Application of Bacillus subtilis B2-GFP to Promote Growth of Sweet Pepper Seedlings
-
摘要:目的 筛选能促进甜椒幼苗生长的枯草芽孢杆菌B2-GFP菌株发酵液适宜浓度,为研发菌肥作用于蔬菜提供依据。方法 以甜椒硕源808为材料,设置枯草芽孢杆菌B2-GFP菌株发酵液T1(1×105 CFU·mL−1)、T2(1×106 CFU·mL−1)、T3(1×107 CFU·mL−1)、T4(1×108 CFU·mL−1)4个浓度梯度处理,每隔7 d向植株浇灌菌株发酵液,连续浇灌3次,每次每株浇灌5 mL,21 d时测定甜椒幼苗生长指标、生物量积累、叶片光合特性、叶绿素荧光参数、根系抗氧化酶活性、根系形态建成及根系活力指标。结果 与对照相比,不同浓度枯草芽孢杆菌B2-GFP菌株发酵液可提高甜椒株高、叶面积、叶绿素含量、植株生物量,以1×106 CFU·mL−1的增幅最大。同时,该浓度显著提高了叶片蒸腾速率(Tr)、气孔导度(Gs)、最大荧光(Fm)、PSⅡ实际光化学效率(ФPSⅡ)和光化学荧光猝灭系数(qP),降低了胞间CO2浓度(Ci)和叶绿素基础荧光(Fo);提高甜椒根系过氧化物酶(POD)、过氧化氢酶(CAT)、超氧化物歧化酶(SOD)、苯丙氨酸解氨酶(PAL)、多酚氧化酶(PPO)活性及根系活力。结论 在甜椒移栽后浇灌1×106 CFU·mL−1B2-GFP菌株发酵液可促进甜椒植株生长和根系形态建成,增强叶片光合能力,提高生物量积累、根系抗氧化酶活性和根系活力。Abstract:Objective Effects of applying Bacillus subtilis B2-GFP culture broth on the growth and physiology of sweet pepper seedlings were studied.Methods In a pot experiment, seedlings of sweet pepper Shuoyuan 808 were treated with B. subtilis B2-GFP culture broths at the concentrations of 1×105 CFU·mL−1 (T1), 1×106 CFU·mL−1 (T2), 1×107 CFU·mL−1 (T3), and 1×108 CFU·mL−1 (T4), along with non-treatment control (CK). The transplanted sweet pepper seedlings were given 5 mL 1×106CFU·mL−1 B2-GFP culture broth every 7 d for 3 times. Growth index, biomass accumulation, leaf photosynthesis, and chlorophyll fluorescence parameters as well as antioxidant enzyme activities, morphological formation, and root vitality of the plants were monitored at 21 d.Results Application of the B2-GFP culture broth increased the plant height and biomass as well as the leaf area and chlorophyll content over CK. The greatest effect was observed under T2, which also accentuated the leaf transpiration rate (Tr), stomatal conductance (Gs), maximum fluorescence (Fm), photosystem II potential Activity (ФPSⅡ), and photochemical fluorescence quenching coefficient (qP) as well as the activities of peroxidase (POD), catalase (CAT), superoxide dismutase (SOD), phenylalanine ammonia lyase (PAL), and polyphenol oxidase (PPO) in the roots but reduced the intercellular CO2 concentration (Ci) and chlorophyll basic fluorescence (Fo).Conclusion When the transplanted sweet pepper seedlings were given 1×106 CFU·mL−1 B2-GFP culture broth, all monitored indicators on the plant growth and root development including leaf photosynthetic parameters and biomass and root antioxidant enzymes activities and vitality were significantly improved in 3 weeks.
-
Keywords:
- Bacillus subtilis /
- sweet pepper /
- growth /
- physiology /
- photosynthesis
-
0. 引言
【研究意义】甜椒(Capsicum frutescens L.)隶属于茄科(Solanaceae)辣椒属(Capsicum),味道温和不辣,其果实富含多种生物活性物质,具备重要的营养和药用特性[1],备受消费者喜爱。近年来,其栽培面积一直呈上升趋势[2],在我国大部分地区都有种植[3],有效推动了甜椒产业的快速发展。甜椒产业化生产具有高度集约化、复种指数高、作物种类单一和肥料施用量大等特点[4,5],随着社会生活水平的提升,人们对甜椒品质的期望也不断提高,大量施用化肥不符合绿色蔬菜种植要求,利用生物肥料替代传统化肥有望推动有机和可持续农业的发展,展现出广阔的发展前景[6]。枯草芽孢杆菌(Bacillus subtilis)是一种促进植物生长的根际细菌,了解其发酵液对甜椒生长和生理特性的具体影响,有助于优化其应用方式,提高甜椒生长发育速度和产量。【前人研究进展】枯草芽孢杆菌是一种常见的、广泛分布在自然环境中的细菌。它可以通过合成植物生长调节剂如:吲哚乙酸(IAA)、细胞分裂素(CTK)、脱落酸(ABA)和可溶性磷酸盐促进莴苣(Lactuca sativa L.)生长[7];菌株TBWR1能显著促进烟草(Nicotiana tabacum L.)株高、叶长、茎围生长和根系生物量增加[8];枯草芽孢杆菌悬浮种衣剂有助于促使辣椒(Capsicum annuum L.)壮苗[9];还可以通过拮抗作用实现生物防治效果,接种枯草芽孢杆菌生物膜对莴苣病原体表现出抗真菌活性[7];菌株TBWR1对烟草青枯病有明显抑制作用,防效达71.1%[8];Y116菌株展现出对核盘菌(Sclerotinia sclerotiorum)生长和菌核形成的显著抑制效果,表明其在防治向日葵(Helianthus annuus)菌核病方面具备潜在的生物防控能力[10]。枯草芽孢杆菌具有诱导植物启动防御机制的能力,能够增强植物对逆境的抵抗能力,从而有助于提高作物的生存率和产量。胡金雪等指出枯草芽孢杆菌对马铃薯疮痂病(Potato common scab)的防效越好,产量越高[11];KRS015的无细胞发酵提取物可作为一种潜在的防治棉花黄萎病(Verticillium dahliae)促生长剂[12];枯草芽孢杆菌表现出对尖孢镰刀菌(Fusarium oxysporum)的生物控制能力,有效保护鹰嘴豆(Cicer)免受病害的侵袭[13]。枯草芽孢杆菌LY-1能保护花生(Arachis hypogaea)免受镰孢菌(Fusarium)的侵染[14]。枯草芽孢杆菌不仅在降低农作物病害发生、提高作物抗性、保护生态环境方面发挥着重要作用,同时在提升农作物产品品质和食品安全方面表现出独特不可替代的效果,因此展现出良好的发展前景。【本研究切入点】目前有关枯草芽孢杆菌B2-GFP在甜椒上的应用效果及其适宜的浓度尚不明确。【拟解决的关键问题】本试验研究不同浓度枯草芽孢杆菌B2-GFP对甜椒幼苗生长和生理特性的影响,旨在为其在甜椒生产上的合理利用提供理论依据。
1. 材料与方法
1.1 试验材料
供试甜椒品种为硕源808,由北京硕源种子有限公司生产;供试菌株为枯草芽孢杆菌B2-GFP,由河南科技大学园艺与植物保护学院烟草行业黄淮烟区烟草病虫害绿色防控重点实验室提供;供试蔬菜育苗基质由莘县益农育苗基质有限公司生产;供试肥料为发酵腐熟纯羊粪,由洛阳农友农业科技有限公司生产;供试土壤采自河南科技大学田园(112°24′59″E,34°36′2″N),为黄壤土,有机质1.145%,全氮1.107%,全磷0.024%,全钾2.906%,pH8.3。
1.2 试验方法
1.2.1 菌株活化及菌液制备
将保存的枯草芽孢杆菌B2-GFP菌株划线接种于LB固体培养基中活化培养24 h,取菌饼转接到LB液体培养基于摇床中振荡培养(30 ℃,200 r·min−1)3 d制成发酵液;用血球计数板计算发酵液浓度,用无菌水将发酵液稀释至1×105、1×106、1×107、1×108 CFU·mL−1。
1.2.2 不同浓度B2-GFP菌株发酵液浇灌甜椒幼苗
将甜椒种子温汤浸种后催芽,种子露白后播于108孔育苗穴盘中,每穴1粒,待幼苗长至4叶1心时移栽到10 cm×10 cm的营养钵中,营养土的土肥比例为7∶3。缓苗后分别给甜椒苗浇灌发酵液,设4个处理,T1、T2、T3、T4分别为1×105、1×106、1×107、1×108 CFU·mL−1,浇灌清水作为对照(CK),每处理20株,重复3次。每隔7 d浇灌1次,每株浇灌量5 mL。21 d时每处理选8株测定各项指标。
1.3 项目测定
1.3.1 生长指标
用直尺测量幼苗基质表面至最高处的高度,记为株高;用游标卡尺测量幼苗基部上方1 cm处的茎直径,记为茎粗;用直尺测量幼苗从上往下第2片完全展开真叶的最大长度、宽度,叶面积的计算公式:叶面积=叶片最大长度×最大宽度×0.75。使用便携式叶绿素测量仪SPAD PLUS对相对叶绿素含量进行测定。
1.3.2 生物量
用清水将甜椒植株清洗干净,吸水纸吸干表面水分,分离地上部和地下部,用天平测定各部分鲜质量;置于烘箱中,先于105 ℃杀青30 min,再85 ℃烘干至恒重,称其干质量。
1.3.3 叶片光合特性
晴天上午10:00选甜椒幼苗顶部第2片完全展开的真叶,使用Li-6400(美国)便携式植物光合作用测定仪对叶片测定净光合速率(Pn)、蒸腾速率(Tr)、气孔导度(Gs)及胞间二氧化碳浓度(Ci)。光强1000 μmol·m−2·s−1,叶温25 ℃,空气湿度60%,叶室CO2浓度为大气CO2浓度。
1.3.4 叶绿素荧光参数
晴天中午12:00选甜椒幼苗顶部第2片完全展开的真叶,提前暗适应25 min,用FluorPen FP110叶绿素荧光测定仪(瞬时脉冲30%,最大脉冲70%)测定叶绿素基础荧光(Fo)、可变荧光(Fv)、最大荧光(Fm)、PSⅡ最大光能转换效率(Fv/Fm)、光化学荧光猝灭系数(qP)、非光化学猝灭效率(NPQ)和PSⅡ实际光化学效率(ФPSⅡ)。
1.3.5 根系抗氧化酶活性
将甜椒根系清洗干净,吸水纸吸干表面水分,参考李合生[15]的方法测定过氧化物酶(POD)、超氧化物歧化酶(SOD)、过氧化氢酶(CAT)、苯丙氨酸解氨酶(PAL)的活性,抗坏血酸过氧化物酶(APX)活性参考Nakano等[16]的方法测定,多酚氧化酶(PPO)活性参考石连旋等[17]的方法测定。
1.3.6 根系生长指标
将甜椒根系清洗干净,使用EPSON根系扫描仪对植物的根系进行分析,包括总根长、根系总表面积、根系总体积、总根尖数、分枝数等指标。
1.3.7 根系活力
将甜椒根系清洗干净,用吸水纸吸干表面水分,参考刘新[18]的TTC法测定。
1.4 数据统计分析
采用Excel 2019软件记录数据,采用IBM SPSS Statistics 26(SPSS Inc,美国)统计软件进行差异显著性分析(P<0.05),用GrapPad Prism 10.1软件作图。
2. 结果与分析
2.1 枯草芽孢杆菌B2-GFP菌株发酵液对甜椒生长指标的影响
甜椒植株的株高、茎粗、叶面积和叶绿素含量可直接反映甜椒的生长状态。从表1可看出,不同浓度枯草芽孢杆菌B2-GFP菌株发酵液处理的甜椒在株高、茎粗、叶面积、叶绿素含量方面与对照均存在差异,其中T2的株高最大,比CK增加22.52%,其次是T1,T4的植株增高效果最小,仅比CK增加1.68%;且T2的茎粗最大,与T1、T3、T4处理的茎粗均有显著差异,T1、T3、T4处理的茎粗均小于CK。T1、T2、T3处理的植株叶面积均与CK有显著性差异,T4与CK差异不显著,且T2处理的植株叶面积最大,比CK增加10.57%;各处理的叶绿素含量均高于CK,T2与CK有显著性差异,T1、T3、T4处理与CK差异均不显著。因此,T2可促进甜椒叶片的生长和叶绿素的积累。
表 1 枯草芽孢杆菌B2-GFP菌株发酵液对甜椒生长指标的影响Table 1. Effect of B2-GFP culture broth application on growth of sweet pepper seedlings处理
Treatment株高
Plant height/cm茎粗
Stem diameter/mm叶面积
Leaf area/cm2叶绿素相对含量
SPADCK 11.90±0.10 d 4.05±0.20 ab 15.79±0.55 c 45.69±0.26 b T1 13.60±0.24 b 3.94±0.10 bc 18.07±1.09 b 47.42±0.79 ab T2 14.58±0.27 a 4.35±0.20 a 20.62±1.16 a 48.12±1.09 a T3 12.98±0.26 c 3.53±0.20 d 18.06±1.19 b 47.67±0.82 ab T4 12.10±0.17 d 3.60±0.25 cd 16.69±0.88 bc 47.58±1.54 ab 同列不同小写字母表示在0.05水平的差异显著性。下表同。
Data with different lowercase letters on same column indicate significant differences at P<0.05. Same for below.2.2 枯草芽孢杆菌B2-GFP菌株发酵液对甜椒生物量的影响
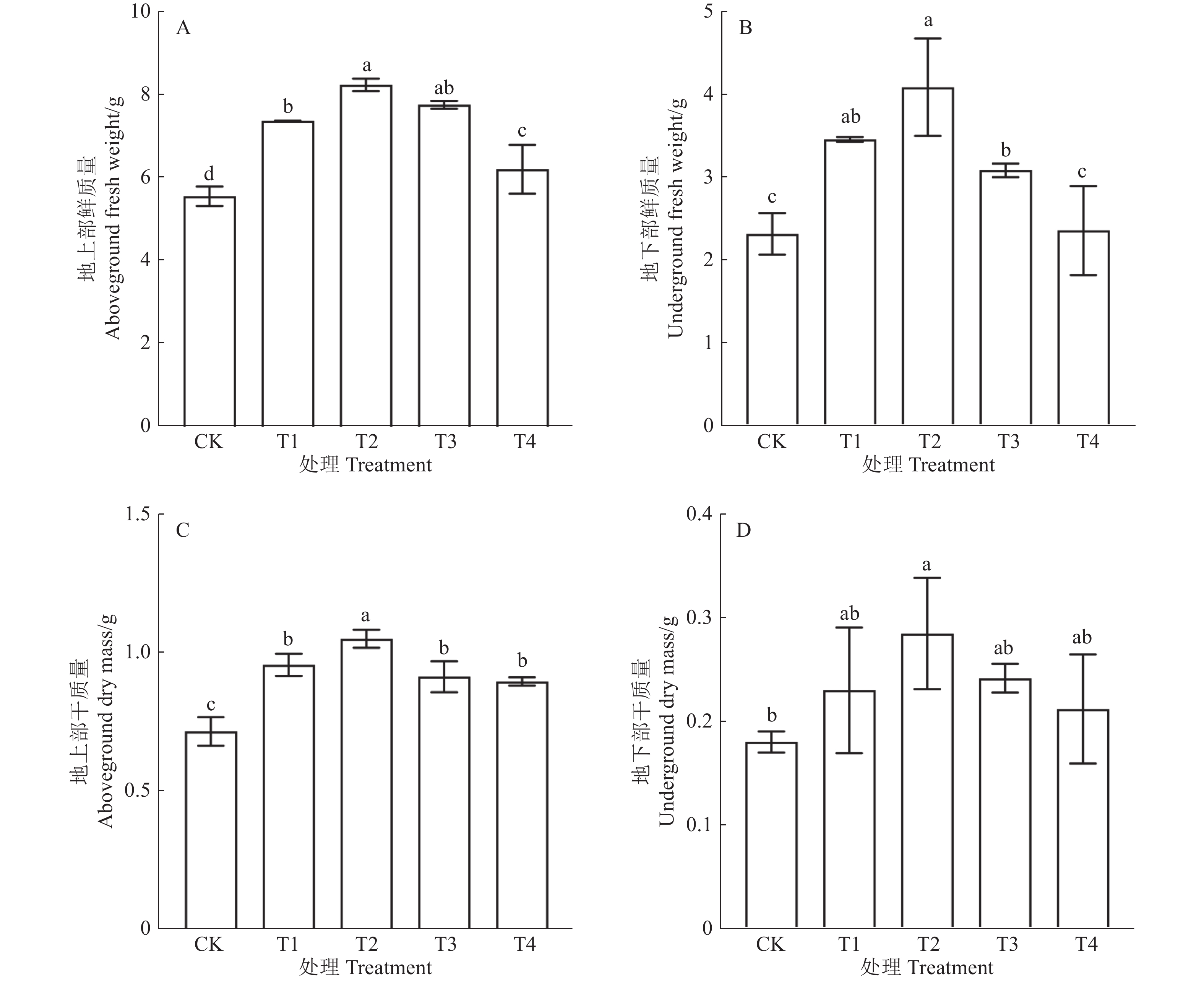
由图1可知,不同浓度枯草芽孢杆菌B2-GFP发酵液灌根处理对甜椒生物量的影响不同。T2的甜椒植株地上和地下部鲜质量及干质量均显著高于CK。各处理的地上部鲜质量均显著高于CK,T2的甜椒植株地上部鲜质量最大,比CK高48.05%,与T1、T4处理差异均达显著水平(图1A);T1、T2、T3处理的甜椒植株地下部鲜质量均显著高于CK,T2的地下部鲜质量最大,比CK高76.15%,T4与CK差异不显著(图1B);各处理植株的地上部干质量都与CK有显著性差异,且T2的地上部干质量最大,比CK高46.74%,与T1、T3、T4差异均显著(图1C);不同处理的植株地下部干质量积累存在差异,但只有T2显著高于CK,比CK高57.96%,CK和T2与T1、T3、T4处理的差异均不显著(图1D)。可见,T2可显著促进甜椒生物量的积累,T4对甜椒地下部生物量的积累促进效果不明显。
2.3 枯草芽孢杆菌B2-GFP菌株发酵液对甜椒叶片光合特性的影响
从图2可以看出,不同浓度B2-GFP菌株发酵液对甜椒叶片光合特性的影响有差异。各处理的叶片净光合速率与对照相比,只有T2与CK有显著性差异,比CK提高63.02%,且T2与T1、T3、T4均有显著性差异(图2A);T2、T3的叶片蒸腾速率均与CK有显著性差异,且T2与其他处理也有显著性差异(图2B);T2、T3的叶片气孔导度均与CK有显著性差异,且T2的叶片气孔导度最大,与对照相比显著提高69.87%,T2与其他处理均有显著性差异(图2C);T1、T2、T3的叶片胞间二氧化碳浓度与CK相比均显著降低,T4与CK之间没有显著性差异,T2的叶片胞间二氧化碳浓度最低,比CK降低9.41%(图2D)。由此说明,T2增强甜椒叶片光合作用效果最好,T4对甜椒叶片光合作用的影响效果较差。
2.4 枯草芽孢杆菌B2-GFP菌株发酵液对甜椒叶片叶绿素荧光参数的影响
从表2可知,与CK相比,T2处理的甜椒叶片Fo显著性降低11.72%;T2、T3处理的Fm均与CK差异性显著,T2数值最大,比CK增加17.64%;各处理的Fv/Fm与CK相比均无显著性差异,T2的值最大,为0.831;T1、T2、T3处理的ФPSⅡ值均比CK大,T2显著提高3.65%;随B2-GFP菌株发酵液浓度的增加qP的值呈现出先升高再降低的趋势,T2的值最大,比CK显著性增加4.48%;各处理的NPQ与CK差异均不显著。T2处理的Fm、ФPSⅡ、Fv/Fm、qP、NPQ数值均比CK高,表明T2处理能降低甜椒叶片非辐射能量和热耗散,提高光合电子链中电子的传递速率。
表 2 枯草芽孢杆菌B2-GFP菌株发酵液对甜椒叶片叶绿素荧光参数的影响Table 2. Effect of B2-GFP culture broth on leaf chlorophyll fluorescence parameters of sweet pepper seedlings处理
Treatment叶绿素基础
荧光Fo最大荧光
FmPSⅡ最大光能
转换效率Fv/FmPSⅡ实际光
化学效率ΦPSⅡ光化学荧光
猝灭系数qP非光化学
猝灭效率NPQCK 3995±140 a 19308±1632 b 0.825±0.004 abc 0.520±0.008 bc 0.67±0.006 b 1.54±0.13 a T1 3811±95 ab 20334±1103 ab 0.827±0.006 ab 0.533±0.012 ab 0.69±0.006 a 1.57±0.25 a T2 3576±197 b 22714±1638 a 0.831±0.001 a 0.539±0.006 a 0.70±0.012 a 1.81±0.16 a T3 3818±163 ab 22610±496 a 0.820±0.002 c 0.525±0.004 abc 0.65±0.015 c 1.94±0.08 a T4 3822±146 ab 21450±2207 ab 0.822±0.001 bc 0.511±0.014 c 0.64±0.010 c 1.69±0.40 a 2.5 枯草芽孢杆菌B2-GFP菌株发酵液对甜椒根系抗氧化酶活性的影响
从图3可以看出,不同浓度枯草芽孢杆菌B2-GFP菌株发酵液对甜椒根系抗氧化酶活性的影响不同。T1、T2、T4处理的甜椒根系POD活性与CK均有显著性差异,且T2的根系POD活性最高,和对照相比,显著提高57.96%,T3与CK之间差异不显著(图3A);各处理对甜椒根系CAT活性的影响不同,除了T4,其他处理均与CK有显著性差异,T2与CK、T1、T3、T4均有显著性差异,与对照相比,显著性提高196.72%(图3B);各处理与对照相比,虽然甜椒根系SOD活性均比CK高,但只有T3与CK之间存在显著性差异,且T3与T1之间也有显著性差异(图3C);T1、T2、T4处理的甜椒根系APX活性均与CK有显著性差异,其中T2相比于CK显著提高50.00%(图3D);T1、T2、T3处理的甜椒根系PAL活性均与CK有显著性差异,T2的甜椒根系PAL活性最大,与CK相比显著提高96.19%,T4与CK之间差异不显著(图3E);各处理的甜椒根系PPO活性与CK之间均有显著性差异,T1、T2之间差异不显著,T1和T2均与T3、T4有显著性差异(图3F)。所以,各处理都有提高甜椒根系抗氧化酶活性的作用,以T2的效果最佳。
2.6 枯草芽孢杆菌B2-GFP菌株发酵液对甜椒根系生长特性的影响
从表3可知,T2处理的甜椒根系总根长最长,为564.47 cm,与CK、T3、T4的差异均显著,T2与T1差异不显著,而T4的甜椒根系总根长比CK短;T1的甜椒根系总表面积最大,为74.20 cm2,其次是T2,T1与T2的差异不显著,T1与CK、T3、T4的差异均显著,T3和T4的甜椒根系总表面积均小于CK;T2的根系总体积最大,与CK、T3、T4的差异均显著,与T1的差异不显著;T2的甜椒根系根尖数与其他处理之间的差异均显著,CK、T1、T3、T4四者间差异均不显著;各处理的根系分叉数有差异,其中T2的根系分叉数最多,与T4有显著性差异;T4的各项根系生长指标均小于CK。同时期甜椒根系的扫描图见图4。由此说明,T2对甜椒幼苗根系的形态建成有促进作用,且效果最好;而T4对甜椒根系生长表现出抑制效果。
表 3 枯草芽孢杆菌B2-GFP菌株发酵液对甜椒根系生长特性的影响Table 3. Effect of B2-GFP culture broth on growth of sweet pepper seedling roots处理
Treatment总根长
Length/cm根总表面积
Surf area/cm2根系总体积
Root volume/cm3根尖数
Tips分叉数
ForksCK 435.24±41.12 b 55.16±5.93 b 0.642±0.092 bc 1737±175 b 2024±651 ab T1 498.32±57.70 ab 74.20±11.64 a 0.757±0.075 ab 1401±182 b 1802±405 ab T2 564.47±48.07 a 70.96±9.45 ab 0.881±0.110 a 2179±273 a 2607±768 a T3 449.93±85.85 b 53.31±7.19 b 0.631±0.134 bc 1553±112 b 2039±793 ab T4 388.92±35.59 b 53.39±9.88 b 0.543±0.097 c 1543±218 b 1405±426 b 2.7 枯草芽孢杆菌B2-GFP菌株发酵液对甜椒根系活力的影响
从图5可知,T2的根系活力最大,为1.828 mg·g−1·h−1,是CK的1.83倍、T1的1.25倍、T3的1.31倍、T4的1.43倍,T2与CK、T1、T3、T4均有显著性差异,TI、T3与CK差异均显著,T4与CK无显著性差异。说明各处理都能提高甜椒幼苗的根系活力,且T2效果最佳。
3. 讨论与结论
在苗期对甜椒进行浇灌不同浓度的B2-GFP菌株发酵液,其产生的影响各有差异。本试验中1×106 CFU·mL−1(T2)B2-GFP菌株发酵液对植株的营养生长有较大的促进作用,使植株更高大粗壮、叶面积增大、叶绿素含量提高、光合特性增强,抗氧化酶活性增强,增强根系活力及促进根系形态建成。试验中1×108 CFU·mL−1(T4)对植株茎粗的生长产生抑制作用,对植株生物量的积累、光合特性、抗氧化酶活性均没有显著增强效果,而且对甜椒根系的生长表现出抑制作用,对根系活力的影响不显著。推测T4的浓度太高,一种可能是高浓度的枯草芽孢杆菌会释放抗生素等抗菌物质,抑制根系正常菌群的生长,影响甜椒幼苗的根系发育、养分吸收和生理代谢,导致甜椒幼苗生长迟缓;另一种可能是高浓度的枯草芽孢杆菌会与甜椒幼苗争夺养分和生长空间,这种竞争会阻止甜椒幼苗获得足够的养分和水分,致使甜椒幼苗生长受限;还有一种可能是枯草芽孢杆菌在高浓度下会产生有毒的代谢产物,直接影响甜椒的光合作用,从而影响甜椒幼苗生长发育。因此,在不同植物上应用枯草芽孢杆菌时,需要合理控制施用浓度,避免造成不利影响。
另外,枯草芽孢杆菌还能恢复过酸过碱的土壤[19],使种植在盐碱地里的冬小麦(Triticum aestivuml)品质和产量得到提升[20]。邱萌萌等[21]研究指出,枯草芽孢杆菌能抑制茄链格孢菌(Alternaria solani)和灰葡萄孢菌(Botrytis cinerea)的生长,且能大大改善土壤真菌菌群的群落结构。枯草芽孢杆菌还对于十字花科(Brassicaceae)作物的肿根病(Clubroot)[22]、西红柿(Solanum lycopersicum)的青枯病(Ralstonia solanacearum)[23]有抑制作用。该试验使用的盆栽土壤是首次用于甜椒的种植,所有处理均未发现甜椒枯萎病(Fusarium oxysporum)、立枯病(Rhizoctonia solani Kuhn)等土传病害,后续将进一步验证B2-GFP菌株发酵液对甜椒土传病害的预防作用。
综上,在甜椒移栽后每隔7 d浇灌一次,连灌3次,每次每株浇灌1×106 CFU·mL−1 B2-GFP菌株发酵液5 mL,对甜椒幼苗的生长有促进作用,同时能增强光合作用,加快根系形态建成,提高根系抗氧化酶活性以及根系活力。该法经济实惠且用量较少,符合我国目前绿色农业减肥减药的政策,适宜推广。
-
表 1 枯草芽孢杆菌B2-GFP菌株发酵液对甜椒生长指标的影响
Table 1 Effect of B2-GFP culture broth application on growth of sweet pepper seedlings
处理
Treatment株高
Plant height/cm茎粗
Stem diameter/mm叶面积
Leaf area/cm2叶绿素相对含量
SPADCK 11.90±0.10 d 4.05±0.20 ab 15.79±0.55 c 45.69±0.26 b T1 13.60±0.24 b 3.94±0.10 bc 18.07±1.09 b 47.42±0.79 ab T2 14.58±0.27 a 4.35±0.20 a 20.62±1.16 a 48.12±1.09 a T3 12.98±0.26 c 3.53±0.20 d 18.06±1.19 b 47.67±0.82 ab T4 12.10±0.17 d 3.60±0.25 cd 16.69±0.88 bc 47.58±1.54 ab 同列不同小写字母表示在0.05水平的差异显著性。下表同。
Data with different lowercase letters on same column indicate significant differences at P<0.05. Same for below.表 2 枯草芽孢杆菌B2-GFP菌株发酵液对甜椒叶片叶绿素荧光参数的影响
Table 2 Effect of B2-GFP culture broth on leaf chlorophyll fluorescence parameters of sweet pepper seedlings
处理
Treatment叶绿素基础
荧光Fo最大荧光
FmPSⅡ最大光能
转换效率Fv/FmPSⅡ实际光
化学效率ΦPSⅡ光化学荧光
猝灭系数qP非光化学
猝灭效率NPQCK 3995±140 a 19308±1632 b 0.825±0.004 abc 0.520±0.008 bc 0.67±0.006 b 1.54±0.13 a T1 3811±95 ab 20334±1103 ab 0.827±0.006 ab 0.533±0.012 ab 0.69±0.006 a 1.57±0.25 a T2 3576±197 b 22714±1638 a 0.831±0.001 a 0.539±0.006 a 0.70±0.012 a 1.81±0.16 a T3 3818±163 ab 22610±496 a 0.820±0.002 c 0.525±0.004 abc 0.65±0.015 c 1.94±0.08 a T4 3822±146 ab 21450±2207 ab 0.822±0.001 bc 0.511±0.014 c 0.64±0.010 c 1.69±0.40 a 表 3 枯草芽孢杆菌B2-GFP菌株发酵液对甜椒根系生长特性的影响
Table 3 Effect of B2-GFP culture broth on growth of sweet pepper seedling roots
处理
Treatment总根长
Length/cm根总表面积
Surf area/cm2根系总体积
Root volume/cm3根尖数
Tips分叉数
ForksCK 435.24±41.12 b 55.16±5.93 b 0.642±0.092 bc 1737±175 b 2024±651 ab T1 498.32±57.70 ab 74.20±11.64 a 0.757±0.075 ab 1401±182 b 1802±405 ab T2 564.47±48.07 a 70.96±9.45 ab 0.881±0.110 a 2179±273 a 2607±768 a T3 449.93±85.85 b 53.31±7.19 b 0.631±0.134 bc 1553±112 b 2039±793 ab T4 388.92±35.59 b 53.39±9.88 b 0.543±0.097 c 1543±218 b 1405±426 b -
[1] KAUR R, KAUR K, SIDHU J S. Drying kinetics, chemical, and bioactive compounds of yellow sweet pepper as affected by processing conditions [J]. Journal of Food Processing and Preservation, 2022, 46(3): e16330.
[2] 项朝阳, 肖小勇, 宋长鸣. 我国蔬菜产业当前的新特点、新问题及对策建议 [J]. 中国蔬菜, 2019, (1):1−6. XIANG Z Y, XIAO X Y, SONG C M. New characteristics, problems and countermeasures of vegetable industry in China [J]. China Vegetables, 2019(1): 1−6. (in Chinese)
[3] 张静. 露地栽培彩色甜椒霜霉病综合防治技术 [J]. 农村新技术, 2023, (7):24−26. DOI: 10.3969/j.issn.1002-3542.2023.07.012 ZHANG J. Integrated control techniques of downy mildew of colored sweet pepper cultivated in open field [J]. New Rural Technology, 2023(7): 24−26. (in Chinese) DOI: 10.3969/j.issn.1002-3542.2023.07.012
[4] HU W Y, ZHANG Y X, HUANG B, et al. Soil environmental quality in greenhouse vegetable production systems in eastern China: Current status and management strategies [J]. Chemosphere, 2017, 170: 183−195.
[5] 付丽军, 张爱敏, 王向东, 等. 生物有机肥改良设施蔬菜土壤的研究进展 [J]. 中国土壤与肥料, 2017, (3):1−5. DOI: 10.11838/sfsc.20170301 FU L J, ZHANG A M, WANG X D, et al. Research progress of bio-organic fertilizer in improving greenhouse vegetable soil [J]. Soil and Fertilizer Sciences in China, 2017(3): 1−5. (in Chinese) DOI: 10.11838/sfsc.20170301
[6] BASU A, PRASAD P, DAS S N, et al. Plant growth promoting rhizobacteria (PGPR) as green bioinoculants: Recent developments, constraints, and prospects [J]. Sustainability, 2021, 13(3): 1140.
[7] SARTI G C, GALELLI M E, ARREGHINI S, et al. Inoculation with biofilm of Bacillus subtilis promotes the growth of Lactuca sativa [J]. Sustainability, 2023, 15(21): 15406.
[8] 杨兴有, 丁安明, 余祥文, 等. 烟草青枯病拮抗菌TBWR1的筛选鉴定及防病促生能力 [J]. 贵州农业科学, 2023, 51(10):58−65. DOI: 10.3969/j.issn.1001-3601.2023.10.007 YANG X Y, DING A M, YU X W, et al. Screening and identification of antagonistic strain TBWR1 against tobacco bacterial wilt and its disease prevention and growth promotion ability [J]. Guizhou Agricultural Sciences, 2023, 51(10): 58−65. (in Chinese) DOI: 10.3969/j.issn.1001-3601.2023.10.007
[9] 胡晨曦, 肖洒, 陈刚, 等. 枯草芽孢杆菌悬浮种衣剂对辣椒幼苗生长和生理特性的影响 [J]. 福建农业学报, 2021, 36(9):1017−1024. DOI: 10.3969/j.issn.1008-0384.2021.9.fjnyxb202109004 HU C X, XIAO S, CHEN G, et al. Effects of seed-coating Bacillus subtilis suspension on growth and physiology of chili pepper seedlings [J]. Fujian Journal of Agricultural Sciences, 2021, 36(9): 1017−1024. (in Chinese) DOI: 10.3969/j.issn.1008-0384.2021.9.fjnyxb202109004
[10] 朱孔艳, 韩升才, 赵榕, 等. 向日葵籽粒拮抗核盘菌的内生菌分离筛选及鉴定 [J]. 作物杂志, 2023, (5):280−284. ZHU K Y, HAN S C, ZHAO R, et al. Isolation and identification of endophytes from sunflower seeds [J]. Crops, 2023(5): 280−284. (in Chinese)
[11] 胡金雪, 樊建英, 相丛超, 等. 枯草芽孢杆菌对马铃薯的促生防病效应 [J]. 中国瓜菜, 2023, 36(10):121−128. DOI: 10.3969/j.issn.1673-2871.2023.10.017 HU J X, FAN J Y, XIANG C C, et al. Effects of Bacillus subtilis on growth promotion and disease control of potato [J]. China Cucurbits and Vegetables, 2023, 36(10): 121−128. (in Chinese) DOI: 10.3969/j.issn.1673-2871.2023.10.017
[12] SONG J, WANG D, HAN D F, et al. Characterization of the endophytic Bacillus subtilis KRS015 strain for its biocontrol efficacy against Verticillium dahliae [J]. Phytopathology, 2024, 114(1): 61−72.
[13] RATHOD K, RANA S, DHANDHUKIA P, et al. Marine Bacillus subtilis as an effective biocontrol agent against Fusarium oxysporum f. sp. ciceris [J]. European Journal of Plant Pathology, 2023, 167(4): 759−770.
[14] LI Y, ZHANG X, HE K, et al. Isolation and identification of Bacillus subtilis LY-1 and its antifungal and growth-promoting effects [J]. Plants, 2023, 12(24): 4158.
[15] 李合生. 植物生理生化实验原理和技术[M]. 北京: 高等教育出版社, 2000. [16] NAKANO Y, ASADA K. Hydrogen peroxide is scavenged by ascorbate-specific peroxidase in spinach chloroplasts [J]. Plant and Cell Physiology, 1981, 22(5): 867−880.
[17] 石连旋, 颜宏. 植物生理学实验指导[M]. 北京: 高等教育出版社, 2013. [18] 刘新. 植物生理学实验指导[M]. 北京: 中国农业出版社, 2015. [19] 彭喜之, 王涛辉, 马珺怡, 等. 微生物菌剂对土壤酸碱性的改良研究[J]. 天津科技, 2021, 48(1):42-45, 48. PENG X Z, WANG T H, MA J Y, et al. Improvement of soil acidity and alkalinity by microbial agents[J]. Tianjin Science & Technology, 2021, 48(1): 42-45, 48. (in Chinese)
[20] 杨璐, 周蓓蓓, 侯亚玲, 等. 枯草芽孢杆菌菌剂对盐胁迫下冬小麦生长与土壤水氮分布的影响 [J]. 排灌机械工程学报, 2021, 39(5):517−524. YANG L, ZHOU B B, HOU Y L, et al. Effects of Bacillus subtilis on growth of winter wheat and distribution of soil water and nitrogen under salt stress [J]. Journal of Drainage and Irrigation Machinery Engineering, 2021, 39(5): 517−524. (in Chinese)
[21] 邱萌萌, 吴玉斌, 陆洪省. 枯草芽孢杆菌对土壤群落结构的影响 [J]. 南方农业, 2021, 15(3):179−181. QIU M M, WU Y B, LU H S. Effect of Bacillus subtilis on soil community structure [J]. South China Agriculture, 2021, 15(3): 179−181. (in Chinese)
[22] 张照然, 何朋杰, 李兴玉, 等. 枯草芽孢杆菌XF-1对十字花科作物体内异硫氰酸苯乙酯含量的影响 [J]. 江西农业学报, 2021, 33(1):23−27. ZHANG Z R, HE P J, LI X Y, et al. Effects of Bacillus subtilis XF-1 on phenethyl isothiocyanate concent in cruciferous crops [J]. Acta Agriculturae Jiangxi, 2021, 33(1): 23−27. (in Chinese)
[23] 甘金佳, 孙成荣, 尹华田, 等. 枯草芽孢杆菌可湿性粉剂防治西红柿青枯病的田间药效试验 [J]. 南方园艺, 2020, 31(6):38−41. DOI: 10.3969/j.issn.1674-5868.2020.06.008 GAN J J, SUN C R, YIN H T, et al. Field efficacy test of Bacillus subtilis wettable powder against tomato bacterial wilt [J]. Southern Horticulture, 2020, 31(6): 38−41. (in Chinese) DOI: 10.3969/j.issn.1674-5868.2020.06.008
-
期刊类型引用(1)
1. 张天翔,林秀香,郑涛,陈振东. 南方设施甜椒病虫害绿色防控技术. 福建热作科技. 2024(04): 50-53 .  百度学术
百度学术
其他类型引用(0)




 下载:
下载: