Cloning and Expression Analysis of Furostanol Glycoside 26-O-β-glucosidase Gene in Anoectochilus roxburhii
-
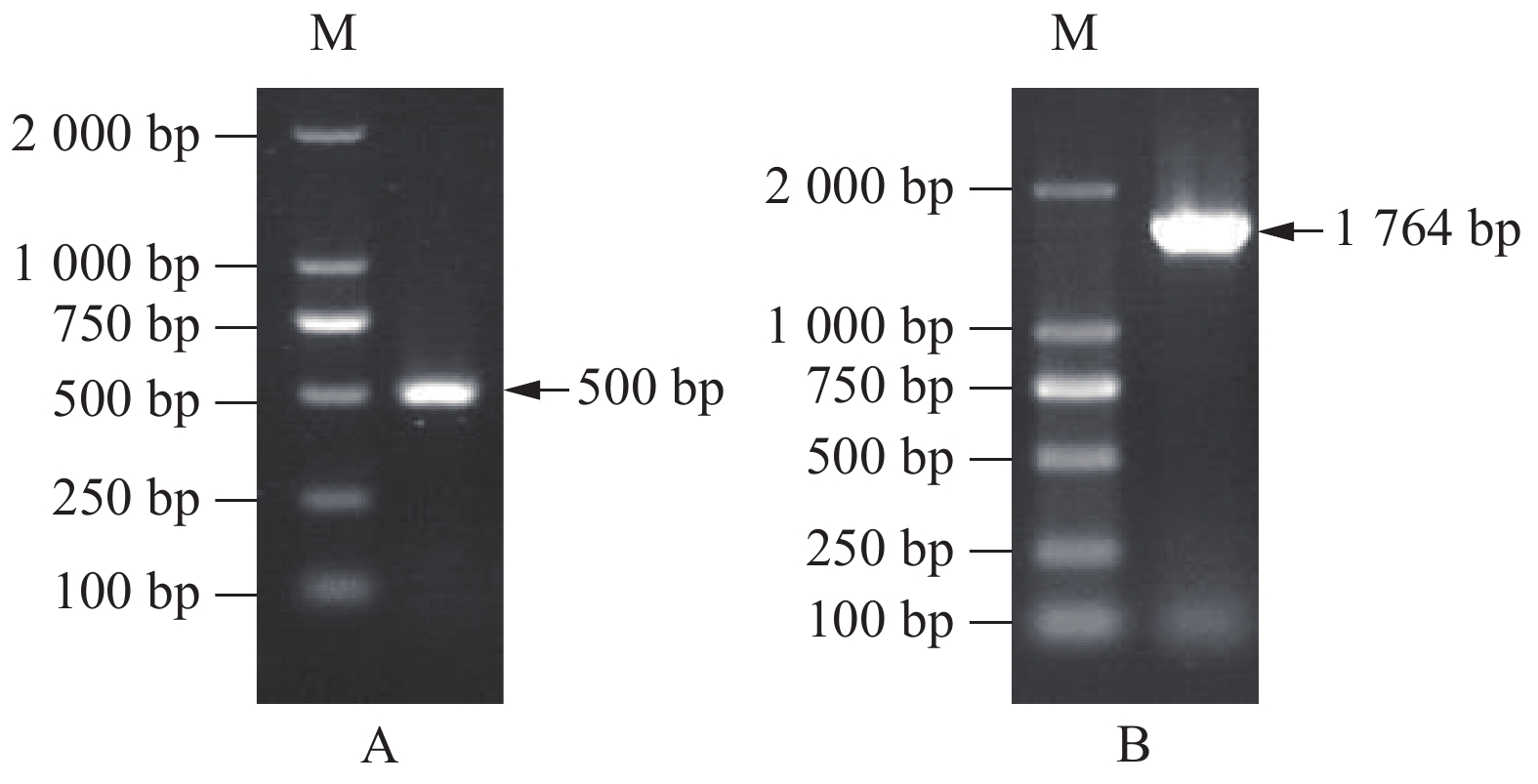
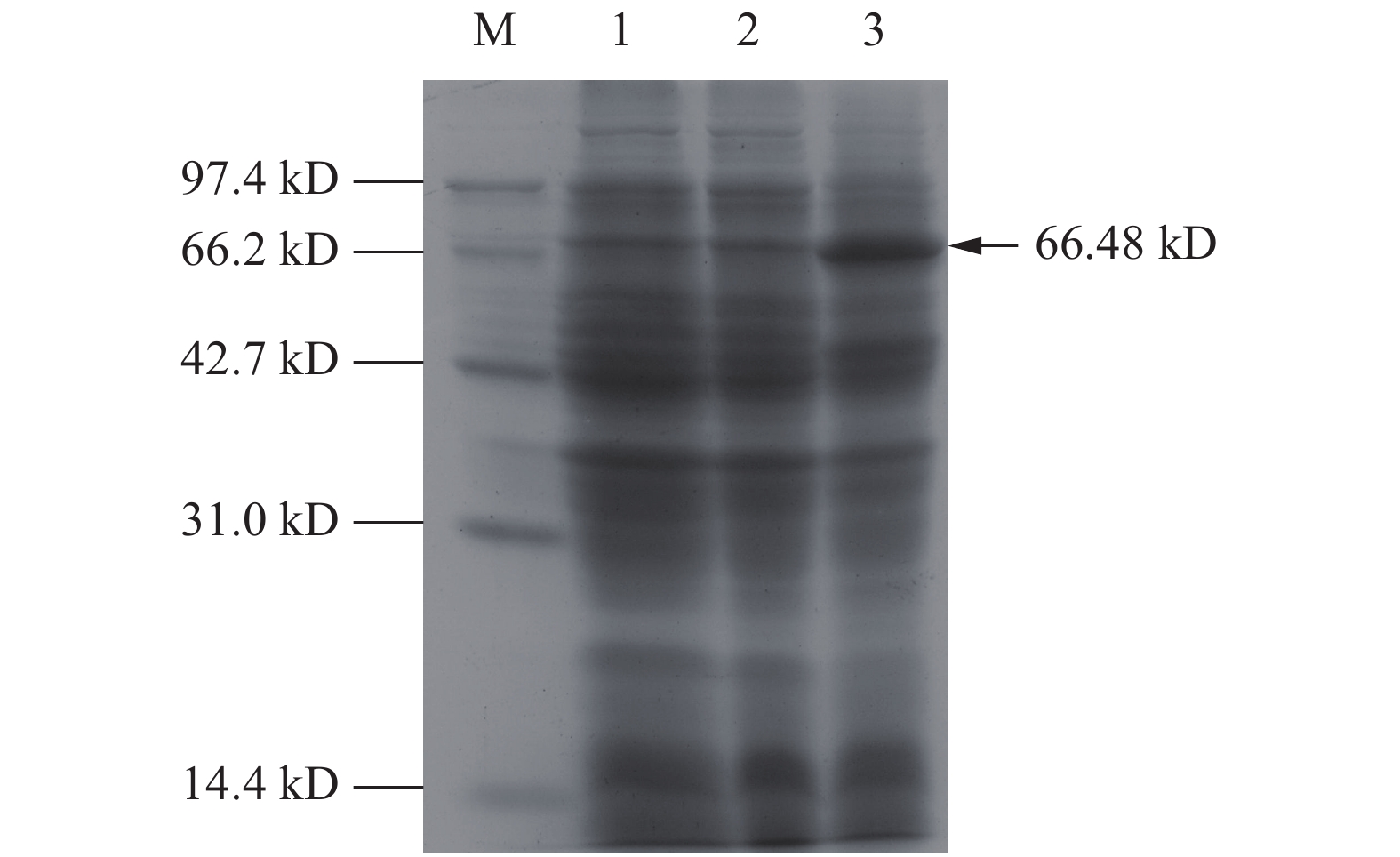
摘要:目的 克隆金线莲(Anoectochilus roxburhii)ArF26G基因的cDNA全长,分析该基因在金线莲茎、叶中的表达模式,以期为进一步了解金线莲甾体皂苷的生物合成代谢调控机制提供参考。方法 利用RACE技术克隆金线莲ArF26G基因cDNA全长,以pET-28a(+)为载体构建原核表达载体并诱导表达,采用荧光定量PCR方法分析不同温度(5、15、25、35℃)和种植时间(1–6个月)ArF26G基因在茎和叶中的表达水平。结果 ArF26G基因的cDNA全长1 982 bp,含有1个1 764 bp的ORF,编码587个氨基酸,编码蛋白具有Glycosyl hydrolase 1(GH1)superfamily蛋白保守区,定位于叶绿体,N端33个氨基酸残基为叶绿体转运肽,分子量为66.48 kD,理论等电点(pI)为5.31,不稳定系数为37.92,属稳定蛋白。构建了pET-28a-ArF26G原核表达载体,并在大肠杆菌(E. coli)BL21(DE3)中成功诱导表达。荧光定量PCR分析结果显示,ArF26G基因在茎中的表达量极显著高于叶,25℃处理表达量最高。金线莲种植时间达4个月时,ArF26G基因在茎中的表达量是25℃处理组培苗茎的11.9倍,种植5个月达到23.3倍。结论 本研究克隆了金线莲ArF26G基因cDNA全长,其表达量在25℃以及种植5个月时表达量最高。
-
关键词:
- 金线莲 /
- 呋甾皂苷26-O-β-糖苷酶 /
- 甾体皂苷 /
- 基因表达
Abstract:Objective In order to further understand the regulatory mechanism of steroidal saponins biosynthesis and metabolism of Anoectochilus roxburhii, the full-length cDNA of ArF26G gene was cloned and its expression pattern in the stem and leaf was analyzed.Method The full-length cDNA of ArF26G gene was cloned by RACE. Prokaryotic expression vector was constructed with pET-28a (+), and induced by IPTG. The expression levels of ArF26G gene in stem and leaf of Anoectochilus roxburhii at different temperatures and planting times were analyzed by fluorescence quantitative PCR.Result The full-length cDNA of ArF26G gene is 1 982 bp with an 1 764 bp ORF, which encoded a protein of 587 amino acids containing a conservative domain of Glycosyl hydrolase 1 (GH1) superfamily. ArF26G is located in chloroplast and a putative chloroplast transit peptide of 33 amino acid residues at the N-terminus. The molecular weight of ArF26G protein is 66.48 kD, and the theoretical isoelectric (pI) is 5.31, and the instability coefficient is 37.92, it is a stable protein. Prokaryotic expression vector pET-28a-ArF26G was constructed and induced successfully by IPTG in E. coli BL21 (DE3). The results of fluorescence quantitative PCR analysis showed that the expression of ArF26G in stem was significantly higher than that in leaf, and the highest expression of tissue culture seedlings was at 25℃. When the planting time was up to 4 months and 5 months, the expression of ArF26G gene in the stem was 11.9 times and 23.3 times as much as that in the stem of tissue culture seedlings treated at 25℃ respectively.Conclusion In this study, the full-length cDNA of ArF26G gene was cloned. The expression of ArF26G gene was the highest at 25℃ or planting for 5 months. -
0. 引言
【研究意义】李(Prunus salicina Lindl.)是我国重要的传统果树。李果实美丽诱人,风味独特,且具有很高的营养价值,深受消费者喜爱。成熟的李果实易软化,难以贮藏运输,不利于优质鲜食李产业的发展。细胞壁结构变化是导致成熟果实软化的重要原因[1]。Expansin作为调节细胞壁的松弛和伸展的一类重要蛋白质,在柿(Diospyros kaki L.‘Fuping Jianshi’)[2]、芒果(Mangifera indica cv. Dashehari)[3]、番荔枝(Annona cherimola Mill)[4]、番茄(Solanum lycopersicum)[5-7]、山番木瓜(Vasconcellea pubescens)[8]和草莓(Fragaria × ananassa)[9]果实成熟和软化中发挥着重要的作用。因此,系统地鉴定和分析李Expansin家族基因对进一步研究Expansin家族基因在李果实成熟过程中的作用具有重要的意义。【前人研究进展】Expansin是一类广泛存在于植物中的细胞壁酶,它通过破坏细胞壁多糖之间的非共价键参与细胞壁松弛和伸展调节[10- 11]。Expansin由一个多基因家族编码,该家族由EXPA(α-expansin)、EXPB(β-expansin)、EXPLA(expansin-like A)和EXPLB(expansin-like B)等4个亚家族组成[12]。典型的Expansin蛋白质在N端有一个长度为20~30个氨基酸残基的信号肽和具有多个保守的半胱氨酸残基和HFD基序的domain1,C端含有一个与第二组花粉过敏原蛋白同源的多糖结合结构域[13-15]。大量研究表明Expansin与植物细胞生长[16]、叶片生长发育[17-18]、根系发育[19-20]、果实发育和质地变化[21-26]等诸多生物学过程密切相关。此外,Expansin还与脱落酸、赤霉素、生长素、油菜素内酯和乙烯等植物激素引起的细胞膨大和细胞壁结构改变有关[27-30]。目前,科研人员已对多种植物的Expansin基因家族进行鉴定与分析,如拟南芥(Arabidopsis thaliana)[31]、烟草(Nicotiana tabacum)[32]、水稻(Oryza sativa)[33]、小麦(Triticum aestivum)[14, 34]、番茄(Solanum lycopersicum)[35]、杨树(Populus trichocarpa)[36]、葡萄(Vitis vinifera)[37]、苹果(Malus × domestica)[38]、桃(Prunus persica)[39]和枣(Ziziphus jujuba Mill.)[13]。【本研究切入点】Expansin在果实发育和成熟中的重要作用已有相关研究,但李Expansin基因家族的鉴定和分析尚未见报道。【拟解决的关键问题】本研究以三月李,以及课题组在前期研究中通过对三月李进行辐射诱变获得的一个果实性状发生显著变化的迟熟突变体[40]为材料,采用生物信息学方法从三月李及其红肉突变体果实成熟过程的转录组数据中鉴定李Expansin家族基因,并对其蛋白质特征、系统进化关系及其在三月李和迟熟突变体果实成熟过程中的表达模式进行比较分析,为研究李Expansin家族基因在果实成熟过程中的功能奠定基础。
1. 材料与方法
1.1 数据来源及Expansin家族基因的鉴定
本研究所使用的数据为本课题组获得的三月李(盛花后95、105和115 d)及其红肉突变体(盛花后95、105、115和125 d)的转录组数据[41]。拟南芥(Arabidopsis thaliana)、水稻(Oryza sativa)和毛果杨(Populus trichocarpa)的Expansin蛋白质序列从EXPANSIN CENTRAL(http://www.personal.psu.edu/fsl/ExpCentral/)下载。以拟南芥、水稻和毛果杨Expansin蛋白质序列为查询序列,采用TBtools[42]的BLAST工具从三月李及其红肉突变体蛋白质数据库中检索Expansin家族成员。同时,从Pfam数据库(http://pfam.xfam.org/)下载DPBB_1和Pollen_allerg_1结构域的HMM模型PF03330和PF01357,并采用HMMER3.0鉴定含有保守结构域DPBB_1和Pollen_allerg_1的蛋白质。
1.2 Expansin家族分析
Expansin家族蛋白质生物信息学分析、保守基序分析与多重序列比对、系统进化树的构建、基因的差异表达模式分析参考文献[40]进行。
2. 结果与分析
2.1 三月李及其红肉突变体Expansin基因家族的鉴定及蛋白质特性分析
为了鉴定三月李及其红肉突变体的Expansin家族成员,以拟南芥(35个)、水稻(58个)和毛果杨(36个)Expansin家族成员的蛋白质序列为查询序列,通过BLAST分析从三月李及其红肉突变体蛋白质数据库中检索Expansin蛋白质,初步鉴定出35个Expansin蛋白质(E-value<1e−5)。随后,采用隐马尔可夫模型进行Expansin蛋白质鉴定,去除不含保守结构域DPBB_1和Pollen_allerg_1的蛋白质。最终得到33个Expansin家族蛋白质(表1)。除了EVM0014217,其余Expansin基因均包含完整的编码序列。李Expansin蛋白质序列的长度在176(EVM0014217)~460 aa(EVM0020356),预测蛋白的相对分子量在19.21~51.33 kD,等电点介于4.62~9.83。蛋白质不稳定系数分析结果表明,除了EVM0026183、EVM0000548、EVM0026545、EVM0018557、EVM0001651和EVM0020356,其余李Expansin蛋白质的不稳定系数均小于40,表明大部分李Expansin蛋白质均为稳定蛋白;平均亲水系数均为负数,表明33个蛋白质均为亲水蛋白质。亚细胞定位预测结果表明,除了EVM0020356可分布于质膜与细胞外,其余李Expansin蛋白质均位于细胞外。
表 1 三月李及其红肉突变体Expansin蛋白质的理化性质和亚细胞定位Table 1. Physicochemical properties and subcellular localization of Expansins in Sanyueli plum and its red-flesh mutant序列编号
Sequnce ID蛋白质长度
Protein length/aa分子量
Molecular weight/kD等电点
pI不稳定系数
Instability index脂肪系数
Aliphatic index平均亲水系数
Grand average of hydropathicity细胞定位
Cell locationEVM0011615 252 26.78 9.36 35.7 64.29 −0.100 Extracellular EVM0015785 252 26.74 6.92 31.32 66.23 −0.108 Extracellular EVM0004461 254 27.27 8.43 30.26 63.43 −0.194 Extracellular EVM0027977 254 27.27 8.43 30.26 63.43 −0.194 Extracellular EVM0009515 257 27.47 8.79 35.46 74.47 −0.039 Extracellular EVM0008468 257 27.50 8.93 34.94 74.47 −0.042 Extracellular EVM0009923 257 27.74 9.14 32.88 67.24 −0.095 Extracellular EVM0010710 258 27.94 8.59 27.91 64.69 −0.066 Extracellular EVM0025415 259 28.39 8.89 22.2 73.9 −0.118 Extracellular EVM0019517 259 28.39 8.89 22.2 73.9 −0.118 Extracellular EVM0022202 259 27.84 9.41 33.23 71.2 −0.010 Extracellular EVM0002390 260 27.99 9.47 34.71 68.65 −0.007 Extracellular EVM0017357 260 28.74 8.07 17.38 66.81 −0.226 Extracellular EVM0018627 261 29.24 9.35 33.36 69.12 −0.338 Extracellular EVM0016646 263 28.99 9.22 35.71 65.32 0.006 Extracellular EVM0026183 265 29.18 9.83 45.17 73.21 −0.057 Extracellular EVM0016777 266 28.74 8.4 33.52 86.54 0.065 Extracellular EVM0010881 282 31.12 9.09 29.38 62.27 −0.388 Extracellular EVM0028371 291 31.89 5.77 39.08 72.03 −0.337 Extracellular EVM0018557 353 37.15 9.24 45.03 76.26 −0.001 Extracellular EVM0001651 367 40.65 9.53 48.28 83.41 −0.018 Extracellular EVM0020356 460 51.33 8.67 46.31 75.07 −0.258 Plasma membrane, Extracellular EVM0014217 176 19.21 4.98 36.08 77.1 −0.137 Extracellular EVM0016078 266 28.47 8.95 28.91 82.44 −0.032 Extracellular EVM0000548 272 28.58 4.62 43.47 76.4 −0.027 Extracellular EVM0006851 280 30.10 5.94 36.92 70.07 −0.168 Extracellular EVM0022596 282 30.33 7.52 35.18 72.02 −0.142 Extracellular EVM0026545 296 31.92 8.62 41.79 67.64 −0.269 Extracellular EVM0024996 260 28.16 8.73 37.26 85.62 0.035 Extracellular EVM0026062 252 28.00 6.87 30.3 69.33 −0.309 Extracellular EVM0028340 252 28.00 6.87 30.3 69.33 −0.309 Extracellular EVM0003805 252 28.00 6.87 30.3 69.33 −0.309 Extracellular EVM0013160 255 27.74 4.78 38.38 75.33 −0.170 Extracellular 2.2 三月李及其红肉突变体Expansin家族蛋白质进化分析
为了解三月李及其红肉突变体Expansin家族蛋白质与桃、拟南芥和水稻的进化关系,采用MEGAX软件构建了拟南芥、水稻、桃和李Expansin家族蛋白质的系统进化树。如图1所示,拟南芥、水稻、桃和李Expansin家族蛋白质可分为4组,分别为EXPA、EXPB、EXPLA和EXPLB。从图1可以看出,每个桃Expansin蛋白质都有与其对应的同源李Expansin蛋白质。EXPA的李Expansin家族蛋白质数量最多,共有22个。其次为EXPB,共含有6个李Expansin家族蛋白质;仅有1个李Expansin蛋白质(EVM0024996)属于EXPLA组。EVM0026062、EVM0028340、EVM0003805和EVM0013160属于EXPLB组。
2.3 三月李及其红肉突变体Expansin家族蛋白质保守结构域分析
对李Expansin蛋白质的保守结构域进行分析,发现33个李Expansin蛋白质均含有DPBB_1和Pollen_allerg_1结构域(图2)。为了进一步了解李Expansin蛋白质的保守结构域,利用在线软件MEME对李Expansin家族蛋白质进行分析,结果表明李Expansin家族蛋白质共含有15个保守基序(图3)。Expansin蛋白质含有的基序数量从5~10个不等。其中,EVM0011615、EVM0028371、EVM0001651、EVM0006851、EVM0022596和EVM0026545含有的基序数量最多(10个),EVM0014217含有的基序数量最少(5个)。所有李Expansin家族蛋白质均含有基序3和5(图3)。除了EVM0014217之外,其他李Expansin家族蛋白质均含有基序1和7(图3)。基序2是EXPA成员特有的基序,基序10为EXPB、EXPLA和EXPLB成员特有的基序,基序12为EXPLA和EXPLB成员特有的基序(图3)。含有基序14的Expansin蛋白质数量最少,仅3个EXPLB成员(EVM0026062、EVM0028340和EVM0003805)含有该基序,EXPA、EXPB和EXPLA均不含该基序(图3)。
![]() 图 3 李Expansin家族蛋白质保守基序及结构域序列Logo注:A:李Expansin家族蛋白质保守元件分布;B:李Expansin家族蛋白质保守元件序列特征。Figure 3. Conserved motifs and domain sequence logo of Expansin familyNote:A:Distribution of the identified motifs in plum Expansin family proteins. B:The sequence constitution of identified motifs in plum Expansin family proteins.
图 3 李Expansin家族蛋白质保守基序及结构域序列Logo注:A:李Expansin家族蛋白质保守元件分布;B:李Expansin家族蛋白质保守元件序列特征。Figure 3. Conserved motifs and domain sequence logo of Expansin familyNote:A:Distribution of the identified motifs in plum Expansin family proteins. B:The sequence constitution of identified motifs in plum Expansin family proteins.为了分析家族蛋白质保守结构域的特征,采用DNAMAN7对Expansin家族蛋白质进行多重序列比对分析。结果表明大多数Expansin蛋白质由3个部分(信号肽、Domain1和Domain3)组成。大部分EXPA成员(EVM0016777除外)和EXPB成员(EVM0016078除外)在Domain1部分都含有一个保守的HFD基序,而EXPLA和EXPLB在对应位置的特征序列则分别为DFV和DFI(图4)。HFD基序两侧存在两个插入片段,分别为EXPA的α-Insertion和EXPB、EXPLA和EXPLB特有的插入片段(图4)。李Expansin家族蛋白质含有多个保守的半胱氨酸和色氨酸(图4)。
2.4 Expansin家族基因在三月李及其红肉突变体果实成熟过程中的表达模式分析
对33个Expansin家族基因的表达模式进行分析,发现三月李及其红肉突变体果实成熟过程中仅有9个Expansin基因存在差异表达,包括7个EXPA(EVM0015785、EVM0010710、EVM0022202、EVM0002390、EVM0016777、EVM0018557和EVM0001651)、1个EXPB(EVM0016078)和1个EXPLA(EVM0024996)(图5)。三月李果肉中EVM0015785和EVM0016777的表达量随果实成熟逐渐降低,但其表达量在红肉突变体果实成熟过程中无显著变化。EVM0010710和EVM0022202在成熟三月李果肉中的表达量也显著降低,而在成熟红肉突变体果肉中的表达量明显升高。红肉突变体果肉中EVM0002390的表达量随果实成熟而升高,但其表达量仅在花后105 d的三月李果肉中显著升高,花后115 d的三月李果肉中的表达量又下降至与花后95 d相当的水平。成熟三月李果肉中EVM0024996的表达量显著升高,而在红肉突变体果实成熟过程中无显著变化。
![]() 图 5 Expansin家族基因在三月李及其红肉突变体果实成熟过程中的表达模式注:上图基于三月李及其红肉突变体果实成熟过程的转录组数据计算得出。所有基因的FPKM值采用每个基因的最大FPKM值进行均一化处理。基因的表达水平由不同大小和颜色的实心圆表示,实心圆越大,表达量越高。右侧的数值为每个基因的最大FPKM值。Figure 5. Expression pattern of Expansins in Sanyueli plum and its red-flesh mutant during fruit ripeningNote:Based on the transcriptome data of Sanyueli and the red-fleshed mutant fruits during ripening. All FPKM values of all genes were normalized with maximum FPKM values of each gene. The expression level of genes was indicated using filled circle with different size and colour. The larger the circle, the higher the expression. The values on the right indicates the highest FPKM value of each gene.
图 5 Expansin家族基因在三月李及其红肉突变体果实成熟过程中的表达模式注:上图基于三月李及其红肉突变体果实成熟过程的转录组数据计算得出。所有基因的FPKM值采用每个基因的最大FPKM值进行均一化处理。基因的表达水平由不同大小和颜色的实心圆表示,实心圆越大,表达量越高。右侧的数值为每个基因的最大FPKM值。Figure 5. Expression pattern of Expansins in Sanyueli plum and its red-flesh mutant during fruit ripeningNote:Based on the transcriptome data of Sanyueli and the red-fleshed mutant fruits during ripening. All FPKM values of all genes were normalized with maximum FPKM values of each gene. The expression level of genes was indicated using filled circle with different size and colour. The larger the circle, the higher the expression. The values on the right indicates the highest FPKM value of each gene.3. 讨论与结论
Expansin不仅是在植物生长发育诸多方面都发挥着重要生物学功能的细胞壁蛋白[17, 18, 20, 22-26],还是研究植物发育进化的重要候选基因[34, 37, 43]。因此,Expansin获得了广泛的关注。本研究从三月李及其红肉突变体果实成熟过程的转录组中鉴定出33个Expansin基因,少于玉米(Zea myas, 93个)[44]、小麦(Triticum aestivum, 87个)[34]、水稻(Oryza sativa, 58个)[33]、烟草(Nicotiana tabacum, 52个)[32]、番茄(Solanum lycopersicum, 43个)[38]、苹果(Malus × domestica, 41个)[38]、杨树(Populus trichocarpa, 36个)[36]、黄瓜(Cucumis sativus, 35个)[45]和模式植物拟南芥(Arabidopsis thaliana, 35个)[31],但多于枣(Ziziphus jujuba Mill., 30个)[13]、葡萄(Vitis vinifera, 29个)[37]及其近缘物种桃(Prunus persica, 27个)[39]。李的近缘物种桃的27个Expansin蛋白质在李转录组中均能找到对应的同源蛋白质,可见本研究鉴定的Expansin基因家族完整性较高,但李基因组中Expansin基因的准确数量还有待通过基因组数据分析进一步确定。研究表明不同Expansin亚家族的成员数量存在很大的差异[32],且大多数情况下EXPA的数量多于EXPB的数量[46]。李Expansin家族的成员组成(22个EXPA、6个EXPBs、1个EXLA和4个EXLB)与拟南芥(26个EXPA、5个EXPB、3个EXLA和1个EXLB)相近,但与水稻(34个EXPA、19个EXPB、4个EXLA和1个EXLB)之间存在较大的差异。不同植物间Expansin家族成员数量和组成的差异可能与植物生长发育和环境适应的不同要求而引起的生物进化有关[35]。
33个李Expansin基因中有9个在三月李及其红肉突变体果实成熟过程中存在差异表达,且表达模式各异。Lu等[35]研究发现不同番茄Expansin家族基因在果实中的表达模式也存在较大的差异。Expansin家族基因在三月李及其红肉突变体果肉中存在多样的表达模式意味着这些基因在果实成熟过程中可能扮演着不同的角色。番茄(Solanum lycopersicum)[47]、草莓(Fragaria × ananassa)[48]、杏(Prunus armeniaca L.)[49]、桃(Prunus persica)[50]、香蕉(Musa acuminate)[51]和山番木瓜(Vasconcellea pubescens)[8]等的研究均表明Expansin的表达与果实软化有关。Palapol等[24]研究发现DzEXP1和DzEXP2的表达与榴莲果实软化呈正相关,乙烯可促进果肉软化和二者的表达,而1-MCP则抑制果肉软化和二者的表达。抑制Sl-EXP1的表达可显著提高番茄果实的硬度,而超表达Sl-EXP1则使番茄果实变软[5, 25]。这些研究均表明Expansin直接或间接参与果实软化。成熟的三月李及其红肉突变体果肉均迅速变软。但值得注意的是,本研究鉴定的9个差异表达Expansin的表达均未呈现与三月李及其红肉突变体果实成熟和软化一致的趋势。Zerpa-Catanho等[52]在番木瓜上也发现了类似结果,分析了成熟相关基因与采后番木瓜软化的关系,发现Expansin与果实软化不存在相关性。不同植物Expansin在果实成熟软化过程中的功能差异可能与物种有关。Expansin在李果实成熟过程中的具体功能及其是否直接参与李果实软化过程还有待进一步研究。
本研究通过生物信息学分析从三月李及其红肉突变体果实成熟过程的转录组数据中鉴定出33个Expansin家族基因,并对Expansin蛋白质的特征和基因表达模式进行分析,为今后进一步研究Expansin家族基因在李果实成熟过程中的功能奠定基础。
-
表 1 PCR引物及其序列
Table 1 PCR primers and sequences
引物名称
Primer name引物序列(5′-3′)
Primer sequence(5′-3′)3F26-F1 GGTTTGTGCCATACTCCGATAG 3F26-F2 GAGTGGTGACTTGAACAATCTG dT-adapt CTGATCTAGAGGTACCGGATCCTTTTTTTTTTTTTTTTT adapt CTGATCTAGAGGTACCGGATCC F26-F TTTGGATCCATGTCTCTGTCCCTGTCTTTTA F26-R GAAGAGCTCTCAATACAATGCAGTGACGCT F26G-F CCAATCCAGCACAAGTAACA F26G-R CCATTGGTAAATACTGACGG ArACT-F GCATAGCCTTCATAGATGGG ArACT-R GAGGACATTCAGCCACTTG 注:下划线碱基为酶切位点。
Note:The underlined bases were the enzyme site. -
[1] 刘星, 余江丽, 刘敏, 等. 近10年甾体皂苷的生物活性研究进展 [J]. 中国中药杂志, 2015, 40(13):2518−2523. LIU X, YU J L, LIU M, et al. Research progress of bioactivity of steroidal saponins in recent ten years [J]. China Journal of Chinese Materia Medica, 2015, 40(13): 2518−2523.(in Chinese)
[2] 黄圆圆, 刘大会, 彭华胜, 等. 15种重楼属植物中8种甾体皂苷的含量测定 [J]. 中国中药杂志, 2017, 42(18):3443−3451. HUANG Y Y, LIU D H, PENG H S, et al. Determination of eight steroidal saponins in 15 kinds of genus Paris [J]. China Journal of Chinese Materia Medica, 2017, 42(18): 3443−3451.(in Chinese)
[3] 旷湘楠, 刘时乔. 麦冬中甾体皂苷类化学成分研究 [J]. 广州化工, 2017, 45(22):85−87. DOI: 10.3969/j.issn.1001-9677.2017.22.030 KUANG X N, LIU S Q. Steroidal saponins from Tuber of Ophiopogon japonicas [J]. Guangzhou Chemical Industry, 2017, 45(22): 85−87.(in Chinese) DOI: 10.3969/j.issn.1001-9677.2017.22.030
[4] 李琳玉, 刘星, 周梦, 等. 小果菝葜根茎的甾体皂苷类化学成分研究 [J]. 中药材, 2017, 40(9):2084−2088. LI L Y, LIU X, ZHOU M, et al. Steroidal saponins from the rhizomes of Smilax davidiana [J]. Journal of Chinese Medicinal Materials, 2017, 40(9): 2084−2088.(in Chinese)
[5] 金明, 仙靓, 孙丽娜, 等. 盾叶薯蓣中甾体皂苷的分离与结构鉴定 [J]. 西北药学杂志, 2017, 32(4):395−399. DOI: 10.3969/j.issn.1004-2407.2017.04.001 JIN M, XIAN L, SUN L N, et al. Isolation and structure identification of steroid saponins from Dioseorea zingiberensis C.H.Wright [J]. Northwest Pharmaceutical Journal, 2017, 32(4): 395−399.(in Chinese) DOI: 10.3969/j.issn.1004-2407.2017.04.001
[6] 尹艳, 关红雨, 张夏楠. 甾体皂苷生物合成相关酶及基因研究进展 [J]. 天然产物研究与开发, 2016, 28(8):1332−1336. YIN Y, GUAN H Y, ZHANG X N. Review on enzymes and genes related to the biosynthesis of steroidal saponins [J]. Natural Product Research and Development, 2016, 28(8): 1332−1336.(in Chinese)
[7] 黄楚君, 蔡金艳, 倪俊, 等. 束花石斛化学成分研究 [J]. 广东药学院学报, 2016, 32(3):279−281. HUANG C J, CAI J Y, NI J, et al. Study on chemical constituents from Dendrobium chrysanthum Wall. ex Lindl [J]. Journal of Guangdong Pharmaceutical University, 2016, 32(3): 279−281.(in Chinese)
[8] 刘海, 杨建琼, 马华谋, 等. 吉祥草中甾体皂苷成分及其抗肿瘤活性研究 [J]. 中药新药与临床药理, 2015, 26(3):348−351. LIU H, YANG J Q, MA H M, et al. Analysis of steroidal saponins from reineckia carnea and their antitumor activities [J]. Traditional Chinese Drug Research and Clinical Pharmacology, 2015, 26(3): 348−351.(in Chinese)
[9] BARILE E, BONANOMI G, ANTIGNANI V, et al. Saponins from Allium minutiflorum with antifungal activity [J]. Phytochemistry, 2007, 68(5): 596−603. DOI: 10.1016/j.phytochem.2006.10.009
[10] INOUE K, SHIBUYA M, YAMAMOTO K, et al. Molecular cloning and bacterial expression of a cDNA encoding furostanol glycoside 26-O-β-glucosidase of Costus speciosus [J]. FEBS Letters, 1996, 389(3): 273−277. DOI: 10.1016/0014-5793(96)00601-1
[11] 王亮, 游松, 蒋雅红, 等. 利用重组F26G酶实现呋甾皂苷向螺甾皂苷的体外生物转化 [J]. 中国药物化学杂志, 2001, 11(6):326−328. DOI: 10.14142/j.cnki.cn21-1313/r.2001.06.004 WANG L, YOU S, JIANG Y H, et al. Bioconversion in vitro from furostanol glycoside to spirostanol glycoside catalyzed by recombinated F26G [J]. Chinese Journal of Medicinal Chemistry, 2001, 11(6): 326−328.(in Chinese) DOI: 10.14142/j.cnki.cn21-1313/r.2001.06.004
[12] NAKAYASU M, KAWASAKI T, LEE H J, et al. Identification of furostanol glycoside 26-O-β-glucosidase involved in steroidal saponin biosynthesis from Dioscorea esculenta [J]. Plant Biotechnology, 2015, 32(4): 299−308. DOI: 10.5511/plantbiotechnology.15.1023b
[13] 张超, 吴建国, 易骏, 等. HPLC-ELSD法测定三种植物基原金线莲的金线莲苷含量 [J]. 食品工业科技, 2017, 38(2):75−78. ZHANG C, WU J G, YI J, et al. Content determination of kinsenoside in Jin-Xian-Lian from three Anoectochilus species by HPLC-ELSD [J]. Science and Technology of Food Industry, 2017, 38(2): 75−78.(in Chinese)
[14] 施满容, 龚林光, 陆志平, 等. 不同地区野生金线莲有效成分含量的比较 [J]. 安徽农学通报, 2016, 22(24):107−110. DOI: 10.3969/j.issn.1007-7731.2016.24.047 SHI M R, GONG L G, LU Z P, et al. The comparison of effective composition content in different localities of wild Anoectochilus roxburhii [J]. Anhui Agricultural Science Bulletin, 2016, 22(24): 107−110.(in Chinese) DOI: 10.3969/j.issn.1007-7731.2016.24.047
[15] 张锦文, 唐菲, 张小琼, 等. 高效液相色谱法测定金线莲中金线莲苷的含量 [J]. 中国医院药学杂志, 2011, 31(4):261−263. ZHANG J W, TANG F, ZHANG X Q, et al. Determination of the content of kinsenoside in Anoectochilus roxburhii (Wall.) Lindl by HPLC [J]. Chinese Journal of Hospital Pharmacy, 2011, 31(4): 261−263.(in Chinese)
[16] 王勇, 陈硕, 卢端萍, 等. 金线莲化学成分的研究 [J]. 中草药, 2017, 48(13):2619−2624. WANG Y, CHEN S, LU D P, et al. Chemical constituents of Anoectochilus roxburhii [J]. Chinese Traditional and Herbal Drugs, 2017, 48(13): 2619−2624.(in Chinese)
[17] 吴丽丽, 梁燕, 许光辉. 金线莲化学成分、药理作用及临床应用研究概述 [J]. 海峡药学, 2014, 26(10):34−37. DOI: 10.3969/j.issn.1006-3765.2014.10.013 WU L L, LIANG Y, XU G H. Advances on investigation of chemical components, pharmacological activities and clinical applications of Anoectochilus roxburhii [J]. Strait Pharmaceutical Journal, 2014, 26(10): 34−37.(in Chinese) DOI: 10.3969/j.issn.1006-3765.2014.10.013
[18] 肖小华, 林彩霞, 吴序栎, 等. 金线莲的化学成分及生物活性研究进展 [J]. 现代食品科技, 2018, 34(5):267−275. XIAO X H, LIN C X, WU X L, et al. Research advance on chemical constituents and biological activities of Anoectochilus roxburhii [J]. Modern Food Science and Technology, 2018, 34(5): 267−275.(in Chinese)
[19] TAMURA K, STECHER G, PETERSON D, et al. MEGA6: molecular evolutionary genetics analysis version 6.0 [J]. Molecular Biology and Evolution, 2013, 30(12): 2725−2729. DOI: 10.1093/molbev/mst197
[20] 林江波, 王伟英, 李海明, 等. 中国水仙锌指蛋白NtPLATZ1的克隆与表达分析 [J]. 西北农林科技大学学报(自然科学版), 2016, 44(10):165−170. LIN J B, WANG W Y, LI H M, et al. Cloning and expression analysis of NtPLATZ1 gene from Narcissus tazetta var. chinensis [J]. Journal of Northwest A & F University(Natural Science Edition), 2016, 44(10): 165−170.(in Chinese)
[21] 林江波, 王伟英, 邹晖, 等. 金线莲3个持家基因表达稳定性分析 [J]. 福建农业学报, 2018, 33(11):1125−1129. LIN J B, WANG W Y, ZOU H, et al. Expression stabilities of three housekeeping genes of Anoectochilus roxburhii [J]. Fujian Journal of Agricultural Sciences, 2018, 33(11): 1125−1129.(in Chinese)
[22] MORANT A V, JØRGENSEN K, JØRGENSEN C, et al. β-Glucosidases as detonators of plant chemical defense [J]. Phytochemistry, 2008, 69(9): 1795−1813. DOI: 10.1016/j.phytochem.2008.03.006
[23] CHEN Y N, WANG L, REN J, et al. The selective biotransformation of furostanol glycosides and their analogs by recombined F-26-O-β-glucosidase [J]. Asian Journal of Traditional Medicines, 2009, 4(1): 7−13.
-
期刊类型引用(2)
1. 林炎娟,叶新福,方智振,周丹蓉. 福红李三个成熟阶段果实营养品质与香气特征分析. 核农学报. 2024(04): 725-735 .  百度学术
百度学术
2. 曾美娟,刘建汀,李祖亮,陈敏氡,叶新如,王彬,朱海生,温庆放. 普通丝瓜GH3基因家族全基因组鉴定及表达分析. 江苏农业科学. 2022(18): 82-87 .  百度学术
百度学术
其他类型引用(0)




 下载:
下载: