A SYBR-Green Ⅰ RT-qPCR Assay for Detecting Enzootic Nasal Tumor Virus in Goats
-
摘要:目的 建立一种快速、敏感的ENTV-2检测方法,用于ENT的早期诊断与流行病学调查。方法 通过生物信息学的方法将ENTV-2与ENTV-1、ERVs、JSRV进行比对,寻找ENTV-2的保守序列并设计1对特异性引物,建立SYBR-Green Ⅰ 实时荧光定量PCR检测方法,对所建立的PCR反应条件进行优化,将PCR扩增产物连接T载体构建的阳性质粒作为标准品,对SYBR-Green Ⅰ 实时荧光定量PCR检测方法的特异性、敏感性和重复性进行验证。结果 建立的检测ENTV-2 qPCR 方法标准曲线呈现良好的线性关系(R2 =0.992);该方法的特异性良好,对ENTV-2可以产生特异性扩增曲线,与ENTV-2高度同源的ERVs没有交叉反应,也无法扩增羊口疮病毒(ORFV)、绵羊肺炎支原体(Mo)、丝状支原体山羊亚种(Mmc)等常见病原;敏感性良好,最低检测限度为7.5×102 copies·μL−1,敏感性可达常规PCR检测方法的100倍;批内、批间的变异系数CV<1%,重复性良好;对81份临床样品的阳性检出率为17.3%。结论 建立的SYBR-Green Ⅰ 实时荧光定量PCR方法特异性良好,敏感性较高,重复性良好,为山羊地方性鼻内肿瘤的早期、快速检测提供了技术支持。
-
关键词:
- 山羊地方性鼻内肿瘤病毒 /
- SYBR-Green Ⅰ /
- 荧光定量 PCR
Abstract:Objective A rapid, sensitive detection method for early diagnosis and epidemiological survey on enzootic nasal tumor (ENT) in goats was established.Method Bioinformatics methods were employed for sequence alignment of ENTV-2 with ENTV-1, ERVs, and JSRV in search for the conserved sequence of the virus. Primers for qPCR were designed to establish a SYBR-Green I RT-qPCR methodology for its detection. Reaction conditions were optimized, and a standard positive plasmid used to determine the specificity, sensitivity, and reproducibility of the newly developed assay.Result A linear standard curve was found for the detection with a R2=0.992. The method specifically detected only ENTV-2, not the highly homologous ERVs, nor amplified ORFV, MO, or Mmc. It showed a detection sensitivity of up to 7.51×102 copies·μL−1, which was 100 times greater than the conventional PCR can deliver, a repeatability with a coefficient variations (CV) of less than 1% on intra- and inter-batch tests, and a positive detection rate of 17.3% on 81 clinical samples.Conclusion The newly established SYBR-Green I RT-qPCR was specific, sensitive, repeatable, and considered adequate for early and rapid detection of ENTV-2 in goats.-
Keywords:
- Enzootic nasal tumor virus of goats(ENTV-2) /
- SYBR-Green Ⅰ /
- RT-qPCR
-
0. 引言
【研究意义】山羊地方性鼻内肿瘤(Enzootic nasal tumor,ENT)是由山羊地方性鼻内肿瘤病毒(Enzootic nasal tumor virus of goats,ENTV-2)导致的鼻甲骨筛骨上皮细胞恶性转化而发生的慢性、进行性、接触性传染病,该病的临床特征主要表现为病羊食欲减退,呼吸困难,鼻漏,鼻腔内出现单侧或两侧性增生物[1-2];后期可导致鼻甲骨变形,眼部突出,病程3个月到1年,通常以死亡为转归;该病的发病率为0.5%~15%,致死率可高达100%,自1939首次于德国报道以来,陆续在欧洲,亚洲,美洲,非洲等地被报道[3-4];国内于1995年首次报道,目前在湖南、四川、重庆、福建等地也有发生[5-7]。该病无特效药物,也没有疫苗用于预防,一旦出现临床症状就只能淘汰,给羊的养殖业造成巨大损失和潜在威胁。由于ENT的临床症状与细菌、支原体、过敏等症状相似,仅通过临床症状难以对病原进行鉴别诊断,因此急需一种敏感、特异的方法对发病羊和羊群进行早期诊断,以便对感染羊进行淘汰,保护健康羊群。【前人研究进展】传统的鉴定方法是通过临床初步判断结合剖检发现鼻腔内赘生物而确诊,但此方法不适用于该病的早期诊断,ENTV-2尚未建立体外培养体系[8],导致血清学检测方法的研究进展缓慢,因此分子生物学检测方法就成为ENT早期诊断的主要研究方向。Cousens C. [9]结合RT-PCR与限制性内切酶分析建立了鉴定ENTV的方法;郝中香等[10]建立了一种快速检测ENTV的RT-PCR方法,该方法最低可检测出6 pg的ENTV;Apostolidi等[11]建立了Taqman实时荧光定量PCR以检测ENTV,该方法可检出到102 RNA转录本;Huang 等[12]建立了基于EvaGreen的实时荧光定量PCR检测方法并报道该方法的灵敏度可以达到3.0×101 copies·μL−1。【本研究切入点】ENTV-2与绵羊肺腺瘤病毒(JSRV)及普遍分布于山羊和绵羊细胞基因组中的内源性反转录病毒(ERVs)高度同源[13]。本研究通过基因信息学方法寻找与上述病毒有较大差异的ENTV-2保守基因。【拟解决的关键问题】通过基因信息学的方法分析17株ENTV-2,并与ENTV-1(Enzootic nasal tumor virus of sheep)、ERVs(Endogenous retroviruses)、JSRV(Jaagsiekte sheep Retrovirus)进行比对,寻找其相对保守片段设计引物,建立检测ENTV-2 的SYBR-Green Ⅰ 实时荧光定量PCR检测方法,以期对ENTV-2进行早期诊断并应用于该病的流行病学调查。
1. 材料与方法
1.1 试验材料
1.1.1 菌(毒)株及临床样品
山羊鼻内肿瘤病毒(ENTV-2)、羊肾细胞、山羊皮肤细胞、绵羊肺细胞、羊口疮病毒(ORFV)、牛冠状病毒(BCV)、绵羊肺炎支原体(Mo)、丝状支原体山羊亚种(Mmc)由本实验室分离鉴定保存,山羊支原体山羊肺炎亚种(Mccp)由兰州兽医研究所储岳峰博士惠赠,81份羊鼻拭子样品,为2017–2019年采集自福建省各地山羊养殖场。
1.1.2 主要试剂和仪器
病毒RNA/DNA提取试剂盒、脱氧核糖核酸酶I(DNaseI)及反转录试剂盒 TransScript® Reverse Transcriptase购自北京全式金生物技术有限公司,Hieff UNICON® Power qPCR SYBR Green Master Mix购自Yeasen Biotech公司,pMD18-T、Nase-Free Water、DNA Marker,均购自宝生物工程(大连)有限公司,胶回收试剂盒、质粒提取试剂盒为天根生化科技有限公司产品;荧光定量 PCR 仪为Eppendorf公司生产。
1.2 试验方法
1.2.1 引物设计合成
根据Genbank上已公布的17株ENTV的LTR区保守的基因片段,应用引物设计软件 DNAStar和Primer Premier 5.0,经NCBI BLAST对比验证,设计1对引物,上游引物S1-140E:GAGATTTCTTACACATGAGAGC下游引物R2-140E:TCCCAGGACTTAACCATTC,引物的特异性目的片段,长度为143 bp。
1.2.2 RNA的提取及反转录
依照EasyPure Viral DNA/RNA Kit 的说明书提取ENTV的RNA,−70 ℃保存,参照TransScript One-STEP gDNA Removal and cDNA synthesis SuperMix 的说明书去除基因组DNA并将RNA反转录为cDNA,−20 ℃保存。
1.2.3 常规PCR
以1.2.2中获得的cDNA为模板,按郝中香等[10]设计的引物和PCR方法进行。
1.2.4 标准品的构建
利用方法1.2.2中获得的cDNA为模板,以方法1.2.1设计的引物对ENTV-2进行 PCR扩增。以20 μL PCR扩增体系:模板1 μL、上、下游引物各l μL(终浓度0.5 μmol·L−1)、Premix Taq 10 μL、加ddH2O 7 μL。反应条件:94 ℃ 2 min;94 ℃ 30s、55 ℃ 15 s、72 ℃15 s,循环数为35;最后 72 ℃延伸10 min。通过凝胶电泳实验将PCR产物回收纯化后克隆至pMDl8-T载体上,然后转化至大肠杆菌DH5a中,扩大培养、提取重组质粒,送生工生物有限公司进行测序。将序列正确的重组质粒作为阳性标准品,并用NanoDrop2000测定标准品的核酸含量。
1.2.5 qPCR反应条件的优化
20 μL反应体系,上下游引物S1-140E与R2-140E(10 μmol·L−1)各1 μL,模板1 μL,SYBR Green Master Mix 10 μL,补水至20 μL。扩增反应条件初步设定为:94 ℃预变性 2 min;94 ℃ 变性15 s,60 ℃ 退火15 s,72 ℃ 延伸15 s,40个循环;最后 72 ℃延伸 5 min。分别用55~65 ℃作为PCR反应的退火温度,引物浓度(0.2、0.4、0.8、1.0、1.5、1.75、2.0 pmol·L−1)对反应条件进行优化,溶解曲线参数按仪器默认参数设置。
1.2.6 qPCR的特异性试验
分别从山羊皮肤细胞、绵羊肺细胞与羊肾细胞中提取DNA作为内源性羊鼻内肿瘤病毒(ERVs)的阳性样本,羊口疮病毒(ORFV)、牛冠状病毒(BCV)、绵羊肺炎支原体(Mo)、丝状支原体山羊亚种(Mmc)、山羊支原体山羊肺炎亚种(Mccp)以及1.2.2中得到的羊鼻内肿瘤病毒(ENTV-2)cDNA为模板,按1.2.5反应体系和优化后的反应条件进行qPCR。
1.2.7 敏感性试验
以方法1.2.4中构建的标准阳性质粒为模板,用1.2.5的方法对其进行扩增,其扩增片段长度为146 bp,初始质量浓度23 ng·μL−1,换算成拷贝数约7.51×109,将其10倍倍比稀释(109~100copies·μL−1)后,从中各取其1 μL 为模板,按最佳条件进行qPCR反应,以确定建立的qPCR的敏感性。同时,用1.2.3中的常规PCR方法与本实验建立的qPCR方法进行比较。
1.2.8 重复性试验
对107、105、103 copies·μL−1的标准品DNA进行批内和批间重复性试验。其中批内重复性试验每个梯度设计3个平行重复,分析批内样品的重复性;同时,对每个梯度再重复3次试验,对比这3次试验结果,分析批间样品的重复性。
1.2.9 临床检测
采用上述qPCR方法,设立阴性、阳性对照,对临床上随机采集的81份山羊鼻子进行检测,并和常规PCR方法进行比较。
1.3 数据统计与分析
平均数、变异系数通过Excel对数据进行整理分析;质粒的分子量换算为拷贝数浓度通过公式:拷贝·μL−1=(ng·μL−1×l0−9)×(6.02×1023)/(DNA length×660)进行换算;其余数据由Eppendorf荧光定量PCR仪自带软件进行分析。
2. 结果与分析
2.1 qPCR条件优化
优化后的反应体系为:SYBR Green I Master Mix 10 μL,上下游引物各0.8 μL,模板1 μL,加去离子水至20 μL。最佳反应条件:94 ℃预变性2 min,94 ℃ 15 s,60 ℃ 15 s,72 ℃ 15 s,40个循环,熔解曲线按仪器默认参数设置,熔解曲线参数:95 ℃ 5 s,60 ℃ 30 s,95 ℃ 15 s,1个循环,退火延伸时检测荧光信号。
2.2 标准品的标准曲线
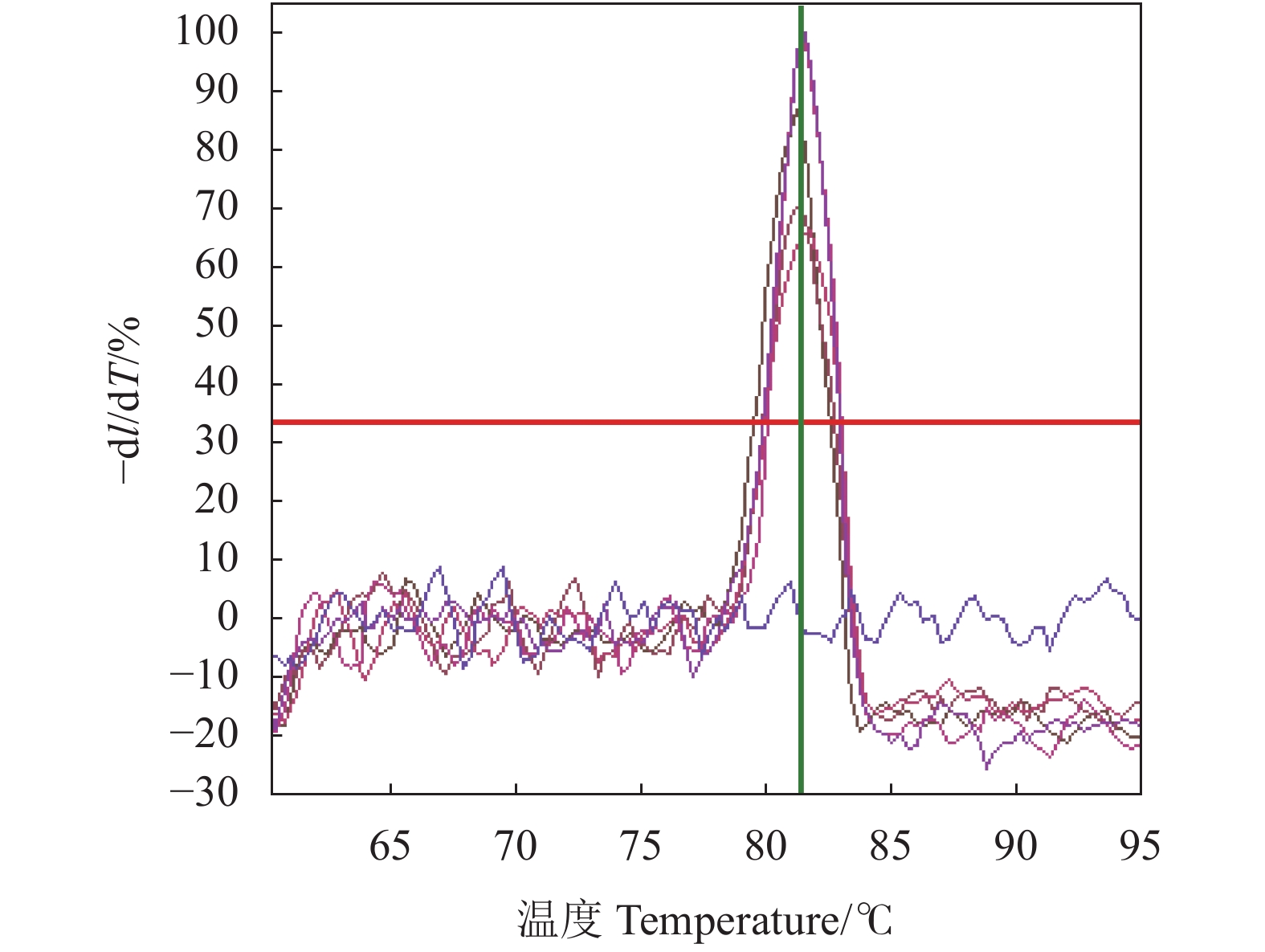
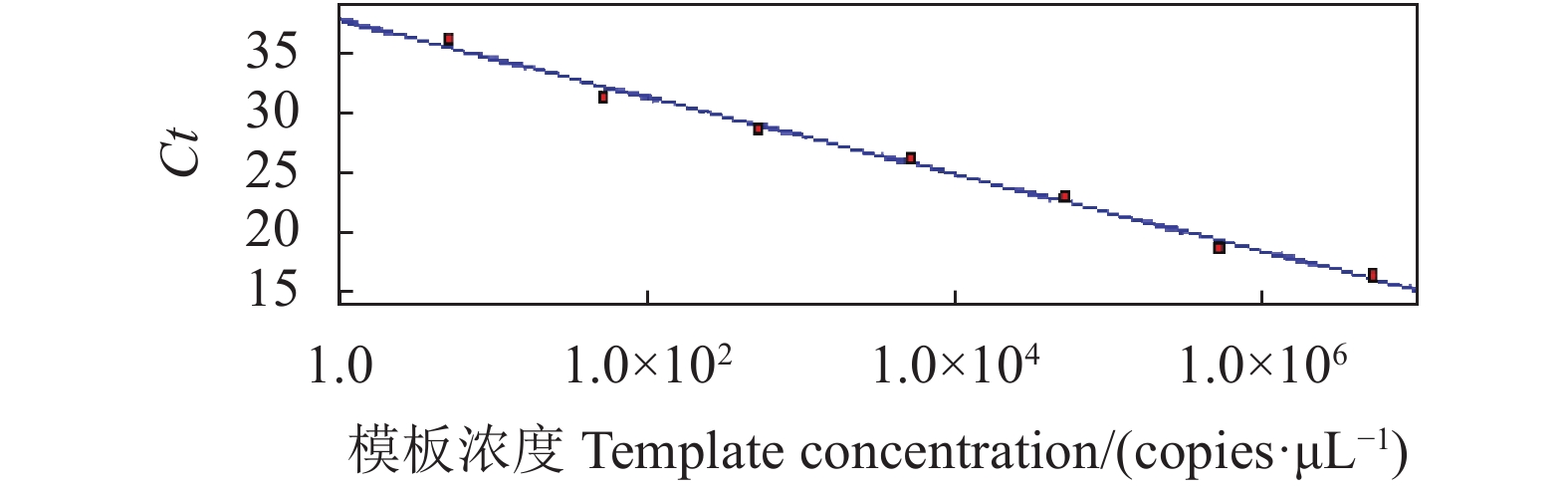
将1.2.4中构建的标准阳性质粒用EASY Dilution按10倍稀释作为模板,进行SYBRGreen I PCR扩增,以模板浓度为X轴,Ct值为Y轴,绘制标准曲线。如图1所示,模板浓度与Ct值的线性关系良好,相关系数R2=0.992,直线方程:y=−3.221×lgx+37.77,溶解曲线由图2可见,熔解曲线TM值1.3±0.2 ℃,无引物二聚体及非特异峰现。
2.3 特异性
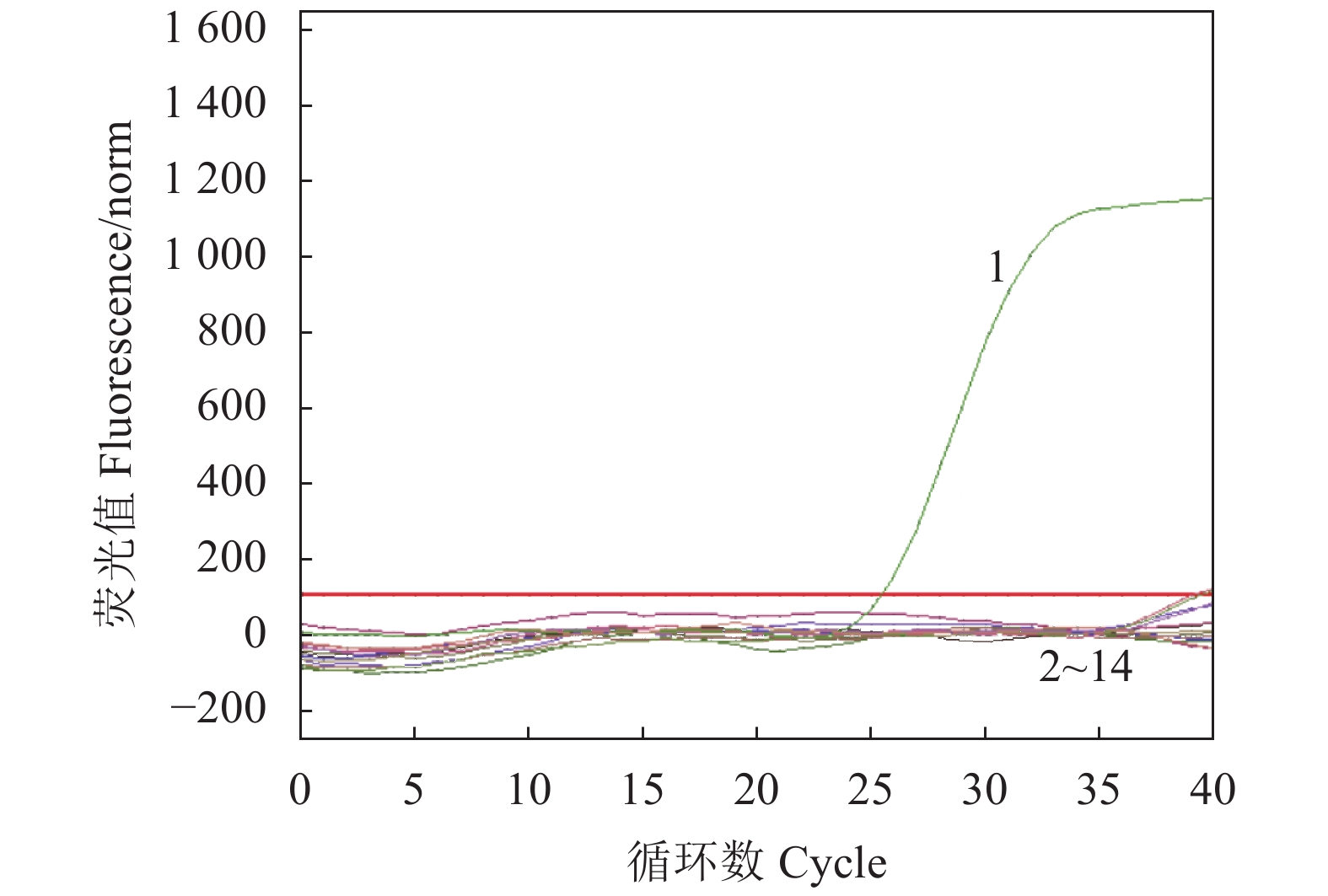
运用建立的ENTV-2 SYBR-Green Ⅰ qPCR方法检测 ENTV-2、山羊皮细胞、山羊肾细胞、绵羊肺细胞、ORFV、BCV、Mo、Mmc、Mccp等病原的基因组DNA,结果仅 ENTV-2呈阳性,其他均为阴性,说明用本方法检测ENTV-2与羊内源性鼻内肿瘤病毒及羊常见病毒均无交叉反应,特异性较好(图3)。
![]() 图 3 ENTV-2 SYBR Green Ⅰ qPCR的特异性注:1:ENTV-2; 2:羊肾1;3:羊肾2;4:羊肾3;5:羊肾4;6:羊肾5;7:山羊皮细胞;8:绵羊肺细胞;9:ORFV; 10:BCV;11:Mo;12:Mmc;13:Mccp;14:H2O。Figure 3. Specificity of SYBR Green Ⅰ RT-qPCR in detecting ENTV-2Note: 1: ENTV-2; 2: kidney cell of goat No. 1; 3: kidney cell of goat No. 2; 4: kidney cell of goat No. 3; 5: kidney cell of goat No. 4; 6: kidney cell of goat No. 5; 7: goat skin cells; 8: sheep lung cells; 9: ORFV; 10: BCV; 11: MO; 12: Mmc; 13: Mccp; 14: H2O.
图 3 ENTV-2 SYBR Green Ⅰ qPCR的特异性注:1:ENTV-2; 2:羊肾1;3:羊肾2;4:羊肾3;5:羊肾4;6:羊肾5;7:山羊皮细胞;8:绵羊肺细胞;9:ORFV; 10:BCV;11:Mo;12:Mmc;13:Mccp;14:H2O。Figure 3. Specificity of SYBR Green Ⅰ RT-qPCR in detecting ENTV-2Note: 1: ENTV-2; 2: kidney cell of goat No. 1; 3: kidney cell of goat No. 2; 4: kidney cell of goat No. 3; 5: kidney cell of goat No. 4; 6: kidney cell of goat No. 5; 7: goat skin cells; 8: sheep lung cells; 9: ORFV; 10: BCV; 11: MO; 12: Mmc; 13: Mccp; 14: H2O.2.4 敏感性
将拷贝数为7.51×109 copies·μL−1的阳性标准质粒从7.51×107 copies·μL−1稀释至7.51×100 copies·μL−1,进行qPCR试验,结果显示敏感性为7.51×102 copies·μL−1,同时以常规PCR方法进行检测,常规PCR的灵敏度为7.51×104 copies·μL−1。
2.5 重复性
对7.51×103、7.51×105和7.51×107 copies·μL−1的阳性标准质粒进行检测,每个浓度设3个重复,进行批内重复性试验;进行批间试验时对同一次试验的每个浓度设3个重复,共检测3次。结果如表1:批内、批间重复试验的变异系数均小于1%,表明该方法重复性良好。
表 1 ENTV-2 荧光定量PCR的重复性Table 1. Repeatability of SYBR-Green I RT-qPCR in detecting ENTV-2Entv阳性质粒含量/
(copies·μL−1)批内重复
Intra-assay reproducibility批间重复
Inter-assay reproducibilityCt±SD CV/% Ct±SD CV/% 7.51×103 25.25±0.15 0.59 25.53±0.16 0.63 7.51×105 18.78±0.11 0.58 19.11±0.17 0.89 7.51×107 12.44±0.12 0.96 12.89±0.12 0.93 2.6 临床样品的检测
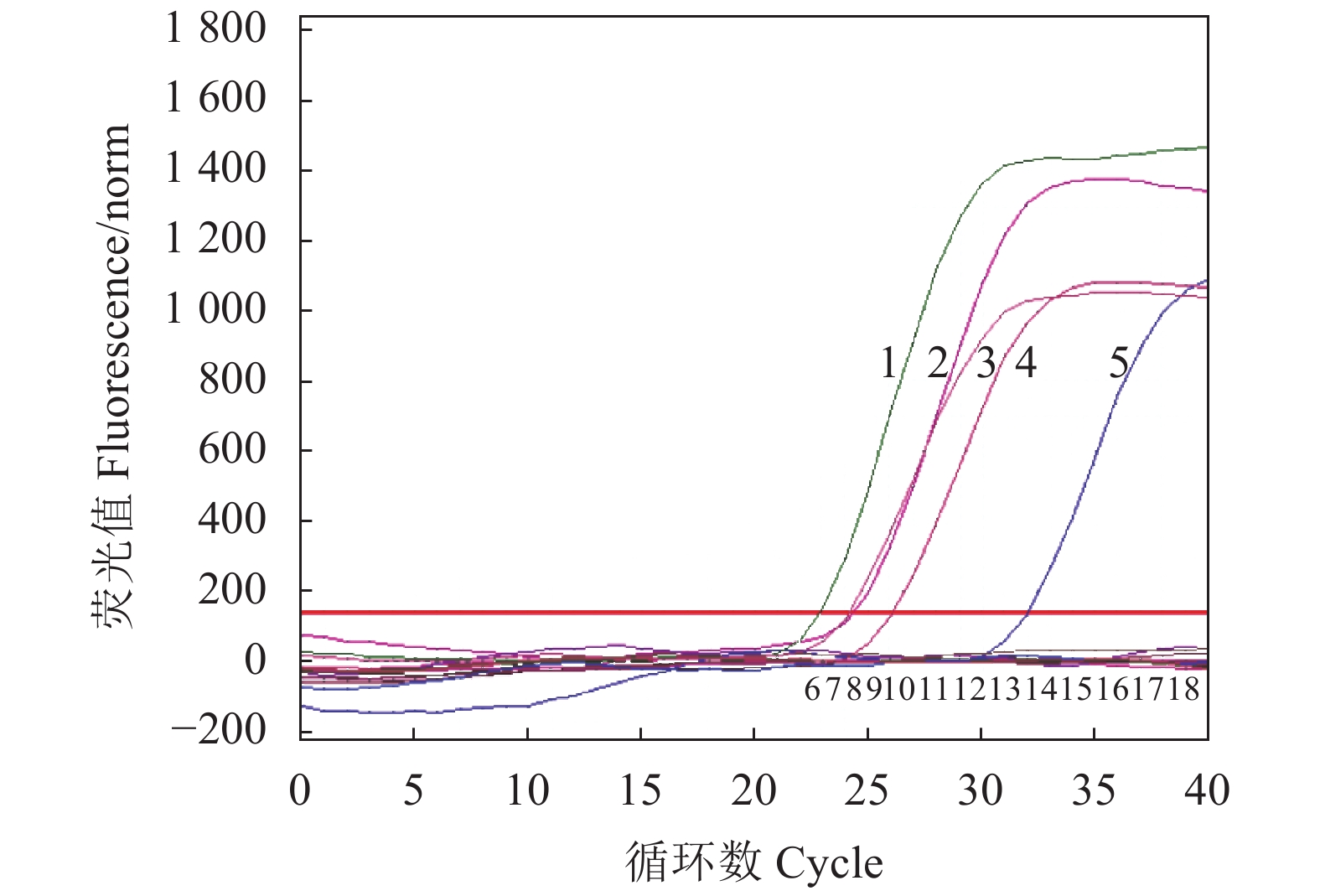
荧光定量PCR的部分结果见图4,对81份临床样品以qPCR方法和常规PCR方法进行平行检测,结果如表2显示,二者同为阳性的数量为10份,二者同为阴性数量为67份,常规PCR检测出10份阳性,71份为阴性,检出率为12.3%,而qPCR方法检出14份阳性,阴性67份,检出率17.3%,说明本研究建立的qPCR方法敏感性高于常规PCR。二者的符合率为95.1%(77/81)。
表 2 SYBR Green I荧光定量PCR和传统PCR法临床样品检测ENTV-2结果比较Table 2. Detections by SYBR-Green Ⅰ RT-qPCR and conventional PCR on clinical samples检测方法
Detecting method荧光定量PCR
SYBR-Green Ⅰ qPCR总计
Sum阳性数量
Positive
number阴性数量
Negative
number常规PCR
Convenional PCR阳性数量
Positive number10 0 10 阴性数量
Negative number4 67 71 总计 Sum 14 67 81 3. 讨论与结论
羊地方性鼻内肿瘤(ENT)是一种在国内外较广泛传播的疾病,除了新西兰和澳大利亚外,大部分国家均有报道。随着国内山羊饲养规模的扩大和活畜贸易的频繁,该病在一些地区频繁发生,其高致死率给羊产业的健康发展带来了严重挑战,尤其影响了羊种质资源。该病毒有较长的潜伏期,在病羊和带毒羊中可长期存在[14],由于缺乏免疫应答,尚无疫苗可用于该病的防治[14],因此,早期的诊断可以及时淘汰病羊,对该病的防控有重要意义。然而,该病的血清学检测方法尚未实现,早期建立的传统PCR方法敏感性不够。本试验通过对ENTV-2已发表的序列与ENTV-1、JSRV、ERVs等进行比对分析,找到了ENTV-2的保守特异性位点,建立了ENTV-2 SYBR-GreenⅠ 荧光定量PCR检测方法。
实时荧光定量PCR具有敏感性高、特异性强等优点,现已广泛应用于分子生物学相关试验,较传统PCR而言,其检测过程只需在荧光定量PCR仪上进行,扩增情况可以实时显示于仪器自带的软件,检测结果可通过Ct值和阳性标准曲线对样品中的DNA进行定性和定量,无需进行凝胶电泳分析,缩短了试验的时间,提高检测的效率,近年来在动物疫病检测中也得到广泛应用,Ortin等[15]、林裕胜等[16-17]对丝状支原体山羊亚种和绵羊肺炎支原体分别建立了SYBR Green I实时荧光定量PCR检测方法,汪伟等[18]建立了SYBR Green Ⅰ荧光定量PCR的方法用于检测山羊关节炎脑炎病毒,Wang Y等[19]应用SYBR Green I实时荧光定量PCR对ORFV进行了检测,付明哲等[20]建立了基于Eva Green染料的实时荧光定量PCR方法检测小反刍兽疫病毒,这些方法的建立不断地完善了羊病的检测体系。由于ENT没有有效的疫苗和治疗药物,一旦在羊场中出现,需要可靠的检测方法和流行病学调查及时清除患病羊,而该病早期的临床症状不明显,易与其他上呼吸道疾病混淆,而且鼻拭子中的病毒含量较低,对敏感性的要求比较高,因此,荧光定量PCR非常适用于该病的检测。本试验建立了ENTV-2的SYBR Green I实时荧光定量PCR检测方法,该方法在7.51×102~7.51×107 copies·μL−1有良好的线性关系(R2=0.992),最低检测限度为7.51×102 copies·μL−1,比传统PCR敏感性高100倍,该方法有较强的特异性,与内源性逆转录病毒(ERVs)、羊口疮病毒(ORFV)等病原均无交叉反应,应用本研究建立的qPCR方法和传统PCR方法对81份临床样品进行检测,检出率分别为17.3%和12.3%,敏感性高于传统PCR方法,而相较于Apostolidi等[11]建立的Taqman实时荧光定量PCR的方法,SYBR Green I实时荧光定量PCR检测方法不需要合成昂贵的探针,只需要合成常规引物,昂贵的探针,相比之下更为经济实用。
目前国内外关于ENTV-2检测方法的报道较少,主要原因在于ENTV-2与ERVs、ENTV-1和JSRV均有较高的同源性,因此本研究通过设计针对ENTV-2特异性的引物,理论上排除了与ERVs、ENTV-1和JSRV交叉的可能性;并且应用山羊皮肤细胞、羊肾细胞、绵羊肺细胞作为对照,结果证明内源性逆转录病毒无法通过该方法扩增出来。ENTV-1和JSRV 2种病毒只感染绵羊,目前尚无报道自然感染山羊的病例,所以试验中没有进行验证,后续研究中应进行验证。ERVs对检测有一定的干扰,可以通过DNase I的酶切反应对宿主基因组DNA进行降解,以排除ERVs的干扰,但是增加该反应有可能带入少量RNase导致病毒RNA部分降解,因此,利用传统PCR进行检测将漏检相当一部分病例,而本研究基于SYBR Green I的实时荧光定量PCR检测方法不仅特异性和重复性好,敏感性也达到7.51×102 copies·μL−1,为ENTV-2感染的早期检测和流行病学调查提供了可靠的方法。
-
图 3 ENTV-2 SYBR Green Ⅰ qPCR的特异性
注:1:ENTV-2; 2:羊肾1;3:羊肾2;4:羊肾3;5:羊肾4;6:羊肾5;7:山羊皮细胞;8:绵羊肺细胞;9:ORFV; 10:BCV;11:Mo;12:Mmc;13:Mccp;14:H2O。
Figure 3. Specificity of SYBR Green Ⅰ RT-qPCR in detecting ENTV-2
Note: 1: ENTV-2; 2: kidney cell of goat No. 1; 3: kidney cell of goat No. 2; 4: kidney cell of goat No. 3; 5: kidney cell of goat No. 4; 6: kidney cell of goat No. 5; 7: goat skin cells; 8: sheep lung cells; 9: ORFV; 10: BCV; 11: MO; 12: Mmc; 13: Mccp; 14: H2O.
表 1 ENTV-2 荧光定量PCR的重复性
Table 1 Repeatability of SYBR-Green I RT-qPCR in detecting ENTV-2
Entv阳性质粒含量/
(copies·μL−1)批内重复
Intra-assay reproducibility批间重复
Inter-assay reproducibilityCt±SD CV/% Ct±SD CV/% 7.51×103 25.25±0.15 0.59 25.53±0.16 0.63 7.51×105 18.78±0.11 0.58 19.11±0.17 0.89 7.51×107 12.44±0.12 0.96 12.89±0.12 0.93 表 2 SYBR Green I荧光定量PCR和传统PCR法临床样品检测ENTV-2结果比较
Table 2 Detections by SYBR-Green Ⅰ RT-qPCR and conventional PCR on clinical samples
检测方法
Detecting method荧光定量PCR
SYBR-Green Ⅰ qPCR总计
Sum阳性数量
Positive
number阴性数量
Negative
number常规PCR
Convenional PCR阳性数量
Positive number10 0 10 阴性数量
Negative number4 67 71 总计 Sum 14 67 81 -
[1] DE LAS HERAS M, GARCIA DE JALON J A, SHARP J M. Pathology of enzootic intranasal tumor in thirty-eight goats [J]. Veterinary Pathology, 1991, 28(6): 474−481. DOI: 10.1177/030098589102800603
[2] VITELLOZZI G, MUGHETTI L, PALMARINI M, et al. Enzootic intranasal tumour of goats in Italy [J]. Journal of Veterinary Medicine(Series B), 2010, 40(7): 459−468.
[3] ÖZMEN Ö, SERPİN N. First case of enzootic nasal adenocarcinoma (Ena) in a sheep in Turkey [J]. Mehmet Akif Ersoy Üniversitesi Veteriner Fakültesi Dergisi, 2016, 1(1): 87.
[4] SID N, BELALMI N E H, BENHAMZA L, et al. First case report of enzootic nasal adenocarcinoma in “Ouled Djellal” ewe in Algeria [J]. Open Veterinary Journal, 2018, 8(1): 9. DOI: 10.4314/ovj.v8i1.3
[5] 雷红宇, 苏建明, 宁玲忠, 等. 一起山羊地方性鼻内肿瘤的调查与诊断 [J]. 动物医学进展, 2006, 27(2):112−114. DOI: 10.3969/j.issn.1007-5038.2006.02.031 LEI H Y, SU J M, NING L Z, et al. Investigation and diagnosis of an Enzootic Nasal Tumor in goats [J]. Progress in Veterinary Medicine, 2006, 27(2): 112−114.(in Chinese) DOI: 10.3969/j.issn.1007-5038.2006.02.031
[6] 耿毅, 汪开毓, 颜其贵, 等. 南江黄羊流行性鼻内腺癌的病理学观察 [J]. 中国兽医学报, 2010, 30(8):1095−1097, 1102. GENG Y, WANG K Y, YAN Q G, et al. Pathomorphologic observation of enzootic intranasal adenocarcinoma in Nanjiang yellow goats [J]. Chinese Journal of Veterinary Science, 2010, 30(8): 1095−1097, 1102.(in Chinese)
[7] 江锦秀, 林裕胜, 江斌, 等. 福建山羊地方性鼻内肿瘤的分子流行病学调查 [J]. 福建农业学报, 2017, 32(8):837−841. JIANG J X, LIN Y S, JIANG B, et al. Molecular epidemiology of enzootic nasal tumor virus on goats in Fujian [J]. Fujian Journal of Agricultural Sciences, 2017, 32(8): 837−841.(in Chinese)
[8] ECKSTRAND C D, CASTILLO D, MCDONNEL S J, et al. Murphy, Genetic variability and in vitro transcriptional permissibility of primary ovine beta-retrovirus pomoter isolates [J]. American Journal of Veterinary Research, 2013, 74: 1421−1427. DOI: 10.2460/ajvr.74.11.1421
[9] COUSENS C, MINGUIJON E, GARCIA M, et al. PCR-based detection and partial characterization of a retrovirus associated with contagious intranasal tumors of sheep and goats [J]. Journal of Virology, 1996, 70(11): 7580−7583. DOI: 10.1128/jvi.70.11.7580-7583.1996
[10] 郝中香, 谢智勇, 廖红, 等. 山羊鼻内肿瘤病毒RT-PCR检测方法的建立 [J]. 中国兽医科学, 2014, 44(9):933−938. HAO Z X, XIE Z Y, LIAO H, et al. Establishment of an RT-PCR method for detection of enzootic nasal tumor virus in goat [J]. Chinese Veterinary Science, 2014, 44(9): 933−938.(in Chinese)
[11] APOSTOLIDI E D, PSALLA D, CHASSALEVRIS T, et al. Development of real-time PCR-based methods for the detection of enzootic nasal tumor virus 2 in goats [J]. Archives of Virology, 2019, 164(3): 707−716. DOI: 10.1007/s00705-018-04138-0
[12] HUANG Q Y, YE C, CHEN T T, et al. EvaGreen-based real-time PCR assay for sensitive detection of enzootic nasal tumor virus 2 [J]. Molecular and Cellular Probes, 2019, 44: 51−56. DOI: 10.1016/j.mcp.2019.02.003
[13] COUSENS C, MINGUIJON E, DALZIEL R G, et al. Complete sequence of enzootic nasal tumor virus, a retrovirus associated with transmissible intranasal tumors of sheep [J]. Journal of Virology, 1999, 73(5): 3986−3993. DOI: 10.1128/JVI.73.5.3986-3993.1999
[14] KAWASAKO K, OKAMOTO M, KUROSAWA T, et al. Enzootic intranasal tumour virus infection in apparently healthy sheep in Japan [J]. Veterinary Record, 2005, 157(4): 118−120. DOI: 10.1136/vr.157.4.118
[15] ORTÍN A, COUSENS C, MINGUIJÓN E, et al. Characterization of enzootic nasal tumour virus of goats: Complete sequence and tissue distribution [J]. The Journal of General Virology, 2003, 84(8): 2245−2252. DOI: 10.1099/vir.0.19125-0
[16] 林裕胜, 江锦秀, 张靖鹏, 等. 绵羊肺炎支原体SYBR Green Ⅰ实时荧光定量PCR检测方法的建立 [J]. 福建农业学报, 2018, 33(10):1054−1058. LIN Y S, JIANG J X, ZHANG J P, et al. Sybr green Ⅰ RT-qPCR assay for Mycoplasma ovipneumoniae detection [J]. Fujian Journal of Agricultural Sciences, 2018, 33(10): 1054−1058.(in Chinese)
[17] 林裕胜, 江锦秀, 张靖鹏, 等. 丝状支原体山羊亚种SYBR Green Ⅰ qRT-PCR快速检测方法的建立 [J]. 农业生物技术学报, 2017, 25(11):1895−1902. LIN Y S, JIANG J X, ZHANG J P, et al. Establishment of a SYBR Green I qRT-PCR for Rapid Detection of Mycoplasma mycoides subsp. capri [J]. Journal of Agricultural Biotechnology, 2017, 25(11): 1895−1902.(in Chinese)
[18] 汪伟, 杜倩, 韩知晓, 等. 山羊关节炎脑炎病毒SYBR Green Ⅰ 荧光定量PCR方法的建立及应用 [J]. 中国兽医科学, 2020, 50(3):294−299. WANG W, DU Q, HAN Z X, et al. Establishment and application of SYBR Green I real-time PCR for CA [J]. Chinese Veterinary Science, 2020, 50(3): 294−299.(in Chinese)
[19] WANG Y, YANG K, BAI C, et al. Development of a SYBR Green I real-time PCR for the detection of the orf virus [J]. Amb Express, 2017, 7(1):1−6.
[20] 付哲, 杨峰, 郝玉青, 等. 小反刍兽疫病毒实时荧光定量PCR检测方法的建立 [J]. 动物医学进展, 2018, 39(11):14−18. FU Z, YANG F, HAO Y Q, et al. Establishment of realtime fluorescence quantitative PCR for PPRV detection [J]. Progress in Veterinary Medicine, 2018, 39(11): 14−18.(in Chinese)
-
期刊类型引用(1)
1. 江锦秀,林裕胜,张靖鹏,游伟,张龙,毛坤明,胡奇林. 山羊地方性鼻内肿瘤病毒MAb的制备及间接ELISA方法的建立. 中国预防兽医学报. 2023(01): 45-50 .  百度学术
百度学术
其他类型引用(1)




 下载:
下载: