Identification and Expressions under Low-temp/Draught Stress of Polyamine Synthesis Genes in Oil Palms
-
摘要:目的 研究多胺合成酶基因在油棕生长发育及非生物胁迫应答中的作用,为油棕抗性品种培育提供理论基础。方法 从油棕基因组中鉴定出15个编码多胺合成酶的基因,并对其进行生物信息学分析和表达模式分析。结果 多胺合成酶的氨基酸长度为318~720,分子量为36.00~46.43 kDa,等电点为4.78~6.31,蛋白不稳定指数为29.26~48.73,脂溶指数为76.46~94.41,总平均亲水性为−0.315~0.082,外显子数目为1~11个,具有特定的蛋白保守基序和保守结构域。进化分析发现油棕多胺合成酶基因可以分为3个家族,EgADCs与水稻的亲缘关系较近,EgACLs、EgSPDSs与椰枣的亲缘关系较近,EgSPMSs与玉米的亲缘关系较近。启动子上鉴定出大量植物激素响应、逆境胁迫响应和光响应的顺式作用元件。组织表达分析发现多胺合成酶基因在油棕不同组织中均有表达;多胺合成酶基因受低温和脱水胁迫的诱导。结论 多胺合成酶基因参与油棕对低温和脱水胁迫的应答,其中EgSPDS1、EgSPDS2、EgSPMS1、EgADC1、EgADC2、EgACL5-2、EgACL5-3、EgSAMDC3-1、EgSAMDC4-1、EgSAMDC4-2和EgACL5-1受低温胁迫的诱导,EgSPDS1、EgSPDS2、EgADC1、EgADC2、EgSAMDC4-1和Eg SAMDC4-2、EgACL5-1受脱水胁迫的诱导。Abstract:Objective Genetic information and resource of low-temp/draught resistant oil palms were studied with respect to the stress responses of polyamines synthase gene in the plants for breeding purposes.Method Bioinformatics of polyamines synthase genes in oil palm were gathered from the genome bank, and their expressions under abiotic stresses analyzed.Result Fifteen polyamines synthase genes were identified from the oil palm genome. There were between 318 and 720 amino acids in the genes with a molecular weight ranging from 36.00 kDa to 46.43 kDa and an isoelectric point between 4.78 and 6.31. The instability indices of the genes were found in between 29.26 and 48.73, the aliphatic indices in between 76.46 and 94.41, the gravy in between −0.315 and 0.082, and the exon number in between 1 and 11. They contained both specific conserved protein motifs and conserved domain. A phylogenetic analysis divided them into 3 families, i.e., EgADCs closely related to rice, EgACLs and EgSPDSs closely related to data palm, and EgSPMSs closely related to maize. Many cis-acting elements that response to phytohormone, stresses, and light were found in the promoters. The expressions of the polyamine synthase genes existed in different tissues of the plant and could be induced by either low temperature or draught stress. Specifically, EgSPDS1, EgSPDS2, EgSPMS1, EgADC1, EgADC2, EgACL5-2, EgACL5-3, EgSAMDC3-1, EgSAMDC4-1, EgSAMDC4-2, and EgACL5-1 were found to be upregulated by the imposed cold stress; while EgSPDS1, EgSPDS2, EgADC1, EgADC2, EgSAMDC4-1 EgSAMDC4-2, and EgACL5-1 by dehydration.Conclusion The polyamine synthase genes were significantly expressed in tissues of the oil palms that could be induced by either low temperature or draught stress. Those responded to the abiotic stresses were identified in this study.
-
Keywords:
- Oil palm /
- polyamine synthase /
- cold /
- dehydration /
- gene expression
-
0. 引言
【研究意义】油棕( Elaeis guineensis )是重要的热带木本油料作物,其果实压榨的棕榈油在食品加工业、轻工业以及生物能源等领域有着广泛的应用[1, 2]。油棕原产于非洲西部的热带雨林中,性喜高温和湿润气候,油棕种植在热带北缘地区常受到低温胁迫的为害,热带地区季节性干旱也会影响油棕的生长和产量[3, 4]。挖掘和鉴定与低温和干旱应答相关的基因,研究油棕的逆境应答分子机制,对油棕遗传改良和栽培选育具有重要的意义。【前人研究进展】多胺是植物由2个或2个以上氨基组成的一种小分子带阳性电荷的脂肪族有机化合物,包括腐胺、精胺、亚精胺、热精胺等[5]。多胺在植物生长发育过程中起着重要的调控作用,参与植物的细胞增殖、形态发生以及对多种生物和非生物胁迫的响应[5]。大量的研究表明多胺的合成受到低温、干旱、盐碱、病原菌侵染等胁迫的诱导[6-8],外源喷施多胺也能显著增强植物对胁迫的耐受能力[9-11]。多胺的合成途径有2条,精氨酸脱羧酶途径和鸟氨酸脱羧酶途径。而在拟南芥中的研究发现其多胺合成主要是通过精氨酸脱羧酶途径[12]。精氨酸在精氨酸脱羧酶(ADC),鲱精胺亚氨基水解酶(AIH),N-氨甲酰腐胺-酰胺水解酶(CPA)3种酶的催化下产生腐胺;腺苷甲硫氨酸在腺苷甲硫氨酸脱羧酶(SAMDC)催化下产生氨丙基;腐胺与氨丙基在亚精胺合成酶(SPDS)的催化下生成亚精胺(Spd);亚精胺在精胺合成酶(SPMS)和热精胺合成酶(ACL5)的作用下分别生成精胺(Spm)和热精胺(Tspm)[13]。其中ADC、SPDS、SPMS、ACL5和SAMDC是该途径中的关键酶,在植物响应非生物及生物胁迫中起着重要的调控作用[14]。在拟南芥中超量表达枳的PtADC1能够促进腐胺的合成和根系生长,进而提高转基因植株对干旱和低温的耐受性[8];超量表达SaADC1能够活化CBF的表达,进而显著提高转基因马铃薯对低温的耐受性[15];在苜蓿中的研究发现超量表达MtADC基因能够促进脯氨酸和精胺,增强对盐害的耐受性[16]。在拟南芥中超量表达羊草的LcSAMDC1基因能够提高转基因植株在低温胁迫下精胺的含量,进而增强抗冷性[17];在拟南芥中超量表达甜菜的BvM14-SAMDC基因能够提高盐胁迫下精胺和亚精胺的含量,增强抗氧化能力,进而提高盐害的耐受性[18]。在茄子中的研究发现SmMYB44通过活化SmSPDS的表达,提高亚精胺的含量,进而增强对茄子青枯病的抗性[19]。【本研究的切入点】随着油棕基因组测序工作的完成,基于全基因组数据库挖掘功能基因成为可能[20]。多胺在植物生长发育和逆境胁迫应答中起着重要的调控作用,而在油棕中的相关研究尚待深入研究。【拟解决的问题】本研究以拟南芥和水稻多胺合成酶的氨基酸序列为参照序列,在油棕基因组中进行比对获得候选基因,再通过染色体定位、数据库功能注释、基因结构、进化树分析确定其家族分类和可能具有的功能,同时采用实时荧光定量PCR分析多胺合成酶基因在油棕低温和脱水胁迫中的表达模式,以期为培育油棕抗性品种奠定理论基础。
1. 材料与方法
1.1 植物材料和胁迫处理
油棕 厚壳种Dura叶片采自中国热带农业科学院国家热带棕榈种植资源圃(东经110.77°,北纬19.53°),采集油棕第17~20位叶片中部的小叶分别置于人工气候箱进行低温和脱水处理模拟低温和干旱胁迫。人工气候箱参数设置为光照(5 000 Lx)16 h,黑暗8 h,低温处理:设置温度为8 ℃,湿度为80%。脱水处理:设置温度为25 ℃,湿度为50%。分别在低温处理0 、6 、12 、24 、36 、48 h取样,在脱水处理0 、0.5 、1、3 、6 、12 h取样,将0 h的叶片作为对照[21]。样品采集后液氮速冻后置于超低温冰箱中用于RNA提取。
1.2 油棕多胺合酶基因的挖掘
从拟南芥基因组数据库(https://www.arabidopsis.org/)下载多胺合成酶的氨基酸序列,从NCBI数据库(https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/genome/?term=rice)中下载水稻多胺合成酶的氨基酸序列,以拟南芥和水稻的多胺合成酶的氨基酸序列作为参考序列,通过BLSATP在油棕基因组数据库中进行比对。利用在线工具ExPAsy(http://www.expasy.org)分析油棕多胺合成酶基因的蛋白质分子量、等电点、蛋白不稳定指数、脂溶指数和总平均亲水性等理化性质。
1.3 油棕多胺合成基因的生物信息学分析
油棕多胺合成酶基因家族的基因结构、蛋白保守基序、保守结构域和染色体定位均采用Tbtool[22]进行可视化分析。采用ClustalW[23]对油棕和其他植物多胺合成酶蛋白质序列进行多重比对,采用MEGA6.0的Neighbor-joining法进行建树,分析进化关系,设置校验值bootstrap为1000。从NCBI数据库中下载油棕多胺合成酶基因CDS上游2000 bp的序列,采用Plant Care[24]进行顺式作用元件分析,采用Tbtool进行可视化[22]。油棕的根(SRR851071)、茎尖(SRR851103)、叶(SRR851096)、花(SRR851108)和花后15周(SRR190698)、17周(SRR190699)、21(SRR190701)和23周(SRR190702)果肉的转录组数据从NCBI的SRA数据库(https://trace.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/Traces/sra/sra.cgi?)中下载。采用RPKM值对转录组数据进行归一化处理,利用基迪奥云平台在线工具(https://www.omicshare.com/tools/)绘制热图。
1.4 油棕多胺合成基因的qRT-PCR分析
总RNA提取参照柱式植物总RNA抽提纯化试剂盒(上海生工)的操作说明进行。cDNA合成参照PrimeScriptTM II 1st Strand cDNA Synthesis(大连宝生物)试剂盒的操作说明进行。qRT-PCR参照SYBR® Select Master Mix(大连宝生物)的操作说明进行。反应体系采用10 μL体系,每个反应加入cDNA模板1 μL,正向引物和反向引物各0.5 μL,SYBR® Select Master Mix 5 μL,双蒸水3 μL。qRT-PCR反应程序为95 ℃预解链2 min,95 ℃解链5 s,退火和延伸20 s,循环40次。每个反应重复4次。引物序列见表1。
表 1 油棕多胺合成酶基因qRT-PCR引物序列Table 1. Sequence of qRT-PCR primer of polyamine synthase genes in oil palms基因 Gene 正向引物 Forward primer 反向引物 Reverse primer 产物长度 Product length EgSPDS1 CCAGCAGGAGTCTTTACGCA CAGCCCCAAGTGTCAGCATA 122 EgSPDS1L TGTCTGCCGCCAAACCTTTA ATGAAACCAATCACCCCGCT 84 EgSPMS1 CCGATTGGTCCAGCTCAAGA AAGCCACATGCTCTCTGCTT 108 EgSPMS2 TGCGCCTGAAGGGATGTATG GGCCTTTCAACAAGTTCCCG 81 EgADCL GAAGGGCAAGTTCGGTCTGA AGCCGATGTGAAAGTGGAGG 107 EgADC GTGATGTTCGAGGGGCTCAA GCACCAGATAGGGCATGGAA 112 EgACL5-1 ACTTGAACGGCGAGTTCCTT AAGAACAACATGCCCTCCCA 135 EgACL5-2 CATGGGGATGGGTTATGGCA ACAAGGAACTCGCCGTTCAA 118 EgACL5-3 CTATGCTGACACTTGGGGCT CGGCAGATGCAAAGGTCTTG 137 EgACL5-4 CCAGCAGGAGTCTTTACGCA CAGCCCCAAGTGTCAGCATA 122 EgSAMDC2 TCAGCGGACGATCCACTCTA TGCTGAGTTGTGCTGGTTCT 96 EgSAMDC3-1 CAGCCTTCTCCCCATCGTAG GATGATGCCGGATCGCCTAT 110 EgSAMDC3-2 TGAAGCCATGGGTCTCAACC CCTTCTTCGACCATGTGCCT 143 EgSAMDC3-3 AGTACTCCCGTGGGACCTTT AAGCCTTACCACCCGAACTG 120 EgSAMDC4-1 GGAGATGACCGAGTTGACGG AATCGTCGAGTATCGGTCGC 121 EgSAMDC4-2 TTACTCGATGAACGGCCTCG CCGGAATACGTTCACGACCT 142 β-actin CTCAACCCCAAGGCGAAC GTAACACCATCTCCCGAGTCAA 100 1.5 数据分析
本研究采用SPSS 13.0进行数据分析,用Ducan检测法进行基因表达的差异显著性分析。图表采用Excel、TBtool和MEGA 6.0绘制。
2. 结果与分析
2.1 油棕多胺合成酶基因的鉴定
分别以拟南芥和水稻多胺合成酶基因的氨基酸序列为参照序列在油棕基因组中比对,获得的15个不同的序列与拟南芥和水稻多胺合成酶基因高度相似。这15个基因分别被命名为亚精胺合成酶(EgSPDS1、EgSPDS2),精胺合成酶(EgSPMS1、EgSPMS2),热精胺合成酶(EgACL5-1,EgACL5-2,EgACL5-3),精氨酸脱羧酶(EgADC1、EgADC2),S-腺苷甲硫氨酸脱羧酶(EgSAMDC1、EgSAMDC2、EgSAMDC3-1、EgSAMDC3-2、EgSAMDC4-1、EgSAMDC4-2)。油棕亚精胺合成酶、精胺合成酶热精胺合成酶、S-腺苷甲硫氨酸脱羧酶的氨基酸长度较短,为300左右,精氨酸脱羧酶的氨基酸长度较长,为700左右。油棕多胺合成酶氨基酸的分子量在36.00~76.58 KDa,等电点在4.80~6.31,偏酸性。EgACLs的蛋白不稳定指数在40以下,为稳定蛋白;其余均大于40,为不稳定蛋白。油棕多胺合成酶脂溶指数在76.46~94.41,平均为83.8。EgADCs的总平均亲水性大于0,EgSAMDC3-1的总平均亲水性为0,其余均小于0(表2)。
表 2 油棕多胺合酶基因的理化性质分析Table 2. Physicochemical properties of polyamine synthase genes in oil palms基因名
Symbol基因登录号
Gene accession基因座登录号
Gene locus氨基酸长度
Number of amino acids分子量(kDa)
Molecular weight等电点
Theoretical pI蛋白不稳定指数
Instability index脂溶指数
Aliphatic index总平均亲水性
GravyEgSPDS1 XM_010943910.3 LOC105060266 346 37.92 4.80 48.15 85.29 −0.094 EgSPDS2 XM_010930791.3 LOC105050680 342 37.52 4.78 48.1 83.16 −0.137 EgSPMS1 XM_010915332.3 LOC105039242 389 42.70 5.31 45.35 81.93 −0.236 EgSPMS2 XM_019849278.2 LOC105040703 363 40.12 5.61 42.47 85.62 −0.131 EgACL5-1 XM_010934133.2 LOC105053105 332 37.74 5.36 30.61 82.20 −0.307 EgACL5-2 XM_010936715.1 LOC105055022 334 37.42 5.91 30.65 78.53 −0.315 EgACL5-3 XM_029263566.1 LOC105041819 318 36.00 5.10 29.26 83.71 −0.291 EgADC1 XM_010910687.3 LOC105035222 720 76.58 5.14 42.79 92.82 0.082 EgADC2 XM_010920850.3 LOC105043339 696 74.08 5.73 42.71 94.41 0.028 EgSAMDC1 XM_019846142.1 LOC105031981 356 38.93 5.47 50.07 85.51 −0.008 EgSAMDC2 XM_010906317.3 LOC105032002 423 46.43 6.05 46.75 80.21 −0.152 EgSAMDC3-1 XM_010930896.3 LOC105050758 402 43.89 4.96 48.73 80.27 −0.083 EgSAMDC3-2 XM_010915747.2 LOC105039560 382 41.89 5.01 44.15 86.05 0.000 EgSAMDC4-1 XM_010923664.3 LOC105045398 340 37.34 6.31 46.89 81.18 −0.082 EgSAMDC4-2 XM_010933625.3 LOC105052707 333 36.27 6.17 46.26 76.46 −0.158 2.2 油棕多胺合成酶的生物信息学分析
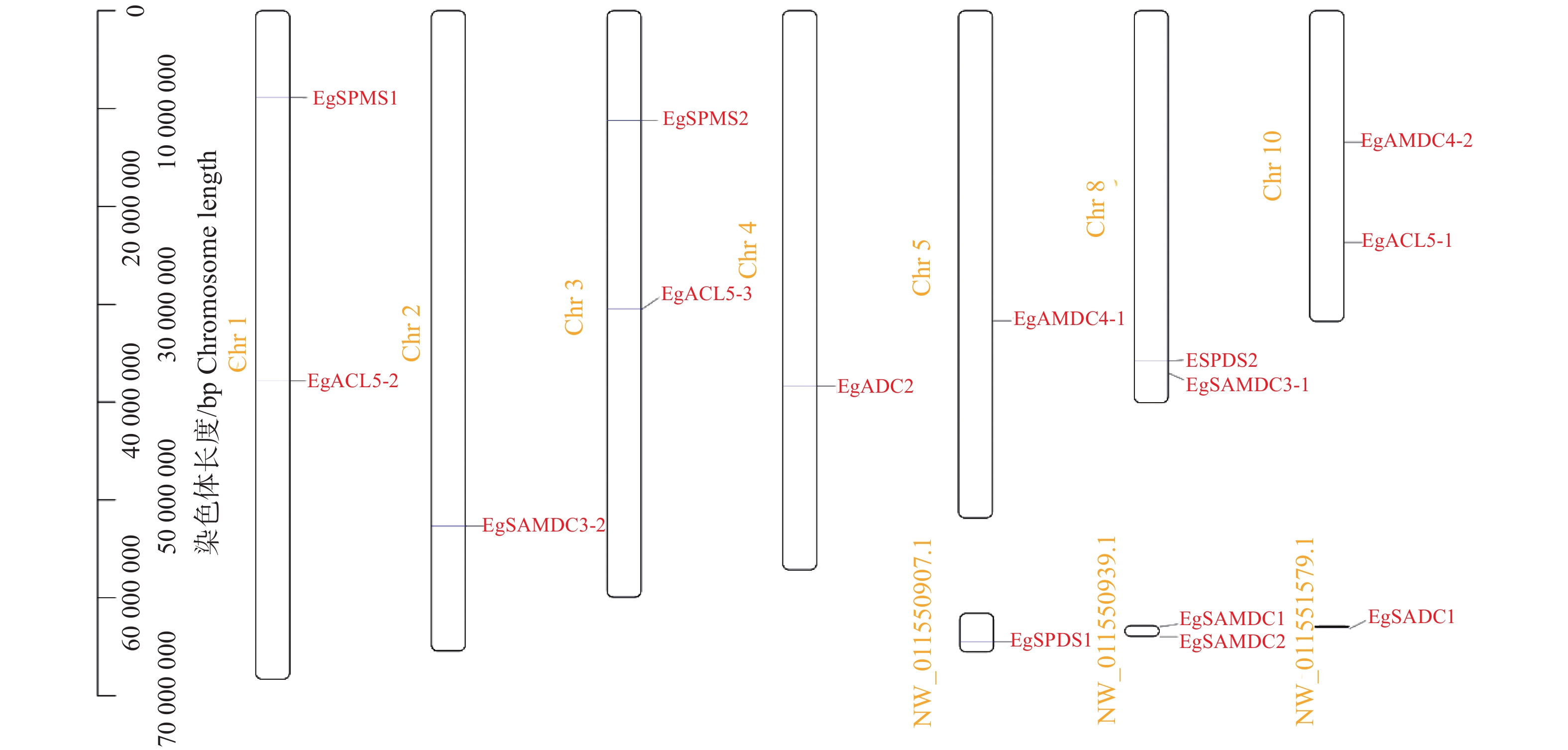
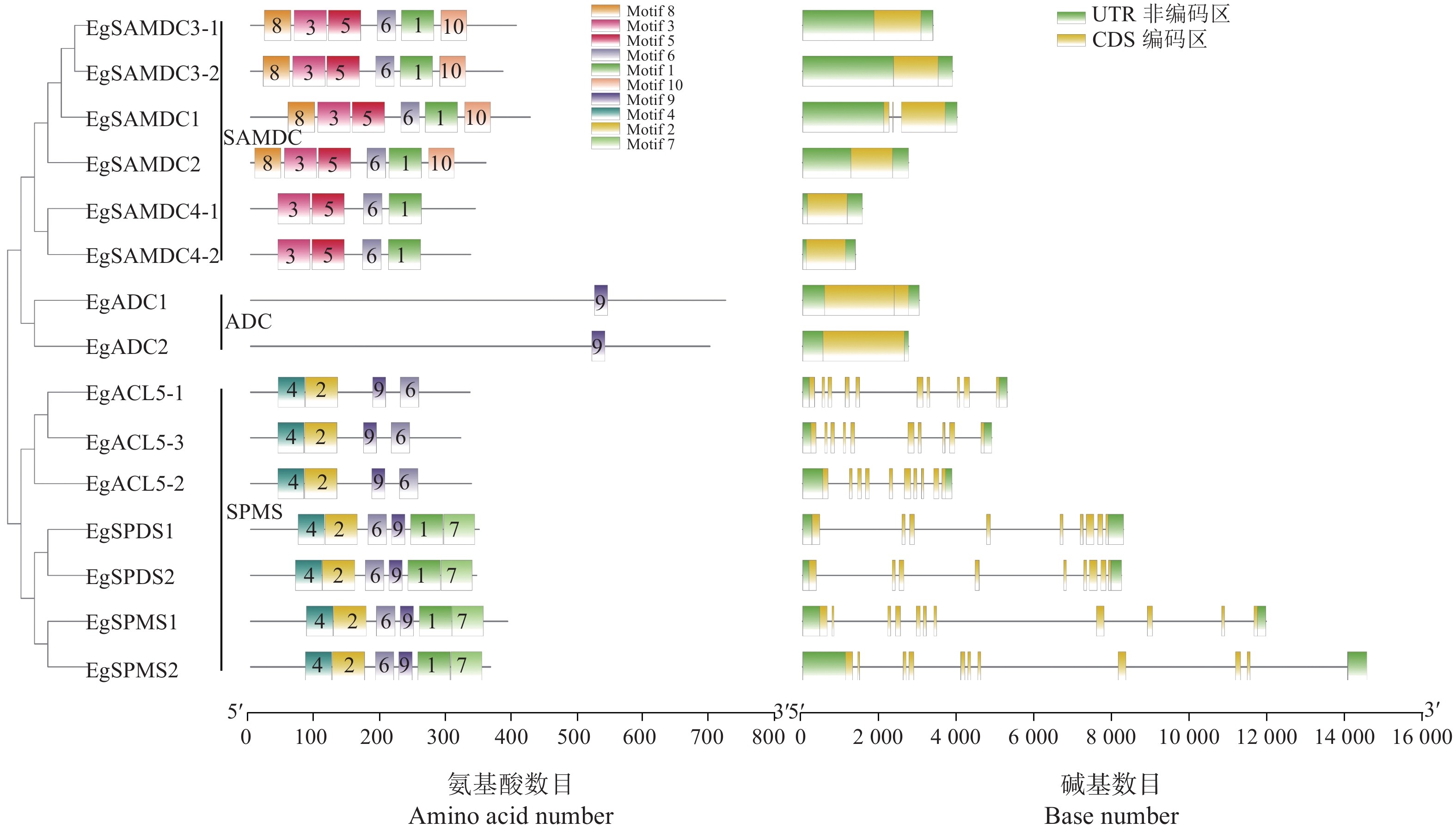
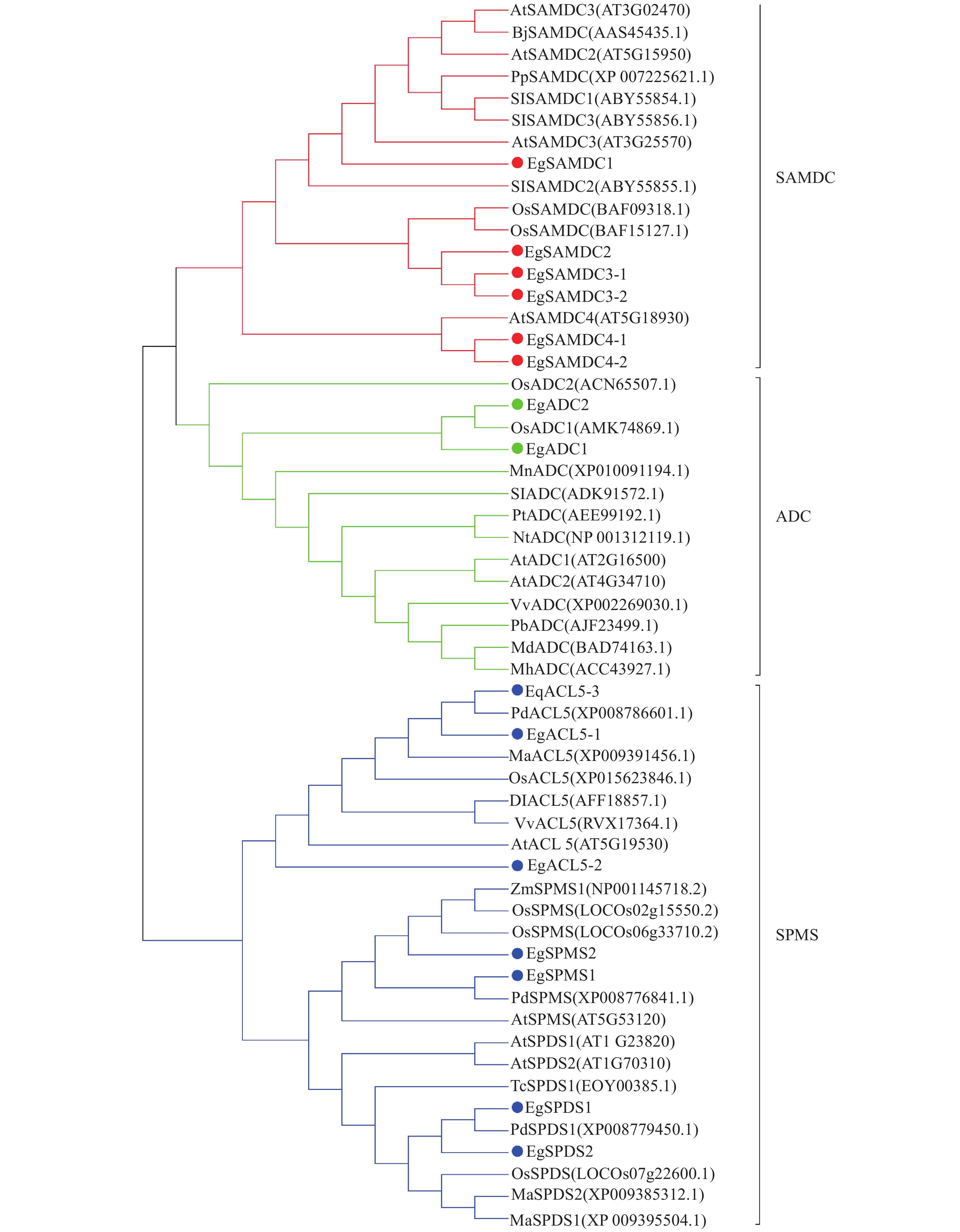
油棕共有16条染色体,对多胺合成酶基因进行染色体定位,发现EgSPMS1和EgACL5-2定位Chr1上,EgSAMDC3-2定位在Chr2上,EgSPMS2和EgACL5-3定位在Chr3上,EgADC2定位在Chr4上,EgSAMDC4-1定位在Chr5上,EgSPDS2和EgSAMDC3-1定位在Chr8上,EgSAMDC4-2和EgACL5-1定位在Chr10上,EgSPDS1、EgSAMDC1、EgSAMDC2和EgADC1未能定位在染色体上,分布在3个Scaffolds上(图1)。利用MEME在线工具分析保守蛋白基序发现:EgSAMDCs含有基序1、3、5、6、8、10,EgADCs含有基序9,EgACL5s含有基序2、4、6、9和EgSPDSs含有基序1、2、4、6、7、9。利用Batch Web CD-Search Tool分析蛋白保守结构域发现:EgSAMDCs含有特定保守域PLN02524,EgADCs含有特定保守域PLN02439,EgACL5s含有特定保守域PLN02823,EgSPDSs含有特定保守域PLN02366(表2)。基因结构分析发现:EgSPDS1和EgSPDS2有9个外显子,EgSPMS1和EgSPMS2有11个外显子,EgACL5-1、EgACL5-2和EgACL5-3有10个外显子,EgSAMDC1有3个外显子,EgADC1有2个外显子,EgADC2、EgSAMDC2、EgSAMDC3-1、EgSAMDC3-2、EgSAMDC4-1、EgSAMDC4-2只有1个外显子,没有内含子(图2)。将油棕的多胺合成酶氨基酸序列和其他植物进行进化分析,发现多胺合成酶基因一共分成3个家族:ADC家族、SPMS家族(包括SPMS,SPDS和ACL5)和SAMDC家族(图3),其中EgSMADCs和EgADCs与水稻的亲缘关系较近,EgACLs和EgSPDSs与椰枣的亲缘关系较近,EgSPMSs与玉米的亲缘关系较近。
在油棕多胺合成基因的启动子中鉴定了大量与光响应、植物激素应答、防卫和逆境胁迫响应相关的顺式作用元件,包括脱落酸响应(47个),赤霉素响应(8个)、光响应(165个)、茉莉酸甲酯响应(21)、伤害响应(3个)、生长素响应(8个)、防卫和和逆境胁迫响应(8个)、低温响应(8个)、水杨酸响应(13个)、干旱响应(8个)(图4),表明油棕多胺合成酶基因参与植物生长、植物激素和环境刺激的应答。
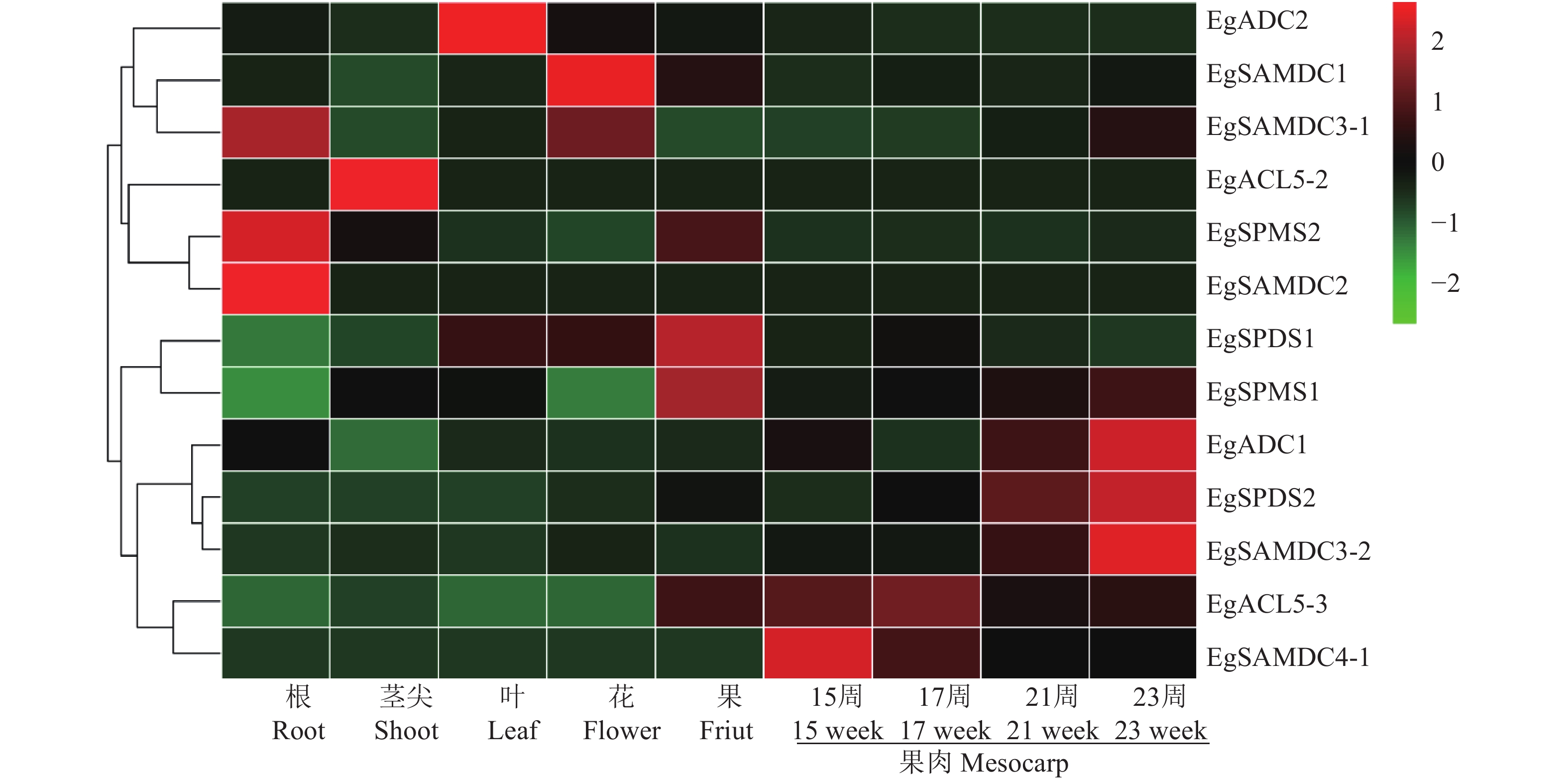
如图5所示,油棕多胺合成酶基因在不同组织中的表达模式差异较大,其中EgSAMDC2、EgSAMDC3-1和EgSPMS2在根中高表达,EgACL5-2在茎尖中高表达,EgADC2在叶中高表达,EgSAMDC1和EgSAMDC3-1在花中高表达,EgSPDS1和EgSPMS1在果中高表达,EgSAMDC4-1在花后15周的果肉中高表达,EgADC1、EgSPDS2和EgSAMDC3-2在花后23周的果肉中高表达。
实时荧光定量PCR结果显示,油棕多胺合成酶基因的表达受到低温和脱水胁迫的诱导表达。EgSPDS2、EgSPMS1、EgADC1、EgADC2、EgACL5-1、EgACL5-2、EgACL5-3、EgSAMDC3-1、EgSAMDC4-1和EgSAMDC4-2在低温处理12 h后达到峰值,然后表达量降低并处于稳定水平(图6)。EgSPMS2、EgSAMDC1和EgSAMDC3-2的表达量则是随着低温处理时间的延长逐渐降低(图6)。EgSPDS1、EgSPDS2、EgADC1、EgADC2、EgSAMDC4-1和Eg SAMDC4-2、EgACL5-1的表达量受脱水胁迫诱导,在脱水1 h达到峰值,然后逐渐降低(图7)。EgSPMS1、EgSPMS2、EgSAMDC3-1和EgSAMDC3-2的表达量随着脱水胁迫时间的延长逐渐降低(图7)。
3. 讨论与结论
随着基因组测序技术的发展和生物信息学研究的不断深入,大量植物完成了全基因组测序,这为植物基因家族的挖掘、鉴定和功能分析提供了有利条件,多胺合成酶基因也在多个物种中鉴定出来[7, 8, 25-27]。油棕作为世界上产油效率最高的油料作物,其多胺合成酶基因的研究尚未见报道,而油棕基因组测序工作的完成[20],为油棕多胺合成酶基因的研究提供了参考。本研究从油棕基因组中鉴定了15个编码多胺合成酶的基因,包括2个SPDS,2个SPMS,2个ADC,3个ACL5和6个SAMDC。油棕多胺合成酶的蛋白长度、分子量、等电点、蛋白不稳定指数、脂溶指数和总平均亲水性、基因结构等基本特性存在较大差异,且都含有特定的保守基序和保守结构域(表2、图2),与海棠、番茄和柑橘中的研究相似[21-27]。进化分析发现油棕多胺合成酶基因与同为单子叶植物的水稻、玉米以及棕榈科植物的椰枣亲缘关系较近(图3)。
油棕多胺合成酶在不同组织中表达量差异很大,表明多胺合成酶在油棕发育的不同阶段起重要的调控作用。EgSAMDC2、EgSAMDC3-1和EgSPMS2在根中的表达量显著高于其他组织(图5),表明多胺参与油棕根系发育的调控,与柑橘中的研究结果类似[21]。EgACL5-2在茎尖中的表达量显著高于其他组织(图5),而茎尖是油棕的顶端生长点,表明热精胺合成酶在油棕的分生组织发育中起重要作用。在棉花中的研究也发现ACL5参与茎的发育,超量表达能够显著提高转基因棉花的株高[28]。在樟子松中研究也发现ACL5参与维管组织发育的调控[24]。EgSPDS1、EgSPDS2、EgSPMS1、EgADC1、EgSAMDC3-2、EgSAMDC4-1在果实中表达量显著高于其他组织(图5),这表明多胺还参与油棕果实发育的调控。番茄中的研究也有类似的结果,精胺和亚精胺在果实发育前期大量积累,腐胺在果实发育后期大量积累,对应的多胺合成酶基因也呈现出相似的表达模式[29]。
油棕原产于非洲几内亚湾的热带河谷地带、性喜温暖、湿润的气候,低温和干旱胁迫会严重影响油棕生长和产量[30, 31]。多胺是植物体内一类低分子量脂肪族胺,广泛参与植物的生长发育和逆境胁迫应答反应,大量研究表明多胺合成酶参与植物对各种生物及非生物胁迫的响应[13, 14, 32],采用基因工程的手段超量表达多胺合成酶基因,能够增强转基因植物对胁迫的耐受性[15, 16, 18, 33]。在本研究中,EgSPDS1、EgSPDS2、EgSPMS1、EgADC1、EgADC2、EgACL5-2、EgACL5-3、EgSAMDC3-1、EgSAMDC4-1、EgSAMDC4-2和EgACL5-1受低温胁迫的诱导(图6),EgSPDS1、EgSPDS2、EgADC1、EgADC2、EgSAMDC4-1和EgSAMDC4-2、EgACL5-1的表达量受脱水胁迫诱导(图7),表明多胺合成酶基因参与油棕对低温和脱水胁迫的应答。同时,在多胺合成酶基因的启动子上也发现大量与脱落酸、茉莉酸甲酯、水杨酸、低温、干旱胁迫响应相关的顺式作用元件(图4),表明油棕的多胺合成酶基因的表达受植物激素和逆境胁迫的调控。本研究对油棕多胺合成酶基因的功能进行了初步的鉴定,在后续的研究中还需要利用转基因技术或基因编辑技术对这些基因的功能和作用机制进行验证。
-
表 1 油棕多胺合成酶基因qRT-PCR引物序列
Table 1 Sequence of qRT-PCR primer of polyamine synthase genes in oil palms
基因 Gene 正向引物 Forward primer 反向引物 Reverse primer 产物长度 Product length EgSPDS1 CCAGCAGGAGTCTTTACGCA CAGCCCCAAGTGTCAGCATA 122 EgSPDS1L TGTCTGCCGCCAAACCTTTA ATGAAACCAATCACCCCGCT 84 EgSPMS1 CCGATTGGTCCAGCTCAAGA AAGCCACATGCTCTCTGCTT 108 EgSPMS2 TGCGCCTGAAGGGATGTATG GGCCTTTCAACAAGTTCCCG 81 EgADCL GAAGGGCAAGTTCGGTCTGA AGCCGATGTGAAAGTGGAGG 107 EgADC GTGATGTTCGAGGGGCTCAA GCACCAGATAGGGCATGGAA 112 EgACL5-1 ACTTGAACGGCGAGTTCCTT AAGAACAACATGCCCTCCCA 135 EgACL5-2 CATGGGGATGGGTTATGGCA ACAAGGAACTCGCCGTTCAA 118 EgACL5-3 CTATGCTGACACTTGGGGCT CGGCAGATGCAAAGGTCTTG 137 EgACL5-4 CCAGCAGGAGTCTTTACGCA CAGCCCCAAGTGTCAGCATA 122 EgSAMDC2 TCAGCGGACGATCCACTCTA TGCTGAGTTGTGCTGGTTCT 96 EgSAMDC3-1 CAGCCTTCTCCCCATCGTAG GATGATGCCGGATCGCCTAT 110 EgSAMDC3-2 TGAAGCCATGGGTCTCAACC CCTTCTTCGACCATGTGCCT 143 EgSAMDC3-3 AGTACTCCCGTGGGACCTTT AAGCCTTACCACCCGAACTG 120 EgSAMDC4-1 GGAGATGACCGAGTTGACGG AATCGTCGAGTATCGGTCGC 121 EgSAMDC4-2 TTACTCGATGAACGGCCTCG CCGGAATACGTTCACGACCT 142 β-actin CTCAACCCCAAGGCGAAC GTAACACCATCTCCCGAGTCAA 100 表 2 油棕多胺合酶基因的理化性质分析
Table 2 Physicochemical properties of polyamine synthase genes in oil palms
基因名
Symbol基因登录号
Gene accession基因座登录号
Gene locus氨基酸长度
Number of amino acids分子量(kDa)
Molecular weight等电点
Theoretical pI蛋白不稳定指数
Instability index脂溶指数
Aliphatic index总平均亲水性
GravyEgSPDS1 XM_010943910.3 LOC105060266 346 37.92 4.80 48.15 85.29 −0.094 EgSPDS2 XM_010930791.3 LOC105050680 342 37.52 4.78 48.1 83.16 −0.137 EgSPMS1 XM_010915332.3 LOC105039242 389 42.70 5.31 45.35 81.93 −0.236 EgSPMS2 XM_019849278.2 LOC105040703 363 40.12 5.61 42.47 85.62 −0.131 EgACL5-1 XM_010934133.2 LOC105053105 332 37.74 5.36 30.61 82.20 −0.307 EgACL5-2 XM_010936715.1 LOC105055022 334 37.42 5.91 30.65 78.53 −0.315 EgACL5-3 XM_029263566.1 LOC105041819 318 36.00 5.10 29.26 83.71 −0.291 EgADC1 XM_010910687.3 LOC105035222 720 76.58 5.14 42.79 92.82 0.082 EgADC2 XM_010920850.3 LOC105043339 696 74.08 5.73 42.71 94.41 0.028 EgSAMDC1 XM_019846142.1 LOC105031981 356 38.93 5.47 50.07 85.51 −0.008 EgSAMDC2 XM_010906317.3 LOC105032002 423 46.43 6.05 46.75 80.21 −0.152 EgSAMDC3-1 XM_010930896.3 LOC105050758 402 43.89 4.96 48.73 80.27 −0.083 EgSAMDC3-2 XM_010915747.2 LOC105039560 382 41.89 5.01 44.15 86.05 0.000 EgSAMDC4-1 XM_010923664.3 LOC105045398 340 37.34 6.31 46.89 81.18 −0.082 EgSAMDC4-2 XM_010933625.3 LOC105052707 333 36.27 6.17 46.26 76.46 −0.158 -
[1] 雷新涛, 曹红星, 冯美利, 等. 热带木本生物质能源树种——油棕 [J]. 中国农业大学学报, 2012, 17(6):185−190. DOI: 10.11841/j.issn.1007-4333.2012.06.023 LEI X T, CAO H X, FENG M L, et al. Oil Palm: a tropical woody tree species as biomass energy [J]. Journal of China Agricultural University, 2012, 17(6): 185−190.(in Chinese) DOI: 10.11841/j.issn.1007-4333.2012.06.023
[2] MAHLIA T M I, ISMAIL N, HOSSAIN N, et al. Palm oil and its wastes as bioenergy sources: a comprehensive review [J]. Environmental Science and Pollution Research International, 2019, 26(15): 14849−14866. DOI: 10.1007/s11356-019-04563-x
[3] ZHOU L, YARRA R, JIN L, et al. Genome-wide identification and expression analysis of MYB gene family in oil palm (Elaeis guineensis Jacq.) under abiotic stress conditions [J]. Environmental and Experimental Botany, 2020, 180: 104245. DOI: 10.1016/j.envexpbot.2020.104245
[4] XIAO Y, ZHOU L, LEI X, et al. Genome-wide identification of WRKY genes and their expression profiles under different abiotic stresses in Elaeis guineensis [J]. PLoS One, 2017, 12(12): e189224.
[5] MICHAEL A J. Biosynthesis of polyamines and polyamine-containing molecules [J]. The Biochemical Journal, 2016, 473(15): 2315−2329. DOI: 10.1042/BCJ20160185
[6] 王广龙, 却枫, 陈伯清, 等. 胡萝卜S-腺苷甲硫氨酸脱羧酶SAMDC基因的克隆及其对非生物胁迫的响应 [J]. 植物生理学报, 2017, 53(3):413−421. WANG G L, QUE F, CHEN B Q, et al. Cloning of S-adenosylmethioine decarboxylase gene SAMDC from Daucus carota and its response to abiotic stresses [J]. Plant Physiology Communications, 2017, 53(3): 413−421.(in Chinese)
[7] 王保全, 张晓娜, 刘继红, 等. 桃树PpADC基因克隆及逆境胁迫表达分析 [J]. 西南师范大学学报(自然科学版), 2020, 45(7):34−41. WANG B Q, ZHANG X N, LIU J H, et al. Cloning and abiotic stress-induced expression of the arginine decarboxylase gene from Prunus persica [J]. Journal of Southwest China Normal University (Natural Science Edition), 2020, 45(7): 34−41.(in Chinese)
[8] 孙培培. 枳精氨酸脱羧酶基因PtADC抗逆功能解析及其调控因子分离与鉴定[D]. 武汉: 华中农业大学, 2014, . SUN P P. Functional charaterization of arginine decarboxylase gene PtADC from Poncirus trifoliata and indentification of the regulators[D]. Wuhan: Huazhong Agricultural University, 2014. (in Chinese).
[9] 杨硕知, 刘球, 吴际友, 等. 外源多胺对红椿S-腺苷甲硫氨酸脱羧酶基因表达的调节作用 [J]. 中南林业科技大学学报, 2019, 39(1):116−123. YANG S Z, LIU Q, WU J Y, et al. Gene cloning and expression analysis of TcSAMDC of Toona ciliata [J]. Journal of Central South University of Forestry & Technology, 2019, 39(1): 116−123.(in Chinese)
[10] 王显瑞, 刘莉莉, 柴晓娇, 等. 外源亚精胺对干旱胁迫下谷子幼苗光合作用及碳水化合物积累的影响 [J]. 作物杂志, 2015(5):100−106. WANG X R, LIU L L, CAI X J, et al. Effects of exogenous spermidine on photosynthesis and carbohydrate accumulation in foxtail millet (Setaria italica) seedlings under drought stress [J]. Crops, 2015(5): 100−106.(in Chinese)
[11] 李丹阳, 闫永庆, 殷媛, 等. 外源Spd和NO对盐胁迫下玉竹脯氨酸代谢途径的影响 [J]. 河南农业科学, 2018, 47(6):111−116. LI D Y, YAN Y Q, YING Y, et al. Effects of spd and NO on proline metabolic pathways of polygonatum odoratum (Mill.) druce under salt stress [J]. Journal of Henan Agricultural Sciences, 2018, 47(6): 111−116.(in Chinese)
[12] HANFREY C, SOMMER S, MAYER M J, et al. Arabidopsis polyamine biosynthesis: absence of ornithine decarboxylase and the mechanism of arginine decarboxylase activity [J]. The Plant Journal, 2001, 27(6): 551−560. DOI: 10.1046/j.1365-313X.2001.01100.x
[13] SHI H, CHAN Z. Improvement of plant abiotic stress tolerance through modulation of the polyamine pathway [J]. Journal of Integrative Plant Biology, 2014, 56(2): 114−121. DOI: 10.1111/jipb.12128
[14] LIU J H, WANG W, WU H, et al. Polyamines function in stress tolerance: from synthesis to regulation [J]. Frontiers in Plant Science, 2015, 6: 827.
[15] KOU S, CHEN L, TU W, et al. The arginine decarboxylase gene ADC1, associated to the putrescine pathway, plays an important role in potato cold-acclimated freezing tolerance as revealed by transcriptome and metabolome analyses [J]. The Plant Journal, 2018, 96(6): 1283−1298. DOI: 10.1111/tpj.14126
[16] HIDALGO-CASTELLANOS J, DUQUE A S, BURGUEÑO A, et al. Overexpression of the arginine decarboxylase gene promotes the symbiotic interaction Medicago truncatula-Sinorhizobium meliloti and induces the accumulation of proline and spermine in nodules under salt stress conditions [J]. Journal of Plant Physiology, 2019, 241: 153034. DOI: 10.1016/j.jplph.2019.153034
[17] LIU Z, LIU P, QI D, et al. Enhancement of cold and salt tolerance of Arabidopsis by transgenic expression of the S-adenosylmethionine decarboxylase gene from Leymus chinensis [J]. Journal of Plant Physiology, 2017, 211: 90−99. DOI: 10.1016/j.jplph.2016.12.014
[18] JI M, WANG K, WANG L, et al. Overexpression of a S-adenosylmethionine decarboxylase from sugar beet M14 increased Araidopsis salt tolerance [J]. International Journal of Molecular Sciences, 2019, 20(8).
[19] QIU Z, YAN S, XIA B, et al. The eggplant transcription factor MYB44 enhances resistance to bacterial wilt by activating the expression of spermidine synthase [J]. Journal of Experimental Botany, 2019, 70(19): 5343−5354. DOI: 10.1093/jxb/erz259
[20] SINGH R, ONGABDULLAH M, LOW E T L, et al. Oil palm genome sequence reveals divergence of interfertile species in old and new worlds [J]. Nature, 2013, 500(7462): 335. DOI: 10.1038/nature12309
[21] 吴昊. 柑橘转录因子CsCBF1和PtrNAC72在调控精氨酸脱羧酶基因表达及抗逆中的功能鉴定[D]. 武汉: 华中农业大学 2017. WU H. Functional characterization of Citrus sinensis CBF1 and NAC72 in regulation of arginine decarboxylase gene expression and stress tolerance[D]. Wuhan: Huazhong Agricultural University, 2017. (in Chinese).
[22] CHEN C, CHEN H, ZHANG Y, et al. TBtools: an integrative toolkit developed for interactive analyses of big biological data [J]. Molecular Plant, 2020, 13(8): 1194−1202. DOI: 10.1016/j.molp.2020.06.009
[23] EDGAR R C, BATZOGLOU S. Multiple sequence alignment [J]. Current Opinion in Structural Biology, 2006, 16(3): 368−373. DOI: 10.1016/j.sbi.2006.04.004
[24] VUOSKU J, MUILU-MÄKELÄ R, AVIA K, et al. Thermospermine synthase (ACL5) and diamine oxidase (DAO) expression is needed for zygotic embryogenesis and vascular development in Scots pine [J]. Frontiers in Plant Science, 2019, 10: 1600. DOI: 10.3389/fpls.2019.01600
[25] 刘荣, 黄海, 韩树全, 等. 芒果精氨酸脱羧酶基因MiADC的克隆及表达分析 [J]. 农业科学与技术(英文版), 2018, 19(2):9−16. LIU R, HUANG H, HAN S Q, et al. Cloning and expression analysis of arginine decarboxylase gene MiADC from mango [J]. Agricultural Science & Technology, 2018, 19(2): 9−16.(in Chinese)
[26] GONG X, DOU F, CHENG X, et al. Genome-wide identification of genes involved in polyamine biosynthesis and the role of exogenous polyamines in Malus hupehensis Rehd. under alkaline stress [J]. Gene, 2018, 669: 52−62. DOI: 10.1016/j.gene.2018.05.077
[27] LIU T, HUANG B, CHEN L, et al. Genome-wide identification, phylogenetic analysis, and expression profiling of polyamine synthesis gene family members in tomato [J]. Gene, 2018, 661: 1−10. DOI: 10.1016/j.gene.2018.03.084
[28] MO H, WANG X, ZHANG Y, et al. Cotton ACAULIS5 is involved in stem elongation and the plant defense response to Verticillium dahliae through thermospermine alteration [J]. Plant cell reports, 2015, 34(11): 1975−1985. DOI: 10.1007/s00299-015-1844-3
[29] TSANIKLIDIS G, KOTSIRAS A, TSAFOUROS A, et al. Spatial and temporal distribution of genes involved in polyamine metabolism during tomato fruit development [J]. Plant Physiology and Biochemistry, 2016, 100: 27−36. DOI: 10.1016/j.plaphy.2016.01.001
[30] WOITTIEZ L S, van WIJK M T, SLINGERLAND M, et al. Yield gaps in oil palm: A quantitative review of contributing factors [J]. European Journal of Agronomy, 2017, 83: 57−77. DOI: 10.1016/j.eja.2016.11.002
[31] CORLEY R H V, TINKER P B. The oil palm[M]. New Jersey: Wiley Blackwell, 2016: 324−327.
[32] ALCÁZAR R, MARCO F, CUEVAS J C, et al. Involvement of polyamines in plant response to abiotic stress [J]. Biotechnology Letters, 2006, 28(23): 1867−1876. DOI: 10.1007/s10529-006-9179-3
[33] KASUKABE Y, HE L, NADA K, et al. Overexpression of spermidine synthase enhances tolerance to multiple environmental stresses and up-regulates the expression of various stress-regulated genes in transgenic Arabidopsis thaliana [J]. Plant & Cell Physiology, 2004, 45(6): 712−722.
-
期刊类型引用(0)
其他类型引用(2)




 下载:
下载: