金小神童’花芽分化过程中可溶性糖和淀粉含量的变化Figure 2. Changes on soluble sugar and starch contents of Golden Elf 'Sun-dust' during flower bud differentiationNote: A-F were stages of undifferentiation, inflorescence primordium differentiation, floret primordium differentiation, sepal primordium differentiation, petal primordium differentiation column and pollinia differentiation.The different lowercase letters in the figure showed significant differences(P < 0.05), the same as fig. 3-4.
图 2 杂交兰‘黄金小神童’花芽分化过程中可溶性糖和淀粉含量的变化Figure 2. Changes on soluble sugar and starch contents of Golden Elf 'Sun-dust' during flower bud differentiationNote: A-F were stages of undifferentiation, inflorescence primordium differentiation, floret primordium differentiation, sepal primordium differentiation, petal primordium differentiation column and pollinia differentiation.The different lowercase letters in the figure showed significant differences(P < 0.05), the same as fig. 3-4.2.3 杂交兰花芽分化过程中可溶性蛋白含量的变化
由图 3可知,杂交兰叶片中的可溶性蛋白含量随着花芽分化进程呈现先上升后下降的趋势,在分化前期不断升高,在萼片原基分化期时,可溶性蛋白含量最高,随后持续下降,直至合蕊柱及花粉块分化期时降到最低值,仅为萼片原基分化期时的22.17%。差异性分析结果显示,可溶性蛋白含量在萼片原基分化期与其他分化时期间具有显著性差异。
2.4 杂交兰花芽分化过程中POD和CAT酶活性的变化
由图 4可知,杂交兰叶片中POD活性和CAT活性随着花芽分化进程均呈现先下降后上升的趋势。POD活性在花芽分化前期缓慢下降,各分化时期无显著性差异,在萼片原基分化期时处于最低值,在花芽分化后期急速上升,各分化时期存在显著性差异,在合蕊柱及花粉块分化期时达到最高值。CAT活性在未分化期时最高,随着花芽分化进程先急剧下降,在小花原基分化期时降到最低值,而后又开始上升,CAT活性在花芽分化各时期差异显著。
3. 讨论与结论
花芽分化是复杂的生理生化和形态分化过程,是植物从营养生长进入生殖生长的关键时期[25]。本研究将杂交兰‘黄金小神童’花芽分化过程分为未分化期、花序原基分化期、小花原基分化期、萼片原基分化期、花瓣原基分化期和合蕊柱及花粉块分化期6个阶段;与蝴蝶兰[23]、黄花美冠兰[26]文心兰[27]花芽分化的研究结果大致相同,而与大花蕙兰[28]、罗汉果[29]的花芽分化过程划分结果有所不同,说明不同植物种类甚至同为兰科植物,其花芽形态分化时期的划分存在较大差异。
植物花芽分化过程中,需要消耗大量的营养物质[30]。有研究表明,碳水化合物是植物完成花芽分化进程的重要物质基础[31-32]。在本研究中,杂交兰叶片中的可溶性糖和淀粉含量随着花芽分化进程,在花芽分化前期不断积累,在小花原基分化期达到峰值,随后开始出现下降,说明叶片中充足的可溶性糖和淀粉含量有利于杂交兰花芽分化的进行。可溶性蛋白是花器官形态建成的物质基础,在花芽分化时需要量较大。韦莉等[23]研究发现,蝴蝶兰花芽分化期间叶片中可溶性蛋白含量先上升后下降;龚湉[33]的研究发现,寒兰叶片中可溶性蛋白含量随花芽分化进程先下降后上升,说明在不同植物花芽分化过程中,可溶性蛋白的变化趋势存在差异。本研究结果显示,杂交兰叶片中可溶性蛋白含量在花芽分化期间呈现先上升后下降的趋势,在萼片原基分化期时达到最高值,说明在花芽分化前期积累足够的蛋白质可为后续花芽分化的推进提供保障。
花芽分化过程中,除了营养物质的积累,还需要一系列酶的参与调控。孔德政等[34]的研究发现,在碗莲花芽分化过程中,莲叶中的CAT活性呈上升趋势,POD活性呈先上升后下降的趋势;艾星梅等[35]的研究结果显示,6个马铃薯品种花芽分化期POD、CAT活性均呈现先升后降的变化趋势;臧纱纱等[36]的研究发现,线辣椒花芽分化过程中,POD活性呈现先降后升的变化趋势。不同植物花芽分化进程中,不同酶活性的变化趋势也存在较大差异。本研究中杂交兰叶片POD和CAT活性随花芽分化进程呈现先下降后上升的趋势,POD活性在萼片原基分化期时处于最低值,在花芽分化后期急速上升;CAT活性在小花原基分化期时降到最低值,而后又开始上升。花芽分化后期POD和CAT活性的上升,可能有效避免杂交兰受到活性氧和氢氧根离子的伤害。
花芽分化是有花植物发育中最为关键的阶段,是在植物体内外因子的共同作用和相互协调下完成的。本研究通过对杂交兰花芽分化过程中的形态及生理变化进行研究,了解杂交兰花芽分化过程中的形态和相关代谢产物含量及酶活性的变化,界定花芽分化的各个阶段,不仅可以为后续制定杂交兰栽培管理措施提供依据,保障杂交兰花芽分化顺利进行,也可以为花期调控和成花机理研究提供基础资料。
-
图 1 不同青贮时间对香茅蛋白质含量占比的影响
注:不同大写字母表示处理间差异极显著(P<0.01),不同小写字母表示处理间差异显著(P<0.05)。图2~7同。
Figure 1. Effect of silage time on protein content of citronella
Note: Data with diffrent capital letters indicate extremely significant difference at 0.01 level,lowercase letters indicate significant difference at 0.05 level.the same as Fig.2-7.
表 1 不同贮藏时间的青贮香茅感官评分
Table 1 Sensory scores on quality of citronella in silage
感官指标
Sernsory index贮藏时间
Silage time/月1 2 3 4 5 6 气味 Odor 14 14 14 10 10 10 结构 Structure 4 2 2 2 1 1 颜色 Color 1 1 0 0 0 0 总分 Total point 19 17 16 12 11 11 等级 Grade 1 1 1 2 2 2 表 2 青贮前香茅的营养成分
Table 2 Nutrient contents of citronella prior to silage
营养成分 Nutrient composition 含量 Content/% 蛋白质 Crude protein 5.48±0.08 氨基酸 Amino Acid 4.02±0.051 粗灰分 Crude ash 8.70±0.043 粗脂肪 Crude fat 1.52±0.017 粗纤维 Crude fiber 34.96±0.482 钙 Calcium 0.54±0.011 磷 Phosphorus 0.29±0.002 -
[1] 杨梦文, 赵琳静, 顾思怡, 等. 香茅化学成分及药理作用的研究进展 [J]. 中成药, 2020, 42(3):714−719. DOI: 10.3969/j.issn.1001-1528.2020.03.031 YANG M W, ZHAO L J, GU S Y, et al. Researchprogress on chemical constituents and pharmacological effects of citronella [J]. Chinese Traditional Patent Medicine, 2020, 42(3): 714−719.(in Chinese) DOI: 10.3969/j.issn.1001-1528.2020.03.031
[2] 刘耀华, 马新耀, 程作慧, 等. 香茅精油对番茄早疫病菌的抑菌作用及抑菌机制 [J]. 应用生态学报, 2017, 28(9):3016−3022. LIU Y H, MA X Y, CHENG Z H, et al. The antimicrobial activity and mechanism of Cymbopogon citratus essential oil against Alternaria solani [J]. Chinese Journal of Applied Ecology, 2017, 28(9): 3016−3022.(in Chinese)
[3] 吴维坚, 李珊珊, 杨敏, 等. 香茅属植物在国内外应用现状及福建省应用展望 [J]. 现代园艺, 2018(15):107−108. WU W J, LI S S, YANG M, et al. The application status of Citronella plants domestic and foreign and its application prospect in Fujian province[ [J]. Xiandai Horticulture, 2018(15): 107−108.(in Chinese)
[4] 杨漓, 谷瑶, 曾永明, 等. 八角、肉桂和香茅加工剩余物发酵配制饲料添加剂对肉鸡和蛋鸡的影响 [J]. 现代农业科技, 2019(6):190−191. YANG L, GU Y, ZENG Y M, et al. Effects of feed additives on chickens and layers prepared by fermentation of processing residues of star anise, cinnamon and Citronella [J]. Modern Agricultural Science and Technology, 2019(6): 190−191.(in Chinese)
[5] 周苗苗, 崔景香. 水分含量和发酵时间对花椰菜茎叶青贮效果的影响 [J]. 饲料研究, 2015(18):70−73. ZHOU M M, CUI J X. Moisturecontentand fermentation time on effects of stem and leaf silage of Cauliflower [J]. Feed Research, 2015(18): 70−73.(in Chinese)
[6] 刘佳杰, 马兰, 周韦, 等. 不同切碎方式及不同青贮时间对饲用苎麻青贮品质影响 [J]. 江西农业大学学报, 2019, 41(4):773−780. LIU J J, MA L, ZHOU W, et al. The effects of different cutting methods and different silage time on the quality of silage for feeding ramie [J]. Acta Agriculturae Universitatis Jiangxiensis, 2019, 41(4): 773−780.(in Chinese)
[7] 张养东, 杨军香, 王宗伟, 等. 青贮饲料理化品质评定研究进展 [J]. 中国畜牧杂志, 2016, 52(12):37−42. DOI: 10.3969/j.issn.0258-7033.2016.12.007 ZHANG Y D, YANG J X, WANG Z W, et al. Progress assessment of chemical indicators of silage [J]. Chinese Journal of Animal Science, 2016, 52(12): 37−42.(in Chinese) DOI: 10.3969/j.issn.0258-7033.2016.12.007
[8] 陈鑫珠, 庄益芬, 张建国, 等. 生物添加剂对水葫芦与甜玉米秸秆混合青贮品质的影响 [J]. 草业学报, 2011, 20(6):195−202. DOI: 10.11686/cyxb20110625 CHEN X Z, ZHUANG Y F, ZHANG J G, et al. Effects of biological additives on the quality of water hyacinth and maize straw mixed silage [J]. Acta Prataculturae Sinica, 2011, 20(6): 195−202.(in Chinese) DOI: 10.11686/cyxb20110625
[9] 刘振宇, 玉柱, 刘忠宽, 等. 无机盐添加剂对窖贮紫花苜蓿品质的影响 [J]. 草业科学, 2010, 27(10):154−159. DOI: 10.3969/j.issn.1001-0629.2010.10.027 LIU Z Y, YU Z, LIU Z K, et al. Effect of Siloguard additives on the quality of Medicago sativa silages in silage Silo [J]. Pratacultural Science, 2010, 27(10): 154−159.(in Chinese) DOI: 10.3969/j.issn.1001-0629.2010.10.027
[10] 陈西风. 综述牛羊青贮饲料的加工利用 [J]. 中国动物保健, 2020, 22(7):63−64. DOI: 10.3969/j.issn.1008-4754.2020.07.054 CHEN X F. Review on the processing and utilization of cattle and sheep silage [J]. China Animal Health, 2020, 22(7): 63−64.(in Chinese) DOI: 10.3969/j.issn.1008-4754.2020.07.054
[11] 蔡敦江, 周兴民, 朱廉, 等. 苜蓿添加剂青贮、半干青贮和与麦秸混贮的研究 [J]. 草地学报, 1997, 5(2):123−127. DOI: 10.11733/j.issn.1007-0435.1997.02.009 CAI D J, ZHOU X M, ZHU L, et al. Study on using additives silage and wilted silage and mixed silage of alfafa [J]. Acta Agrestia Sinica, 1997, 5(2): 123−127.(in Chinese) DOI: 10.11733/j.issn.1007-0435.1997.02.009
[12] 冯骁骋, 格根图, 李长春, 等. 青贮条件对天然牧草青贮饲料饲用品质的影响 [J]. 西北农林科技大学学报(自然科学版), 2013, 41(5):9−13. FENG X C, GE G T, LI C C, et al. Influence of silage condition on the natural grass silage feeding quality [J]. Journal of Northwest A & F University (Natural Science Edition), 2013, 41(5): 9−13.(in Chinese)
[13] 陈荣, 刘利林, 刘雪彦, 等. 菊芋青贮饲料的制作与品质分析鉴定 [J]. 饲料研究, 2020, 43(5):76−78. CHEN R, LIU L L, LIU X Y, et al. Production and quality analysis and identification of Jerusalem artichoke silage [J]. Feed Research, 2020, 43(5): 76−78.(in Chinese)
[14] 高海娟, 刘泽东, 孙蕊, 等. 不同贮藏时间对苜蓿青贮品质的影响 [J]. 中国饲料, 2019(23):95−98. GAO H J, LIU Z D, SUN R, et al. The effects of different storage time on alfalfa silage quality [J]. China Feed, 2019(23): 95−98.(in Chinese)
[15] 李茂, 字学娟, 吕仁龙, 等. 添加乳酸菌和纤维素酶对王草青贮品质和瘤胃降解率的影响 [J]. 中国畜牧杂志, 2020, 56(7):161−165. LI M, ZI X J, LYU R L, et al. Effects of adding lactobacillus Plantarum and Cellulase on silage qualityof King grass and rumen degradation rate [J]. Chinese Journal of Animal Science, 2020, 56(7): 161−165.(in Chinese)
[16] 姚焰础, 刘作华, 杨飞云, 等. 柑橘皮渣的营养组成及其在畜禽饲料中的应用研究进展 [J]. 养猪, 2013(1):17−21. DOI: 10.3969/j.issn.1002-1957.2013.01.006 YAO Y C, LIU Z H, YANG F Y, et al. Nutrition composition of citrus peel residue and its application in animal feed [J]. Swine Production, 2013(1): 17−21.(in Chinese) DOI: 10.3969/j.issn.1002-1957.2013.01.006
[17] 丁倩, 殷钟意, 郑旭煦, 等. 柑橘皮渣青贮试验及其在小尾寒羊饲喂中的应用研究 [J]. 云南农业大学学报(自然科学), 2020, 35(2):262−268. DING Q, YIN Z Y, ZHENG X X, et al. Silage experiment of Citrus peel residue and its application in feeding small-tailed Han sheep [J]. Journal of Yunnan Agricultural University (Natural Science), 2020, 35(2): 262−268.(in Chinese)
[18] 闫峻, 王文杰, 高玉鹏, 等. 玉米秸秆青贮饲料贮存期的营养品质变化规律 [J]. 西北农业学报, 2009, 18(4):57−60. DOI: 10.7606/j.issn.1004-1389.2009.04.013 YAN J, WANG W J, GAO Y P, et al. Variation law of corn straw silage nutritional quality in different storage periods [J]. Acta Agriculturae Boreali-Occidentalis Sinica, 2009, 18(4): 57−60.(in Chinese) DOI: 10.7606/j.issn.1004-1389.2009.04.013
[19] 刘东华. 青贮饲料的调制及其营养变化 [J]. 黑龙江畜牧兽医, 2013(4):111. LIU D H. Silagepreparation and itsnutritionchanges [J]. Heilongjiang Animal Science and Veterinary Medicine, 2013(4): 111.(in Chinese)
[20] 李春霞. 饲料中钙、磷含量对动物机体的影响 [J]. 养殖技术顾问, 2014(4):55−55. LI C X. Effect of feed Ca and Pcontents on animal body [J]. Technical Advisor for Animal Husbandry, 2014(4): 55−55.(in Chinese)
[21] 艾丹, 郭春华, 徐亚欧, 等. 四川阿坝县秋季牧草钙磷等矿物元素特征及其与土壤钙磷含量的关系 [J]. 草地学报, 2011, 19(6):1060−1063. DOI: 10.11733/j.issn.1007-0435.2011.06.029 AI D, GUO C H, XU Y O, et al. Mineral element characteristics of autumn forage in aba County and the relationships with ca, P contents of soil [J]. Acta Agrestia Sinica, 2011, 19(6): 1060−1063.(in Chinese) DOI: 10.11733/j.issn.1007-0435.2011.06.029
-
期刊类型引用(14)
1. 陈露,李青女,郑佳桐,王奕晴,翟俊文,吴沙沙. 兰科植物花期调控技术及分子机理研究进展. 植物遗传资源学报. 2025(01): 1-13 .  百度学术
百度学术
2. 刘贝宁,陈发兴. 多效唑和乙烯利对西克刺桐花芽分化及成花基因表达的影响. 福建农业学报. 2024(04): 427-437 .  本站查看
本站查看
3. 李腾基,付志恵,陈鑫,黄洁衔,黄紫钦,张建霞. 不同植物生长调节剂对墨兰成花生理和开花性状的影响. 分子植物育种. 2024(17): 5777-5786 .  百度学术
百度学术
4. 黄洁衔,李腾基,黄紫钦,逯有法,张建霞. 墨兰花芽形态分化及生理特性研究. 北方园艺. 2023(03): 56-63 .  百度学术
百度学术
5. 金洲,卢山,江俊浩,李寿仁,张楠,江晓钰,吴凡. 园艺植物花芽分化影响因素及机理研究进展. 园艺学报. 2023(05): 1151-1164 .  百度学术
百度学术
6. 张超,李彤妤,裴珂,段九菊. 乙炔催花对观赏凤梨糖代谢的影响. 核农学报. 2023(12): 2478-2484 .  百度学术
百度学术
7. 周荣,贺琪馨,陆楚桥. 植物生长调节剂对建兰开花的调控作用研究. 广东农业科学. 2023(09): 165-172 .  百度学术
百度学术
8. 温玥,郝志超,孙天雨,苏淑钗,王湘南. 油茶花芽分化过程中营养物质和内源激素的变化规律. 经济林研究. 2023(04): 31-39 .  百度学术
百度学术
9. 张英杰,李奥,吕云飞,孙纪霞,刘民晓,张京伟,刘学庆,刘晓华,郭文姣,郭对田. 蝴蝶兰成花过程内源激素含量的变化和植物生长调节剂的作用. 热带亚热带植物学报. 2022(01): 104-110 .  百度学术
百度学术
10. 孔兰,林榕燕,樊荣辉,林兵,方能炎,钟淮钦. 杂交兰花瓣类黄酮成分分析及其对花色的影响. 西北植物学报. 2022(10): 1711-1719 .  百度学术
百度学术
11. 段秋笛,杨旭,赵焱,卢丽晶,崔秀伟,梁宏伟. 连香树花芽发育过程中的生理生化特性研究. 湖北农业科学. 2022(22): 89-93 .  百度学术
百度学术
12. 吴洁秋,朱根发,王凤兰,杨凤玺. 竹叶兰花器官发育过程及生理特性研究. 热带作物学报. 2021(01): 140-148 .  百度学术
百度学术
13. 李霖,李婷婷,杨坤,张志忠,吴菁华. 低温抑制中国水仙花芽分化的生理生化机制. 福建农业学报. 2021(04): 412-417 .  本站查看
本站查看
14. 董晓晓,别沛婷,袁涛. 3个牡丹品种花芽分化过程形态及叶片碳水化合物质量分数变化. 东北林业大学学报. 2020(07): 34-39 .  百度学术
百度学术
其他类型引用(4)





 下载:
下载: