Isolation and Application of Microbes Capable of Decomposing Tea Dregs
-
摘要:目的 筛选高温高效分解茶渣的菌株,为茶渣开发利用提供理论依据。方法 利用高温特殊生境分离方法,从废弃茶渣中分离筛选较高产纤维素酶和蛋白酶的高温菌,对其中高产酶活力的菌株进行形态学、生理生化特性以及生长特性等研究;并克隆其16S rDNA基因序列和菌株gyrB基因测序,进行系统发育学分析;同时对该菌株分解茶渣效果进行验证。结果 试验表明,分离筛选获得分解茶渣的高温菌5株,其中Fb菌产生的纤维素酶、蛋白酶的活力均最高。Fb属贝莱斯芽孢杆菌(Bacillus velezensis),可耐受55℃高温,最适生长条件:42~45 ℃、pH 5.0~7.0、16 h、盐度1.0%~6.0%、装液量0.12 mL·min−1、摇床转速120 r·min−1。茶渣添加Fb菌发酵7 d后,与对照组比,粗蛋白提高14.88%(P<0.05);除胱氨酸、蛋氨酸和组氨酸发酵外,其他14种氨基酸含量均显著提高(P<0.05),且氨基酸总量提高5.98%;粗纤维下降9.69%,其中性洗涤纤维、酸性洗涤纤维和木质素分别下降10.72%、4.47%和11.37%(P<0.05)。结论 首次报道贝莱斯芽孢杆菌Fb能高效分解茶渣,提高茶渣的营养价值。Abstract:Objective Microorganisms that can efficiently decompose tea dregs at high temperature were screened for potential waste treatment application.Method A high temperature special habitat separation method was employed to isolate cellulase and protease-producing bacteria on tea dregs. Morphological, physiochemical, and growth characteristics of selected strains were examined prior to 16S rDNA cloning for sequencing. Gene sequences of the candidates, along with gyrB, were subjected to phylogenetic analysis for species identification. Decomposing capacity of the isolated strains on tea dregs was determined for final selection.Results Five thermophiles exhibiting the desired properties were isolated. Among them, Fb showed the highest enzymatic activities and was found to be a strain of Bacillus velezensis. It was further characterized with a high temperature tolerance up to 55 ℃ and the optimal culture conditions of 42-45 ℃, pH 5.0-7.0, 16 h incubation, 1.0-6.0% salinity, 30 mL 250 min−1 filling volume, and 120 rpm shaker speed. After Fb inoculation and incubation for 7 d, the crude protein in the resulting tea dregs significantly increased by 14.88% (P<0.05), the contents of 14 amino acids, except cystine, methionine, and histidine, significantly increased (P<0.05), the total amino acids increased by 5.98%, the crude fiber decreased by 9.69%, and the neutral detergent fiber, acid detergent fiber, and lignin decreased by 10.72%, 4.47%, and 11.37%, respectively (P<0.05).Conclusion For the first time, B. velezensis Fb was identified to be capable of efficiently decomposing tea dregs with a significantly improved nutritional profile on the substrate. It could conceivably become a bioagent for treating the waste material.
-
Keywords:
- Tea dregs /
- Bacillus velezensis /
- isolation /
- protein /
- cellulose
-
0. 引言
【研究意义】茶渣是茶饮料、速溶茶和茶单宁产业等加工茶叶后产生的残渣,据统计,仅茶饮料和速溶茶公司每年产生的茶渣就达16万t[1]。研究表明,干基的茶渣粗蛋白质含量为17%~25%,是一种良好的蛋白质饲料资源[2-4]。日本的佐野满昭[5]在饲料中添加3%的茶渣喂养肉鸡,可提高鸡肉的嫩度和脂溶性抗氧化物(VE、VC)含量,降低鸡肉脂质过氧化物含量。徐瑞等[6]研究表明,在日粮中添加2%的茶叶渣能提高育肥猪的生长性能,改善猪肉的色泽和保水性能。吴慧敏[7]研究发现在蛋鸡的日粮中添加1%~2%的茶渣不仅显著增加产蛋数和蛋重观察蛋鸡的生产性能,还能显著提高血清中的GSH-Px,T-SOD,IgA,IgM含量,同时显著的降低血清中的胆固醇含量。马帮军[8]研究表明,猪日粮中添加茶粉1%~3%会降低猪的平均日增重,但显著降低猪背膘厚度,减少脂肪在猪胴体中的沉积。潘发明[9]等则认为饲粮中添加茶渣比例过高,会影响适口性,降低绵羊采食量。主要原因是茶渣粗纤维含量高,畜禽纤维素酶活力低,不利于消化吸收;另一原因,刚出产的茶渣水分达到80%不易储藏和运输,因此仅有小部分的茶渣作为饲料源利用,绝大部分茶渣被丢弃或掩埋;这不仅造成资源浪费,而且造成生态环境污染[10-11]。【前人研究进展】为了更好利用茶渣资源,刘姝等[12]利用木霉等组合微生物发酵茶渣,在30 ℃下发酵4~8 d后发现,饲料中粗蛋白测定含量>25%,比对照提高了20%,其营养价值达到了仔猪配合饲料中粗蛋白的含量。胡桂萍等[13]以提取茶多酚后的茶渣为发酵原料,利用乳杆菌、枯草芽孢杆菌、酵母菌和米曲霉菌进行常温(25~35 ℃)的厌氧固态发酵5~7 d,测定发现发酵产品中粗蛋白含量达29.49%。倪星虹[14]以混合菌种经温度28 ℃发酵7 d后,测定发现茶渣发酵产物中蛋白质含量提高了60.78%。朱飞等[1]利用黑曲霉在添加5%玉米粉的茶渣中进行固态发酵,经自然pH、37 ℃、8 d条件下发酵后,茶渣的营养价值显著提高。贝莱斯芽孢杆菌(Bacillus velezensis)是2005年由Ruiz-Garcia等[15]新命名的一种生防菌,是芽孢杆菌属的一个新种[16-19]。国内外已有学者研究表明Bacillus veiezensis能产生具有广谱抗菌活性的次生代谢产物,包括纤维素酶、蛋白酶以及多种抗菌的活性物质,是用来增加作物产量、维护生态环境和农业生态系统的首选生物药剂[20-26]。贝莱斯芽孢杆也作为水产养殖的益生菌[27]。 Liu X Y等[28]对从海洋微生物中筛选到菌株Bacillus velezensis H3的发酵培养基和拮抗物质进行研究,发现该菌株的活性物质是一种替代性的表面活性素,有较高的研究价值。【本研究切入点】茶渣经发酵后虽然能在一定程度上提高茶渣的营养价值,但发酵温度均不超过37 ℃,发酵效率低,时间长,易被杂菌污染。因此有必要筛选能适合高效分解茶渣的高温菌株。但鲜见贝莱斯芽孢杆菌(Bacillus velezensis)在降解工农业副产物的研究报道。【拟解决的关键问题】本研究从堆积废弃茶渣中分离获得既耐高温又能产生高酶活的贝莱斯芽孢杆菌Fb,对其进行形态学、生理生化以及分子生物学鉴定,同时研究其最适的生长条件,分解茶渣的效果,为后续的茶渣开发研究奠定理论的基础。
1. 材料与方法
1.1 试验材料
LB培养液(L):酵母粉10 g,蛋白胨10 g,牛肉浸膏5 g,NaCl 10 g,pH 5.5~6.0。
纯化固体培养基:LB培养液中时加入20 g琼脂粉。
分离固体培养基:取新鲜茶渣50 g加蒸馏水500 ml蒸煮30 min,过滤后的茶渣液定容到200 ml,加入4 g琼脂粉。
液体发酵培养基:同LB培养液。
茶渣:采集于某地的茶饮料车间。将发酵前后的茶渣烘干,粉碎并过0.25 mm孔径筛,用四分法取样100 g。
主要仪器:LRH-250A生化培养箱,CRY-200恒温摇床,Multiskan MK3酶标仪,FOSS全自动凯氏定氮仪Kjeltec8400,FOSS2010纤维测定仪,menbarPureA300全自动氨基酸分析仪。
试剂:酵母粉、蛋白胨、NaCl等均为AR级、茚三酮染色剂、缓冲液、氨基酸标准液和稀释液均为德国menbarPure公司。
1.2 试验方法
1.2.1 菌株的培养与分离
从某地多年堆积的茶渣处取样品10 g,加入盛有50 mL LB培养液的250 mL锥形瓶中,在42 ℃、120 r·min−1条件下富集培养24 h,取2 mL培养物接种到新鲜的LB培养液,以相同的条件重复培养3次。富集培养物在分离固体培养基上划线培养,42 ℃培养24 h。挑取生长明显的菌落进行复筛。将初筛菌落在纯化固体培养基上划线分离3次,以获得纯培养物,并依据菌种在分离固体培养基的生长情况,挑取有不同形态特征的单菌落,于42 ℃ LB培养基上分别扩繁后加20%甘油混匀,于−80 ℃条件下保存。
1.2.2 菌株产酶能力测定
将菌株活化24 h后挑取1环至液体发酵培养液中,42 ℃、120 r·min−1条件下培养48 h后,测定发酵液的蛋白酶、纤维素酶的活力。采用蒽酮比色法测定纤维素酶(CL)催化羧甲基纤维素钠降解产生的还原糖的含量[29]。每mL样本每分钟催化产生1 μg葡萄糖定义为一个酶活力单位(U)。酸性蛋白酶(ACP)、中性蛋白酶(NP)和碱性蛋白酶(AKP)的测定按照GB/T 23527—2009和相关文献[30-31]执行。
1.2.3 菌落与菌体形态特征观察
菌株平板划线42 ℃分别培养16 h和25 h,在自然光下观察菌落形态;革兰氏染色后,观察菌株形态[32-33]。
1.2.4 菌株生理生化特性
1.2.5 分子鉴定
菌株的分子鉴定用16S rDNA和gyrB基因进行[36]。利用NCBI网站的BLAST功能对所测的16S rDNA和gyrA序列进行同源性分析,确定亲缘关系,使用MEGA 5.0软件Neighbor-Joining[37-38]构建系统发育树,进行1 000次的相似度重复计算。
1.2.6 菌株生长特性
测量菌株的生长曲线,判断最适生长温度[39];对其生长条件进行单因素试验如表1方案,分析不同因素对菌株生长的影响,其他培养条件和培养基相同,间隔2 h取样用酶标仪在波长630 nm测吸光度。每组设3个重复。
表 1 菌株生长条件单因素试验Table 1. Single factor test on growth conditions of bacteria因素
Factors添加水平
Level培养温度
Incubation temperature/℃30、33、36、39、42、45、48、51、54、57、60 装液量
Liquid loading quantity/mL10、15、20、25、30、35、40、45、50、55、60 摇床转速
Shaking speed/r·min−1100、120、140、160、180、200 培养时间
Fermentation time/h2、4、6、8、10、12、14、16、18、20 初始pH值
The initial pH4.0、4.5、5.0、5.5、6.0、6.5、7.0、7.5、8.0、8.5、9.0 盐度
Salinity/%0、0.5、1.0、1.5、2.0、2.5、3.0、3.5、4.0、4.5、5.0、5.5、6.0、6.5、7.0 注:盐度是指海水中溶解物质质量与海水质量的比值。
Note: Salinity refers to the ratio of dissolved substances in water to water.1.2.7 茶渣降解分析
用回接方法,验证菌株对茶渣降解效果:对照组不添加菌剂;发酵组用LB菌株培养液进行扩大培养制成种子,将培养好的种子接入新鲜茶渣中,搅拌均匀使其菌浓度约为1×106 CFU·g−1;对照组和发酵组各装入9个1 L的三角瓶,每瓶装量200 mg。两组同时放入42~45 ℃下的培养箱中;每天摇动三角瓶5 s,发酵7 d结束测定茶渣营养成分的变化。
常规成分测定[40]:粗蛋白、粗纤维和粗灰分分别按GB/T 6432—1994、GB/T 6433—2006和GB/T 6438—2007规定的方法执行。纤维的成分测定[40]:中性洗涤纤维(NDF)、酸性洗涤纤维(ADF)和酸性洗涤木质素(ADL)测定根据GB/T 20806—2006和GB/T 20805—2006方法。氨基酸测定[41]:按GB/T 18246—2000方法,采用全自动氨基酸分析仪(menbarPureA300)进行测定。
1.2.8 数据分析
所得数据用SPSS 16.0软件进行分析,F检验分析;采用氨基酸分析仪自带软件处理数据。
2. 结果与分析
2.1 菌株产酶能力比较
对5株菌的发酵液进行分析,产纤维素酶(CL)活力由高到低分别是DJ、8106、Fb、8116、HLH;酸性蛋白酶(ACP)活力由高到低分别是8106、8116、DJ、HLH、Fb;中性蛋白酶(NP)活力由高到低分别是8106、HLH、8116、DJ、Fb;碱性蛋白酶(AKP)活力由高到低分别是Fb、8116、8106、DJ、HLH(表2)。可见Fb菌产四种酶的活力均较强。
表 2 菌株酶活力比较Table 2. Enzyme activities of selected strains菌号
The
fungusCL活力
(U)
Cellulose
enzymeACP活性
(U)
Acid protease
activityNP活性
(U)
Neutral protease
activityAKP活性
(U)
Alkaline protease
activityDJ 191.58 21.59 40.23 23.35 Fb 198.33 22.90 41.24 44.36 8116 178.46 23.08 28.25 33.06 8106 189.95 24.44 30.90 27.85 HLH 154.34 16.61 54.17 18.76 2.2 菌落与菌体形态特征
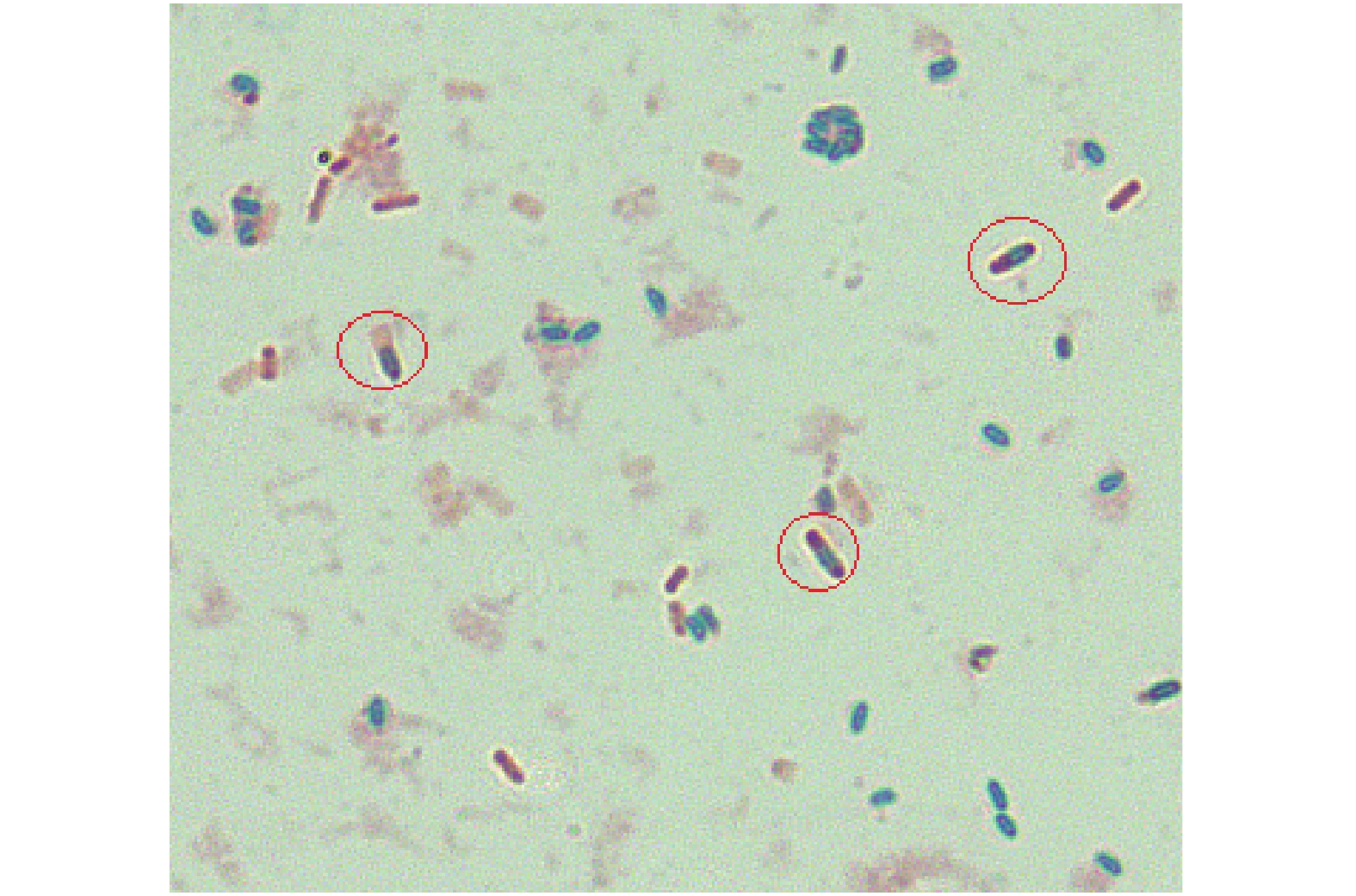
Fb菌在自然光下,LB培养基,42 ℃培养16 h,其菌落浅黄色,圆形,表面干燥,不透明,边缘不整齐,如图1。菌体呈杆状,(0.4~0.6) μm×(0.9~4.0) μm,单个或成对排列,菌体形态如图2;芽胞近圆形,近中部生见图3圆圈标记。
2.3 菌株生理生化特性
由表3可知,Fb菌株能水解七叶苷;吲哚试验阳性;可在β-木糖苷酶、苯丙氨酸芳胺酶、α-半乳糖苷酶、丙氨酸-苯丙氨酸-脯氨酸芳胺酶、L-吡咯烷酮芳胺酶等酶中生长;能利用D-甘露醇、D-甘露糖、古老糖、D-海藻糖、D-葡萄糖、D-核糖等多种糖作为碳源生长;但不能利用肌醇、L-鼠李糖、菊粉、环糊精、N-乙酰-D-氨基葡萄糖、D-塔格糖、糖原、麦芽三糖、D-松三糖等。Fb菌株能在低剂量的抗生素中生长,不能在高剂量的卡那霉素耐药(0.2 g·L−1)、竹桃霉素耐药(0.1 g·L−1)、多粘菌素B耐药(0.031 g·L−1)等培养基生长。
表 3 Fb菌株生理生化特性Table 3. Characteristics of Fb项目
Items结果
Result项目
Items结果
Result项目
Items结果
Result项目
Items结果
Resultβ-木糖苷酶
β-xylosidase+ L-赖氨酸芳胺酶
L-lysine aromatase− L-天冬氨酸芳胺酶
L-aspartate aromatase− 亮氨酸芳胺酶
Leucine aromatase− 苯丙氨酸芳胺酶
Phenylalanine aramidase+ L-脯氨酸芳胺酶
L-proline aramidase− β-半乳糖苷酶
β-galactosidase− L-吡咯烷酮芳胺酶
L-pyrrolidone aramidase+ α-半乳糖苷酶
α-Galactosidase+ 丙氨酸芳胺酶
Alanine Aramidase− 酪氨酸芳胺酶
Tyrosine Aramidase− β-N-乙酰氨基葡糖苷酶
β-N-Acetylglucosaminidase− 丙氨酸-苯丙氨酸-脯氨酸芳胺酶
Alanine-phenylalanine-proline arylaminease+ 环糊精
Cyclodextrin− D-半乳糖
D-galactose− 糖原
Glycogen− 肌醇Inositol − 甲基-α-D-吡喃葡萄糖苷酸化
Methyl-α-D-glucopyranosylation+ ELLMAN 试剂 − 甲基-D-木糖苷
Methyl-D-xylosid− α-甘露糖苷酶
α-mannosidase− 麦芽三糖
Maltotriose− 甘氨酸芳胺酶
Glycine arylaminease− D-甘露醇
D-mannitol+ D-甘露糖
D-mannose+ D-松三糖
D-matsutriose− N-乙酰-D-氨基葡萄糖
N-acetyl-D-glucosamine− 古老糖
Ancient sugar+ L-鼠李糖
L-Rhamnose− β-葡糖苷酶
β-glucosidase+ β-甘露糖苷酶
β-mannosidase-phos− 磷酰胆碱
Phorylcholine− 丙酮酸盐
Pyruvate+ α-葡萄糖苷酶+
α-glucosidase− D-塔格糖
D-tagatose− D-海藻糖
D-trehalose+ 菊粉
Inulin− D-葡萄糖
D-glucose+ D-核糖
D-ribose+ 腐胺同化
Putrescine assimilation− 吲哚
Indole+ 卡那霉素耐药
Kanamycin resistance− 竹桃霉素耐药
Oleander resistance− 七叶苷水解
Aescin hydrolysis+ 红四氮唑
Red tetrazolium− 多粘菌素B耐药
Polymyxin B resistance− 注:“+”表示阳性,“-”表示阴性;ELLMAN试剂用于检测游离的巯基(-SH)。
Note: 1: + positive; − negative. 2: ELLMAN reagent for free sulfhydryl (-SH) detection.2.4 菌株的分子鉴定
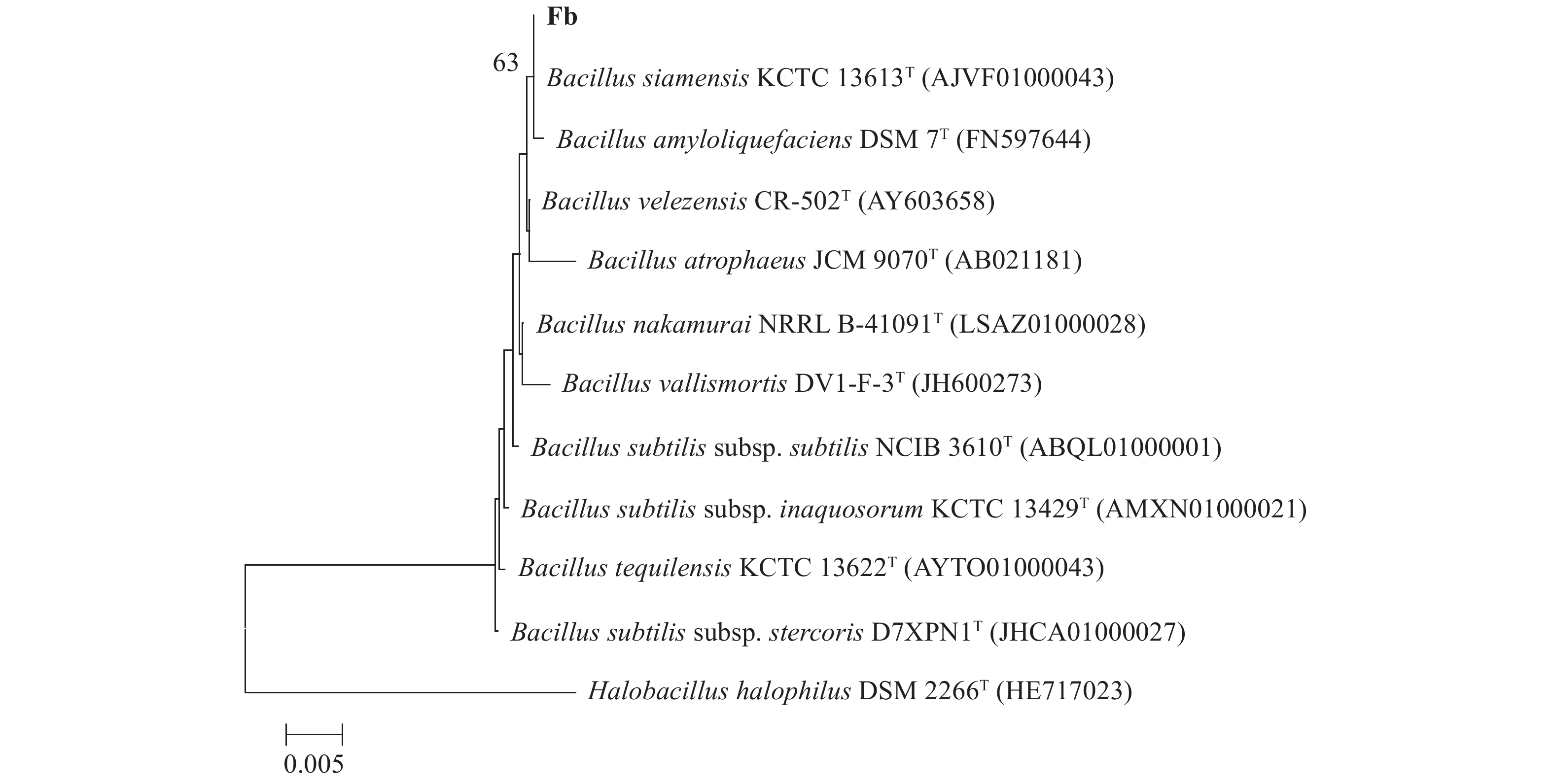
利用NCBI数据库中的Blast程序分析结果表明,Fb菌株与Bacillus siamensis KCTC 13613T(AJVF01000043)和Bacillus amyloliquefaciens DSM 7T(FN597644)菌株的同源性最高,相似性达到99.93%。采用MEGA 5.0软件,邻位链接法显示Fb菌株与相关种的16S rDNA序列系统发育树(图4)。菌株gyrB测序分析表明,序列长1 176 bp。MEGA 5.0软件分析结果表明,其与Bacillus velezensis BCRC 17467T(DQ903176)的同源性较高,相似性达到100%。同理将该菌株与其他种属明确的10株菌的gyrB基因构建系统发育树(图5)。
结合菌株形态学、生理生化特性以及16S rDNA和gyrB的序列比较分析,将Fb菌株鉴定为贝莱斯芽孢杆菌(Bacillus velezensis)。
2.5 菌株生长特征
2.5.1 Fb菌的生长曲线
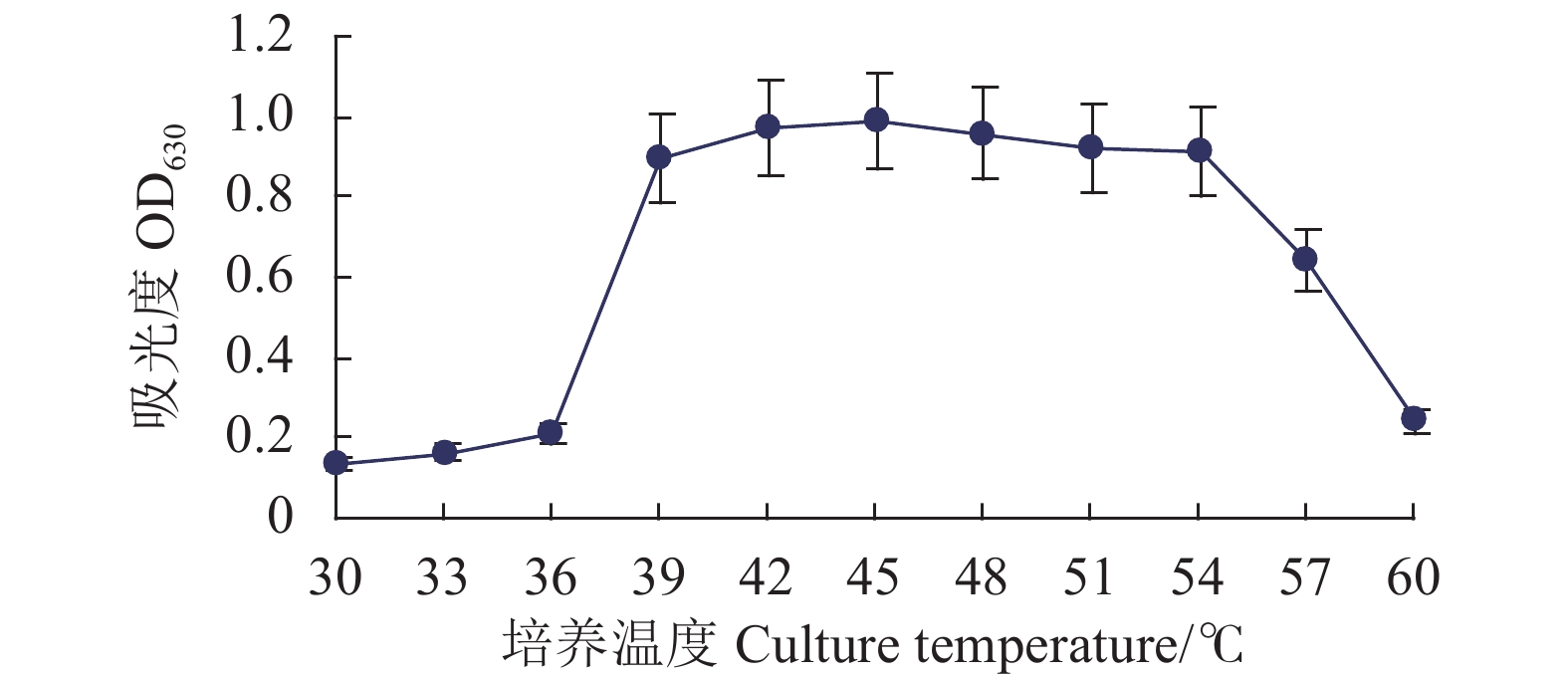
从图6可以看出,随着培养温度的提高,菌株的细胞分裂加快,吸光值增加;Fb菌可在30~60 ℃下生长,其最适的生长温度为39~54 ℃。
2.5.2 装液量和摇床转速对Fb菌生长的影响
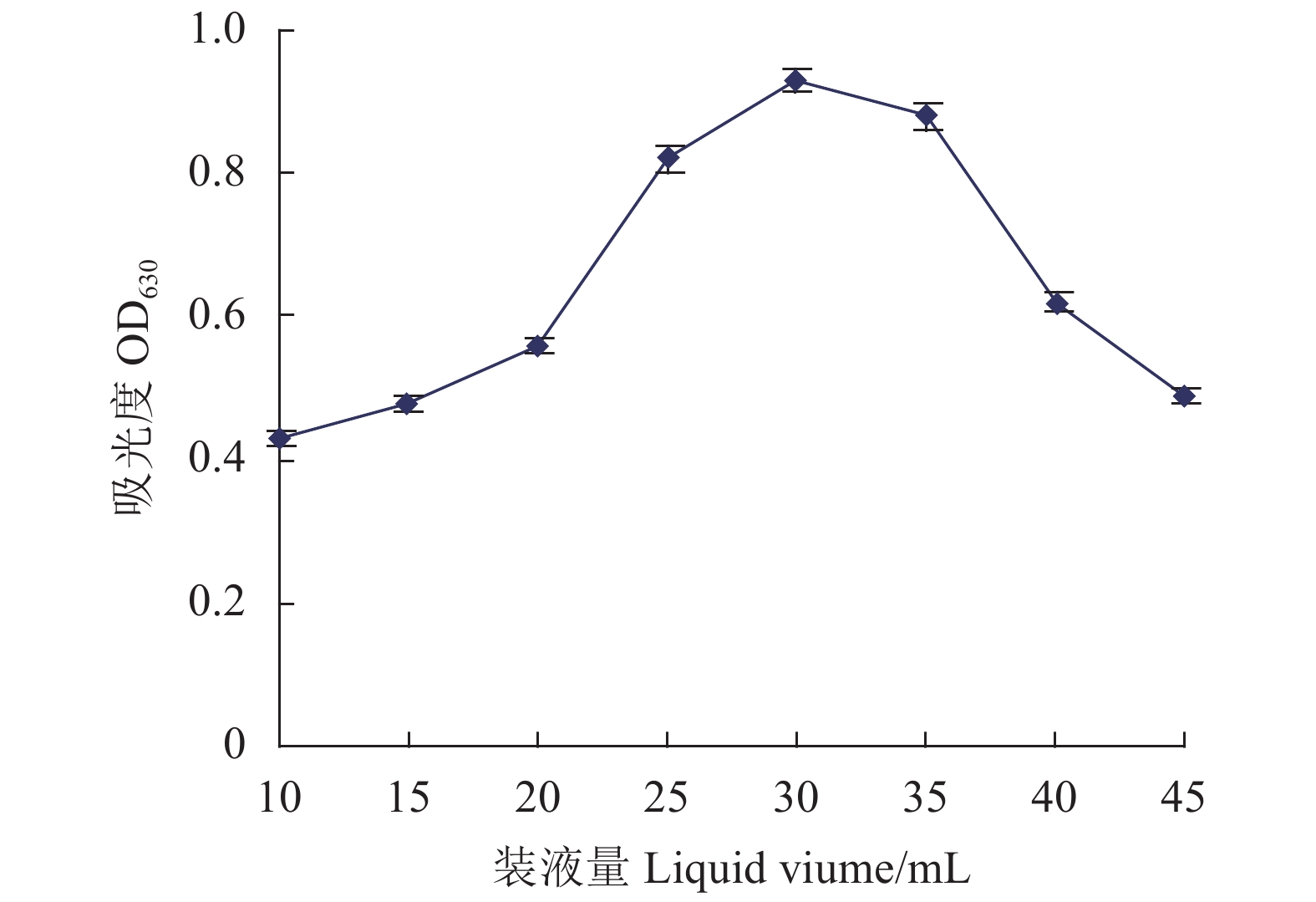
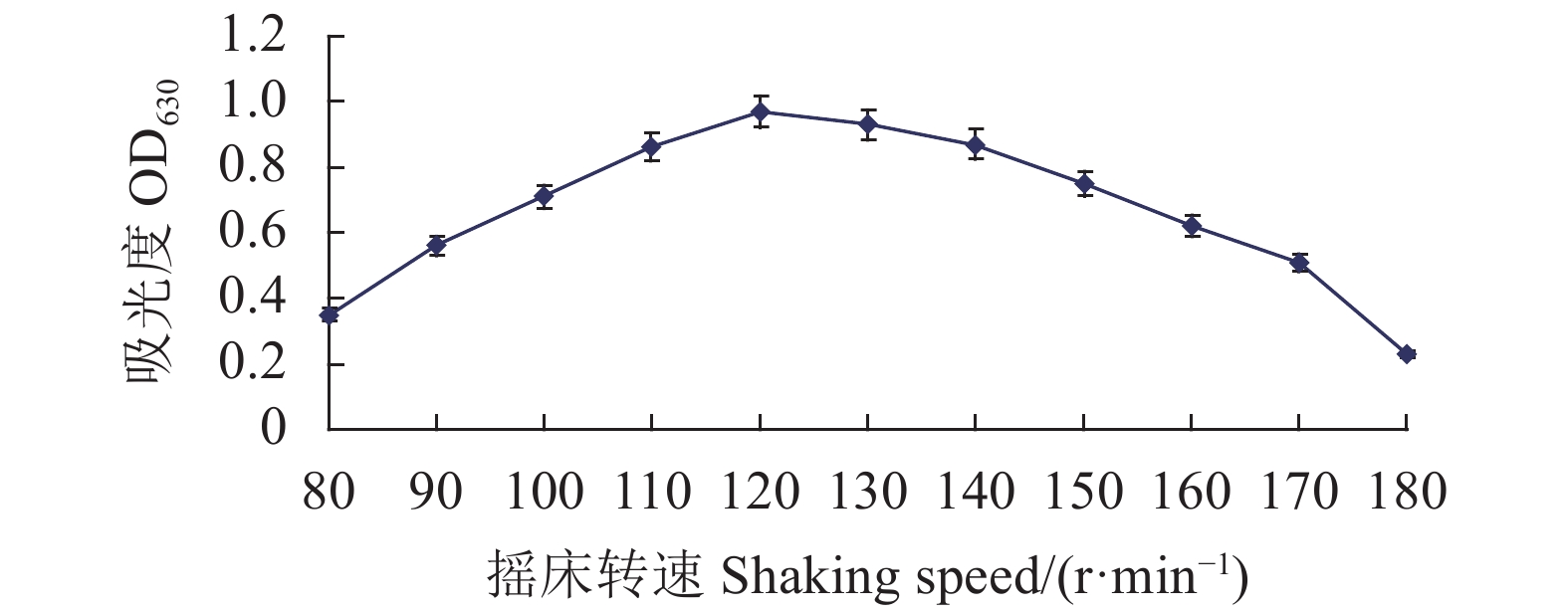
摇床转速120 r·min−1时,随着装液量的增加,菌液的吸光值升高,至装液量30 mL时,Fb菌的吸光值达最高:0.97;再提高装液量,吸光值逐渐降低(图7)。从图8可知,装液量30 mL时,随着摇床转速的提高,吸光值升高,摇床转速为120 r·min−1时,Fb菌的吸光值达最高:0.98;再提高摇床转速,吸光值逐渐降低。表明Fb菌液体培养最佳装液量和摇床转速分别为30 mL和120 r·min−1。
2.5.3 培养时间对Fb菌生长的影响
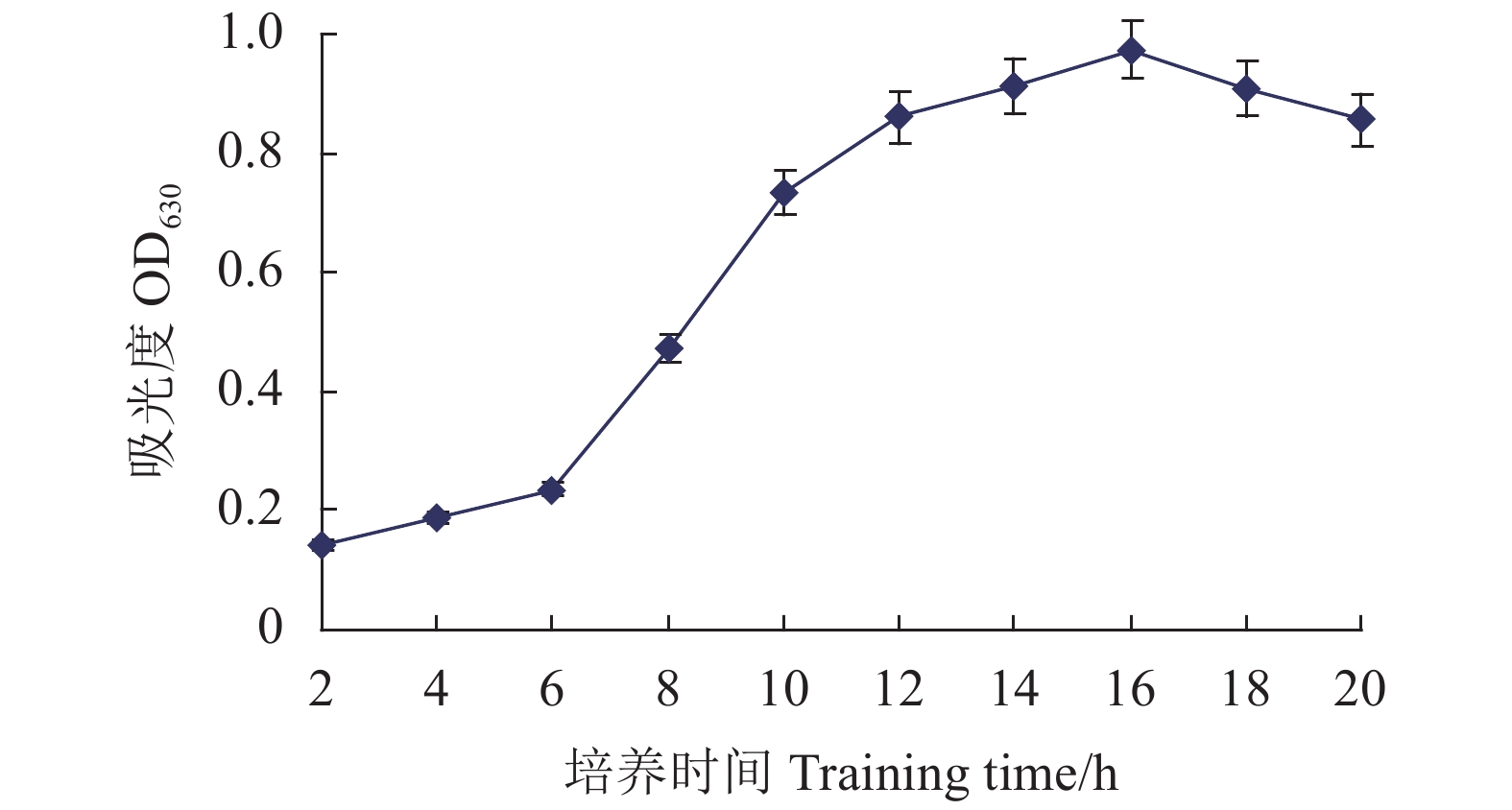
图9为Fb菌在培养温度42 ℃下的生长曲线。0~6 h是菌体适应新环境的迟缓期,细胞分裂增殖缓慢;6~16 h为生长繁殖迅速的对数生长期;16 h的菌体吸光值最高0.974;16~18 h为稳定生长期;18 h后由于自溶酶作用或有毒代谢产物积累,细胞进入衰亡期裂解菌体吸光值随之下降。表明Fb菌的最适培养时间为16 h。
2.5.4 初始pH对Fb菌生长的影响
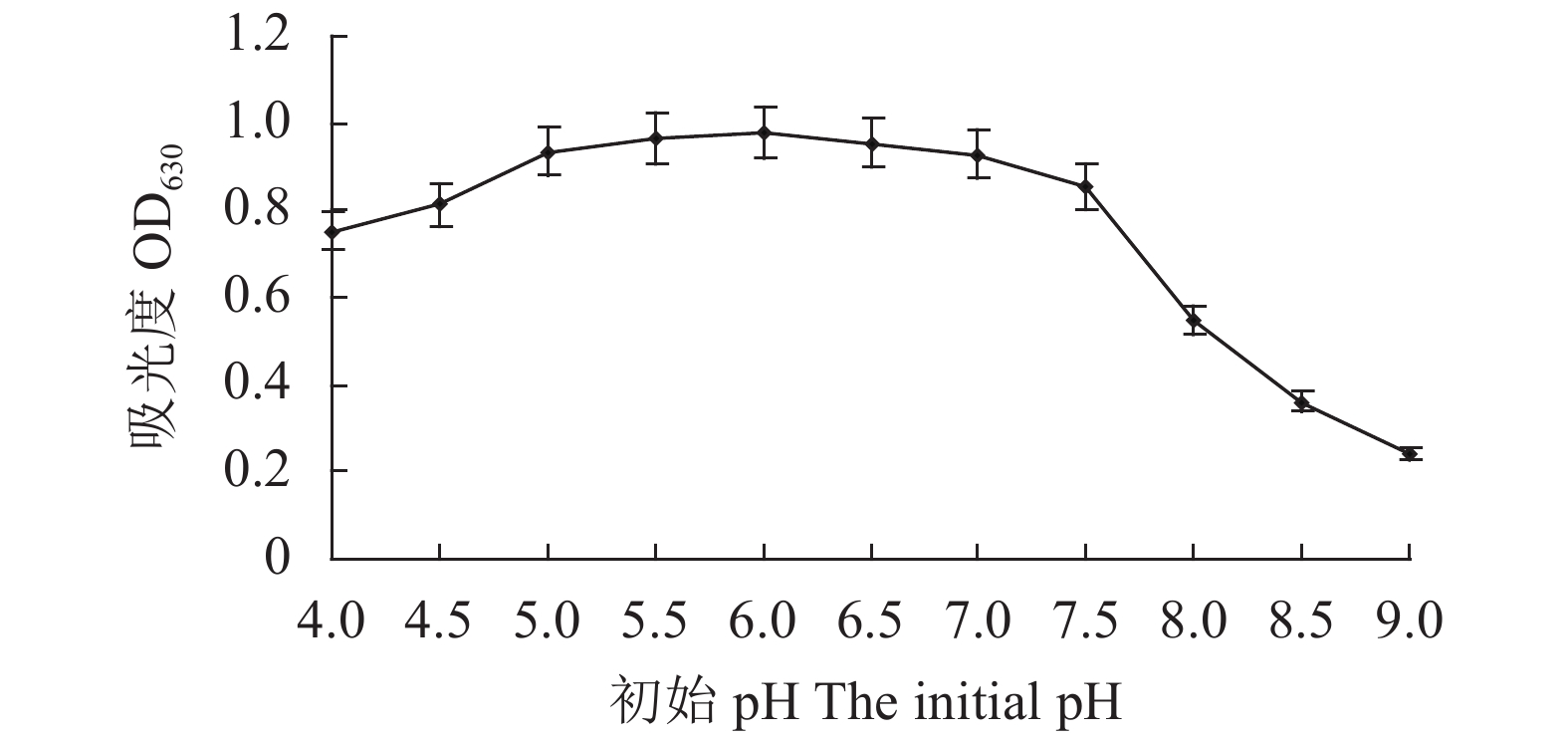
从图10可以看出,培养基初始pH 4.0~5.0时,菌体吸光值随pH的提高而提高;培养基初始pH 5.0~7.0范围内,Fb菌生物量较高且各组间差异不显著,均高0.93;再逐渐提高培养基的初始pH培养时,菌体吸光值随之下降;表明Fb菌的培养基最适初始pH为5.0~7.0。
2.5.5 盐度对Fb菌生长的影响
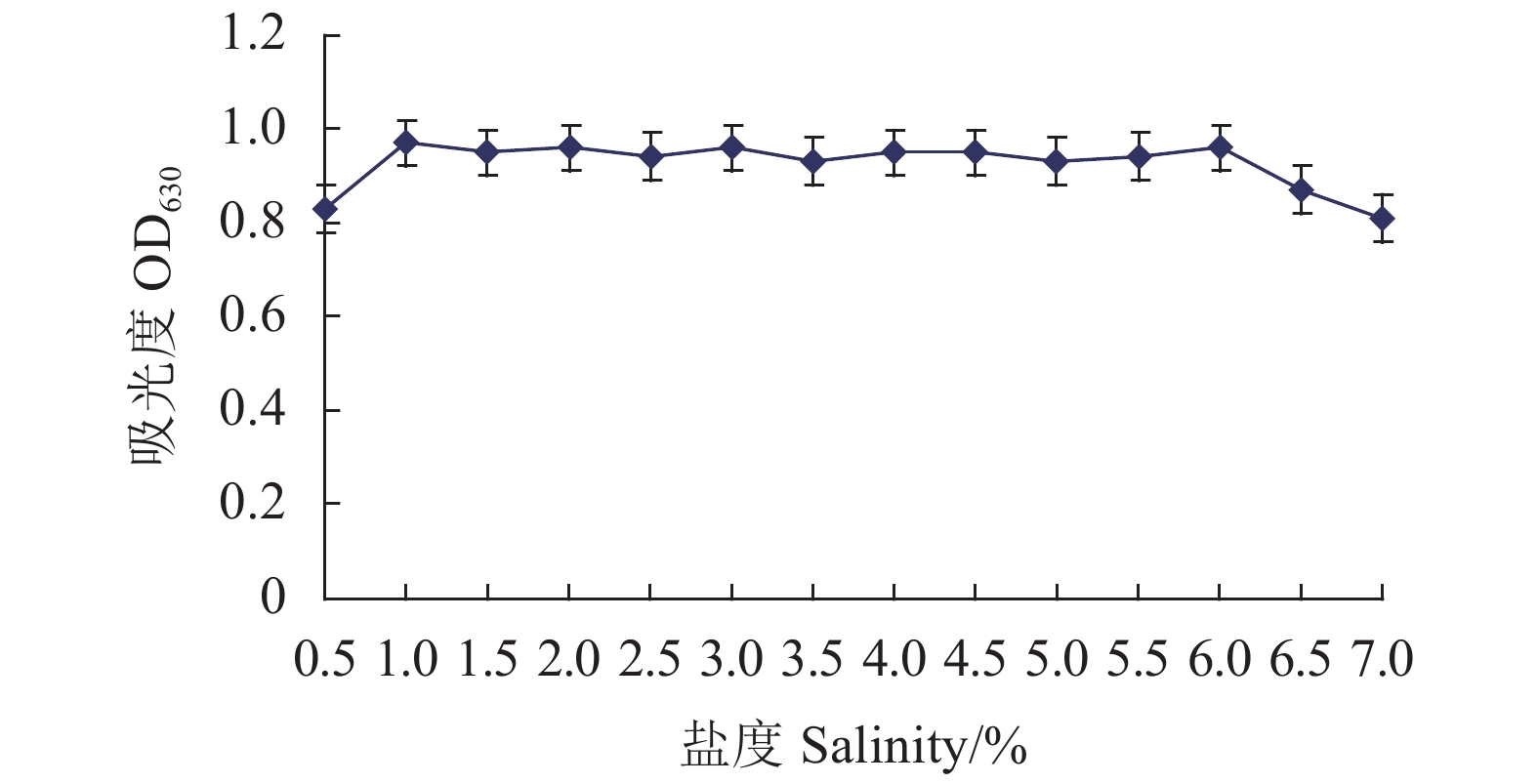
从图11可以看出,培养液的盐度从0.0增加到1.0%,菌株的吸光值也从0.46增加到0.92;培养液的盐度为1.0%~6.0%,菌株的吸光值均大于0.92,无显著差异;6.0%~7.0%菌株的吸光值下降至0.81。
2.6 菌株对茶渣降解效果
从茶渣常规营养成分分析看出(表4),发酵组比对照组粗蛋白提高14.88%,水分和粗纤维分别下降42.06%和9.69%,均存在显著差异。
表 4 茶渣常规营养成分的变化(n=9)Table 4. Changes in nutritional composition of tea dregs with Fb inoculation (dry base, n=9)(单位:%) 项目 Items 水分 Moisture 粗蛋白 Crude protein 粗纤维 Crude fiber 灰分 Ash 对照组 Control group 63.12±1.96 a 18.42±1.13 b 17.75±1.09 a 5.21±0.79 a 发酵组 Fermentation group 36.57±1.72 b 21.16±1.23 a 16.03±1.43 b 5.17±0.51 a 注:粗蛋白、粗纤维和灰分为干基所测值;同列数据后相同字母表示差异不显著(P>0.05),相邻或相隔字母分别表示差异显著(P<0.05)或差异极显著(P<0.01)。下表同。
Note: Crude protein, crude fiber and ash are measured on a dry basis;the same letter in the same column indicates that the difference is not significant(P>0.05), and the adjacent or spaced letters indicate that the difference is significant(P<0.05)or extremely significant(P<0.01). The same as follows.从茶渣纤维成分分析发现(表5),发酵组比对照组的中性洗涤纤维、酸性洗涤纤维和木质素分别下降10.72%、4.47%和11.37%,均存在显著差异。
表 5 茶渣纤维成分的比较(干基, n=9)Table 5. Change on fiber composition of tea dregs by treatment (dry base, n=9)(单位:%) 项目
Items中性洗涤纤维
Neutral detergent
fiber酸性洗涤纤维
Acid washing
fiber木质素
Lignin对照组
Control group50.75±1.62 a 44.12±1.62 a 2.11±1.62 a 发酵组
Fermentation group45.31±1.38 b 42.15±1.16 b 1.87±1.21 b 从茶渣氨基酸的组分和含量可以看出(表6),除胱氨酸、蛋氨酸和组氨酸发酵前后无差异外,两组均为谷氨酸含量最高,其次天冬氨酸;除胱氨酸、蛋氨酸和组氨酸发酵外,其他14种氨基酸含量均显著提高(P<0.05);氨基酸总量的变化与粗蛋白的变化一致,发酵后其含量提高5.98%,差异显著。
表 6 茶渣处理前后氨基酸含量的比较(干基, n=9)Table 6. Change on amino acid composition of tea dregs by treatment(单位:%) 项目
Items对照组
Control group发酵组
Fermentation group天冬氨酸 Asp 2.14±0.18 b 2.29±0.13 a 苏氨酸 Thr 1.09±0.05 b 1.14±0.03 a 丝氨酸 Ser 1.14±0.11 b 1.20±0.02 a 谷氨酸 Glu 2.76±0.12 b 2.95±0.13 a 甘氨酸 Gly 1.25±0.07 b 1.34±0.02 a 丙氨酸 Ala 1.36±0.04 b 1.43±0.05 a 胱氨酸 Cys 0.11±0.01 a 0.11±0.02 a 缬草氨酸 Val 1.38±0.03 b 1.47±0.03 a 精氨酸 Arg 1.34±0.05 b 1.41±0.06 a 甲硫(蛋)氨酸 Met 0.09±0.01 a 0.11±0.01 a 异亮氨酸 Iso 1.11±0.05 b 1.16±0.04 a 赖氨酸 Lys 1.65±0.02 b 1.77±0.06 a 亮氨酸 Leu 2.14±0.02 b 2.24±0.01 a 酪氨酸 Tyr 0.85±0.02 b 0.91±0.03 a 苯丙氨酸 Phe 1.33±0.03 b 1.38±0.01 a 组氨酸 His 0.05±0.01 a 0.05±0.01 a 脯氨酸 Pro 1.11±0.04 b 1.20±0.03 a 总量 Total 20.92 b 22.17 a 以上结果表明Fb菌能高效分解茶渣,显著提高茶渣的营养价值,更好实现茶渣饲料资源化利用。
3. 讨论与结论
研究表明,在固态发酵中,适宜的水分和原料粒度能够保证发酵基质深层微生物对氧气的需求,疏松多孔的基质能促进微生物的代谢废物及时排出,基质内部的养分也可随着自由水通过原料间隙扩散到基质表面,满足基质表面微生物对营养的需求,有利于微生物正常繁殖并保持高产酶活性状态[1, 42]。对于含水率高的物料,一般选择吸水性强的铺料如麦麸等来降低物料的含水率;或选择中高温菌发酵利于物料中水分蒸发。刘姝等[12]、胡桂萍等[13]、倪星虹[14]和朱飞等[1]均在茶渣中添加不同种类和比例的铺料进行发酵。本研究获得贝莱斯芽孢杆菌Fb属高温菌,在不添加任何铺料条件下,新鲜茶渣茶渣经其7 d发酵后水分下降了42.06%(P<0.05),可有效解决水分过高的问题。这种利用高温菌发酵分解高水分茶渣的方法不仅能降低生产成本,而且能发酵产生的生物热加大物料水分蒸发鲜见报道。
本研究中,利用高温特殊生境分离方法,从废弃茶渣中分离到有分解茶渣作用的高温菌5株,其中Fb菌能产生具有较强酶活力的纤维素酶、酸性蛋白酶、中性蛋白酶和碱性蛋白酶;与胡宝东等[43]从酱香型大曲中分离获得的甲基营养型芽孢杆菌(即贝莱斯芽孢杆菌)FBKL1.0190相似。Fb菌经菌落形态、菌株形态、生理生化特性的研究及分子鉴定为贝莱斯芽孢杆菌(Bacillus velezensis);可耐受55 ℃的高温,最适生长条件为:42~45 ℃、pH 5.0~7.0、16 h、盐度1.0%~6.0%、装液量0.12 mL·min−1、摇床转速120 r·min−1。茶渣经Fb菌株发酵后,与对照组比,粗蛋白提高14.88%(P<0.05);除胱氨酸、蛋氨酸和组氨酸发酵外,其他14种氨基酸含量均显著提高(P<0.05),且氨基酸总量提高5.98%(P<0.05);这与朱飞等[1]的结果一致,与李芳蓉[44]和张沛[45]的结果相近。另,本研究中茶渣经Fb菌株发酵后与对照组相比粗纤维及其中性洗涤纤维、酸性洗涤纤维和木质素分别下降9.69%、10.72%、4.47%和11.37%(P<0.05),这与张楠[46]和陈奕业[47]研究的结果相似。此外,本研究分离的Fb菌株的生长温度均高于他们的发酵菌株,这不仅可减少其他杂菌生长,而且可提高发酵效率。由此可见,Fb菌能有效分解茶渣,提高茶渣的营养价值。但该菌株在发酵分解茶渣的过程中能否产生一些抗菌的活性物质或表面活性素还有待后续的研究。
-
表 1 菌株生长条件单因素试验
Table 1 Single factor test on growth conditions of bacteria
因素
Factors添加水平
Level培养温度
Incubation temperature/℃30、33、36、39、42、45、48、51、54、57、60 装液量
Liquid loading quantity/mL10、15、20、25、30、35、40、45、50、55、60 摇床转速
Shaking speed/r·min−1100、120、140、160、180、200 培养时间
Fermentation time/h2、4、6、8、10、12、14、16、18、20 初始pH值
The initial pH4.0、4.5、5.0、5.5、6.0、6.5、7.0、7.5、8.0、8.5、9.0 盐度
Salinity/%0、0.5、1.0、1.5、2.0、2.5、3.0、3.5、4.0、4.5、5.0、5.5、6.0、6.5、7.0 注:盐度是指海水中溶解物质质量与海水质量的比值。
Note: Salinity refers to the ratio of dissolved substances in water to water.表 2 菌株酶活力比较
Table 2 Enzyme activities of selected strains
菌号
The
fungusCL活力
(U)
Cellulose
enzymeACP活性
(U)
Acid protease
activityNP活性
(U)
Neutral protease
activityAKP活性
(U)
Alkaline protease
activityDJ 191.58 21.59 40.23 23.35 Fb 198.33 22.90 41.24 44.36 8116 178.46 23.08 28.25 33.06 8106 189.95 24.44 30.90 27.85 HLH 154.34 16.61 54.17 18.76 表 3 Fb菌株生理生化特性
Table 3 Characteristics of Fb
项目
Items结果
Result项目
Items结果
Result项目
Items结果
Result项目
Items结果
Resultβ-木糖苷酶
β-xylosidase+ L-赖氨酸芳胺酶
L-lysine aromatase− L-天冬氨酸芳胺酶
L-aspartate aromatase− 亮氨酸芳胺酶
Leucine aromatase− 苯丙氨酸芳胺酶
Phenylalanine aramidase+ L-脯氨酸芳胺酶
L-proline aramidase− β-半乳糖苷酶
β-galactosidase− L-吡咯烷酮芳胺酶
L-pyrrolidone aramidase+ α-半乳糖苷酶
α-Galactosidase+ 丙氨酸芳胺酶
Alanine Aramidase− 酪氨酸芳胺酶
Tyrosine Aramidase− β-N-乙酰氨基葡糖苷酶
β-N-Acetylglucosaminidase− 丙氨酸-苯丙氨酸-脯氨酸芳胺酶
Alanine-phenylalanine-proline arylaminease+ 环糊精
Cyclodextrin− D-半乳糖
D-galactose− 糖原
Glycogen− 肌醇Inositol − 甲基-α-D-吡喃葡萄糖苷酸化
Methyl-α-D-glucopyranosylation+ ELLMAN 试剂 − 甲基-D-木糖苷
Methyl-D-xylosid− α-甘露糖苷酶
α-mannosidase− 麦芽三糖
Maltotriose− 甘氨酸芳胺酶
Glycine arylaminease− D-甘露醇
D-mannitol+ D-甘露糖
D-mannose+ D-松三糖
D-matsutriose− N-乙酰-D-氨基葡萄糖
N-acetyl-D-glucosamine− 古老糖
Ancient sugar+ L-鼠李糖
L-Rhamnose− β-葡糖苷酶
β-glucosidase+ β-甘露糖苷酶
β-mannosidase-phos− 磷酰胆碱
Phorylcholine− 丙酮酸盐
Pyruvate+ α-葡萄糖苷酶+
α-glucosidase− D-塔格糖
D-tagatose− D-海藻糖
D-trehalose+ 菊粉
Inulin− D-葡萄糖
D-glucose+ D-核糖
D-ribose+ 腐胺同化
Putrescine assimilation− 吲哚
Indole+ 卡那霉素耐药
Kanamycin resistance− 竹桃霉素耐药
Oleander resistance− 七叶苷水解
Aescin hydrolysis+ 红四氮唑
Red tetrazolium− 多粘菌素B耐药
Polymyxin B resistance− 注:“+”表示阳性,“-”表示阴性;ELLMAN试剂用于检测游离的巯基(-SH)。
Note: 1: + positive; − negative. 2: ELLMAN reagent for free sulfhydryl (-SH) detection.表 4 茶渣常规营养成分的变化(n=9)
Table 4 Changes in nutritional composition of tea dregs with Fb inoculation (dry base, n=9)
(单位:%) 项目 Items 水分 Moisture 粗蛋白 Crude protein 粗纤维 Crude fiber 灰分 Ash 对照组 Control group 63.12±1.96 a 18.42±1.13 b 17.75±1.09 a 5.21±0.79 a 发酵组 Fermentation group 36.57±1.72 b 21.16±1.23 a 16.03±1.43 b 5.17±0.51 a 注:粗蛋白、粗纤维和灰分为干基所测值;同列数据后相同字母表示差异不显著(P>0.05),相邻或相隔字母分别表示差异显著(P<0.05)或差异极显著(P<0.01)。下表同。
Note: Crude protein, crude fiber and ash are measured on a dry basis;the same letter in the same column indicates that the difference is not significant(P>0.05), and the adjacent or spaced letters indicate that the difference is significant(P<0.05)or extremely significant(P<0.01). The same as follows.表 5 茶渣纤维成分的比较(干基, n=9)
Table 5 Change on fiber composition of tea dregs by treatment (dry base, n=9)
(单位:%) 项目
Items中性洗涤纤维
Neutral detergent
fiber酸性洗涤纤维
Acid washing
fiber木质素
Lignin对照组
Control group50.75±1.62 a 44.12±1.62 a 2.11±1.62 a 发酵组
Fermentation group45.31±1.38 b 42.15±1.16 b 1.87±1.21 b 表 6 茶渣处理前后氨基酸含量的比较(干基, n=9)
Table 6 Change on amino acid composition of tea dregs by treatment
(单位:%) 项目
Items对照组
Control group发酵组
Fermentation group天冬氨酸 Asp 2.14±0.18 b 2.29±0.13 a 苏氨酸 Thr 1.09±0.05 b 1.14±0.03 a 丝氨酸 Ser 1.14±0.11 b 1.20±0.02 a 谷氨酸 Glu 2.76±0.12 b 2.95±0.13 a 甘氨酸 Gly 1.25±0.07 b 1.34±0.02 a 丙氨酸 Ala 1.36±0.04 b 1.43±0.05 a 胱氨酸 Cys 0.11±0.01 a 0.11±0.02 a 缬草氨酸 Val 1.38±0.03 b 1.47±0.03 a 精氨酸 Arg 1.34±0.05 b 1.41±0.06 a 甲硫(蛋)氨酸 Met 0.09±0.01 a 0.11±0.01 a 异亮氨酸 Iso 1.11±0.05 b 1.16±0.04 a 赖氨酸 Lys 1.65±0.02 b 1.77±0.06 a 亮氨酸 Leu 2.14±0.02 b 2.24±0.01 a 酪氨酸 Tyr 0.85±0.02 b 0.91±0.03 a 苯丙氨酸 Phe 1.33±0.03 b 1.38±0.01 a 组氨酸 His 0.05±0.01 a 0.05±0.01 a 脯氨酸 Pro 1.11±0.04 b 1.20±0.03 a 总量 Total 20.92 b 22.17 a -
[1] 朱飞, 苏娣, 冉雷, 等. 黑曲霉固态发酵改善茶渣营养价值的研究 [J]. 动物营养学报, 2018, 30(10):4269−4278. DOI: 10.3969/j.issn.1006-267x.2018.10.054 ZHU F, SU D, RAN L, et al. Nutritional improvement of tea residue by solid-state fermentation with Aspergillus niger [J]. Chinese Journal of Animal Nutrition, 2018, 30(10): 4269−4278.(in Chinese) DOI: 10.3969/j.issn.1006-267x.2018.10.054
[2] 郑清梅, 陈昆平, 钟艳梅, 等. 4类茶叶及其茶渣主要成分的测定与分析 [J]. 广东农业科学, 2015, 42(6):14−20. DOI: 10.3969/j.issn.1004-874X.2015.06.003 ZHENG Q M, CHEN K P, ZHONG Y M, et al. Determination and analysis of main components of four kinds of tea and their tea wastes [J]. Guangdong Agricultural Sciences, 2015, 42(6): 14−20.(in Chinese) DOI: 10.3969/j.issn.1004-874X.2015.06.003
[3] 叶勇. 茶饲料的应用及发展前景 [J]. 中国茶叶, 2000(4):14−15. YE Y. Application and development prospects of tea feed [J]. China Tea, 2000(4): 14−15.(in Chinese)
[4] 刘红云, 梁慧玲. 茶渣用作饲料的研究 [J]. 饲料研究, 2004(9):19−20. DOI: 10.3969/j.issn.1002-2813.2004.09.006 LIU H Y, LIANG H L. Research on the use of tea residue as feed [J]. Feed Research, 2004(9): 19−20.(in Chinese) DOI: 10.3969/j.issn.1002-2813.2004.09.006
[5] 佐野满昭, 孙希琪. 茶添加到家畜饲料中的利用效果 [J]. 农业新技术新方法译丛, 1996, 0(2):32−33. SANO MANZHAO, SUN X Q. Utilization effect of tea added to livestock feed [J]. Translation of new agricultural technologies and methods, 1996, 0(2): 32−33.(in Chinese)
[6] 徐瑞, 王改琴, 邬本成, 等. 茶叶渣对育肥猪生产性能及猪肉品质的影响 [J]. 黑龙江畜牧兽医, 2017(10):73−75, 286. XU R, WANG G Q, WU B C, et al. Effect of tea residue on fattening pig performance and pork quality [J]. Heilongjiang Animal Science and Veterinary Medicine, 2017(10): 73−75, 286.(in Chinese)
[7] 吴慧敏. 茶渣、茶末对蛋鸡生产性能及鸡蛋品质的影响研究[D]. 福州: 福建农林大学, 2016. WU H M. Study on the effect of tea residue and the tea dust on production performance and egg quality[D]. Fuzhou: Fujian Agriculture and Forestry University, 2016. (in Chinese)
[8] 舒庆龄, 赵和涛. 茶渣饲养肉用鸡效果研究 [J]. 安徽农业科学, 1995(4):355−356. SHU Q L, ZHAO H T. Research on the effect of tea residues in breeding chicken for meat [J]. Journal of Anhui Agricultural Sciences, 1995(4): 355−356.(in Chinese)
[9] 潘发明, 李发弟, 郝正里, 等. 茶渣单宁含量对绵羊养分消化利用与氮代谢参数的影响 [J]. 畜牧兽医学报, 2012, 43(1):71−81. PAN F M, LI F D, HAO Z L, et al. Effects of tannin content in residue of tea-leaves on digestion and utilization of nutrients and metabolic parameters of nitrogen in sheep [J]. Chinese Journal of Animal and Veterinary Sciences, 2012, 43(1): 71−81.(in Chinese)
[10] 傅志民, 吴永福. 废弃茶渣综合再利用研究进展 [J]. 中国茶叶加工, 2011(1):17−20. FU Z M, WU Y F. Research on multi-purpose utilization of used waste tea leaves [J]. China Tea Processing, 2011(1): 17−20.(in Chinese)
[11] 谢月琴, 罗君谊, 陈婷, 等. 茶渣资源再利用研究概况 [J]. 中国农学通报, 2019, 35(33):141−145. DOI: 10.11924/j.issn.1000-6850.casb18060083 XIE Y Q, LUO J Y, CHEN T, et al. Reuse of tea residue resources: A review [J]. Chinese Agricultural Science Bulletin, 2019, 35(33): 141−145.(in Chinese) DOI: 10.11924/j.issn.1000-6850.casb18060083
[12] 刘姝, 涂国全. 茶渣经微生物固体发酵成饲料的初步研究 [J]. 江西农业大学学报, 2001(1):130−133. DOI: 10.3969/j.issn.1000-2286.2001.01.029 LIU S, TU G Q. A preliminary study on the microbial feed by solid fermentation of tea residue [J]. Acta Agriculturae Universitis Jiangxiensis, 2001(1): 130−133.(in Chinese) DOI: 10.3969/j.issn.1000-2286.2001.01.029
[13] 胡桂萍, 杨广, 欧阳雪灵. 茶渣发酵蛋白饲料辅料优选及成本分析 [J]. 重庆理工大学学报(自然科学), 2017, 31(5):86−90, 142. HU G P, YANG G, OUYANG X L. Optimation of supplemental material in microbial fermentation of tea residue and its costs analysis [J]. Journal of Chongqing University of Technology (Natural Science), 2017, 31(5): 86−90, 142.(in Chinese)
[14] 倪星虹. 茶渣提取蛋白及饲料化利用的初步研究[D]. 南京: 南京农业大学, 2011. NI X H. Studys of the protein extract and utilization of producing protein feed from tea residues[D]. Nanjing: Nanjing Agricultural University, 2011. (in Chinese)
[15] 方呈祥. 中国高等学校菌种目录[M]. 北京: 化学工业出版社, 2009. [16] JAIN D K, COLLINS-THOMPSON D L, LEE H, et al. A drop-collapsing test for screening surfactant-producing microorganisms [J]. Journal of Microbiological Methods, 1991, 13(4): 271−279. DOI: 10.1016/0167-7012(91)90064-W
[17] PINCHUK I V, BRESSOLLIER P, SOROKULOVA I B, et al. Amicoumacin antibiotic production and genetic diversity of Bacillus subtilis strains isolated from different habitats [J]. Research in Microbiology, 2002, 153(5): 269−276. DOI: 10.1016/S0923-2508(02)01320-7
[18] WANG L T, LEE F L, TAI C J, et al. Bacillus velezensis is a later heterotypic synonym of Bacillus amyloliquefaciens [J]. International Journal of Systematic and Evolutionary Microbiology, 2008, 58(Pt 3): 671−675.
[19] 王伟, 李术娜, 李红亚, 等. 番茄灰霉病拮抗细菌的筛选与X-75菌株鉴定 [J]. 园艺学报, 2010, 37(2):307−312. WANG W, LI S N, LI H Y, et al. Screening of antagonistic bacteria against Botrytis cinerea and identification of strain X-75 [J]. Acta Horticulturae Sinica, 2010, 37(2): 307−312.(in Chinese)
[20] 王青华, 孙晓晖, 唐旭, 等. 深海贝莱斯芽孢杆菌DH82的筛选、鉴定及其抗菌粗蛋白性质分析 [J]. 海洋通报, 2019, 38(1):63−69. WANG Q H, SUN X H, TANG X, et al. Screening and identification of Bacillus velezensis strain DH82 and the characterization of the crude antimicrobial protein [J]. Marine Science Bulletin, 2019, 38(1): 63−69.(in Chinese)
[21] 杜淑涛, 李术娜, 朱宝成. 白菜黑斑病拮抗细菌Bacillus velezensis DL-59的筛选鉴定及田间防效实验 [J]. 河北农业大学学报, 2010, 33(6):51−56. DOI: 10.3969/j.issn.1000-1573.2010.06.011 DU S T, LI S N, ZHU B C. Screening and identification of antagonistic strain DL-59 of Bacillus velezensis against Alternaria brassicae and biocontrol efficiency [J]. Journal of Agricultural University of Hebei, 2010, 33(6): 51−56.(in Chinese) DOI: 10.3969/j.issn.1000-1573.2010.06.011
[22] 李生樟, 陈颖, 杨瑞环, 等. 一株拮抗黄单胞菌的贝莱斯芽孢杆菌的分离和鉴定 [J]. 微生物学报, 2019, 59(10):1969−1983. LI S Z, CHEN Y, YANG R H, et al. Isolation and identification of a Bacillus velezensis strain against plant pathogenic Xanthomonas spp [J]. Acta Microbiologica Sinica, 2019, 59(10): 1969−1983.(in Chinese)
[23] KANJANAMANEESATHIAN M, WIWATTANAPATAPEE R, ROTNIAM W, et al. Application of a suspension concentrate formulation of Bacillus velezensis to control root rot of hydroponicallygrown vegetables [J]. New Zealand Plant Protection, 2013, 66: 229−234. DOI: 10.30843/nzpp.2013.66.5556
[24] 张彩文, 程坤, 张欣, 等. 贝莱斯芽胞杆菌(Bacillus velezensis)分类学及功能研究进展 [J]. 食品与发酵工业, 2019, 45(17):258−265. ZHANG C W, CHENG K, ZHANG X, et al. Taxonomy and functions of Bacillus velezensis: A review [J]. Food and Fermentation Industries, 2019, 45(17): 258−265.(in Chinese)
[25] PAN H Q, LI Q L, HU J C. The complete genome sequence of Bacillus velezensis 9912D reveals its biocontrol mechanism as a novel commercial biological fungicide agent [J]. Journal of Biotechnology, 2017, 247: 25−28. DOI: 10.1016/j.jbiotec.2017.02.022
[26] KIM S Y, LEE S Y, WEON H Y, et al. Complete genome sequence of Bacillus velezensis M75, a biocontrol agent against fungal plant pathogens, isolated from cotton waste [J]. Journal of Biotechnology, 2017, 241: 112−115. DOI: 10.1016/j.jbiotec.2016.11.023
[27] 王金燕, 李彬, 王印庚, 等. 刺参养殖池塘一株贝莱斯芽孢杆菌的分离及其生理特性 [J]. 中国水产科学, 2018, 25(3):567−575. DOI: 10.3724/SP.J.1118.2018.17383 WANG J Y, LI B, WANG Y G, et al. Screening and characteristic analysis of Bacillus velezensis from sea cucumber(Apostichopus japonicus) ponds [J]. Journal of Fishery Sciences of China, 2018, 25(3): 567−575.(in Chinese) DOI: 10.3724/SP.J.1118.2018.17383
[28] LIU X Y, REN B, CHEN M, et al. Production and characterization of a group of bioemulsifiers from the marine Bacillus velezensis strain H3 [J]. Applied Microbiology and Biotechnology, 2010, 87(5): 1881−1893. DOI: 10.1007/s00253-010-2653-9
[29] TOMAZ C T, QUEIROZ J A. Fractionation of Trichoderma reesei cellulases by hydrophobic interaction chromatography on phenyl-sepharose [J]. Biotechnology Letters, 2004, 26(3): 223−227. DOI: 10.1023/B:BILE.0000013719.92024.04
[30] 中华人民共和国国家质量监督检验检疫局, 中国国家标准化管理委员会.饲料添加剂酸性蛋白酶活力的测定分光光度法: GB/T 28715—2012 [S].北京: 中国标准出版社, 2012. [31] 中华人民共和国国家技术监管局.蛋白酶制剂: GB/T 23527—2009[S].北京: 中国标准出版社, 2009. [32] 杨健, 何永林, 刘晔华. 微生物教学中常用细菌染色方法的改进 [J]. 川北医学院学报, 2003(4):165. DOI: 10.3969/j.issn.1005-3697.2003.04.150 YANG J, HE Y L, LIU Y H. Improvement of commonly used bacterial staining methods in microbiology teaching [J]. Journal of North Sichuan Medical College, 2003(4): 165.(in Chinese) DOI: 10.3969/j.issn.1005-3697.2003.04.150
[33] 布坎南 R E,吉本斯 N E.伯杰细菌鉴定手册[M].8版.中国科学院微生物研究所《伯杰细菌鉴定手册》翻译组,译.北京: 科学出版社,1984. [34] 沈萍. 微生物学实验[M]. 北京: 高等教育出版社, 2004. [35] 东秀珠, 蔡妙英. 常见细菌系统鉴定手册[M]. 北京: 科学出版社, 2001: 364−398. [36] 郝云婕, 韩素贞. gyrB基因在细菌系统发育分析中的应用 [J]. 生物技术通报, 2008(2):39−41. HAO Y J, HAN S Z. Application of gyrB gene in bacterial phylogenetic analysis [J]. Biotechnology Bulletin, 2008(2): 39−41.(in Chinese)
[37] TANG X L, ZHAI L, LIN Y F, et al. Halomonas alkalicola sp. nov., isolated from a household product plant [J]. International Journal of Systematic and Evolutionary Microbiology, 2017, 67(5): 1546−1550. DOI: 10.1099/ijsem.0.001757
[38] PHENG S, LEE J J, EOM M K, et al. Paucibacter oligotrophus sp. nov., isolated from fresh water, and emended description of the genus Paucibacter [J]. International Journal of Systematic and Evolutionary Microbiology, 2017, 67(7): 2231−2235. DOI: 10.1099/ijsem.0.001931
[39] 卫扬保. 微生物生理学[M]. 北京: 高等教育出版社, 1989. [40] 王加启, 于建国. 饲料分析与检验[M]. 北京: 中国计量出版社, 2004. [41] 于泓, 牟世芬. 氨基酸分析方法的研究进展 [J]. 分析化学, 2005(3):398−404. DOI: 10.3321/j.issn:0253-3820.2005.03.028 YU H, MOU S F. Method development for amino acid analysis [J]. Chinese Journal of Analytical Chemistry, 2005(3): 398−404.(in Chinese) DOI: 10.3321/j.issn:0253-3820.2005.03.028
[42] BHATTACHARYA S S, GARLAPATI V K, BANERJEE R. Optimization of laccase production using response surface methodology coupled with differential evolution [J]. New Biotechnology, 2011, 28(1): 31−39. DOI: 10.1016/j.nbt.2010.06.001
[43] 胡宝东, 邱树毅, 周鸿翔, 等. 酱香型大曲的理化指标、水解酶系、微生物产酶的关系研究 [J]. 现代食品科技, 2017, 33(2):99−106. HU B D, QIU S Y, ZHOU H X, et al. Relationships among physiochemical indices and hydrolyzing enzyme systems and enzymes-produced-ability in Jiangxiang daqu [J]. Modern Food Science and Technology, 2017, 33(2): 99−106.(in Chinese)
[44] 李芳蓉, 陈鑫, 张建军. 红芪药渣固态发酵生产蛋白饲料的探讨 [J]. 中央民族大学学报(自然科学版), 2019, 28(1):47−51. LI F R, CHEN X, ZHANG J J. Discussion on the production of protein feed by solid ferm entation of Hedysarum polybotrys hand. -Mazz. Residue [J]. Journal of Minzu University of China (Natural Sciences Edition), 2019, 28(1): 47−51.(in Chinese)
[45] 张沛, 杨国辉, 魏丽娟, 等. 稻壳粉固态发酵生产蛋白饲料的工艺研究 [J]. 中国饲料, 2015(8):25−27, 38. ZHANG P, YANG G H, WEI L J, et al. Study on the technology of protein feed frim rice husk powder fermented by solid slate [J]. China Feed, 2015(8): 25−27, 38.(in Chinese)
[46] 张楠, 张凌云. 茶渣在自然发酵与添加外源微生物发酵过程中的理化动态研究[C]//2009年中国茶叶科技创新与产业发展学术研讨会论文集. 重庆, 2009: 428-435. [47] 陈奕业, 朱妮, 梁瑶, 等. 不同添加剂对凉茶渣发酵品质的影响 [J]. 家畜生态学报, 2020, 41(2):55−59. DOI: 10.3969/j.issn.1673-1182.2020.02.010 CHEN Y Y, ZHU N, LIANG Y, et al. Effect of additives on quality of herbal tea residue fermentation [J]. Journal of Domestic Animal Ecology, 2020, 41(2): 55−59.(in Chinese) DOI: 10.3969/j.issn.1673-1182.2020.02.010
-
期刊类型引用(1)
1. 张建新,陈永艳,和子涵,武婧玉,李梦,黄梦媛,孟晓林,常绪路,冯军厂. 鲤源产β-甘露聚糖酶Bacillus velezensis HF-14109的分离鉴定及其酶学和生物学特性研究. 微生物学报. 2022(08): 3062-3078 .  百度学术
百度学术
其他类型引用(1)




 下载:
下载: