Duplex PCR Detection on Pasteurella multocida Serogroup F Strain in Rabbits
-
摘要:目的 建立检测兔源F型多杀性巴氏杆菌的双重PCR检测方法,为兔巴氏杆菌病的诊断提供技术支持。方法 根据多杀性巴氏杆菌kmt1基因和F型多杀性巴氏杆菌fcbD基因的保守序列分别设计了2对引物进行双重PCR扩增,对双重PCR检测方法的退火温度和混合引物浓度进行优化,并对方法的特异性、敏感性、重复性和准确性进行验证。结果 该双重PCR方法最优反应条件为:退火温度60 ℃、混合引物浓度0.8 μmol·L−1。该双重PCR方法能扩增出兔源F型多杀性巴氏杆菌的kmt1基因片段(260 bp)和fcbD基因片段(490 bp)、兔源A和D型多杀性巴氏杆菌的kmt1基因片段(260 bp),对兔源支气管败血波氏杆菌、肺炎克雷伯菌、大肠杆菌、金黄色葡萄球菌和阴性对照均为阴性,无交叉反应,特异性较强。该方法对兔源F型多杀性巴氏杆菌的最低检出限为1×103拷贝·μL−1,敏感性高。应用该方法对90份病死兔肺脏样品进行批内和批间重复性试验,结果均一致,重复性好。应用该双重PCR方法和已报道的多重PCR方法同时检测87份已知结果的呼吸道病死兔肺脏样品,结果显示双重PCR方法检测结果和已报道的多重PCR方法检测结果与已知结果的符合率分别为97.70%和94.25%,双重PCR方法检测结果与已报道的多重PCR方法检测结果的符合率为93.10%,双重PCR方法的准确性更高。结论 针对多杀性巴氏杆菌kmt1基因和F型多杀性巴氏杆菌fcbD基因建立的双重PCR检测方法具有良好的特异性、敏感性、重复性和准确性,为兔源F型多杀性巴氏杆菌的快速检测提供了技术支撑。Abstract:Objective A duplex PCR assay for rapid detecting Pasteurella multocida serogroup F strain in rabbits was developed.Methods Primer concentration and annealing temperature for the duplex PCR were optimized based upon two sets of specific primers targeting the conserved sequences of kmt1 of P. multocida and fcbD of P. multocida serogroup F strain. Specificity, sensitivity, and accuracy of the methodology were tested for its applicability.Results The optimized conditions for the assay included 0.8 μmol·L−1 on the primer concentration and 60 ℃ for the annealing temperature. The assay detection was specific for P. multocida serogroup A, D, and F strains and free of cross-reactions with Bordetella bronchiseptica, Klebsiella pneumonia, Escherichia coli, Staphylococcus aureus, and negative control. A highly sensitive detection limit up to 1×103 copies·μL−1 on genomic DNA of P. multocida serogroup F isolate was achieved. In the repeated intra- and inter-assays on 90 lung specimens from dead diseased rabbits, the assay variation coefficients were identical. By using 87 lung samples collected from known infection cases, the newly developed duplex PCR assay and reported multiplex PCR assay yield agreements of 97.70% and 94.25% with the known results, respectively. Moreover, the current duplex PCR determination also yielded an agreement of 93.10% on the measurements with the reported from a multiplex PCR assay.Conclusion The newly established duplex PCR assay based on the specific primers targeting the conserved sequences of kmt1 of P. multocida as well as fcbD of P. multocida serogroup F strain was tested to be highly specific, sensitive, repeatable, and accurate in detecting the pathogenic P. multocida serogroup F strain in rabbits.
-
Keywords:
- rabbit /
- Pasteurella multocida serogroup F strain /
- kmt1 gene /
- fcbD gene /
- duplex PCR assay
-
0. 引言
【研究意义】兔巴氏杆菌病是由多杀性巴氏杆菌感染兔引起的一种传染病。该病一年四季均可发生,且所有日龄的兔均可发病。临床上,兔巴氏杆菌病以呼吸道症状多见,也可见中耳炎和结膜炎[1-2]。该病是兔的常发病和多发病,是危害兔产业发展的重要疾病。根据多杀性巴氏杆菌的荚膜抗原可将其分为5种血清型,即A、B、D、E和F型[3]。其中,A和D型菌株是兔群中的优势流行菌株[4-5]。【前人研究进展】F型多杀性巴氏杆菌最早在美国的火鸡中发现[6],该菌株主要感染禽类[7],其感染能引起禽霍乱[8]。然而,研究表明国内外兔群中也存在F型多杀性巴氏杆菌,且该菌株对兔具有强致病性[9-11]。由此可见,兔群中F型多杀性巴氏杆菌的出现,使兔巴氏杆菌病的病因更加复杂,也使该病的确诊更加困难。因此,实现对F型多杀性巴氏杆菌的快速检测,掌握其在兔群中的流行情况,对兔产业的发展具有重要意义。【本研究切入点】目前,用于F型多杀性巴氏杆菌的实验室检测方法有细菌分离鉴定和多重PCR[3, 10]。多杀性巴氏杆菌营养需求高、生长较缓慢,容易受其他生长较快的细菌污染。多重PCR用于多杀性巴氏杆菌的荚膜分型[3],反应体系中包含6对引物,对反应体系的组成和反应条件都要求很高,否则会出现非特异性扩增或假阴性结果。【拟解决的关键问题】为了建立一种快速且简便的F型多杀性巴氏杆菌检测方法,本研究根据多杀性巴氏杆菌kmt1基因和F型多杀性巴氏杆菌fcbD基因的保守序列分别设计了2对特异性引物,建立了检测F型多杀性巴氏杆菌的双重PCR检测方法,为兔源F型多杀性巴氏杆菌的快速检测提供技术支撑。
1. 材料与方法
1.1 材料
1.1.1 主要试剂
2×PCR Mix、pEASY-T1克隆载体、细菌基因组DNA提取试剂盒和胶回收试剂盒购自北京全式金生物技术有限公司。
1.1.2 菌株
兔源A、D和F型多杀性巴氏杆菌(Pasteurella multocida)、支气管败血波氏杆菌(Bordetella bronchiseptica)、肺炎克雷伯菌(Klebsiella pneumonia)、大肠杆菌(Escherichia coli)、金黄色葡萄球菌(Staphylococcus aureus)由本实验室分离保存。
1.2 方法
1.2.1 引物设计
根据GenBank中公布的多杀性巴氏杆菌kmt1基因(登录号:KX348143)和F型多杀性巴氏杆菌的fcbD基因(登录号:AF302467),利用Primer Premier 5.0软件设计了2对分别针对kmt1基因和fcbD基因保守序列的特异性引物,kmt1基因引物序列为:kmt1-F:5′-gttttatgccacttgaaatgggaa-3′/kmt1-R:5′-taagaaacgtaactcaacatggaaatatt-3′;fcbD基因引物序列为:fcbD-F:5′-ctaaagatcttgttcttgctccattg-3′/fcbD-R:5′-tctgcggtaatattatgagtatccac-3′,扩增的目的片段分别为260 bp和490 bp。引物由上海铂尚生物技术有限公司合成。
1.2.2 单重PCR方法的建立及扩增产物的鉴定
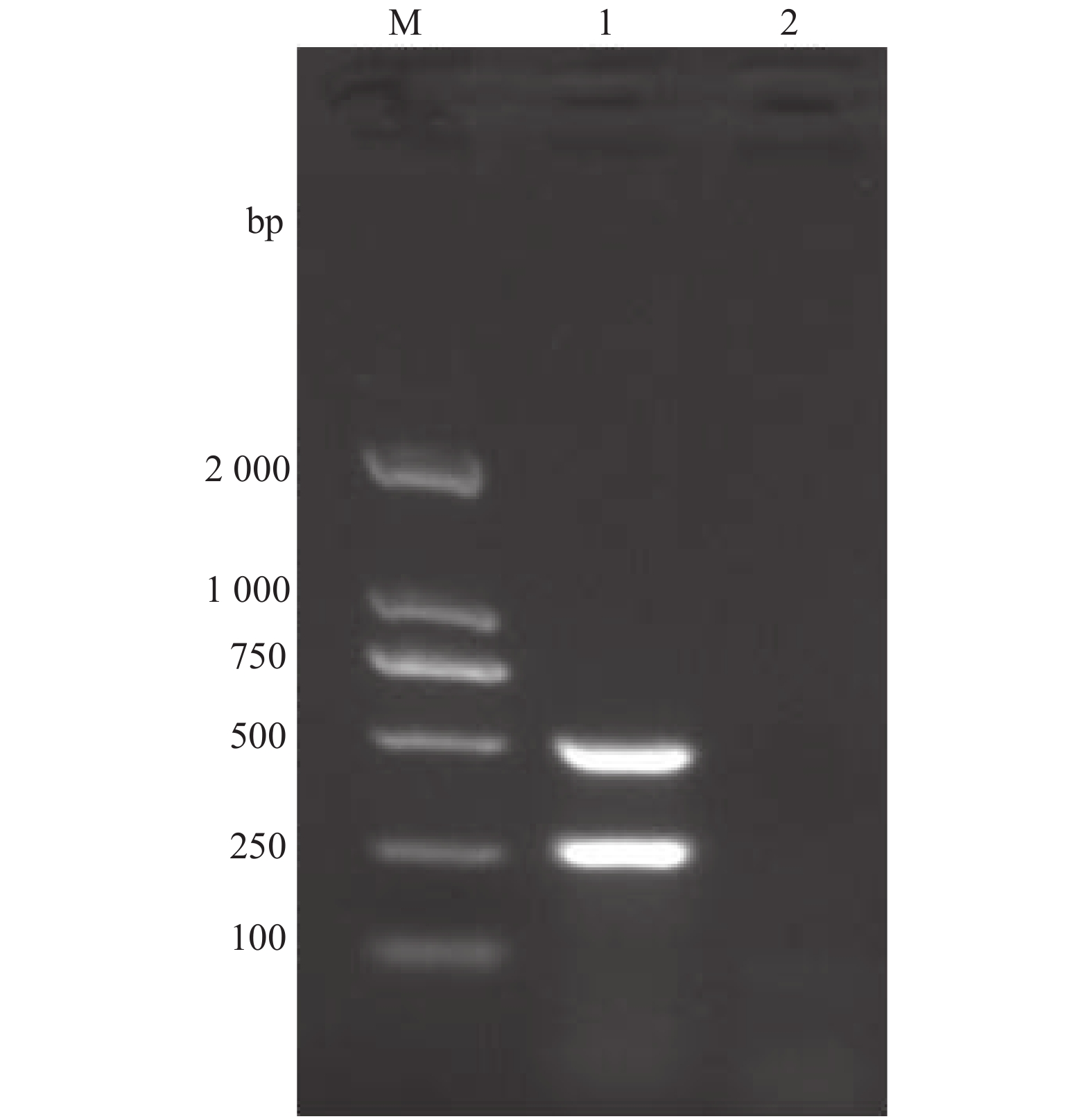
以提取的兔源F型多杀性巴氏杆菌基因组DNA为模板,分别利用kmt1基因和fcbD基因引物进行单重PCR扩增。单重PCR反应体系为:2×PCR Mix 25 μL,基因组DNA 1 μL,上下游引物(10 μmol·L−1)各2 μL,灭菌ddH2O 20 μL,共50 μL反应体系。单重PCR反应程序为95 ℃ 5 min;95 ℃ 30 s、59 ℃ 30 s、72 ℃ 30 s,35个循环;72 ℃ 10 min。PCR产物纯化后克隆至pEASY-T1克隆载体,送上海铂尚生物技术有限公司测序。
1.2.3 双重PCR方法的建立及反应条件的优化
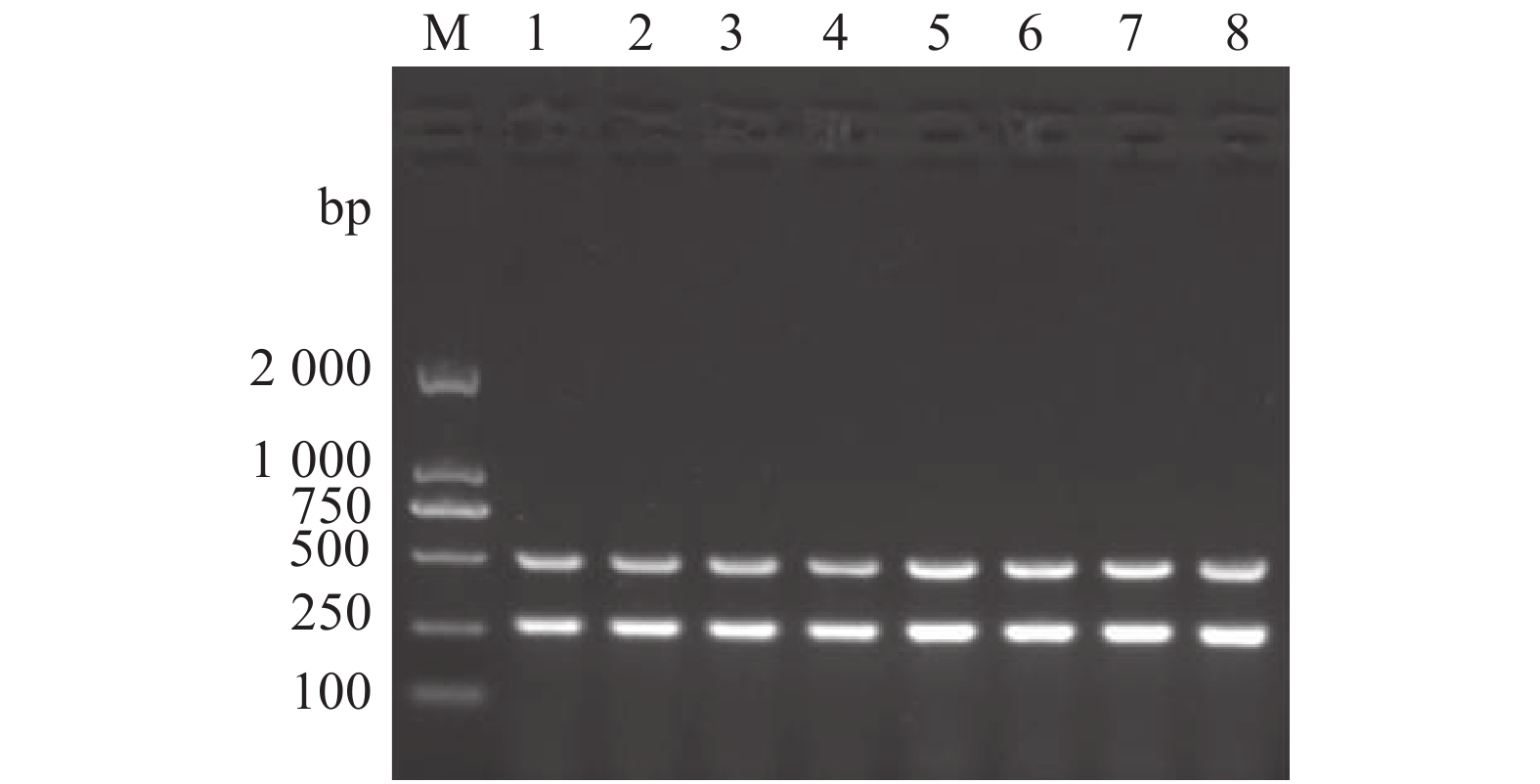
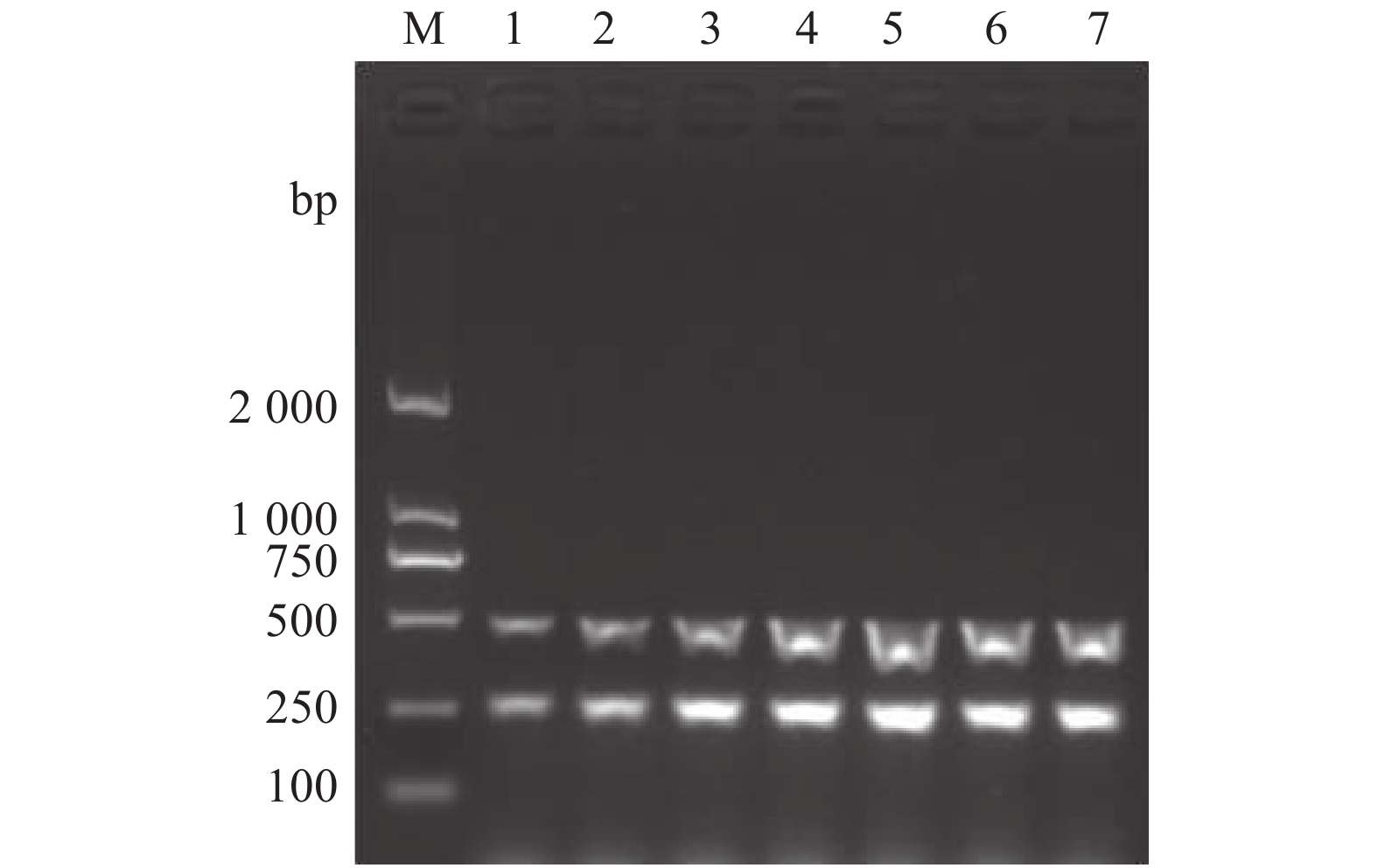
将kmt1基因和fcbD基因引物调整至40 μmol·L−1,等体积混匀后作为双重PCR的引物。双重PCR反应体系为:2×PCR Mix 25 μL,兔源F型多杀性巴氏杆菌基因组DNA 1 μL,混合引物4 μL,灭菌ddH2O 20 μL,共50 μL反应体系。双重PCR反应程序为95 ℃ 10 min;95 ℃ 30 s、59 ℃ 90 s、72 ℃ 2 min,35个循环;72 ℃ 10 min。在此基础上,设置双重PCR方法的退火温度在54~60 ℃、混合引物终浓度在0.4、0.5、0.6、0.7、0.8、0.9、1.0 μmol·L−1进行优化,确定最佳的退火温度和引物浓度。
1.2.4 双重PCR方法的特异性试验
分别以提取的兔源A、D和F型多杀性巴氏杆菌、支气管败血波氏杆菌、肺炎克雷伯菌、大肠杆菌、金黄色葡萄球菌的基因组DNA为模板,应用建立的双重PCR方法进行检测,设置阴性对照(灭菌ddH2O),评估该双重PCR方法的特异性。
1.2.5 双重PCR方法的敏感性试验
将荚膜F型多杀性巴氏杆菌的基因组DNA 10倍倍比稀释,使双重PCR反应体系中DNA模板的含量为1×107~1×100拷贝·μL−1,设置阴性对照(灭菌ddH2O),评估该方法的敏感性。
1.2.6 双重PCR方法的重复性试验
取90份已知结果的病死兔肺脏样品,平均分为3组,每组30份(A型多杀性巴氏杆菌样品5份,D型多杀性巴氏杆菌5份,F型多杀性巴氏杆菌5份,支气管败血波氏杆菌3份,肺炎克雷伯菌3份,大肠杆菌3份,金黄色葡萄球菌3份,阴性样品3份)。利用细菌基因组DNA提取试剂盒分别提取样品的基因组DNA,平均分为3份,利用建立的双重PCR方法分3次检测(每次检测90份),每次检测时每份样品重复3次,统计批内和批间变异系数,评估该双重PCR方法的重复性。
1.2.7 双重PCR方法的初步应用
选取从龙岩、三明、南平、福州和宁德5个地区收集的87份已知结果的呼吸道病死兔肺脏样品,应用本实验建立的双重PCR方法和已报道的多重PCR方法[3]同时对87份临床样品进行检测。统计检测结果,比较两种PCR方法检测结果与已知结果的一致性以及两种PCR方法检测结果的一致性。
2. 结果与分析
2.1 单重PCR方法的建立及扩增产物的鉴定
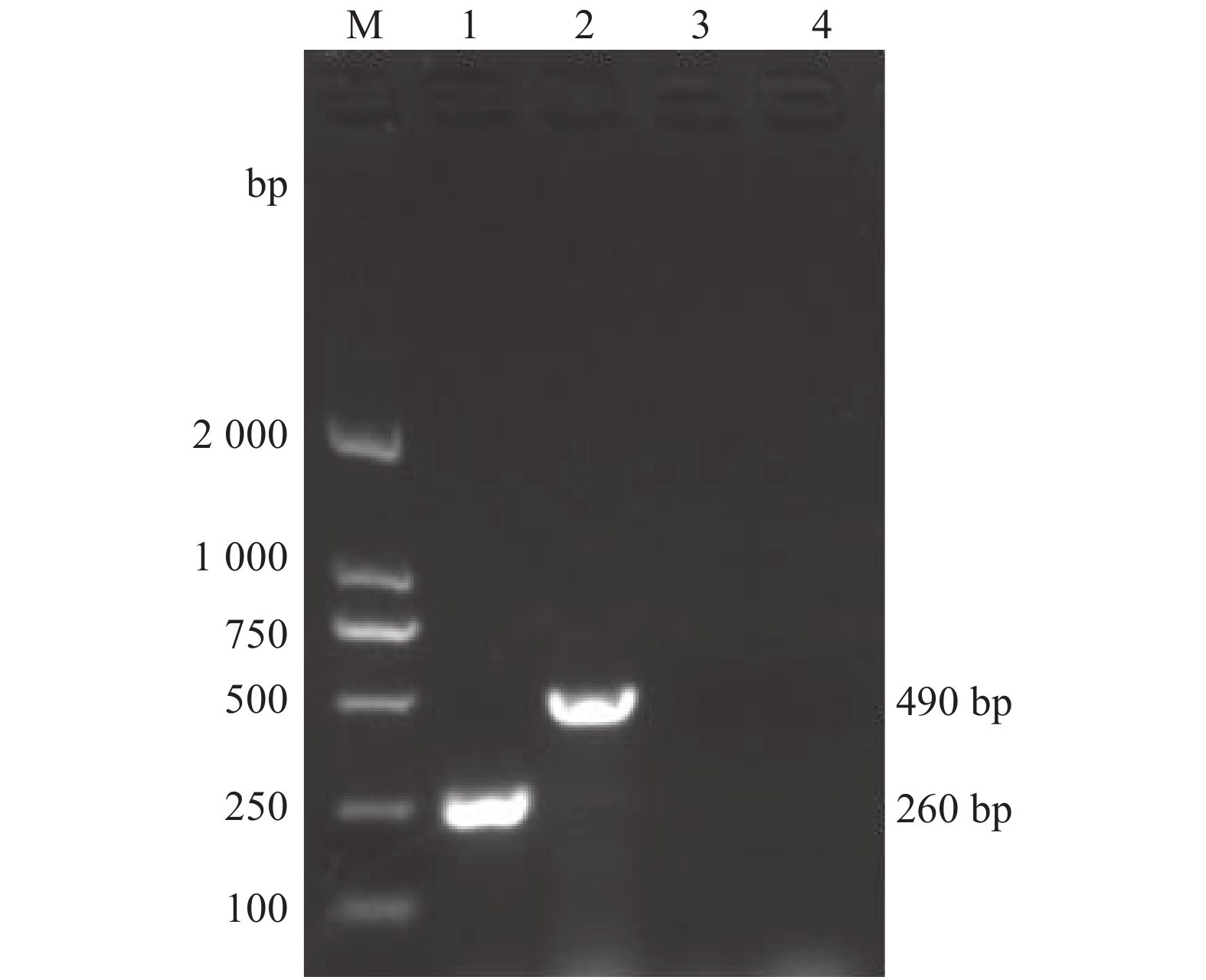
以兔源F型多杀性巴氏杆菌的基因组DNA为模板,利用设计的kmt1基因和fcbD基因引物分别进行单重PCR扩增。结果显示,扩增产物分别为260 bp和490 bp(图1),与预期目的片段大小相符。将上述2条目的片段克隆至pEASY-T1克隆载体并测序,测序结果显示2条目的片段序列与相应参考基因的序列同源性均为100%。
2.2 双重PCR方法的建立及反应条件的优化
以兔源F型多杀性巴氏杆菌的基因组DNA为模板,应用kmt1基因和fcbD基因引物进行双重PCR扩增。结果显示,在同一反应体系中,2对引物均能特异地扩增出相应的目的片段(图2)。在此基础上,进一步对双重PCR的退火温度和引物浓度进行优化。结果显示,当退火温度为54~60 ℃时,该双重PCR的扩增效果均较好(图3);当混合引物浓度为0.8 μmol·L−1时(图4),双重PCR扩增效果最好。退火温度高,则特异性强。因此,确定该双重PCR的最佳反应条件为退火温度60 ℃,混合引物浓度0.8 μmol·L−1。
2.3 双重PCR方法的特异性
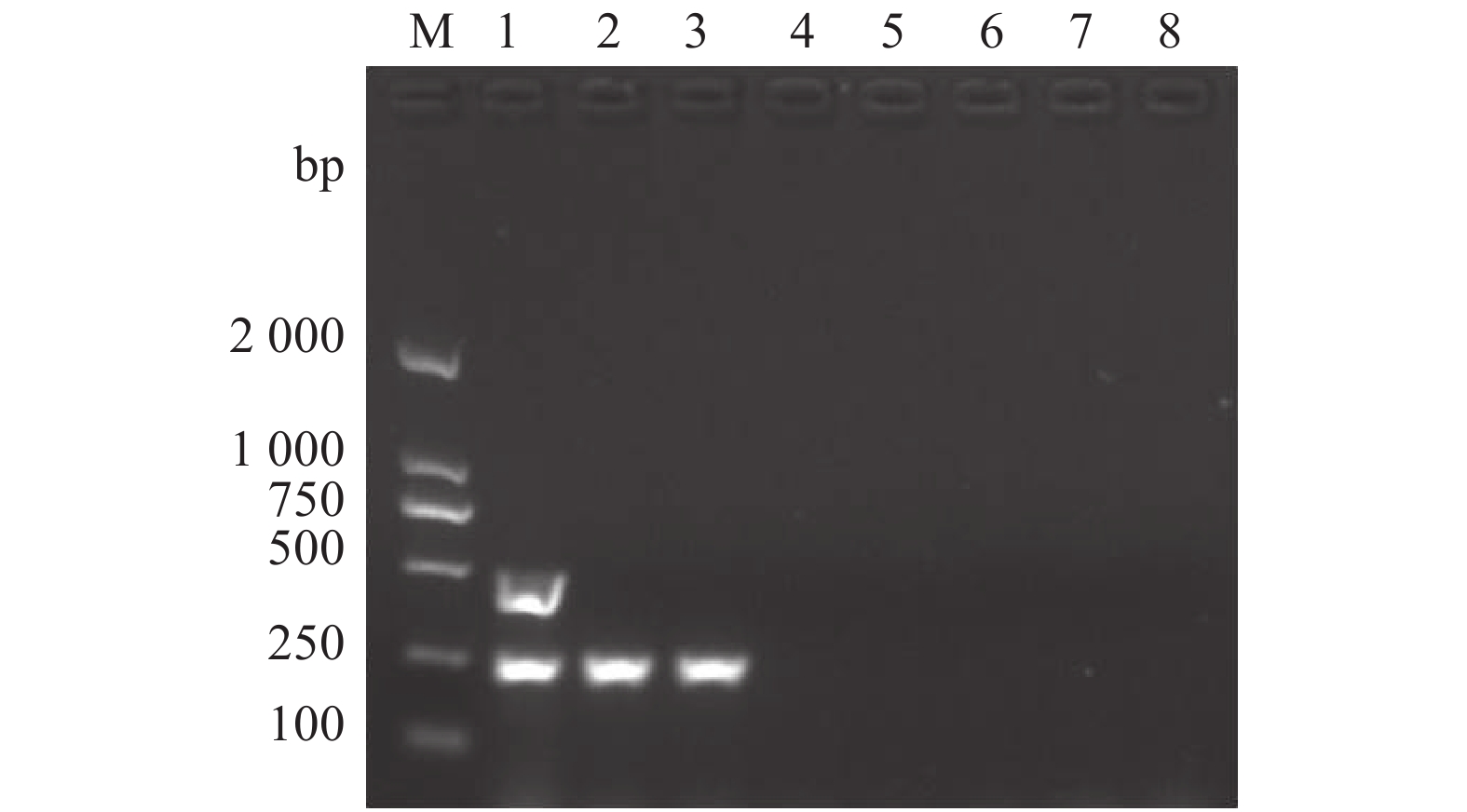
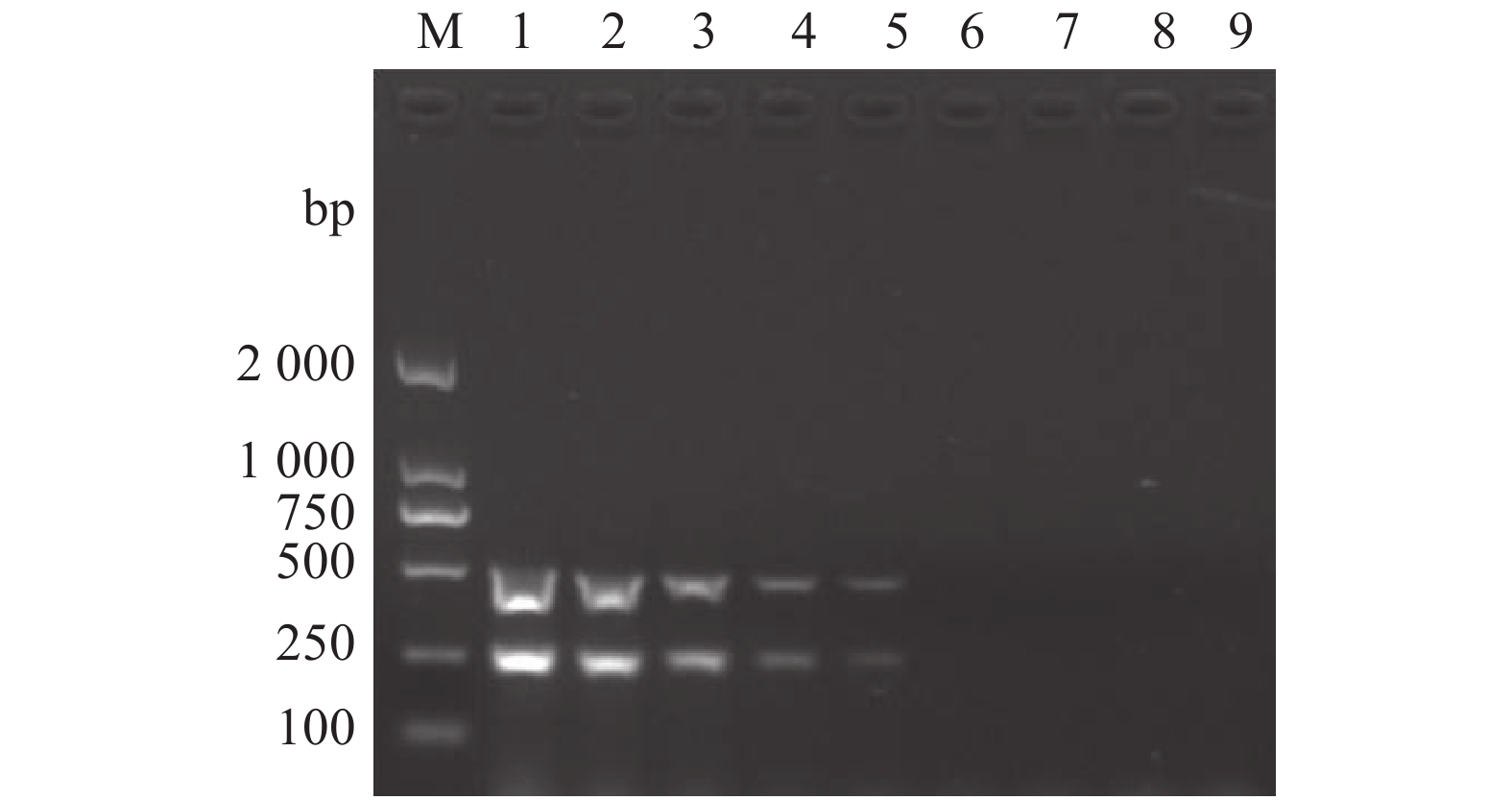
利用建立的双重PCR能同时特异地扩增出兔源F型多杀性巴氏杆菌的kmt1基因片段和fcbD基因片段,能扩增出兔源A型和D型多杀性巴氏杆菌的kmt1基因片段,对兔源支气管败血波氏杆菌、肺炎克雷伯菌、大肠杆菌、金黄色葡萄球菌和阴性对照(灭菌ddH2O)则为阴性(图5)。结果表明,该双重PCR方法具有较强的特异性。
![]() 图 5 双重PCR检测方法特异性试验注:M: DNA Marker;1:F型多杀性巴氏杆菌;2:A型多杀性巴氏杆菌;3:D型多杀性巴氏杆菌;4:支气管败血波氏杆菌;5:肺炎克雷伯菌;6:大肠杆菌;7:金黄色葡萄球菌;8:阴性对照Figure 5. Specificity of duplex PCR assayNote: M: DNA marker; 1: serogroup F strain of P. multocida; 2: serogroup A strain of P. multocida; 3: serogroup D strain of P. multocida; 4:B. bronchiseptica; 5: K. pneumonia; 6: E. coli; 7: S. aureus; 8: negative control.
图 5 双重PCR检测方法特异性试验注:M: DNA Marker;1:F型多杀性巴氏杆菌;2:A型多杀性巴氏杆菌;3:D型多杀性巴氏杆菌;4:支气管败血波氏杆菌;5:肺炎克雷伯菌;6:大肠杆菌;7:金黄色葡萄球菌;8:阴性对照Figure 5. Specificity of duplex PCR assayNote: M: DNA marker; 1: serogroup F strain of P. multocida; 2: serogroup A strain of P. multocida; 3: serogroup D strain of P. multocida; 4:B. bronchiseptica; 5: K. pneumonia; 6: E. coli; 7: S. aureus; 8: negative control.2.4 双重PCR方法的敏感性
将兔源F型多杀性巴氏杆菌的基因组DNA 10倍倍比稀释(1×107~1×100拷贝·μL−1)。结果显示,该双重PCR的最低检测限为1×103拷贝·μL−1基因组DNA(图6),表明该双重PCR具有良好的敏感性。
2.5 双重PCR方法的重复性
应用建立的双重PCR对90份已知结果的病死兔肺脏样品(3组,每组30份)分3批次进行批内和批间重复性试验。结果显示,重复性试验批内和批间结果均一致,表明该双重PCR具有良好的重复性。
2.6 双重PCR方法的初步应用
应用建立的双重PCR方法和已报道的多重PCR方法同时对87份已知结果(A型多杀性巴氏杆菌阳性样品30份,D型多杀性巴氏杆菌阳性样品9份,F型多杀性巴氏杆菌阳性样品8份,支气管败血波氏杆菌阳性样品11份,肺炎克雷伯菌阳性样品2份,大肠杆菌阳性样品1份,金黄色葡萄球菌阳性样品3份,阴性样品23份)的呼吸道病死兔肺脏样品进行检测。结果显示,双重PCR检测出多杀性巴氏杆菌阳性样品49份(其中F型多杀性巴氏杆菌阳性样品8份),阴性样品38份。多重PCR检测出多杀性巴氏杆菌阳性样品43份(其中A型多杀性巴氏杆菌阳性样品30份,D型多杀性阳性样品7份,F型多杀性巴氏杆菌阳性样品6份),阴性样品39份,非特异扩增样品5份。双重PCR方法检测结果和已报道的多重PCR方法检测结果与已知结果的符合率分别为97.70%和94.25%。双重PCR方法检测结果与已报道的多重PCR方法检测结果的符合率为93.10%。上述结果表明,本试验建立的双重PCR方法准确性高,具有较好的临床应用价值。
3. 讨论与结论
多杀性巴氏杆菌感染是引起兔呼吸道疾病的重要病原之一,常常引起致死性感染。临床上,致死性病例以50~70日龄的商品兔、怀孕后期母兔和哺乳母兔多见,给养兔业造成严重的经济损失[12]。兔巴氏杆菌病主要由A和D型多杀性巴氏杆菌感染引起[4-5]。F型多杀性巴氏杆菌首次分离自火鸡[6],主要在禽类中流行病且致病性强[7-8]。然而,在国内外兔群中也发现有该菌的存在,且其感染能引起兔的严重致死性呼吸道疾病[9-11]。由此可见,F型多杀性巴氏杆菌在兔群中的出现使兔巴氏杆菌病病因更加复杂,导致该病的确诊更加困难。
本试验根据多杀性巴氏杆菌的kmt1基因和F型多杀性巴氏杆菌fcbD基因的保守序列分别设计了2对特异性引物,建立了检测F型多杀性巴氏杆菌的双重PCR方法。kmt1基因是多杀性巴氏杆菌的种特异性基因,以该基因为目的基因能建立检测多杀性巴氏杆菌的特异性PCR检测方法[13-14]。fcbD基因编码F型多杀性巴氏杆菌荚膜中的软骨素,是F型菌株中的特异性基因,以该基因为目的基因能建立鉴定F型多杀性巴氏杆菌荚膜血清型的多重PCR方法[3]。由此可见,以kmt1基因和fcbD基因为目的基因能建立特异的检测兔源F型多杀性巴氏杆菌的双重PCR检测方法。本试验建立的双重PCR方法快速简便,不仅克服了细菌分离鉴定的费时,还克服了多杀性巴氏杆菌荚膜分型多重PCR方法的费力。此外,该双重PCR方法特异性强、重复性好、准确性高,具有很好的临床应用价值,为掌握兔群中F型多杀性巴氏杆菌的流行情况提供了有力的技术手段。
-
图 5 双重PCR检测方法特异性试验
注:M: DNA Marker;1:F型多杀性巴氏杆菌;2:A型多杀性巴氏杆菌;3:D型多杀性巴氏杆菌;4:支气管败血波氏杆菌;5:肺炎克雷伯菌;6:大肠杆菌;7:金黄色葡萄球菌;8:阴性对照
Figure 5. Specificity of duplex PCR assay
Note: M: DNA marker; 1: serogroup F strain of P. multocida; 2: serogroup A strain of P. multocida; 3: serogroup D strain of P. multocida; 4:B. bronchiseptica; 5: K. pneumonia; 6: E. coli; 7: S. aureus; 8: negative control.
-
[1] 王锦祥, 孙世坤, 陈冬金, 等. 一株致兔结膜炎多杀性巴氏杆菌的分离和鉴定 [J]. 中国养兔, 2020(5):9−11. DOI: 10.3969/j.issn.1005-6327.2020.05.003 WANG J X, SUN S K, CHEN D J, et al. Isolation and identification of Pasteurella multocida causing conjunctivitis in rabbits [J]. Chinese Journal of Rabbit Farming, 2020(5): 9−11.(in Chinese) DOI: 10.3969/j.issn.1005-6327.2020.05.003
[2] 林毅, 李兴玉, 张先慧, 等. 三个品种肉兔人工感染兔巴氏杆菌的抗病性比较研究 [J]. 中国养兔, 2013(6):8−9, 31. DOI: 10.3969/j.issn.1005-6327.2013.06.002 LIN Y, LI X Y, ZHANG X H, et al. A comparative study of the difference of the disease resistance to pasterrella multocida among three kinds of rabbits [J]. Chinese Journal of Rabbit Farming, 2013(6): 8−9, 31.(in Chinese) DOI: 10.3969/j.issn.1005-6327.2013.06.002
[3] TOWNSEND K M, BOYCE J D, CHUNG J Y, et al. Genetic organization of Pasteurella multocida cap loci and development of a multiplex capsular PCR typing system [J]. Journal of Clinical Microbiology, 2001(39): 924−929.
[4] GARCÍA-ALVAREZ A, CHAVES F, FERNÁNDEZ A, et al. An ST11 clone of Pasteurella multocida, widely spread among farmed rabbits in the Iberian Peninsula, demonstrates respiratory niche association [J]. Infection Genetics and Evolution, 2015(34): 81−87.
[5] WANG J X, SANG L, SUN S K, et al. Characterization of Pasteurella multocida isolated from dead rabbits with respiratory disease in Fujian, China [J]. BMC Veterinary Research, 2019, 15(1): 438. DOI: 10.1186/s12917-019-2191-3
[6] RIMLER R B, RHOADES K R. Serogroup F, a new capsule serogroup of Pasteurella multocida [J]. Journal of Clinical Microbiology, 1987, 25(4): 615−618. DOI: 10.1128/JCM.25.4.615-618.1987
[7] RHOADES K R, RIMLER R B. Capsular groups of Pasteurella multocida isolated from avian hosts [J]. Avian Diseases, 1987, 31(4): 895−898. DOI: 10.2307/1591048
[8] JONAS M, MORISHITA T Y, ANGRICK E J., et al Characterization of nine Pasteurella multocida isolates from avian cholera outbreaks in Indonesia [J]. Avian Diseases, 2001, 45(1): 34−42. DOI: 10.2307/1593009
[9] MASSACCI F R, MAGISTRALI C F, CUCCO L, et al. Characterization of Pasteurella multocida involved in rabbit infections [J]. Veterinary Microbiology, 2018, 213: 66−72. DOI: 10.1016/j.vetmic.2017.11.023
[10] 张娜, 李书光, 陈金龙, 等. 兔F型多杀性巴氏杆菌的分离鉴定及其致病性 [J]. 中国兽医科学, 2012, 42(7):685−689. ZHANG N, LI S G, CHEN J L, et al. Isolation, identification and pathogenicity of Pasteurella multocida serogroup F from rabbits [J]. Veterinary Science in China, 2012, 42(7): 685−689.(in Chinese)
[11] JAGLIC Z, JEKLOVA E, LEVA L, et al. Experimental study of pathogenicity of Pasteurella multocida serogroup F in rabbits [J]. Veterinary Microbiology, 2008, 126(1-3): 168−177. DOI: 10.1016/j.vetmic.2007.06.008
[12] 王锦祥, 桑雷, 孙世坤, 等. 一株兔源多杀性巴氏杆菌的分离鉴定及荚膜血清分型 [J]. 中国养兔, 2019(1):4−6. WANG J X, SANG L, SUN S K, et al. Identification and capsule serotyping of a Pasteurella multocida isolated from rabbit [J]. Chinese Journal of Rabbit Farming, 2019(1): 4−6.(in Chinese)
[13] 许腾林, 邢桂玲, 刘家森, 等. 多杀性巴氏杆菌TaqMan荧光定量PCR检测方法的建立与应用 [J]. 中国预防兽医学报, 2018, 40(8):706−710. XU T L, XING G L, LIU J S, et al. Development and application of TaqMan real-time PCR assay for the detection of Pasteurella multocida [J]. Chinese Journal of Preventive Veterinary Medicine, 2018, 40(8): 706−710.(in Chinese)
[14] 唐先春, 吴斌, 刘国平, 等. 应用双重PCR检测产毒素多杀性巴氏杆菌 [J]. 中国兽医学报, 2005, 25(4):374−375. DOI: 10.3969/j.issn.1005-4545.2005.04.013 TANG X C, WU B, LIU G P, et al. Detection of toxigenic Pasteurella multocida by Diplex pcr [J]. Chinese Journal of Veterinary Science, 2005, 25(4): 374−375.(in Chinese) DOI: 10.3969/j.issn.1005-4545.2005.04.013
-
期刊类型引用(5)
1. 徐翔飞,黄盼,崔雪梅,黄叶娥,季权安,韦强,肖琛闻,鲍国连,刘燕. 猪大肠埃希菌和沙门氏菌双重PCR检测方法的建立. 浙江农业科学. 2023(04): 957-963 .  百度学术
百度学术
2. 王锦祥,林松华,陈冬金,孙世坤,陈岩锋,高承芳,桑雷,谢喜平. 兔源F型多杀性巴氏杆菌荧光定量PCR检测方法的建立. 中国预防兽医学报. 2023(02): 156-160 .  百度学术
百度学术
3. 申秋平,徐佳豪,王新茹,庄林林. 多杀性巴氏杆菌快速检测方法研究进展. 现代畜牧科技. 2023(08): 23-28 .  百度学术
百度学术
4. 王锦祥,付环茹,孙世坤,陈冬金,高承芳,桑雷,谢喜平. 兔源A型多杀性巴氏杆菌双重PCR检测方法的建立. 福建畜牧兽医. 2023(05): 20-23 .  百度学术
百度学术
5. 王锦祥,孙世坤,陈岩峰,陈冬金,桑雷,谢喜平. 兔源F型多杀性巴氏杆菌环介导等温扩增快速检测方法的建立. 中国兽医学报. 2022(03): 490-495 .  百度学术
百度学术
其他类型引用(0)




 下载:
下载: