Micromorphology of Leaves and Pollens of Wild Tea (Camellia sinensis) Germplasms from Shouning, Fujian
-
摘要:目的 观察福建寿宁野生茶树种质资源叶片和花粉的微形态,为茶树野生种质资源发掘、鉴定提供参考依据。方法 以福鼎大白茶为对照,利用冷场发射扫描电镜对4份福建寿宁野生茶树种质资源叶片和花粉微形态特征进行观察,对茶树叶片气孔、茸毛和花粉极轴长、赤道轴长等进行数据统计及分析。结果 4份野生茶树种质的叶片叶上表皮纹饰有平展型、皱脊型、波浪型3种;叶片下表皮气孔皆为长卵形,具异性气孔(腺鳞)且气孔密度相对栽培种较小;茸毛长度为(280.75±107.65)~(616.95±132.52)μm,且不同种长度差异明显,茸毛纹饰皆为平滑型;不同于栽培种,野生茶树种质资源叶片茸毛表层均有脱落现象。4份野生茶树花粉均具三孔沟,属N3P4C5类型,其花粉大小在(427.69±153.94)~(1205.07±237.80)μm2,皆小于福鼎大白茶。花粉极面观有近圆形和三裂近三角形2种,赤道面观各不相同,花粉形状有超长球形和近球形2种,花粉纹饰均为疣状。结论 4份野生茶树和福鼎大白茶的叶片和花粉微形态特征有一定的共性和特异性。Abstract:Objective Foliar and pollen micromorphology of wild tea germplasms from Shouning, Fujian was examined and recorded for references on the natural resource.Method Field emission scanning electron microscopy (FE-SEM) was used to observe the micro-structures of the leaves and pollens of 4 tea germplasms collected from Shouning. Twelve morphological characteristics on the leaves and 10 on the pollens were obtained for analysis.Result The leaf-surface stomates of these plants were oval in shape with glandular scales less densely scattered than the cultivated cultivars. The trichome lengths ranged between(280.75±107.65) μm and (616.95±132.52) μm with significant differences among the germplasms. The surface of trichome was smooth. The adaxial epidermal wax ornamentation was either flat, wrinkled or wavy in appearance. The pollens were all tricolporate of the N3P4C5 type with a size in between (427.69±153.94) μm2 and (1205.07±237.80) μm2, which was smaller than those of Fudingdabaicha tea. They had two kinds of polar view, suborbicular and trifid subtriangular; their equatorial views differed; their shapes, ellipsoid or subsphaeroidal; and, their ornamentations, verrucate. As compared to Fudingdabaicha, the 4 wild germplasms had certain distinct foliar and pollen micromorphological characteristics, which could serve for the differentiation of the species.
-
Keywords:
- Camellia sinensis /
- germplasm resource /
- Shouning /
- leaf /
- pollen /
- micromorphology
-
0. 引言
【研究意义】中国作为茶树Camellia sinensis (L.) O. Kuntze的原产中心和分布中心,拥有丰富的茶树种质资源[1]。茶树属山茶科山茶属[2],为多年生常绿木本植物,一般为灌木,在热带地区也有乔木型。寿宁地理坐标为北纬27°11′~27°41′,东经119°14′~119°44′,位于福建东北部,属于闽东地区。闽东是福建省茶叶的主产地之一,产茶历史悠久,野生茶、苦茶等茶树种质资源丰富[3-6]。这些野生茶树资源的发掘,为进一步研究茶树起源、进化和选育新品种提供了宝贵的材料。【前人研究进展】近年来,植物叶片和花粉的超微结构在系统分类、演化等研究中已成为植物学领域的重要途径[7-10]。茶树叶片是人们采摘的主要部位,叶片与茶树品种的产量、品质、抗逆性等有密切关系。植物叶片的结构不仅反映了植物与环境的相互作用,其微形态特征也与植物的遗传、分类有着密切的联系[11-14]。植物花粉的形态特征由基因控制,具有很强的遗传保守性和稳定性,环境因素对其形态影响的较少,从而形成种的特异性与科属间的共同特征。花粉的形态特征可用于分类和推论演化趋势方面的研究[15]。【本研究切入点】尽管中国的茶树种质资源比较丰富,但对野生茶树种质资源的叶片及花粉微形态观察少有研究报道,同时,许多野生茶树种质资源的分类鉴别也还未确定。【拟解决的关键问题】本研究以福鼎大白茶为对照,采用扫描电镜对4份寿宁野生茶种质资源的叶片、花粉微形态进行观察,探明寿宁野生茶叶片、花粉微形态特征,以期为福建茶树种质资源的分类鉴定提供参考依据。
1. 材料与方法
1.1 试验材料及仪器试剂
4份野生茶树种质资源均来自福建省寿宁县,以福鼎大白茶为对照,其基本信息见表 1。于2018年11月采摘其叶片及花。主要仪器与试剂:SU-8010型冷场发射扫描电镜(日立公司,日本);E-1010型离子溅射仪(日立公司,日本);FD-1-50型真空冷冻干燥机(北京博医康实验仪器有限公司);DHG-9240A型可编程电热烘箱(上海一恒科学仪器有限公司);2.5%的戊二醛;pH=6.8的磷酸缓冲液;50%、70%、80%、90%和100%的乙醇;100%的叔丁醇。
表 1 供试茶树种质资源主要特征Table 1. Main characteristics of tea germplasms1.2 样品处理方法
用真空冷冻干燥[16-17]的方法处理茶树叶片,具体方法如下:在茶树叶片中部取3 mm×3 mm大小的叶片,将其置于2.5%的戊二醛溶液中并在4℃冰箱中固定5 h;再分别用50%、70%、80%、90%乙醇进行脱水,每次时间为15 min;之后用100%乙醇脱水4~5次,每次时间为15 min;最后将叶片材料置于100%叔丁醇中浸泡15 min后,放入真空冷冻干燥机进行干燥。花粉具体处理方法如下:直接将试验用花置于可编程烘箱干燥处理。之后将处理过的茶树叶片及花粉粘在双面导电胶上,在其表面喷金镀膜80 s,电镜观察。
1.3 测量指标及方法
对茶树叶片的12个性状(内外气孔长宽、气孔数量、气孔开度、气孔器大小、茸毛长、茸毛直径、茸毛密度、叶腹纹饰和茸毛纹饰)进行观察和统计。对茶树花粉的10个性状(赤道轴长E、极轴长P、萌发沟长L、赤道面观、极面观、外壁纹饰、P×E、P/E和L/P)进行观察和统计。每个性状测量重复15次[18]。
1.4 统计与分析
采用软件Image-Pro、SPSS22.0[19]对数据进行统计分析。
2. 结果与分析
2.1 寿宁野生茶树叶片微形态特征
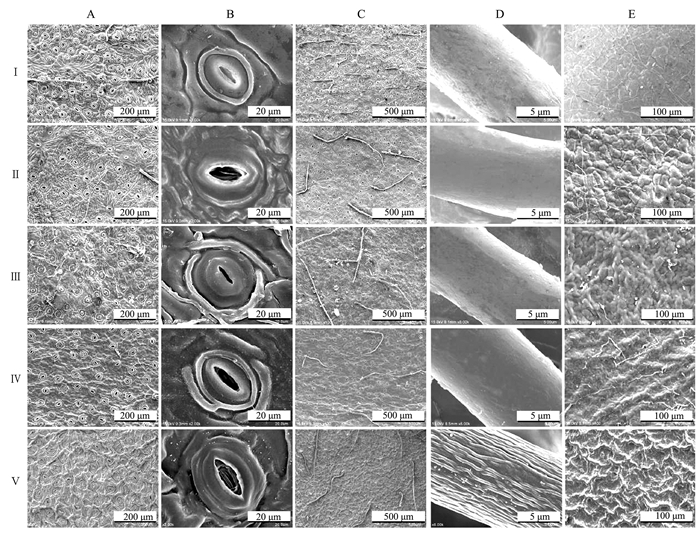
5份茶树叶片背面均具表皮毛,4份野生茶树茸毛纹饰都为平滑型,福鼎大白茶为长条纹形;气孔都为长卵形,具有异性气孔(腺鳞),叶表蜡质纹饰有波浪状、平展状和皱脊状3种类型(图 1)。
![]() 图 1 寿宁野生茶树叶片微形态电子显微观察结果注:Ⅰ为地洋001,Ⅱ为地洋002,Ⅲ为芎坑001,Ⅳ为芎坑002,Ⅴ为福鼎大白茶。图 3同。A为气孔整体观,B为气孔,C茸毛整体观,D为茸毛,E为蜡质纹饰。Figure 1. SEM of tea leafNote:Ⅰ.Diyang 001, Ⅱ.Diyang 002, Ⅲ.Xiongkeng 001, Ⅳ.Xiongkeng 002, Ⅴ.Fudingdabaicha.The same as Fig. 3. A.Stomatal wholeness, B.Stomatal wholeness, C.Villi wholeness, D.Villi wholeness, E.Waxy texture.
图 1 寿宁野生茶树叶片微形态电子显微观察结果注:Ⅰ为地洋001,Ⅱ为地洋002,Ⅲ为芎坑001,Ⅳ为芎坑002,Ⅴ为福鼎大白茶。图 3同。A为气孔整体观,B为气孔,C茸毛整体观,D为茸毛,E为蜡质纹饰。Figure 1. SEM of tea leafNote:Ⅰ.Diyang 001, Ⅱ.Diyang 002, Ⅲ.Xiongkeng 001, Ⅳ.Xiongkeng 002, Ⅴ.Fudingdabaicha.The same as Fig. 3. A.Stomatal wholeness, B.Stomatal wholeness, C.Villi wholeness, D.Villi wholeness, E.Waxy texture.由表 2可知,5份茶树叶片内气孔长在(10.42±2.00)~(17.42±1.31)μm,其中芎坑002和地洋002的内气孔相对较长,且显著长于其他3份茶树,芎坑001的内气孔长度相对最短。内气孔宽在(3.17±0.80)~(7.20±2.09)μm,地洋002与芎坑002的内气孔相对较宽,且显著宽于其他3份茶树,芎坑001的内气孔相对最窄。外气孔长在(22.20±1.65)~(27.86±2.20)μm,地洋002的外气孔相对最长,与福鼎大白茶、芎坑002差异不显著,与其他2份茶树差异显著,芎坑001的外气孔相对最短。外气孔宽在(16.42±1.22)~(20.94±2.31)μm,福鼎大白茶的外气孔相对最宽,显著宽于其他4份茶树,地洋001的外气孔相对最窄。气孔开度在(0.32±0.14)~(0.47±0.41),福鼎大白茶的气孔开度相对最大,与地洋002差异不显著,与其他3份野生茶树差异显著。气孔器大小在(394.07±57.96)~(577.79±105.90)μm2,福鼎大白茶与地洋002的气孔器相对较大,且显著大于其他3份野生茶树,芎坑001的气孔器相对最小。气孔密度在(127.41±13.60)~(239.57±28.31)个·mm-2,福鼎大白茶和地洋001的气孔密度相对较大,且显著大于其他3份野生茶树,地洋002的气孔密度相对最小。4份野生茶树的气孔器大小均小于福鼎大白茶(福鼎大白与地洋002没有显著差异)。
表 2 寿宁野生茶树叶片气孔微形态特征Table 2. Stomatal micromorphology of tea leaf种质资源
Germplasm内气孔长
Inner stomatal
length/μm内气孔宽
Inner stomatal
width/μm外气孔长
Outer stomatal
length/μm外气孔宽
Outer stomatal
width/μm气孔开度
Stomatal
aperture气孔器大小
Stomach
size/μm2气孔密度
Stomatal
density(个·mm-2)产地
OriginⅠ 13.88±1.77b 4.77±1.44b 24.46±1.21b 16.42±1.22c 0.34±0.10b 402.03±41.27c 229.09±18.19a 福建寿宁 Ⅱ 17.21±2.17a 7.2±2.09a 27.86±2.20a 18.92±2.31b 0.42±0.13a 530.41±94.96ab 127.41±13.60b 福建寿宁 Ⅲ 10.42±2.00c 3.17±0.80c 22.2±1.65c 17.69±1.63bc 0.32±0.14b 394.07±57.96c 132.14±20.93b 福建寿宁 Ⅳ 17.42±1.31a 6.11±1.27ab 26.26±1.85ab 18.34±1.73b 0.35±0.06b 481.87±58.64b 141.88±14.55b 福建寿宁 Ⅴ 13.38±4.51b 5.31±3.06b 27.56±3.67a 20.94±2.31a 0.47±0.41a 577.79±105.90a 239.57±28.31a 福建福鼎 注:同列数据后不同小写字母表示在0.05水平下差异显著。表 3、4同。
Note:Different lowercase letters in a same column represent significant difference at 5% level. The same as table 3,4.由表 3可知,茸毛长度在(280.75±107.65)~(616.95±132.52)μm,福鼎大白茶的茸毛相对最长,显著长于其他4份野生茶树,地洋001的茸毛长度相对最短。茸毛粗度在(8.06±2.14)~(12.04±3.38)μm,芎坑001的茸毛相对最粗,芎坑002的茸毛相对最细。茸毛密度在(2.17±1.13)~(9.41±2.87)根·mm-2,地洋001的茸毛密度相对最大,且显著大于其他4份茶树,芎坑001的茸毛密度相对最小。与福鼎大白茶相比,4份野生茶树的叶片茸毛显著较短,茸毛粗度差异不大。地洋001的茸毛密度相对最大,且显著大于福鼎大白茶和其他3份野生茶树。
表 3 寿宁野生茶树叶片茸毛微形态特征Table 3. Trichome micromorphology of tea leaf种质资源
Germplasm茸毛长度
Trichome length/μm茸毛粗度
Trichome diameter/μm茸毛密度
Trichome density/(根·mm-2)产地
OriginⅠ 280.75±107.65c 8.22±2.22ab 9.41±2.87a 福建寿宁 Ⅱ 327.47±139.86c 9.18±1.96ab 6.11±1.58b 福建寿宁 Ⅲ 519.30±203.63b 12.04±3.38a 2.17±1.13c 福建寿宁 Ⅳ 307.54±107.81c 8.06±2.14b 2.18±0.72c 福建寿宁 Ⅴ 616.95±132.52a 9.36±0.89ab 6.67±1.27b 福建福鼎 从叶片纹饰方面来看,地洋001的叶腹面纹饰是平展状为一类,地洋002和芎坑001的纹饰为皱脊状属于一类,芎坑002和福鼎大白茶为波浪状属于一类。在电镜观察中发现,4份野生茶树种质资源的叶背和叶腹面均有很多丝状体(图 1)。
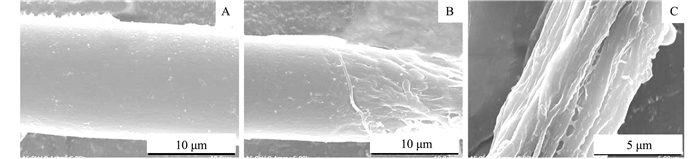
在对叶表皮的电镜观察中发现,4份野生茶树种质资源的大多数茸毛表层均有脱落的现象,且脱落的位置大多集中在茸毛的中下部长度(图 2)。茸毛的形态特征变化与品种、抗性等有密切关系[20],同时根据实际情况推测可能与茶树的生长环境有关。
2.2 寿宁野生茶树花粉微形态特征
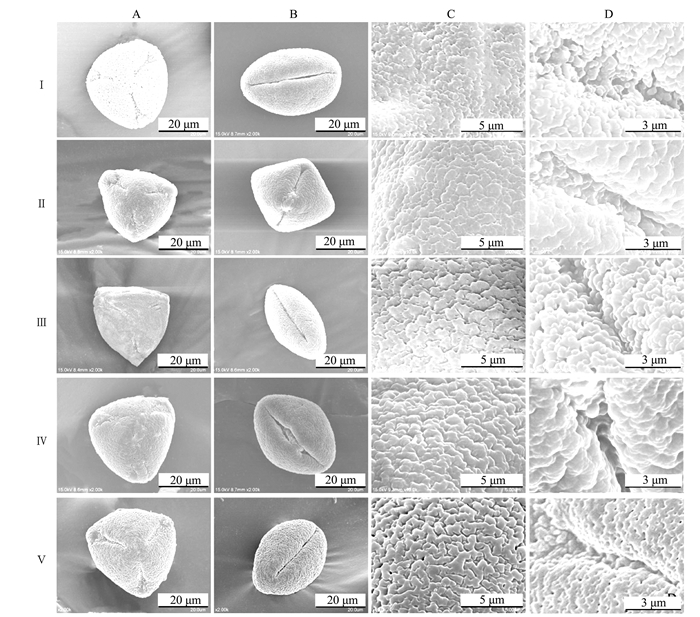
参考王开发等[21]和王伏雄[22]的方法,5份茶树的花粉均为单粒花粉,花粉均具三孔沟,孔沟均沿赤道方向120°均匀分布,为N3P4C5型(N为萌发孔的数目、P为萌发孔的位置、C为萌发孔的特征)花粉(图 3)。按照王开发等[21]提出的花粉最长轴分类标准,5份茶树花粉极轴长均值为25~50 μm,属于中等长度花粉。5份茶树花粉的极面观除地洋001为近圆形外,其他4份茶树均为三裂近三角形,赤道面观有超长球形、近扁球形外、近长球形、长椭圆形4种。三孔沟花粉的形状包括近球形(P/E值在0.75~1.33)、长球形(P/E值在1.33~2.00)及超长球形(P/E值>2)。地洋001的P/E值(2.04±0.49)最大,其花粉形状为超长球形,其他4份茶树花粉的P/E值均在0.75~1.33,花粉形状为近球形。
地洋001花粉外壁纹饰为微小疣状无穿孔,地洋002为光滑疣状并有较多穿孔,芎坑001和芎坑002都为粗糙疣状并有少量穿孔,福鼎大白茶为光滑疣状无穿孔。5份茶树花粉萌发沟内均具有块状或颗粒状纹饰。
由表 4可知,5份野生茶树种质资源的花粉极轴长(P)在(27.60±4.39)~(35.68±7.29)μm,其中福鼎大白茶极轴相对最长,与地洋002差异不显著,但显著长于其他3份野生茶树。赤道轴长(E)在(14.74±4.10)~(33.81±2.01)μm,地洋002的赤道轴相对最长,与地洋002差异不显著,但显著长于其他3份野生茶树。萌发沟长(L)在(19.81±3.35)~(25.94±2.22)μm,其中地洋002的萌发沟最长,与芎坑001差异不显著,显著长于其他3份茶树。花粉大小(P×E)在(427.69±153.94)~(1205.07±237.80)μm2,福鼎大白茶的花粉最大,与地洋002差异不显著,但显著大于其他3份野生茶树。花粉形状(P/E)的比值在(0.94±0.15)~(2.04±0.49),地洋001的极轴长/赤道轴长(P/E)值较大,其他几种花粉极轴长/赤道轴长(P/E)值较小且无显著差异。沟极比(L/P)在(0.54±0.16)~(0.93±0.19),其中芎坑001的沟极比(L/P)相对最大,福鼎大白茶沟极比(L/P)相对最小。
表 4 寿宁野生茶树花粉形态性状指标Table 4. Pollen morphology of tea cultivars种质资源
Germplasm极轴长(P)
Length of
polaraxis/μm赤道轴长(E)
Length of
equator axis/μm萌发沟长(L)
Length of germi-
nation colpus/μm花粉大小
P×E
/μm2花粉形状
P/E萌发沟长/
极轴长
L/P极面观
Polar view赤道面观
Equatorial
view外壁纹饰
Outer wall
decorationⅠ 28.55±3.32b 14.74±4.10c 23.23±3.34b 427.69±153.94c 2.04±0.49a 0.83±0.15ab 近圆形 超长球形 疣状无穿孔 Ⅱ 31.68±2.08ab 33.06±2.80ab 25.94±2.22a 1064.73±143.03ab 0.95±0.10b 0.82±0.06ab 三裂近三角形 近扁球形 疣状多穿孔 Ⅲ 27.60±4.39b 28.92±3.12b 24.77±3.14ab 814.70±168.30b 0.94±0.15b 0.93±0.19a 三裂近三角形 近长球形 疣状少量穿孔 Ⅳ 30.93±4.20b 31.06±3.22b 21.97±4.72bc 931.12±145.89b 0.98±0.18b 0.74±0.18b 三裂近三角形 近长球形 疣状少量穿孔 Ⅴ 35.68±7.29a 33.81±2.01a 19.81±3.35c 1205.07±237.80a 1.06±0.24b 0.54±0.16c 三裂近三角形 长椭圆形 疣状无穿孔 花粉观察结果表明,5份花粉都为中等大小花粉。地洋001、芎坑001和芎坑002的花粉均小于福鼎大白茶,地洋002与其无显著差别。其中地洋001的花粉最小,福鼎大白茶花粉大小约为地洋001的花粉大小的3~4倍。据束际林[23]用扫描电镜对34个野生茶树花粉的研究结果显示,野生茶树花粉的平均直径显著小于栽培种的平均直径,因此推测地洋001可能相对较为原始。其中地洋001的极轴长显著大于赤道轴长,且极轴长大约为赤道轴长的2倍,其余4份茶树则是赤道轴长大于极轴长,且两者相差不多。地洋001花粉形状与其他3份野生花粉差异较大,地洋001的花粉为超长球形,其他3份均为近球形。
地洋002、芎坑001、芎坑002与福鼎大白茶的极面观相似,都为三裂近三角形。地洋001极面观为近圆形,与其余4份茶树极面观差异较大,外壁纹饰都为疣状,其中地洋001与福鼎大白茶外壁纹饰均无穿孔,地洋002、芎坑001、和芎坑002都有穿孔(图 3)。
3. 讨论与结论
叶片微形态的差异一方面是植物物种本身特有的特征的体现,另一方面也是环境对其作用的体现。肖寒等[24]对云锦杜鹃亚组叶表皮微形态观察研究结果表明其毛被、气孔器及其周围纹饰的多样性和相似性可为分类学提供一定证据。这与本研究结果具有一致性。本研究结果表明,5份茶树的叶表蜡质纹饰有波浪状、平展状和皱脊状3种类型,表明了茶树叶片蜡质纹饰的多样性。4份野生茶树叶片背面均有圆形细长或短粗状的表皮毛,呈不规则分布,气孔器都为长卵形;茸毛长度、茸毛密度、气孔器大小、气孔密度等特征性状指标在不同品种间有一定差异性。这表明茶树茸毛、气孔、蜡质纹饰等可作为茶树分类及鉴别的重要形态性状[25-26]。本研究发现所供野生茶树的茸毛长度均显著小于栽培种,且4份野生茶树的大多数茸毛表层均有脱落的现象。福鼎大白茶是国家级优质茶树品种,茸毛特多、耐寒性强等是其较突出的优良性状,而地洋001茸毛密度显著大于福鼎大白茶。这表明茶树种质资源叶片形态结构关乎茶树抗性和品质[27-28]。
不同植物种类的花粉在长期的进化过程中往往形成独特的形态特征,这些形态特征具有很强的遗传保守性和稳定性,可以为植物的起源、分类、亲缘关系及杂交育种亲本的选配等方面提供重要依据[29]。Al-Hakimi等[30]对柳杉属9种植物的花粉和种子微形态的研究结果表明花粉纹饰、外壁厚度等特征有助于区分属内物种。本研究中4份野生茶树的花粉外壁纹饰都为疣状有穿孔或无穿孔,具有共性和差异性。束际林[23]对云南花粉形态的研究发现野生型茶树花粉大小小于一般栽培型茶树花粉。在本研究中野生茶树花粉大小都为中等花粉,但显著小于福鼎大白茶栽培种,表明野生茶树花粉大小显著小于栽培种,与前人结论相符。
本研究涉及的4份野生茶树种质资源与1份茶树栽培品种的叶片茸毛密度、长度、气孔密度和与花粉大小、外壁纹饰等微形态特征在不同品种间既有统一性,又有多样性差异,可为茶树种间分类、鉴别、系统关系探讨、良种选育提供参考依据,后续研究可通过分子生物学等手段对其分类鉴定和亲缘关系做进一步探讨。
-
图 1 寿宁野生茶树叶片微形态电子显微观察结果
注:Ⅰ为地洋001,Ⅱ为地洋002,Ⅲ为芎坑001,Ⅳ为芎坑002,Ⅴ为福鼎大白茶。图 3同。A为气孔整体观,B为气孔,C茸毛整体观,D为茸毛,E为蜡质纹饰。
Figure 1. SEM of tea leaf
Note:Ⅰ.Diyang 001, Ⅱ.Diyang 002, Ⅲ.Xiongkeng 001, Ⅳ.Xiongkeng 002, Ⅴ.Fudingdabaicha.The same as Fig. 3. A.Stomatal wholeness, B.Stomatal wholeness, C.Villi wholeness, D.Villi wholeness, E.Waxy texture.
表 1 供试茶树种质资源主要特征
Table 1 Main characteristics of tea germplasms
表 2 寿宁野生茶树叶片气孔微形态特征
Table 2 Stomatal micromorphology of tea leaf
种质资源
Germplasm内气孔长
Inner stomatal
length/μm内气孔宽
Inner stomatal
width/μm外气孔长
Outer stomatal
length/μm外气孔宽
Outer stomatal
width/μm气孔开度
Stomatal
aperture气孔器大小
Stomach
size/μm2气孔密度
Stomatal
density(个·mm-2)产地
OriginⅠ 13.88±1.77b 4.77±1.44b 24.46±1.21b 16.42±1.22c 0.34±0.10b 402.03±41.27c 229.09±18.19a 福建寿宁 Ⅱ 17.21±2.17a 7.2±2.09a 27.86±2.20a 18.92±2.31b 0.42±0.13a 530.41±94.96ab 127.41±13.60b 福建寿宁 Ⅲ 10.42±2.00c 3.17±0.80c 22.2±1.65c 17.69±1.63bc 0.32±0.14b 394.07±57.96c 132.14±20.93b 福建寿宁 Ⅳ 17.42±1.31a 6.11±1.27ab 26.26±1.85ab 18.34±1.73b 0.35±0.06b 481.87±58.64b 141.88±14.55b 福建寿宁 Ⅴ 13.38±4.51b 5.31±3.06b 27.56±3.67a 20.94±2.31a 0.47±0.41a 577.79±105.90a 239.57±28.31a 福建福鼎 注:同列数据后不同小写字母表示在0.05水平下差异显著。表 3、4同。
Note:Different lowercase letters in a same column represent significant difference at 5% level. The same as table 3,4.表 3 寿宁野生茶树叶片茸毛微形态特征
Table 3 Trichome micromorphology of tea leaf
种质资源
Germplasm茸毛长度
Trichome length/μm茸毛粗度
Trichome diameter/μm茸毛密度
Trichome density/(根·mm-2)产地
OriginⅠ 280.75±107.65c 8.22±2.22ab 9.41±2.87a 福建寿宁 Ⅱ 327.47±139.86c 9.18±1.96ab 6.11±1.58b 福建寿宁 Ⅲ 519.30±203.63b 12.04±3.38a 2.17±1.13c 福建寿宁 Ⅳ 307.54±107.81c 8.06±2.14b 2.18±0.72c 福建寿宁 Ⅴ 616.95±132.52a 9.36±0.89ab 6.67±1.27b 福建福鼎 表 4 寿宁野生茶树花粉形态性状指标
Table 4 Pollen morphology of tea cultivars
种质资源
Germplasm极轴长(P)
Length of
polaraxis/μm赤道轴长(E)
Length of
equator axis/μm萌发沟长(L)
Length of germi-
nation colpus/μm花粉大小
P×E
/μm2花粉形状
P/E萌发沟长/
极轴长
L/P极面观
Polar view赤道面观
Equatorial
view外壁纹饰
Outer wall
decorationⅠ 28.55±3.32b 14.74±4.10c 23.23±3.34b 427.69±153.94c 2.04±0.49a 0.83±0.15ab 近圆形 超长球形 疣状无穿孔 Ⅱ 31.68±2.08ab 33.06±2.80ab 25.94±2.22a 1064.73±143.03ab 0.95±0.10b 0.82±0.06ab 三裂近三角形 近扁球形 疣状多穿孔 Ⅲ 27.60±4.39b 28.92±3.12b 24.77±3.14ab 814.70±168.30b 0.94±0.15b 0.93±0.19a 三裂近三角形 近长球形 疣状少量穿孔 Ⅳ 30.93±4.20b 31.06±3.22b 21.97±4.72bc 931.12±145.89b 0.98±0.18b 0.74±0.18b 三裂近三角形 近长球形 疣状少量穿孔 Ⅴ 35.68±7.29a 33.81±2.01a 19.81±3.35c 1205.07±237.80a 1.06±0.24b 0.54±0.16c 三裂近三角形 长椭圆形 疣状无穿孔 -
[1] 王平盛, 虞富莲.中国野生大茶树的地理分布、多样性及其利用价值[J].茶叶科学, 2002, 22(2): 105-108. DOI: 10.3969/j.issn.1000-369X.2002.02.003 WANG P S, YU F L. The Geographic Distribution, Diversity and Utilization of Wild Tea Camellias in China[J]. Journal of Tea Science, 2002, 22(2): 105-108.(in Chinese) DOI: 10.3969/j.issn.1000-369X.2002.02.003
[2] 汪劲武.两个姐妹科--茶科和猕猴桃科[J].生命世界, 1985(5):33-35. http://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTotal-ZWZA198505027.htm WANG J W. Two sister families-Theaceae and Actinidiaceae Gilg & Werderm[J].Life World, 1985(5):33-35. (in Chinese) http://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTotal-ZWZA198505027.htm
[3] 郭元超, 姚信恩, 肖丽平, 等.仙墩山野生茶树考查报告[J].茶叶科学简报, 1984(1):6-11. http://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTotal-CYKJ198401002.htm GUO Y C, YAO X E, XIAO L P, et al.Investigation report of wild tea trees in Xiandun Mountain[J]. Tea Science Briefing, 1984(1):6-11.(in Chinese) http://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTotal-CYKJ198401002.htm
[4] 郭元超, 叶乃兴, 肖丽平.太姥山野生茶树考查报告[J].茶叶科学简报, 1985(1):8-10. http://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTotal-CYKJ198501002.htm GUO Y C, YE N X, XIAO L P. Taicha Mountain Wild Tea Tree Examination[J].ReportTea Science Briefing, 1984(1):6-11.(in Chinese) http://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTotal-CYKJ198501002.htm
[5] 周玉璠, 吴洪新, 阮克錞, 等.宁德市陆续发现茶的野生资源[J].福建茶叶, 1994(3):8-10. http://www.wanfangdata.com.cn/details/detail.do?_type=perio&id=QK199400063882 ZHOU Y P, WU H X, RUAN K C, et al.Ningde City successively discovered the wild resources of tea[J]. Tea In Fujian, 1994(3):8-10.(in Chinese) http://www.wanfangdata.com.cn/details/detail.do?_type=perio&id=QK199400063882
[6] 杨如兴, 陈芝芝, 张磊, 等.福建野生茶树种质资源保护与利用[J].茶叶学报, 2017, 58(3):96-101. DOI: 10.3969/j.issn.1007-4872.2017.03.003 YANG R X, CHEN Z Z, ZHANG L, et al.Conservation and Utilization of Wild Tea Germplasm in Fujian[J]. Acta Tea Sinica, 2017, 58(3):96-101.(in Chinese) DOI: 10.3969/j.issn.1007-4872.2017.03.003
[7] SOSNOVSKY Y, NACHYCHKO V, PROKOPIV A, et al. Leaf architecture in Rhododendron subsection Rhododendron (Ericaceae) from the Alps and Carpathian Mountains: Taxonomic and evolutionary implications[J]. Flora, 2017, 230:26-38. DOI: 10.1016/j.flora.2017.03.003
[8] FIRETTI LEGGIERI F, LOHMANN L G, SEMIR J, et al. Using leaf anatomy to solve taxonomic problems within the Anemopaegma arvense species complex (Bignonieae, Bignoniaceae)[J]. Nordic Journal of Botany, 2015, 32(5):620-631. http://www.wanfangdata.com.cn/details/detail.do?_type=perio&id=181eaaf801f72b97e40593de8aa1674b
[9] 汤雨岛, 廖晨阳, 周波.常绿杜鹃亚属麻花杜鹃亚组11种3变种植物叶片微形态特征及其分类学意义[J].西北植物学报, 2016, 36(8): 1600-1607. http://d.old.wanfangdata.com.cn/Periodical/xbzwxb201608014 TANG Y D, LIAO C Y, ZHOU B. Leaf Micromorphological Characteristics and Taxonomic Significance of 11 Species, 3 Varieties in Subsect.Maculifera, Subgen.Hymenanthes(Ericaceae)[J]. Acta BotanicaBoreali-Occidentalia Sinica, 2016, 36(8): 1600-1607.(in Chinese) http://d.old.wanfangdata.com.cn/Periodical/xbzwxb201608014
[10] 陈常颂, 彭艾, 钟秋生, 等. 34份茶树种质的花粉形态特征研究[J].福建农业学报, 2012, 27(11):1219-1226. DOI: 10.3969/j.issn.1008-0384.2012.11.014 CHEN C S, PENG A, ZHONG Q S, et al.Morphological Studies on Pollen of Camellias for 34 Species (Camellia Sinensis)[J]. Fujian Journal of Agricultural Sciences, 2012, 27(11):1219-1226.(in Chinese) DOI: 10.3969/j.issn.1008-0384.2012.11.014
[11] SUR G L, KEATING R, SNOW N, et al. Leaf Micromorphology Aids Taxonomic Delineation within the Hypervariable Genus Metrosideros (Myrtaceae) on O'ahu[J]. Pacific Science, 2018, 72(3):345-362. DOI: 10.2984/72.3.6
[12] FORTINI P, ANTONECCHIA G, MARZIO P D, et al. Role of micromorphological leaf traits and molecular data in taxonomy of three sympatric white oak species and their hybrids (Quercus L.)[J]. Giornale Botanico Italiano, 2013, 149(3):546-558. http://www.researchgate.net/publication/259397440_Role_of_micromorphological_leaf_traits_and_molecular_data_in_taxonomy_of_three_sympatric_white_oak_species_and_their_hybrids_(Quercus_L.)
[13] 胡蕙露, 杨景华, 陈慧, 等.若干科观赏植物花粉形态电镜观察与比较[J].安徽农业大学学报, 2001(3): 320-325. DOI: 10.3969/j.issn.1672-352X.2001.03.024 HU H L, YANG J H, CHEN H, et al. The SEM Investigation on Structure and Shape of Ornamental Plant's Pollen in Several Families[J]. Journal of Anhui Agricultural University, 2001(3): 320-325.(in Chinese) DOI: 10.3969/j.issn.1672-352X.2001.03.024
[14] FURNESS C A, GREGORY T, RUDALL P J. Pollen Structure and Diversity in Liliales[J]. International Journal of Plant Sciences, 2015, 176(8):000-000. http://www.wanfangdata.com.cn/details/detail.do?_type=perio&id=3e547f1e70000bd2447a5eb1d6bd198e
[15] 张永芳, 胡超琼, 杨勇, 等.柿属8种植物花粉形态观察[J].园艺学报, 2016(6): 1167-1174. http://d.old.wanfangdata.com.cn/Periodical/yyxb201606015 ZHANG Y F, HU C Y, YANG Y, et al. Pollen Morphology Observation of Eight Resources in Diospyros[J]. Acta Horticulturae Sinica, 2016(6): 1167-1174.(in Chinese) http://d.old.wanfangdata.com.cn/Periodical/yyxb201606015
[16] 杨国一, 于文涛, 蔡春平, 等.茶树叶片扫描电镜样品制备方法的比较研究[J].江苏农业科学, 2018, 46(3): 95-98. http://d.old.wanfangdata.com.cn/Periodical/jsnykx201803024 YANG G Y, YU W T, CAI C P, et al. Comparative Study on Preparation Methods of Scanning Electron Microscope Samples of Tea Leaves[J]. Jiangsu Agricultural Sciences, 2018, 46(3): 95-98.(in Chinese) http://d.old.wanfangdata.com.cn/Periodical/jsnykx201803024
[17] 侯燕鸣, 胡剑江, 方蔷, 等.扫描电镜的不同含水量植物叶片样品的处理及观察方法研究[J].分析仪器, 2011(5): 45-48. DOI: 10.3969/j.issn.1001-232X.2011.05.011 HOU Y M, HU J J, FANG Q, et al. Study on sample treatment methods of plant leaves with different water contents for SEM[J]. Analytical Instrumentation, 2011(5): 45-48.(in Chinese) DOI: 10.3969/j.issn.1001-232X.2011.05.011
[18] 戴志聪, 杜道林, 司春灿, 等.用扫描仪及Image J软件精确测量叶片形态数量特征的方法[J].广西植物, 2009, 29(3):342-347. DOI: 10.3969/j.issn.1000-3142.2009.03.013 DAI Z C, DU D L, SI C C, et al, A method to exactly measure the morphological quantity of leaf using Scanner and Image J Software[J].Guihaia, 2009, 29(3):342-347.(in Chinese) DOI: 10.3969/j.issn.1000-3142.2009.03.013
[19] 谢微微, 于文涛, 杨国一, 等. 14个茶树品种的花粉微形态观察[J].南方农业学报, 2018, 49(9): 1698-1704. DOI: 10.3969/j.issn.2095-1191.2018.09.03 XIE W W, YU W T, YANG G Y, Micromorphological observation on pollen of 14 cultivars of tea tree (Camellia sinensis) [J].Journal of Southern Agriculture, 2018, 49(9): 1698-1704.(in Chinese) DOI: 10.3969/j.issn.2095-1191.2018.09.03
[20] 尹鹏, 刘威, 王广铭, 等.茶树芽叶茸毛及茶毫研究进展[J].河南农业, 2016(27): 44-46. DOI: 10.3969/j.issn.1006-950X.2016.27.023 YIN P, LIU W, WANG G M, et al, Advances in research on tea tree bud leaf trichomes and teapubescence[J].Agriculture of Henan, 2016(27): 44-46.(in Chinese) DOI: 10.3969/j.issn.1006-950X.2016.27.023
[21] 王开发, 王宪曾.孢粉学概论[M].北京:北京大学出版社, 1983. WANG K F, WANG X Z. Introduction to Playnology[M]. Beijing:Peking University Press, 1983. (in chinese)
[22] 王伏雄.中国植物花粉形态(第2版)[M].北京:科学出版社, 1995. WANG F X. Pollen Flora of China (Second Edition)[M]. Beijing:Science Press, 1995. (in chinese)
[23] 束际林.云南茶树种质资源花粉形态的研究[J].中国茶叶, 1990(4):12-13. http://www.wanfangdata.com.cn/details/detail.do?_type=perio&id=QK000001157224 SHU J L. Study on Pollen Morphology of Yunnan Tea Tree Germplasm Resources[J].China Tea, 1990(4):12-13.(in Chinese) http://www.wanfangdata.com.cn/details/detail.do?_type=perio&id=QK000001157224
[24] 肖寒, 白洁.常绿杜鹃亚属云锦杜鹃亚组26种植物叶片微形态特征及其分类学意义[J].四川大学学报(自然科学版), 2013, 50(2). http://d.old.wanfangdata.com.cn/Periodical/scdxxb201302030 XIAO H, BAI J. Leaf micromorphological characteristics and taxonomic significance of twenty-six species of Subsect. Fortunea, subgen.Hymenanthe (Ericaceae)[J].Journal of Sichuan University(Natural Science Edition), 2013, 50(2). (in Chinese) http://d.old.wanfangdata.com.cn/Periodical/scdxxb201302030
[25] 郭元超.茶树茸毛的形态特征与演化特点[J].茶叶科学简报, 1993(3): 1-4. http://www.cqvip.com/QK/91310X/199303/4001506630.html GUO Y C. Morphological characteristics and evolution characteristics of tea tree trichomes[J].ReportTea Science Briefing, 1993(3): 1-4.(in Chinese) http://www.cqvip.com/QK/91310X/199303/4001506630.html
[26] 杨国一, 于文涛, 郑晶, 等.乌龙茶种质叶片微形态特征的扫描电镜观察[J].南方农业学报, 2018, 49(10): 2020-2027. DOI: 10.3969/j.issn.2095-1191.2018.10.18 YANG G Y, YU W T, ZHENG J, et al, Scanning electron microscopy observation on foliar micromorphology of Oolong tea germplasms[J].Journal of Southern Agriculture, 2018, 49(10): 2020-2027.(in Chinese) DOI: 10.3969/j.issn.2095-1191.2018.10.18
[27] 邱勇娟, 李火坤, 陈佳, 等.扶绥野生茶树叶片结构与生产性状分析[J].南方农业学报, 2015, 46(2):286-292. DOI: 10.3969/jissn.2095-1191.2015.2.286 QIU Y J, LI H K, CHEN J, et al, Leaf structure and production trait of wild tea(Camellia sinensis) from Fusui county[J].Journal of Southern Agriculture, 2015, 46(2):286-292.(in Chinese) DOI: 10.3969/jissn.2095-1191.2015.2.286
[28] 袁弟顺, 叶乃兴, 刘金英, 等.白茶品种茸毛的生化特性[J].福建农林大学学报(自然科学版), 2010, 39(4):356-360. http://d.old.wanfangdata.com.cn/Periodical/fjnydxxb201004005 YUAN D S, YE N X, LIU J Y, et al, Biochemical characteristics of white tea pubescence[J].Journal of Fujian Agriculture and Forestry University(Natural Science Edition), 2010, 39(4):356-360.(in Chinese) http://d.old.wanfangdata.com.cn/Periodical/fjnydxxb201004005
[29] 孙崇波, 向林, 施季森, 等.兰科5属常见栽培品种花粉块形态的扫描电镜观察[J].园艺学报, 2010, 37(12): 1969-1974. http://d.old.wanfangdata.com.cn/Periodical/yyxb201012010 SUN C B, XIANG L, SHI J S, et al, Scanning Electron Microscope Observation on Pollinium Morphology of Five Most Common Cultivated Orchid Genera (Orchidaceae)[J].Acta Horticulturae Sinica, 2010, 37(12): 1969-1974.(in Chinese) http://d.old.wanfangdata.com.cn/Periodical/yyxb201012010
[30] Al-HAKIMI A S, FARIDAH Q Z, ABKULWAHAB A S, et al. Pollen and seed morphology of, Barleria, L. (Barlerieae: Ruellioideae: Acanthaceae) of Yemen[J]. South African Journal of Botany, 2018, 116:185-191. DOI: 10.1016/j.sajb.2018.03.010
-
期刊类型引用(8)
1. 王攀,于文涛,蔡春平,刘财国,王泽涵,叶乃兴. 福建云霄秃房野生茶树群体花器官微形态特征研究. 江苏农业科学. 2023(05): 155-162 .  百度学术
百度学术
2. 徐梦婷,魏明秀,陈潇敏,卢明基,吴文晞,陈晓岚,高水练,叶乃兴. 寿宁长叶1号等茶树新品系儿茶素和氨基酸组分分析. 茶叶学报. 2022(01): 20-26 .  百度学术
百度学术
3. 陈潇敏,章进汕,金珊,邵淑贤,刘永崇,吴文晞,王鹏杰,赵峰,叶乃兴. 福建大田茶树品种资源生化成分特征分析与评价. 南方农业学报. 2022(02): 381-390 .  百度学术
百度学术
4. 曾珊珊,陈潇敏,邵淑贤,廖龙华,吴文晞,赵峰,叶乃兴. 福建苦茶资源不同叶位儿茶素及嘌呤生物碱组分分析. 茶叶学报. 2022(02): 65-72 .  百度学术
百度学术
5. 樊晓静,于文涛,蔡春平,王泽涵,林浥,张琛,叶乃兴. 茶树种质资源花器官微形态特征观察. 南方农业学报. 2021(03): 700-710 .  百度学术
百度学术
6. 刘丹,张洪卫,厉锋,刘启虎,李文清. 济南市野生代茶林木种质资源研究初探. 安徽农学通报. 2020(07): 49-50 .  百度学术
百度学术
7. 陈晓岚,魏明秀,卢明基,孙君,刘登勇,樊晓静,郭永春,叶乃兴. 寿宁县野生茶树种质资源生物学性状分析. 茶叶学报. 2020(01): 10-14 .  百度学术
百度学术
8. 王泽涵,于文涛,樊晓静,方德音,蔡捷英,王元勋,叶乃兴. 福建秃房野生茶种质资源新纪录及其子房微形态观察. 福建农业学报. 2020(08): 830-836 .  本站查看
本站查看
其他类型引用(6)




 下载:
下载: