Establishing a Primary Core Collection of Chinese Yam Germplasms in Fujian
-
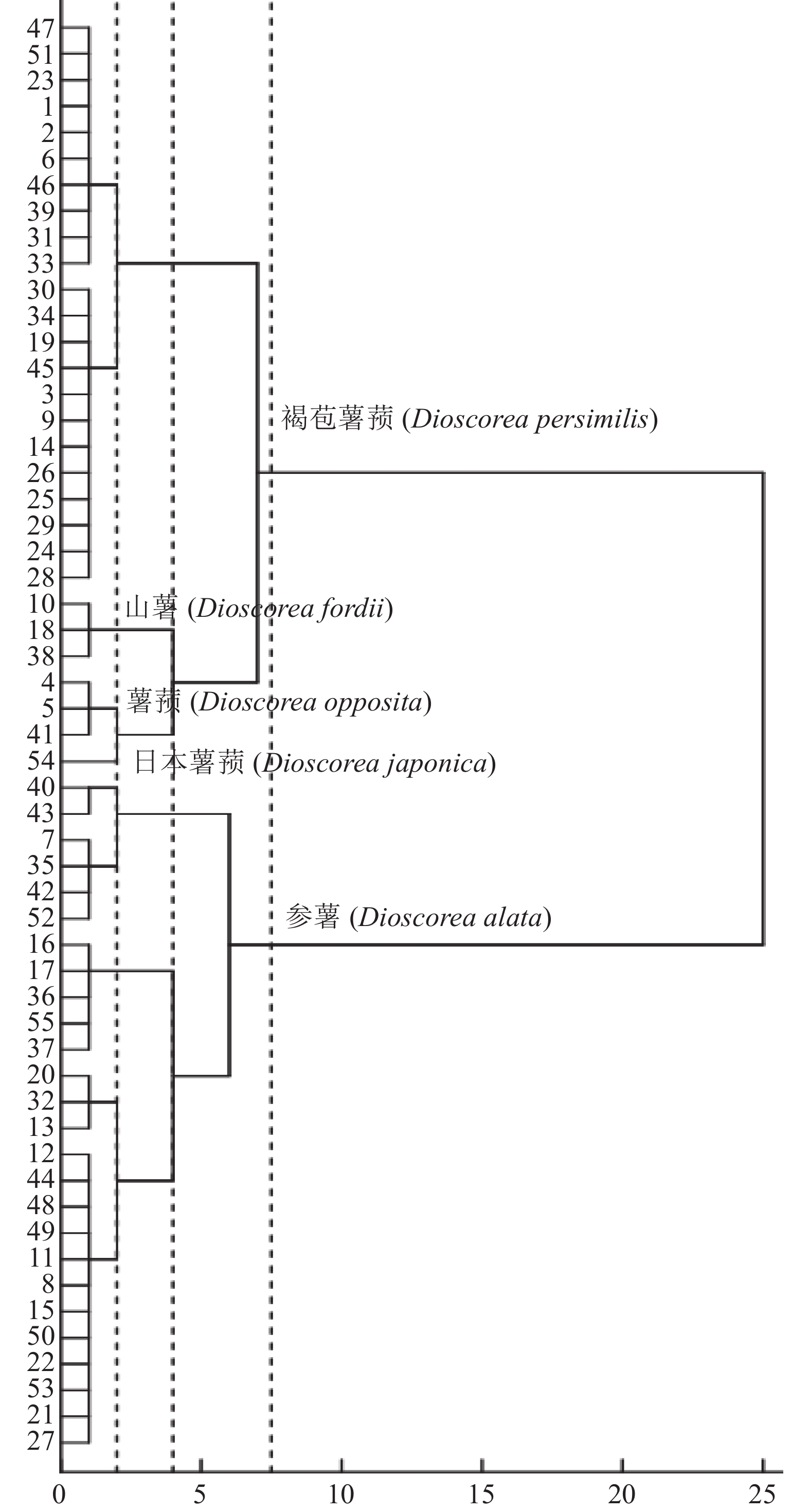
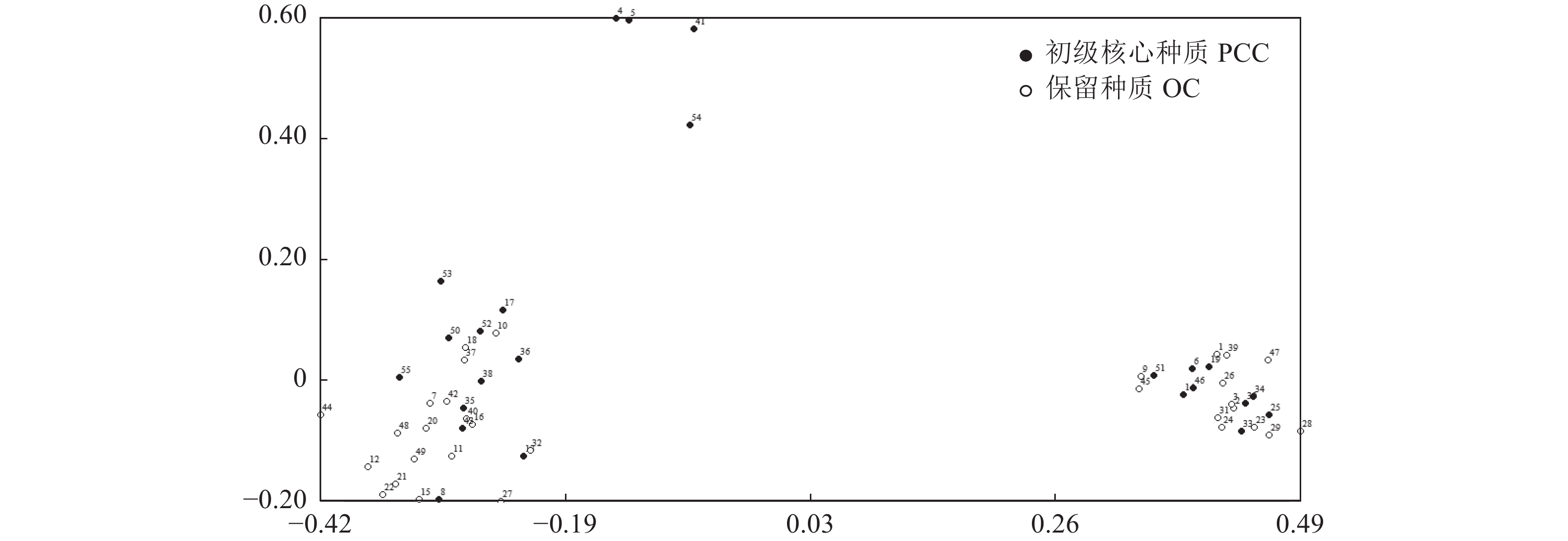
摘要:目的 构建福建省山药初级核心种质,为福建地方山药资源的保存、品种选育提供理论依据。方法 以55份福建省地方主栽山药资源为材料,调查20个农艺性状,包括7个数量性状和13个描述型性状,采用离差平方和法进行聚类,根据聚类结果采用优先取样法构建初级核心种质,同时采用统计学方法及ISSR分子标记等对其代表性进行评价。结果 构建的初级核心种质数量占原种质的43.6%,在降低冗余的同时保留了选育品种和有突出特点或地方特色的资源。初级核心种质和原种质各性状的均值、方差、变异系数、香农多样性指数无显著性差异。数量性状除茎粗外,核心种质保留了原种质变异范围的84.9%~100%。描述性指标除最弱的生长势外,核心种质保留了原种质的全部等级分布。初级核心种质和原种质的ISSR分子标记的等位基因数量、有效等位基因数量、香农多样性信息指数、Nei’s基因多样性指数无显著差异,且初级核心种质的多态位点保留率达到原种质的98.6%。基于农艺性状的主成分分析和基于ISSR分子标记的主坐标分析均确认了核心种质的代表性。结论 构建的福建省山药初级核心种质能够较好地代表原种质的遗传多样性,有助于福建地方山药资源的保存和开发利用。Abstract:Objective A primary core collection of Chinese yam germplasms in Fujian was established for conserving and breeding the natural resources.Method Fifty-five locally cultivated Chinese yams were categorized according to 7 quantitative and 13 descriptive traits. A cluster analysis was conducted on the data using the squared Euclidean distance method to develop a germplasm collection by priority sampling. The representativeness of the Primary Core Collection on Chinese Yams (PCCCY) was statistically evaluated using the agronomic traits as well as ISSR molecular markers.Result PCCCY received 43.6% of the previous collection. It reduced the redundancy of the old version but retained the breeding varieties as well as the germplasms of outstanding characteristics or unique local features. No significant differences were found in the means, variances, coefficients of variation, and Shannon-Wiener index between the PCCCY and the previous collection on various traits. On the quantitative traits, other than stem thickness, the PCCCY preserved 84.9% to 100% of the variation range of the previous collection. Whereas the entire original descriptive traits, except the weakest growth vigor, were kept intact. No significant differences in the number of ISSR molecular marker alleles, effective alleles, Shannon-Wiener index, and Nei’s genetic diversity index were found between the two collections. And 98.6% of the polymorphic loci in the original version were retained. The principal component analysis based on agronomic traits and the principal coordinate analysis based on ISSR molecular markers confirmed a high representativeness on the varieties by the newly established PCCCY.Conclusion The primary core collection established by this study for the Chinese yam germplasms in the province satisfactorily represented the genetic diversity of the natural resource. The PCCCY was deemed to facilitate future efforts in conserving and utilizing the local Chinese yam species.
-
Keywords:
- Chinese yam /
- primary core collection /
- agronomic traits /
- ISSR marker /
- Fujian Province
-
0. 引言
【研究意义】双孢蘑菇Agaricus bisporus又名蘑菇、白蘑菇、洋蘑菇等,属于担子菌门、担子菌纲、伞菌科、伞菌目、蘑菇属,是一种世界性栽培和消费的食药用菌[1-4]。闽南地区是国内双孢蘑菇生产的主产区[5],截至目前当地双孢蘑菇栽培仍以农户个体式的季节性生产为主,栽培菌株包括As2796、W192、福蘑38等,均是福建省农业科学院食用菌研究所选育品种;2010年前后陆续有人尝试利用空调等温控措施反季节栽培双孢蘑菇,目前工厂化生产双孢蘑菇运行较好的企业包括福建金明食品有限公司、漳州市新发生物科技有限公司、漳州市九冬蘑菇产业园等,栽培菌株几乎都是W192。尤其对工厂化生产企业,生产品种单一存在一定经营风险。未来双孢蘑菇生产的发展趋势必然是工厂化周年生产。随着市场的发展,对多样化、高品质的双孢蘑菇需求日益旺盛,亟需更多优良的双孢蘑菇品种。杂交育种是现代食用菌育种的常规手段, 也是目前较有效的育种方法[6-9]。杂交育种成功一个非常重要的关键因素是选择合适的亲本[10-13]。因此,收集拟用于育种的双孢蘑菇品种,评价其生物学性状,分析其遗传背景,可为后期的杂交育种亲本筛选提供依据。【前人研究进展】拮抗反应是体细胞不亲和性的具体表现[14],可用于食用菌遗传特异性的鉴定,日本的食用菌品种登记制度也将其列为一个重要指标[15]。通过拮抗反应判断菌株间的亲缘关系,操作方便,结果也较直观、易辨认,但也存在一些缺陷,如不容易区分遗传背景近似的菌株[16-17],而且观察拮抗线时存在主观因素,因此鉴定菌株时采用拮抗反应需结合分子标记等方法。近年来,已陆续有学者利用分子标记技术对双孢蘑菇种质资源进行分类鉴定、辅助育种。王翠等[18]通过SRAP等3种分子标记,结合农艺性状的表型,表明特定标记与双孢蘑菇产、质量性状具有明显的关联性。林媛等[19]利用RAPD标记对40个双孢蘑菇品种进行亲缘关系鉴定,王金斌等[20]采用SSR分子标记鉴定了双孢蘑菇栽培菌株,王新新等[21]采用SSR标记对国内外不同来源的双孢蘑菇种质建立了分子身份证,顾敏等[22]对31份As2796的单孢分离株和8份代表性双孢蘑菇栽培菌株进行遗传多样性研究。【本研究切入点】闽南地区双孢蘑菇栽培菌株较单一,本研究以不同途径引进的9个双孢蘑菇菌株为试验材料,利用体细胞不亲和性试验和SSR分子标记对其进行亲缘关系的探讨,旨在为进一步收集保护双孢蘑菇种质资源、杂交亲本选择等提供理论依据和技术支撑。【拟解决的关键问题】本研究采用体细胞不亲和性试验和SSR分子标记相结合对收集的9个双孢蘑菇菌株进行鉴定与分析,以期更准确更科学鉴定收集的双孢蘑菇菌株,明确其亲缘关系,为后续的杂交育种亲本选择等研究工作奠定基础。
1. 材料与方法
1.1 试验材料
供试双孢蘑菇菌株具体见表1。
表 1 供试的双孢蘑菇菌株编号Table 1. Sample codes for A. bisporus germplasms编号
No.菌株名称
Strain来源
Origin1 As2796 漳州市农科所 2 W2000 福建省农科院 3 W192 福建省农科院 4 福蘑38 福建省农科院 5 福蘑52 福建省农科院 6 福蘑58 福建省农科院 7 901 制种户 8 A15 制种户 9 HK 香港 1.2 试验试剂
DNA提取试剂盒、琼脂糖H、SSR引物等由生工生物工程(上海)股份有限公司提供;6×DNA Loading Dye、DNA Ladder Mix(100-3000 bp)、POP-7TM Polymer、HiDiFormamide等购自ThermoFisher。
1.3 供试培养基
100 g马铃薯+60 g双孢蘑菇二次发酵晒干草粪料+20 g葡萄糖+18 g琼脂。
1.4 试验方法
1.4.1 培养基制作
将草粪料和去皮、切块的马铃薯分别放入锅中,分别加水0.5 L,在加热器上加热至沸腾,维持约20~30 min,用2层纱布趁热在量杯上过滤,滤液待用;将2种滤液混合,小火加热,逐步加入糖和琼脂,混匀,水补足至1 L,分装,121 ℃高压蒸汽灭菌20 min。
1.4.2 体细胞不亲和性试验
体细胞不亲和性试验参考文献[14]的方法进行。
1.4.3 供试菌株DNA提取
采用Ezup 柱式真菌基因组DNA抽屉试剂盒提取DNA。
1.4.4 PCR反应体系与条件
参考文献[21-23],选用12个SSR引物对供试菌株进行扩增。引物信息具体见表2,PCR反应体系组成:10 mmol·L−1 dNTPs 0.4 μL,5 U Taq酶0.3 μL,100 ng DNA 1.0 μL,10 μmol·L−1的上、下游引物各 1 μL,Taq Buffer(含MgCl2)2.5 μL,加ddH2O 至 25 μL。PCR扩增程序为:95 ℃预变性3 min:94 ℃变性30 s,60 ℃退火30 s,72 ℃延伸30 s,共10个循环;94 ℃变性30 s,55 ℃退火30 s,72 ℃延伸30 s,共35个循环;72 ℃延伸8 min,4 ℃ 保存。
表 2 供试菌株鉴定所用SSR引物Table 2. SSR primers for variety identification引物名
Primer序列(5′ to 3′)
Sequence(5′ to 3′)5′端修饰
5′end modification重复基序
Repeat motifs片段大小/bp
Fragment size退火温度/℃
Annealing temperatureAbSSR005-F CTCTGGGATATGGACGAGGA 5′6-FAM (GATGAG)6 118 56 AbSSR013-F GACTGCCTGATTGACGGATT 5′HEX (TA)6 162 57 AbSSR015-F CTCGAGTCGACGAAGGAAAC 5′HEX (GA)7 238 58 AbSSR016-F TGTCTGGTTTTGCTCACGTC 5′HEX (TC)12 242 55 AbSSR018-F TGGCTCTTTACAGCCTTGGT 5′6-FAM (CAT)6 122 55 AbSSR084-F CGACCCATCATCAACTTCCT 5′HEX (GAA)6 234 59 AbSSR6-F ACCACATTCTGGAAAACGAA 5′HEX (GCT)8 181 55 AbSSR36-F CGTTGATGGAGTTCACTGAG 5′HEX (GAAG)4(GAAAAG)(GAAG) 148 58 L11-F ATAAAAAAGCATAATCACAAATG 5′6-FAM (TC)13 228 50 L15-F GCAGGTCCAGTGTGAACGG 5′6-FAM (TCC)8 192 57 L17-F ATCCAATTCACCAACCAGC 5′6-FAM (A)11gagaataagaaattgaaaattg(A)16 186 52 L23-F CTTTTCAGGGGAAGACAACG 5′6-FAM (GTG)7 174 55 1.4.5 电泳检测和 STR检测
将扩增好的PCR产物进行琼脂糖凝胶电泳(2 μL样品+6 μL溴酚蓝),300 V电压下12 min,获取鉴定胶图,通过胶图确定模板浓度,加水稀释到毛细管电泳所需浓度,按照相关流程进行STR检测。
1.5 数据分析
体细胞不亲和性试验结果的判断参照NY/T1845-2010。使用Gene mapper4.1软件分析SSR数据,用MVSP软件进行聚类分析,并形成供试菌株的遗传聚类图。
2. 结果与分析
2.1 供试菌株的体细胞不亲和性分析
供试菌株间的拮抗反应存在一定差异,如图1所示。福蘑52、901、As2796等3个菌株间的拮抗反应明显,表现为菌丝隆起。W192和W2000无拮抗反应,这2个菌株与福蘑52拮抗反应明显,表现为拮抗线。福蘑58和W2000无拮抗反应,这2个菌株与901拮抗反应明显,表现为沟状。
根据体细胞不亲和性试验结果,拮抗反应具体结果见表3。可以看出,901与A15之间没有拮抗线,但与其他菌株均存在较明显的拮抗线,分为一组;HK、福蘑52两两之间及与其他菌株之间均有较明显拮抗反应,这2个菌株的亲缘关系可能较远,HK分为一组,福蘑52分为另外一组;W192、W2000、As2796、福蘑58两两之间没有明显拮抗线,初步认为这些菌株之间亲缘关系较近,分为一组;As2796与W192等没有明显拮抗线,但菌丝明显不同,单独分为一组。因此,通过体细胞不亲和性试验可以初步将供试菌株分成 5 组。
表 3 供试菌株间的拮抗反应情况Table 3. Antagonistic reactions among tested germplasms菌株
StrainAs2796
As2796W2000
W2000W19
2W192福蘑38
Fomo 38福蘑52
Fomo 52福蘑58
Fomo 58901 A15 HK As2796 As2796 − W2000 W2000 − − W192 W192 − − − 福蘑38 Fomo 38 − − − − 福蘑52 Fomo 52 + + + + − 福蘑58 Fomo 58 − − + − + − 901 + + + + + + − A15 + + + + + + − − HK + + + + + + + + − 注:‘+’表示有拮抗性;‘−’表示无拮抗
Note: + presence of antagonism; − absence of antagonism.2.2 供试菌株遗传相似系数分析
遗传相似系数是表示群体或个体间相似程度的度量值,相似系数越大,样本的遗传关系越近,反之则越远。本研究结果表明,9个供试菌株的遗传相似系数变幅较大(0.432~0.905),平均值为0.6721;其中W192与福蘑38、W2000遗传相似系数最大,表明这3个菌株在这9个引进菌株群体中的亲缘关系最近;而W192与901遗传相似系数最小,表明这两个菌株的亲缘关系最远。W192、W2000、福蘑58、福蘑38、As2796之间的遗传相似系数均≥0.8,远大于平均值,表明这几个菌株间的亲缘关系较近;从遗传相似系数数值分布可以看出(表4),遗传相似系数≥0.9占比8.3%,遗传相似系数≤0.5占比11.1%,遗传相似系数0.8~0.89、0.7-0.79、0.6-0.69、0.5-0.59占比各约20%,表明这9个菌株间具有一定的遗传多样性,遗传丰富度较高。
表 4 相似性系数Table 4. List of similarity coefficients菌株
Strain福蘑38
Fomo 38福蘑52
Fomo 52福蘑58
Fomo 58901 A15 As2796 HK W192 W2000 福蘑38 Fomo 38 1 福蘑52 Fomo 52 0.615 1 福蘑58 Fomo 58 0.9 0.595 1 901 0.541 0.588 0.629 1 A15 0.462 0.722 0.486 0.765 1 As2796 0.821 0.667 0.865 0.529 0.556 1 HK 0.526 0.686 0.5 0.667 0.743 0.571 1 W192 0.905 0.718 0.8 0.432 0.564 0.821 0.632 1 W2000 0.81 0.769 0.8 0.486 0.615 0.821 0.684 0.905 1 2.3 亲缘关系分析
如图2所示,结合相似性系数矩阵表,以相似性系数0.76为阈值,可将供试菌株分成4个类群,第一类群只有一个样本HK;第二类群有2个样本A15与901;第三类群只有一个样本福蘑52;第四类群最多,有5个样本,其中W2000,W192和福蘑38在相似性为86%的地方聚为一类,其中W192和福蘑38的相似性有91%;样本AS2796和福蘑58相似性只有87%。
3. 讨论与结论
形态标记是人们最早利用的遗传标记类型[24]。但对食用菌等大型真菌而言,其子实体表型受外部环境因素影响大,因此单纯借助形态学指标区分菌株间亲缘关系难度较大。通过体细胞不亲和性试验可以初步判断菌株间的亲缘关系。本试验的拮抗反应较明显,如HK、福蘑52两两之间及与其他菌株之间的拮抗反应均较明显,说明这2个菌株的亲缘关系较远;As2796、W192、W2000、As2796、福蘑58两两之间没有拮抗反应,说明这些菌株之间的亲缘关系较近;901与A15两个菌株均由国外育种公司选育而成,相互没有拮抗反应,二者亲缘关系可能较近,但与其他菌株之间的拮抗反应均较明显,表明这2个菌株与其他供试菌株的亲缘关系较远,这与菌种来源是相符的。
DNA分子标记目前已广泛用于食用菌品种鉴定[15-16,18-22]。SSR具有等位变异高、共显性、简便、快速、稳定的特点[25]。SSR技术在农作物品种鉴定、遗传多样性分析、辅助分子育种等方面得到大量应用[20-28]。本研究结合相似性系数矩阵表,以相似性系数0.76为阈值,可将供试菌株分成4个类群,表明这9个双孢蘑菇菌株具有一定的遗传多样性与遗传丰富度。
有研究报道体细胞不亲和性试验的分类结果与分子标记聚类分析的结果基本相同。唐传红等的[16]利用拮抗试验和RAPD分子标记技术分析了供试菌株的亲缘关系,结果表明2种方法的鉴定结论是一致。杏鲍菇[29],黑木耳[30-31]等的研究结果也佐证了这一结论。但杨和川等[15]对29个金针菇进行遗传多样性分析结果表明,大部分拮抗对峙试验结果与聚类分析结果一致,也存在不一致的。因此采用多种鉴定方法对供试菌株进行综合分析,可以得出更准确结论。本研究综合体细胞不亲和性试验和SSR分子标记技术两种方法对供试的9个双孢蘑菇菌株进行鉴定分析,结果表明两种方法所得到的结果基本一致。如HK与其他供试菌株均存在明显拮抗线,SSR分子标记聚类结果也显示HK与其他菌株平均相似系数仅为0.626,单独聚为一类;A15和901二者之间不存在拮抗反应,而与其他供试菌株均存在不同程度的拮抗反应,聚类分析结果显示A15和901相似系数为0.765,与其他菌株平均相似系数分别为0.614和0.579,这两个菌株遗传背景相近,而与其他供试菌株亲缘关系较远。
不同DNA分子标记方法的开发原理是有一定区别的,有时不同分子标记方法的聚类分析结果会存在一定的差异。杨军[32]综合ISSR和RAPD两种分子标记鉴定分析供试灰树花菌株,结果表明利用2种分子标记比单独使用分子标记鉴定的结果更准确。本研究是综合拮抗反应试验的分类结果与分子标记聚类分析的结果,可以考虑进一步采用其他分子标记验证本试验结果。
-
表 1 55份山药资源编号、名称和基原
Table 1 Codes, names, and origins of 55 Chinese yam germplasms
编号
No.种质资源名称
Germplasm resource name基原
Origins编号
No.种质资源名称
Germplasm resource name基原
Origins1 麻沙硬壳薯
Masha hard-shelled yam褐苞薯蓣
D. persimilis29 宁化三黄村徐引2号
Ninghua Sanhuang Xu Yin No.2褐苞薯蓣
D. persimilis2 麻沙土薯
Masha local yam褐苞薯蓣
D. persimilis30 清流雪薯*
Qingliu snow yam褐苞薯蓣
D. persimilis3 麻沙小叶永安薯
Masha small-leaf yong'an yam褐苞薯蓣
D. persimilis31 明溪土薯
Mingxi local yam褐苞薯蓣
D. persimilis4 麻沙六月薯*
Mosha June yam薯蓣
D. opposita32 明溪红皮白肉
Mingxi red skin white pulp参薯
D. alata5 麻沙七月薯*
Mosha July yam薯蓣
D. opposita33 明溪淮山1号*
Mingxi Huaishan No.1褐苞薯蓣
D. persimilis6 麻沙1号山药*
Masha No.1 yam褐苞薯蓣
D. persimilis34 安砂小叶薯*
Ansha small-leaf yam褐苞薯蓣
D. persimilis7 麻沙大薯
Masha big yam参薯
D. alata35 安砂大叶薯*
Ansha large-leaf yam参薯
D. alata8 麻沙紫薯*
Masha purple yam参薯
D. alata36 建宁紫山药*
Jianning purple yam参薯
D. alata9 麻沙大叶永安薯
Masha large-leaf yong'an yam褐苞薯蓣
D. persimilis37 三明三元紫山药
Sanming Sanyuan purple yam参薯
D. alata10 麻沙江西薯
Mashajiang sweet yam山薯
D. fordii38 马铺1号山药*
Mapu No.1 yam山薯
D. fordii11 浦城紫山药
Pucheng purple yam参薯
D. alata39 屏南麻沙薯
Pingnan Masha yam褐苞薯蓣
D. persimilis12 连城紫山药
Liancheng purple yam参薯
D. alata40 屏南牛腿薯
Pingnan beef leg yam参薯
D. alata13 连城红皮白肉*
Liancheng red skin white pulp参薯
D. alata41 屏南棉薯*
Pingnan soft yam薯蓣
D. opposita14 宣和雪薯*
Xuanhe snow yam褐苞薯蓣
D. persimilis42 福安白石板大薯
Fu'an Baishiban yam参薯
D. alata15 新罗紫山药
Xinluo purple yam参薯
D. alata43 福安前洋糯米薯*
Fu'an Qianyang yam参薯
D. alata16 武平1号紫山药
Wuping No.1 purple yam参薯
D. alata44 永春紫山药
Yongchun purple yam参薯
D. alata17 武平2号紫山药*
Wuping No.2 purple yam参薯
D. alata45 永春锦溪村土薯
Yongchun Jinxi local yam褐苞薯蓣
D. persimilis18 长汀野药薯
Changting wild yam山薯
D. fordii46 安溪山格淮山*
Anxi Shange Huaishan褐苞薯蓣
D. persimilis19 长汀淮山*
Changting Huaishan褐苞薯蓣
D. persimilis47 德化淮山
Dehua Huaishan褐苞薯蓣
D. persimilis20 长汀红皮白肉
Changting red skin white pulp参薯
D. alata48 德化紫薇紫山药
Dehua Ziwei purple yam参薯
D. alata21 长汀紫山药
Changting purple yam参薯
D. alata49 德化1号紫山药
Dehua No.1 purple yam参薯
D. alata22 长汀紫玉淮山
Changting purple jade Huaishan参薯
D. alata50 德化2号紫山药*
Dehua No.2 purple yam参薯
D. alata23 宁化石寮村土薯
Ninghua Shiliao local yam褐苞薯蓣
D. persimilis51 德化芹峰淮山*
Dehua Qinfeng Huaishan褐苞薯蓣
D. persimilis24 宁化早熟
Ninghua precocious yam褐苞薯蓣
D. persimilis52 马铺3号*
Mapu No.3 yam参薯
D. alata25 宁化晚熟*
Ninghua late maturation yam褐苞薯蓣
D. persimilis53 马铺6号紫山药*
Mapu No.6 purple yam参薯
D. alata26 宁化三黄村奶薯
Ninghua Sanhuang milk yam褐苞薯蓣
D. persimilis54 马铺日本薯蓣*
Mapu Japanese yam日本薯蓣 D.japonica 27 宁化三黄村紫薯
Ninghua Sanhuang purple yam参薯
D. alata55 马铺7号紫山药*
Mapu No.7 purple yam参薯
D. alata28 宁化三黄村徐引1号
Ninghua Sanhuang Xu Yin No.1褐苞薯蓣
D. persimilis*表示初级核心种质资源。
* indicates primary core collection.表 2 描述性指标的分级和赋值
Table 2 Grading and assignments of descriptive traits
性状
Characters分级与赋值
Grading and assignment生长势 GP 1=弱Weak;2=较弱Relatively weak;3=中Mdium;4=较强Relatively strong;5=强Strong 茎蔓狭翅 SNW 1=无No;2=黄绿色Yellow-green;3=紫色 Purple 基部茎刺 SBT 1=无No;2=有Yes 叶柄近叶端颜色 PLC 1=黄绿色Yellow-green;2=紫色 Purple 叶形 LS 1=戟形Halberd shape;2=长心形Long heart shape;3=心形Heart shape;4=披针形Lanceolate 叶面网脉 LSRV 1=不明显Inapparent;2=明显Apparent 零余子 Bulbil 1=无No;2=有Yes 开花 Flowering 1=无No;2=有Yes 块茎形状 TS 1=短棒状Short bar shape;2=长棒状Long bar shape;3=短圆柱形Short cylindrical shape;4=长圆柱形Long cylindrical shape;5=不规则块状 Irregular shape 表皮光滑度 SS 1=光滑Smooth;2=较光滑Relatively smooth;3=较粗糙Relatively rough;4=粗糙Rough 须根数 FRN 1=少Only a little;2=较少Not many;3=多many 块茎肉色 TFC 1=白White;2=黄白Yellow with white;3=全紫色Purple;4=不均匀紫色Uneven purple;5=仅内皮层紫色Only the endothelium is purple 肉质褐变性 FB 1=易Easy;2=不易Hard 表 3 原种质与初级核心种质7个数量性状的平均值、方差、极差和变异系数的比较
Table 3 Mean, variance, range, and CV of 7 quantitative traits of previous collection and PCCCY
性状
Characters平均值 Mean 方差 Variance 极差 Range 变异系数 CV/% 原种质 OC 初级核心种质 PCC 原种质 OC 初级核心种质 PCC 原种质 OC 初级核心种质 PCC 原种质 OC 初级核心种质 PCC 茎粗SD/mm 3.22 3.27 0.63 0.65 2.1~6.3 2.1~5.0 24.58 24.73 叶长LL/cm 14.63 13.88 9.41 10.81 6.6-21.2 6.6~19.0 20.97 20.49 叶宽LW/cm 8.39 8.35 4.48 6.15 3.0~13.6 3.0~13.6 25.23 24.30 块茎长TL cm 50.29 54.13 483.01 552.69 16.4~97.4 20.5~97.4 43.70 43.43 块茎直径TD/mm 65.01 67.85 1641.53 2207.23 5.2~230.0 32~230 62.32 69.25 龙头长TTL/cm 5.43 5.87 17.68 21.69 0~15.6 0~15.6 77.39 79.30 块茎鲜重TFW/g 917.00 984.77 366456.52 451101.78 262.5~3111.7 262.53~2813.7 66.01 68.20 表 4 原种质与初级核心种质13个描述型性状的等级分布和香农指数的比较
Table 4 Grade distribution of 13 descriptive traits and Shannon-Weaver indexes of PCCCY and previous collection
性状
Characters等级分布
Grade distribution香浓多样性指数
Shannon-Weaver index原种质
OC初级核心种质
PCC原种质
OC初级核心种质
PCC生长势 GP 1~5 2-5 1.11 1.01 茎蔓狭翅 SNW 1~3 1~3 0.98 0.96 基部茎刺 SBT 1~2 1~2 0.21 0.17 叶柄近叶端颜色 PLC 1~2 1~2 0.68 0.64 叶形 LS 1~4 1~4 0.85 1.12 叶面网脉 LSRV 1~2 1~2 0.67 0.66 零余子有无 BON 1~2 1~2 0.52 0.60 开花与否 FON 1~2 1~2 0.69 0.68 块茎形状 TS 1~5 1~5 1.48 1.51 表皮光滑度 SS 1~4 1~4 0.97 0.92 须根数 FRN 1~4 1~4 1.24 1.32 块茎肉色 TFC 1~5 1~5 1.27 1.23 肉质褐变性 FB 1~2 1~2 0.26 0.29 表 5 供试ISSR引物及其扩增的多态性
Table 5 Polymorphisms and amplified products of ISSR primers
编号
No.引物名称
Primer name引物序列
Primer sequences多态位点
Polymorphic sites总位点
Total sites多态性比率
Polymorphism ratio/%1 UBC807 AGA GAG AGA GAG AGA GT 16 17 94.12 2 UBC808 AGA GAG AGA GAG AGA GC 12 14 85.71 3 UBC810 GAG AGA GAG AGA GAG AT 14 15 93.33 4 UBC811 GAG AGA GAG AGA GAG AC 14 14 100.00 5 UBC818 CAC ACA CAC ACA CAC AG 16 16 100.00 6 UBC825 ACA CAC ACA CAC ACA CT 14 14 100.00 7 UBC827 ACA CAC ACA CAC ACA CG 16 16 100.00 8 UBC834 AGA GAG AGA GAG AGA GYT 12 12 100.00 9 UBC856 ACA CAC ACA CAC ACA CYA 17 17 100.00 10 UBC864 ATG ATG ATG ATG ATG ATG 14 14 100.00 平均 Average 14.5 14.9 97.32 表 6 原种质与初级核心种质的分子遗传多样性参数比较
Table 6 Grade distribution on molecular genetic diversity parameters of PCCCY and previous collection
遗传信息
genetic information样本数
Sample size等位基因数Na 有效等位基因数Ne 多样性指数He 香农多样性信息指数I 多态位点
Polymorphic sites多态位点率
Polymorphic site rate /%原种质 OC 55 1.9732± 0.1622 1.6015±0.3239 0.3461±0.1488 0.5147±0.1871 145 97.32 初级核心种质 PCC 24 1.9597± 0.1973 1.6288±0.3118 0.3594±0.1425 0.5307±0.1810 143 95.97 表 7 原种质和初级核心种质主成分分析的特征值及累计贡献率
Table 7 Characteristic values and cumulative contribution rates of PCCCY and previous collection based on principal component analysis
主成份
Main component原种质 OC 初级核心种质 PCC 特征值
Eigenvalues贡献率
Contribution rate/%累积贡献率
Cumulative contribution rate/%特征值
Eigenvalues贡献率
Contribution rate/%累积贡献率
Cumulative contribution rate/%1 9.163 45.814 45.814 9.378 46.890 46.890 2 2.756 13.780 59.595 3.176 15.879 62.769 3 2.284 11.419 71.014 1.954 9.772 72.541 4 1.456 7.282 78.296 1.373 6.865 79.406 5 1.013 5.063 83.359 1.130 5.649 85.055 -
[1] 张武君, 刘保财, 陈菁瑛, 等. 福建省山药产业发展现状及对策 [J]. 福建农业科技, 2019(4):38−42. DOI: 10.13651/j.cnki.fjnykj.2019.04.011 ZHANG W J, LIU B C, CHEN J Y, et al. Current situation and countermeasures of yam industry in Fujian Province [J]. Fujian Agricultural Science and Technology, 2019(4): 38−42.(in Chinese) DOI: 10.13651/j.cnki.fjnykj.2019.04.011
[2] FRANKEL O H. Genetic perspectives of germplasm conservation[M]//ARBER W, LIMENSEE K, PEACICK W J, et al. Genetic manipulation: genetic manipulation impact on man and society. Cambridge, UK: Cambridge University Press, 1984.
[3] BROWN A H D. Core collections: A practical approach to genetic resources management [J]. Genome, 1989, 31(2): 818−824. DOI: 10.1139/g89-144
[4] 陈伊航, 唐朝臣, 张雄坚, 等. 基于表型性状和SSR分子标记构建甘薯核心种质 [J]. 作物学报, 2023, 49(5):1249−1261. CHEN Y H, TANG C C, ZHANG X J, et al. Construction of core collection of sweetpotato based on phenotypic traits and SSR markers [J]. Acta Agronomica Sinica, 2023, 49(5): 1249−1261.(in Chinese)
[5] ESNAULT F, PELLÉ R, DANTEC J P, et al. Development of a potato cultivar (Solanum tuberosum L. ) core collection, a valuable tool to prospect genetic variation for novel traits [J]. Potato Research, 2016, 59(4): 329−343. DOI: 10.1007/s11540-016-9332-x
[6] OLIVEIRA E J, FERREIRA C F, SANTOS V S, et al. Development of a cassava core collection based on single nucleotide polymorphism markers [J]. Genetics and Molecular Research, 2014, 13(3): 6472−6485. DOI: 10.4238/2014.August.25.11
[7] GIRMA G, BHATTACHARJEE R, LOPEZ-MONTES A, et al. Re-defining the yam (Dioscorea spp. ) core collection using morphological traits [J]. Plant Genetic Resources:Characterization and Utilization, 2018, 16(3): 193−200. DOI: 10.1017/S1479262117000144
[8] MAHALAKSHMI V, NG Q, ATALOBHOR J, et al. Development of a West African yam Dioscorea spp. core collection [J]. Genetic Resources and Crop Evolution, 2007, 54(8): 1817−1825. DOI: 10.1007/s10722-006-9203-4
[9] 刘向宇. 山药种质资源遗传多样性分析及核心种质的构建[D]. 呼和浩特: 内蒙古农业大学, 2015. LIU X Y. Genetic diversity analysis and core collection construction in yam (Dioscorea spp. )[D]. Hohhot: Inner Mongolia Agricultural University, 2015. (in Chinese)
[10] 杨帆. 基于形态学标记和SSR分子标记的山药种质资源遗传多样性分析及核心种质库构建[D]. 呼和浩特: 内蒙古农业大学, 2022. YANG F. Genetic diversity analysis and core collection construction of yam (Dioscorea thunb) based on morphological and SSR markers[D]. Hohhot: Inner Mongolia Agricultural University, 2022. (in Chinese)
[11] 张武君, 陈菁瑛, 刘保财, 等. 37份福建山药地方品种主要性状遗传变异研究 [J]. 福建农业学报, 2019, 34(11):1246−1254. ZHANG W J, CHEN J Y, LIU B C, et al. Genetic variations on major traits of 37 Chinese yam germplasms [J]. Fujian Journal of Agricultural Sciences, 2019, 34(11): 1246−1254.(in Chinese)
[12] 李丽红, 华树妹, 陈芝华, 等. 福建山药地方品种表型性状的遗传多样性研究 [J]. 云南农业大学学报(自然科学), 2016, 31(2):257−262. DOI: 10.16211/j.issn.1004-390X(n).2016.02.010 LI L H, HUA S M, CHEN Z H, et al. Phenotypic genetic diversity research on Dioscorea landraces of Fujian Province [J]. Journal of Yunnan Agricultural University (Natural Science), 2016, 31(2): 257−262.(in Chinese) DOI: 10.16211/j.issn.1004-390X(n).2016.02.010
[13] 华树妹, 涂前程, 雷伏贵. 福建山药种质资源遗传多样性的RAPD分析 [J]. 植物遗传资源学报, 2009, 10(2):195−200. DOI: 10.13430/j.cnki.jpgr.2009.02.028 HUA S M, TU Q C, LEI F G. Genetic diversity of Dioscorea polystachya Turcz. revealed by RAPD markers [J]. Journal of Plant Genetic Resources, 2009, 10(2): 195−200.(in Chinese) DOI: 10.13430/j.cnki.jpgr.2009.02.028
[14] 闫彩霞, 王娟, 张浩, 等. 基于表型性状构建中国花生地方品种骨干种质 [J]. 作物学报, 2020, 46(4):520−531. DOI: 10.3724/SP.J.1006.2020.94101 YAN C X, WANG J, ZHANG H, et al. Developing the key germplasm of Chinese peanut landraces based on phenotypic traits [J]. Acta Agronomica Sinica, 2020, 46(4): 520−531.(in Chinese) DOI: 10.3724/SP.J.1006.2020.94101
[15] 杨帆, 张艳芳, 王锦华, 等. 山药种质资源SSR分析及初级核心种质库的构建 [J]. 北方农业学报, 2022, 50(2):18−27. DOI: 10.12190/j.issn.2096-1197.2022.02.03 YANG F, ZHANG Y F, WANG J H, et al. SSR analysis of Chinese yam(Dioscorea opposita Thunb. )germplasm resources and construction of primary core collection [J]. Journal of Northern Agriculture, 2022, 50(2): 18−27.(in Chinese) DOI: 10.12190/j.issn.2096-1197.2022.02.03
[16] 牟书靓, 牛海龙, 张春宵, 等. 结合农艺性状和SSR标记构建吉林省花生初级核心种质 [J]. 吉林农业大学学报, 2017, 39(4):392−402. DOI: 10.13327/j.jjlau.2017.3325 MU S J, NIU H L, ZHANG C X, et al. Construction of peanut primary core germplasm in Jilin Province by agronomic traits and SSR markers [J]. Journal of Jilin Agricultural University, 2017, 39(4): 392−402.(in Chinese) DOI: 10.13327/j.jjlau.2017.3325
[17] 董玉琛, 曹永生, 张学勇, 等. 中国普通小麦初选核心种质的产生 [J]. 植物遗传资源学报, 2003, 4(1):1−8. DOI: 10.3969/j.issn.1672-1810.2003.01.002 DONG Y C, CAO Y S, ZHANG X Y, et al. Establishment of candidate core collections in Chinese common wheat germplasm [J]. Journal of Plant Genetic Resources, 2003, 4(1): 1−8.(in Chinese) DOI: 10.3969/j.issn.1672-1810.2003.01.002
[18] 李金龙, 范昱, 赵梦雨, 等. 基于表型性状和SSR分子标记构建甜荞初级核心种质 [J]. 植物遗传资源学报, 2021, 22(5):1240−1247. DOI: 10.13430/j.cnki.jpgr.20210308001 LI J L, FAN Y, ZHAO M Y, et al. Construction of primary core collection of buckwheat germplasm resources based on phenotypic traits and SSR [J]. Journal of Plant Genetic Resources, 2021, 22(5): 1240−1247.(in Chinese) DOI: 10.13430/j.cnki.jpgr.20210308001
[19] 刘向宇, 霍秀文, 杨明, 等. 山药种质资源的ISSR分析及初级核心种质库的构建 [J]. 西北植物学报, 2015, 35(5):915−921. DOI: 10.7606/j.issn.1000-4025.2015.05.0915 LIU X Y, HUO X W, YANG M, et al. Genetic diversity analysis and primary core collection construction in yam (Dioscorea opposita thunb.) by ISSR marker [J]. Acta Botanica Boreali-Occidentalia Sinica, 2015, 35(5): 915−921.(in Chinese) DOI: 10.7606/j.issn.1000-4025.2015.05.0915
[20] WU W Q, CHEN C, ZHANG Q, et al. A comparative assessment of diversity of greater yam (Dioscorea alata) in China [J]. Scientia Horticulturae, 2019, 243: 116−124. DOI: 10.1016/j.scienta.2018.08.016
[21] BAI Q S, CAI Y L, HE B X, et al. Core set construction and association analysis of Pinus massoniana from Guangdong Province in Southern China using SLAF-seq [J]. Scientific Reports, 2019, 9: 13157. DOI: 10.1038/s41598-019-49737-2
[22] 苏群, 王虹妍, 刘俊, 等. 基于SSR荧光标记构建睡莲核心种质 [J]. 园艺学报, 2023, 50(10):2128−2138. DOI: 10.16420/j.issn.0513-353x.2022-0902 SU Q, WANG H Y, LIU J, et al. Construction of core collection of Nymphaea based on SSR fluorescent markers [J]. Acta Horticulturae Sinica, 2023, 50(10): 2128−2138.(in Chinese) DOI: 10.16420/j.issn.0513-353x.2022-0902
[23] 王倩, 张立媛, 许月, 等. 黍稷高基元EST-SSR标记开发及200份核心种质资源遗传多样性分析 [J]. 作物学报, 2023, 49(8):2308−2327. WANG Q, ZHANG L Y, XU Y, et al. High motif EST-SSR markers development and genetic diversity evaluation for 200 core germplasms in proso millet [J]. Acta Agronomica Sinica, 2023, 49(8): 2308−2327.(in Chinese)
[24] 曾晓璇. 山药种质资源整理研究[D]. 武汉: 湖北中医药大学, 2021 ZENG X X. Study on germplasm resources arrangement of Shanyao[D]. Wuhan: Hubei University of Chinese Medicine, 2021. (in Chinese)
[25] 彭枫, 李阳, 戴雨柔, 等. 基于表型性状的菠菜核心种质构建 [J]. 上海师范大学学报(自然科学版), 2022, 51(1):9−19. PENG F, LI Y, DAI Y R, et al. Construction of spinach’s core germplasms based on its phenotypic traits [J]. Journal of Shanghai Normal University (Natural Sciences), 2022, 51(1): 9−19.(in Chinese)
[26] 郑福顺, 王晓敏, 李国花, 等. 宁夏地区番茄种质资源核心种质构建策略 [J]. 浙江农业学报, 2022, 34(9):1877−1888. DOI: 10.3969/j.issn.1004-1524.2022.09.07 ZHENG F S, WANG X M, LI G H, et al. Construction strategy of core collections of tomato germplasm resources in Ningxia, China [J]. Acta Agriculturae Zhejiangensis, 2022, 34(9): 1877−1888.(in Chinese) DOI: 10.3969/j.issn.1004-1524.2022.09.07
[27] 刘遵春, 张春雨, 张艳敏, 等. 利用数量性状构建新疆野苹果核心种质的方法 [J]. 中国农业科学, 2010, 43(2):358−370. DOI: 10.3864/j.issn.0578-1752.2010.02.017 LIU Z C, ZHANG C Y, ZHANG Y M, et al. Study on method of constructing core collection of Malus sieversii based on quantitative traits [J]. Scientia Agricultura Sinica, 2010, 43(2): 358−370.(in Chinese) DOI: 10.3864/j.issn.0578-1752.2010.02.017
[28] 于树涛, 孙泓希, 任亮, 等. 基于花生感官品质的核心种质资源构建 [J]. 花生学报, 2020, 49(2):67−72. DOI: 10.14001/j.issn.1002-4093.2020.02.011 YU S T, SUN H X, REN L, et al. Construction of core resource for peanut germplasms based on indicators of sensory quality [J]. Journal of Peanut Science, 2020, 49(2): 67−72.(in Chinese) DOI: 10.14001/j.issn.1002-4093.2020.02.011
[29] 张馨方, 张树航, 李颖, 等. 利用SSR标记构建板栗初级核心种质 [J]. 中国农业大学学报, 2021, 26(12):89−101. DOI: 10.11841/j.issn.1007-4333.2021.12.09 ZHANG X F, ZHANG S H, LI Y, et al. Construction of primary core collection of Castanea mollissima Bl. using SSR molecular markers [J]. Journal of China Agricultural University, 2021, 26(12): 89−101.(in Chinese) DOI: 10.11841/j.issn.1007-4333.2021.12.09
[30] 李自超, 张洪亮, 孙传清, 等. 植物遗传资源核心种质研究现状与展望 [J]. 中国农业大学学报, 1999, 4(5):51−62. DOI: 10.3321/j.issn:1007-4333.1999.05.010 LI Z C, ZHANG H L, SUN C Q, et al. Status and prospects of core collection in plant germplasm resource [J]. Journal of China Agricultural University, 1999, 4(5): 51−62.(in Chinese) DOI: 10.3321/j.issn:1007-4333.1999.05.010
-
期刊类型引用(3)
1. 连燕萍,赵光辉,吴振强,袁滨,柯丽娜,张志鸿. 卵孢小奥德蘑菌株的拮抗及ISSR遗传分析. 热带农业科学. 2023(01): 15-20 .  百度学术
百度学术
2. 袁滨,柯丽娜,连燕萍,赵光辉,林德锋,陈光祥. 适宜温控菇房的双孢蘑菇菌株筛选. 热带农业科学. 2022(03): 16-19 .  百度学术
百度学术
3. 卓蕾,向成丽,肖杰,叶媛丽. SSR标记在植物种质资源鉴定的应用进展. 现代园艺. 2021(15): 9-11 .  百度学术
百度学术
其他类型引用(0)




 下载:
下载: