Effect of Magnesium on Endogenous Hormones, Medicinal Material Yield, and l-Borneol Accumulation of Growing Blumea balsamifera Plants
-
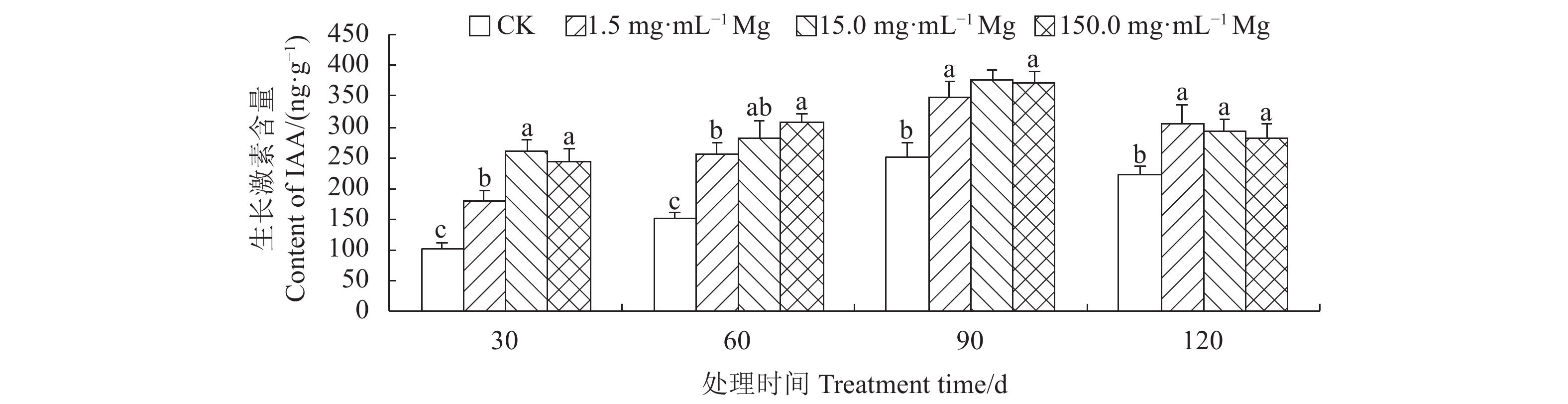
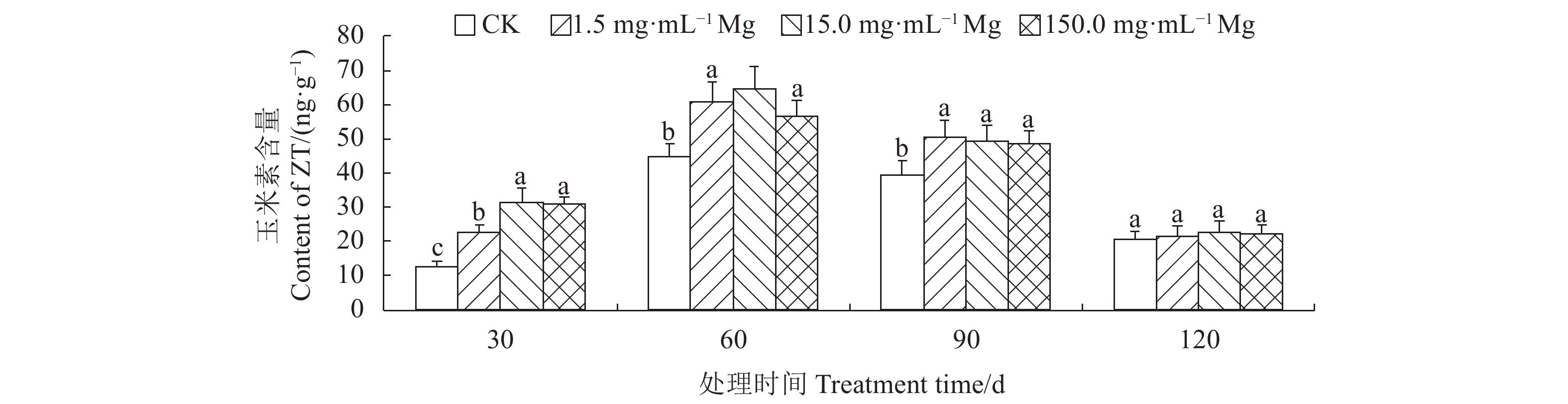
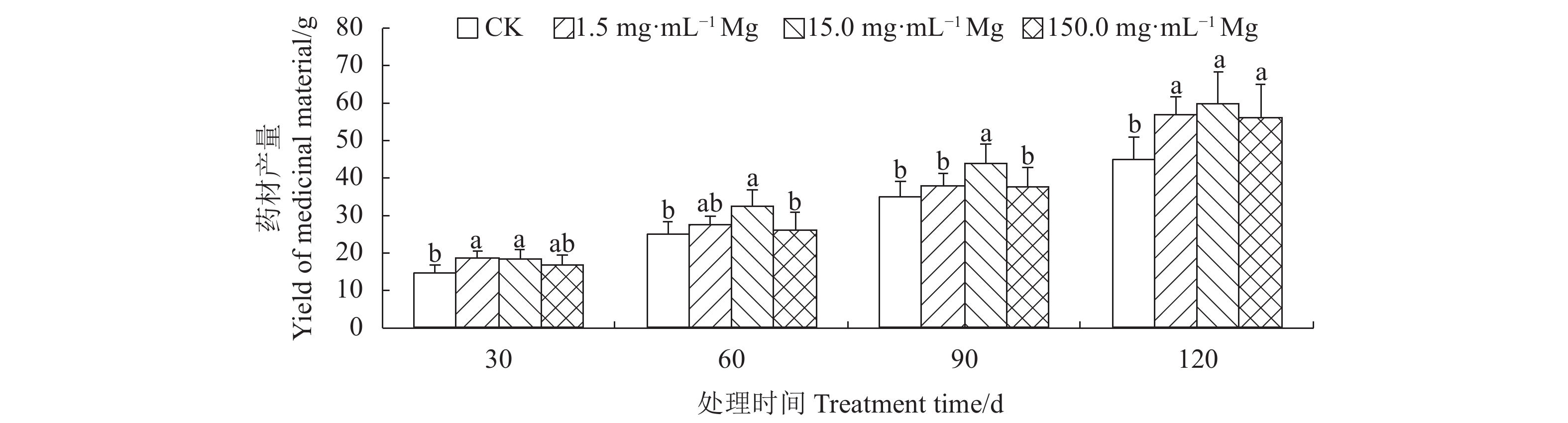
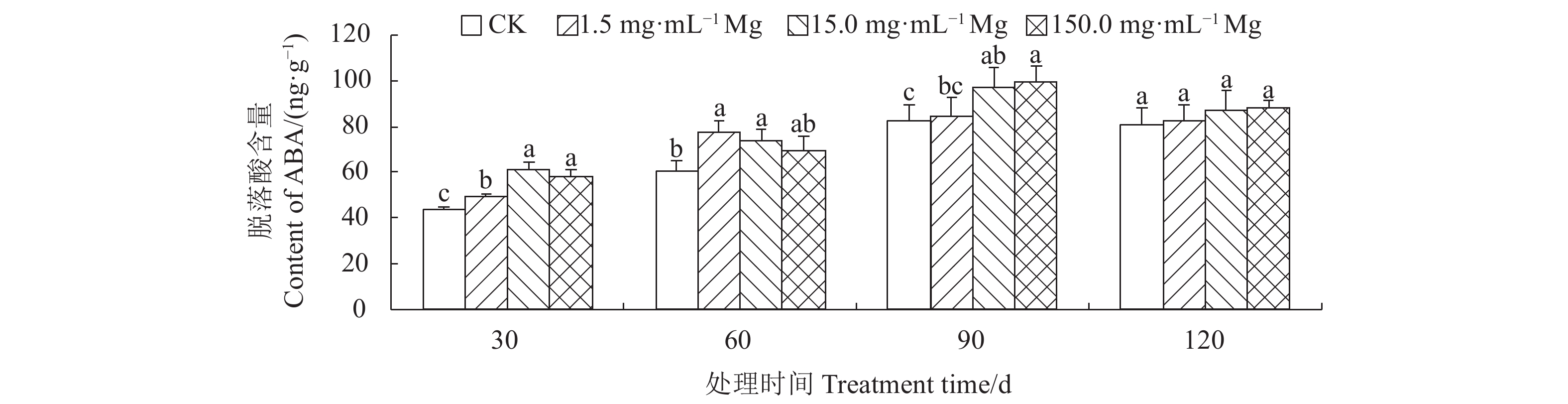
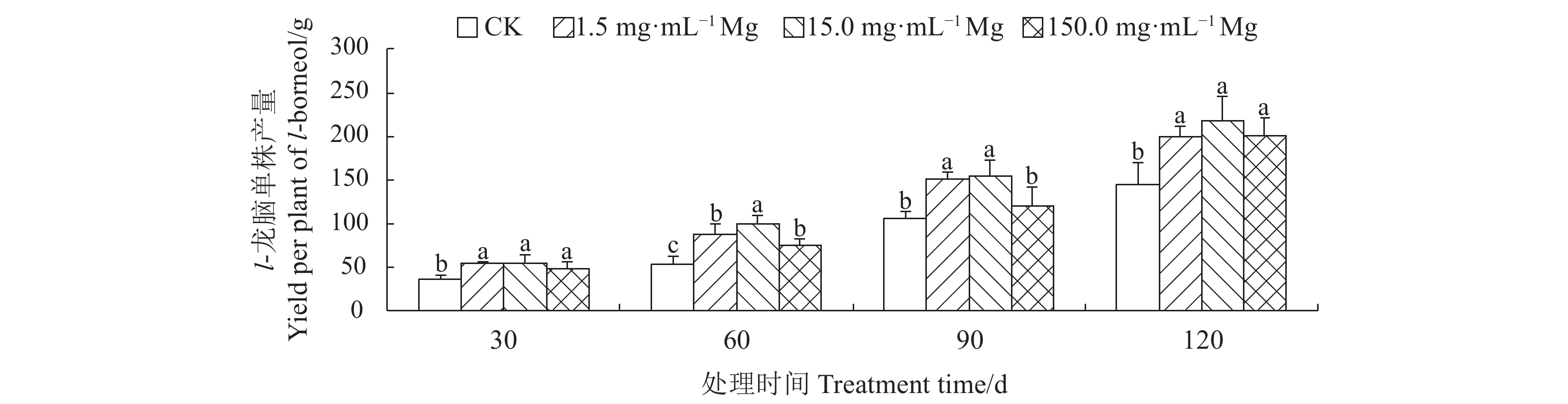
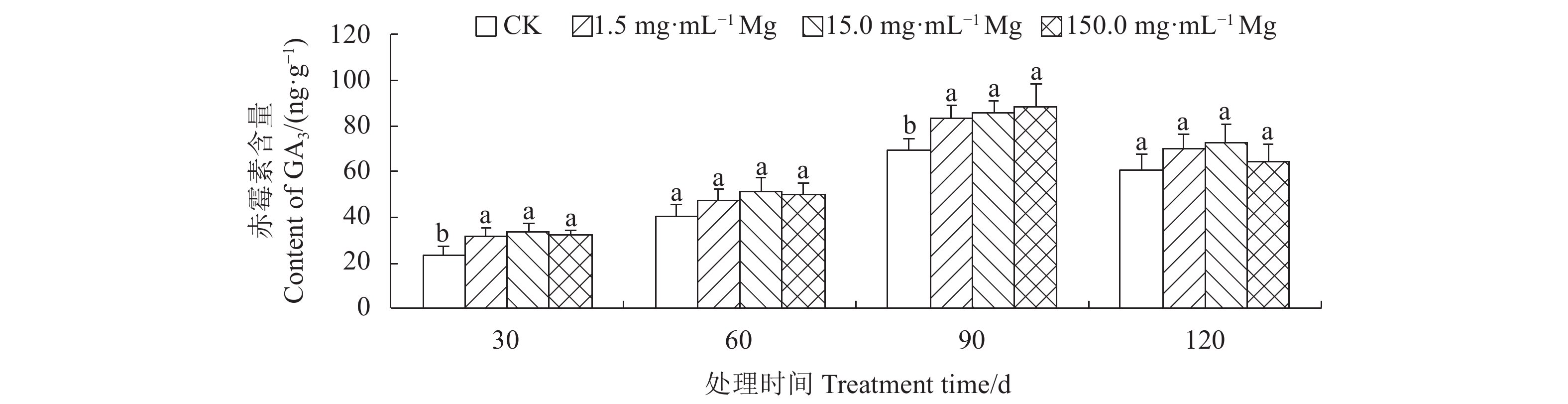
摘要:目的 明确施镁对生长期艾纳香内源激素、产量和有效成分l-龙脑积累的影响情况。方法 以1年生艾纳香种子苗为试验材料,用七水合硫酸镁提供镁元素,共设置4个镁水平,分别为0.0(CK)、1.5、15.0、150.0 mg·mL−1,采用酶联免疫吸附法分别测定艾纳香叶片赤霉素(GA3)、生长素(IAA)、脱落酸(ABA)、玉米素(ZR)等4种内源激素含量。使用电子秤测定艾纳香药材产量,利用GC测定生长期不同阶段艾纳香叶片有效成分l-龙脑百分含量,通过计算确定l-龙脑单株产量。结果 在处理第30 d、60 d和第90 d时,不同施镁水平显著增加了艾纳香中GA3、IAA、ABA和ZR等4种内源激素含量,显著增加了生长期艾纳香药材产量,其中1.5 、15.0 mg·mL−1镁水平影响效果最显著。在处理第60 d和第90 d时,不同施镁水平下艾纳香中l-龙脑百分含量差异极显著(P<0.01),在处理第60 d时,CK组l-龙脑百分含量最低,较1.5、15.0 和150.0 mg·mL−1镁处理组分别显著降低了34.37%、35.48%和25.00%。在处理第90 d时,1.5 mg·mL−1镁处理组l-龙脑百分含量显著高于其他处理组,在处理第30 d和第120 d时,各处理间差异不具有统计学意义(P>0.05)。在整个处理过程中,与CK相比,其他3个施镁水平均显著提高了l-龙脑单株产量(P<0.05)。结论 在处理第30 d,不同施镁水平显著促进了艾纳香内源激素、产量和l-龙脑百分含量和单株产量的积累。在处理第60 d、90 d和第120 d时,1.5、15.0 mg·mL−1镁素的作用效果较明显,对提高艾纳香药材产量和品质有显著的促进作用。Abstract:Objective Effects of magnesium (Mg) application on the endogenous hormones, medicinal material yield, and active componentl-borneol accumulation of Blumea balsamifera (L.) DC. during growth periods were studied.Method One-year-old seedlings of B. balsamifera were treated with MgSO4·7H2O to provide the plants with Mg at levels of 0.0, 1.5, 15.0 or 150.0 mg·mL−1. Spanning across the growth periods of the plants, contents of gibberellic acid (GA3), auxin (IAA), abscisic acid (ABA), and zeatin (ZR) in leaf were determined by the enzyme linked immunosorbent assay; yield of medicinal material on an electronic scale; and, contents of l-borneol by GC. The combined total l-borneol in life cycle was calculated as the per plant yield of the active component.Result On the 30th, 60th, and 90th day after the treatments, the 4 endogenous hormones and medicinal material yield of the treated plants significantly increased. The greatest effects were observed at the application levels of 1.5 or 15.0 mg·mL−1. Sampled on the 60th and 90th day, the l-borneol contents in leaf significantly differed by the varied treatments the plants received (P<0.01). The lowest content showed up in the leaves tested on the 60th day after the 0.0 mg·mL−1 control treatment, while 1.5 mg·mL−1 had 34.37%, 15.0 mg·mL−1 applications rendered 35.48%, and 150.0 mg·mL−1 resulted in 25.00% on l-borneol. At the end of 90d, the l-borneol in leaf under 1.5 mg·mL−1 treatment was significantly higher than those under other treatments, but no statistically significant differences found among the treatments on the 30th or the 120th day (P>0.05). All Mg applications significantly increased the per plant yields on l-borneol (P<0.05).Conclusion The Mg applications significantly boosted the endogenous hormones, medicinal material yield, and l-borneol production of the individual B. balsamifera plant in 30 d. On the 60th, 90th, and 120th day, the applications at the rates of 1.5 and 15.0 mg·mL−1 seemed more apparent in promoting the yield of the medicinal material and the content of l-borneol than either control or the highest dosage.
-
Keywords:
- magnesium /
- Blumea balsamifera /
- endogenous hormones /
- yield /
- l-borneol
-
-
-
[1] 国家中医药管理局《中华本草》编委会. 中华本草(1-10卷)[M]. 上海: 上海科技教育出版社, 1999. [2] 王丹, 蓝惠萍, 张影波, 等. 镁对两年生艾纳香生物量、抗氧化酶活性及有效成分积累的影响 [J]. 热带农业科学, 2018, 38(7):50−56. WANG D, LAN H P, ZHANG Y B, et al. The effect of magnesium on biomass, antioxidant enzyme activities, and active component accumulation of two years old Blumea balsamifera [J]. Chinese Journal of Tropical Agriculture, 2018, 38(7): 50−56.(in Chinese)
[3] 国家药典委员会. 中华人民共和国药典[M]. 北京: 中国医药科技出版社, 2015. [4] 李璞, 陈宇琼, 黄火强. 艾纳香化学成分与药理活性研究进展 [J]. 实用中医内科杂志, 2012, 26(13):3−4, 6. LI P, CHEN Y Q, HUANG H Q. Research progress on chemical constituents and biological activities of Blumea balsamifera (L.)/DC [J]. Journal of Practical Traditional Chinese Internal Medicine, 2012, 26(13): 3−4, 6.(in Chinese)
[5] 李小婷, 王丹, 庞玉新, 等. 左旋龙脑对UVB辐射后小鼠皮肤光损伤的影响 [J]. 中国现代中药, 2017, 19(4):518−524. LI X T, WANG D, PANG Y X, et al. eeffects of L-borneol on UVB-induced Photo-damages in skin of balb/c mice [J]. Modern Chinese Medicine, 2017, 19(4): 518−524.(in Chinese)
[6] SILVA D M D, DE SOUZA K R D, VILAS BOAS L V, et al. The effect of magnesium nutrition on the antioxidant response of coffee seedlings under heat stress [J]. Scientia Horticulturae, 2017, 224: 115−125. DOI: 10.1016/j.scienta.2017.04.029
[7] CANIZELLA B T, MOREIRA A, MORAES L A C, et al. Efficiency of magnesium use by common bean varieties regarding yield, physiological components, and nutritional status of plants [J]. Communications in Soil Science and Plant Analysis, 2015, 46(11): 1376−1390. DOI: 10.1080/00103624.2015.1043452
[8] 林敏霞, 张晓东, 邱美欢, 等. 植物镁素生理功能及镁素营养诊断和施用 [J]. 热带农业科学, 2016, 36(3):39−43. LIN M X, ZHANG X D, QIU M H, et al. Physiological function, nutrition diagnosis and application of the magnesium element on plant [J]. Chinese Journal of Tropical Agriculture, 2016, 36(3): 39−43.(in Chinese)
[9] 王丹, 范佐旺, 庞玉新, 等. 外源镁对冬季迟缓期的艾纳香生物量和有效成分含量的影响 [J]. 中国实验方剂学杂志, 2015, 21(4):75−79. WANG D, FAN Z W, PANG Y X, et al. Effect of exogenous magnesium on biomass and contents of effective constituents of Blumea balsamifera in slow growth period of winter [J]. China Journal of Experimental Traditional Medical Formulae, 2015, 21(4): 75−79.(in Chinese)
[10] 何元农, 丁映, 洗福荣, 等. 肥料种类对艾纳香生物产量和有效成分含量的影响 [J]. 贵州农业科学, 2005, 33(5):53−57. HE Y N, DING Y, XIAN F R, et al. Effects of different fertilizers on biological yield and active ingredient content of Blumea balsamifera [J]. Guizhou Agricultural Sciences, 2005, 33(5): 53−57.(in Chinese)
[11] 何元农, 柴立, 丁映, 等. 艾纳香产量和有效成分含量对氮素营养的反应 [J]. 贵州农业科学, 2006, 34(2):28−30. HE Y N, CHAI L, DING Y, et al. Effect of N nutrition on yield and active ingredient in Blumea balsamifera [J]. Guizhou Agricultural Sciences, 2006, 34(2): 28−30.(in Chinese)
[12] 王丹, 马青松, 范佐旺, 等. 赤霉素对冬季迟缓期艾纳香生长和有效成分含量的影响 [J]. 贵州农业科学, 2015, 43(11):153−156. WANG D, MA Q S, FAN Z W, et al. Effects of gibberellin on growth and contents of effective constituents in Blumea balsamifera in slow growth period of winter [J]. Guizhou Agricultural Sciences, 2015, 43(11): 153−156.(in Chinese)
[13] WANG D, MA Q S, FAN Z W, et al. The effect of calcium element on biomass and contents of effective constituents in BlumeaBalsamifera in slow growth period of winter [J]. Agricultural Science & Technology, 2016, 17(2): 358−361, 437.
[14] 蓝惠萍, 王丹, 杨全, 等. 氮磷钾配施对艾纳香产量及品质的影响 [J]. 贵州农业科学, 2017, 45(1):107−111. LAN H P, WANG D, YANG Q, et al. Effects of combined application of NPK fertilizers on yield and quality of Blumea balsamifera [J]. Guizhou Agricultural Sciences, 2017, 45(1): 107−111.(in Chinese)
[15] 王丹, 蓝惠萍, 张影波, 等. 镁素处理对艾纳香药材生物量和营养元素积累的影响 [J]. 热带作物学报, 2018, 39(11):2126−2131. WANG D, LAN H P, ZHANG Y B, et al. The effect of magnesium on biomass and accumulation of nutrient elements in Blumeabalsamifera [J]. Chinese Journal of Tropical Crops, 2018, 39(11): 2126−2131.(in Chinese)
[16] YANG J C, ZHANG J H, WANG Z Q, et al. Hormonal changes in the grains of rice subjected to water stress during grain filling [J]. Plant Physiology, 2001, 127(1): 315−323. DOI: 10.1104/pp.127.1.315
[17] 罗庆华, 李振宙, 林俊清, 等. 氮肥用量对苦荞内源激素、产量和品质的影响 [J]. 福建农业学报, 2019, 34(3):271−277. LUO Q H, LI Z Z, LIN J Q, et al. Effects of nitrogen application level on endogenous hormones, yield and quality of Tartary buckwheat [J]. Fujian Journal of Agricultural Sciences, 2019, 34(3): 271−277.(in Chinese)
[18] 敖兰吉亚, 季祥, 邵盈, 等. 山药块茎生长期5种内源激素含量变化对块茎膨大的影响 [J]. 福建农业学报, 2019, 34(3):284−292. AOLAN J Y, JI X, SHAO Y, et al. Correlation between endogenous hormones and Tuber growth of Dioscorea opposite thunb [J]. Fujian Journal of Agricultural Sciences, 2019, 34(3): 284−292.(in Chinese)
[19] QIU L H, CHEN R F, LUO H M, et al. Effects of exogenous GA_3 and DPC treatments on levels of endogenous hormone and expression of key gibberellin biosynthesis pathway genes during stem elongation in sugarcane [J]. Sugar Tech, 2019, 21(6): 936−948. DOI: 10.1007/s12355-019-00728-7
[20] 周开兵, 周晓超, 苏阳, 等. 叶面镁营养促进妃子笑荔枝果皮着色的生理成因 [J]. 热带作物学报, 2016, 37(9):1752−1758. ZHOU K B, ZHOU X C, SU Y, et al. The physiological causes of foliar Mg application enhance the fruit pigmentation of Litchi chinensis sonn. cv feizixiao [J]. Chinese Journal of Tropical Crops, 2016, 37(9): 1752−1758.(in Chinese)
[21] BATTAL P. Effects of some mineral nutrients on gibberellic acid levels in maize plants (ZEA MAYS L) [J]. Economic Botany, 2004, 58(2): 195−203. DOI: 10.1663/0013-0001(2004)058[0195:EOSMNO]2.0.CO;2
[22] REHMAN H U, ALHARBY H F, ALZAHRANI Y, et al. Magnesium and organic biostimulant integrative application induces physiological and biochemical changes in sunflower plants and its harvested progeny on sandy soil [J]. Plant Physiology and Biochemistry, 2018, 126: 97−105. DOI: 10.1016/j.plaphy.2018.02.031
[23] 靳晓琳, 马翠兰, 陈立松. 植物缺镁研究进展 [J]. 亚热带农业研究, 2012, 8(2):118−122. JIN X L, MA C L, CHEN L S. Research progress on magnesium deficiency in plants [J]. Subtropical Agriculture Research, 2012, 8(2): 118−122.(in Chinese)
[24] 吕世保, 王戈, 白羽祥, 等. 不同施镁量对烤烟K326生长和产质量的影响 [J]. 安徽农业科学, 2017, 45(26):41−43. LYU S B, WANG G, BAI Y X, et al. Effects of magnesium on growth and yield and quality of flue-cured tobacco K326 [J]. Journal of Anhui Agricultural Sciences, 2017, 45(26): 41−43.(in Chinese)
[25] 苏阳. 荔枝果皮钾、钙和镁含量变化与着色发育的关系[D]. 海南大学, 2015. SU Y. Study on the relationships between the changes in the contents of potassium and calcium and magnesium in Litchi pericarps and the pericarp, s coloring[D]. Haikou: Hainan Uuniversity, 2015. (in Chinese)
[26] 莫兴春, 李金玲, 赵致, 等. 钙镁元素缺乏对太子参产量和品质的影响 [J]. 中国现代中药, 2014, 16(7):547−550, 555. MO X C, LI J L, ZHAO Z, et al. Effects on the yield and quality of Pseudostellaria heterophylla by treatments of calcium and magnesium deficiency [J]. Modern Chinese Medicine, 2014, 16(7): 547−550, 555.(in Chinese)
[27] 李佳, 曹先梅, 刘立云, 等. 镁对槟榔幼苗光合特性和叶绿体超微结构的影响 [J]. 植物营养与肥料学报, 2019, 25(11):1949−1956. LI J, CAO X M, LIU L Y, et al. Effects of different magnesium nutrition levels on photosynthetic characteristics and chloroplast ultrastructure of areca palm seedlings [J]. Journal of Plant Nutrition and Fertilizers, 2019, 25(11): 1949−1956.(in Chinese)
[28] 袁剑龙, 杨丽丽, 王玉萍, 等. 低镁胁迫对马铃薯试管苗碳水化合物积累和分配的影响 [J]. 干旱地区农业研究, 2018, 36(4):200−206. YUAN J L, YANG L L, WANG Y P, et al. Effect of the accumulation and distribution of carbohydrates of potato seedling under low magnesium stress [J]. Agricultural Research in the Arid Areas, 2018, 36(4): 200−206.(in Chinese)
[29] 白琳, 官玲亮, 陈松笔, 等. 茉莉酸甲酯对艾纳香活性成分、抗氧化酶活力以及内源激素含量的影响 [J]. 中草药, 2019, 50(1):203−209. BAI L, GUAN L L, CHEN S B, et al. Effects of methyle jasmonate on active components, anti-oxidant enzyme activities and endogenous hormone content in Blumea balsamifera [J]. Chinese Traditional and Herbal Drugs, 2019, 50(1): 203−209.(in Chinese)
[30] KARP F, ZHAO Y X, SANTHAMMA B, et al. Inhibition of monoterpene cyclases by inert analogues of geranyl diphosphate and linalyl diphosphate [J]. Archives of Biochemistry and Biophysics, 2007, 468(1): 140−146. DOI: 10.1016/j.abb.2007.09.008
[31] HYATT D C, YOUN B, ZHAO Y, et al. Structure of limonene synthase, a simple model for terpenoid cyclase catalysis [J]. PNAS, 2007, 104(13): 5360−5365. DOI: 10.1073/pnas.0700915104
[32] PETERS R J, CROTEAU R B. Alternative termination chemistries utilized by monoterpene cyclases: Chimeric analysis of bornyl diphosphate, 1,8-cineole, and sabinene synthases [J]. Archives of Biochemistry and Biophysics, 2003, 417(2): 203−211. DOI: 10.1016/S0003-9861(03)00347-3
[33] WHITTINGTON D A, WISE M L, URBANSKY M, et al. Nonlinear partial differential equations and applications: Bornyl diphosphate synthase: Structure and strategy for carbocation manipulation by a terpenoid cyclase [J]. PNAS, 2002, 99(24): 15375−15380. DOI: 10.1073/pnas.232591099
[34] 徐应文. 鱼腥草单萜次生代谢研究[D]. 四川农业大学, 2012. XU Y W. Monoterpene secondary metabolites in Houttuyniacordata Thunb.[D]. Yaan: Sichuan Agricultural University, 2012. (in Chinese)
-
期刊类型引用(5)
1. 侯赛赛,仝姗姗,王鹏企,谢冰雪,张瑞芳,王鑫鑫. 生物炭和秸秆对不同作物生长性状和养分吸收的影响. 中国农业科技导报(中英文). 2025(04): 179-191 .  百度学术
百度学术
2. 吕海龙,魏镛频,郭子军,谢淑琴,张旦,曹力强,吴丹,王姣敏. 生物炭对芹菜幼苗生长及基质理化性状的影响. 中国果菜. 2024(01): 54-57+84 .  百度学术
百度学术
3. 兰子叶,桂阳,朱国胜,李彪,刘宏宇,黄万兵,杨通静,龚光禄. 不同土壤改良措施对连作红托竹荪菌丝生长的影响. 食药用菌. 2024(05): 351-358 .  百度学术
百度学术
4. 杨如意,郭应成,况帅,徐艳丽,宋文静. 不同类型生物质炭对保山植烟土壤理化性质及酶活性的影响. 山东农业科学. 2024(11): 92-99 .  百度学术
百度学术
5. 张晓波,闫烨. 生物炭施用对菊花连作土壤性质及其生长的影响. 江苏农业科学. 2024(22): 162-167 .  百度学术
百度学术
其他类型引用(3)




 下载:
下载: