Cloning and Preliminary Functional Verification of VfNHX1 in Vicia faba L.
-
摘要:目的 探究蚕豆(Vicia faba L.)VfNHX1基因在响应盐胁迫过程中的作用。方法 通过3′和5′RACE方法,从蚕豆中克隆了1个Na+/H+逆向转运蛋白编码基因VfNHX1,并对其进行了生物信息学分析、亚细胞定位、盐胁迫下的表达分析和初步功能验证。结果 (1)该基因全长
2255 bp,CDS编码区长1 629 bp,编码542个氨基酸;(2)生物信息学分析显示,该蛋白有10个跨膜区,不具有信号肽,是一个结构稳定的膜蛋白,且包含1个NHX 蛋白家族特有的Na-H Exchanger结构域;亚细胞定位分析显示VfNHX1定位在液泡膜上;(3)实时荧光定量PCR(qRT-PCR)分析显示,在NaCl处理后,叶片中VfNHX1表达量呈现先降低后升高,随即又下降的变化趋势,且在12 h时达最高值;根中VfNHX1表达量先降低后升高,在48 h时表达量显著升高(P<0.01);(4)酵母生长试验结果表明,VfNHX1 可以提高盐敏感酵母突变体AXT4K对高盐的耐受能力。结论 VfNHX1基因能够响应盐胁迫,是蚕豆潜在抗盐功能基因。-
关键词:
- 蚕豆 /
- Na+/H+逆向转运蛋白 /
- 基因克隆 /
- 盐胁迫 /
- 功能验证
Abstract:Objective Role of VfNHX1 of faba bean in response to salt stress was studied.Methods A Na+/H+ reverse transporter protein-encoding gene, VfNHX1, was cloned from Vicia faba L. by 3' and 5' RACE for a bioinformatics analysis, subcellular localization determination, expression under salt stress, and a preliminary verification on the function.Results (1) VfNHX1 sequence was2255 bp with a CDS coding region of1629 bp encoding 542 amino acids. (2) As a stable transmembrane protein, VfNHX1 had 10 transmembrane regions without signal peptide and contained a typical Na-H exchanger conserved functional domain of NHX family. It was in the vacuolar membrane. (3) In the leaves, the expression of VfNHX1 under NaCl stress determined by qRT-PCR showed a trend of decreasing, then increasing, followed by decreasing with a peak reached in 12 h. In the roots, the expression declined initially and then rose significantly at 48 h (P<0.01). (4) The presence of VfNHX1 in a yeast growth experiment indeed heightened the NaCl tolerance of the salt-sensitive yeast mutant AXT4K.Conclusion VfNHX1 in V. faba L. was able to respond to salt stress and could be a functional gene to boost the salt resistance of the plant.-
Keywords:
- Vicia faba L. /
- Na+/H+ antiporter /
- cloning /
- salt stress /
- functional verification
-
0. 引言
【研究意义】土壤盐渍是限制植物生长和作物生产的主要非生物因素之一,它会引起渗透胁迫、离子胁迫和氧化应激,导致植物生长和发育受阻[1]。盐渍土富含钠离子、氯离子以及碳酸盐(包括碳酸氢盐),其中氯化钠是由Na+和Cl− 组成的毒性最强的盐,占盐渍土中可溶性盐总量的50%以上[2]。盐渍化土壤(盐含量0.5%以上)中过高的土壤盐分严重制约了农业生产和粮食安全,农用地的盐碱化主要是由于土壤中盐分的积累造成的[3]。世界范围内,不能被人类有效利用的盐碱地面积已经超过10亿公顷[4],由于化肥的使用,未来预计约有50 %的农业用地将受到盐碱化的影响[5]。因此,培育耐盐碱作物成为应对这一问题可行且有效的途径。为了应对盐胁迫,植物进化出了多种抗逆机制,液泡膜Na+/H+逆向转运蛋白被认为在调节细胞离子组成和电解质平衡中起关键作用[6]。将Na+区隔化在液泡中,不仅可以清除细胞质中潜在的有毒离子,还可以提高细胞的渗透压来对抗渗透胁迫,主要的质子泵、H - ATP酶和焦磷酸酶为该过程提供动力[7]。【前人研究进展】目前,已有多个植物液泡膜Na+/H+逆向转运蛋白基因被克隆,这些基因与植物耐盐性的关系也得到了证实。例如,转化了盐爪爪Kf NHX1 基因的拟南芥种子在盐胁迫下的萌发率明显高于野生型[8],200 mmol·L−1 NaCl 胁迫处理15 d后野生型拟南芥叶片枯黄,转基因植株的生长表型较好。在含有50 mmol·L−1 NaCl和8 mmol·L−1 NaHCO3的MS培养基中,野生型拟南芥的根生长受到明显抑制,而转化了羊草LcNHX1基因的拟南芥株系的生长状态明显优于野生型[9]。过表达盐地碱蓬SsNHX1基因的转基因玉米植株在NaCl质量分数增加至1%时表现出较低的生长迟缓和生理损伤,与野生型相比在叶片中积累了更多的Na+和K+[10]。上述结果表明液泡膜Na+/H+逆向转运蛋白可以提高植物对盐碱胁迫的耐受能力。蚕豆(Vicia faba L.)是世界上最重要的豆科作物之一[11]。与鹰嘴豆(Cicer arietinum)、豌豆(Pisum sativum)和兵豆(Vicia lens)等其他冷季豆类相比,其高蛋白质含量(干物质的18%~35%)使其成为满足未来蛋白质需求的合适候选作物[12]。【本研究切入点】蚕豆生物固氮率高,是很好的轮作恢复作物,作为绿肥还田后还能改善土壤结构和肥力[13],能够很好地改良盐碱土地。但在谷物豆类中,蚕豆对非生物胁迫特别敏感,经常遭受严重的产量损失。目前,关于蚕豆耐盐基因NXH家族的序列和功能分析尚未见报道。因此,克隆和鉴定蚕豆液泡膜Na+/H+逆向转运蛋白基因,对了解蚕豆的耐盐机制具有重要意义。【拟解决的关键问题】本研究结合课题组前期蚕豆耐盐转录组数据,以蚕豆种质2014-04为材料,扩增获得蚕豆VfNHX1基因,对其进行生物信息学分析、基因表达特性分析、亚细胞定位分析和功能验证,以期为解析蚕豆VfNHX1响应盐胁迫分子机制及耐盐蚕豆育种提供理论依据。
1. 材料与方法
1.1 植物材料
参试材料由青海大学农林科学院提供,课题组前期通过相对发芽率及平均隶属函数划分耐盐等级等方法筛选后发现蚕豆材料2014-04属于耐盐性优良的蚕豆种质资源。容易经过盐分诱导而获得盐分响应基因,因此本研究选用2014-04为试验材料。选取长势一致的幼苗,分别用0、50、100、 150 mmol·L−1 NaCl处理7 d后发现:在100 mmol·L−1 NaCl处理时,参试蚕豆的生理及表型与对照组有明显的区别,浓度大于100 mmol·L−1时,蚕豆材料容易出现死亡表型,参考 Ouzounidou等[14]的研究结果,本研究将100 mmol·L−1 NaCl作为后续基因克隆及实时荧光定量表达分析所用材料的处理浓度。
用蒸馏水浸种4 d,待种子出芽后移栽至装有等量营养土和蛭石(体积比为 2∶1)的花盆中,生长在16 h/8 h光周期下,光照强度为 250 μmol·m2·s−1,温度为 24 ℃,湿度70%。待完全长出两对真叶后开始盐处理,对照组和处理组各设置3个重复,以蒸馏水为对照,用100 mmol·L−1 NaCl 溶液直接浇灌于花盆中,以花盆中土壤全部浸透而盐溶液不外渗为标准。经课题组前期预试验并参考陈江飞[15]和唐欣[16]等的研究结果,本研究选取 0 、4、8、12、24、48 h为处理时间,于处理后取叶和根保存于−80 ℃保存备用,用于基因克隆及实时荧光定量。
1.2 试验方法
1.2.1 RNA提取及cDNA合成
使用天根多糖多酚总RNA提取试剂盒提取蚕豆叶片和根部组织总RNA,用超微量核酸蛋白测定仪(NanoPhotometer® NP80,IMPLEN)检测RNA浓度和纯度,选取OD260/OD280在1.8~2.1(高质量RNA的标准)之间的RNA,用1.0%琼脂糖凝胶电泳检测其完整性;最后使用Prime Script TM II 1st cDNA Synthesis Kit将 RNA 反转录合成 cDNA 。合成的cDNA通过内参引物检测cDNA 质量,挑选条带单一且清晰的cDNA于−20 ℃保存备用。
1.2.2 VfNHX1基因的克隆
以cDNA为模板,设计克隆蚕豆VfNHX1基因中间片段的引物(表1),PCR反应条件:95 ℃,8 min;95 ℃,30 s、55.5 ℃,30 s、72 ℃,70 s、30个循环;72 ℃,10 min。反应结束后将PCR产物电泳检测,切下目的片段使用琼脂糖凝胶DNA回收试剂盒(增强型,天根)做胶回收,并连接到pTOPO载体进行测序分析(引物合成与测序均由天津金唯智公司完成),获得中间片段。
表 1 VfNHX1基因克隆及荧光定量PCR引物Table 1. Primers for VfNHX1 cloning and qRT-PCR引物名称
Primer引物序列
Primer sequence (5′→3′)用途
ApplicationNHX1-127F CTTGAGGAGAATCGGTGGATGAA 中间片段克隆
Intermediate fragment cloningNHX1-1270R GTGCTTGTGATCATGATTGCATTG 中间片段克隆
Intermediate fragment cloningNHX1-5′-GSP1 CGTAAGCACTGAGCAGACCTGTCAAAACGC 5′第一轮引物
5′ first round primersNHX1-5′-NGSP1 GGTGTCTCGTCTTGATTTAGCACCTGCAACG 5′第二轮引物
5′ second round primersNHX1-3′-GSP2 CAAGCACTCTCCTTGGCGTTTTGACAGGTC 3′第一轮引物
3′ first round primersNHX1-3′-NGSP2 CCTGTCGTTTGTTGCCGAGATCTTCATCTTCC 3′第二轮引物
3′ second round primersUPM CTAATACGACTCACTATAGGGCAAGCAGTGGTATCAACGCAGAGT 3′5′第一轮引物
3′5′ first round primersUPS CTAATACGACTCACTATAGGGC 3′5′第二轮引物
3′5′ second round primersNHX1-438F TGATGCTACCTCAGTGGTGCTT 荧光定量PCR
qRT-PCRNHX1-622R AGTGCCTGCCAATGTAGAGC 荧光定量PCR
qRT-PCRELF1A-F GTGAAGCCCGGTATGCTTGT 内参基因
Reference geneELF1A-R CTTGAGATCCTTGACTGCAACATT 内参基因
Reference gene设计引物(表1),以合成的5′、3′-RACE-Ready cDNA为模板,分别扩增蚕豆VfNHX1基因的5′片段和3′片段,反应程序采用降落PCR技术。反应条件:94 ℃,30 s、72 ℃,3 min、5个循环;94 ℃,30 s、70 ℃,30 s、72 ℃,3 min、5个循环;72 ℃,30 s、58 ℃,30 s、72 ℃,3 min、25个循环。反应结束后凝胶电泳检测,切胶回收后构建载体测序,将得到的序列用DNAMAN软件拼接后获得蚕豆VfNHX1基因完整序列。
1.2.3 实时荧光定量PCR(qRT-PCR)
使用实时荧光定量PCR仪(LightCycler®480,Roche)检测VfNHX1基因在蚕豆根、叶中的表达,选用蚕豆ELF1A基因为内参基因(表1),荧光定量PCR引物见表1。反应条件:94 ℃预变性30 s;94 ℃变性5 s,60 ℃退火30 s,40个循环;94 ℃,5 s,60 ℃,1 min;50 ℃降温30 s。每个样品设置3个重复,应用2−ΔΔCt方法[17]计算VfNHX1基因相对表达量,用LSD法(图11同)分别对叶和根的相对表达量进行多重比较,使用Excel进行数据处理与绘图。
1.2.4 生物信息学分析
使用生物信息学分析在线工具(表2)对VfNHX1蛋白的跨膜区、保守结构域、蛋白序列信号肽、亚细胞定位、二级结构、三级结构及理化性质进行预测分析。在NCBI查找与VfNHX1基因同源的其他物种的相关序列,利用 DNAMAN 软件对所获得的序列进行多序列比对后在MEGA11.0软件中用Neighbor-Joining(NJ)法构建进化树。
表 2 生物信息学分析网站Table 2. Bioinformatics analysis website用途 Function 网址 Website 蛋白质信号肽分析
Analysis of protein signal peptidehttps://services.healthtech.dtu.dk/services/signalp-6.0/ 蛋白质跨膜结构
Protein transmembrane structurehttp://pfam-legacy.xfam.org/ 蛋白质亚细胞定位
Protein subcellular localizationhttp://www.csbio.sjtu.edu.cn/bioinf/plant-multi/ 保守结构域分析
Conservative domain analysishttps://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/Structure/cdd/wrpsb.cgi 蛋白质二级结构预测
Protein secondary structure predictionhttps://npsaprabi.ibcp.fr/cgibin/npsa_automat.pl?page=npsa%20_sopma.html 蛋白质三级结构预测
Protein tertiary structure predictionhttps://swissmodel.expasy.org 蛋白质理化性质
Physicochemical properties of proteinhttps://web.expasy.org/protparam/ 数据可视化
Data visualizationhttps://www.chiplot.online/ 1.2.5 亚细胞定位
使用Primer Premier 5.0确定pBI121-EGFP质粒及VfNHX1基因CDS序列(去除终止密码子)的双酶切位点并设计带保护碱基的特异性引物。使用高保真酶进行 PCR扩增后用Xba I和Sma I双酶切目的基因和载体,用T4连接酶4 ℃过夜连接(连接比,V载体∶V目的基因=3∶1)。将连接产物转化进大肠杆菌感受态细胞DH5α,在含有卡那霉素(50 µg·mL−1)的LB固体培养板上进行抗性筛选,挑取单菌落进行菌液PCR验证和双酶切验证,选取条带合适的菌落重新摇菌后使用天根快速质粒小提试剂盒提质粒并送测序。
将测序结果正确的融合载体转入农杆菌感受态细胞GV3101中,在LB固体培养板上进行抗性筛选。挑取阳性克隆接种于含有50 µg·mL−1利福平、卡那霉素和40 µg·mL−1硫酸庆大霉素的LB液体培养基中,28 ℃过夜培养后离心富集菌体。将菌体重悬于预先配置好的诱导培养基中(200 mmol·L−1,MgCl2 10 mmol·L−1,MES 10 mmol·L−1,乙酰丁香酮(Acetosyringone, AS)),选取4周龄的本氏烟草(Nicotiana benthamiana)叶片,使用无针头的注射器缓慢将菌液注入烟草叶片背部下表皮细胞。黑暗条件下培养24 h后,光照培养48 h,使用激光共聚焦显微镜(NIKON A1R+)进行亚细胞定位观察。
1.2.6 酵母生长试验
为了在酵母中研究VfNHX1基因的功能,将VfNHX1基因构建到酵母表达载体pDR196上(融合载体的构建方法同上,本次双酶切位点为Sma I和Eco RI,抗性筛选使用氨苄霉素),并转化进对盐分高度敏感的突变型酵母AXT4K(ena1-4Δ::HIS3, nha1Δ::LEU2, nhx1Δ:: TRP1, kha1Δ::KanMX6)中,同时转化空载体pDR196作为阴性对照。将用于生长试验的酵母菌株起始浓度调整为OD600 nm=0.12,十倍梯度稀释(100、101、102、103)后吸取4 μL菌液分别点在含有0、150、200 mmol·L−1 NaCl 的 YPD 板上,置于 30 ℃培养箱内培养3 d。液体酵母试验步骤同上,将涂板步骤改为将梯度稀释后的菌液4 μL加入含有10 mL YPD液体培养基(NaCl浓度同上)的15 mL离心管中于恒温摇床中培养(30 ℃,180 r·min−1),设置3个重复,每隔12 h取样250 μL点样于96孔板中(3个重复),使用赛默飞Varioskan LUX多功能酶标读数仪测样品OD600 nm值,共测72 h,使用Excel处理数据并绘图。
2. 结果与分析
2.1 VfNHX1基因的克隆
前期获得的RNA和cDNA如图1和图2所示,扩增得到的中间片段目的条带和3′ -RACE和5′-RACE扩增产物电泳结果如图3所示。切胶构建载体测序后将得到的3段序列拼接并分析发现:蚕豆VfNHX1基因cDNA全长
2 255 bp,包含1个完整的ORF,CDS编码区1 629 bp,位于第315~1943 bp处;5′-UTR序列305 bp,3′-UTR序列323 bp;编码542个氨基酸;对其编码的蛋白在NCBI数据库比对后发现该蛋白属于NHX蛋白家族。2.2 VfNHX1同源蛋白序列比对及系统发育进化关系分析
VfNHX1蛋白进化树如图4所示,蚕豆VfNHX1蛋白与紫花苜蓿(Mcdicago sative)MsNHX1蛋白及其亚种镰刀紫花苜蓿(Mcdicago sative supsb.) MssNHX1蛋白进化关系最近;其次,蚕豆VfNHX1与木豆(Cajanus cajan)CcNHX1蛋白以及大豆(Glycinc max)GmNHX1蛋白的进化关系较近。对蚕豆VfNHX1蛋白和亲缘关系较近物种的蛋白质多序列比对(图5)后发现:其蛋白序列与紫花苜蓿(ADB27460.1)、木豆(XP_020209643.1)、大豆(NP_001237166.2)氨基酸序列相似度最高,分别为93.36%、 86.72%和86.63%。
2.3 VfNHX1蛋白的理化性质及氨基酸组成
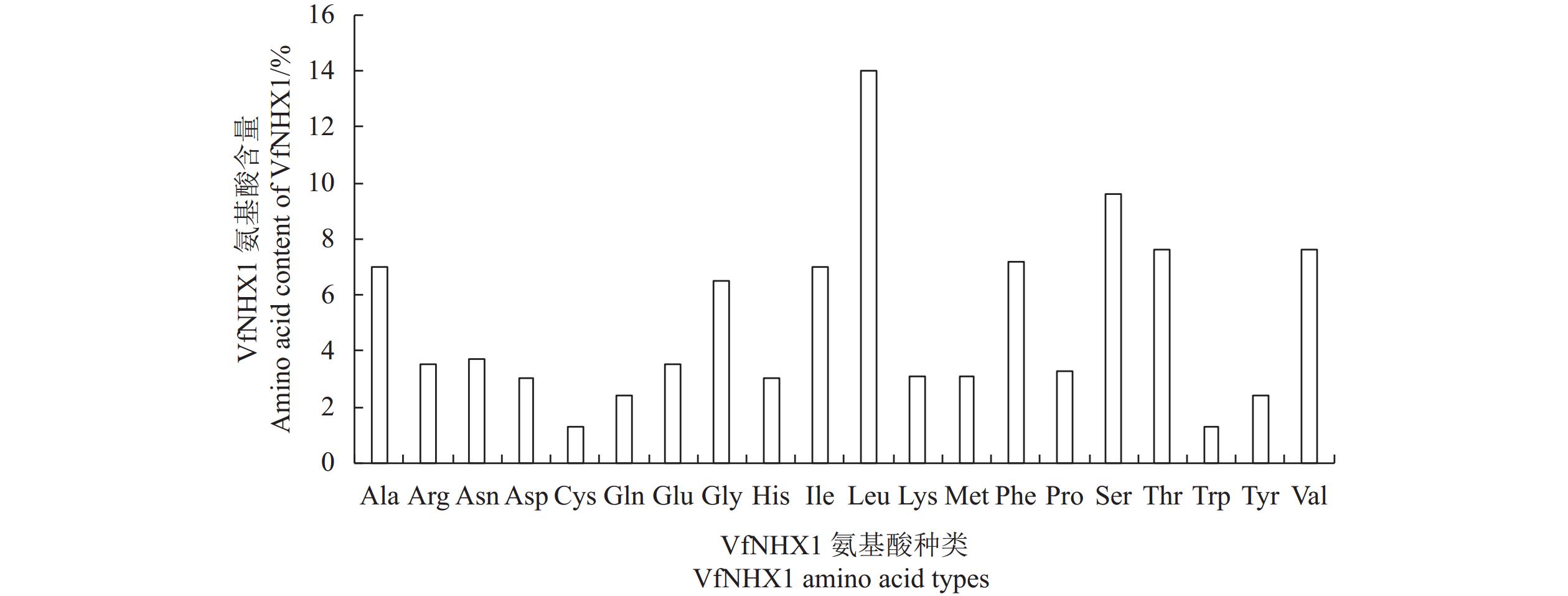
利用Expasy-Prot Param tool对VfNHX1蛋白的理化分析结果表明,其相对分子质量为59.81 kDa,理论等电点为7.70;氨基酸组成如图6所示,其中亮氨酸含量最多(76, 14.0%),丝氨酸次之(52, 9.6%);再次为苏氨酸、缬氨酸(41, 7.6%);苯丙氨酸(39, 7.2%);丙氨酸、异亮氨酸(38, 7.0%)。不稳定指数为36.57,说明该蛋白较稳定。
2.4 VfNHX1蛋白的跨膜结构、信号肽及保守结构域分析
利用SignalP-6.0软件分析结果显示VfNHX1蛋白序列没有信号肽存在,且不属于分泌蛋白(图7A)。TMHMM和Pfam软件进行蛋白跨膜结构分析表明,VfNHX1含有10个跨膜结构域,各跨膜结构位置如(图7B)蓝色下划线所示,其中N端在细胞质膜一侧的概率为
0.9555 。利用CDD和Chiplot在线软件对VfNHX1蛋白的保守结构域进行分析后发现,VfNHX1蛋白的第47~445个氨基酸之间包含一个Na+/H+逆向转运蛋白所特有的Na-H Exchanger结构域(图7C),该结构域内有4个Na+/H+ exchanger signature,其对应的氨基酸序列位置如图7B红色标记部分所示。2.5 蚕豆VfNHX1的蛋白结构分析
利用SOPMA在线软件进行二级结构预测,结果显示VfNHX1蛋白二级结构是以α-螺旋(43.36%)和无规则卷曲(34.13%)为主,其次延伸链(19.0%)、β-转角(3.51%)(图8A);用SWISS-MODEL在线软件预测蛋白的三级结构(图8B),发现VfNHX1三级结构与编码Na+/H+逆向转运蛋白的Q0IJ87.1.A(大豆)模型结构相似,相似度高达88.31%,覆盖度为0.77。
2.6 VfNHX1亚细胞定位分析
先使用PSORT/Plant-mPLocserver-SJTU预测发现VfNHX1定位在液泡膜,为进一步确定VfNHX1的亚细胞定位情况,经转化烟草进行瞬时表达分析, 结果显示VfNHX1蛋白定位在液泡膜上(图9),与预测结果一致。表明 VfNHX1 蛋白主要在液泡膜中发挥功能。综上所述,VfNHX1是一个定位于液泡膜上的Na+/H+逆向转运蛋白。
2.7 VfNHX1基因的表达分析
实时荧光定量PCR检测VfNHX1在蚕豆不同组织中的表达结果如图10所示,在100 mmol·L−1的NaCl胁迫下,随着盐胁迫处理时间延长,VfNHX1基因在叶片中的相对表达量呈现波浪形变化趋势,在盐处理12 h时达到了峰值,随后随着处理时间的延长呈现下降趋势;根中的相对表达量在处理时间到达48 h时显著上调(P<0.01),约为叶中该基因相对表达量的8倍。结果表明蚕豆VfNHX1基因的表达受盐胁迫调控,且表现出组织差异性。
2.8 VfNHX1在酵母中的功能研究
酵母生长试验结果如图11显示,酵母突变体AXT4K在含有NaCl的固体培养介质上长势较差,而同等条件下野生型酵母W303-1B可以正常生长,表达了VfNHX1的酵母突变体AXT4K长势优于AXT4K(图11A);酵母液体生长试验显示表达了VfNHX1的酵母突变体AXT4K的生长曲线明显优于AXT4K(图11B)。以上结果表明,VfNHX1可以提高酵母盐敏感突变体AXT4对盐胁迫的耐受能力,暗示其可能在酵母细胞内调节Na+的动态平衡。
3. 讨论与结论
研究表明,Na+/H+逆向转运蛋白定位在质膜(如冬箭筈豌豆 NHX1[18]和滨豇豆 VmNHX [19])、液泡膜(如长叶红砂RtNHX1[20]和珠美海棠Mz2NHX1[21])或内膜(如拟南芥的AtNHX5-6[22])上,是依赖跨膜离子梯度的在植物Na+稳态方面起重要作用的跨膜转运蛋白[23]。定位在不同位置上的Na+/H+逆向转运蛋白对Na+的转运效果不同,已有研究结果表明编码液泡膜Na+/H+逆向转运蛋白的基因过表达入模式植物拟南芥后比质膜Na+/H+逆向转运蛋白对植株耐盐性的改善贡献大,其耐盐育种开发潜力也最大[6]。本研究结果表明,VfNHX1定位于液泡膜并在其上发挥功能的典型Na+/H+逆向转运蛋白。
植物通过根部吸收水分和营养物质以维持正常生长,其生长发育是环境与基因共同作用的结果,也是植物最先遭受逆境胁迫的部位,而叶片是液泡集中和发挥区隔化作用的主要器官[24]。在盐胁迫下,NHX1通常表现为转录上调响应,但主要表达部位不同,如藜麦CqNHX1[25]、高糖甜菜 BvNHX1[26]以及烟草NtNHX1[27]等基因主要在叶片中表达,而筇竹QtNHX1[28]和海马齿 SpNHX1[29]基因在根中的表达量较高。为了解蚕豆VfNHX1基因在盐胁迫下的表达特点,本研究中NaCl 处理后,蚕豆根中VfNHX1表达量在各个时间段均表现出显著上调或下调,而叶片中该基因的表达在8 h和12 h无明显变化,这说明VfNHX1基因的表达具有组织特异性,表明蚕豆主要通过根部细胞液泡膜上的Na+/H+逆向转运蛋白响应盐胁迫。
酿酒酵母作为一种在实验系统研究方面具有许多内在优势的模式生物,为高等真核生物基因的异源表达提供一个检测系统[30]。通过酵母试验已明确NHX1直接参与Na+转运过程,不同植物来源NHX1基因的转入,可恢复nhx1缺失型酵母菌株的Na+转运功能[9,31−32]。因此,利用酵母异源表达系统对蚕豆NHX1进行功能验证,仍有重要意义。蚕豆VfNHX1可以使突变体酵母菌株AXT4K在含150 mmol·L−1 NaCl或200 mmol·L−1 NaCl的YPD培养基上恢复生长,与对照组相比,显著增加了其对NaCl胁迫的耐受性,说明VfNHX1基因能够恢复突变体酵母菌株AXT4K对Na+转运功能。
综上所述,试验结果初步表明VfNHX1参与蚕豆盐胁迫响应过程,是蚕豆潜在抗盐功能基因。然而,蚕豆VfNHX1在盐胁迫过程的具体作用方式仍需进一步的转基因试验证实。蚕豆目前没有再生体系,在未来的研究工作中,我们将在拟南芥中异源表达VfNHX1基因,进一步鉴定VfNHX1基因功能特性。
-
表 1 VfNHX1基因克隆及荧光定量PCR引物
Table 1 Primers for VfNHX1 cloning and qRT-PCR
引物名称
Primer引物序列
Primer sequence (5′→3′)用途
ApplicationNHX1-127F CTTGAGGAGAATCGGTGGATGAA 中间片段克隆
Intermediate fragment cloningNHX1-1270R GTGCTTGTGATCATGATTGCATTG 中间片段克隆
Intermediate fragment cloningNHX1-5′-GSP1 CGTAAGCACTGAGCAGACCTGTCAAAACGC 5′第一轮引物
5′ first round primersNHX1-5′-NGSP1 GGTGTCTCGTCTTGATTTAGCACCTGCAACG 5′第二轮引物
5′ second round primersNHX1-3′-GSP2 CAAGCACTCTCCTTGGCGTTTTGACAGGTC 3′第一轮引物
3′ first round primersNHX1-3′-NGSP2 CCTGTCGTTTGTTGCCGAGATCTTCATCTTCC 3′第二轮引物
3′ second round primersUPM CTAATACGACTCACTATAGGGCAAGCAGTGGTATCAACGCAGAGT 3′5′第一轮引物
3′5′ first round primersUPS CTAATACGACTCACTATAGGGC 3′5′第二轮引物
3′5′ second round primersNHX1-438F TGATGCTACCTCAGTGGTGCTT 荧光定量PCR
qRT-PCRNHX1-622R AGTGCCTGCCAATGTAGAGC 荧光定量PCR
qRT-PCRELF1A-F GTGAAGCCCGGTATGCTTGT 内参基因
Reference geneELF1A-R CTTGAGATCCTTGACTGCAACATT 内参基因
Reference gene表 2 生物信息学分析网站
Table 2 Bioinformatics analysis website
用途 Function 网址 Website 蛋白质信号肽分析
Analysis of protein signal peptidehttps://services.healthtech.dtu.dk/services/signalp-6.0/ 蛋白质跨膜结构
Protein transmembrane structurehttp://pfam-legacy.xfam.org/ 蛋白质亚细胞定位
Protein subcellular localizationhttp://www.csbio.sjtu.edu.cn/bioinf/plant-multi/ 保守结构域分析
Conservative domain analysishttps://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/Structure/cdd/wrpsb.cgi 蛋白质二级结构预测
Protein secondary structure predictionhttps://npsaprabi.ibcp.fr/cgibin/npsa_automat.pl?page=npsa%20_sopma.html 蛋白质三级结构预测
Protein tertiary structure predictionhttps://swissmodel.expasy.org 蛋白质理化性质
Physicochemical properties of proteinhttps://web.expasy.org/protparam/ 数据可视化
Data visualizationhttps://www.chiplot.online/ -
[1] 罗达, 宋锋惠, 卢明艳, 等. 盐胁迫对平欧杂种榛根系生理生化特性的影响 [J]. 东北林业大学学报, 2024, 52(4):29−33,45. DOI: 10.3969/j.issn.1000-5382.2024.04.005 LUO D, SONG F H, LU M Y, et al. Effects of salt stress on the physiological and biochemical characteristics of ping’ou hybrid hazelnut root systems [J]. Journal of Northeast Forestry University, 2024, 52(4): 29−33,45. (in Chinese) DOI: 10.3969/j.issn.1000-5382.2024.04.005
[2] SHELKE D B, NIKALJE G C, CHAMBHARE M R, et al. Na+ and Cl− induce differential physiological, biochemical responses and metabolite modulations in vitro in contrasting salt-tolerant soybean genotypes [J]. 3 Biotech, 2019, 9(3): 91. DOI: 10.1007/s13205-019-1599-6
[3] 朱晨晨, 史昆, 何沁坤, 等. 混合盐碱胁迫对紫花苜蓿幼苗生理和基因表达的影响 [J]. 草地学报, 2024, 32(4):1044−1054. ZHU C C, SHI K, HE Q K, et al. Effects of mixed saline-alkali stress on physiology and gene expression of alfalfa seedlings [J]. Acta Agrestia Sinica, 2024, 32(4): 1044−1054. (in Chinese)
[4] ZHANG H L, YU F F, XIE P, et al. A Gγ protein regulates alkaline sensitivity in crops [J]. Science, 2023, 379(6638): eade8416. DOI: 10.1126/science.ade8416
[5] KUMAR A, SINGH S, GAURAV A K, et al. Plant growth-promoting bacteria: Biological tools for the mitigation of salinity stress in plants [J]. Frontiers in Microbiology, 2020, 11: 1216. DOI: 10.3389/fmicb.2020.01216
[6] KARIM R, BOUCHRA B, FATIMA G, et al. Plant NHX antiporters: From function to biotechnological application, with case study [J]. Current Protein & Peptide Science, 2021, 22(1): 60−73.
[7] 万玺宏, 张会龙, 朱建峰, 等. 液泡膜转运蛋白在植物耐盐性调控中的作用 [J]. 植物生理学报, 2024, 60(2):295−310. WAN X H, ZHANG H L, ZHU J F, et al. The role of tonoplast transporters in the regulation of salt tolerance in plants [J]. Plant Physiology Journal, 2024, 60(2): 295−310. (in Chinese)
[8] 银芳柳, 毛晓菲, 曾幼玲. 盐生植物盐爪爪液泡膜钠氢反向运输载体基因(KfNHX1)遗传转化拟南芥的耐盐性鉴定 [J]. 新疆农业科学, 2021, 58(3):565−572. YIN F L, MAO X F, ZENG Y L. Salt-tolerant identification of genetic transformation in Arabidopsis with the KfNHX1 gene from the halophyte Kalidium foliatum [J]. Xinjiang Agricultural Sciences, 2021, 58(3): 565−572. (in Chinese)
[9] 李晓薇, 郭嘉, 王鑫, 等. 羊草液泡膜Na+/H+逆向转运蛋白基因LcNHX1的克隆及功能分析 [J]. 中国草地学报, 2017, 39(5):1−9. LI X W, GUO J, WANG X, et al. Cloning and functional analysis of a vacuolar Na+/H+ antiporter gene LcNHX1 from Leymus chinensis [J]. Chinese Journal of Grassland, 2017, 39(5): 1−9. (in Chinese)
[10] HUANG Y, ZHANG X X, LI Y H, et al. Overexpression of the Suaeda salsa SsNHX1 gene confers enhanced salt and drought tolerance to transgenic Zea mays [J]. Journal of Integrative Agriculture, 2018, 17(12): 2612−2623. DOI: 10.1016/S2095-3119(18)61998-7
[11] BIMURZAYEV N, SARI H, KURUNC A, et al. Effects of different salt sources and salinity levels on emergence and seedling growth of faba bean genotypes [J]. Scientific Reports, 2021, 11: 18198. DOI: 10.1038/s41598-021-97810-6
[12] NASRALLAH A K, ATIA M A M, ABD EL-MAKSOUD R M, et al. Salt priming as a smart approach to mitigate salt stress in faba bean (Vicia faba L. ) [J]. Plants, 2022, 11(12): 1610. DOI: 10.3390/plants11121610
[13] ÁLVAREZ-IGLESIAS L, PUIG C G, REVILLA P, et al. Faba bean as green manure for field weed control in maize [J]. Weed Research, 2018, 58(6): 437−449. DOI: 10.1111/wre.12335
[14] OUZOUNIDOU G, ILIAS I F, GIANNAKOULA A, et al. Effect of water stress and NaCl triggered changes on yield, physiology, biochemistry of broad bean (Vicia faba) plants and on quality of harvested pods [J]. Biologia, 2014, 69(8): 1010−1017. DOI: 10.2478/s11756-014-0397-1
[15] 陈江飞, 余津铭, 杨建坤, 等. 茶树Na+/H+逆向转运蛋白基因CsNHX1、CsNHX2的克隆及表达分析 [J]. 茶叶科学, 2018, 38(6):559−568. DOI: 10.3969/j.issn.1000-369X.2018.06.002 CHEN J F, YU J M, YANG J K, et al. Cloning and expression analysis of Na+/H+Antiporter gene CsNHX1 and CsNHX2 in tea plant(Camellia sinensis) [J]. Journal of Tea Science, 2018, 38(6): 559−568. (in Chinese) DOI: 10.3969/j.issn.1000-369X.2018.06.002
[16] 唐欣, 王瑞辉, 杨秀艳, 等. 唐古特白刺液泡膜Na+/H+逆向运输蛋白基因NtNHX1的克隆与表达分析 [J]. 林业科学, 2014, 50(3):38−44. TANG X, WANG R H, YANG X Y, et al. Isolation and expression analysis of a vacuolar membrane Na+/H+ antiporter gene NtNHX1 from Nitraria tangutorum [J]. Scientia Silvae Sinicae, 2014, 50(3): 38−44. (in Chinese)
[17] 陈心仪, 吴成英, 贺海皓, 等. 滇水金凤4CL基因的克隆及表达分析 [J]. 福建农业学报, 2024, 39(1):40−48. CHEN X Y, WU C Y, HE H H, et al. Cloning and expression of 4CLs in Impatiens uliginosa [J]. Fujian Journal of Agricultural Sciences, 2024, 39(1): 40−48. (in Chinese)
[18] 姚娜, 云岚, 艾芊, 等. 冬箭筈豌豆耐盐基因NHX1克隆及表达分析[J]. 草地学报, 2024, 32(5): 1401-1409 YAO N, YUN L, AI Q, et al. Cloning and expression analysis of salt-tolerant gene NHX1 in Vicia villosa Roth[J]. Acta Agrestia Sinica, 2024, 32(5): 1401-1409. (in Chinese)
[19] 李霞, 孔丹宇, 刘传鑫, 等. 滨豇豆VmNHX基因克隆与表达分析 [J]. 分子植物育种, 2024, 22(2):402−413. LI X, KONG D Y, LIU C X, et al. Cloning and expression analysis of VmNHX gene in Vigna marina [J]. Molecular Plant Breeding, 2024, 22(2): 402−413. (in Chinese)
[20] 董禄禄, 秦晓春, 党振华. 长叶红砂液泡膜Na+/H+逆向转运蛋白基因的克隆及表达特性 [J]. 西北植物学报, 2015, 35(11):2164−2170. DOI: 10.7606/j.issn.1000-4025.2015.11.2164 DONG L L, QIN X C, DANG Z H. Isolation and expression of vacuolar membrane Na+/H+ antiporter gene in reaumuriatrigyna [J]. Acta Botanica Boreali-Occidentalia Sinica, 2015, 35(11): 2164−2170. (in Chinese) DOI: 10.7606/j.issn.1000-4025.2015.11.2164
[21] 张永利, 孟晓烨, 孙婷梅, 等. 珠美海棠Mz 2NHX1基因的克隆和序列分析 [J]. 江苏农业科学, 2015, 43(9):20−25. ZHANG Y L, MENG X Y, SUN T M, et al. Cloning and sequence analysis of Mz 2NHX1 gene from Malus jumeiensis [J]. Jiangsu Agricultural Sciences, 2015, 43(9): 20−25. (in Chinese)
[22] 邱全胜. 拟南芥NHX5和NHX6: 离子平衡与蛋白质运输 [J]. 中国科学: 生命科学, 2017, 47(8):839−846. DOI: 10.1360/N052016-00351 QIU Q S. Arabidopsis NHX5 and NHX6: Ion homeostasis and protein transport [J]. Scientia Sinica (Vitae), 2017, 47(8): 839−846. (in Chinese) DOI: 10.1360/N052016-00351
[23] 李源, 蔡勤安, 马瑞, 等. 植物Na+/H+逆向转运蛋白研究进展 [J]. 山东农业科学, 2022, 54(10):143−152. LI Y, CAI Q A, MA R, et al. Research progress of plant Na+/H+ antiporter [J]. Shandong Agricultural Sciences, 2022, 54(10): 143−152. (in Chinese)
[24] 边晨凯, 龙定沛, 刘雪琴, 等. 桑树Na+/H+逆向转运蛋白基因(MnNHX1)的克隆与耐盐力表达 [J]. 林业科学, 2015, 51(8):16−25. BIAN C K, LONG D P, LIU X Q, et al. Cloning and expression to salt stress of Na+/H+ antiporter gene(MnNHX1) in mulberry tree [J]. Scientia Silvae Sinicae, 2015, 51(8): 16−25. (in Chinese)
[25] 许浩宇, 赵颖, 阮倩, 等. 不同混合盐碱下藜麦幼苗的抗性研究 [J]. 草业学报, 2023, 32(1):122−130. DOI: 10.11686/cyxb2021500 XU H Y, ZHAO Y, RUAN Q, et al. Resistance of quinoa seedlings under different salt-alkali stress levels [J]. Acta Prataculturae Sinica, 2023, 32(1): 122−130. (in Chinese) DOI: 10.11686/cyxb2021500
[26] 李宁宁, 孙亚卿, 李国龙. 高糖甜菜BvNHX1基因的克隆及表达特性分析 [J]. 分子植物育种, 2021, 19(16):5250−5257. LI N N, SUN Y Q, LI G L. Cloning and expression analysis of BvNHX1 from beta vulgaris with high sucrose [J]. Molecular Plant Breeding, 2021, 19(16): 5250−5257. (in Chinese)
[27] 高玉龙, 宋中邦, 李梅云, 等. 烟草NtNHX1-3基因的克隆及表达特性 [J]. 西北植物学报, 2018, 38(12):2201−2206. DOI: 10.7606/j.issn.1000-4025.2018.12.2201 GAO Y L, SONG Z B, LI M Y, et al. Cloning and expression characteristics of tobacco NtNHX1-3 Gene [J]. Acta Botanica Boreali-Occidentalia Sinica, 2018, 38(12): 2201−2206. (in Chinese) DOI: 10.7606/j.issn.1000-4025.2018.12.2201
[28] 李玥, 肖如雪, 芮蕊, 等. 筇竹Na+/H+逆向转运蛋白基因克隆与表达分析 [J]. 分子植物育种, 2021, 19(10):3235−3242. LI Y, XIAO R X, RUI R, et al. Cloning and expression analysis on QtNHX1 gene from Qiongzhuea tumidinoda [J]. Molecular Plant Breeding, 2021, 19(10): 3235−3242. (in Chinese)
[29] 喻珊, 胡艳平, 丛心黎, 等. 海马齿Na+/H+逆转运蛋白基因SpNHX1的克隆及表达模式 [J]. 热带生物学报, 2015, 6(2):127−133. DOI: 10.3969/j.issn.1674-7054.2015.02.004 YU S, HU Y P, CONG X L, et al. Isolation and expression analysis of Na+/H+ antiporter gene SpNHX1 from Sesuvium portulacastrumand L. [J]. Journal of Tropical Biology, 2015, 6(2): 127−133. (in Chinese) DOI: 10.3969/j.issn.1674-7054.2015.02.004
[30] 王立光, 陈军, 叶春雷, 等. 酿酒酵母BJ3505 NHX1基因突变株的构建及功能验证 [J]. 生物技术通报, 2018, 34(12):152−158. WANG L G, CHEN J, YE C L, et al. Mutant construction and functional validation of NHX1 in Saccharomyces cerevisiae BJ3505 [J]. Biotechnology Bulletin, 2018, 34(12): 152−158. (in Chinese)
[31] 刘威, 李慧, 蔺经, 等. 杜梨PbNHX1基因的克隆、表达分析及功能验证 [J]. 果树学报, 2018, 35(2):137−146. LIU W, LI H, LIN J, et al. Cloning, expression and functional analysis of PbNHX1 gene in Pyrus betulaefolia [J]. Journal of Fruit Science, 2018, 35(2): 137−146. (in Chinese)
[32] 赵云霞, 郭丹丽, 魏艳玲, 等. 新疆无苞芥Na+/H+逆向转运蛋白基因OpNHX1的克隆、表达分析与功能验证 [J]. 生物技术通报, 2014, (7):74−80. ZHAO Y X, GUO D L, WEI Y L, et al. Cloning, expressing and functional analysis of Na+/H+ antiporter gene OpNHX1 from Olimarabidopsis pumila in Xinjiang [J]. Biotechnology Bulletin, 2014(7): 74−80. (in Chinese)




 下载:
下载: