Deep Eutectic Solvents Extraction of Polyphenols from Tieguanyin Tea Optimized by Response Surface Method
-
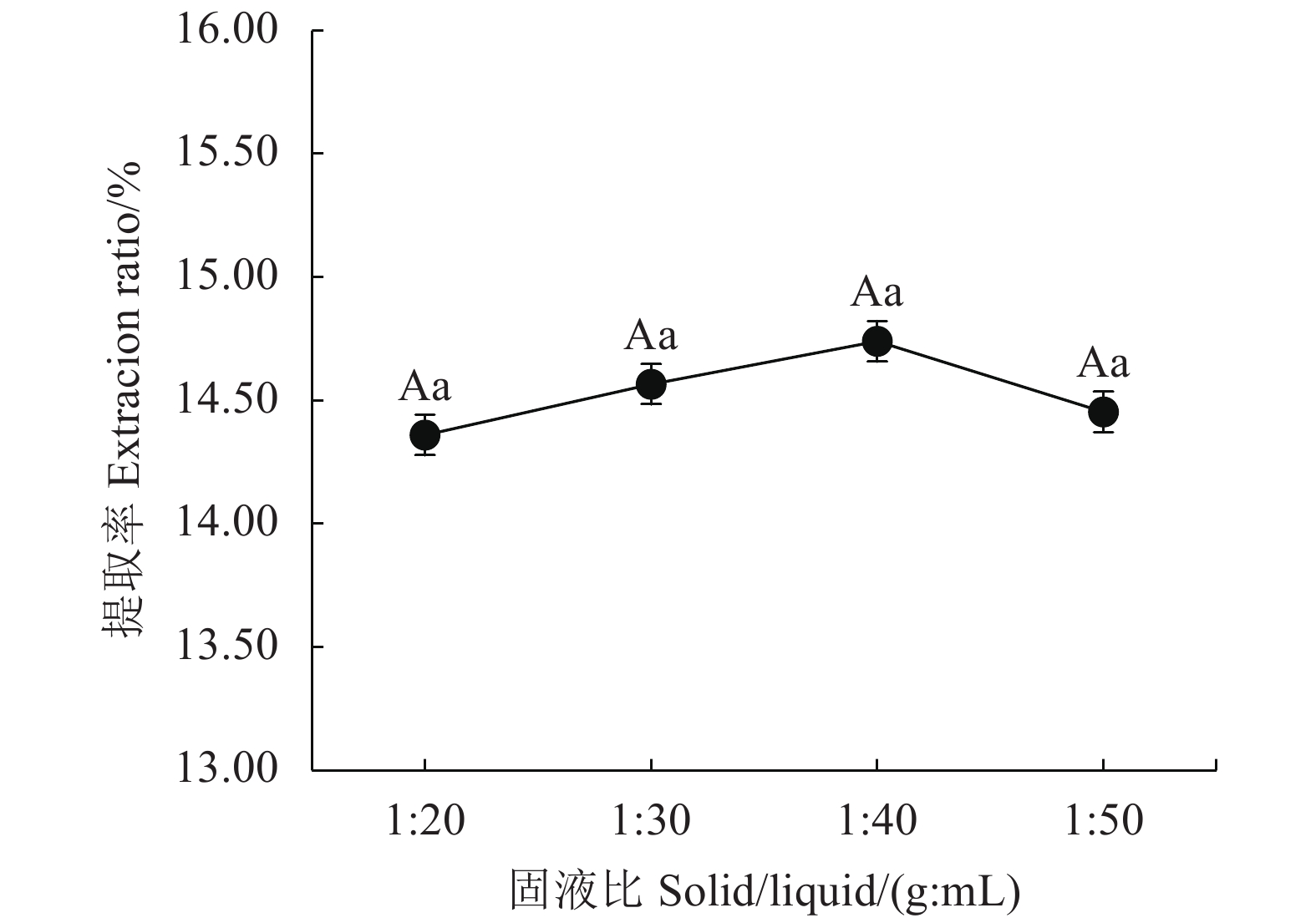
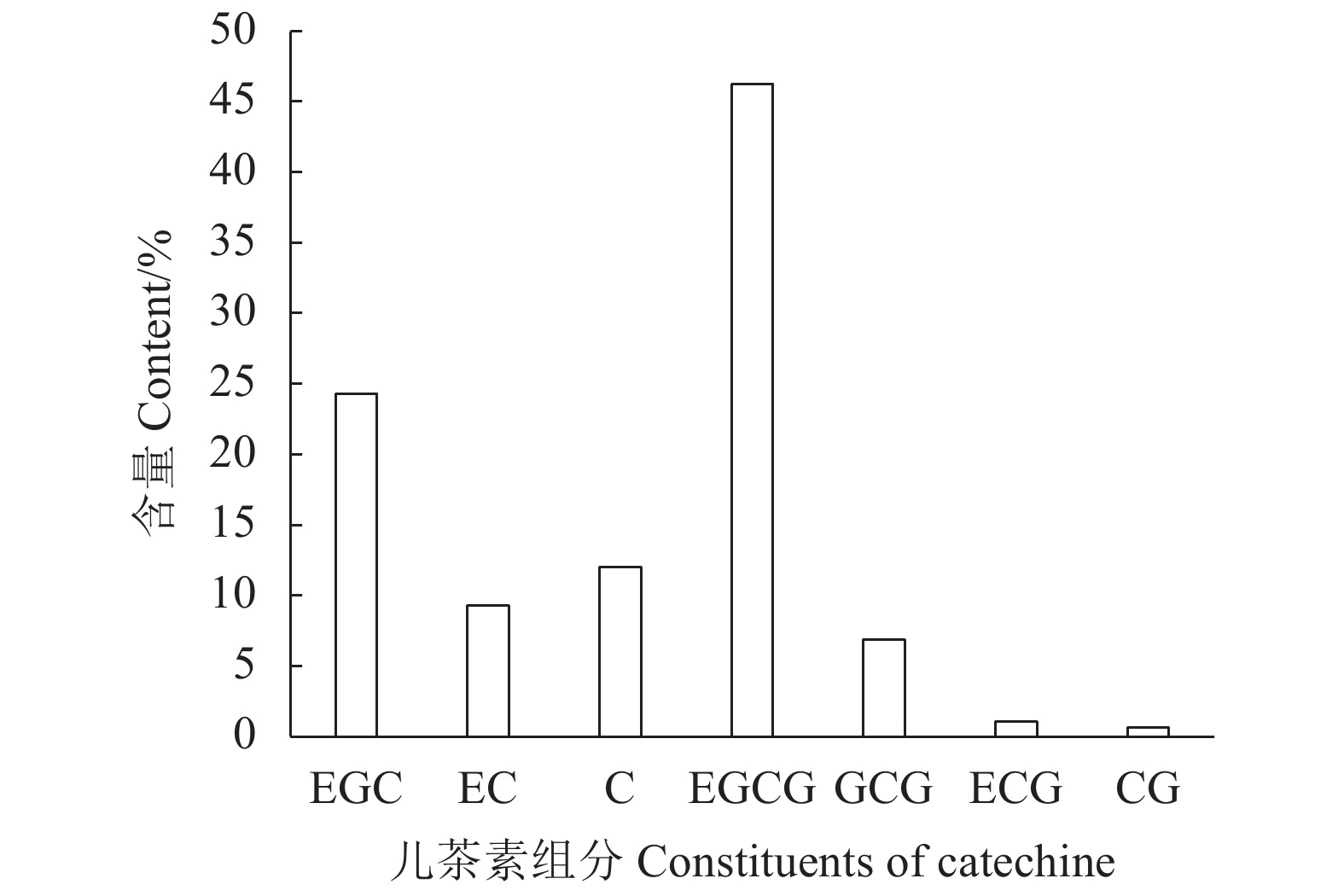
摘要:目的 探索一种绿色、环保、安全、高效的铁观音茶多酚提取新方法,为茶多酚绿色提取提供新的技术参考。方法 以铁观音成品茶为原料,采用新型绿色溶剂——低共熔溶液提取茶多酚;首先筛选出最优的低共熔溶液提取体系,然后在单因素试验的基础上,通过响应面法优化,研究时间、温度、溶液含水率对提取率的影响,得出最佳提取条件并分析其主要成分;最后通过测定DPPH自由基清除率分析茶多酚的抗氧化能力。结果 筛选出最适的茶多酚低共熔溶液提取体系为:乳酸-甜菜碱,其次得到最佳单因素提取条件为提取时间40 min、提取温度60℃、含水率30%、摩尔比2 ∶ 1、固液比1 ∶ 40(g : mL);响应面优化分析得到最佳提取条件为:时间46.79 min、温度62.48℃、溶液含水率32.15%,在此条件下茶多酚提取率为15.42%。通过高效液相色谱分析茶多酚组分,其中没食子酸含量占1.40%,儿茶素类物质占84.99%,其他组分占13.61%。低共熔溶液法提取的茶多酚DPPH自由基半清除浓度(IC50)值73.89 μg·mL−1,比抗坏血酸提高了37.80%。结论 采用响应面法优化得出的低共熔溶液提取茶多酚最佳工艺条件,可有效提高铁观音茶多酚提取率。Abstract:Objective A green, environmentally friendly, safe and efficient process to extract polyphenols from tea was explored and optimized using the response surface method.Methods Tieguanyin tea was used for the extraction with deep eutectic solvents (DESs). After the DES was selected and a single factor experiment conducted, the time, temperature and water content in solvent were optimized for the process with respect of polyphenol extraction rate by a response surface experimentation. Antioxidant capacity of the extract was determined according to the DPPH radical scavenging rate.Results Lactic acid and betaine of a molar ratio of 2:1 with a water content of 30% and a substrate-to-solvent ratio of 1:40 (g:mL) were chosen for the extraction at 60oC for 40 min. The response surface method optimized the process to apply a moisture content of 32.15% of DESs for a 46.79 min-extraction at 62.48℃ with a yield of polyphenols at 15.42%. The polyphenol extract was analyzed by HPLC to show a gallic acid content of 1.40%, catechins of 84.99%, and the remainders of 13.61%. The semi-scavenging concentration (IC50) of the extract was 73.89 μg·mL-1, which was 37.80% higher than that of ascorbic acid.Conclusion The newly developed DESs extraction significantly improved the polyphenol extraction rate from Tieguanyin tea over the conventional process.
-
Keywords:
- deep eutectic solvents /
- Tieguanyin /
- tea polyphenol /
- antioxidant activity /
- chemical analysis
-
0. 引言
【研究意义】海带(Laminaria japonica Aresch)又名纶布、昆布,素有“海上之蔬”、“含碘冠军”的美誉,是我国重要的经济海藻,产量位居世界首位[1]。海带虽然价格低廉,但富含碘、甘露醇、维生素A、维生素B族、维生素C、牛磺酸、多糖等功效成分[2],海带含有多种生物活性物质,如海带多糖、昆布氨酸、牛磺酸等,其中海带多糖具有调节免疫、抗肿瘤、抗凝血、抗氧化、降血脂(糖)等独特的功效,在食品、医药、化妆品、农业等方面都具有广阔的应用前景[3-4]。采用自然日晒方法将海带加工成干制品是海带加工的主要方式,但自然日晒方法受自然环境因素的影响,存在易霉变及活性成分损失大等问题,成品品质良莠不齐。因此研发可提高海带干制品质量的现代干燥技术具有重要意义。【前人研究进展】干燥方法会影响干制产品的质量,同样的原料采用不同的干燥方法可以生产出品质完全不同的产品[5]。微波具有穿透性,因此真空微波干燥技术可以有效控制生鲜食品干燥过程的干缩,提高干制品的复水速率和复水比[6],减少多糖等功效成分的损失,并提高其抗氧化活性[7];微波辅助提取技术也可以提高多糖等功效成分的提取率[8];而且不同的微波功率密度对于物料干燥特性和蛋白质等营养成分保留率都有较大的影响[9-10]。【本研究切入点】已有研究表明微波处理可以提高海带多糖的提取率[11],而且真空微波应用于海带干燥加工可以有效改善干制品的复水性等品质指标[6];然而关于干燥加工,特别是不同微波功率密度的真空微波干燥对海带多糖的影响还未见报道。【拟解决的关键问题】本研究采用自然日晒、热风干燥、真空干燥,以及两种不同微波功率密度真空微波-真空组合干燥5种方法对新鲜海带进行干燥,研究不同干燥方法对海带多糖的得率及其特性的影响,旨在为获取高品质海带的干燥方法提供理论依据。
1. 材料与方法
1.1 试验材料
新鲜海带由莆田市后海垦区现代农业发展有限公司提供。
1.2 仪器与设备
RX-16ZK多功能真空微波干燥箱(带电热管加热功能,广州荣兴工业微波设备有限公司产品),DHG-9070A 型电热恒温鼓风干燥箱(上海一恒科技有限公司),NDJ-8S 型数显黏度计(上海菁海仪器有限公司),UV-1900紫外可见分光光度计(上海翱艺仪器有限公司)等。
1.3 试验方法
1.3.1 原料处理
新鲜海带用自来水洗净,切除根部及周边较薄部分,切成1 cm×5 cm规格的海带条,沥去表面水分后用保鲜袋包装,置于5℃冰箱冷藏备用。
1.3.2 干燥试验
(1)2 W·g−1真空微波-真空组合干燥(VM-VD1)
2 000 g鲜海带条以厚度约0.6 cm薄层平铺于带硅胶垫的聚四氟乙烯盘内,在微波功率4 kW、压力−0.085~−0.090 MPa、温度(50±2)℃条件下干燥至海带条含水量30%左右,关闭微波,开启电热管,继续在压力−0.085~−0.090 MPa、电热管功率8 kW、温度(60±2)℃条件下干燥至终点。
(2)4 W·g−1真空微波-真空组合干燥(VM-VD2)
微波功率改为8 kW,其余同1.3.2(1)。
(3)真空干燥(VD)
2 000 g鲜海带条以厚度约0.6 cm薄层平铺于带硅胶垫的聚四氟乙烯网盘上,在压力−0.085~−0.090 MPa、电热管功率8 kW、温度(60±2)℃条件下干燥至终点。
(4)热风干燥(AD)
2 000 g鲜海带条以厚度约0.6 cm薄层平铺于带硅胶垫的聚四氟乙烯网盘上,置于预热到设定温度的恒温鼓风干燥箱内,在温度(60±1)℃、开启鼓风开关的条件下干燥至终点。
(5)自然日晒(ND)
2 000 g鲜海带条以厚度约0.6 cm薄层平铺于带硅胶垫的聚四氟乙烯网盘上,白天置于阳光强烈照射的通风处,夜晚收至室内,晒3 d后至终点。
1.3.3 海带粉制备
海带条水分含量低于8%为干燥终点,将不同干燥方法制备的干海带条粉碎至80目备用。
1.3.4 试验指标及测定方法
(1)海带多糖制备及多糖得率测定
海带多糖的提取参考余华等的方法[12],称取一定重量的海带粉,加25倍蒸馏水于90℃水浴提取6 h,混合液冷却后5 000 r·min−1离心15 min,沉淀中加入海带粉15倍蒸馏水重复提取1次,合并上清液,浓缩至原体积的1/5,加入浓缩液5倍体积的95%乙醇,5℃静置过夜,5 000 r·min−1离心5 min,沉淀冷冻干燥得到海带粗多糖。海带粗多糖用蒸馏水配制成2.0 mg·mL−1的海带粗多糖溶液备用。
多糖含量采用苯酚-硫酸比色法[13]测定。吸取l.0 mL海带粗多糖溶液于具塞试管中,加入1.0 mL 6%苯酚溶液,摇匀后加入5.0 mL浓硫酸,混匀后沸水浴10 min,冷却至室温,于490 nm处测吸光值。以葡萄糖标准品作标准曲线,计算多糖含量。
海带多糖得率(%)=海带粗多糖质量海带干粉质量×多糖含量×100% (2)海带多糖硫酸根含量的测定
采用明胶-氯化钡法测量[14]。称取一定重量的冻干海带粗多糖样品(约20 mg),加入15 mL浓HCl和4.5 mL浓HNO3硝化至微黄色止,消化液定容到50 mL,取2.5 ml硝化液,加入2.5 ml 明胶-氯化钡溶液混匀,静置15 min,于360 nm处测定吸光值。以硫酸钾标准品作标准曲线,计算海带多糖样品中硫酸根含量。
(3)海带多糖黏度的测定
用蒸馏水配制20.0 mg·mL−1的海带粗多糖溶,在20±2℃条件下,选用旋转黏度计2号转子,转速30 r·min−1测定海带多糖黏度。
(4)海带多糖清除羟自由基(·OH)活性的测定
参考孙玉军等的方法[15],在4 mL海带多糖溶液中,分别加入9 mmol·L−1 FeSO4、9 mmol·L−1水杨酸-乙醇溶液和8.8 mmol·L−1 H2O2各0.5 mL,在37℃下反应0.5 h,以蒸馏水代替海带多糖溶液作为空白对照,于510 nm波长处测吸光度值。
清除率计算公式:
⋅OH清除率(%)=A0−AA0×100% 式中:A0
为空白对照管的吸光度值; A为样品管的吸光度值。
(5)海带多糖清除超氧阴离子自由基(O2−·)活性的测定
参考孙玉军等的方法[15],吸取50 mmol·L−1、pH 8.0的Tis-HCl缓冲液4.5 mL,25℃水浴20 min,加入4.0 mL海带粗多糖溶液和0.1 mL 25 mmol·L−1邻苯三酚溶液(以10 mmol·L−1的HCl配制),混匀,25℃反应5 min,加入1 mL 8 mol·L−1HCl终止反应,以Tis-HCl缓冲液代替样品作为空白对照,在300 nm波长处测定吸光度值。
清除率计算公式:
O2−⋅清除率(%)=A0−AA0×100% 式中:A0空白对照管的吸光度值;
A为样品管的吸光度值。
1.3.5 统计分析
所有试验均重复3次,结果取平均值±标准差表示,采用Origin 8.5和SPSS 24软件进行数据处理。
2. 结果与分析
2.1 干燥方法对海带多糖得率的影响
不同干燥方法对海带多糖的得率(图1)有显著影响(P<0.05);多糖得率由小到大的顺序依次为:自然日晒、热风干燥、真空干燥、2 W·g−1真空微波-真空组合干燥、4 W·g−1真空微波-真空组合干燥。即采用自然日晒海带的多糖得率最低,为7.87%;而采用4 W·g−1真空微波-真空组合干燥海带的多糖得率最高,为13.83%。该结果表明,不同干燥方法会显著影响海带多糖的得率,其中自然日晒会导致海带多糖有较大的损失;而较高的微波功率密度(4 W·g−1)有利于提高海带多糖得率。
2.2 干燥方法对海带多糖SO42−含量的影响
不同干燥方法对海带多糖SO42−含量的影响见图2。海带多糖SO42−含量由小到大的顺序依次为:自然日晒、热风干燥、真空干燥、4 W·g−1真空微波-真空组合干燥、2 W·g−1真空微波-真空组合干燥。采用自然日晒海带的多糖SO42−含量最低,为5.71%,明显低于其他方法干燥海带的多糖SO42−含量(P<0.05);而采用2 W·g−1真空微波-真空组合干燥海带的多糖SO42− 含量最高(8.79%),明显高于自然日晒、热风干燥和真空干燥的海带样品(P<0.05),但与4 W·g−1微波功率密度的真空微波-真空组合干燥海带的多糖SO42−含量差异不显著(P>0.05)。
2.3 干燥方法对海带多糖黏度的影响
黏度可以粗略反映出多糖的组分及分子量情况,对于相同浓度的海带多糖溶液,多糖分子量大则其黏度高,反之则低。由图3可以看出,采用真空干燥和热风干燥海带的多糖黏度显著高于自然日晒和两种真空微波-真空组合干燥海带的多糖黏度(P<0.05);而采用4 W·g−1真空微波-真空组合干燥海带的多糖黏度最低。相对热风干燥和真空干燥,自然日晒海带的多糖黏度较低,说明海带在自然日晒过程中其多糖降解率较高;两种真空微波-真空组合干燥海带的多糖黏度较低,而且较高的微波功率密度(4 W·g−1)组合干燥海带的多糖黏度显著低于较低的微波功率密度(2 W·g−1)组合干燥海带的多糖黏度(P<0.05),说明微波干燥会导致海带多糖的降解,而且微波功率密度越高其降解作用越强。
2.4 干燥方法对海带多糖体外抗氧化活性的影响
不同干燥方法对海带多糖清除羟自由基和超氧阴离子自由基活性的影响分别见图4和图5。其清除率由大到小的顺序均为:2 W·g−1真空微波-真空组合干燥、4 W·g−1真空微波-真空组合干燥、真空干燥、热风干燥、自然日晒。该结果表明,干燥方法对海带多糖的体外抗氧化活性有显著的影响(P<0.05);自然日晒会导致海带多糖的体外抗氧化活性大幅降低;相对于热风干燥,真空干燥可减缓海带多糖体外抗氧化活性的损失;真空微波-真空组合干燥海带多糖的体外抗氧化活性较高,而且较高的微波功率密度(4 W·g−1)干燥的海带多糖体外抗氧化活性较低(P<0.05),说明较高的微波功率密度会造成海带多糖体外抗氧化活性的损失。
![]() 图 5 干燥方法对海带多糖清除超氧阴离子自由基(O2−·)能力的影响注:图柱顶部不同小写字母表示处理间差异显著(P<0.05)。Figure 5. Effect of drying methods on superoxide anion radical scavenging activity of polysaccharide in dried L. japonicaNote: Data with different lowercase letters on top of a column indicate significant differences among treatments at P<0.05.
图 5 干燥方法对海带多糖清除超氧阴离子自由基(O2−·)能力的影响注:图柱顶部不同小写字母表示处理间差异显著(P<0.05)。Figure 5. Effect of drying methods on superoxide anion radical scavenging activity of polysaccharide in dried L. japonicaNote: Data with different lowercase letters on top of a column indicate significant differences among treatments at P<0.05.3. 讨论与结论
多糖是生物体内普遍存在的一类生物大分子,具有特殊的生物活性;干燥过程会导致多糖的损失,而且干燥温度越高、时间越长,损失率越高[16]。自然日晒海带的多糖得率、SO42−含量、黏度和体外抗氧化活性低于热风干燥和真空干燥样品,应该是由于受阳光中紫外线及环境中微生物等因素的影响而导致海带多糖发生降解所致。相对于热风干燥,真空干燥可保持海带较低的品温,从而减少多糖的损失;段梦颖等[17]研究也发现真空干燥的聚合草多糖得率、SO42−含量、黏度均高于热风干燥样品。真空微波-真空组合干燥海带的多糖得率、SO42−含量和抗氧化活性较高,而黏度较低,这可能是由于微波干燥时间短,多糖损失少,但微波对多糖具有降解作用所致[18]。对于两种不同微波功率密度的真空微波-真空组合干燥,增大微波功率密度虽然可以提高海带多糖的得率,但也会降低多糖的SO42−含量、黏度和体外抗氧化活性,这是由于较高的微波功率密度对海带细胞结构的破坏作用较强,有利于胞内多糖的溶出[19],从而提高其得率,但也会导致海带多糖因过度降解而损失。
从海带中提取的粗多糖主要包括褐藻胶、褐藻糖胶和褐藻淀粉,其中褐藻糖胶是一种硫酸多糖,也是海带多糖中主要的生物活性成分[20],因此硫酸根含量是考察海带多糖生物活性的重要指标之一[21]。此外,多糖的生物活性与其分子量及其分布有关[22],而黏度可以粗略地反映出多糖的组分及分子量情况。多糖分子量大则黏度高,而黏度过高不利于多糖在体内的扩散和吸收,会降低其生物活性,因此对多糖进行适度降解,有利于提高其生物活性[23]。
真空微波-真空组合干燥技术可以有效减少干燥过程海带多糖的损失,但微波会导致海带多糖的降解,而且微波功率密度越高,其降解作用越强。因此,只有适宜微波功率密度的真空微波-真空组合干燥才是生产高品质海带干制品的有效途径。
-
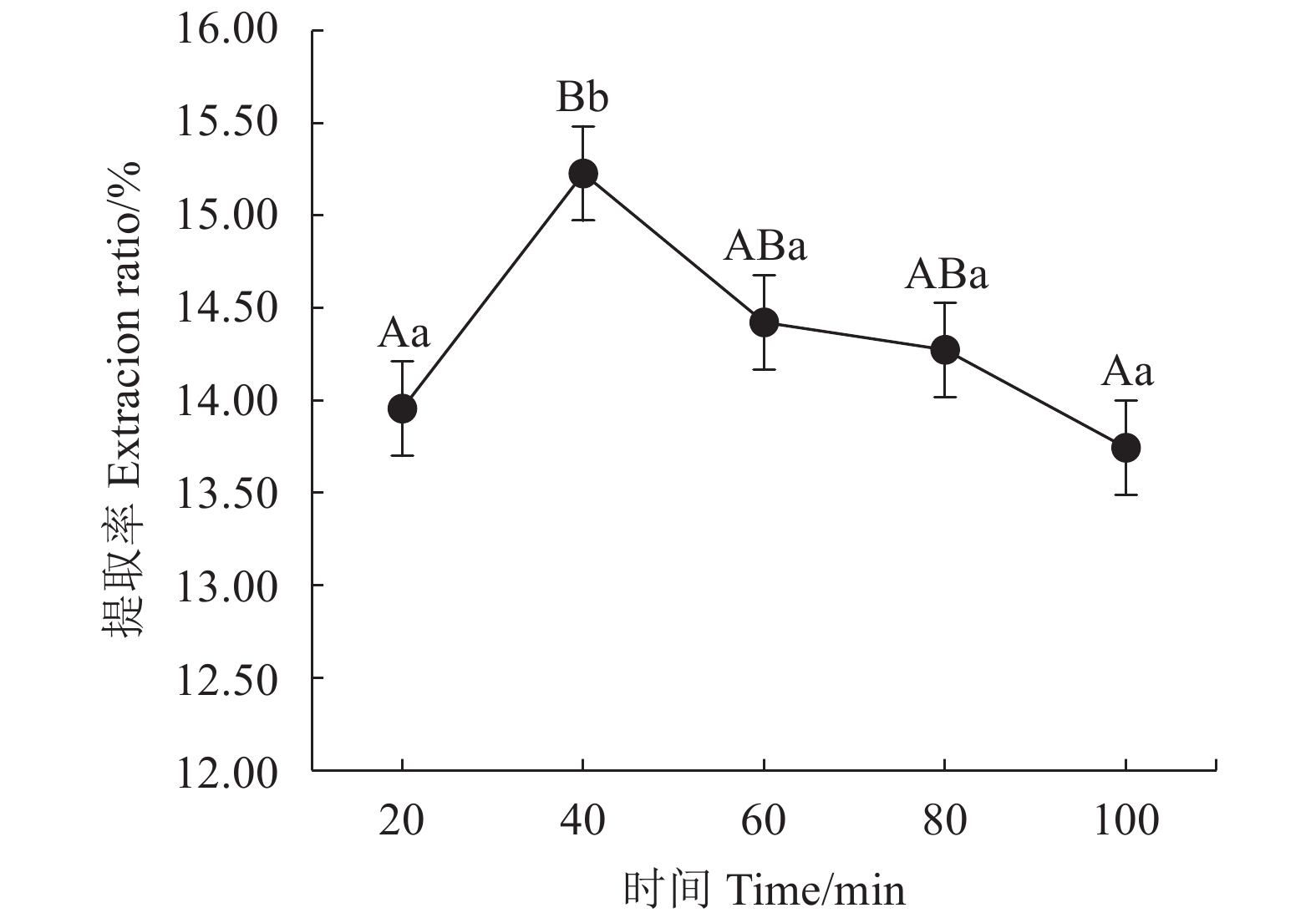
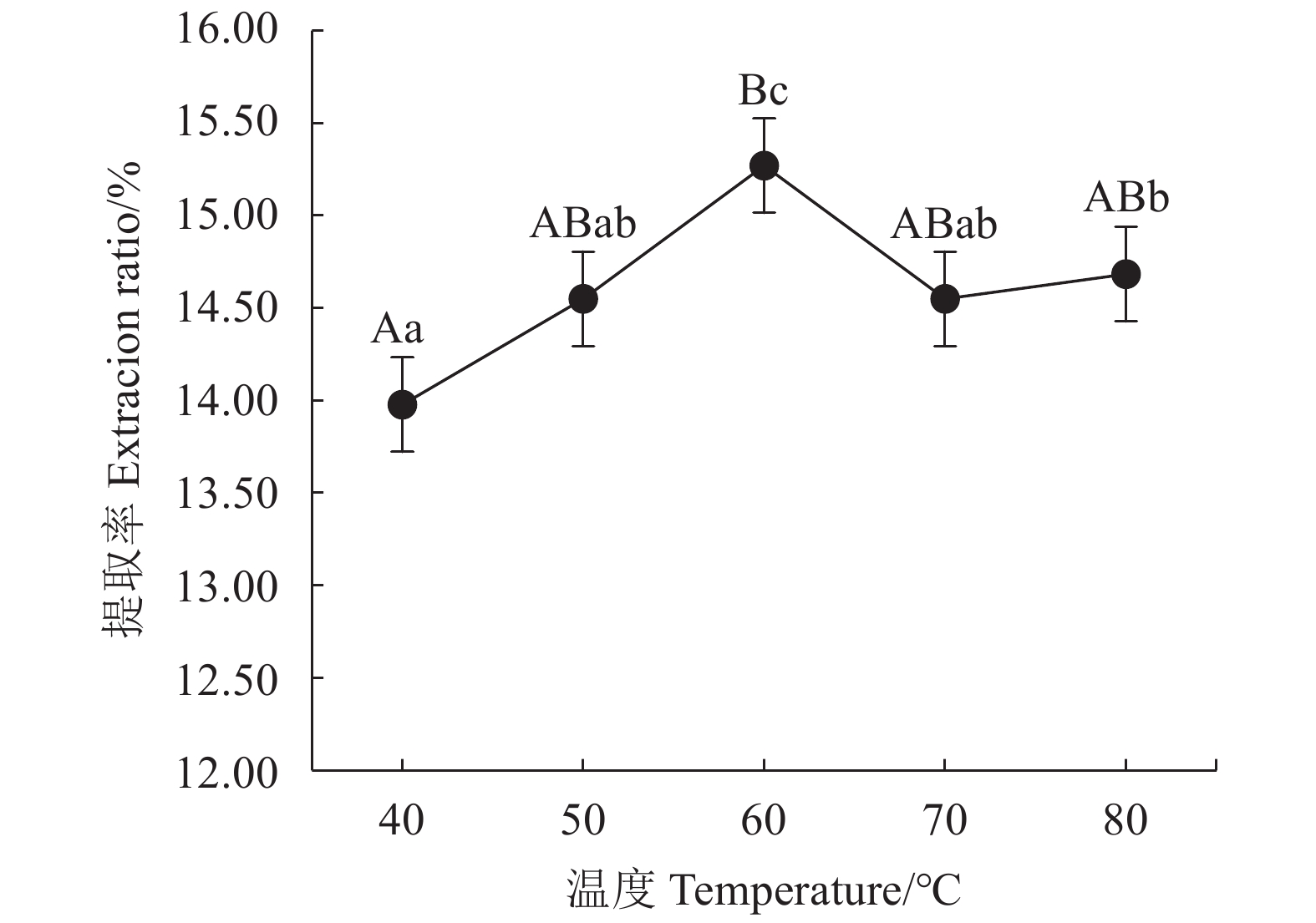
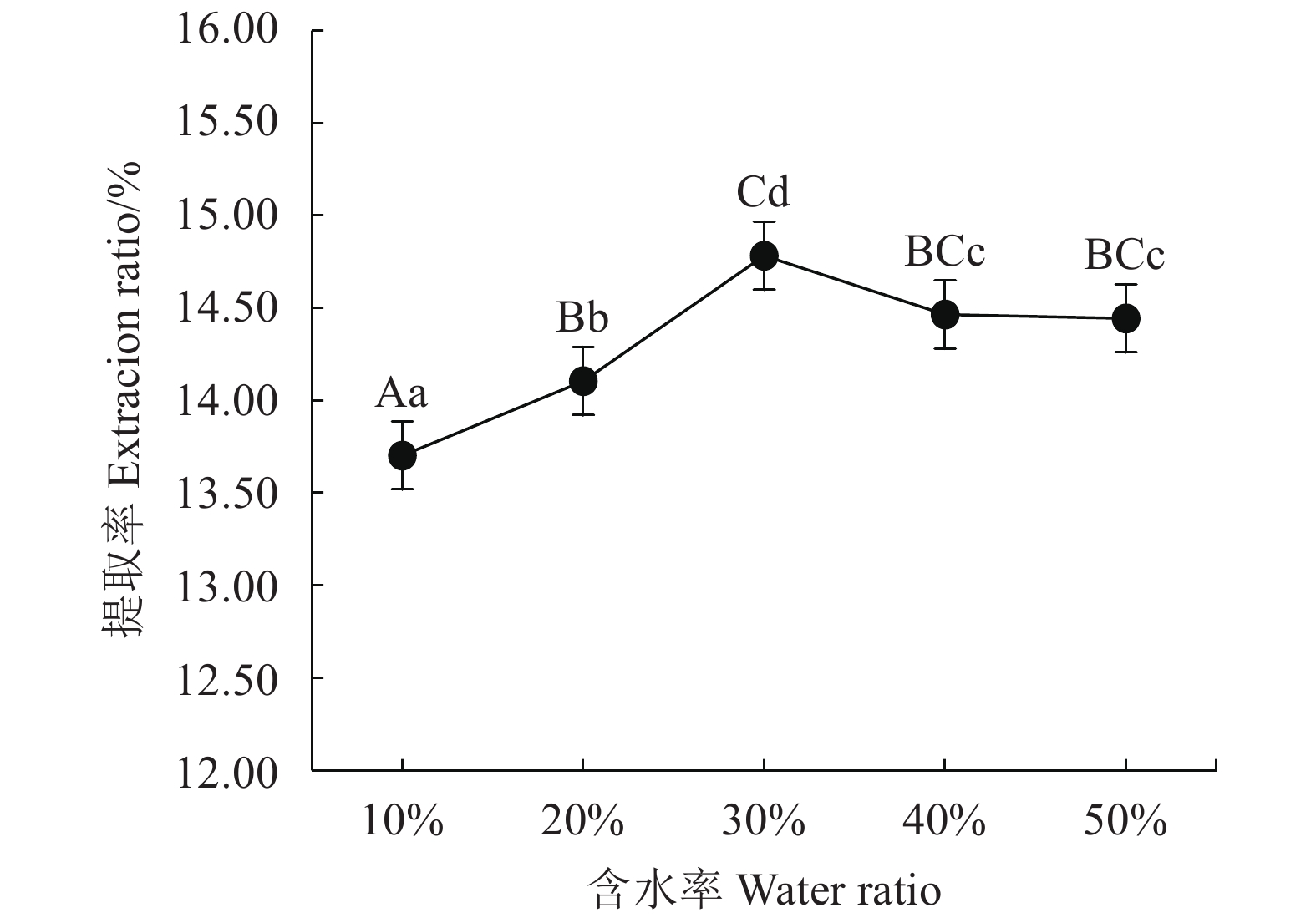
表 1 Box-Behnken试验因素水平及编码
Table 1 Factors and coding levels in Box-Behnken experiment
水平
Levels因素 Factors A时间
Time/minB温度
Temperature/℃C溶液含水率
Water raito of solvent/%−1 20 50 20 0 40 60 30 1 60 70 40 表 2 不同低共熔溶液体系提取茶多酚
Table 2 DESs for polyphenol extraction
名称
Name提取率
Extraction ratio/%相对水提取提高
Aqueous extraction ratio exceeded by DES/%水 Water 8.61±0.27Aa 果糖/氯化胆碱
Fructose/Choline chloride12.47±0.74Bb 44.90 乳酸/氯化胆碱
Lacticacid/Choline chloride12.69±0.81Bb 47.36 苹果酸/甜菜碱
Malicacid/Choline chloride12.68±0.68 Bb 47.24 柠檬酸/甜菜碱
Citricacid/Betaine12.79±0.54Bb 48.59 乳酸/甜菜碱
Lacticacid/Betaine14.40±0.53 Cc 67.29 注:同列数据后不同大、小写字母表示差异极显著(P<0.01)或差异显著(P<0.05)。
Note: Different uppercase and lowercase letters in the same column indicate extremely significant differences (P<0.01) and significant differences (P<0.05).表 3 响应面优化结果
Table 3 Response surface experiment and results
序号
NumberA时间
TimeB温度
TemperatureC含水率
Water ratioY提取率
Extraction ratio/%1 0 0 0 15.46 2 −1 0 1 14.68 3 0 0 0 15.33 4 0 0 0 15.40 5 −1 0 −1 13.93 6 0 −1 −1 13.62 7 −1 −1 0 14.37 8 1 0 −1 14.63 9 0 0 0 15.27 10 1 1 0 15.07 11 1 −1 0 14.74 12 0 1 1 14.88 13 0 1 −1 14.57 14 −1 1 0 14.86 15 0 −1 1 14.76 16 0 0 0 15.39 17 1 0 1 15.01 表 4 方差分析
Table 4 Regression statistical analysis
来源
Source平方和
Sum of square自由度
Degree of freedom均方
Mean squareF值
F valueP值
P value显著性
Significance模型 Model 4.13 9 0.46 48.03 <0.000 1 ** A时间 Time 0.32 1 0.32 33.89 0.000 6 ** B温度 Temperature 0.45 1 0.45 46.7 0.000 2 ** C含水率 Water raito 0.83 1 0.83 87.03 <0.000 1 ** AB 6.40×10−3 1 6.40×10−3 0.67 0.440 2 AC 0.034 1 0.034 3.58 0.100 4 BC 0.17 1 0.17 18.01 0.003 8 ** A2 0.27 1 0.27 28.08 0.001 1 ** B2 0.54 1 0.54 56.29 0.000 1 ** C2 1.3 1 1.3 135.65 <0.000 1 ** 残差 Resdual 0.067 7 9.561×10−3 失拟项 Lack of fit 0.046 3 0.015 2.92 0.164 纯误差 Pure error 0.021 4 5.250×10−3 总和 Cor total 4.2 16 注:*,P<0.05,表示显著差异;**,P<0.01,表示极显著差异。
Note: *, P<0.05, indicating significant difference; **, P<0.01, indicating extremely significant difference. -
[1] 黄欢, 赵展恒, 王玉娇, 等. 铁观音加工过程中咖啡碱、茶多酚、游离氨基酸含量变化研究 [J]. 福建农业学报, 2014, 29(3):282−285. DOI: 10.3969/j.issn.1008-0384.2014.03.017 HUANG H, ZHAO Z H, WANG Y J, et al. Study on the content change of caffeine, tea polyphenols and free amino acids in the Tie-Guanyin oolong tea machining process [J]. Fujian Journal of Agricultural Sciences, 2014, 29(3): 282−285.(in Chinese) DOI: 10.3969/j.issn.1008-0384.2014.03.017
[2] 冯欢欢, 陈识文, 高梦祥. β-环糊精结合响应面法优化茶多酚的提取工艺 [J]. 食品科技, 2014, 39(11):212−216. FENG H H, CHEN S W, GAO M X. Optimization of the extraction process of tea polyphenols from tea dust by response surface methodology and β-CD [J]. Food Science and Technology, 2014, 39(11): 212−216.(in Chinese)
[3] 陆爱霞, 姚开, 吕远平, 等. 茶多酚提取和应用研究进展 [J]. 食品科技, 2003, 28(2):53−55. DOI: 10.3969/j.issn.1005-9989.2003.02.020 LU A X, YAO K, Lü Y P, et al. Extraction and application of tea polyphenols [J]. Food Science and Technology, 2003, 28(2): 53−55.(in Chinese) DOI: 10.3969/j.issn.1005-9989.2003.02.020
[4] 赵晶晶, 刘宝友, 魏福祥. 低共熔离子液体的性质及应用研究进展 [J]. 河北工业科技, 2012, 29(3):184−189. DOI: 10.7535/hbgykj.2012yx0316 ZHAO J J, LIU B Y, WEI F X. Property and application of eutectic ionic liquid [J]. Hebei Journal of Industrial Science and Technology, 2012, 29(3): 184−189.(in Chinese) DOI: 10.7535/hbgykj.2012yx0316
[5] 杨申明, 王振吉, 王波. 白竹山云雾茶中茶多酚提取工艺研究 [J]. 食品工业, 2014, 35(8):4−8. YANG S M, WANG Z J, WANG B. Study on extraction technology of tea polyphenol from baizhu mountain tea [J]. The Food Industry, 2014, 35(8): 4−8.(in Chinese)
[6] 李思睿, 董慧茹. 溶剂浮选法分离富集茶叶中茶多酚的研究 [J]. 分析科学学报, 2007, 23(5):571−574. DOI: 10.3969/j.issn.1006-6144.2007.05.019 LI S R, DONG H R. Study on the separation and concentration of tea polyphenols in tea by solvent sublation [J]. Journal of Analytical Science, 2007, 23(5): 571−574.(in Chinese) DOI: 10.3969/j.issn.1006-6144.2007.05.019
[7] 韦星船, 陈小宏, 王琪莹. 微波-离子沉淀法提取茶叶中茶多酚的工艺研究 [J]. 食品科技, 2007, 32(8):132−138. DOI: 10.3969/j.issn.1005-9989.2007.08.037 WEI X C, CHEN X H, WANG Q Y. Study on the extract technology of tea polyphenol by microwave radiation and Ion co-precipitation [J]. Food Science and Technology, 2007, 32(8): 132−138.(in Chinese) DOI: 10.3969/j.issn.1005-9989.2007.08.037
[8] 张效林, 薛伟明, 李平, 等. 树脂吸附法分离茶多酚及咖啡碱 [J]. 化学工程, 2001, 29(3):15−19. DOI: 10.3969/j.issn.1005-9954.2001.03.003 ZHANG X L, XUE W M, LI P, et al. Adsorptive separation based on resins for tea-polyphenols and caffeine [J]. Chemical Engineering(China), 2001, 29(3): 15−19.(in Chinese) DOI: 10.3969/j.issn.1005-9954.2001.03.003
[9] PAN X J, NIU G G, LIU H Z. Microwave-assisted extraction of tea polyphenols and tea caffeine from green tea leaves [J]. Chemical Engineering and Processing: Process Intensification, 2003, 42(2): 129−133. DOI: 10.1016/S0255-2701(02)00037-5
[10] 张素霞. 茶多酚提取工艺的研究 [J]. 食品科技, 2010, 35(8):267−270. ZHANG S X. Study on extraction process of the tea polyphenols [J]. Food Science and Technology, 2010, 35(8): 267−270.(in Chinese)
[11] 于基成, 金莉, 薄尔琳, 等. 超临界CO2萃取技术在茶多酚提取中的应用 [J]. 食品科技, 2007, 32(1):85−87. DOI: 10.3969/j.issn.1005-9989.2007.01.024 YU J C, JIN L, BO E L, et al. Application of supercritical fluid extraction technique on tea polyhenols [J]. Food Science and Technology, 2007, 32(1): 85−87.(in Chinese) DOI: 10.3969/j.issn.1005-9989.2007.01.024
[12] 代忠波. 茶饮料萃取技术研究现状 [J]. 饮料工业, 2013, 16(9):39−45. DAI Z B. An overview of tea leaf extraction technologies for RTD tea beverages [J]. Beverage Industry, 2013, 16(9): 39−45.(in Chinese)
[13] 张咪, 汤小芳. 乙醇/硫酸铵双水相体系萃取茶叶中茶多酚的研究 [J]. 广东化工, 2013, 40(14):26−28, 32. DOI: 10.3969/j.issn.1007-1865.2013.14.013 ZHANG M, TANG X F. The study of ethanol/ammonium sulfate aqueous two-phase extraction of tea polyphenols in tea [J]. Guangdong Chemical Industry, 2013, 40(14): 26−28, 32.(in Chinese) DOI: 10.3969/j.issn.1007-1865.2013.14.013
[14] 韦露, 樊友军. 低共熔溶剂及其应用研究进展 [J]. 化学通报, 2011, 74(4):333−339. WEI L, FAN Y J. Progress of deep eutectic solvents and their applications [J]. Chemistry, 2011, 74(4): 333−339.(in Chinese)
[15] 崔琦. 沙棘叶中主要黄酮类成分的提取富集工艺研究[D]. 哈尔滨: 东北林业大学, 2016. CUI Q. Study on extraction and enrichment of main flavonoids from Sea buckthorn leaves[D]. Harbin: Northeast Forestry University, 2016. (in Chinese)
[16] OZTURK B, PARKINSON C, GONZALEZ-MIQUEL M. Extraction of polyphenolic antioxidants from orange peel waste using deep eutectic solvents [J]. Separation and Purification Technology, 2018, 206: 1−13. DOI: 10.1016/j.seppur.2018.05.052
[17] 李婷婷. 微波辅助低共熔溶剂提取黄芩中主要黄酮成分研究[D]. 哈尔滨: 东北林业大学, 2014. LI T T. Study on extraction of main flavonoids from Scutellaria baicalensis Georgi by microwave-assisted eutectic solvent. Harbin: Northeast Forestry University, 2014. (in Chinese)
[18] XU B J, CHANG S K C. A comparative study on phenolic profiles and antioxidant activities of legumes as affected by extraction solvents [J]. Journal of Food Science, 2007, 72(2): S159−S166. DOI: 10.1111/j.1750-3841.2006.00260.x
[19] 李堆淑. 复合酶提取绿茶茶多酚工艺及其抑菌性 [J]. 广西林业科学, 2019, 48(2):229−234. DOI: 10.3969/j.issn.1006-1126.2019.02.017 LI D S. Compound enzyme extraction of green tea polyphenols and its bacteriostasis [J]. Guangxi Forestry Science, 2019, 48(2): 229−234.(in Chinese) DOI: 10.3969/j.issn.1006-1126.2019.02.017
[20] 李加兴, 陈选, 邓佳琴, 等. 黄秋葵黄酮的提取工艺和体外抗氧化活性研究 [J]. 食品科学, 2014, 35(10):121−125. DOI: 10.7506/spkx1002-6630-201410022 LI J X, CHEN X, DENG J Q, et al. Extraction and antioxidant activity in vitro of okra flavonoids [J]. Food Science, 2014, 35(10): 121−125.(in Chinese) DOI: 10.7506/spkx1002-6630-201410022
[21] BI W T, TIAN M L, ROW K H. Evaluation of alcohol-based deep eutectic solvent in extraction and determination of flavonoids with response surface methodology optimization [J]. Journal of Chromatography A, 2013, 1285: 22−30. DOI: 10.1016/j.chroma.2013.02.041
[22] 洪姗. 儿茶素分子定向修饰及其抗氧化构效关系研究[D]. 杭州: 浙江大学, 2015. HONG S. Development of specific modification methods for catechins and structure and antioxidant activity relationship investigation[D]. Hangzhou: Zhejiang University, 2015. (in Chinese)
[23] 韦献雅, 殷丽琴, 钟成, 等. DPPH法评价抗氧化活性研究进展 [J]. 食品科学, 2014, 35(9):317−322. DOI: 10.7506/spkx1002-6630-201409062 WEI X Y, YIN L Q, ZHONG C, et al. Advances in the DPPH radical scavenging assay for antioxidant activity evaluation [J]. Food Science, 2014, 35(9): 317−322.(in Chinese) DOI: 10.7506/spkx1002-6630-201409062
-
期刊类型引用(0)
其他类型引用(1)








 下载:
下载: