Study on the ecological characteristics and spatial pattern of Chreonoma atritarsis larvae in Camellia oleifera
-
摘要:目的 油茶蓝翅天牛的发生危害与生态环境因子关系密切,掌握该天牛幼虫的生态学特性及其空间分布规律是估计虫口密度、害虫预测预报的基础,可为害虫生态控制提供理论依据。方法 通过对江西主要油茶基地蓝翅天牛幼虫危害情况的系统调查,应用6种聚集度指标和2种回归模型研究了蓝翅天牛幼虫种群的空间格局,运用SPSS 统计软件分析了蓝翅天牛幼虫的发生与林分因子等生态环境的关系。结果 油茶蓝翅天幼虫种群的空间分布格局是均匀分布,种群中生物个体之间是相互排斥的。林分郁闭度、林下植被覆盖度是影响油茶蓝翅天牛有虫株率的2个关键林分因子,林分郁闭度与有虫株率呈极显著负相关,而林下植被覆盖度与有虫株率呈极显著正相关;林下植被覆盖度、林分郁闭度、林内林缘、树高、树龄这5个因子是油茶蓝翅天牛风险评估的关键因子。同时,坡向、坡位对蓝翅天牛有虫株率也存在不同程度的影响。油茶蓝翅天牛幼虫在油茶树枝干上的分布具有较强的选择性,喜欢选择3~6 a枝龄、1.5~2.2 cm枝径、枝角小于60°、枝下高40~59 cm的枝条处蛀食为害。结论 本研究结果丰富了油茶蓝翅天牛的空间分布研究内容,表明该天牛幼虫的均匀分布空间格局是由该虫的生物学、生态学与环境因素共同作用的结果,探明了影响该天牛幼虫发生危害的关键林分因子及其在枝干上的分布规律,对指导预测预报及生物防治具有实用价值。Abstract:Objective The occurrence and damage of Chreonoma atritarsis are closely related to its ecological environment factors. The ecological characteristics and spatial distribution of C. atritarsis larvae are the basis for estimating the population density and pest prediction, which can provide theoretical basis for pest ecological control.Method Based on the systematic investigation on the damage of C. atritarsis larvae in the main Camellia oleifera bases in Jiangxi Province, the spatial pattern of C. atritarsis larvae was studied by using six aggregation indexes and two regression models. The relationship between the occurrence of C. atritarsis larvae and ecological factors was analyzed by using SPSS statistical software.Result The results showed that the spatial distribution pattern of the larva population was uniform, and the individuals in the population were mutually exclusive. Forest canopy density and understory vegetation coverage are the two key factors affecting the pest population rate of C. oleifera. The relationship between forest canopy density and pest population rate is extremely significant negative correlation, while understory vegetation coverage and pest population rate are extremely significant positive correlation. Understory vegetation coverage, forest canopy density, forest edge, tree height and tree age were the key factors for risk assessment of C. atritarsis. At the same time, slope aspect and slope position also had different effects on the percentage of infected plants. The distribution of C. atritarsis. larvae on the branches of C. oleifera was highly selective. They preferred to choose the branches with the age of 3-6 a, diameter of 1.5-2.2 cm, angle less than 60°, and height within 40-59 cm.Conclusion The results of this study enriched the research content of spatial distribution of C. atritarsis, and showed that the spatial pattern of uniform distribution of C. atritarsis larvae was the result of the joint action of biological, ecological and environmental factors. The key forest factors affecting the occurrence and damage of C. atritarsis larvae and their distribution on branches were explored, which had practical value for guiding prediction and biological control.
-
Keywords:
- Camellia oleifera /
- Chreonoma atritarsis /
- larva /
- ecology /
- spatial distribution /
- stand factor /
- ecological factor /
- branch
-
0. 引言
【研究意义】昆虫种群消长的原因,特别是害虫种群暴发的成因一直是昆虫生态学研究及其预测预报的重要内容。虽然昆虫内在的繁殖倾向是其主要内因,但其随时随地受到种种外界生态条件的制约和影响[1-2],但对于“各类生态因素究竟是如何影响与抑制着种群内在的增殖倾向?是否存在着某类特殊的生态因素起着调节种群密度的作用?”等问题,对于控制种群密度的主导因素,各昆虫生态学家有不同的观点:生物因素、气象因素、生态因素综合作用、自动调节。这也正是油茶蓝翅天牛(Chreonoma atritarsis)生态学研究亟需解决的问题。【前人研究进展】近年来,油茶蓝翅天牛在江西有逐渐增加的趋势,部分油茶林受害严重,经济效益和生态效益均受到很大影响[3],虽然各地采取了一些积极措施,但蓝翅天牛种群仍在各地不时暴发成灾[3 - 4],究其原因,除蓝翅天牛自身内在的繁殖力外,可能还与气象因子、林分因素、地势、地形、地被物、天敌等油茶林生物群落情况以及栽培管理密切相关。关于蓝翅天牛发生危害与生态环境的关系,王跃连[5]简要分析了密度、郁闭度与油茶蓝翅天牛等蛀干害虫在广东发生数量的关系;王邵军等[3]认为,一般树龄较大、树势衰老、管理粗放(多年不修剪)的油茶园发生较严重;石兴昌等[6]调查认为,贵州省黎平县油茶蓝翅天牛在林缘遮荫处、杂草处、山阴坡地、种植密度大、海拔500 m 以下中幼林的油茶园发生偏重,暖冬、春秋气候因子宜适的情况下,虫口密增加,发生偏重。然而,这些研究均是单因素分析或仅是定性分析,未曾综合定量分析。在自然界中,各个生态因子并不是单独起作用,而是各个因子的综合相互作用[1]。可见,单个生态因素的作用并不能决定蓝翅天牛的发生与消长。另外,空间分布型是昆虫种群的重要属性之一,了解害虫的空间分布规律是估计虫口密度、害虫预测预报技术的基础,可为害虫生态控制提供理论依据。研究蓝翅天牛的发生危害分布规律,尤其是幼虫的空间格局及幼虫在枝干中的分布习性在生物防治上具有重要意义,张显政等通过对湖南溆浦县1个基地的调查后认为蓝翅天牛幼虫是聚集分布[7]。幼虫种群聚集分布的原因一般是由其本身特性及环境因素共同作用造成,而江西的油茶蓝翅天牛幼虫空间分布和种群空间格局尚待深入研究。【本研究切入点】因此,从生态学角度来研究蓝翅天牛与林分因子、立地因子等生态因子的相互关系,对多个生态因子的影响进行综合分析,并在此基础上筛选出影响蓝翅天牛危害程度的关键因子,即探明其适合油茶生长发育而不利于害虫危害的生态因子,是蓝翅天牛生态防控和预测预报的重要任务。【拟解决的关键问题】本研究通过解剖蓝翅天牛危害的油茶枝条,结合林间虫情、生态因子调查,研究蓝翅天牛幼虫空间格局及其在油茶树枝干上的分布规律,探讨影响油茶林蓝翅天牛有虫株率的关键林分因子,旨在了解蓝翅天牛的生态学特性及危害特性,为科学地释放天敌开展生物防治及风险评估提供依据。
1. 材料与方法
1.1 调查时间、地点及品种
调查时间:2019年3月至2020年12月21日。
调查地点:江西省信丰县古坡镇(25°21′10″N, 115°04′56″E, 海拔110 m),崇义县杰坝乡(25°50′26″N, 114°17′02″E, 海拔248 m)和杨眉镇(25°41′51″N, 114°27′27″E, 海拔402 m),万安县百嘉镇(26°32′56″N, 114°45′22″E, 海拔120 m),永丰县罗铺垦殖场(27°15′51″N, 115°21′03″E, 海拔100 m),宜春市袁州区西村(27°43′25″N, 114°11′34″E, 海拔80 m),万载县三兴镇(28°12′09″N, 114°31′28″E, 海拔116 m)。
调查品种:赣无系列油茶,树龄 4~20 a。
调查地情况:信丰古陂点:山坡地(坡度30°左右),长势良好,树龄 8~17 a,平均密度1 112 株·hm−2,郁闭度0.31 ~0.43;崇义杰坝点:山坡地(坡度50°左右),长势良好,树龄 4~20 a,平均密度2 346 株·hm−2,郁闭度0.49 ~0.57;崇义杰坝点:山坡地(坡度60°左右),长势良好,树龄 10~20 a,平均密度2 174 株·hm−2,郁闭度0.61 ~0.66;万安百嘉点:山坡地(坡度20°左右),长势一般,树龄 7~14 a,平均密度970 株·hm−2,郁闭度0.51~0.61;永丰罗铺点:山坡地(坡度40°左右),长势良好,树龄 8~12 a,平均密度1 719 株·hm−2,郁闭度0.27 ~0.35;袁州西村点:山坡地(坡度30°左右),长势良好,树龄 6~10 a,平均密度1 541 株·hm−2,郁闭度0.33 ~0.41;万载三兴点:平坡地(坡度10°左右),长势良好,树龄 6~11 a,平均密度1 570 株·hm−2,郁闭度0.39 ~0.52。
1.2 调查方法
在上述县区油茶种植基地,在油茶林分踏查的基础上,设置样地进行详查。每基地按大五点对角线取样法,设置5块样地,每样地 30 m × 30 m,逐株详查,详细记录坡位、坡向、坡度、主林层郁闭度、林龄、种植密度、林下植被覆盖度(灌木和草本层的总覆盖度)等林分因子,测量并记录受害株树龄、树高、冠幅及受害枝枝条径粗、枝高、枝条部位、枝向、枝角(枝条与垂直主茎的角度)等。
同时,统计每样地有虫株数、每株受害枝枝数、每枝环蛀圈数、幼虫数,测量幼虫头宽和体长等。
1.3 蓝翅天牛危害程度分级标准
依据林业有害生物危害程度分级标准[8],确定蓝翅天牛幼虫危害程度分级标准:
轻微:有虫株率 ≤ 10%;中等:10%<有虫株率 ≤ 20%;严重:有虫株率>20%。
计算公式:有虫株率(%)=(有虫株数/调查株数)× 100%;
虫口密度(条/株)=调查总活虫数/调查株数。
1.4 生态因子数据无量纲化及分析处理
依据唐艳龙的数据量化格式[9],对于定性记载的生态因子,采用等级数量化处理:坡向,取“东向”= 1,“南向”= 2,“西向”= 3,“北向”= 4;坡位,“取“下坡”= 1,“中坡”= 2,“上坡”= 3;“林内” = 1,“林缘”= 2。
利用公式x = xi / max(即每一个变量值除以该变量取值的最大值)(i = 1, 2, …5)进行数据无量纲化处理。数据及图表均用 Excel 2007 及 SPSS 22.0分析处理。
1.5 空间分布型分析方法
主要参数测定法:根据林间调查数据,采用以下 6 种聚集度指标计算、判断幼虫种群聚集度:扩散系数(C)、负二项分布(K)、平均拥挤度(m*)、丛生指标(I)、聚块性指标(m*/m)、久野指数 Cassie指标(CA)。计算公式参照佟友贵等[10-13]的方法进行计算,差别标准见表1。
表 1 蓝翅天牛幼虫空间分布型差别标准Table 1. Difference standard of spatial distribution pattern of Chreonoma atritarsis larvae项目 C K m* I m*/m CA 分布型 Distributional pattern m = V = 1 >8 = m = 0 = 1 = 0 随机分布 Random distribution m<V >1 0<K<8 >m >0 >1 >0 聚集分布 Aggregation distribution m>V <1 <0 <m <0 <1 <0 均匀分布 Uniform distribution 注:m:虫口密度 ;V:方差
Note: m: Population density、V: Varianc2. 结果与分析
2.1 蓝翅天牛幼虫的空间格局
2.1.1 空间分布的主要参数测定法
6个样地(上述6个县油茶基地)的调查数据及其分析:虫口密度、样本方差及幼虫种群空间分布格局参数如表 2所示,各样地的扩散系数C<1、负二项分布K<0、丛生指标I<0、聚块性指标(m*/m)<1、久野指数 Cassie指标(CA)<0,另外,根据沈佐锐的观点[14],当方差值V<平均值m时,表示种群中生物个体之间是相互排斥的,空间格局为均匀分布。这些指标值均表明,油茶蓝翅天牛幼虫在各样地的空间分布型为均匀分布。
表 2 各样地油茶蓝翅天牛幼虫聚集度指标值Table 2. Index values of larval aggregation degree of Chreonoma atritarsis in Camellia oleifera样地
Plot调查株数
Plant number虫口密度
Population density/
(头·株−1)方差
Variance扩散系数
diffusion
coefficient负二项分布
Negative binomial
distribution平均拥挤度
Average
congestion丛生指标
Cluster
index聚块性指标
Agglomerate
indexCA指标
CA index分布型判断
Distributional
patternm V C K m* I m*/m CA 1 253 0.6367 0.099 0.155 −0.754 0.364 −0.273 0.572 −1.326 均匀分布 Uniformity 2 162 0.4250 0.048 0.113 −0.479 0.342 −0.083 0.804 −2.087 均匀分布 Uniformity 3 471 0.6911 0.189 0.273 −0.951 0.079 −0.612 0.115 −1.051 均匀分布 Uniformity 4 331 0.1367 0.002 0.015 −0.139 0.134 −0.002 0.983 −7.208 均匀分布 Uniformity 5 205 0.1920 0.004 0.021 −0.196 0.187 −0.005 0.974 −5.100 均匀分布 Uniformity 6 463 0.3867 0.015 0.039 −0.402 0.362 −0.024 0.937 −2.486 均匀分布 Uniformity Total 1885 0.4525 0.116 0.256 −0.608 0.241 −0.212 0.532 −1.643 均匀分布 Uniformity 2.1.2 空间分布的回归分析测定法
(1)Taylor 幂法则。根据表2的虫口平均密度(m)、方差(V)数据,再以lgV和lgm作线性回归,计算得出回归方程为:lgV = 2.742 lgm−0.417。lgV 与lgm的相关性达到极显著水平(R = 0.981, P = 0.001<0.01),说明所建模型成立。
根据lga = −0.417<0,b=2.742>1,m<1,说明蓝翅天牛幼虫在油茶林是均匀分布的。
(2)Iwao m*-m的回归分析法。由表2 的各样地虫口平均密度(m)、平均拥挤度(m*)作简单线性回归,得回归方程:m* = 0.209 + 0.087m,相关系数R = 0.9154。
根据 a = 0.209>0, 说明分布的基本成分是个体群,1>b = 0.087>0,说明蓝翅天牛幼虫在油茶林是均匀分布的。
2.2 影响油茶林蓝翅天牛有虫株率的关键林分因子
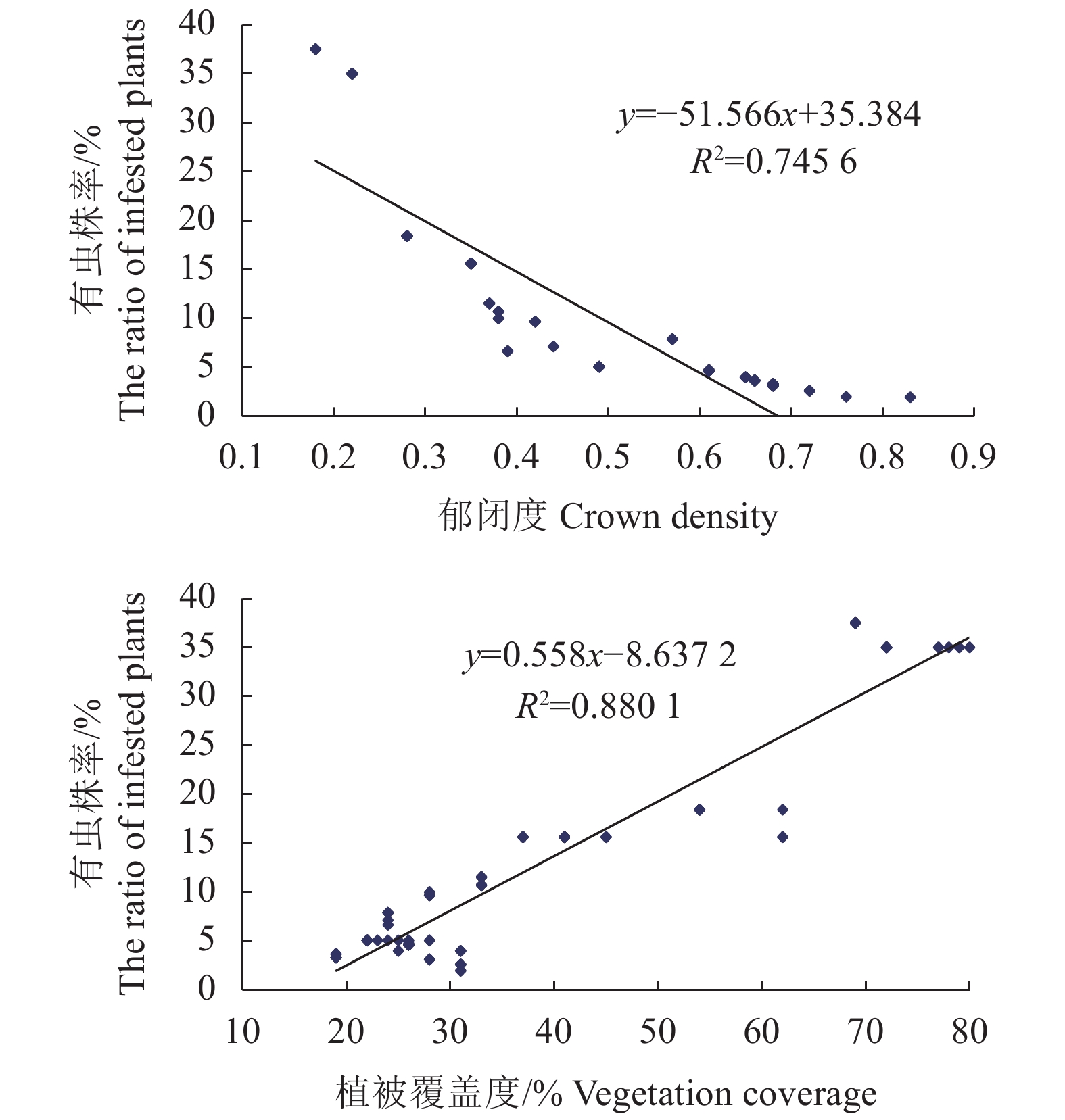
各林分因子及其代号,以及各因子与油茶林蓝翅天牛有虫株率的逐步回归分析结果如表3所示,与油茶林有虫株率相关性大(相关系数大)的林分因子是郁闭度(R = −0.864)、林下植被覆盖度(R = 0.938),且两者P = 0.000<0.01,说明林分郁闭度与有虫株率呈极显著负相关,而林下植被覆盖度与有虫株率呈极显著正相关(图1),可见,林分郁闭度、林下植被覆盖度是影响油茶蓝翅天牛有虫株率的2个关键林分因子。
表 3 各林分因子与油茶林有虫株率的逐步回归分析结果Table 3. The results of stepwise regression analysis between stand factors and the percentage of infested plants因子
Factors树龄
Tree age/a树高
Tree height/m冠幅
Crown width/m2坡向
Aspect坡位
Slope position林内林缘
Forest within
and edged密度
Density/
(株·hm−2)郁闭度
Canopy
density植被盖度
Vegetation
coverage/%x1 x2 x3 x4 x5 x6 x7 x8 x9 均值 Mean 9.609 2.187 5.368 0.511 0.634 0.778 1621.233 0.468 35.684 相关系数R Pearson Correlation 0.175 −0.111 0.149 −0.078 −0.022 −0.135 −0.256 −0.864 0.938 P值 Sig. 0.044 0.203 0.088 0.370 0.798 0.121 0.003 0.000 0.000 各因子与有虫株率(y)的逐步回归分析得到多元线性回归模型:y = 5.933 + 0.423x9 – 19.308x8 – 2.751x6 – 0.342x3 + 1.489x2。经F检验,该预测模型达到极显著水平(F = 59.98; df = 9 132; P = 0.000<0.01)。因此,林下植被覆盖度x9、林分郁闭度x8、林内林缘x6、树高x3、树龄x2这5个因子是风险评估的关键因子,应用该模型对蓝翅天牛的发生进行风险评估是可靠的。
2.3 坡向、坡位对油茶林蓝翅天牛有虫株率的影响
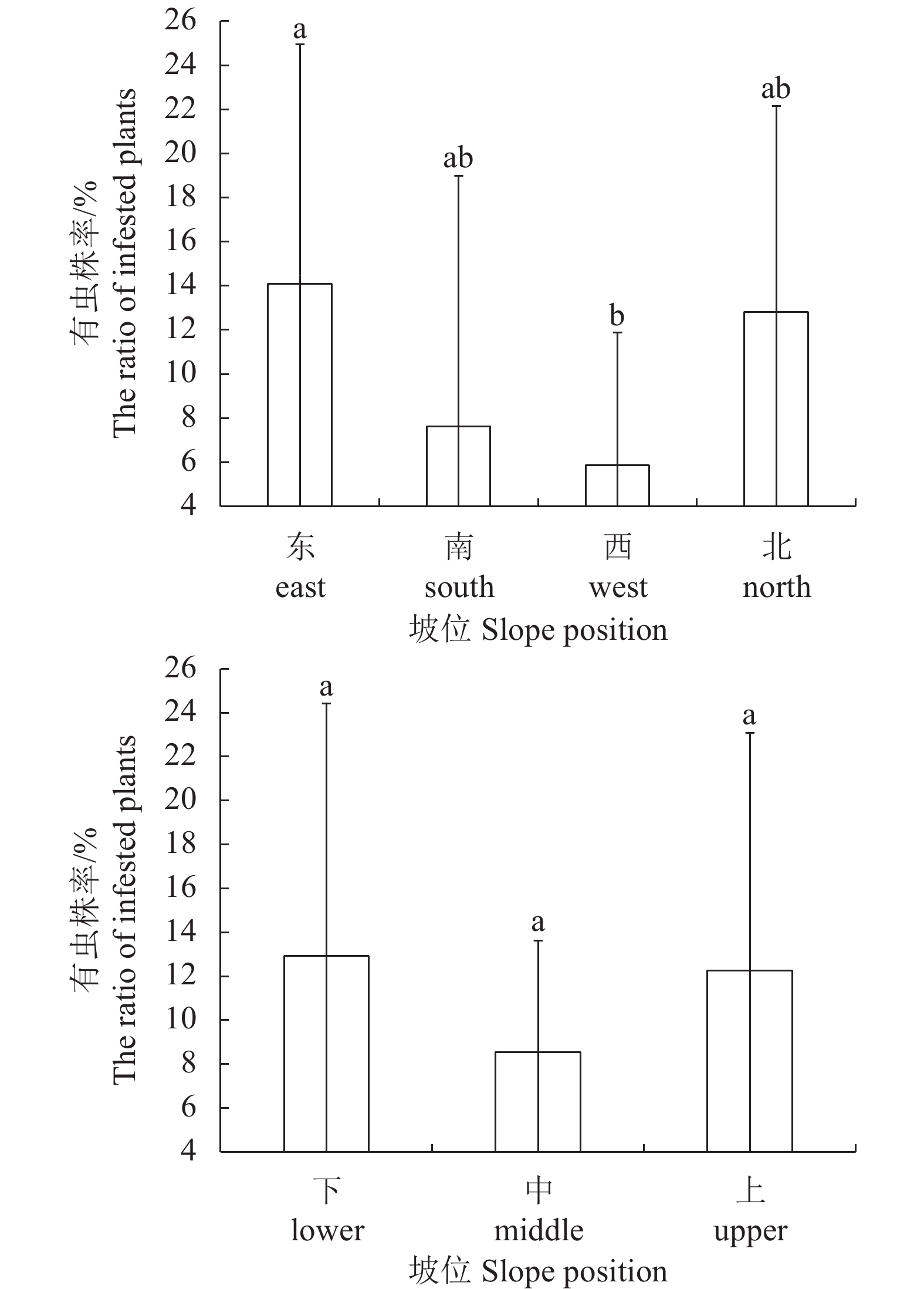
虽然坡向坡位不是影响油茶林蓝翅天牛有虫株率的关键因子,但不同坡向、不同坡位对蓝翅天牛有虫株率存在不同程度的影响(图2)。就坡向而言,东向坡的油茶林有虫株率最高(14.09 ± 10.85),其次是北向坡(12.81 ± 9.34),但两者的有虫株率差异未达显著水平(P>0.05),有虫株率最小的是西向坡(5.85 ± 6.03),且与东向坡的差异达显著水平(P<0.05)。就坡位而言,有虫株率的大小顺序是:下坡位>上坡位>中坡位,但三者间的差异未达显著水平。
2.4 蓝翅天牛幼虫在油茶树枝干上的分布
调查结果显示,蓝翅天牛幼虫在油茶树枝干上的危害存在选择性,枝条年龄(枝龄)、枝条径粗(枝径)、分枝角度(枝角)、枝下高、枝条部位、枝条方位等的不同,幼虫的数量存在差异,即幼虫在枝干上分布具有自己的嗜好(表4)。
表 4 蓝翅天牛幼虫在油茶枝干上的选择分布Table 4. Selection and distribution of Chreonoma atritarsis larvae on Camellia oleifera branches枝龄
Branch
age/a幼虫数占比
Proportion of
larvae/%枝径
Branch
diameter/cm幼虫数占比
Proportion of
larvae/%枝高
Branch
height/cm幼虫数占比
Proportion of
larvae/%枝角
Branch
angle/℃幼虫数占比
Proportion of
larvae/%枝向
Branch
direction幼虫数占比
Proportion of
larvae/%1~2 0.75 c 0.7~1.0 0.75 d 0~19 3.76 c 0~9 15.04 ab 正北 Due north 18.05 a 3~4 30.83 a 1.1~1.4 11.28 b 20~39 14.29 ab 10~19 14.29 ab 垂直 Vertical 12.03 b 5~6 34.59 a 1.5~1.8 27.82 a 40~59 24.81 a 20~29 15.79 ab 正东 Due east 18.05 a 7~8 14.29 b 1.9~2.2 29.32 a 60~79 18.80 ab 30~39 21.05 a 东北 Northeast 3.76 c 9~10 8.27 bc 2.3~2.6 13.53 b 80~99 19.55 ab 40~49 11.28 b 东南 Southeast 7.52 bc 11~12 2.26 c 2.7~3.0 6.02 c 100~119 9.02 b 50~59 11.28 b 正南 Due south 11.28 b 13~14 6.02 bc 3.1~3.4 4.51 c 120~139 3.01 c 60~69 8.27 bc 正西 Due west 15.79 ab 15~16 2.26 c 3.5~3.8 5.26 c 140~159 3.76 c 70~79 2.26 d 西北 Northwest 6.77 bc 17~ 0.75 c 3.9~ 1.54 d 160~179 3.01 c 80~90 0.75 d 西南 Southwest 6.77 bc 注:同列不同小写字母表示差异显著(SNK法, P<0.05)。
Note: Different lowercase letters in the same column show significant difference(SNK, P<0.05).从表4可见,蓝翅天牛幼虫多分布在枝龄3~6 a的枝干上,幼虫数占调查幼虫总数的65.41%,显著高于其他枝龄的枝干(P<0.05);油茶枝条的直径(枝径)不同对该天牛幼虫数量有显著影响(R = 0.5523; F = 57.4910;df =1 132;P = 0.0000<0. 01),该天牛幼虫最喜欢选择在直径1.5~2.2 cm的枝条上危害,占比57.14%,达一半以上;枝条离地高度(枝下高)对该天牛幼虫数量也有显著影响(R = 0.4802; F = 39.2672; df =1 132; P = 0.0000<0. 01),在40~59 cm枝高的枝条处幼虫数量最多,即蓝翅天牛比较喜欢选择在离地高40~59 cm的枝条位置钻蛀为害;油茶分枝与垂直主枝的角度(枝角)也显著影响着蓝翅天牛幼虫数量(R = 0.5180; F = 48.0477; df =1 132;P = 0.0000<0.01),幼虫喜欢选择在枝角<59°的枝干上为害,说明该天牛幼虫喜欢在向上角度较小的枝条上蛀食;幼虫取食对枝条方向的选择没有特别嗜好,东、南、西、北各个方向的占比均相当,差异均未达显著水平(P>0. 05),但主枝(即垂直方向)相对较少;而对枝条部位的选择,蓝翅天牛幼虫则更喜欢选择在枝条的中段及下段,其幼虫数量均显著高于枝条上段(P<0. 05)。
可见,油茶蓝翅天牛幼虫在油茶树枝干上的分布具有较强的选择性,喜欢选择枝角小于60°、枝龄3~6 a、枝径1.5~2.2 cm、枝下高40~59 cm的枝条处蛀食为害。
3. 讨论与结论
油茶蓝翅天牛幼虫空间分布格局是种群有效利用资源的一个重要特征。本研究表明,油茶蓝翅天牛幼虫空间分布的基本成分是个体群,个体群之间是相互排斥的,其空间格局为均匀分布。本研究结果与绝大多数天牛幼虫呈聚集分布的结果不同[15-18],这主要是由蓝翅天牛本身的种群内在增殖倾向、分散产卵等生物学特性决定,也是由幼虫危害习性等生态学特性和油茶林不同生境共同作用的结果。但同是油茶蓝翅天牛,本研究结果表明其幼虫是均匀分布,而张显政等[7]则认为是聚集分布,这可能是由蓝翅天牛自身的生物学特性决定的:幼虫种群空间分布型是动态的,在低密度时(本研究虫口密度均值为0.452 5头·株−1)呈均匀分布,而在高密度时(张显政报道的虫口密度均值为1.241 4头·株−1)呈聚集分布。或许也可能是两省油茶林的生态环境因子不同所造成的,有待深入研究。
害虫的发生危害与生态因子关系密切,油茶蓝翅天牛也不例外。本研究表明,蓝翅天牛幼虫危害油茶林有虫株率与林分郁闭度、林下植被覆盖度均有显著的相关性,是影响油茶蓝翅天牛有虫株率的2个关键林分因子。这与诸瑞龙等、王跃连、石兴昌等的报道一致[4–6],郁闭度较大时,蓝翅天天牛等蛀害虫数量较少,郁闭度小、杂草多(植被覆盖度高)的油茶林,有虫株率高,抚育管理差或林地荒芜的林分被害率高。
虽然单个的因子并不能决定害虫的发生,但这些因子的综合作用,给害虫的发生提供了有利的环境条件[19–20]。本研究表明,林下植被覆盖度、林分郁闭度、林内林缘、树高、树龄这5个因子是油茶蓝翅天牛风险评估的关键因子。同时,坡向、坡位对蓝翅天牛有虫株率也存在不同程度的影响。
本研究表明,油茶蓝翅天牛幼虫在油茶树枝干上的分布具有较强的选择性,喜欢选择枝龄3~6 a、枝径1.5~2.2 cm、枝角小于60°、枝下高40~59 cm的枝条处蛀食为害。其原因主要是与幼虫取食为害习性有关,幼虫孵化后蛀入皮层,自下而上旋绕蛀食一圈, 再蛀入木质部和髓部,并向上蛀食隧道,幼虫发育进度与其为害进程密切相关,枝龄、枝径太小则营养不足,幼虫将过早完成环蛀过程,幼虫太小造成蛀入木质部艰难;枝龄、枝径太大,因环蛀时间过长往往造成幼虫不能按时完成环蛀,而且因枝径太大造成幼虫蛀入木质部的距离增大,将影响幼虫生长发育。这一点与前人的报道基本一致[3, 21]。曾家丽等 [21]报道的蓝翅天牛幼虫蛀食的最适枝枝龄与本研究相同,但其枝径比本研究的更小些(1.0~1.5 cm),这可能的原因是36年的油茶管理相对粗放(“7~8年生油茶未进行修剪”[21]),而本研究所调查的油茶是精细化管理,精于修剪及施肥,营养条件更好,生长发育更快,正如申巍研究所证实“修剪和施肥对油茶枝条粗度有明显促进作用” [22],所以在同样的枝龄下,现在的枝条比以前长得更粗更脆嫩,所以造成该天牛以前喜欢选择1.0~1.5 cm枝径而现在则更喜欢1.5~2.2 cm枝径的枝条。大于60°的枝条大多为水平枝、下垂枝,受光条件差,营养条件差,纤细,不利于该天牛幼虫生长发育,所以,油茶蓝翅天牛幼虫多喜欢选择枝角小于60°的枝条蛀食。
本研究对油茶蓝翅天牛幼虫生态学及空间分布特性的研究在一定程度上可指导虫情测报和生态防控策略的制定。但本研究仅调查、分析了立地、林分因子等生境与幼虫发生危害的关系,未获得气象数据,未分析气象因子对幼虫发生危害的影响。因此,应进一步探讨害虫的发生与温湿度等气象条件的关系,从气候、寄主、林分、群落等不同层次,揭示油茶蓝翅天牛种群暴发机制,以期为害虫的预测预报、综合防控提供更可靠的参考依据,从而更好地服务于油茶产业生产经营管理。
-
表 1 蓝翅天牛幼虫空间分布型差别标准
Table 1 Difference standard of spatial distribution pattern of Chreonoma atritarsis larvae
项目 C K m* I m*/m CA 分布型 Distributional pattern m = V = 1 >8 = m = 0 = 1 = 0 随机分布 Random distribution m<V >1 0<K<8 >m >0 >1 >0 聚集分布 Aggregation distribution m>V <1 <0 <m <0 <1 <0 均匀分布 Uniform distribution 注:m:虫口密度 ;V:方差
Note: m: Population density、V: Varianc表 2 各样地油茶蓝翅天牛幼虫聚集度指标值
Table 2 Index values of larval aggregation degree of Chreonoma atritarsis in Camellia oleifera
样地
Plot调查株数
Plant number虫口密度
Population density/
(头·株−1)方差
Variance扩散系数
diffusion
coefficient负二项分布
Negative binomial
distribution平均拥挤度
Average
congestion丛生指标
Cluster
index聚块性指标
Agglomerate
indexCA指标
CA index分布型判断
Distributional
patternm V C K m* I m*/m CA 1 253 0.6367 0.099 0.155 −0.754 0.364 −0.273 0.572 −1.326 均匀分布 Uniformity 2 162 0.4250 0.048 0.113 −0.479 0.342 −0.083 0.804 −2.087 均匀分布 Uniformity 3 471 0.6911 0.189 0.273 −0.951 0.079 −0.612 0.115 −1.051 均匀分布 Uniformity 4 331 0.1367 0.002 0.015 −0.139 0.134 −0.002 0.983 −7.208 均匀分布 Uniformity 5 205 0.1920 0.004 0.021 −0.196 0.187 −0.005 0.974 −5.100 均匀分布 Uniformity 6 463 0.3867 0.015 0.039 −0.402 0.362 −0.024 0.937 −2.486 均匀分布 Uniformity Total 1885 0.4525 0.116 0.256 −0.608 0.241 −0.212 0.532 −1.643 均匀分布 Uniformity 表 3 各林分因子与油茶林有虫株率的逐步回归分析结果
Table 3 The results of stepwise regression analysis between stand factors and the percentage of infested plants
因子
Factors树龄
Tree age/a树高
Tree height/m冠幅
Crown width/m2坡向
Aspect坡位
Slope position林内林缘
Forest within
and edged密度
Density/
(株·hm−2)郁闭度
Canopy
density植被盖度
Vegetation
coverage/%x1 x2 x3 x4 x5 x6 x7 x8 x9 均值 Mean 9.609 2.187 5.368 0.511 0.634 0.778 1621.233 0.468 35.684 相关系数R Pearson Correlation 0.175 −0.111 0.149 −0.078 −0.022 −0.135 −0.256 −0.864 0.938 P值 Sig. 0.044 0.203 0.088 0.370 0.798 0.121 0.003 0.000 0.000 表 4 蓝翅天牛幼虫在油茶枝干上的选择分布
Table 4 Selection and distribution of Chreonoma atritarsis larvae on Camellia oleifera branches
枝龄
Branch
age/a幼虫数占比
Proportion of
larvae/%枝径
Branch
diameter/cm幼虫数占比
Proportion of
larvae/%枝高
Branch
height/cm幼虫数占比
Proportion of
larvae/%枝角
Branch
angle/℃幼虫数占比
Proportion of
larvae/%枝向
Branch
direction幼虫数占比
Proportion of
larvae/%1~2 0.75 c 0.7~1.0 0.75 d 0~19 3.76 c 0~9 15.04 ab 正北 Due north 18.05 a 3~4 30.83 a 1.1~1.4 11.28 b 20~39 14.29 ab 10~19 14.29 ab 垂直 Vertical 12.03 b 5~6 34.59 a 1.5~1.8 27.82 a 40~59 24.81 a 20~29 15.79 ab 正东 Due east 18.05 a 7~8 14.29 b 1.9~2.2 29.32 a 60~79 18.80 ab 30~39 21.05 a 东北 Northeast 3.76 c 9~10 8.27 bc 2.3~2.6 13.53 b 80~99 19.55 ab 40~49 11.28 b 东南 Southeast 7.52 bc 11~12 2.26 c 2.7~3.0 6.02 c 100~119 9.02 b 50~59 11.28 b 正南 Due south 11.28 b 13~14 6.02 bc 3.1~3.4 4.51 c 120~139 3.01 c 60~69 8.27 bc 正西 Due west 15.79 ab 15~16 2.26 c 3.5~3.8 5.26 c 140~159 3.76 c 70~79 2.26 d 西北 Northwest 6.77 bc 17~ 0.75 c 3.9~ 1.54 d 160~179 3.01 c 80~90 0.75 d 西南 Southwest 6.77 bc 注:同列不同小写字母表示差异显著(SNK法, P<0.05)。
Note: Different lowercase letters in the same column show significant difference(SNK, P<0.05). -
[1] 张孝羲. 昆虫生态及预测预报[M]. 北京: 农业出版社, 1985. [2] 孙儒泳. 动物生态学原理(第2版)[M]. 北京: 北京师范大学出版社, 1996. [3] 王邵军, 彭九生. 江西油茶蓝翅天牛生物学特征及其生态控制技术 [J]. 林业实用技术, 2011(6):41−43. WANG S J, PENG J S. Biological characteristics and ecological control techniques of Chreonoma atritarsis of Camellia oleifera in Jiangxi [J]. Practical Forestry Technology,, 2011(6): 41−43.(in Chinese)
[4] 诸瑞龙, 金德胜, 徐凌浩. 油茶枝干害虫—红颈蓝翅天牛 [J]. 江西植保, 1982(3):28. ZHU R L, JIN D S, XU L H. Red necked blue winged longicorn, a pest on branches and stems of Camellia oleifera [J]. Jiangxi Plant Protection, 1982(3): 28.(in Chinese)
[5] 王跃连. 密度、郁闭度与油茶蛀干害虫发生数量的关系 [J]. 中南林业调查规划, 1983(2):28−32. WANG Y L. The relationship between density, canopy density and the number of stem borers in Camellia oleifera [J]. Central South Forest Inventory and Planning, 1983(2): 28−32.(in Chinese)
[6] 石兴昌, 吴运辉, 李振东, 等. 油茶黑跗眼天牛防治技术调查研究 [J]. 绿色科技, 2020(11):103−105. SHI X C, WU Y H, LI Z D, et al. Investigation and study on control techniques of Chreonoma atritarsis [J]. Journal of Green science and technology, 2020(11): 103−105.(in Chinese)
[7] 张显政, 成小飞. 蓝翅眼天牛幼虫空间分布型及用双重抽样调查幼虫密度研究初报 [J]. 湖南林业科技, 1988(2):59−61. ZHANG X Z, CHENG X F. Study on spatial distribution pattern of Chreonoma atritarsis larvae and density of larvae by double sampling [J]. Hunan Forestry Science & Technology, 1988(2): 59−61.(in Chinese)
[8] 关继东. 林业有害生物控制技术[M]. 北京: 中国林业出版社, 2007. [9] 唐艳龙. 栗山天牛的生态学特性及其生物防治技术研究[D]. 北京: 中国林业科学研究院, 2011. TANG Y L. Studies on the ecology of Massicus raddei (Coleoptera: Cerambycidae)and its biological control[D]. Beijing: Chinese Academy of Forestry Sciences, 2011. (in Chinese).
[10] 佟友贵, 张开存, 杨欣, 等. 桉树枝瘿姬小蜂幼虫空间分布型研究 [J]. 中国科技信息, 2013(10):95, 105. TONG Y G, ZHANG K C, YANG X, et al. Study on spatial distribution pattern of Leptocybe invasa larvae [J]. China Science and Technology Information, 2013(10): 95, 105.(in Chinese)
[11] 赵丹阳, 叶燕华, 方天松, 等. 油茶象甲幼虫发生及空间分布型研究 [J]. 广东农业科学, 2015, 42(12):78−81. DOI: 10.3969/j.issn.1004-874X.2015.12.016 ZHAO D Y, YE Y H, FANG T S, et al. Occurrence and spatial distribution patterns of Curculio chinensis larvae [J]. Guangdong Agricultural Sciences, 2015, 42(12): 78−81.(in Chinese) DOI: 10.3969/j.issn.1004-874X.2015.12.016
[12] 王小强, 刘虹伶, 蒲德强, 等. 四川凉山烟区烟蚜种群空间分布型及抽样技术研究 [J]. 中国烟草科学, 2017, 38(6):34−40. WANG X Q, LIU H L, PU D Q, et al. Spatial distribution pattern and sampling technique of Myzus persicae in Liangshan tobacco regions of Sichuan Province [J]. Chinese Tobacco Science, 2017, 38(6): 34−40.(in Chinese)
[13] 冯雪莹, 张毅波, 黄玉翠, 等. 雄安新区及其周边地区烟粉虱的种群动态及空间分布格局 [J]. 中国农业科技导报, 2019, 21(10):115−124. FENG X Y, ZHANG Y B, HUANG Y C, et al. Population dynamics and spatial distribution of Bemisia tabaci in Xiongan New Area and its surrounding areas [J]. Journal of Agricultural Science and Technology, 2019, 21(10): 115−124.(in Chinese)
[14] 沈佐锐. 关于Taylor幂法则的统计学讨论 [J]. 生态学杂志, 1990, 9(6):64−67. SHEN Z R. A statistical discussion on taylor's power law [J]. Chinese Journal of Ecology, 1990, 9(6): 64−67.(in Chinese)
[15] 过婉珍. 茶天牛发生的田间调查及防治 [J]. 福建茶叶, 2010, 32(1):15−16. DOI: 10.3969/j.issn.1005-2291.2010.01.005 GUO W Z. Field investigation and control of Aeolesthes induta [J]. Tea in Fujian, 2010, 32(1): 15−16.(in Chinese) DOI: 10.3969/j.issn.1005-2291.2010.01.005
[16] 王晓红. 锈色粒肩天牛生物学、生态学特性与生物防治技术研究[D]. 北京: 中国林业科学研究院, 2011. WANG X H. Studies on biology, ecology and biocontrol techniques of Apriona swainsoni Hope (Coleoptera: Cerambycidae)[D]. Beijing: Chinese Academy of Forestry Sciences, 2011. (in Chinese).
[17] 戚裕锋. 星天牛幼虫空间分布型及抽样技术 [J]. 福建林业科技, 2016, 43(4):97−99, 124. QI Y F. Spatial distribution pattern and sampling techniques of Anoplophora chinensis larvae [J]. Journal of Fujian Forestry Science and Technology, 2016, 43(4): 97−99, 124.(in Chinese)
[18] 陈潜, 许志春, 张连生, 等. 褐梗天牛幼虫和成虫空间分布的地统计学研究 [J]. 生态学报, 2018, 38(3):975−983. CHEN Q, XU Z C, ZHANG L S, et al. Geostatistical analysis of the spatial distribution of Arhopalus rusticus larvae and adults [J]. Acta Ecologica Sinica, 2018, 38(3): 975−983.(in Chinese)
[19] 唐艳龙, 温小遂, 杨清培, 等. 影响萧氏松茎象发生的关键小气候因子 [J]. 南京林业大学学报(自然科学版), 2009, 33(5):117−120. TANG Y L, WEN X S, YANG Q P, et al. Key microclimate factors related to the outbreak of Hylobitelus xiaoi Zhang [J]. Journal of Nanjing Forestry University (Natural Sciences), 2009, 33(5): 117−120.(in Chinese)
[20] 唐艳龙, 杨清培, 温小遂, 等. 萧氏松茎象发生与湿地松林地枯落物及土壤物理性质的关系 [J]. 林业科学研究, 2010, 23(4):554−559. TANG Y L, YANG Q P, WEN X S, et al. The relationship between physical characteristics of litterfall and soil in slash pine plantation and the occurring of Hylobitelus xiaoi Zhang [J]. Forest Research, 2010, 23(4): 554−559.(in Chinese)
[21] 曾家丽, 邓白罗, 石卓功. 油茶枝条状态对油茶蓝翅天牛产卵易感性的初步研究 [J]. 经济林研究, 1984, 2(1):73−79. ZENG J L, DENG B L, SHI Z G. A preliminary study on the oviposition susceptibility of Chreonoma atritarsis [J]. Economic forest research, 1984, 2(1): 73−79.(in Chinese)
[22] 申巍. 修剪施肥对油茶生长结实特性影响研究[D]. 重庆: 西南大学, 2008. SHEN W. Studies on effects of pruning and fertilization on Camellia oleifera growth and fruiting bearing characteristics[D]. Chongqing: Southwest University, 2008. (in Chinese).
-
期刊类型引用(5)
1. 陈元生,黄建林,罗致迪,潘友粮. 油茶织蛾幼虫生态学特性及其发生测报研究. 生物灾害科学. 2024(01): 7-12 .  百度学术
百度学术
2. 覃艳妮,余宏昌,兰俊幸,王旭,刘有莲. 油茶林相思拟木蠹蛾和黑跗眼天牛羽化孔空间生态位分析. 广西农学报. 2024(05): 86-95 .  百度学术
百度学术
3. 雷艳红,蓝应亮,陈元生,罗致迪. 油茶蓝翅天牛的生物调控技术研究与示范. 现代农业科技. 2023(14): 79-82 .  百度学术
百度学术
4. 陈元生,周嘉颖,肖小华,罗致迪,彭小文. 林间花斑花绒寄甲幼虫种群动态及空间分布格局. 环境昆虫学报. 2023(03): 688-694 .  百度学术
百度学术
5. 苏湘宁,陈勤,章玉苹,刘伟玲,李传瑛,廖章轩,黄少华. 潮州单丛茶树天牛种群动态、空间分布型及成虫交配和产卵行为研究. 南方农业学报. 2022(02): 364-371 .  百度学术
百度学术
其他类型引用(2)




 下载:
下载: