Pathogen Identification and Fungicide Evaluation for Sclerotinia Stem Rot of Gerbera jamesonii
-
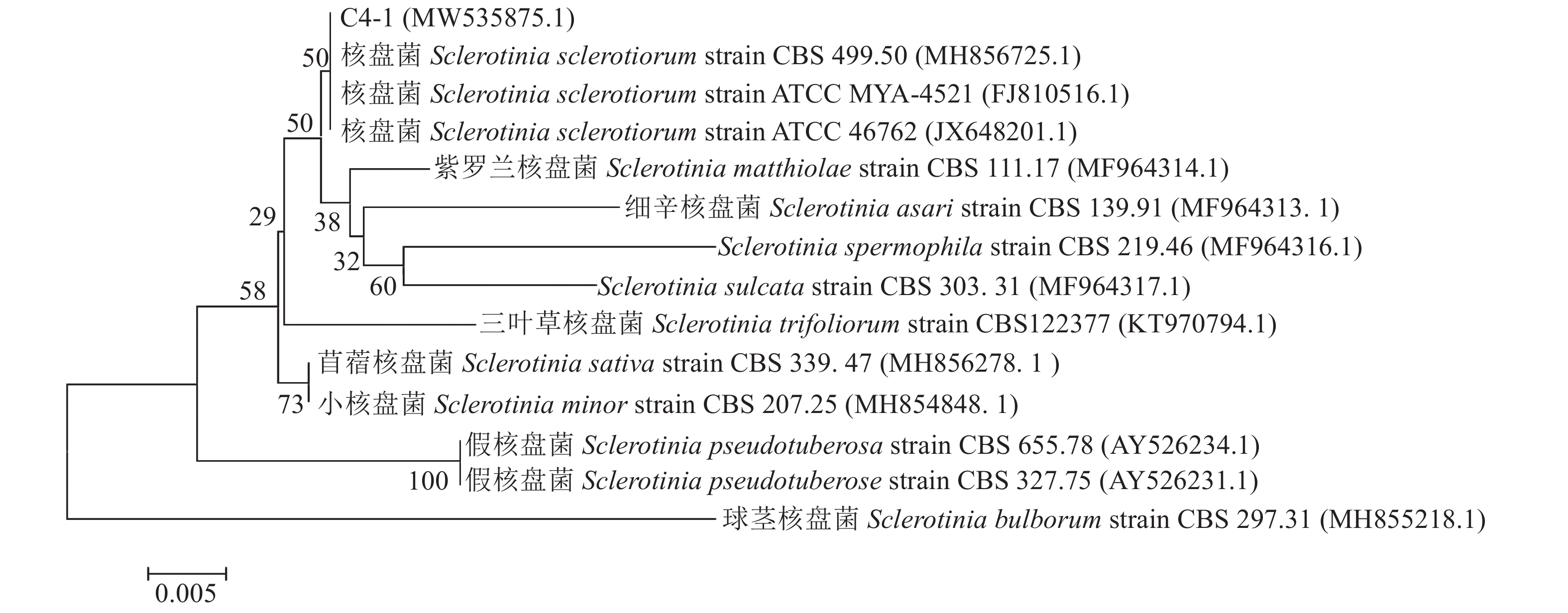
摘要:目的 分离鉴定福建省非洲菊种植过程中的主要病害菌核病的病原,筛选几种有效防治药剂进行轮换使用,避免农药的滥用及延缓病菌产生抗药性。方法 采用组织分离法分离非洲菊菌核病病原菌,经病原菌株形态学、ITS分子鉴定及柯赫氏法则验证,确定致病的病原种类,并利用室内毒力测定法筛选对菌核病病原毒力高的药剂。结果 分离获得1个非洲菊菌核病菌株C4-1;形态学、ITS及柯赫氏法则验证鉴定C4-1菌株为核盘菌Sclerotinia sclerotiorum;室内毒力测定结果显示,5种杀菌剂中25%咪鲜胺对核盘菌菌株C4-1的抑菌作用最强,EC50值为0.0324 μg·mL−1;其次为50%啶酰菌胺、40%菌核净、15%三唑醇,EC50值分别为1.0337、1.8362、6.9408 μg·mL−1;50%多菌灵的抑菌作用最弱,EC50值为22.4349 μg·mL−1。结论 分离鉴定出福建省非洲菊菌核病病原为核盘菌Sclerotinia sclerotiorum,咪鲜胺、啶酰菌胺、菌核净对核盘菌毒力强,防治非洲菊菌核病过程中可轮换使用。Abstract:Objective The pathogen of sclerotinia stem rot, a major disease of Gerbera jamesonii cultivated in Fujian, was identified. Effective fungicides that could be alternatively applied to curtail drug resistance were evaluated.Method The causative pathogen of sclerotinia stem rot was isolated from tissue of the diseased plant and verified by Koch’s rule as well as morphological observation and ITS sequence of the microbe. Toxicities of selected fungicides were determined in the laboratory.Result The isolated strain, C4-1, was identified as the culprit to be Sclerotinia sclerotiorum. Among the fungicides, hymexazol with an EC50 of 0.032 4 μg·mL−1 was most potent in inhibiting the pathogen growth. It was followed by boscalid with an EC50 of 1.033 7 μg·mL−1, dimetachlone with an EC50 values of 1.8362 μg·mL−1, triadimenol with an EC50 of 6.9408 μg·mL−1, and carbendazim the least effective agent with anEC50 of 22.434 9 μg·mL−1.Conclusion S. sclerotiorumwas isolated and identified as the pathogen that caused the sclerotinia stem rot disease on G. jamesonii in the province. Of the fungicides evaluated, hymexazol, boscalid, and dimetachlone, could be used alternatively for the disease control to minimize drug resistance by the pathogen.
-
Keywords:
- Gerbera jamesonii /
- sclerotinia stem rot /
- Sclerotinia sclerotiorum /
- identification /
- toxicity test
-
0. 引 言
【研究意义】猪繁殖与呼吸综合征(PRRS,俗称猪蓝耳病)是由猪繁殖与呼吸综合征病毒(PRRSV)引起的急性传染病。该病主要造成妊娠母猪流产、死胎等繁殖障碍和仔猪呼吸道疾病,并导致仔猪死亡率升高,生长发育受阻,高死亡率,既能垂直传播又能水平传播[1-2]。2007年前后我国各地陆续发生高致病性PRRS。高致病性PRRS已成为困扰养猪业的最主要的疫病之一,给养猪业造成了巨大的经济损失[3]。PRRSV主要感染猪的巨噬细胞,主要损伤肺脏及其他免疫器官,导致免疫力下降,从而引起免疫抑制,感染猪不仅引起免疫抑制,还会影响其他疫苗免疫,增加感染其他疾病的几率,如容易感染猪流行性腹泻、非洲猪瘟及各种细菌性疾病等。【前人研究进展】目前预防PRRS最有效的措施仍是疫苗免疫,科学的免疫至关重要[4-5]。我国市面上以PRRS活疫苗和灭活疫苗为主,其中活疫苗毒株主要有CH-1R株、JXA1-R株、VR2332株等,灭活疫苗毒株主要有CH-1a株,还有些新型PRRS疫苗,如活载体疫苗、亚单位疫苗等。PRRS活疫苗可诱导体液免疫和细胞免疫,免疫持续期长,其免疫效果比灭活苗好。灭活疫苗需多次免疫、免疫剂量大、副作用较大,不能快速激发产生细胞免疫反应,产生体液免疫迟缓,免疫持续期短,因而单独使用PRRS灭活疫苗免疫仔猪群,免疫效果差,难以很好地防控PRRS[6]。早期市面上防控PRRS以免疫PRRS活疫苗为主,但是PRRS活疫苗的不安全性仍然影响着猪群的稳定。近年来,由于非洲猪瘟疫情的影响,养猪场更加重视蓝耳活疫苗可能对猪群不稳定的影响。故而许多厂家陆续推出安全性更高的蓝耳病灭活疫苗,且也得到了一定的认可,并取得了一定的效果,但褒贬不一。【本研究切入点】目前有些厂家推荐使用PRRS活疫苗与灭活疫苗组合的免疫方案,至于PRRS活疫苗与灭活疫苗哪种组合免疫方案最佳,有待深入研究。【拟解决的关键问题】本研究设计PRRS活疫苗与灭活疫4种不同组合方式免疫仔猪,通过抗体水平、细胞因子水平以及攻毒保护试验,对比不同组合的免疫效果,以期为市场制定PRRS的疫苗防控方案提供参考。
1. 材料与方法
1.1 材料
1.1.1 供试疫苗、强毒、稀释液
PRRS活疫苗(CH-1R株)A及稀释液,PRRS灭活疫苗(CH-1a株)A,由福州牧邦生物科技有限公司提供(A厂家);PRRS活疫苗(CH-1R株)B及稀释液,PRRS灭活苗(CH-1a株)B,PRRS强毒(NVDC-JXA1株),由兆丰华生物科技(福州)有限公司提供(B厂家)。
1.1.2 主要检测试剂盒与试剂
PRRS GP5、M蛋白抗体ELISA检测试剂盒购自海博莱动物保健品有限公司(HIPRA公司);PRRS N蛋白抗体检测试剂盒购自爱德士生物科技股份有限公司(EDXX);血液RNA提取试剂盒购自Bioteke公司;反转录试剂盒与实时荧光定量PCR试剂盒购自Novoprotein公司;taco TMDNA/RNA Extraction Kit购自金瑞鸿捷(厦门)生物科技有限公司;AMV反转录酶、HPRI、Random primer和dNTPs (2.5 mmol·L−1)、PMD-18T、EASY Dilution(for Real Time PCR)购自宝生物工程(大连)有限公司;AceQ®Universal U+ probe Master Mix V2购自南京诺唯赞生物科技有限公司;引物由福州博尚生物技术有限公司合成。
1.1.3 试验用猪
28~35日龄仔猪,购自永泰桃园猪场。
1.2 试验方法
1.2.1 试验猪筛选及分组
选择同品种的4~5窝体重相近、饲养管理条件相同的28–35 d仔猪,经PRRSV、猪瘟病毒(CSFV)、猪圆环病毒2型(PCV-2)、猪伪狂犬病毒(PRV)抗原与抗体检测,选以上病原抗原抗体均为阴性的仔猪25头,免疫前将25头仔猪逐头做好编号,并随机分为5个组,分别为:免疫组A、B、C、D,E组为空白对照组,每组5头仔猪,各组均饲养于单独的猪栏。攻毒前仔猪在正压猪舍隔离饲养,攻毒时仔猪转至负压区猪舍进行隔离饲养。
1.2.2 试验猪免疫与攻毒
免疫:仔猪购回后在动物房猪舍正压区饲养,然后采血进行PRRS抗原抗体检测,并观察3 d,精神、体况均正常后进行免疫接种。各组免疫信息见表1。
表 1 各组免疫信息Table 1. Information table of immune in each group组别
Group数量
Total /头第一次免疫
The first immunization第二次免疫(一免后14 d)
Second immunization
(14 days after the first immunization)疫苗类型
Vaccines免疫方法
Immune type剂量
Dose/(mL·头−1)疫苗类型
Vaccines免疫方法
Immune type剂量
Dose/(mL·头−1)A组 A Group 5 PRRS活疫苗(A) 肌注 2 PRRS灭活疫苗(A) 肌注 2 B组 B Group 5 PRRS活疫苗(B) 肌注 2 PRRS灭活疫苗(B) 肌注 2 C组 C Group 5 PRRS灭活疫苗(A) 肌注 2 PRRS灭活疫苗(A) 肌注 2 D组 D Group 5 PRRS灭活疫苗(B) 肌注 2 PRRS灭活疫苗(B) 肌注 2 E组 E Group 5 灭菌生理盐水 肌注 2 灭菌生理盐水 肌注 2 攻毒:各组分别于二免后28 d用PRRS强毒(NVDC-JXA1株)进行攻毒,每只滴鼻2 mL(含105.2TCID50·头−1),攻毒后每日观察各组仔猪的体温变化、采食量以及是否有其他异常情况,观察21 d,攻毒后21 d,对各组仔猪进行剖检,并仔细观察脏器的病变情况。
1.2.3 血样采集与处理
1)细胞因子检测血样采集。各组试验仔猪于免前、一免后1、3、5、7 d进行外周血抗凝采样,每只采血2 mL,做好标记,置于−20 ℃冰柜保存,用于检测细胞因子(IL-2、IFN-γ、IFN-α、TNF-α)含量。
2)抗体检测血样采集。各组试验仔猪于免前、二免后7、14、21、28 d进行采血,并将所采血样于37 ℃ 放置2 h,移至4 ℃冰箱过夜,然后2 000 r·min−1离心5 min,吸取上层血清,保存于−20 ℃冰柜,待检测血清中抗体用。
1.2.4 细胞因子检测
将各组用于检测细胞因子的血样用荧光定量PCR方法(染料法)检测各细胞因子含量。
1)引物设计与合成。参照GenBank中登录的IL-2、IFN-γ、IFN-α、TNF-α基因序列,通过Primer Permier 5.0和Oligo 7.0软件设计、合成3对特异性引物,同时设计内参基因(GAPDH)。引物由福州博尚生物技术有限公司合成。相关引物序列见表2。
表 2 相关引物序列表Table 2. Sequence table of related primers引物名称
Primers names引物序列(5′-3′)
Sequences (5′-3′)GAPDH-F TATGATTCCACCCACGGCAAG GAPDH-R CCACAACATACGTAGCACCAG IL-2-F AAGATGCAGCTCTTGTGTTGC IL-2- R TCAACAGCAGTTACTGTCTCA IFN-α-F AATCTCTCCCTTCTCCTGCCT IFN-α-R CAGGAGGAAGAATGGGCTTGT IFN-γ-F CAGAAGCTAACTCTCTCCGAA IFN -γ-R TCTGACTTCTCTTCCGCTTT TNF-α-F GAAGACACACCCCCGAACAGG TNF-α-R CGGCACTGAGTCGATCATCC 2)总RNA的提取及cDNA的合成。按照病毒DNA/RNA核酸提取试剂盒说明书提取总病毒核酸并进行反转录,反转录体系:5×AMV Buffer 2 µL,dNTP Mix(10 mmoL·L−1) 1 µL,随机引物1 µL,RNA 3.5 µL,AMV酶 1 µL,反转录酶抑制剂0.5 µL,ddH2O补足至10 µL,42 ℃作用1 h,进行反转录合成cDNA,−20 ℃保存备用。
3)细胞因子含量检测。以上述保存的cDNA为模板,用所设计的特异性引物分别对IL-2、IFN-γ、IFN-α、TNF-α因子及GAPDH内参进行qPCR扩增,反应体系20 μL:TBGreen®Premix EX TaqTMII(2×)10 μL、上下游引物(10 μmol·mL−1)各0.4 μL、cDNA 2 μL、补充ddH2O至终体积为20 μL。qPCR反应条件:95 ℃ 2 min;95 ℃ 15 s,58 ~60 ℃ 15 s,72 ℃ 10 s,40个循环,添加熔解曲线,同时设置阴性对照。
1.2.5 蓝耳抗体检测
将各组血清样本按照一定比例进行稀释后加入到96孔ELISA检测板,100 μL·孔−1,37 ℃作用一段时间后,PBST洗板,拍干;加入一定比例稀释的标记抗体,100 μL·孔−1,37 ℃作用一段时间后,PBST洗板,拍干;加入终止液进行读值。具体步骤参照试剂盒说明书。
1.2.6 体温观察
各组仔猪攻毒后21 d内每天上午检测体温,并记录。
1.2.7 剖检及观察
将攻毒21 d后各组仔猪进行安乐死,然后剖检,并仔细观察肺脏病变情况。发病判定标准为攻毒后仔猪出现体温升高(≥40 ℃),至少持续4日,食欲减退和明显呼吸道症状;剖检观察仔猪的肺的心叶、间叶、隔叶等出现不同程度的花斑状肉样实变;部分仔猪脾脏头部肿大、淋巴结中度到重度肿大。
1.3 数据统计方法
采用SPSS 17.0 软件进行单因素方差分析,将免疫后各时间点的处理组各细胞因子含量数据进行bonferroni多重比较。
2. 结果与分析
2.1 细胞因子含量检测结果与分析
2.1.1 IL-2表达量
IL-2 在机体中具有抗病毒、抗肿瘤和增强机体免疫功能等作用,是细胞免疫的一项评价指标。从图1可看出,对照组与C组IL-2含量免疫后开始快速下降,至3 d后保持较低的水平,而A、B、D组免疫后先上升,然后缓慢下降,在1、3、5 d仍能保持较高的水平;各时间点B组表达量均高于其他组。图1显示,除了3 d的C组,其他免疫组的各时间组的IL-2含量均显著高于对照组,A、B、D组在各时间点的IL-2含量均显著高于C组,A、B组在3 d时又显著高于其他免疫组,B组在各时间点均显著高于其他组。可见,从IL-2表达水平上看PRRS活疫苗与灭活疫苗组合处理的A组、B组优于灭活苗组合组C、D组,B厂家疫苗免疫组优于A厂家疫苗免疫组。
2.1.2 IFN-γ表达量
IFN-γ具有免疫调节作用,可促进抗原呈递和提高巨噬细胞溶酶体活性,还可以抑制PRRSV在巨噬细胞中的复制,促进细胞免疫应答的效应因子。从图2可看出, 对照组与A组的IFN-γ含量免疫后基本保持较低的水平,B、C、D组均免疫后先上升然后下降,而后又上升,在7 d时升至最高值,B组的含量上升与下降幅度比C、D组小,C、D两组为两次免灭活苗组变化曲线极为相近,整体上升较高,5 d、7 d时上升特别高。图2显示,A组在各时间点的IFN-γ含量均与对照组比差异不显著,在免后3 d、5 d、7 d时C、D组的IFN-γ含量均上升至较高水平,并与其他组比较差异显著。可见,从IFN-γ表达水平上看,灭活疫苗组合组C、D组优于活疫苗与灭活疫苗组合组A、B组,能更好地提高IFN-γ含量,可能与灭活疫苗抗原含量高有关。
2.1.3 IFN-α表达量
IFN-α在机体中主要参与响应病毒感染的先天性免疫,具有广泛的抗病毒、抗肿瘤和免疫调节作用。从图3可看出,对照组的IFN-α含量在免后呈显著下降趋势,均在低含量水平,而B组IFN-α的含量在免后基本呈快速上升趋势,在免后7 d达到极高的水平;A、C、D组免后有所上升,然后上下波动,各时间点含量较低,但均高于对照组;图3显示,B组在免后各时间点IFN-α含量显著高于其他各组,A、C组在7 d时显著高于对照组和D组。可见,从IFN-α表达水平上看,活疫苗与灭活疫苗组合组B组优于其他组,能快速提高IFN-α含量。
2.1.4 TNF-α表达量
TNF-α可促进细胞增殖分化、免疫调节、炎症介导、抗肿瘤等作用,可协同IFN-γ抵抗病毒感染。从图4 可看出,对照组的TNF-α含量反复下降后又上升波动,整体含量不高,其他组各时间点的含量均高于对照组,只有C组不断上升,其他组均有下降和上升的变化,其中A组在7 d时上升最高,均高于其他组;图4显示,除了D组免后3 d的TNF-α与对照组差异不显著,其他各组不同时间点的TNF-α含量均显著高于对照组,1 d时D组显著高于其他各组,7 d时A组显著高于其他各组,7 d时B、C、D组又显著高于对照组。可见,各组的TNF-α含量在免后均有不同程度的上升和波动,没有特别的规律,B厂家灭活疫苗组合组D组在一免后1 d时显著高于其他各组,A厂家活疫苗与灭活疫苗组合组A组在7 d时显著高于其他各组,说明B厂家灭活苗产生的炎症反应较大。
2.2 血清中抗体检测结果与分析
从表3、表4中可以看出,活疫苗与灭活苗组合A组、B组,较早出现抗体转阳,且阳性率较灭活疫苗组合组C、D组高;A、B组中B厂家疫苗组整体阳性率高于A厂家疫苗组,C、D组中D组B厂家的整体阳性率又高于C组A厂家的。从GP5蛋白抗体与N蛋白抗体来看,GP蛋白抗体稍晚于N蛋白抗体产生,且整体阳性率也稍低于N蛋白抗体。可见,B厂家活疫苗与灭活苗组合组B组的GP5与N蛋白抗体阳性率最高,免疫效果最好。
表 3 不同疫苗组免疫后GP5蛋白抗体阳性率Table 3. Positive rates of antibodies against GP5 proteins after immunization in different groups(单位:%) 组别
Group一免前
Before first immunization一免后14 d
14th d after first immunization二免后7 d
7th d after second immunization二免后14 d
14th d after second immunization二免后21 d
21th d after second immunization二免后28 d
28th d after second immunizationA组 Group A 0 0 20 60 80 100 B组 Group B 0 0 20 80 100 100 C组 Group C 0 0 0 0 20 20 D组 Group D 0 0 20 20 40 60 E组(对照)Group E (Control) 0 0 0 0 0 0 表 4 不同疫苗组免疫后N蛋白抗体阳性率Table 4. Positive rate of N protein antibody in different groups after immunization(单位:%) 组别
Group一免前
Before the first immunization一免后14 d
14th d after the first immunization二免后7 d
7thd after second immunization二免后14 d
14thd after second immunization二免后21 d
21thd after second immunization二免后28 d
28th d after second immunizationA组 Group A 0 0 40 60 100 100 B组 Group B 0 0 60 80 100 100 C组 Group C 0 0 0 20 20 40 D组 Group D 0 0 20 40 60 60 E组(对照)Group E (Control) 0 0 0 0 0 0 从图5、图6可以看出,各组的抗体均从二免后7 d开始上升,活疫苗与灭活苗组合A组、B组,二免后抗体快速上升,至二免后28 d达到最高值。灭活疫苗组合组C、D组,从二免后7 d开始缓慢上升,至二免后28 d达到最高值,A、B组的抗体水平高于C、D组,同时可以看出,B厂家活疫苗与灭活疫苗组合组及灭活疫组合组抗体水平均高于A厂家疫苗组合组。可见B厂家活疫苗与灭活苗组合组B组产生的GP5和N蛋白抗体水平均最高。
![]() 图 5 不同组免后GP5蛋白抗体水平1-14 d代表一免后14 d,2-7 d代表二免后7 d,2-14 d,代表二免后14 d,2-21 d,代表二免后21 d,2-28 d代表二免后28 d。Figure 5. GP5 protein antibody levels in different groups after immunization1-14 d represents the 14th day after the first immunization,2-7 d represents the 7th day after the second immunization,2-14 d represents the 14th day after the second immunization,2-21 d represents the 21st day after the second immunization,2-28 d represents the 28th day after the second immunization.
图 5 不同组免后GP5蛋白抗体水平1-14 d代表一免后14 d,2-7 d代表二免后7 d,2-14 d,代表二免后14 d,2-21 d,代表二免后21 d,2-28 d代表二免后28 d。Figure 5. GP5 protein antibody levels in different groups after immunization1-14 d represents the 14th day after the first immunization,2-7 d represents the 7th day after the second immunization,2-14 d represents the 14th day after the second immunization,2-21 d represents the 21st day after the second immunization,2-28 d represents the 28th day after the second immunization.![]() 图 6 不同组免后N蛋白抗体水平1-14 d代表1免后14 d,2-7 d代表2免后7 d,2-14 d,代表2免后14 d,2-21 d,代表2免后21 d,2-28 d代表2免后28 dFigure 6. N protein antibody levels in different groups after immunization1-14 d represents the 14th day after the first immunization,2-7 d represents the 7th day after the second immunization,2-14 d represents the 14th day after the second immunization,2-21 d represents the 21st day after the second immunization,2-28 d represents the 28th day after the second immunization
图 6 不同组免后N蛋白抗体水平1-14 d代表1免后14 d,2-7 d代表2免后7 d,2-14 d,代表2免后14 d,2-21 d,代表2免后21 d,2-28 d代表2免后28 dFigure 6. N protein antibody levels in different groups after immunization1-14 d represents the 14th day after the first immunization,2-7 d represents the 7th day after the second immunization,2-14 d represents the 14th day after the second immunization,2-21 d represents the 21st day after the second immunization,2-28 d represents the 28th day after the second immunization2.3 攻毒后体温变化与攻毒保护结果
从图7可以看出,免疫组在攻毒后7 d内体温均上升,升至40 ℃左右,并上下波动,部分上升至41 ℃,7 d后开始下降,逐渐回到常温;灭活疫苗组合组C、D组整体升温比活疫苗与灭活疫苗组合组A、B组高,C组高温的在一周至两周之间持续保持41 ℃的高温。对照组攻毒后体温开始上升,前3 d在40 ℃左右,然后继续上升,第4天开始升至41 ℃以上,持续高温,大约到13 d后才下降至40 ℃左右,然后继续下降,15 d下降至接近常温。可见,活疫苗与灭活疫苗组合A组、B组相对灭活疫苗组合C组、D组体温上升较小,持续时间也短。B疫苗厂家的活疫苗与灭活疫苗组合组B组体温上升幅度最小,且最快降至正常体温。
刘义等[7]研究中,NVDC-JXA1强毒株攻毒后病变主要表现为肺部尖叶、膈叶明显实变或花斑状病变,部分出现淋巴结肿大充血,脾脏肿大。从表5、图8可以看出,对照攻毒组全部病变,整个肺呈明显花斑状病变等典型的实变,A、B组攻毒后的肺部病变较C、D组轻微,B组中5头剖检肺部无明显病变,A组中只有1头肺部出现明显病变,C组中有3头肺部出现明显的花斑状病变,D组中有2头出现肺部尖叶、膈叶明显实变或花斑状病变,免疫组病变部位比对照组轻,肺部局部出现肉变。可见,不同疫苗组合进行攻毒有一定的保护效果,活疫苗与灭活疫苗组合组攻毒保护率高于灭活疫苗组合组,其中B疫苗厂家活疫苗与灭活疫苗组合组B组攻毒保护率最高,可达100%保护。
表 5 不同组攻毒保护率Table 5. Challenge protection rate of different groups组别
Group攻毒保护率
Challenge protection rate/%A组 Group A 80 B组 Group B 100 C组 Group C 40 D组 Group D 60 E组(对照) Group E(control) 0 3. 讨论与结论
PRRS疫苗的免疫保护主要是细胞免疫和体液免疫,活疫苗产生细胞免疫强,同时可产生体液免疫,灭活疫苗主要以产生体液免疫为主[8]。从本试验结果可看出,PRRS活疫苗与灭活疫苗组合与灭活苗组合组比可更早产生抗体,并产生更高的抗体水平,攻毒保护率也更高,这可能与活疫苗早期激活了机体的细胞免疫,并产生了免疫记忆有关,后面再免灭活疫苗时,机体能快速识别免疫记忆,从而快速产生抗体水平,并缩短抗体的空档期。刘海珍等[9-10]试验结果表明,仔猪用猪繁殖与呼吸综合征活疫苗与灭活疫苗组合免疫,第一次使用活疫苗免疫,第二次使用灭活疫苗免疫,免疫后抗体阳性率和抗体水平均显著高于两次灭活疫苗组合免疫组,结果与本试验结果一致。
本试验结果表明不同厂家PRRS灭活疫苗产生抗体水平存在较大的差异,可能与不同厂家的生产工艺及使用的佐剂不同有关,对于PRRS灭活疫苗可能需要选择合适的佐剂来辅助提升抗体水平,从而提升免疫效果,所以近年来利用佐剂提高蓝耳疫苗的免疫效果和交叉保护效果成为一大研究热点[10]。
NVDC-JXA1毒株在PRRS不同毒株中属于强毒株,仔猪攻毒后以升温并持续保持高温、呼吸困难、肺部典型的花斑状实变为主要特征,并以此特征作为攻毒后病变不保护的标准。JXA1毒株虽然为强毒株,但对照组攻毒后仔猪也基本不出现死亡情况,只是体温上升持续高温,肺部出现典型的PRRS病变。
从各组攻毒后的体温变化可以看出,免PRRS活疫苗与灭活疫苗组合组在攻毒后7 d内体温不会升至41 ℃,而单独两次免灭活疫苗组在7 d内有不少体温升至41 ℃以上,同时从整体攻毒的免疫保护率看,PRRS活疫苗与灭活疫苗组合组攻毒保护率比单独两次灭活疫苗组高,可能与接种活疫苗可较早产生细胞免疫、免疫力相对较强有关,也可能与活疫苗辅助使用了佐剂,产生一些非特异性免疫有关。
PRRSV中含有中和表位蛋白GP2、GP3、GP4、GP5和M蛋白,其中 GP5 是产生中和抗体的主要靶蛋白,其含有B细胞表位和T细胞表位,可诱导中和抗体的产生[11-12],而N蛋白为核衣壳蛋白,不含中和表位,产生的N蛋白抗体为非中和抗体,N蛋白抗体水平高低,并不能代表疫苗免疫的保护水平[13],本试验选用了两种抗体检测试剂盒,一种为检测GP5蛋白抗体,另一种为N蛋白抗体,对比了试验各组的两种抗体检测结果,可以看出,N蛋白抗体的产生早于GP5蛋白抗体,免疫后同样的时间N蛋白抗体也相对更高。从本试验的GP5蛋白抗体和N蛋白抗体结果结合攻毒保护结果看,GP5蛋白抗体和N蛋白抗体越高攻毒保护率也越高,但本试验设计的最后一次检测GP5蛋白抗体和N蛋白抗体为二免后的28 d,关于二免28 d后两种抗体的消长情况未知,所以N蛋白抗体水平高是否能代表疫苗的保护水平有待进一步研究。
在机体免疫反应中IL-2、IFN-γ、IFN-α、TNF-α细胞因子起着重要的作用,发挥着增强细胞免疫或体液免疫、抗病毒、抗肿瘤和增强机体免疫功能等作用。任向阳等[14]研究表明疫苗免疫后产生细胞免疫早于体液免疫,从免疫猪瘟疫苗后1~5 d的攻毒结果看,3 d就可以产生较好的保护,4 d就可以产生100%保护,说明疫苗免疫后早期可以产生较强细胞免疫力。本试验检测细胞因子主要在于对比疫苗免疫早期的细胞因子含量变化。从试验结果可以看出,活疫苗与灭活疫苗组合组A、B组所产生的IL-2比灭活疫苗组合组C、D组高;灭活疫苗组合所产生的IFN-γ比活疫苗与灭活苗组合含量高,可能在免疫后的短时间内机体中灭活疫苗抗原含量比活疫苗高有关;B厂家的活疫苗与灭活疫苗组合B组在7 d时IFN-α含量特别高,A厂家的活疫苗与灭活疫苗组合A组在7 d产生的TNF-α量特别高,可能与不同厂家的疫苗效价及使用的稀释液有关。通过人工表达的IFN-α通过淋巴结注射,以及经肌肉注射,作为PRRS活疫苗的佐剂,均可增强PRRS弱毒疫苗诱导机体免疫反应的能力,产生的中和抗体和特异性抗体均明显升高[10],所以在制备蓝耳病疫苗时可考虑使用可提高IL-2、IFN-γ、IFN-α、TNF-α含量的佐剂,从而提高PRRS疫苗的免疫效果。
本试验对免后攻毒只监测体温的变化与肺脏的病变观察,对于攻毒的强毒在血液中及在肺脏中的能存活多久,具体不同时间的病毒载量未做检测和研究。William等的试验结果表明疫苗接种可以有效减少攻毒猪的肺脏病毒含量[15]。病毒载量的检测对于了解PRRS强毒在机体内的增殖与病毒衰减有着重要的意义,有待于进一步研究。
正确使用PRRS疫苗是PRRS免疫预防的关键,要根据弱毒活疫苗和灭活疫苗的不同使用特点应用不同的免疫方案[16]。本试验表明,使用PRRS活疫苗与灭活疫苗组合免疫效果优于使用灭活疫苗组合组,产生IL-2的含量高,更早产生抗体,并能产生更高的抗体,有更高的攻毒保护率。对于PRRS阳性场可参考使用蓝耳病活疫苗与灭活疫苗组合免疫,后期再长期使用灭活疫苗加强免疫,可达到较好的PRRS防控效果,并配合生物安全防控和严格的饲养管理可达到最终净化PRRS的目的。对于阴性仔猪、肥育猪场可以考虑PRRS活疫苗与灭活疫苗组合免疫方法,如果考虑保持猪场抗原阴性,也可以考虑使用灭活疫苗重复免疫的方法,对于阴性种猪场可以考虑使用灭活苗重复免疫的方法。
-
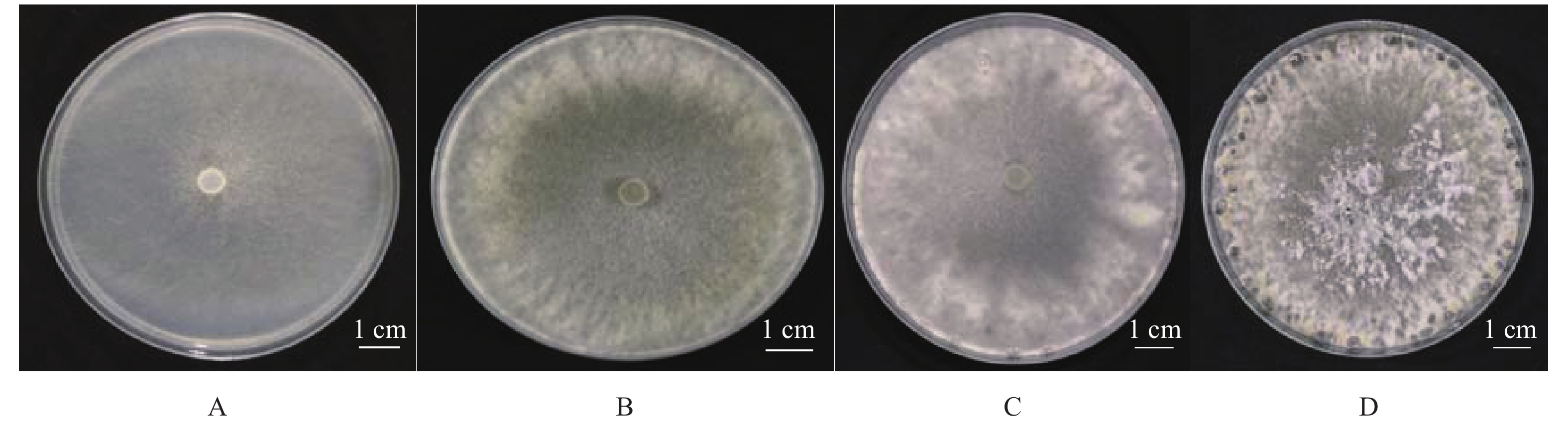
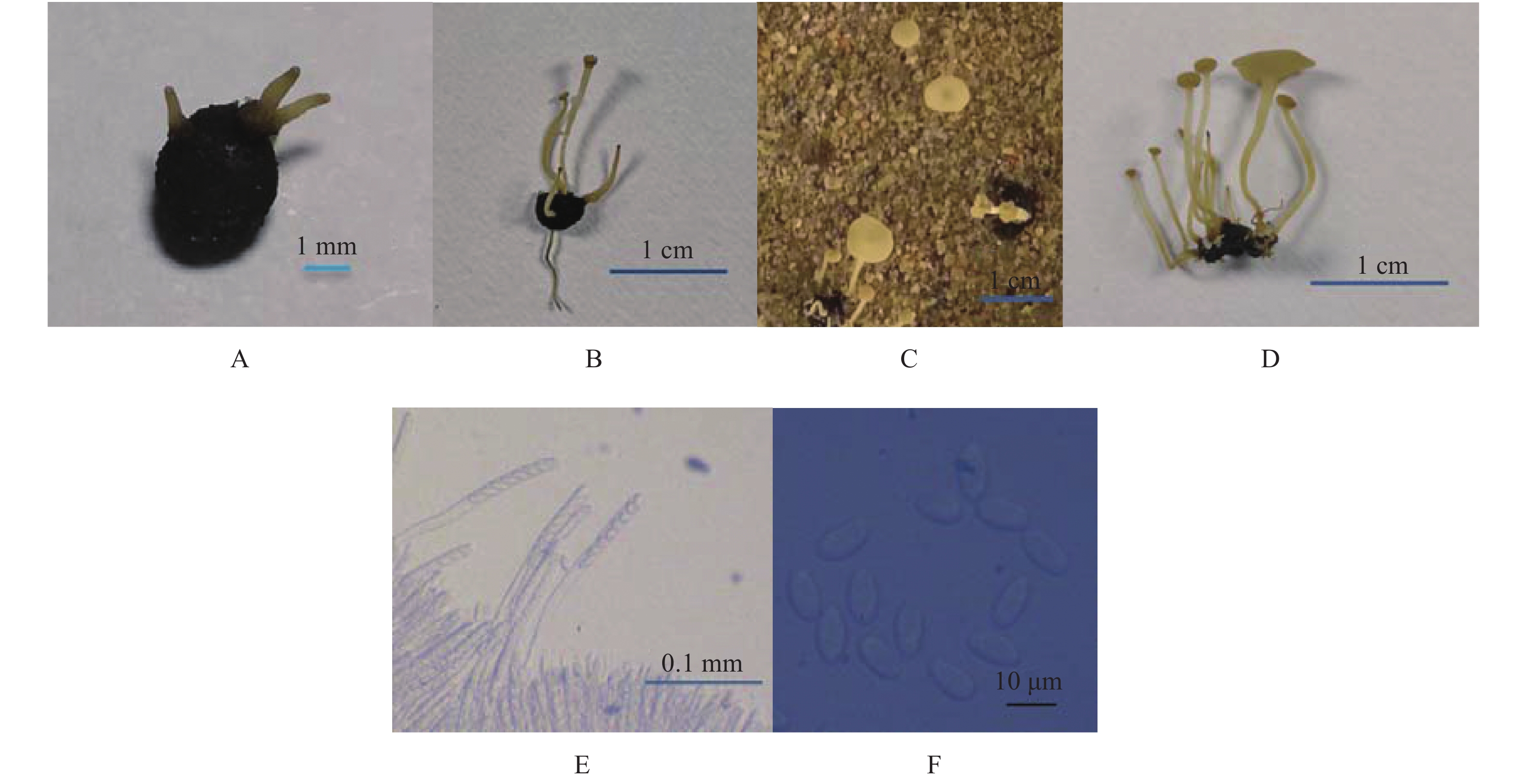
图 3 菌核的萌发过程及子囊和子囊孢子的形态
注:A,菌核萌发初期 ;B,子囊盘开始形成; C,子囊盘形成 ;D,一个菌核萌发形成多个子囊盘; E,子囊盘形态 ;F,子囊孢子形态。
Figure 3. Germination process of sclerotia and the morphology of asci and ascospores
Note: A, primary stage of sclerotia germination; B, apothecia being formed; C, formed apothecia; D, geminated sclerotia with several apothecia; E, apothecia morphology; F, ascospore morphology.
表 1 供试杀菌剂母液及使用浓度
Table 1 Original and applied concentrations of fungicides under study
杀菌剂
Fungicide剂型
Pesticide formulation生产厂家
Manufacturer母液质量浓度
Initial concentration/
(μg·mL−1)处理质量浓度
Treatment mass concentration/
(μg·mL−1)50% 多菌灵
50% Carbendazim可湿性粉剂
Wettable Powder江苏蓝丰生物化工股份有限公司
Jiangsu Lanfeng Biochemical Co., Ltd.1000 3.125,6.25,12.5,25,50 25% 咪鲜胺
25% Prochloraz水乳剂
Emulsion in Water江苏辉丰生物农业股份有限公司
Jiangsu Huifeng Bio-agriculture Co., Ltd.1000 0.0125,0.25,0.05,0.1,0.2 50% 啶酰菌胺
50% Boscalid水分散粒剂
Water Dispersible Granule巴斯夫(中国)有限公司
BASF China Co., Ltd.1000 1.25,2.5,5,10,20 40% 菌核净
40% Dimethachlon可湿性粉剂
Wettable Powder江西禾益化工股份有限公司
Jiangxi Heyi Chemical Co., Ltd.1000 0.5,1,2,4,8 15% 三唑醇
15% Triadimenol可湿性粉剂
Wettable Powder江苏剑牌农化股份有限公司
Jiangsu Sword Agrochemical Co., Ltd.1000 1.25,2.5,5,10,20 表 2 5种杀菌剂对非洲菊核盘菌菌株C4-1的毒力
Table 2 Toxicities of 5 fungicides on S. sclerotiorum C4-1
杀菌剂
Fungicide剂型
Pesticide Formulation毒力回归方程
Virulent regression equation相关系数
Correlation coefficient, rEC50值
EC50 value/(μg·mL−1)50% 多菌灵
50% Carbendazim可湿性粉剂
Wettable powdery=0.2272x−0.5196 0.9757 22.4349 25% 咪鲜胺
25% Prochloraz水乳剂
Emulsion in watery=0.1849x+1.4149 0.9698 0.0324 50% 啶酰菌胺
50% Boscalid水分散粒剂
Water dispersible granuley=0.1067x+0.4949 0.9756 1.0337 40% 菌核净
40% Dimethachlon可湿性粉剂
Wettable powdery=0.3821x+0.1650 0.9858 1.8362 15% 三唑醇
15% Triadimenol可湿性粉剂
Wettable powdery=0.2489x−0.1957 0.9947 6.9408 -
[1] 肖建梅. 非洲菊组培技术 [J]. 中国花卉园艺, 2005(8):14−15. XIAO J M. Tissue Culture of Gerbera Jamesonii [J]. China Flowers & Horticulture, 2005(8): 14−15.(in Chinese)
[2] 郭方其, 陈文海, 叶琪明, 等. 不同非洲菊品种在浙北地区的适应性评价 [J]. 浙江农业科学, 2020, 61(10):2056−2059. GUO F Q, CHEN W H, YE Q M, et al. Evaluation of Adaptability of Different Gerbera jamesonii Cultivars in Northern Zhejiang Province [J]. Journal of Zhejiang Agricultural Sciences, 2020, 61(10): 2056−2059.(in Chinese)
[3] MATHERON M E. First Report of Sclerotinia sclerotiorum on African Daisy in Arizona [J]. Plant Disease, 1994(78): 924D.
[4] WOLCAN S M. Occurrence of Crown Rot of Gazania and Gerbera Caused by Scleroticnia sclerotiorum in Argentina [J]. Journal of Plant Pathology, 2004, 86(3): 263−264.
[5] FOLK G, TUSNÁDI CS K. A New Disease of Gerbera in Hungary, Sclerotinia Wilt [J]. Növényvédelem, 1985, 21(12): 557−561.
[6] VIGODSKY H. Methods for Controlling Sclerotinia Rot of Gerbera and Studies on the Disease Cycle in Israel [J]. lsrael J agric Res, 1969, 19: 185−194.
[7] 周韦成, 赵建军. 上海地区非洲菊真菌病害鉴定 [J]. 生物灾害科学, 2015, 38(4):339−344. DOI: 10.3969/j.issn.2095-3704.2015.04.014 ZHOU W C, ZHAO J J. Identification of Pathogenic Fungi Gerbera jamesonii in Shanghai [J]. Biological Disaster Science, 2015, 38(4): 339−344.(in Chinese) DOI: 10.3969/j.issn.2095-3704.2015.04.014
[8] 王涛. 非洲菊病虫害综合防治技术 [J]. 中国植保导刊, 2004, 24(5):25−26. DOI: 10.3969/j.issn.1672-6820.2004.05.010 WANG T. Integrated Pest Control Techniques of Gerbera jamesonii [J]. China Plant Protechion, 2004, 24(5): 25−26.(in Chinese) DOI: 10.3969/j.issn.1672-6820.2004.05.010
[9] 刘峰. 非洲菊主要病害及其防治 [J]. 特种经济动植物, 2004, 7(9):40. DOI: 10.3969/j.issn.1001-4713.2004.09.036 LIU F. The Main Diseases and Control of Gerbera jamesonii [J]. Special Economic Animal and Plant, 2004, 7(9): 40.(in Chinese) DOI: 10.3969/j.issn.1001-4713.2004.09.036
[10] 张志轩, 王洪习, 汪妮. 豫北地区非洲菊鲜切花常见病虫害及综合防治技术 [J]. 现代园艺, 2007(6):25−27. DOI: 10.3969/j.issn.1006-4958.2007.06.016 ZHANG Z X, WANG H X, WANG N. Common Diseases and Pests of Gerbera Cut Flower in Northern Henan and Integrated Control Techniques [J]. Modern Horticulture, 2007(6): 25−27.(in Chinese) DOI: 10.3969/j.issn.1006-4958.2007.06.016
[11] 夏朝水. 福建主栽非洲菊品种资源的综合评价与应用[D]. 福州: 福建农林大学, 2014. XIA C S. Comprehensive Evaluation and Application of Fujian Main Cultivated Varieties of Gerbera jamesonii Resources [D]. Fuzhou: Fujian Agriculture and Forestry University, 2014. (in Chinese)
[12] 方中达. 植病研究方法[M]. 3版. 北京: 中国农业出版社, 1998. [13] 孙敬贤, 张鲁刚. 大白菜菌核病病原菌鉴定及其主要生物学特性 [J]. 华北农学报, 2015, 30(S):321−328. SUN J X, ZHANG L G. Identification and Main Biological Characteristics of Sclerotinia Rot Pathogen in Chinese Cabbage [J]. Acta Agriculturae Boreali-Sinica, 2015, 30(S): 321−328.(in Chinese)
[14] 张薇, 魏海雷, 张力群, 等. 紫花苜蓿菌核病病原鉴定及其主要生物学特性 [J]. 草业学报, 2005, 14(2):69−75. DOI: 10.3321/j.issn:1004-5759.2005.02.013 ZHANG W, WEI H L, ZHANG L Q, et al. Identification and Control of Medicago sativa Sclerotinia Stem Rot Occurred in South Jiangsu Hilly Area [J]. Acta Prataculturae Sinica, 2005, 14(2): 69−75.(in Chinese) DOI: 10.3321/j.issn:1004-5759.2005.02.013
[15] 刘春来, 文景芝, 杨明秀, 等. rDNA-ITS在植物病原真菌分子检测中的应用 [J]. 东北农业大学学报, 2007, 38(1):101−106. DOI: 10.3969/j.issn.1005-9369.2007.01.022 LIU C L, WEN J Z, YANG M X, et al. Application of rDNA-ITS in Molecular Test of Phytopathogenic fungi [J]. Journal of Northeast Agricultural University, 2007, 38(1): 101−106.(in Chinese) DOI: 10.3969/j.issn.1005-9369.2007.01.022
[16] 李克宁, 龚贤弟. 荷兰进口的扶郎花上发生严重菌核病 [J]. 植物检疫, 1987, 1(4):316. LI K N, GONG X D. Severe Sclerotinia on Gerbera Imported from the Netherlands [J]. Plant Quarantine, 1987, 1(4): 316.(in Chinese)
[17] 卢灿华, 蔺忠龙, 甄安忠, 等. 香料烟灰霉病和菌核病病原鉴定及室内药剂筛选 [J]. 中国烟草科学, 2020, 41(6):68−75. LU C H, LIN Z L, ZHEN A Z, et al. Causal Pathogen Identification of Gray Mold Rot and Sclerotinia Rot on Oriental Tobacco and Indoor Screening of Fungicides [J]. Chinese Tobacco Science, 2020, 41(6): 68−75.(in Chinese)
[18] 孙雅楠, 哀嘉彬, 唐爱妙, 等. 浙江桑葚菌核病的病原菌鉴定及其对4种杀菌剂的抗性检测 [J]. 果树学报, 2020, 37(12):1934−1940. SUN Y N, AI J B, TANG A M, et al. Identification of Pathogenic Fungi Causing Mulberry Fruit Sclerotiniose and Their Resistance to Four Fungicides in Zhejiang [J]. Journal of Fruit Science, 2020, 37(12): 1934−1940.(in Chinese)
[19] 顾玉阳, 王黎娜, 袁娟, 等. 扁豆菌核病病原菌鉴定及其生物学特性 [J]. 中国蔬菜, 2020(10):68−76. GU Y Y, WANG L N, YUAN J, et al. Identification of Hyacinth Bean Sclerotinia Pathogen and Its Biological Characteristics [J]. China Vegetables, 2020(10): 68−76.(in Chinese)
[20] BOLAND G J, HALL R. Index of plant hosts of Sclerotinia sclerotiorum [J]. Canadian Journal of Plant Pathology, 1994, 16(2): 93−108. DOI: 10.1080/07060669409500766
[21] 桂勇武, 高年春, 魏启舜. 非洲菊常见病虫害综合防治技术 [J]. 现代农业科技, 2006(20):52−53. DOI: 10.3969/j.issn.1007-5739.2006.20.043 GUI Y W, GAO N C, WEI Q S. Integrated Control Techniques of Common Diseases and Pests of Gerbera [J]. Modern Agricultural Science and Technology, 2006(20): 52−53.(in Chinese) DOI: 10.3969/j.issn.1007-5739.2006.20.043
[22] 吴仁锋, 杨绍丽. 蔬菜菌核病的识别及防治 [J]. 长江蔬菜, 2016(5):42−43. DOI: 10.3865/j.issn.1001-3547.2016.05.020 WU R F, YANG S L. Identification and Control of Sclerotinia sclerotiorum of Vegetables [J]. Journal of Changjiang Vegetables, 2016(5): 42−43.(in Chinese) DOI: 10.3865/j.issn.1001-3547.2016.05.020
[23] 乔昕, 余洋, 陈杰, 等. 川渝地区油菜菌核病菌对多菌灵的抗性监测及抗性机理研究 [J]. 西南大学学报(自然科学版), 2016, 38(5):26−30. QIAO X, YU Y, CHEN J, et al. Molecular Mechanism and Monitoring on Carbendazim Resistance of Sclerotinia sclerotiorum Obtained from the Blight Stems of Rape in Chongqing and Sichuan [J]. Journal of Southwest University (Natural Science), 2016, 38(5): 26−30.(in Chinese)
[24] 乔广行, 李兴红, 周莹, 等. 北京地区不同寄主蔬菜菌核病菌抗药性比较 [J]. 江苏农业科学, 2014, 42(12):155−157. QIAO G X, LI X H, ZHOU Y, et al. Comparative Study on Resistance to Drugs of Sclerotinia sclerotiorum with Different Host Vegetables [J]. Jiangsu Agricultural Sciences, 2014, 42(12): 155−157.(in Chinese)
-
期刊类型引用(0)
其他类型引用(2)




 下载:
下载: