Transcriptome-based EST-SSR Search for Analysis on Lemon Genetic Diversity
-
摘要:目的
以柠檬转录组数据为基础开发EST-SSR标记并进行遗传多样性分析。
方法利用MISA软件对柠檬转录组进行SSR位点搜索,用Primer 3.0设计和筛选引物,并绘制49份柠檬的聚类图。
结果共鉴定到
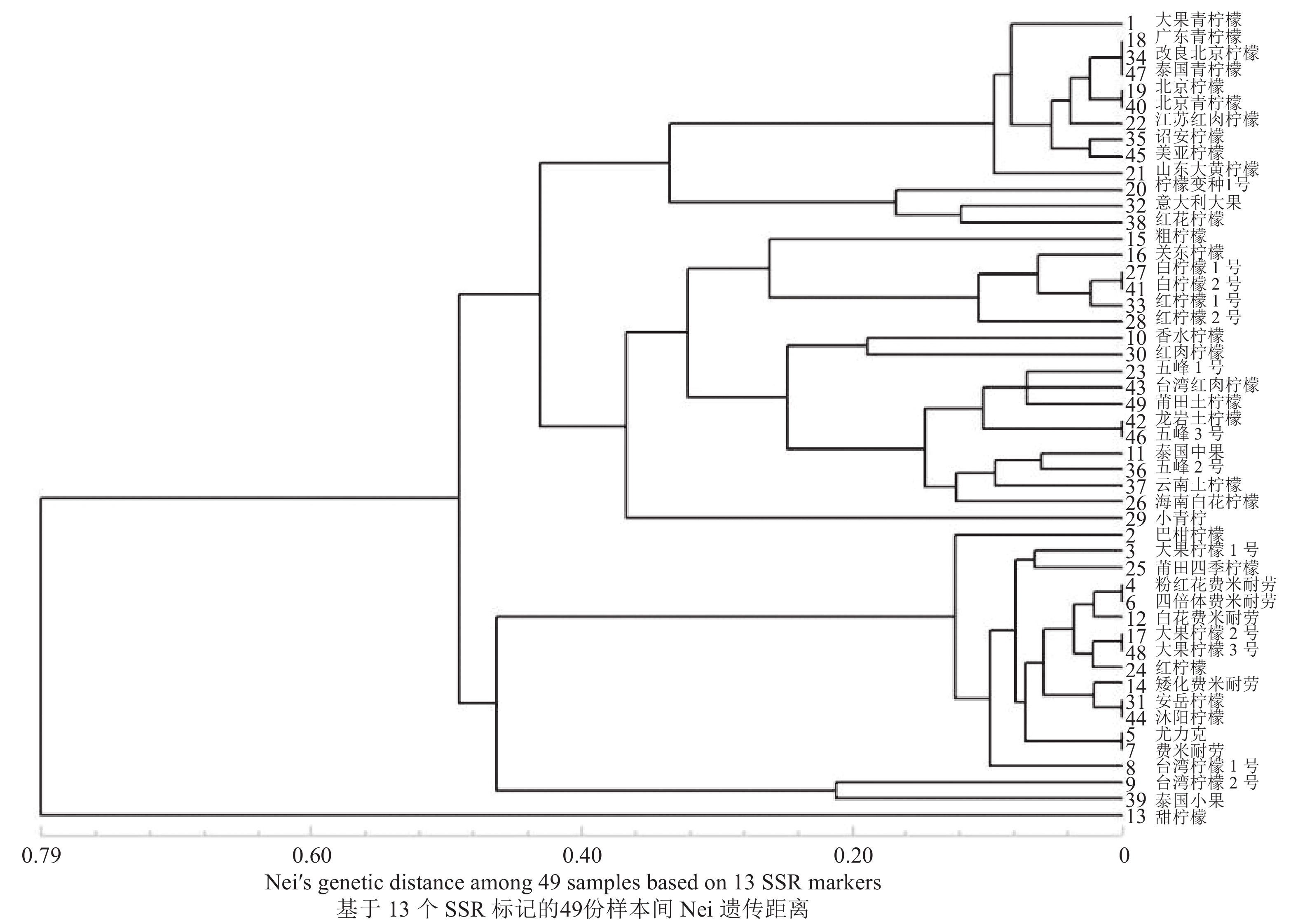
40 193 个SSR位点,SSR分布频率为35.67%,平均分布距离为1.39 kb;柠檬转录组中SSR序列以单、三、二核苷酸重复类型为主,分别占80.91%、9.20%和8.67%,其优势基元分别为A/T、AG/CT和AAG/CTT;共设计出4561 对引物,选取其中24对进行有效性验证,筛选到13对多态性引物;扩增得到47个等位基因,有效等位基因均值为3.615;观察杂合度、期望杂合度和引物多态信息含量的均值为0.637、0.516和0.528;在遗传距离0.40时可将供试材料划分为五大类,聚类结果与传统的形态学分类结果大体一致。结论本研究开发的13对EST-SSR引物能将供试材料进行有效区分,与传统分类学相吻合,并揭示了供试材料间具有丰富的遗传多样性,为柠檬种质资源后续开发及利用提供参考依据。
Abstract:ObjectiveEST-SSRs of lemon were searched based on transcriptome data to analyze the genetic diversity of the plant.
MethodSSR loci of lemon transcriptomes were screened using MISA to design primers by Primer 3.0. A clustering of 49 species was secured.
ResultOf the
40193 SSR loci identified, a distribution frequency of 35.67% and an average distribution distance of 1.39 kb were found in the sequences of 80.91% mono-, 9.20% tri-, and 8.67% dinucleotide repeat types with the dominant motifs of A/T, AG/CT, and AAG/CTT, respectively. Twenty-four of the4561 pairs of primers were selected for validity verification, and 13 by being polymorphic. The amplified 47 alleles had a mean effective value of 3.615 with the mean Ho, He, and PIC of 0.637, 0.516, and 0.528, respectively. At the genetic distance of 0.40, the lemon cultivars were clustered into 5 categories, which were generally consistent with that obtained by the traditional morphological classification.ConclusionThirteen pairs of EST-SSR primers were selected to classify 49 lemon specimens. The resulting clustering agreed with traditional taxonomy. The displayed rich genetic diversity rendered these cultivars an adequate germplasm collection for the development and utilization of lemon plants.
-
Keywords:
- lemon /
- transcriptome /
- EST-SSRs /
- cluster analysis
-
-
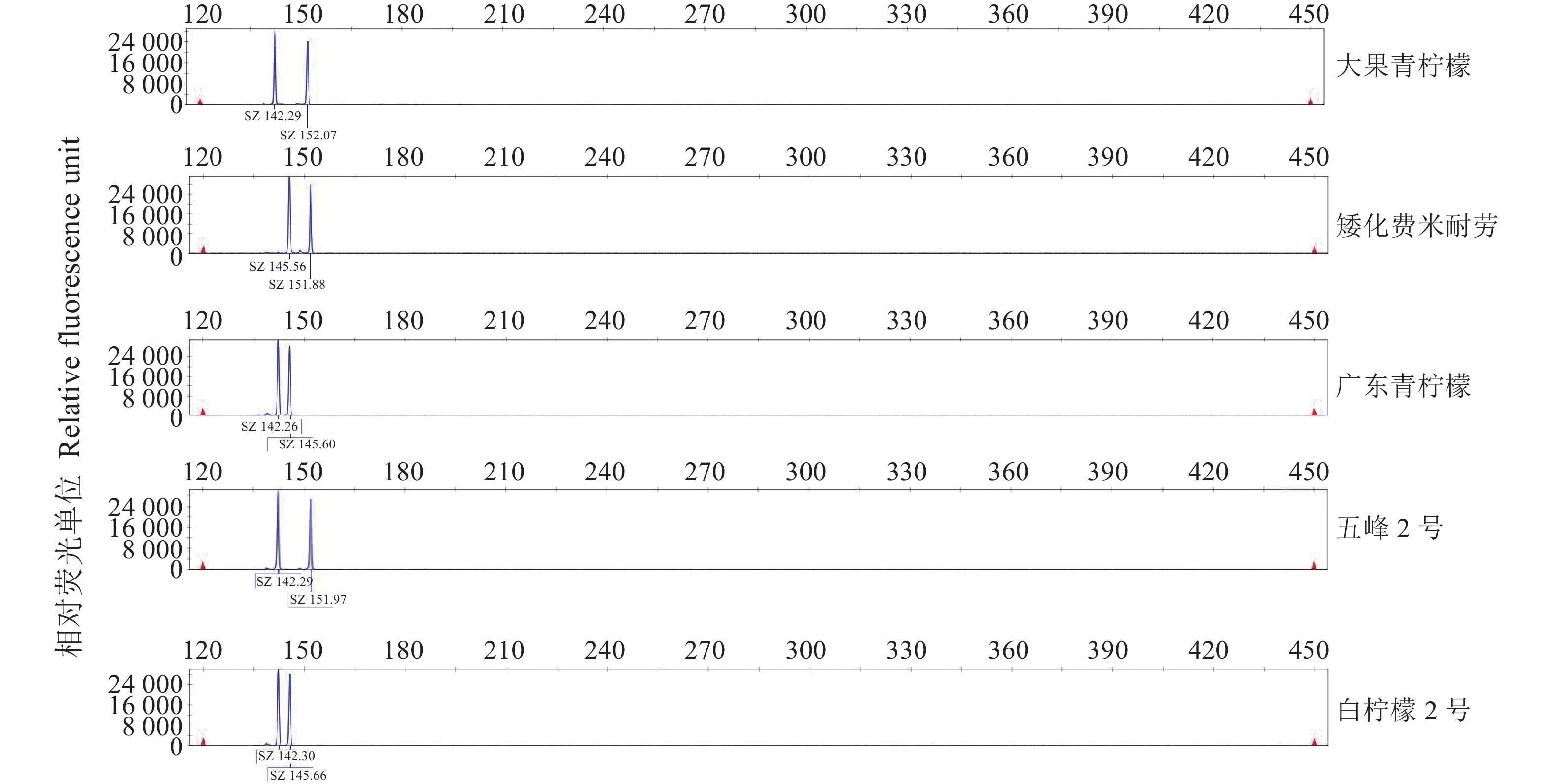
表 1 柠檬材料
Table 1 List of lemon specimens
编号 Code 名称 Name 学名 Scientific name 编号 Code 名称 Name 学名 Scientific name 1 大果青柠檬 C. limon (L.) Burm. f. 26 海南白花柠檬 Citrus medica L. 2 巴柑柠檬 C. bergamia Risso. 27 白柠檬1号 C. limonia Osb. 3 大果柠檬1号 C. limon (L.) Burm. f. 28 红柠檬2号 C. limonia Osb. 4 粉红花费米耐劳 C. limon (L.) Burm. f. 29 小青柠 C. limon (L.) Burm. f. 5 尤力克 C. limon (L.) Burm. f. 30 红肉柠檬 Citrus medica L. var.sarcodactylis Swingle 6 四倍体费米耐劳 C. limon (L.) Burm. f. 31 安岳柠檬 C. limon (L.) Burm. f. 7 费米耐劳 C. limon (L.) Burm. f. 32 意大利大果 C. limon (L.) Burm. f. 8 台湾柠檬1号 C. limon (L.) Burm. f. 33 红柠檬1号 C. limonia Osb. 9 台湾柠檬2号 C.aurantifolia (Christm.) Swingle 34 改良北京柠檬 C. limon (L.) Burm. f. 10 香水柠檬 C. limon (L.) Burm. f. 35 诏安柠檬 C. limon (L.) Burm. f. 11 泰国中果 C. limon (L.) Burm. f. 36 五峰2号 Citrus medica L. 12 白花费米耐劳 C. limon (L.) Burm. f. 37 云南土柠檬 Citrus medica L. 13 甜柠檬 C. limon (L.) Burm. f. 38 红花柠檬 C. limon (L.) Burm. f. 14 矮化费米耐劳 C. limon (L.) Burm. f. 39 泰国小果 C. limon (L.) Burm. f. 15 粗柠檬 C.jambhiri Lush. 40 北京青柠檬 C. limon (L.) Burm. f. 16 关东柠檬 C. limon (L.) Burm. f. 41 白柠檬2号 C. limon (L.) Burm. f. 17 大果柠檬2号 C. limon (L.) Burm. f. 42 龙岩土柠檬 Citrus medica L. 18 广东青柠檬 C. limon (L.) Burm. f. 43 台湾红肉柠檬 C. limon (L.) Burm. f. 19 北京柠檬 C. limon (L.) Burm. f. 44 沐阳柠檬 C. limon (L.) Burm. f. 20 柠檬变种1号 C. limon (L.) Burm. f. 45 美亚柠檬 C. limon (L.) Burm. f. 21 山东大黄柠檬 C. limon (L.) Burm. f. 46 五峰3号 Citrus medica L. 22 江苏红肉柠檬 C. limon (L.) Burm. f. 47 泰国青柠檬 C. limon (L.) Burm. f. 23 五峰1号 Citrus medica L. 48 大果柠檬3号 C. limon (L.) Burm. f. 24 红柠檬 C. limon (L.) Burm. f. 49 莆田土柠檬 Citrus medica L. 25 莆田四季柠檬 C. limon (L.) Burm. f. 表 2 柠檬转录组中SSR序列分布
Table 2 SSR sequences of lemon transcriptomes
条目 Items 数量 Number 比例 Percentage/% 检索序列总数
Retrieved sequences68118 碱基总长度
Total base length/Gb55.73 检测到的SSR总数
SSRs detected40193 含SSR 标记的序列数
Number of sequences containing SSR markers24297 35.67 有1 个SSR 的序列数
Number of sequences with 1 SSR5481 8.05 有≥2个SSR 的序列数
Number of sequences with≥ 2 SSRs8000 11.74 复合SSR 的序列数
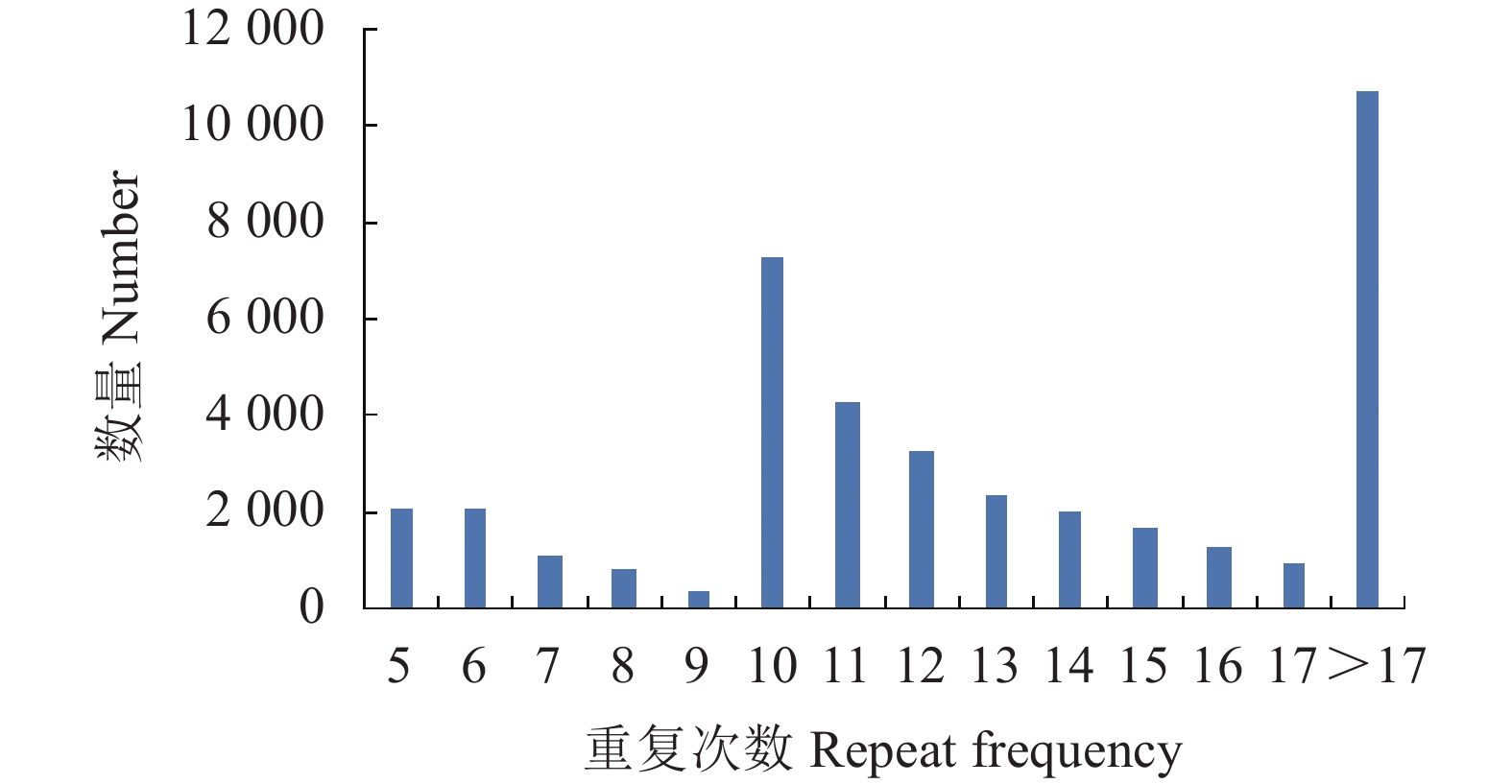
Number of composite SSR sequences10816 15.88 表 3 柠檬转录组SSR序列分布情况
Table 3 SSR sequence distribution in transcriptomes of lemon specimens
SSR类型
SSR type数量
Number比例
Percentage/%出现频率
Distribution
frequency/%平均距离
Average
distance/kb单核苷酸
Mono-nucleotide32520 80.91 47.74 1.71 二核苷酸
Di-nucleotide3484 8.67 5.11 16.00 三核苷酸
Tri-nucleotide3696 9.20 5.43 15.08 四核苷酸
Tetra-nucleotide331 0.82 0.49 168.37 五核苷酸
Penta-nucleotide66 0.16 0.10 844.38 六核苷酸
Hexa-nucleotide96 0.24 0.14 580.51 总计 Total 40193 100.00 59.00 1.39 表 4 柠檬转录组SSR重复基元分布
Table 4 SSR motif distribution in lemon transcriptomes
重复类型
Repeat types类型数目
Number of types重复基元
Repeat motifs数目
Number发生频率
Frequency/%比例
Proportion/%单核苷酸
Mononucleotide2 A/T 30978 45.48 77.07 C/G 1542 2.26 3.84 二核苷酸
Dinucleotide4 AG/CT 2180 3.20 5.42 AT/AT 658 0.97 1.64 AC/GT 633 0.93 1.57 CG/CG 13 0.02 0.03 三核苷酸
Trinucleotide10 AAG/CTT 995 1.46 2.48 AAT/ATT 686 1.01 1.71 AGC/CTG 505 0.74 1.26 ATC/ATG 469 0.69 1.17 其他类型
Other types1041 1.44 2.59 四核苷酸
Tetra-nucleotide24 AAAT/ATTT 91 0.13 0.23 AAAG/CTTT 88 0.13 0.22 AAAC/GTTT 22 0.03 0.05 ACTG/AGTC 16 0.02 0.04 其他类型
Other types114 0.17 0.28 五核苷酸
Penta-nucleotide15 AAAAG/CTTTT 19 0.03 0.05 AAAAC/GTTTT 6 0.01 0.01 AAAAT/ATTTT 6 0.01 0.01 AACTC/AGTTG 6 0.01 0.01 AGCTC/AGCTG 6 0.01 0.01 其他类型
Other types23 0.03 0.06 六核苷酸
Hexa-nucleotide35 AAGGAG/CCTTCT 10 0.01 0.02 ACCAGC/CTGGTG 10 0.01 0.02 AAAAAC/GTTTTT 6 0.01 0.01 ACCTCC/AGGTGG 6 0.01 0.01 其他类型
Other types64 0.09 0.16 表 5 柠檬转录组13对SSR多态性引物信息
Table 5 Information on 13 pairs of polymorphic SSR primers in lemon transcriptomes
引物编号
Primer No.来源
Gene ID引物系列
Primer sequences(5′-3′)SSR基元
SSR motif有效等位基因
Effective
allele观测杂合度
Observed
heterozygosity期望杂合度
Expected
heterozygosity多态信息含量
Polymorphism
information contentCil-5 TRINITY_DN21626_c0_g1_i1 F:AGGTACGGAACAGGACGATTTC
R:GTCCCACCACCCATGATCATC(TGG) 8 3 0.429 0.351 0.404 Cil-6 TRINITY_DN22713_c0_g1_i3 F:TGGAGGGGAATTGCAGAGAAAT
R:CAAAAGCGTCTGATTCGGATAA(AG) 18 3 0.841 0.664 0.657 Cil-7 TRINITY_DN22780_c0_g1_i1 F:ACAGAGCCGCCGTCGTAATT
R:ACGCTGATGAAGAAGGCTGCTG(ACA) 10 4 0.746 0.566 0.570 Cil-9 TRINITY_DN20983_c0_g1_i1 F:TTGTTTGTTGCAGCTCGATACA
R:GCCGACACCAATTACAGACTTT(GTCT) 6 4 0.317 0.309 0.365 Cil-11 TRINITY_DN21948_c0_g3_i2 F:ACCATCTAAGGGCTTCGTTTTA
R:GTAACGGCTTGCACTCCATCAA(TCGA) 6 2 0.143 0.187 0.215 Cil-12 TRINITY_DN14061_c0_g1_i3 F:CTGCTCGGAGGTAGGGAATTG
R:CGAAGGTGGTGGTTAAGC(TTGA) 7 3 0.762 0.495 0.491 Cil-13 TRINITY_DN39739_c0_g1_i1 F:GCCGTCTCCAGAGCGCAAATT
R:AACACTCACAATCATGCCGCGA(TCT) 8 4 0.905 0.641 0.622 Cil-14 TRINITY_DN12772_c0_g1_i1 F:TCCCCTTTTCTTTGGCGTTCTT
R:TGGGATCATAGCCGGAGTACAA(TCT) 8 4 0.698 0.507 0.507 Cil-15 TRINITY_DN15845_c0_g2_i1 F:GGTTTGTCCCTTGCTGTAAAA
R:CCGGACCTGAAAACTACTCTAT(AC) 10 4 0.746 0.601 0.589 Cil-16 TRINITY_DN22015_c0_g2_i4 F:TGGACACAGCGGCCATTTTGT
R:CGAACCCGTCCCATCTGCATAA(GAGC) 6 2 0.683 0.479 0.474 Cil-17 TRINITY_DN11400_c1_g1_i1 F:AGCCGAATGAGGAACCGAAGAA
R:GCGGTAAATTAGTGGAGGTTGC(TCCCT) 5 5 0.730 0.798 0.793 Cil-19 TRINITY_DN23736_c6_g2_i1 F:CCGACTTTCTTCCCGTCTTCTA
R:GGGATTTAGGCGAGGACAATGA(TCA) 8 3 0.413 0.373 0.436 Cil-24 TRINITY_DN22258_c1_g2_i1 F:GGCGGTGATGTGGGCGAAATA
R:TCCTACTGCTTTGTCACCTTCT(GGA) 8 6 0.873 0.74 0.746 平均值 Average 3.615 0.637 0.516 0.528 -
[1] 高俊燕,周东果,岳建强,等. 费米耐劳柠檬引种研究初报[J]. 西南农业学报,2008,21(3) :760−763. DOI: 10.3969/j.issn.1001-4829.2008.03.047 GAO J Y,ZHOU D G,YUE J Q,et al. Original research on the performance of the Femminello lemon introduced into Dehong state[J]. Southwest China Journal of Agricultural Sciences,2008,21(3) :760−763. (in Chinese) DOI: 10.3969/j.issn.1001-4829.2008.03.047
[2] 李进学,高俊燕,付小猛,等. 云南柠檬产业发展的优势与潜力[J]. 热带农业科学,2017,37(10) :99−104,110. LI J X,GAO J Y,FU X M,et al. Advantages and potential of lemon industry in Yunnan Province[J]. Chinese Journal of Tropical Agriculture,2017,37(10) :99−104,110. (in Chinese)
[3] 沈兆敏,柠檬优质丰产栽培[M]. 北京:金盾出版社,2002:1–8. [4] 周齐铭,彭长江,计长远. 柠檬栽培技术[M]. 成都:四川科学技术出版社,2005:7–8. [5] 马丽丽,解凯东,叶俊丽,等. 基于SSR标记的早花柠檬亲缘关系分析[J]. 果树学报,2013,30(3) :381−385,506. MA L L,XIE K D,YE J L,et al. Phylogenetic relationship for early flowering lemon by SSR markers[J]. Journal of Fruit Science,2013,30(3) :381−385,506. (in Chinese)
[6] 张树伟. 香水柠檬无籽成因和相关基因的分离与鉴定[D]. 南宁:广西大学,2014. ZHANG S W. Causes of Seedless Forming and identifiction of seedless related genes from ‘Xiangshui’ lemon[D]. Nanning:Guangxi University,2014. (in Chinese)
[7] 尤桂春,林文忠,武竞超,等. 柠檬种质资源表型性状遗传多样性分析[J]. 中国南方果树,2020,49(06) :34−39. YOU G C,LIN W Z,WU J C,et al. Analysis genetic diversity of lemon germplasm resources with phenotypic traits[J]. South China Fruits,2020,49(06) :34−39. (in Chinese)
[8] 谢倩,张诗艳,江来,等. 橄榄转录组SSR信息分析及分子标记开发与应用[J]. 园艺学报,2023,50(11) :2350−2364. XIE Q,ZHANG S Y,JIANG L,et al. Analysis of Canarium album transcriptome SSR information and molecular marker development and application[J]. Acta Horticulturae Sinica,2023,50(11) :2350−2364. (in Chinese)
[9] 秦玥,朱高浦,郭欢欢,等. 扁桃EST-SSR分子标记开发及遗传多样性评价[J]. 林业科技通讯,2023(6) :20−25. QIN Y,ZHU G P,GUO H H,et al. Development of EST-SSR molecular marker and evaluation of genetic diversity in Prunus communis[J]. Forest Science and Technology,2023(6) :20−25. (in Chinese)
[10] 郭俊,朱婕,谢尚潜,等. 油梨转录组SSR分子标记开发与种质资源亲缘关系分析[J]. 园艺学报,2020,47(8) :1552–1564. GUO J,ZHU J,XIE S Q,et al. Development of SSR molecular markers based on transcriptome and analysis of genetic relationship of germplasm resources in Avocado[J]. Acta Horticulturae Sinica,2020,47(8) :1552−1564. (in Chinese)
[11] 毛娟,梁国平,卢世雄,等. 葡萄EST-SSR标记的开发及其在遗传多样性分析中的应用[J]. 中外葡萄与葡萄酒,2019(6) :12−19. MAO J,LIANG G P,LU S X,et al. Development of the EST-SSRs marker and application on genetic diversity analysis from grapevine[J]. Sino-Overseas Grapevine & Wine,2019(6) :12–19. (in Chinese)
[12] 潘丽芹,李纪元,李绍翠,等. 基于山茶转录组的SSR标记开发及亲缘关系分析[J]. 北京林业大学学报,2019,41(7) :111–120. PAN L Q,LI J Y,LI S C,et al. Development of SSR markers based on transcriptome of Camellia japonica and analysis of genetic relationship[J]. Journal of Beijing Forestry University,2019,41(7) :111−120. (in Chinese)
[13] 杨仕美,乔光,毛永亚,等. 基于火龙果转录组测序的SSR标记开发及种质亲缘关系分析[J]. 分子植物育种,2018,16(24) :8096−8110. YANG S M,QIAO G,MAO Y Y,et al. SSR markers development and genetic relationship analysis of germplasm based on transcriptomic sequencing of Pitaya[J]. Molecular Plant Breeding,2018,16(24) :8096−8110. (in Chinese)
[14] 饶龙兵,杨汉波,郭洪英,等. 基于桤木属转录组测序的SSR分子标记的开发[J]. 林业科学研究,2016,29(6) :875−882. RAO L B,YANG H B,GUO H Y,et al. Development of SSR molecular markers based on transcriptome sequences of alnus[J]. Forest Research,2016,29(6) :875−882. (in Chinese)
[15] 李太强,刘雄芳,万友名,等. 滇东南濒危植物长梗杜鹃转录组微卫星特征分析[J]. 林业科学研究,2017,30(4) :533−541. LI T Q,LIU X F,WANG Y M,et al. Characteristic analysis of microsatellites in the transcriptome of Rhododendron Longipedicellatum,an endangered species endemic to southeastern Yunnan,china[J]. Forest Research,2017,30(4) :533−541. (in Chinese)
[16] 孙禄娟,何建军,汪军成,等. 基于全长转录组测序的盐生草SSR标记开发及其遗传多样性分析[J]. 草业学报,2022,31(8) :199−210. SUN L J,HE J J,WANG J C,et al. Development of SSR markers based on full-length transcriptome sequencing and genetic diversity analysis of Halogeton glomeratus[J]. Acta Prataculturae Sinica,2022,31(8) :199−210. (in Chinese)
[17] 杨丹丹,马玲玲,李亚,等. 楸树EST-SSR标记开发及种质资源的遗传多样性分析[J]. 分子植物育种,2020,18(4) :1216−1223. YANG D D,MA L L,LI Y,et al. Development of EST-SSR marker and genetic diversity of germplasm sesources in Catalpa bungei[J]. Molecular Plant Breeding,2020,18(4) :1216−1223. (in Chinese)
[18] 杜庆章. 利用连锁与连锁不平衡联合作图解析毛白杨重要性状的等位遗传变异[D]. 北京:北京林业大学,2014. DU Q Z. Dissection of allelic variation underlying important traits in Populus tomentos Carr.by usingjoint linkage and linkage disequilibrium mapping[D]. Beijing:Beijing Forestry University,2014. (in Chinese)
[19] 陈红,杨迤然. 贵州李资源遗传多样性及亲缘关系的ISSR分析[J]. 果树学报,2014,31(2) :175−180. CHEN H,YANG Y R. Genetic diversity and relationship of Plum resources in Guizhou analysed by ISSR markers[J]. Journal of Fruit Science,2014,31(2) :175−180. (in Chinese)
[20] 张起,安华明. 贵州砂梨种质资源遗传多样性的ISSR分析[J]. 果树学报,2015,32(1) :6−12. ZHANG Q,AN H M. Genetic diversity of Pyrus pyrifolia resources distributed in Guizhou province revealed by ISSR markers[J]. Journal of Fruit Science,2015,32(1) :6−12. (in Chinese)
[21] 陈孝赏,汤紫依,何海叶,等. 基于ISSR标记的姜种质资源遗传多样性分析[J]. 分子植物育种,2024,22(20) :6757−6766. CHEN X S,TANG Z Y,HE H Y,et al. Genetic diversity analysis of Ginger (Zingiber officinale) germplasm resources based on ISSR molecular marker[J]. Molecular Plant Breeding,2024,22(20) :6757−6766. (in Chinese)
[22] 宋喜娥,李英慧,常汝镇,等. 中国栽培大豆(Glycine max (L.) Merr.) 微核心种质的群体结构与遗传多样性[J]. 中国农业科学,2010,43(11) :2209−2219. SONG X E,LI Y H,CHANG R Z,et al. Population structure and genetic diversity of mini core collection of Cultivated Soybean (Glycine max (L.) Merr.) in china[J]. Scientia Agricultura Sinica,2010,43(11) :2209−2219. (in Chinese)
[23] 杨晓明. 柑橘亚科植物系统发育基因组学及野生枸橼、宜昌橙谱系地理学研究[D]. 武汉:华中农业大学,2017. YANG X M. The phylogenomic of aurantioideae and phylogeography of Wild Citron(Citrus medica) and Ichang Papeda(Citrus ichangensls) [D]. Wuhan:Huazhong Agricultural University,2017. (in Chinese)
[24] 李小孟. 柑橘及其近缘属植物的分子进化与栽培柑橘的起源研究[D]. 重庆:西南大学,2010. LI X M. Molecular phylogeny of the true citrus fruit trees group (Aurantioideae,Rutaceae) and the origin of cultivated citrus[D]. Chongqing:Southwest University,2010. (in Chinese)




 下载:
下载: