Properties of Mixed Pig Manure Residue and Sewage Sludge Composts
-
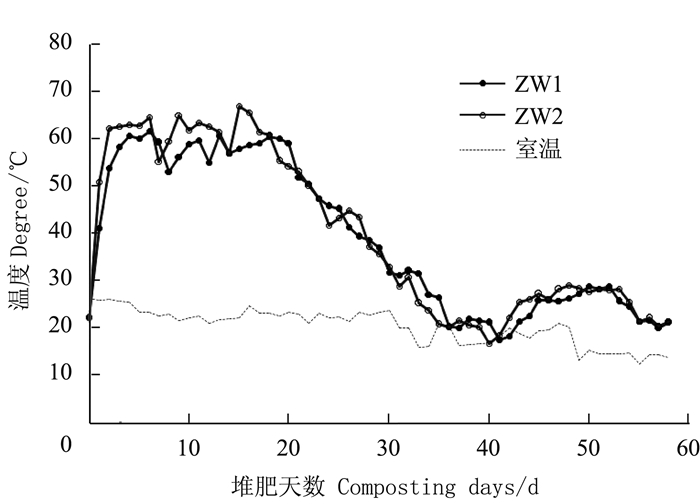
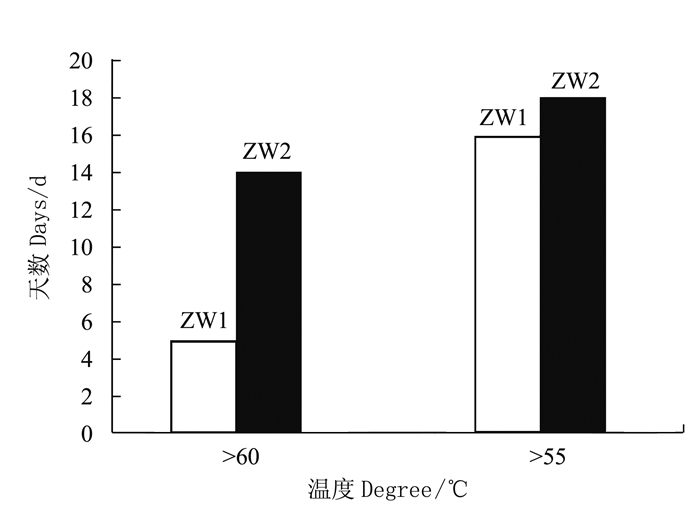
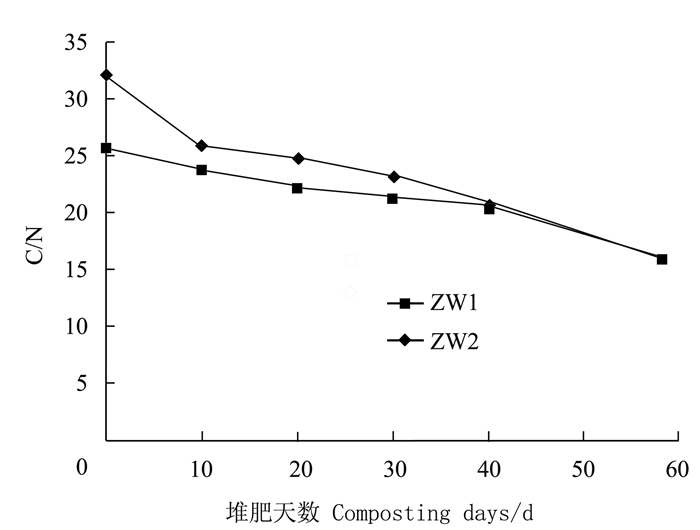
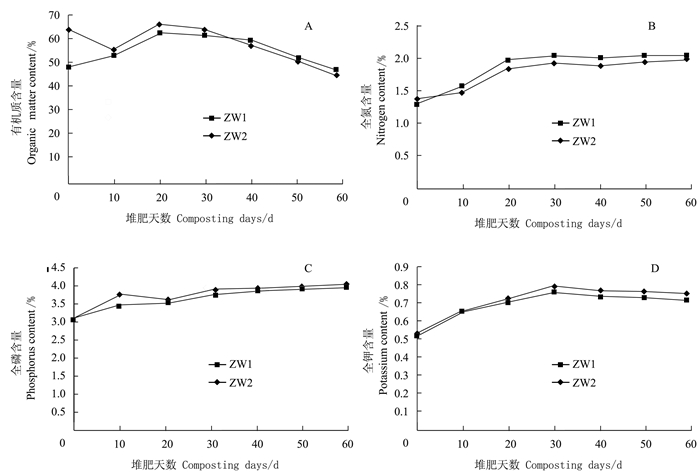
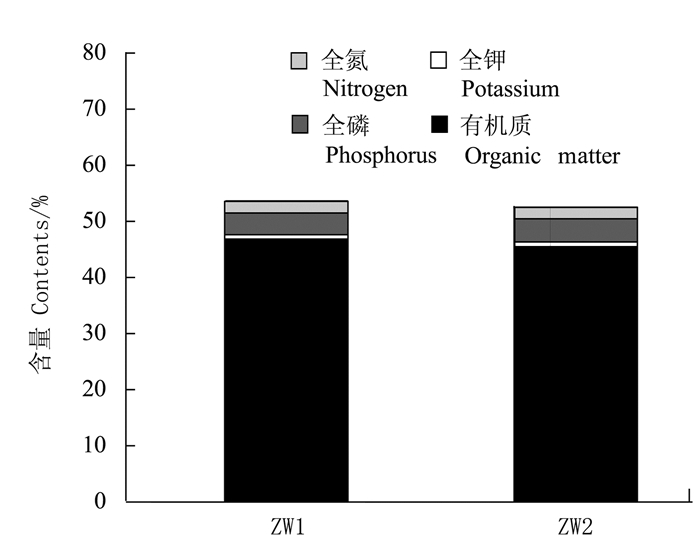
摘要:目的 研究不同配比猪粪渣/生活污泥堆肥过程养分及重金属含量变化,开发城市生活污泥堆肥化处置调理剂,实现猪粪渣资源化利用。方法 以规模化养猪场粪污经固液分离后得到的渣滓为调理剂,与城市生活污泥进行条垛式堆肥,分别设置猪粪渣、生活污泥质量配比6:10(ZW1处理,C/N=25)和6:5(ZW2处理,C/N=30)两组不同处理,研究不同物料配比处理堆肥过程温度、C/N、养分含量(全氮、全磷、全钾)、有机质含量和重金属(Cu、Zn、Cd和Pb)含量的变化。结果 ZW2处理的堆体高温期持续时间长于ZW1处理;两个处理的C/N均逐渐下降并最终趋于一致,且堆肥结束后ZW2处理(C/N=30)的有机碳含量降幅达到28.6%,而ZW1处理(C/N=25)的降幅仅为2.1%,说明猪粪渣中的碳源较容易被微生物分解和转化;堆肥过程中全氮、全磷和全钾随有机碳含量的降低表现为增加的趋势;不同处理的堆肥产品的重金属(Cu、Zn、Cd和Pb)含量在堆肥后均有所提高;堆制58 d后,各处理堆肥无害化程度、养分含量和重金属Cd、Pb含量均达到NY525-2012的要求。结论 猪粪渣可以作为城市生活污泥堆肥的调理剂,且猪粪渣、生活污泥质量配比为6:5的堆肥效果更优。Abstract:Objective Waste from pig farms and municipal sewer were mixed and composted to evaluate its utilization as a safe, organic substrate for agricultural applications.Method Manure residue from large pig farms after solid-liquid separation was mixed with municipal sewage sludge for the composting. Two mixing ratios of manure residue:sewage sludge, i.e., a low C/N treatment of 6:10 (ZW1) and a high C/N treatment of 6:5 (ZW2), were applied for the experiment. The changes on temperature, C/N ratio as well as the nutrients (total nitrogen, total phosphorus, total potassium and organic matters) and heavy metals (Cu, Zn, Cd and Pb) contents of the mixtures during the fermentation process were monitored for evaluation.Result The thermophilic phase of ZW2 lasted longer than that of ZW1. After composting, the organic carbon content of ZW2 (C/N=30) decreased by 28.6%, while that of ZW1 (C/N=25) merely 2.1%, indicating that the carbon source in pig manure was easily decomposed by microorganisms. As the fermentation progressed, the total nitrogen, phosphorus and potassium increased, and the heavy metals increased in the mixtures. After 58 d of composting, both resulting materials met the national standards for nutrients content and safety on heavy metals.Conclusion The mass ratio of 6:5 (C/N=30) between the pig manure residue and the sewage sludge was considered appropriate for composting to produce an applicable fertilizer.
-
Keywords:
- composting /
- pig manure /
- sewage sludge /
- C/N /
- heavy metal
-
0. 引言
【研究意义】猪伪狂犬病(Porcine pseudorabies, PR)是危害我国养猪产业的重要急性传染性疫病之一。不同饲养阶段生猪在感染猪伪狂犬病毒(Porcine pseudorabies virus, PRV)后的临床表现不同:仔猪出现中枢神经系统紊乱,死亡率高达100%;育肥猪出现呼吸道症状;妊娠母猪则表现为流产、产死胎和木乃伊胎[1]。该病宿主范围广泛,可以感染并导致多种哺乳动物发病,如猪(Sus scrofa)、牛(Bovine)[2]、羊(Ovis aries)[3]、猫(Felis catus)[3]、狗(Canis lupus familiaris)和兔子(Leporidae)[4],同时对水貂(Neovison vison)也具有一定的致病性[5],发病率和死亡率都很高[6]。虽然疫苗是该病防控的主要手段,但是科学检测与预警才是防控的第一要素。【前人研究进展】目前PRV的检测方法主要包括酶联免疫吸附试验、病毒分离鉴定、普通PCR和荧光定量PCR等。酶联免疫吸附试验是将抗原或抗体固定到聚苯乙烯等固相载体上,利用抗原抗体特异性反应进行定性或定量检测的方法[7],易于批量自动化操作,但是对环境和温度以及专业仪器要求较高,检测试剂价格高[7]。病毒的分离鉴定操作复杂、耗时长,对成本和技术要求高,不利于猪伪狂犬病的快速诊断,也不适合在资源有限的环境、基层和现场即时检测,难以满足生产实践中快速诊断的要求[8]。普通PCR需要使用琼脂糖凝胶电泳观察结果,操作繁琐且费时[9]。荧光定量PCR虽然简化了检测流程并具有更优异的检测性能,但目前其相关试剂及仪器成本较高,操作复杂,难以推广[10]。可见传统检测方法对实验室条件及仪器要求高且耗费时间长,在临床快检应用中存在一定局限性[11]。RAA具有操作简单、扩增时间短、支持多样化数据读取等优点[12],不需要特殊仪器和专业实验室,支持现场恒温快速检测,更容易在临床实践中应用,具有较强的推广性[13]。【本研究切入点】虽然已有学者建立了伪狂犬病毒荧光重组酶介导核酸扩增快速检测方法[14],但其检测灵敏度还有待提高。【拟解决的关键问题】本研究针对PRV的gE基因设计了特异性引物和探针,基于荧光 RAA 技术建立高灵敏度且快速检测PRV的方法,为现场PRV检测提供新的技术手段。
1. 材料与方法
1.1 试验样品
40份疑似PRV感染临床样品为2018–2023年采自福建省18个家庭农场(表1),由本实验室收集并保存。
表 1 疑似伪狂犬病料收集的来源信息Table 1. Tissue collection of suspected diseased pigs地区
Region样本数(份)/来源猪场(个)
Samples/Farms宁德 Ningde 4/2 泉州 Quanzhou 5/3 漳州 Zhangzhou 10/4 南平 Nanping 12/5 龙岩 Longyan 9/4 合计 Total 40/18 1.2 试验材料、试剂与仪器
病毒RNA/DNA核酸提取试剂盒购自杭州博日科技股份有限公司,RAA核酸扩增试剂(荧光型)购自杭州众测生物科技有限公司,pUC57-gE质粒由本实验室构建并保存。LightCycler®96荧光PCR检测仪,北京君意东方电泳设备有限公司。猪繁殖与呼吸综合征病毒(Porcine reproductive and respiratory syndrome virus, PRRSV)、猪流行性腹泻病毒(Porcine epidemic diarrhea virus, PEDV)、猪轮状病毒(Porcine rotavirus, PoRV)、猪传染性胃肠炎病毒(Transmissible gastroenteritis virus, TGEV)、猪圆环病毒2型(Porcine circovirus 2, PCV2)、猪圆环病毒3型(Porcine circovirus 3, PCV3)核酸均由本实验室保存。
1.3 引物设计与合成
根据GenBank中PRV gE基因(NC_006151.1)参考序列,并用NCBI BLAST比对选取保守区域,利用Oligo 7和Primer 5设计RAA引物及nfo探针(表2)。引物和探针由尚亚生物技术有限公司(福州)合成。
表 2 PRV荧光RAA引物与探针Table 2. Primers and probes of PRV for fluorescent RAA引物/探针
Primer/Probe引物序列(5'-3')
Sequence(5'-3')用途
UsagePRV-F1 CGATCTACGTGGACGGCATCACGACGCCG 识别并结合到PRV-gE DNA片段的特定区域,启动扩增过程。 PRV-R1 TAGTAGTCCTCGTGCGTGGGCAGGCTGGTGTA PRV-F2 CGAGTACGTCACGGTCATCAAGGAGCTGAC PRV-R2 GCTGGTGTACACCGGAGAGAGCATGTGCGT PRV-Probe GCTGTTTGTGCTGGCGCTGGGCTCCTTCG[FAM-dT]
[THF]A[BHQ1-dT]GACGTGCGTCGTC-C3用于检测和量化扩增过程中产生的特定核酸序列 1.4 荧光RAA引物筛选
将上游与下游引物进行两两组合,获得4组反应引物对,按照荧光型RAA核酸扩增试剂盒说明书,建立50.0 μL扩增反应体系,向装有重组酶及聚合酶的RAA反应管加入缓冲液A Buffer 25.0 μL,上下游引物各2.0 μL,探针0.6 μL,ddH2O 12.9 μL,DNA模板5.0 μL。充分混匀溶解,最后向检测管中加入B Buffer 2.5 μL,充分混匀后低速离心5 s,将上述反应管放入荧光PCR检测仪(LightCycler®96)中反应,通过反应结果筛选出最佳引物对。
1.5 荧光RAA反应体系建立及优化
将筛选的最佳引物对进行稀释,设置终浓度为 1、2.5、5、7.5、10 μmol·L−1,使用上述50 μL RAA 反应体系,通过RAA扩增筛选出最佳引物浓度;将反应温度设定为37、38、39、40、41、42、43、44 ℃进行RAA反应,以筛选出最佳反应温度。
1.6 荧光RAA敏感性试验
通过NanoDrop 2000测定pUC57-gE质粒浓度,根据质粒浓度计算拷贝数,拷贝数/(copies·μL−1)=6.02×1023×浓度(ng·μL−1)×10−9/(碱基数×660)[14],得出重组质粒pUC57-gE的拷贝数为 1.11×1011 copies·μL−1。将重组质粒pUC57-gE进行10倍倍比稀释,获得1.11×100~ 1.11×107 copies·μL−1 8个浓度。将这8个浓度的标准品分别作为模板,ddH2O为阴性对照,进行荧光RAA反应,以评价该检测方法的敏感性。
1.7 荧光RAA特异性试验
以PRRSV、PEDV、PoRV、TGEV、PCV2和PCV3的DNA或cDNA为模板,ddH2O为阴性对照,进行荧光RAA反应,以评价该检测方法的特异性。
1.8 荧光RAA重复性试验
取重组质粒浓度为1.11×104、1.11×105、1.11×106 copies·μL−1分别进行3次组内和3次组间重复性试验,评价该检测方法的重复性。
1.9 临床样品检测
提取40份临床样品DNA,用本研究建立的荧光RAA方法检测,并与常规聚合酶链式反应(PCR)方法进行对比,比较分析两种检测方法的结果,计算两种检测方法的符合度,以评价建立的检测方法的实际应用效果。
2. 结果与分析
2.1 荧光RAA引物筛选
按照引物组合(PRV-F1/PRV-R1、PRV-F2/PRV-R2、PRV-F1/PRV-R2、PRV-F2/PRV-R1)的顺序分别进行RAA扩增反应,并设置ddH2O阴性对照。通过RAA扩增得到的引物筛选结果如图1,发现只有PRV-F1/PRV-R1引物对PRV质粒能有效扩增,可检测到荧光信号,因此根据扩增结果选择引物对(PRV-F1/PRV-R1)进行后续试验。
2.2 荧光RAA反应条件的优化
不同浓度的引物和探针浓度RAA反应结果(图2、图3)显示,引物浓度为10 μmol·L−1时最早检测到荧光信号,扩增效率最高,而探针浓度从10 μmol·L−1降低至2.5 μmol·L−1时扩增效率逐步提高,而从2.5 μmol·L−1降低至1 μmol·L−1时扩增效率明显下降,当探针浓度为2.5 μmol·L−1时最早检测到荧光信号,扩增效率最高,因此RAA最佳引物浓度为10 μmol·L−1,探针浓度为2.5 μmol·L−1。
不同温度下荧光RAA反应结果(图4)显示,37 ~ 44 ℃均能有效扩增,当温度从37 ℃增加至43 ℃时扩增效率逐步提高,而从43 ℃增加至44 ℃时扩增效率下降,在43 ℃时,最早检测到荧光信号,且荧光信号强,扩增效率最高,因此RAA最佳反应温度为43 ℃。
2.3 特异性试验
分别以提取的PRRSV、PEDV、PoRV、TGEV、PCV2和PCV3核酸为模板,利用优化后的反应体系进行RAA反应,结果(图5)显示除PRV表现出明显的扩增曲线外,其他病毒及阴性对照均未出现扩增曲线,说明本试验建立的荧光RAA检测方法特异性强,不受其他猪源病毒影响。
2.4 敏感性试验
不同浓度的重组质粒pUC57-gE的RAA反应结果(图6)显示,荧光RAA方法能鉴别检测到的最低质粒浓度为1.11×102 copies·μL−1,说明本次试验中所对应的最低检出拷贝数为111 copies·μL−1。
2.5 重复性试验
以1.11×104 、1.11×105、1.11×106 copies·μL−1 浓度的质粒标准品pUC57-gE为模板,分别进行组内、组间重复性试验。结果(表3)显示,该3个浓度均能有效扩增,起峰差异小,组内、组间变异系数都低于5%,说明该方法重复性好。
表 3 荧光重复性试验结果Table 3. Repeatability of fluorescent RAA质粒浓度
Plasmid
concentration/
(copies·μL−1)组内变异试验
Intra-assay variability组间变异试验
Inter-assay variability循环数
¯X+SD变异系数CV/% 循环数
¯X+SD变异系数CV/% 1.11×104 16.9±0.33 1.98 17.27±0.77 4.52 1.11×105 15.09±0.34 2.31 12.09±0.49 4.09 1.11×106 9.38±0.25 2.76 8.74±0.30 3.45 2.6 临床样品检测
对40份疑似PRV临床样品分别使用荧光RAA和常规聚合酶链式反应(PCR)方法检测,RAA检测设置了一个阳性对照和一个阴性对照,结果显示,RAA检测方法的检出阳性率为15%(6/40),临床样品6、临床样品14、临床样品21、临床样品27、临床样品31和临床样品34出现扩增曲线,其余34个临床样品及阴性对照均未出现扩增曲线。与常规聚合酶链式反应(PCR)方法的阳性检出率一致(6/40)(图7),说明本试验建立的荧光RAA检测方法可靠性强,可以在临床检测中运用。
![]() 图 7 临床样品PRV的PCR和RAA检测A:临床样品RAA结果。B:临床样品PCR结果;M:DL 2000 Marker;1:阴性对照;2:阳性对照;3~42:临床样品。Figure 7. PRV detections by conventional PCR and fluorescent RAA on clinical samplesA: results on clinical samples by fluorescent RAA; B: results on clinical samples by conventional PCR; M: DL 2000 marker; 1: negative control ; 2: positive control ; 3–42: clinical samples.
图 7 临床样品PRV的PCR和RAA检测A:临床样品RAA结果。B:临床样品PCR结果;M:DL 2000 Marker;1:阴性对照;2:阳性对照;3~42:临床样品。Figure 7. PRV detections by conventional PCR and fluorescent RAA on clinical samplesA: results on clinical samples by fluorescent RAA; B: results on clinical samples by conventional PCR; M: DL 2000 marker; 1: negative control ; 2: positive control ; 3–42: clinical samples.3. 讨论
猪伪狂犬病感染会导致新生仔猪死亡,母猪繁殖障碍,尽管大部分猪场进行了疫苗接种,但是由PRV引起的新生仔猪神经症状乃至死亡的案例仍有发生[15]。2011 以来,我国有29个省市出现了PRV变异株,伪狂犬病“老病新发”,给我国养猪业造成了巨大的经济损失[16]。RAA是基于重组酶聚合酶扩增技术(Recombinase polymerase amplification, RPA)发展起来的一项新技术,所用的Bsu聚合酶主要来源于细菌和真菌[17],与RPA相比,RAA的重组酶来源范围更广,且RAA技术在我国具有产权优势,价格低廉,对检测环境和设备要求低,并且不需要复杂的热循环仪,因此可以在资源有限的现场使用。本研究根据PRV的gE基因序列设计引物与探针,建立了PRV实时荧光RAA检测方法,该方法只能扩增PRV核酸,对其他猪源病毒均无扩增,表明该方法特异性强;该方法检测到的最低拷贝数为111 copies·μL−1,灵敏度比已报道的PRV实时荧光检测重组酶聚合酶扩增方法(real-time RPA法)和侧向流试纸条法(RPA LFD法)高[18];重复性试验显示,组内和组间试验的变异系数均小于5%,表明该方法可重复性强。
兰德松等[19]报道,辽宁省2017年的PRV阳性率为11.20%(82/732),2018年PRV阳性率为7.54%(42/557)。汪一平等[20]报道豫西地区2017年PRV阳性率为20.69%、2018年PRV阳性率为19.05%。Sun等[15]对2012–2017年收集的中国27个省份疑似PRV感染猪场的样本进行了PRV的核酸检测,平均阳性率为8.27%,2012–2017年PRV的阳性率分别为11.92%(153/
1284 )、12.19%(225/1846)、6.70%(169/2523 )、11.10%(269/2424 )、5.57%(147/2640 )和6.90%(382/5539 )。PRV变异毒株的出现,导致传统Bartha-K61活疫苗无法产生完全的保护作用,使得PR在我国再次大规模流行。但疫苗免疫接种仍是防控PRV感染的有效手段,随着伪狂犬疫苗免疫次数的加强、生物安全体系的不断完善和净化工作的开展,总体上猪伪狂犬病毒感染阳性率呈逐年下降的趋势。本研究收集的2018–2023年疑似PRV的40份临床样品检测结果显示,PRV阳性率为15%(6/40),其阳性率高于先前的报道,这可能与病料的收集、采集的样本类型有关,本研究收集的样品是临床上疑似PRV感染的家庭农场,其防控技术较弱,存在免疫空白或免疫检测不到位等因素影响。综上,本研究建立了一种以PRV的gE基因为靶点的荧光RAA快速检测方法,可快速检测PRV的感染,并具有简便、稳定、特异性强、灵敏度高等优点,适用于临床猪伪狂犬病的监测和流行病学调查,为实现快速准确检测PRV提供依据,对猪伪狂犬病的防治具有重要意义。
-
表 1 试验设计及物料配比
Table 1 Test design and mixing ratios of materials
处理编号
Treatment物料配比
Material ratio含水率
Moisture content/%猪粪渣
Pig manure /kg污泥
Sewage sludge/kg碳氮比
C/NZW1 6:10 68.60 240 400 25:1 ZW2 6:5 67.47 240 200 30:1 表 2 原料及堆肥中重金属含量
Table 2 Heavy metal contents in raw materials and composts
样品
Sample铜Cu/
(mg·kg-1)锌Zn/
(mg·kg-1)镉Cd/
(mg·kg-1)铅Pb/
(mg·kg-1)原料
Component猪粪渣 230 55 0.16 7.40 污泥 240 55 0.82 71.14 堆肥前
Before compostingZW1 240 54 0.47 37.22 ZW2 240 54 0.47 33.75 堆肥后
After compostingZW1 273 65 0.56 38.61 ZW2 262 64 0.52 35.48 -
[1] 李琼, 华珞, 徐兴华, 等.城市污泥农用的环境效应及控制标准的发展现状[J].中国生态农业学报, 2011, 19(2):468-476. http://d.old.wanfangdata.com.cn/Periodical/stnyyj201102040 LI Q, HUA L, XU X H, et al. A review on environmental effects and control criteria of biosolid agricultural application[J]. Chinese Journal of Eco-Agriculture, 2011, 19(2):468-476.(in Chinese) http://d.old.wanfangdata.com.cn/Periodical/stnyyj201102040
[2] 郭广慧, 陈同斌, 杨军, 等.中国城市污泥重金属区域分布特征及变化趋势[J].环境科学学报, 2014, 34(10):2455-2461. http://d.old.wanfangdata.com.cn/Periodical/hjkxxb201410001 GUO G H, CHEN T B, YANG J, et al. Regional distribution characteristics and variation of heavy metals in sewage sludge of China[J]. Acta Scientiae Circumstantiae, 2014, 34(10):2455-2461.(in Chinese) http://d.old.wanfangdata.com.cn/Periodical/hjkxxb201410001
[3] 陈镇新, 檀笑, 解启来, 等.不同辅料配比对城市污泥堆肥效果及重金属形态转化的影响[J].江苏农业科学, 2017, 45(1):227-234. http://d.old.wanfangdata.com.cn/Periodical/jsnykx201701064 CHEN Z X, TAN X, XIE Q L, et al. Effects of different additives ratios on efficiency and heavy metal forms during sewage sludge composting process[J]. Jiangsu Agricultural Sciences, 2017, 45(1):227-234.(in Chinese) http://d.old.wanfangdata.com.cn/Periodical/jsnykx201701064
[4] 吴飞龙, 叶美锋, 吴晓梅, 等.添加菌糠对猪粪渣堆肥过程及氨排放的影响[J].农业环境科学学报, 2017, 36(3):598-604. http://d.old.wanfangdata.com.cn/Periodical/nyhjbh201703024 WU F L, YE M F, WU X M, et al. Effects of mushroom bran addition on the process and NH3 emissions of swine feces residue composting[J]. Journal of Agro-Environment Science, 2017, 36(3):598-604.(in Chinese) http://d.old.wanfangdata.com.cn/Periodical/nyhjbh201703024
[5] OZDEMIR S, DEDE O H, DEDE G. Comparison of the composting performance of four different sewage sludge amendments[J]. Compost Science & Utilization, 2014, 22(4): 207-215. http://cn.bing.com/academic/profile?id=ac2fbaf8f5bf1fcc3ca0e3513d086b1c&encoded=0&v=paper_preview&mkt=zh-cn
[6] 牛明杰, 郑国砥, 朱彦莉, 等.城市污泥与调理剂混合堆肥过程中有机质组分的变化[J].植物营养与肥料学报, 2016, 24(4):1016-1023. http://d.old.wanfangdata.com.cn/Periodical/zwyyyflxb201604017 NIU M J, ZHENG G D, ZHU Y L, et al. Dynamic of organic matter fractions during sewage sludge and bulking agent composting[J]. Journal of Plant Nutrition and Fertilizers, 2016, 24(4): 1016-1023.(in Chinese) http://d.old.wanfangdata.com.cn/Periodical/zwyyyflxb201604017
[7] 胡伟桐, 余雅琳, 李喆, 等.不同调理剂对生物沥浸污泥堆肥氮素损失的影响[J].农业环境科学学报, 2015, 34(12):2379-2385. DOI: 10.11654/jaes.2015.12.018 HU W T, YU Y L, LI Z, et al. Effects of Different Organic Bulking Agents on Nitrogen Loss During Composting of Dewatered Bioleached Sludge on a Commercial Scale[J]. Journal of Agro-Environment Science, 2015, 34(12):2379-2385.(in Chinese) DOI: 10.11654/jaes.2015.12.018
[8] 吴珍珍, 舒增年, 黄健.以菇渣和猪粪为调理剂的城市污泥堆肥效果研究[J].浙江农业学报, 2015, 27(12):2171-2176. DOI: 10.3969/j.issn.1004-1524.2015.12.20 WU Z Z, SHU Z N, HUANG J. Effect of mushroom resedue and pig manure as conditioner ou aerobic composting of sewage sludge[J]. Acta Agriculturae Zhejiangensis. 2015, 27(12): 2171-2176.(in Chinese) DOI: 10.3969/j.issn.1004-1524.2015.12.20
[9] 郑玉琪, 陈同斌, 高定, 等.城市污泥堆肥添加猪粪的功效研究[J].中国给水排水, 2006, 22(9):105-108. DOI: 10.3321/j.issn:1000-4602.2006.09.028 ZHENG Y Q, CHEN T B, GAO D, et al. Influence of adding pig manure on urban sludge composting[J]. China Water & Wastewater, 2006, 22(9): 105-108.(in Chinese) DOI: 10.3321/j.issn:1000-4602.2006.09.028
[10] WICHUK K M, MCCARTNEY D. Compost stability and maturity evaluation—a literature review[J]. Canadian Journal of Civil Engineering, 2010, 37(11): 1505-1523. DOI: 10.1139/L10-101
[11] LI S, LI D, LI J, et al. Evaluation of humic substances during co-composting of sewage sludge and corn stalk under different aeration rates[J]. Bioresource Technology, 2017, 245(Pt A): 1299-1302. http://www.wanfangdata.com.cn/details/detail.do?_type=perio&id=43d080f1f2e2677f1aea34bb674c4786
[12] XU S, REUTER T, GILROYED B H, et al. Biodegradation of prions in compost[J]. Environmental Science & Technology, 2014, 48(12): 6909-6918. http://cn.bing.com/academic/profile?id=7a89d355a5451e90cc3c746f5fb95d7e&encoded=0&v=paper_preview&mkt=zh-cn
[13] YAACOBY T, GOLDWASSER Y, PAPORISH A, et al. Germination of Phelipanche aegyptiaca and Cuscuta campestris seeds in composted farm manure[J]. Crop Protection, 2015, 72: 76-82. DOI: 10.1016/j.cropro.2015.03.005
[14] 秦莉, 沈玉君, 李国学, 等.不同CN比堆肥碳素物质变化规律研究[J].农业环境科学学报, 2010, 29(7):1388-1393. http://d.old.wanfangdata.com.cn/Periodical/nyhjbh201007025 QIN L, SHEN Y J, LI G X, et al. C matter change of composting with different C/N[J]. Journal of Agro-Environment Science, 2010, 29(7):1388-1393.(in Chinese) http://d.old.wanfangdata.com.cn/Periodical/nyhjbh201007025
[15] BERNAL M P, ALBURQUERQUE J A, MORAL R. Composting of animal manures and chemical criteria for compost maturity assessment. A review[J]. Bioresource Technology, 2009, 100(22): 5444-5453. DOI: 10.1016/j.biortech.2008.11.027
[16] 杨帆, 欧阳喜辉, 李国学, 等.膨松剂对厨余垃圾堆肥CH4、N2O和NH3排放的影响[J].农业工程学报, 2013, 29(18):226-233. DOI: 10.3969/j.issn.1002-6819.2013.18.027 YANG F, OUYANG X H, LI G X, et al.Effect of bulking agent on CH4, N2O and NH3 emissions in kitchen waste composting[J]. Transactions of the Chinese Society of Agricultural Engineering (Transactions of the CSAE), 2013, 29(18):226-233.(in Chinese) DOI: 10.3969/j.issn.1002-6819.2013.18.027
[17] 李云蓓, 李伟光.不同类型的外加碳源对污泥堆肥过程氮素损失的影响[J].土木建筑与环境工程, 2014, 36(2):104-109. http://d.old.wanfangdata.com.cn/Periodical/cqjzdxxb201402016 LI Y B, LI W G. Influence of Carbon-Rich Amendments on Nitrogen Losses During Sewage Sludge Composting[J]. Journal of Civil, Architectural & Environmental Engineering, 2014, 36(2):104-109.(in Chinese) http://d.old.wanfangdata.com.cn/Periodical/cqjzdxxb201402016
[18] 罗一鸣, 李国学, FRANK SCHUCHARDT, 等.过磷酸钙添加剂对猪粪堆肥温室气体和氨气减排的作用[J].农业工程学报, 2012, 28(22):235-242. DOI: 10.3969/j.issn.1002-6819.2012.22.033 LUO Y M, LI G X, FRANK SCHUCHARDT, et al. Effects of additive superphosphate on NH3, N2O and CH4 emissions during pig manure composting[J]. Transactions of the Chinese Society of Agricultural Engineering (Transactions of the CSAE), 2012, 28(22):235-242.(in Chinese) DOI: 10.3969/j.issn.1002-6819.2012.22.033
[19] 鲍艳宇, 娄翼来, 颜丽, 等.不同畜禽粪便好氧堆肥过程中重金属Pb、Cd、Cu、Zn的变化特征及其影响因素分析[J].农业环境科学学报, 2010, 29(9):1820-1826. http://d.old.wanfangdata.com.cn/Periodical/nyhjbh201009031 BAO Y Y, LOU Y L, YAN L, et al. Dynamic change characteristic of heavy metals Pb, Cu and Zn during aerobic composting of different manure and the analysis of effect factors[J]. Journal of Agro-Environment Science, 2010, 29(9):1820-1826.(in Chinese) http://d.old.wanfangdata.com.cn/Periodical/nyhjbh201009031
[20] ZHOU H, MENG H, ZHAO L, et al. Effect of biochar and humic acid on the copper, lead, and cadmium passivation during composting[J]. Bioresource Technology, 2018, 258: 279-286. DOI: 10.1016/j.biortech.2018.02.086
-
期刊类型引用(3)
1. 郑丁瑀,王珏,常瑞雪,陈清. 堆肥工艺钝化粪肥中重金属及其形态变化的研究进展. 农业资源与环境学报. 2021(05): 778-786 .  百度学术
百度学术
2. 努尔比耶柯孜·麦麦提,张春友,薛娇,陈聪. 堆肥过程中腐殖质钝化重金属的作用机理研究进展. 农业与技术. 2021(20): 27-30 .  百度学术
百度学术
3. 查金,贾宇锋,刘政洋,刘建国,罗云,华锐,周平,宗世荣,李云驹,祁光霞. 市政污泥堆肥对矿山废弃地生态恢复影响的研究进展. 环境科学研究. 2020(08): 1901-1910 .  百度学术
百度学术
其他类型引用(7)




 下载:
下载: