Identification and Analysis of Expansins in the Transcriptome of Sanyueli Plum and Its Red-flesh Mutant
-
摘要:目的 Expansin是广泛存在于植物中的一类细胞壁蛋白,通过调节细胞壁柔韧性在植物生长发育过程中发挥作用。本研究旨在分析Expansin基因家族特征及其在果实成熟过程中的表达模式,并比较Expansin基因在三月李及其红肉突变体之间的差异表达。方法 基于三月李及其红肉突变体果实成熟过程的转录组数据,采用生物信息学分析方法进行Expansin家族基因鉴定与分析。结果 鉴定出33个李Expansin基因家族成员,编码蛋白长度在176~460 aa,分子量在19.21~51.33 kD,等电点4.62~9.83,大部分为位于细胞外的稳定亲水蛋白。系统进化树分析表明李Expansin家族成员可分为4个组:22个EXPA、6个EXPB、1个EXPLA和4个EXPLB。所有李Expansin蛋白质均具有保守的DPBB_1和Pollen_allerg_1结构域。保守基序分析表明,同一组Expansin成员具有相似的基序组成。9个Expansin基因在三月李及其红肉突变体果实成熟过程中差异表达。结论 Expansin在三月李及其红肉突变体果实成熟过程中的表达模式存在显著差异。本研究结果可为解析李Expansin家族基因在果实成熟过程中的功能奠定基础。
-
关键词:
- 李 /
- 转录组 /
- expansin家族 /
- 生物信息学分析 /
- 表达分析
Abstract:Objective Characteristics and expressions of Expansins, the widely existing gene family associated with plant cell wall, were studied during the fruit ripening stage to decipher the genetic functions relating to ripening of the plum fruits.Method Transcriptomes of fruits of Sanyueli ( Prunus salicina Lindl.) and its red-flesh mutant were used to identify Expansin genes as well as for a bioinformatic and expression comparison of identified genes.Result Thirty-three Expansins, with individual protein containing 176 to 460 amino acids, a molecular weight ranging from 19.21kD to 51.33kD, and an isoelectric point varying from 4.62 to 9.83, were identified from the fruit transcriptome data. Most of them were stable hydrophilic proteins located in the extracellular space. Phylogenetic analysis revealed that plum Expansin family included 22 EXPAs, 6 EXPBs, 1 EXPLA, and 4 EXPLBs. All of the proteins had DPBB_1 and Pollen_allerg_1 domains, and, within a same classification, they shared same conserved motif composition. Nine Expansins were differentially expressed in Sanyueli and the mutant during fruit ripening. The expressions of EVM0015785, EVM0016777, EVM0010710, EVM0022202, EVM0002390, and EVM0024996 significantly differed between Sanyueli and the red-flesh mutant.Conclusion The information obtained was to be used for further study on the functions of the Expansin family during ripening of plum fruits.-
Keywords:
- Plum /
- transcriptome /
- expansin family /
- bioinformatics analysis /
- expression analysis
-
0. 引言
【研究意义】李(Prunus salicina Lindl.)是我国重要的传统果树。李果实美丽诱人,风味独特,且具有很高的营养价值,深受消费者喜爱。成熟的李果实易软化,难以贮藏运输,不利于优质鲜食李产业的发展。细胞壁结构变化是导致成熟果实软化的重要原因[1]。Expansin作为调节细胞壁的松弛和伸展的一类重要蛋白质,在柿(Diospyros kaki L.‘Fuping Jianshi’)[2]、芒果(Mangifera indica cv. Dashehari)[3]、番荔枝(Annona cherimola Mill)[4]、番茄(Solanum lycopersicum)[5-7]、山番木瓜(Vasconcellea pubescens)[8]和草莓(Fragaria × ananassa)[9]果实成熟和软化中发挥着重要的作用。因此,系统地鉴定和分析李Expansin家族基因对进一步研究Expansin家族基因在李果实成熟过程中的作用具有重要的意义。【前人研究进展】Expansin是一类广泛存在于植物中的细胞壁酶,它通过破坏细胞壁多糖之间的非共价键参与细胞壁松弛和伸展调节[10- 11]。Expansin由一个多基因家族编码,该家族由EXPA(α-expansin)、EXPB(β-expansin)、EXPLA(expansin-like A)和EXPLB(expansin-like B)等4个亚家族组成[12]。典型的Expansin蛋白质在N端有一个长度为20~30个氨基酸残基的信号肽和具有多个保守的半胱氨酸残基和HFD基序的domain1,C端含有一个与第二组花粉过敏原蛋白同源的多糖结合结构域[13-15]。大量研究表明Expansin与植物细胞生长[16]、叶片生长发育[17-18]、根系发育[19-20]、果实发育和质地变化[21-26]等诸多生物学过程密切相关。此外,Expansin还与脱落酸、赤霉素、生长素、油菜素内酯和乙烯等植物激素引起的细胞膨大和细胞壁结构改变有关[27-30]。目前,科研人员已对多种植物的Expansin基因家族进行鉴定与分析,如拟南芥(Arabidopsis thaliana)[31]、烟草(Nicotiana tabacum)[32]、水稻(Oryza sativa)[33]、小麦(Triticum aestivum)[14, 34]、番茄(Solanum lycopersicum)[35]、杨树(Populus trichocarpa)[36]、葡萄(Vitis vinifera)[37]、苹果(Malus × domestica)[38]、桃(Prunus persica)[39]和枣(Ziziphus jujuba Mill.)[13]。【本研究切入点】Expansin在果实发育和成熟中的重要作用已有相关研究,但李Expansin基因家族的鉴定和分析尚未见报道。【拟解决的关键问题】本研究以三月李,以及课题组在前期研究中通过对三月李进行辐射诱变获得的一个果实性状发生显著变化的迟熟突变体[40]为材料,采用生物信息学方法从三月李及其红肉突变体果实成熟过程的转录组数据中鉴定李Expansin家族基因,并对其蛋白质特征、系统进化关系及其在三月李和迟熟突变体果实成熟过程中的表达模式进行比较分析,为研究李Expansin家族基因在果实成熟过程中的功能奠定基础。
1. 材料与方法
1.1 数据来源及Expansin家族基因的鉴定
本研究所使用的数据为本课题组获得的三月李(盛花后95、105和115 d)及其红肉突变体(盛花后95、105、115和125 d)的转录组数据[41]。拟南芥(Arabidopsis thaliana)、水稻(Oryza sativa)和毛果杨(Populus trichocarpa)的Expansin蛋白质序列从EXPANSIN CENTRAL(http://www.personal.psu.edu/fsl/ExpCentral/)下载。以拟南芥、水稻和毛果杨Expansin蛋白质序列为查询序列,采用TBtools[42]的BLAST工具从三月李及其红肉突变体蛋白质数据库中检索Expansin家族成员。同时,从Pfam数据库(http://pfam.xfam.org/)下载DPBB_1和Pollen_allerg_1结构域的HMM模型PF03330和PF01357,并采用HMMER3.0鉴定含有保守结构域DPBB_1和Pollen_allerg_1的蛋白质。
1.2 Expansin家族分析
Expansin家族蛋白质生物信息学分析、保守基序分析与多重序列比对、系统进化树的构建、基因的差异表达模式分析参考文献[40]进行。
2. 结果与分析
2.1 三月李及其红肉突变体Expansin基因家族的鉴定及蛋白质特性分析
为了鉴定三月李及其红肉突变体的Expansin家族成员,以拟南芥(35个)、水稻(58个)和毛果杨(36个)Expansin家族成员的蛋白质序列为查询序列,通过BLAST分析从三月李及其红肉突变体蛋白质数据库中检索Expansin蛋白质,初步鉴定出35个Expansin蛋白质(E-value<1e−5)。随后,采用隐马尔可夫模型进行Expansin蛋白质鉴定,去除不含保守结构域DPBB_1和Pollen_allerg_1的蛋白质。最终得到33个Expansin家族蛋白质(表1)。除了EVM0014217,其余Expansin基因均包含完整的编码序列。李Expansin蛋白质序列的长度在176(EVM0014217)~460 aa(EVM0020356),预测蛋白的相对分子量在19.21~51.33 kD,等电点介于4.62~9.83。蛋白质不稳定系数分析结果表明,除了EVM0026183、EVM0000548、EVM0026545、EVM0018557、EVM0001651和EVM0020356,其余李Expansin蛋白质的不稳定系数均小于40,表明大部分李Expansin蛋白质均为稳定蛋白;平均亲水系数均为负数,表明33个蛋白质均为亲水蛋白质。亚细胞定位预测结果表明,除了EVM0020356可分布于质膜与细胞外,其余李Expansin蛋白质均位于细胞外。
表 1 三月李及其红肉突变体Expansin蛋白质的理化性质和亚细胞定位Table 1. Physicochemical properties and subcellular localization of Expansins in Sanyueli plum and its red-flesh mutant序列编号
Sequnce ID蛋白质长度
Protein length/aa分子量
Molecular weight/kD等电点
pI不稳定系数
Instability index脂肪系数
Aliphatic index平均亲水系数
Grand average of hydropathicity细胞定位
Cell locationEVM0011615 252 26.78 9.36 35.7 64.29 −0.100 Extracellular EVM0015785 252 26.74 6.92 31.32 66.23 −0.108 Extracellular EVM0004461 254 27.27 8.43 30.26 63.43 −0.194 Extracellular EVM0027977 254 27.27 8.43 30.26 63.43 −0.194 Extracellular EVM0009515 257 27.47 8.79 35.46 74.47 −0.039 Extracellular EVM0008468 257 27.50 8.93 34.94 74.47 −0.042 Extracellular EVM0009923 257 27.74 9.14 32.88 67.24 −0.095 Extracellular EVM0010710 258 27.94 8.59 27.91 64.69 −0.066 Extracellular EVM0025415 259 28.39 8.89 22.2 73.9 −0.118 Extracellular EVM0019517 259 28.39 8.89 22.2 73.9 −0.118 Extracellular EVM0022202 259 27.84 9.41 33.23 71.2 −0.010 Extracellular EVM0002390 260 27.99 9.47 34.71 68.65 −0.007 Extracellular EVM0017357 260 28.74 8.07 17.38 66.81 −0.226 Extracellular EVM0018627 261 29.24 9.35 33.36 69.12 −0.338 Extracellular EVM0016646 263 28.99 9.22 35.71 65.32 0.006 Extracellular EVM0026183 265 29.18 9.83 45.17 73.21 −0.057 Extracellular EVM0016777 266 28.74 8.4 33.52 86.54 0.065 Extracellular EVM0010881 282 31.12 9.09 29.38 62.27 −0.388 Extracellular EVM0028371 291 31.89 5.77 39.08 72.03 −0.337 Extracellular EVM0018557 353 37.15 9.24 45.03 76.26 −0.001 Extracellular EVM0001651 367 40.65 9.53 48.28 83.41 −0.018 Extracellular EVM0020356 460 51.33 8.67 46.31 75.07 −0.258 Plasma membrane, Extracellular EVM0014217 176 19.21 4.98 36.08 77.1 −0.137 Extracellular EVM0016078 266 28.47 8.95 28.91 82.44 −0.032 Extracellular EVM0000548 272 28.58 4.62 43.47 76.4 −0.027 Extracellular EVM0006851 280 30.10 5.94 36.92 70.07 −0.168 Extracellular EVM0022596 282 30.33 7.52 35.18 72.02 −0.142 Extracellular EVM0026545 296 31.92 8.62 41.79 67.64 −0.269 Extracellular EVM0024996 260 28.16 8.73 37.26 85.62 0.035 Extracellular EVM0026062 252 28.00 6.87 30.3 69.33 −0.309 Extracellular EVM0028340 252 28.00 6.87 30.3 69.33 −0.309 Extracellular EVM0003805 252 28.00 6.87 30.3 69.33 −0.309 Extracellular EVM0013160 255 27.74 4.78 38.38 75.33 −0.170 Extracellular 2.2 三月李及其红肉突变体Expansin家族蛋白质进化分析
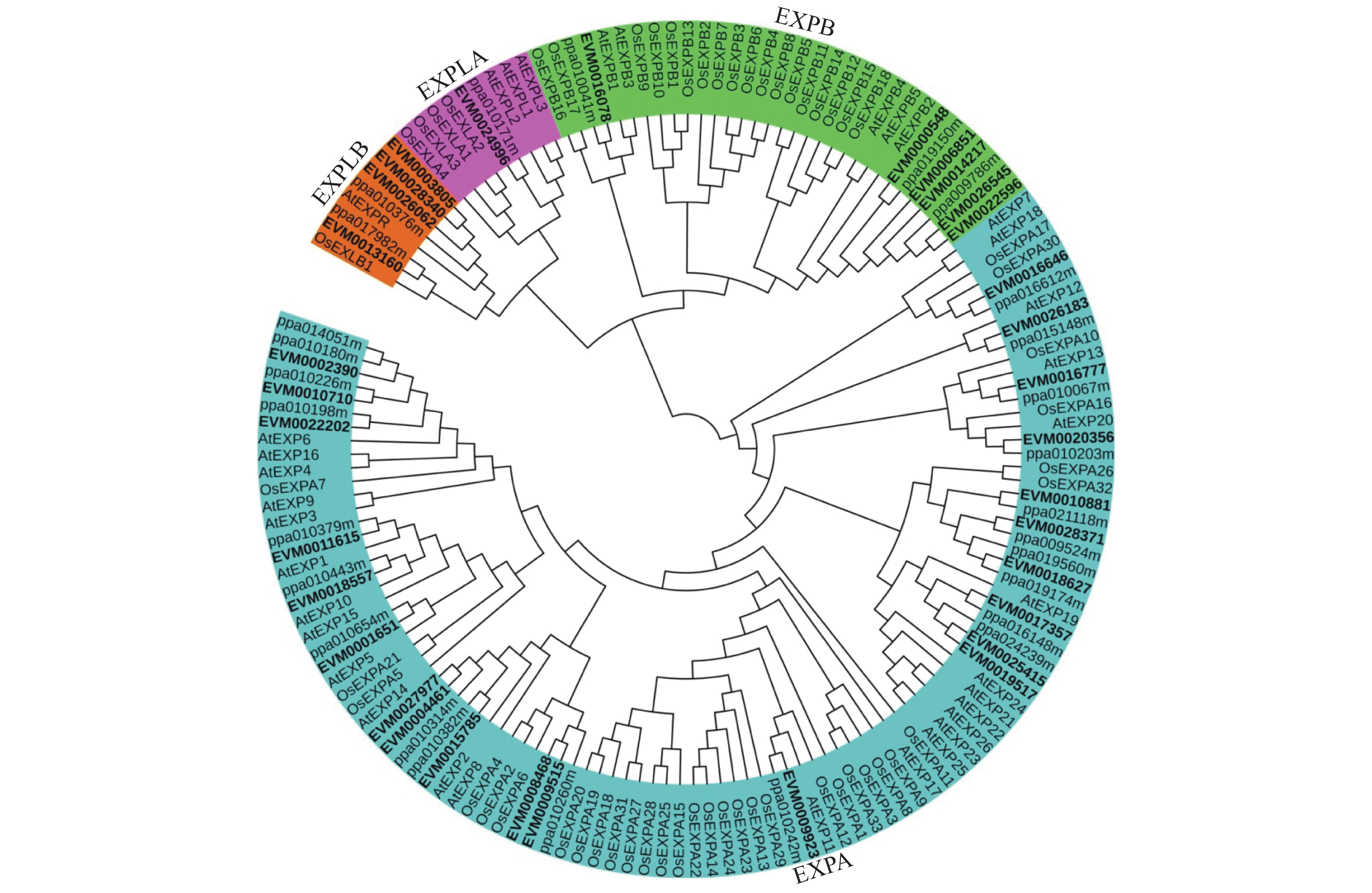
为了解三月李及其红肉突变体Expansin家族蛋白质与桃、拟南芥和水稻的进化关系,采用MEGAX软件构建了拟南芥、水稻、桃和李Expansin家族蛋白质的系统进化树。如图1所示,拟南芥、水稻、桃和李Expansin家族蛋白质可分为4组,分别为EXPA、EXPB、EXPLA和EXPLB。从图1可以看出,每个桃Expansin蛋白质都有与其对应的同源李Expansin蛋白质。EXPA的李Expansin家族蛋白质数量最多,共有22个。其次为EXPB,共含有6个李Expansin家族蛋白质;仅有1个李Expansin蛋白质(EVM0024996)属于EXPLA组。EVM0026062、EVM0028340、EVM0003805和EVM0013160属于EXPLB组。
2.3 三月李及其红肉突变体Expansin家族蛋白质保守结构域分析
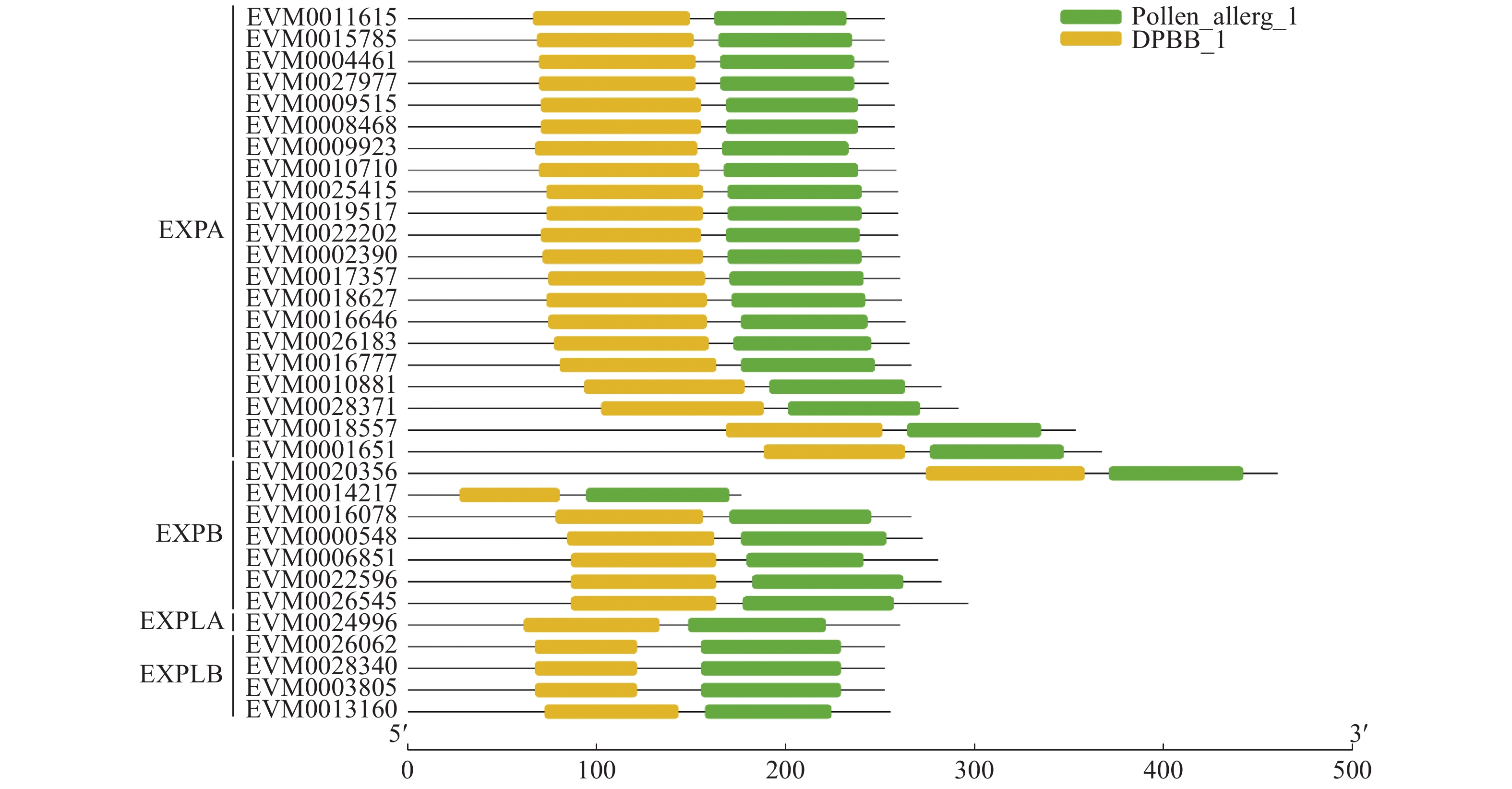
对李Expansin蛋白质的保守结构域进行分析,发现33个李Expansin蛋白质均含有DPBB_1和Pollen_allerg_1结构域(图2)。为了进一步了解李Expansin蛋白质的保守结构域,利用在线软件MEME对李Expansin家族蛋白质进行分析,结果表明李Expansin家族蛋白质共含有15个保守基序(图3)。Expansin蛋白质含有的基序数量从5~10个不等。其中,EVM0011615、EVM0028371、EVM0001651、EVM0006851、EVM0022596和EVM0026545含有的基序数量最多(10个),EVM0014217含有的基序数量最少(5个)。所有李Expansin家族蛋白质均含有基序3和5(图3)。除了EVM0014217之外,其他李Expansin家族蛋白质均含有基序1和7(图3)。基序2是EXPA成员特有的基序,基序10为EXPB、EXPLA和EXPLB成员特有的基序,基序12为EXPLA和EXPLB成员特有的基序(图3)。含有基序14的Expansin蛋白质数量最少,仅3个EXPLB成员(EVM0026062、EVM0028340和EVM0003805)含有该基序,EXPA、EXPB和EXPLA均不含该基序(图3)。
![]() 图 3 李Expansin家族蛋白质保守基序及结构域序列Logo注:A:李Expansin家族蛋白质保守元件分布;B:李Expansin家族蛋白质保守元件序列特征。Figure 3. Conserved motifs and domain sequence logo of Expansin familyNote:A:Distribution of the identified motifs in plum Expansin family proteins. B:The sequence constitution of identified motifs in plum Expansin family proteins.
图 3 李Expansin家族蛋白质保守基序及结构域序列Logo注:A:李Expansin家族蛋白质保守元件分布;B:李Expansin家族蛋白质保守元件序列特征。Figure 3. Conserved motifs and domain sequence logo of Expansin familyNote:A:Distribution of the identified motifs in plum Expansin family proteins. B:The sequence constitution of identified motifs in plum Expansin family proteins.为了分析家族蛋白质保守结构域的特征,采用DNAMAN7对Expansin家族蛋白质进行多重序列比对分析。结果表明大多数Expansin蛋白质由3个部分(信号肽、Domain1和Domain3)组成。大部分EXPA成员(EVM0016777除外)和EXPB成员(EVM0016078除外)在Domain1部分都含有一个保守的HFD基序,而EXPLA和EXPLB在对应位置的特征序列则分别为DFV和DFI(图4)。HFD基序两侧存在两个插入片段,分别为EXPA的α-Insertion和EXPB、EXPLA和EXPLB特有的插入片段(图4)。李Expansin家族蛋白质含有多个保守的半胱氨酸和色氨酸(图4)。
2.4 Expansin家族基因在三月李及其红肉突变体果实成熟过程中的表达模式分析
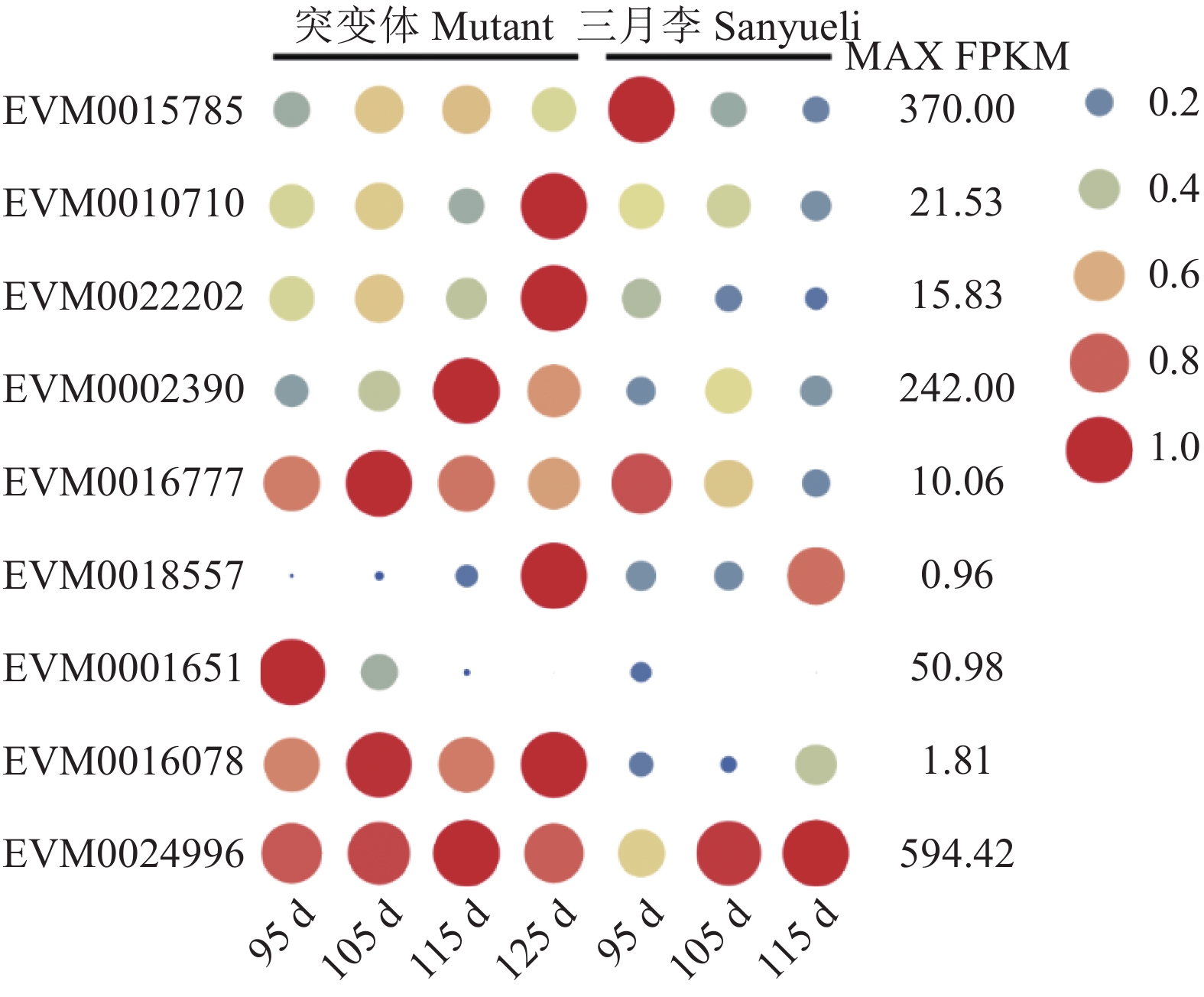
对33个Expansin家族基因的表达模式进行分析,发现三月李及其红肉突变体果实成熟过程中仅有9个Expansin基因存在差异表达,包括7个EXPA(EVM0015785、EVM0010710、EVM0022202、EVM0002390、EVM0016777、EVM0018557和EVM0001651)、1个EXPB(EVM0016078)和1个EXPLA(EVM0024996)(图5)。三月李果肉中EVM0015785和EVM0016777的表达量随果实成熟逐渐降低,但其表达量在红肉突变体果实成熟过程中无显著变化。EVM0010710和EVM0022202在成熟三月李果肉中的表达量也显著降低,而在成熟红肉突变体果肉中的表达量明显升高。红肉突变体果肉中EVM0002390的表达量随果实成熟而升高,但其表达量仅在花后105 d的三月李果肉中显著升高,花后115 d的三月李果肉中的表达量又下降至与花后95 d相当的水平。成熟三月李果肉中EVM0024996的表达量显著升高,而在红肉突变体果实成熟过程中无显著变化。
![]() 图 5 Expansin家族基因在三月李及其红肉突变体果实成熟过程中的表达模式注:上图基于三月李及其红肉突变体果实成熟过程的转录组数据计算得出。所有基因的FPKM值采用每个基因的最大FPKM值进行均一化处理。基因的表达水平由不同大小和颜色的实心圆表示,实心圆越大,表达量越高。右侧的数值为每个基因的最大FPKM值。Figure 5. Expression pattern of Expansins in Sanyueli plum and its red-flesh mutant during fruit ripeningNote:Based on the transcriptome data of Sanyueli and the red-fleshed mutant fruits during ripening. All FPKM values of all genes were normalized with maximum FPKM values of each gene. The expression level of genes was indicated using filled circle with different size and colour. The larger the circle, the higher the expression. The values on the right indicates the highest FPKM value of each gene.
图 5 Expansin家族基因在三月李及其红肉突变体果实成熟过程中的表达模式注:上图基于三月李及其红肉突变体果实成熟过程的转录组数据计算得出。所有基因的FPKM值采用每个基因的最大FPKM值进行均一化处理。基因的表达水平由不同大小和颜色的实心圆表示,实心圆越大,表达量越高。右侧的数值为每个基因的最大FPKM值。Figure 5. Expression pattern of Expansins in Sanyueli plum and its red-flesh mutant during fruit ripeningNote:Based on the transcriptome data of Sanyueli and the red-fleshed mutant fruits during ripening. All FPKM values of all genes were normalized with maximum FPKM values of each gene. The expression level of genes was indicated using filled circle with different size and colour. The larger the circle, the higher the expression. The values on the right indicates the highest FPKM value of each gene.3. 讨论与结论
Expansin不仅是在植物生长发育诸多方面都发挥着重要生物学功能的细胞壁蛋白[17, 18, 20, 22-26],还是研究植物发育进化的重要候选基因[34, 37, 43]。因此,Expansin获得了广泛的关注。本研究从三月李及其红肉突变体果实成熟过程的转录组中鉴定出33个Expansin基因,少于玉米(Zea myas, 93个)[44]、小麦(Triticum aestivum, 87个)[34]、水稻(Oryza sativa, 58个)[33]、烟草(Nicotiana tabacum, 52个)[32]、番茄(Solanum lycopersicum, 43个)[38]、苹果(Malus × domestica, 41个)[38]、杨树(Populus trichocarpa, 36个)[36]、黄瓜(Cucumis sativus, 35个)[45]和模式植物拟南芥(Arabidopsis thaliana, 35个)[31],但多于枣(Ziziphus jujuba Mill., 30个)[13]、葡萄(Vitis vinifera, 29个)[37]及其近缘物种桃(Prunus persica, 27个)[39]。李的近缘物种桃的27个Expansin蛋白质在李转录组中均能找到对应的同源蛋白质,可见本研究鉴定的Expansin基因家族完整性较高,但李基因组中Expansin基因的准确数量还有待通过基因组数据分析进一步确定。研究表明不同Expansin亚家族的成员数量存在很大的差异[32],且大多数情况下EXPA的数量多于EXPB的数量[46]。李Expansin家族的成员组成(22个EXPA、6个EXPBs、1个EXLA和4个EXLB)与拟南芥(26个EXPA、5个EXPB、3个EXLA和1个EXLB)相近,但与水稻(34个EXPA、19个EXPB、4个EXLA和1个EXLB)之间存在较大的差异。不同植物间Expansin家族成员数量和组成的差异可能与植物生长发育和环境适应的不同要求而引起的生物进化有关[35]。
33个李Expansin基因中有9个在三月李及其红肉突变体果实成熟过程中存在差异表达,且表达模式各异。Lu等[35]研究发现不同番茄Expansin家族基因在果实中的表达模式也存在较大的差异。Expansin家族基因在三月李及其红肉突变体果肉中存在多样的表达模式意味着这些基因在果实成熟过程中可能扮演着不同的角色。番茄(Solanum lycopersicum)[47]、草莓(Fragaria × ananassa)[48]、杏(Prunus armeniaca L.)[49]、桃(Prunus persica)[50]、香蕉(Musa acuminate)[51]和山番木瓜(Vasconcellea pubescens)[8]等的研究均表明Expansin的表达与果实软化有关。Palapol等[24]研究发现DzEXP1和DzEXP2的表达与榴莲果实软化呈正相关,乙烯可促进果肉软化和二者的表达,而1-MCP则抑制果肉软化和二者的表达。抑制Sl-EXP1的表达可显著提高番茄果实的硬度,而超表达Sl-EXP1则使番茄果实变软[5, 25]。这些研究均表明Expansin直接或间接参与果实软化。成熟的三月李及其红肉突变体果肉均迅速变软。但值得注意的是,本研究鉴定的9个差异表达Expansin的表达均未呈现与三月李及其红肉突变体果实成熟和软化一致的趋势。Zerpa-Catanho等[52]在番木瓜上也发现了类似结果,分析了成熟相关基因与采后番木瓜软化的关系,发现Expansin与果实软化不存在相关性。不同植物Expansin在果实成熟软化过程中的功能差异可能与物种有关。Expansin在李果实成熟过程中的具体功能及其是否直接参与李果实软化过程还有待进一步研究。
本研究通过生物信息学分析从三月李及其红肉突变体果实成熟过程的转录组数据中鉴定出33个Expansin家族基因,并对Expansin蛋白质的特征和基因表达模式进行分析,为今后进一步研究Expansin家族基因在李果实成熟过程中的功能奠定基础。
-
图 3 李Expansin家族蛋白质保守基序及结构域序列Logo
注:A:李Expansin家族蛋白质保守元件分布;B:李Expansin家族蛋白质保守元件序列特征。
Figure 3. Conserved motifs and domain sequence logo of Expansin family
Note:A:Distribution of the identified motifs in plum Expansin family proteins. B:The sequence constitution of identified motifs in plum Expansin family proteins.
图 5 Expansin家族基因在三月李及其红肉突变体果实成熟过程中的表达模式
注:上图基于三月李及其红肉突变体果实成熟过程的转录组数据计算得出。所有基因的FPKM值采用每个基因的最大FPKM值进行均一化处理。基因的表达水平由不同大小和颜色的实心圆表示,实心圆越大,表达量越高。右侧的数值为每个基因的最大FPKM值。
Figure 5. Expression pattern of Expansins in Sanyueli plum and its red-flesh mutant during fruit ripening
Note:Based on the transcriptome data of Sanyueli and the red-fleshed mutant fruits during ripening. All FPKM values of all genes were normalized with maximum FPKM values of each gene. The expression level of genes was indicated using filled circle with different size and colour. The larger the circle, the higher the expression. The values on the right indicates the highest FPKM value of each gene.
表 1 三月李及其红肉突变体Expansin蛋白质的理化性质和亚细胞定位
Table 1 Physicochemical properties and subcellular localization of Expansins in Sanyueli plum and its red-flesh mutant
序列编号
Sequnce ID蛋白质长度
Protein length/aa分子量
Molecular weight/kD等电点
pI不稳定系数
Instability index脂肪系数
Aliphatic index平均亲水系数
Grand average of hydropathicity细胞定位
Cell locationEVM0011615 252 26.78 9.36 35.7 64.29 −0.100 Extracellular EVM0015785 252 26.74 6.92 31.32 66.23 −0.108 Extracellular EVM0004461 254 27.27 8.43 30.26 63.43 −0.194 Extracellular EVM0027977 254 27.27 8.43 30.26 63.43 −0.194 Extracellular EVM0009515 257 27.47 8.79 35.46 74.47 −0.039 Extracellular EVM0008468 257 27.50 8.93 34.94 74.47 −0.042 Extracellular EVM0009923 257 27.74 9.14 32.88 67.24 −0.095 Extracellular EVM0010710 258 27.94 8.59 27.91 64.69 −0.066 Extracellular EVM0025415 259 28.39 8.89 22.2 73.9 −0.118 Extracellular EVM0019517 259 28.39 8.89 22.2 73.9 −0.118 Extracellular EVM0022202 259 27.84 9.41 33.23 71.2 −0.010 Extracellular EVM0002390 260 27.99 9.47 34.71 68.65 −0.007 Extracellular EVM0017357 260 28.74 8.07 17.38 66.81 −0.226 Extracellular EVM0018627 261 29.24 9.35 33.36 69.12 −0.338 Extracellular EVM0016646 263 28.99 9.22 35.71 65.32 0.006 Extracellular EVM0026183 265 29.18 9.83 45.17 73.21 −0.057 Extracellular EVM0016777 266 28.74 8.4 33.52 86.54 0.065 Extracellular EVM0010881 282 31.12 9.09 29.38 62.27 −0.388 Extracellular EVM0028371 291 31.89 5.77 39.08 72.03 −0.337 Extracellular EVM0018557 353 37.15 9.24 45.03 76.26 −0.001 Extracellular EVM0001651 367 40.65 9.53 48.28 83.41 −0.018 Extracellular EVM0020356 460 51.33 8.67 46.31 75.07 −0.258 Plasma membrane, Extracellular EVM0014217 176 19.21 4.98 36.08 77.1 −0.137 Extracellular EVM0016078 266 28.47 8.95 28.91 82.44 −0.032 Extracellular EVM0000548 272 28.58 4.62 43.47 76.4 −0.027 Extracellular EVM0006851 280 30.10 5.94 36.92 70.07 −0.168 Extracellular EVM0022596 282 30.33 7.52 35.18 72.02 −0.142 Extracellular EVM0026545 296 31.92 8.62 41.79 67.64 −0.269 Extracellular EVM0024996 260 28.16 8.73 37.26 85.62 0.035 Extracellular EVM0026062 252 28.00 6.87 30.3 69.33 −0.309 Extracellular EVM0028340 252 28.00 6.87 30.3 69.33 −0.309 Extracellular EVM0003805 252 28.00 6.87 30.3 69.33 −0.309 Extracellular EVM0013160 255 27.74 4.78 38.38 75.33 −0.170 Extracellular -
[1] BRUMMELL D A. Cell wall disassembly in ripening fruit [J]. Functional Plant Biology, 2006, 33(2): 103−119. DOI: 10.1071/FP05234
[2] 孙振营, 韩叶, 李秀芳, 等. 柿采后丙烯和1-甲基环丙烯处理对两个扩展蛋白基因表达的影响 [J]. 园艺学报, 2014, 41(6):1089−1095. SUN Z Y, HAN Y, LI X F, et al. Effects of propylene and 1-methylcyclopropene on expression of two EXP genes in persimmon fruits [J]. Acta Horticulturae Sinica, 2014, 41(6): 1089−1095.(in Chinese
[3] SANE V A, CHOURASIA A, NATH P. Softening in mango (Mangifera indica cv. Dashehari) is correlated with the expression of an early ethylene responsive, ripening related expansin gene, MiExpA1 [J]. Postharvest Biology and Technology, 2005, 38(3): 223−230. DOI: 10.1016/j.postharvbio.2005.07.008
[4] SHEN W B, LI C R, CHEN J Y, et al. Expansin gene expression in cherimoya fruit is correlated with flesh firmness during fruit ripening and softening [J]. The Journal of Horticultural Science and Biotechnology, 2009, 84(3): 333−339. DOI: 10.1080/14620316.2009.11512527
[5] BRUMMELL, HARPSTER, CIVELLO, et al. Modification of expansin protein abundance in tomato fruit alters softening and cell wall polymer metabolism during ripening [J]. The Plant Cell, 1999, 11(11): 2203−2216. DOI: 10.1105/tpc.11.11.2203
[6] MINOIA S, BOUALEM A, MARCEL F, et al. Induced mutations in tomato SlExp1 alter cell wall metabolism and delay fruit softening [J]. Plant Science, 2016, 242: 195−202. DOI: 10.1016/j.plantsci.2015.07.001
[7] JIANG F L, LOPEZ A, JEON S, et al. Disassembly of the fruit cell wall by the ripening-associated polygalacturonase and expansin influences tomato cracking [J]. Horticulture Research, 2019, 6(1): 17. DOI: 10.1038/s41438-018-0105-3
[8] GAETE-EASTMAN C, FIGUEROA C R, BALBONTÍN C, et al. Expression of an ethylene-related expansin gene during softening of mountain papaya fruit (Vasconcellea pubescens) [J]. Postharvest Biology and Technology, 2009, 53(1): 58−65.
[9] VALENZUELA-RIFFO F, PARRA-PALMA C, RAMOS P, et al. Molecular and structural insights into FaEXPA5, an alpha-expansin protein related with cell wall disassembly during ripening of strawberry fruit [J]. Plant Physiology and Biochemistry, 2020, 154: 581−589. DOI: 10.1016/j.plaphy.2020.06.010
[10] COSGROVE D J. Growth of the plant cell wall [J]. Nature Reviews Molecular Cell Biology, 2005, 6(11): 850−861. DOI: 10.1038/nrm1746
[11] COSGROVE D J. Plant expansins: Diversity and interactions with plant cell walls [J]. Current Opinion in Plant Biology, 2015, 25: 162−172. DOI: 10.1016/j.pbi.2015.05.014
[12] SAMPEDRO J, COSGROVE D J. The expansin superfamily [J]. Genome Biology, 2005, 6(12): 242. DOI: 10.1186/gb-2005-6-12-242
[13] HOU L, ZHANG Z Y, DOU S H, et al. Genome-wide identification, characterization, and expression analysis of the expansin gene family in Chinese jujube (Ziziphus jujuba Mill.) [J]. Planta, 2019, 249(3): 815−829. DOI: 10.1007/s00425-018-3020-9
[14] HAN Z S, LIU Y L, DENG X, et al. Genome-wide identification and expression analysis of expansin gene family in common wheat (Triticum aestivum L.) [J]. BMC Genomics, 2019, 20(1): 1−19. DOI: 10.1186/s12864-018-5379-1
[15] YENNAWAR N H, LI L C, DUDZINSKI D M, et al. Crystal structure and activities of EXPB1 (Zea m 1), a β-expansin and group-1 pollen allergen from maize [J]. PNAS, 2006, 103(40): 14664−14671. DOI: 10.1073/pnas.0605979103
[16] LI Y, JONES L, MCQUEEN-MASON S. Expansins and cell growth [J]. Current Opinion in Plant Biology, 2003, 6(6): 603−610. DOI: 10.1016/j.pbi.2003.09.003
[17] GOH H H, SLOAN J, DORCA-FORNELL C, et al. Inducible repression of multiple expansin genes leads to growth suppression during leaf development [J]. Plant Physiology, 2012, 159(4): 1759−1770. DOI: 10.1104/pp.112.200881
[18] LÜ P, KANG M, JIANG X Q, et al. RhEXPA4, a rose expansin gene, modulates leaf growth and confers drought and salt tolerance to Arabidopsis [J]. Planta, 2013, 237(6): 1547−1559. DOI: 10.1007/s00425-013-1867-3
[19] CHO H T, COSGROVE D J. Regulation of root hair initiation and expansin gene expression in Arabidopsis [J]. The Plant Cell, 2002, 14(12): 3237−3253. DOI: 10.1105/tpc.006437
[20] CHE J, YAMAJI N, SHEN R F, et al. An Al-inducible expansin gene, OsEXPA10 is involved in root cell elongation of rice [J]. The Plant Journal, 2016, 88(1): 132−142. DOI: 10.1111/tpj.13237
[21] HAYAMA H, SHIMADA T, FUJII H, et al. Ethylene-regulation of fruit softening and softening-related genes in peach [J]. Journal of Experimental Botany, 2006, 57(15): 4071−4077. DOI: 10.1093/jxb/erl178
[22] SCHLOSSER J, OLSSON N, WEIS M, et al. Cellular expansion and gene expression in the developing grape (Vitis vinifera L.) [J]. Protoplasma, 2008, 232(3): 255−265.
[23] NARDI C F, VILLARREAL N M, ROSSI F R, et al. Overexpression of the carbohydrate binding module of strawberry expansin2 in Arabidopsis thaliana modifies plant growth and cell wall metabolism [J]. Plant Molecular Biology, 2015, 88(1): 101−117.
[24] PALAPOL Y, KUNYAMEE S, THONGKHUM M, et al. Expression of expansin genes in the pulp and the dehiscence zone of ripening durian (Durio zibethinus) fruit [J]. Journal of Plant Physiology, 2015, 182: 33−39. DOI: 10.1016/j.jplph.2015.04.005
[25] PERINI M A, SIN I N, VILLARREAL N M, et al. Overexpression of the carbohydrate binding module from Solanum lycopersicum expansin 1(Sl-EXP1) modifies tomato fruit firmness and Botrytis cinerea susceptibility [J]. Plant Physiology and Biochemistry, 2017, 113: 122−132. DOI: 10.1016/j.plaphy.2017.01.029
[26] XIE H, CHEN J Y, YUAN R C, et al. Differential expression and regulation of expansin gene family members during fruit growth and development of ‘Shijia’ longan fruit [J]. Plant Growth Regulation, 2009, 58(3): 225−233. DOI: 10.1007/s10725-009-9370-3
[27] COX M C H, BENSCHOP J J, VREEBURG R A M, et al. The roles of ethylene, auxin, abscisic acid, and gibberellin in the hyponastic growth of submerged Rumex palustris petioles [J]. Plant Physiology, 2004, 136(2): 2948−2960. DOI: 10.1104/pp.104.049197
[28] PARK C H, KIM T W, SON S H, et al. Brassinosteroids control AtEXPA5 gene expression in Arabidopsis thaliana [J]. Phytochemistry, 2010, 71(4): 380−387. DOI: 10.1016/j.phytochem.2009.11.003
[29] VREEBURG R A M, BENSCHOP J J, PEETERS A J M, et al. Ethylene regulates fast apoplastic acidification and expansin A transcription during submergence-induced petiole elongation in Rumex palustris [J]. The Plant Journal, 2005, 43(4): 597−610. DOI: 10.1111/j.1365-313X.2005.02477.x
[30] LEE A, GIORDANO W, HIRSCH A M. Cytokinin induces expansin gene expression in Melilotus alba Desr. wild-type and the non-nodulating, non-mycorrhizal (Nod-Myc-) mutant Masym3 [J]. Plant Signaling & Behavior, 2008, 3(4): 218−223.
[31] LEE Y, CHOI D, KENDE H. Expansins: ever-expanding numbers and functions [J]. Current Opinion in Plant Biology, 2001, 4(6): 527−532. DOI: 10.1016/S1369-5266(00)00211-9
[32] DING A M, MAROWA P, KONG Y Z. Genome-wide identification of the expansin gene family in tobacco (Nicotiana tabacum) [J]. Molecular Genetics and Genomics, 2016, 291(5): 1891−1907. DOI: 10.1007/s00438-016-1226-8
[33] 施杨, 徐筱, 李昊阳, 等. 水稻扩展蛋白家族的生物信息学分析 [J]. 遗传, 2014, 36(8):809−820. SHI Y, XU X, LI H Y, et al. Bioinformatics analysis of the expansin gene family in rice [J]. Hereditas, 2014, 36(8): 809−820.(in Chinese
[34] LI N N, PU Y Y, GONG Y C, et al. Genomic location and expression analysis of expansin gene family reveals the evolutionary and functional significance in Triticum aestivum [J]. Genes & Genomics, 2016, 38(11): 1021−1030.
[35] LU Y, LIU L F, WANG X, et al. Genome-wide identification and expression analysis of the expansin gene family in tomato [J]. Molecular Genetics and Genomics, 2016, 291(2): 597−608. DOI: 10.1007/s00438-015-1133-4
[36] 李昊阳, 施杨, 丁亚娜, 等. 杨树扩展蛋白基因家族的生物信息学分析 [J]. 北京林业大学学报, 2014, 36(2):59−67. LI H Y, SHI Y, DING Y N, et al. Bioinformatics analysis of expansin gene family in poplar genome [J]. Journal of Beijing Forestry University, 2014, 36(2): 59−67.(in Chinese
[37] DAL SANTO S, VANNOZZI A, TORNIELLI G B, et al. Genome-wide analysis of the expansin gene superfamily reveals grapevine-specific structural and functional characteristics [J]. PLoS One, 2013, 8(4): e62206. DOI: 10.1371/journal.pone.0062206
[38] ZHANG S Z, XU R R, GAO Z, et al. A genome-wide analysis of the expansin genes in Malus × domestica [J]. Molecular Genetics and Genomics, 2014, 289(2): 225−236. DOI: 10.1007/s00438-013-0796-y
[39] 张倩, 曹珂, 朱更瑞, 等. 桃EXPANSIN基因家族序列特征及其在根结线虫侵染后的诱导表达分析 [J]. 果树学报, 2018, 35(1):1−10. ZHANG Q, CAO K, ZHU G R, et al. The sequence characters of EXPANSIN genes and the analysis of their induced expression after the infection of root-knot Nematodes in peach [J]. Journal of Fruit Science, 2018, 35(1): 1−10.(in Chinese
[40] 方智振, 叶新福, 周丹蓉, 等. 辐射三月李红肉迟熟突变体的ISSR分析 [J]. 核农学报, 2016, 30(2):209−215. FANG Z Z, YE X F, ZHOU D R, et al. ISSR analysis on red-flesh and late-ripening mutant of Sanyue plum (Prunus salicina Lindl.) induced by irradiation [J]. Journal of Nuclear Agricultural Sciences, 2016, 30(2): 209−215.(in Chinese
[41] 方智振, 姜翠翠, 周丹蓉, 等. 基于转录组的‘三月李’及其红肉突变体ARF基因家族鉴定及分析 [J]. 应用与环境生物学报, 2019, 25(6):1388−1395. FANG Z Z, JIANG C C, ZHOU D R, et al. Analysis of the ARF gene family of 'Sanyueli' plum (Prunus salicina Lindl.) and its red-fleshed mutant based on transcriptome [J]. Chinese Journal of Applied & Environmental Biology, 2019, 25(6): 1388−1395.(in Chinese
[42] CHEN C J, CHEN H, ZHANG Y, et al. TBtools: an integrative toolkit developed for interactive analyses of big biological data [J]. Molecular Plant, 2020, 13(8): 1194−1202. DOI: 10.1016/j.molp.2020.06.009
[43] CAREY R E, COSGROVE D J. Portrait of the expansin superfamily in Physcomitrella patens: Comparisons with angiosperm expansins [J]. Annals of Botany, 2007, 99(6): 1131−1141. DOI: 10.1093/aob/mcm044
[44] 姜志磊, 周琳, 武奉慈, 等. 玉米扩展蛋白Expansin基因家族定位及基因表达模式分析 [J]. 生物技术进展, 2018, 8(1):34−40. JIANG Z L, ZHOU L, WU F C, et al. Analysis of location and expression pattern of maize expansin gene family [J]. Current Biotechnology, 2018, 8(1): 34−40.(in Chinese
[45] 郝西, 理向阳, 腊贵晓, 等. 黄瓜扩展蛋白基因家族的鉴定与生物信息学分析 [J]. 分子植物育种, 2015, 13(10):2280−2289. HAO X, LI X Y, LA G X, et al. Identification and bioinformatic analysis of the expansin gene family in cucumber [J]. Molecular Plant Breeding, 2015, 13(10): 2280−2289.(in Chinese
[46] ZHANG J F, XU Y Q, DONG J M, et al. Genome-wide identification of wheat (Triticum aestivum) expansins and expansin expression analysis in cold-tolerant and cold-sensitive wheat cultivars [J]. PLoS One, 2018, 13(3): e0195138. DOI: 10.1371/journal.pone.0195138
[47] ROSE J K C, LEE H H, BENNETT A B. Expression of a divergent expansin gene is fruit-specific and ripening-regulated [J]. PNAS, 1997, 94(11): 5955−5960. DOI: 10.1073/pnas.94.11.5955
[48] HARRISON E P, MCQUEEN-MASON S J, MANNING K. Expression of six expansin genes in relation to extension activity in developing strawberry fruit [J]. Journal of Experimental Botany, 2001, 52(360): 1437−1446. DOI: 10.1093/jexbot/52.360.1437
[49] MBÉGUIÉ-A-MBÉGUIÉ D, GOUBLE B, GOMEZ R M, et al. Two expansin cDNAs from Prunus armeniaca expressed during fruit ripening are differently regulated by ethylene [J]. Plant Physiology and Biochemistry, 2002, 40(5): 445−452. DOI: 10.1016/S0981-9428(02)01391-8
[50] HAYAMA H, ITO A, MORIGUCHI T, et al. Identification of a new expansin gene closely associated with peach fruit softening [J]. Postharvest Biology and Technology, 2003, 29(1): 1−10. DOI: 10.1016/S0925-5214(02)00216-8
[51] TRIVEDI P K, NATH P. MaExp1, an ethylene-induced expansin from ripening banana fruit [J]. Plant Science, 2004, 167(6): 1351−1358. DOI: 10.1016/j.plantsci.2004.07.005
[52] ZERPA-CATANHO D, ESQUIVEL P, MORA-NEWCOMER E, et al. Transcription analysis of softening-related genes during postharvest of papaya fruit (Carica papaya L. ‘Pococí’ hybrid) [J]. Postharvest Biology and Technology, 2017, 125: 42−51. DOI: 10.1016/j.postharvbio.2016.11.002
-
期刊类型引用(9)
1. 郭河麟,郭河燕,石玉琴,辛镇忠,王翔,杨佳丽,王腾飞,王愈. 壶瓶枣裂果多糖咀嚼片配方优化及其体外抗氧化活性研究. 保鲜与加工. 2025(02): 87-98 .  百度学术
百度学术
2. 王晨,冯作山,苏合拉提·吐尔逊太,杨莲,胡长江,刘明臣,李硕,尼格尔热依·亚迪卡尔. 青熟期托克逊杏咀嚼片湿法压片法的制备工艺研究. 食品研究与开发. 2024(06): 174-183 .  百度学术
百度学术
3. 周迪,姚可欣,于清华,吕博威,王永奇,于建. 双层包埋维生素A微胶囊的压片性能和稳定性研究. 中国食品添加剂. 2024(09): 188-196 .  百度学术
百度学术
4. 丁雯,崔慧莹,高振珅,王慧,王悦尚. 吡喹酮咀嚼片的制备及其质量评价. 山东畜牧兽医. 2024(09): 1-4+7 .  百度学术
百度学术
5. 赵宇慧,张丽,宋玉霞,甘晓燕,聂峰杰,巩檑. 响应面法优化肉苁蓉咀嚼片配方及品质检测. 食品工业. 2022(01): 130-135 .  百度学术
百度学术
6. 刘淑敏,张淑君,梁绮晴,陈文泉,阮艳红,杨娟. 白芸豆甘蔗渣咀嚼片直接压片法的制备工艺研究. 食品研究与开发. 2021(17): 93-100 .  百度学术
百度学术
7. 戴春. 麦麸膳食纤维对控制中老年糖尿病患者血糖效果研究. 中国食物与营养. 2020(03): 57-60 .  百度学术
百度学术
8. 汤葆莎,赖谱富,李怡彬,吴俐,翁敏劼,郑恒光. 芙蓉李咀嚼片酚类物组成及其生物活性. 福建农业学报. 2020(07): 788-794 .  本站查看
本站查看
9. 刘伟,杨华峰,屈世龙,杜荣荣,薛淑花,李芳,孔令明. 基于模糊数学评价结合混料设计优化葡萄籽超微粉压片糖果工艺. 新疆农业大学学报. 2020(04): 281-289 .  百度学术
百度学术
其他类型引用(7)




 下载:
下载: