Expression of Antioxidant Enzyme Genes in Rice under PEG-simulated Drought-stress
-
摘要:目的 干旱是影响水稻生产的重要环境因素之一,在干旱条件下水稻植株体内会发生一系列的抗逆反应,其中参与防御反应的关键酶基因表达会发生明显的变化。因此,本研究拟分析干旱胁迫处理后抗氧化酶类基因的表达变化,为进一步研究水稻抗旱机制提供理论参考。方法 采用质量体积比为0(CK)、18%、20%、22%、24%、26%的聚乙二醇(PEG6000)对三叶一心期的籼稻航2号植株进行干旱胁迫处理,筛选适合处理籼稻航2号的PEG6000质量体积比;进一步采用PEG6000对航2号植株进行干旱胁迫处理,分别于处理0、2、4、8、12、24、48、72 h取样;并用SYBR Green I荧光定量PCR(qRT-PCR)分析PEG6000处理不同时间段后植株中抗氧化酶类基因表达,包括过氧化氢酶(CATA、CATB、CATC)、过氧化物酶(POX5.1、POX1)、超氧化物歧化酶(plastidic Cu/Zn-SOD,cytosolic Cu/Zn-SOD)、抗坏血酸过氧化物酶(APX)、谷胱甘肽还原酶(GR)基因的表达变化。结果 根据表型观察和植株存活率,筛选出籼稻航2号对PEG6000的耐受临界质量体积比为22%;qRT-PCR结果表明PEG6000胁迫处理后9个基因的表达均出现上调,大部分基因表达都呈先上调后下调的趋势,且一般PEG处理4 h之后基因表达出现较明显上调,说明这些基因均不同程度地参与了PEG胁迫反应;其中,过氧化氢酶A基因(CATA)表达变化最显著,处理8 h表达量上调至处理0 h的28倍。结论 PEG6000胁迫处理后主要的抗氧化酶类基因表达发生了明显的变化。
-
关键词:
- 水稻 /
- 聚乙二醇(PEG6000) /
- 干旱胁迫 /
- 抗氧化酶基因 /
- 表达分析
Abstract:Objective Expression of antioxidant enzyme genes of rice in response to drought-stress was studied.Method Simulated drought conditions using PEG6000 on Indica rice Hang 2 were used for the experimentation. The plants at 3-leaf stage were initially treated with 0% (CK), 18%, 20%, 22%, 24% or 26% PEG6000 to determine the appropriate concentration for the subsequent test. Under the selected PEG6000 treatment level, plant samples were collected at 0, 2, 4, 8, 12, 24, 48 and 72 h for analysis. The expressions of antioxidant enzyme genes (i.e., CATA, CATB and CATC), peroxidase genes (i.e., POX5.1 and POX1), superoxide dismutase genes (i.e., plastidic Cu/Zn-SOD and cytosolic Cu/Zn-SOD), ascorbate peroxidase gene (i.e., APX), and glutathione reductase gene (i.e., GR) of the rice plants were determined by qRT-PCR.Result Based on the phenotype and survival rate of the rice plants in the preliminary test, 22% PEG6000 was chosen for the simulation experiment. The results of qRT-PCR showed that all 9 genes were upregulated initially under the treatment but downregulated afterward. Most of the genes significantly upregulated 4 h after treatment showing a response of the genes to the stress. In particular, CATA exhibited a most significant change at 8 h which was 28 times of that at 0 h.Conclusion The expression of antioxidant enzyme genes significantly reacted to the PEG6000 treatment.-
Keywords:
- rice /
- PEG6000 /
- drought stress /
- antioxidant enzymes genes /
- expression analysis
-
0. 引言
【研究意义】无花果Ficus carica L.是桑科榕属植物,栽培简易、适应性强,在光照充足,冬无严寒,又常有海风海雾吹拂滋润的海洋性气候地区种植尤为适宜[1],富含多种维生素[2]、氨基酸和矿质元素[3]。果实中的糖含量是影响果实品质和果实风味最主要的因素之一,无花果的品质形成多依赖于无花果果实中的糖的积累。‘波姬红’为福建地区主栽无花果品种,但在福建引种时间短,果实品质易受多种因素影响,且栽培技术落后,果实品质良莠不齐。钾是无花果果实生长发育中基础元素之一,对无花果的生理生长和生理代谢有着重要的作用。因此,研究无花果果实糖积累规律,揭示钾元素对无花果糖代谢调控机制,对提高无花果果实品质和产量都具有重要意义。【前人研究进展】钾元素在土中易流失,果实发育期间钾肥补施十分重要。大量研究表明,增施钾肥可以提高果实中的可溶性糖含量,促进果实色泽的形成[4-6]。迄今为止,关于果实糖代谢的研究已经在李[7]、柑橘[8]、香蕉[9]、芒果[10]等果树上有了大量研究,关于钾肥对果实糖代谢影响的研究,已经在苹果[11]、草莓[12]、番茄[13]等园艺作物上有了相关报道。【本研究切入点】关于增施钾肥对无花果果实糖含量及糖代谢相关酶活性影响的研究鲜见报道。【拟解决的关键问题】本试验以2年生的‘波姬红’无花果为试材,研究不同施钾水平对无花果果实糖积累的调控机制,以期为合理施肥,提高无花果果实品质和产量提供理论依据。
1. 材料与方法
1.1 试验材料
本试验以2年生的大棚‘波姬红’无花果苗为试验材料,在福建省莆田市天兰种植基地进行。试验土壤为砂质壤土,施肥前土壤营养状况为:土壤pH 6.07,碱解氮118.3 mg·kg−1,速效磷211.0 mg·kg−1,速效钾139.3 mg·kg−1,有机质21.75 g·kg−1。
2019年4月,选择大棚中生长状况一致、健康无病害的植株,进行挂牌标记。试验共设4个处理,施钾量分别为:CK(0 g·株−1)、K1(125 g·株−1)、K2(250 g·株−1)、K3(375 g·株−1)。每个处理的每个重复选10棵果树,重复3次。钾肥分3个时期施用,分别于5月13日(果实快速膨大期Ⅰ前,施总钾肥量的40%)、6月16日(果实快速膨大期Ⅱ前,施总钾肥量的30%)、7月13日(果实采收前,施总钾肥量的30%)各施肥1次。施肥方式采用浇施,取相应量的肥料兑水施入,对照施入等量的清水,并进行常规管理。
样品采集于晴朗天气的上午进行,采样从5月23日开始,每次采样间隔15 d,每个试验处理的每个重复取果20个,直至果实成熟。
1.2 试验方法
1.2.1 可溶性糖提取
可溶性糖的提取参考李春丽[14]的方法。
1.2.2 可溶性总糖与淀粉含量的测定
可溶性总糖含量采用王学奎等[15]的方法测定。淀粉含量采用北京索莱宝科技有限公司淀粉含量测定试剂盒测定。
1.2.3 高效液相色谱(HPLC)测定可溶性糖组分
测定糖含量的色谱条件参考龚江美[16]的方法,并略有改动。测定仪器为ACQUITY UPLC®(美国WATERS公司)超高效液相色谱仪,检测器为AUtech 3300型蒸发光散射检测器(美国奥泰公司),配置配有自动进样器、四元溶剂管理器,进样量2 μL。色谱柱采用Waters ACQUITY UPLC BEH Amide氨基柱,2.1 X 100 mm,1.7 μm,柱温35℃,流动相为A:乙腈,B:含0.2%(体积分数)的氨水,A:B=79%:21%,流速:0.2 mL·min−1,所测蔗糖、果糖、葡萄糖的标准样品均为色谱纯级标准品,购自北京索莱宝科技有限公司。
1.2.4 无花果果实糖代谢相关酶活性的测定
酸性转化酶(AI)、中性转化酶(NI)、蔗糖磷酸合成酶(SPS)、蔗糖合酶(SS)的提取参考Keller and Ludlow[17]方法。酸性和中性转化酶的活性测定参考Rui Zhou[18]的方法。蔗糖磷酸合成酶、蔗糖合成酶活性测定参考赵智中[19]的方法。α-淀粉酶和β-淀粉酶活性采用酶联免疫吸附法测定,ELISA 试剂盒购置于上海通蔚生物科技有限公司。
1.3 数据分析
利用Excel 2016和DPS v14.10进行数据统计和差异性分析,用SPSS 20.0进行相关性分析。
2. 结果与分析
2.1 不同施钾水平对无花果不同生长期可溶性总糖含量的影响
由图1可以看出,无花果果实可溶性糖含量随生长发育逐渐上升,增加速率整体呈“快-慢-快-慢”的趋势。与对照相比,增施钾肥可以有效提高各个时期无花果果实中的可溶性糖含量,以K2整体表现最好。在成熟期时,K1、K2、K3处理的无花果果实中的可溶性糖含量分别达到14.74%、15.56%、14.97%,比CK组高1.2%、6.4%、2.7%。其中K2、K3与CK之间的差异均达显著水平。
2.2 不同施钾水平对无花果不同生长期可溶性糖组分及淀粉含量的影响
由图2可知,果糖(图2-A)与葡萄糖(图2-B)是果实中主要的可溶性糖,其含量在果实发育前期增长幅度较小,后期迅速升高。蔗糖(图2-C)含量相对较低,整体呈先下降后上升的趋势。施钾处理对3种可溶性糖含量的影响在果实发育前期不明显,中后期差异较大,其中以K2表现最好。至果实成熟期,K1、K2、K3的果糖和葡萄糖含量分别达到31.4 mg·g−1、31.7 mg·g−1;37.3 mg·g−1、40.2 mg·g−1;34.3 mg·g−1、35.3 mg·g−1,比对照提高了2.8%、4.1%;22.2%、40.3%;12.2%、32.0%,其中K2、K3与处理组之间的差异均达极显著水平。蔗糖含量分别达0.11 mg·g−1、0.13 mg·g−1、0.11 mg·g−1,比对照提高了11.6%、28.6%、14.5%,其中K1、K3与对照组之间的差异达显著水平,K2与对照组之间的差异达极显著水平。
淀粉(图2-D)含量与可溶性糖含量的变化趋势相反,除了在果实发育前期,淀粉含量有短暂的升高,整体呈下降趋势。在坐果后30 d(5月23日),3个处理组的淀粉含量均大于对照组,其中以K3最高,达11.1 mg·g−1,对照组与处理组之间的差异均达极显著水平。至坐果后45 d(6月8日)时,CK与K1的淀粉含量有明显上升,而K2与K3的淀粉含量明显下降,这表明增施钾肥可以加速淀粉的合成和降解速率。至果实成熟期,K2、K3的淀粉含量与CK之间的差异达极显著,K1与CK之间的差异不显著。
2.3 不同施钾水平对无花果蔗糖代谢相关酶活性的影响
2.3.1 不同施钾水平对无花果果实转化酶活性的影响
图3-A显示,随着果实的发育,AI的活性整体呈逐渐上升的趋势,变化较小。3个处理组的AI活性整体大于对照组。在果实发育前期,处理之间的差异并不明显,从坐果后45 d(6月8日)起,K2的AI活性开始显著高于其他几组处理,其中坐果后75 d(7月8日)、坐果后90 d(7月23日)K2与其他处理的AI活性差异达极显著。
图3-B显示,NI随着果实的成熟活性先降低至坐果后75 d(7月8日)迅速回升。在果实发育前期(坐果后30 -60 d),对照与处理之间的差异较小,至坐果后75 d(7月8日),3个处理组的NI活性均显著大于对照组。3个处理中,K2的NI活性在坐果后30 d(5月23日)和坐果后75 d(7月8日)都显著大于其他2个处理组,在坐果后90 d(7月23日)显著大于K1和CK,整体表现最好。K1和K3之间的差异并不显著。
2.3.2 不同施钾水平对无花果果实蔗糖合酶分解方向活性的影响
如图4所示,SS(分解方向)的活性随果实的生长发育总体呈先下降后上升的趋势。3个处理组的SS活性在果实发育前期(坐果后30 d和坐果后45 d)大于对照组,后期处理和对照间的差异没有明显的规律。3个处理间以K2的SS分解方向活性最高,坐果后75 d(7月8日)K2与其他处理组间的差异达到显著水平,其中坐果后45 d(6月8日)、坐果后90 d(7月23日)差异均极显著。
2.3.3 不同施钾水平对无花果蔗糖合酶合成方向活性的影响
由图5可知,SS(合成方向)的活性随果实生长发育呈先下降后上升的趋势,至果实成熟期,又有略微下降。在整个果实发育期间,处理组的SS活性普遍高于对照组,其中在坐果后45 d(6月8日)和坐果后90 d(7月23日)差异最大,但整体上处理和对照之间的差异不显著。3个处理之间以K2活性最高,在坐果后45 d(6月8日)和坐果后75 d(7月8日),K2与其他2组处理之间的差异都达到显著水平。
2.3.4 不同施钾水平对无花果蔗糖磷酸合酶活性的影响
由图6可知,随着果实的生长发育,SPS的活性总体呈先上升后下降的趋势。处理组的酶活性在各个时期均大于对照组,且差异显著。3个处理组之间的差异也体现在果实发育的各个时期。处理组中K2的活性最高,在果实发育的整个过程中都显著高于其他2个处理组,可以看出增施钾肥对SPS的活性有显著影响。
2.3.5 不同施钾水平对无花果淀粉酶活性的影响
由图7-A可知,处理组α-淀粉酶的活性整体上随果实发育逐渐升高,在坐果后75 d(7月8日)达到峰值,至果实成熟期,酶活又有轻微下降。而对照组的酶活性虽有上下波动,但变化不大。处理组和对照组之间酶活性在各个时期都表现出显著差异。3个处理组之间以K2的酶活性最高,在坐果后45 d(6月8日),75 d(7月8日)和90 d(7月23日),都显著高于其他2个处理组。
由图7-B可知,β-淀粉酶在处理组中的酶活性变化与α-淀粉酶相同,活性整体上逐渐升高,在坐果后75 d达到峰值,至果实成熟期,酶活又有轻微下降。对照组的活性在果实发育早期上升,至坐果后60 d下降,之后开始缓慢上升。处理组与对照组之间酶活性的差异除在坐果后45 d差异不明显外,在其他各个时期都差异显著。3个处理之间以K2的酶活性最高,在坐果后30 d、60 d和75 d都显著高于其他2个个处理组。
2.4 相关性分析
2.4.1 不同发育时期施钾水平与无花果果实糖代谢酶的相关性分析
如表1所示,不同施钾水平与无花果中AI(r5/23=0.791**,r7/8=0.583*,r7/23=0.611*),NI(r7/23=0.954**),SS分解方向(r5/23=0.897**,r6/8=0.788**,r7/8=0.876**),SPS(r5/23=−0.599*,r6/8=0.581*,r6/23=0.768**,r7/8=0.815**,r7/23=0.754**),α-淀粉酶(r5/23=0.738**,r6/8=0.842**,r6/23=0.622*,r7/8=0.707*),β-淀粉酶(r6/23=0.865**,r7/8=0.825**,r7/23=0.922**)活性具有极显著正相关。这表明,增施钾肥对提高无花果中AI、NI、SS分解方向、SPS、α-淀粉酶、β-淀粉酶的活性有显著的影响。
表 1 不同发育时期施钾水平与无花果果实糖代谢酶的相关性分析Table 1. Correlation between sugar metabolic enzymes in figs and K applications at fruit development stages项目
Item指标
Indices日期 Date (M/D) 5/23 6/8 6/23 7/8 7/23 施钾水平
K applicationAI 0.791** −0.039 0.073 0.583* 0.611* NI 0.095 0.504 0.325 0.253 0.954** SS分解方向 0.897** 0.788** −0.299 0.876** −0.1 SS合成方向 0.233 0.163 0.125 0.094 0.517 SPS 0.599* 0.581* 0.768** 0.815** 0.754** α-淀粉酶 0.738** 0.842** 0.622* 0.707* 0.641 β-淀粉酶 0.338 0.182 0.865** 0.825** 0.922** 注:*和**表示相关系数分别在0.05和0.01水平显著。表2同。
Note: * and * * indicate significant correlation coefficients at 0.05 and 0.01 levels, respectively. The same as Table 2.2.4.2 无花果果实中糖含量与糖代谢相关酶的相关性分析
如表2所示,果糖和葡萄糖在各个施钾水平下与NI活性之间都呈极显著正相关,与AI活性在K1和K3处理中呈显著正相关,在K2处理中呈极显著正相关,而在CK处理中没有表现出明显的相关性;在CK和K1处理中与SS分解方向酶活性之间存在显著或极显著正相关性,在K2处理中与SS分解方向酶活性之间存在显著正相关性,而在K3处理中与SS分解方向酶活性之间相关性并不明显;在CK中与α-淀粉酶与β-淀粉酶活性之间的相关性并不明显,在K1处理中与α-淀粉酶与β-淀粉酶活性之间存在显著或极显著正相关性,在K2和K3处理中与α-淀粉酶与β-淀粉酶活性之间存在极显著正相关性。
表 2 无花果果实中糖含量与糖代谢相关酶的相关性分析Table 2. Correlation between sugar content and enzymes related to sugar metabolism in figs项目
Items中性转化酶
NI酸性转化酶
AI蔗糖合酶分解方向
SS decomposition direction蔗糖合酶合成方向
SS synthesis direction蔗糖磷酸合成酶
SPSα-淀粉酶
α-amylaseβ-淀粉酶
β-amylaseCK 果糖 Fructose 0.92** 0.22 0.794** 0.588* 0.41 0.437 −0.07 葡萄糖 Glucose 0.909** 0.236 0.777** 0.589* 0.401 0.409 −0.09 蔗糖 Sucrose 0.141 −0.771** −0.146 −0.109 0.482 −0.296 0.391 淀粉 Starch −0.929** −0.162 −0.786** −0.604* −0.129 −0.33 0.438 K1 果糖 Fructose 0.913** 0.572* 0.647** 0.811** 0.681** 0.708** 0.566* 葡萄糖 Glucose 0.897** 0.527* 0.625* 0.813** 0.608* 0.634* 0.532* 蔗糖 Sucrose 0.701** 0.215 0.32 0.547** 0.148 0.138 0.241 淀粉 Starch −0.879** −0.482 −0.595* −0.82** −0.738** −0.803** −0.371 K2 果糖 Fructose 0.867** 0.821** 0.516* 0.732** 0.818** 0.897** 0.882** 葡萄糖 Glucose 0.852** 0.812** 0.528* 0.746** 0.797** 0.881** 0.823** 蔗糖 Sucrose 0.439 0.408 0.576* 0.153 −0.308 0.129 −0.026 淀粉 Starch −0.718** −0.732** −0.340 −0.456 −0.712** −0.925** −0.783** K3 果糖 Fructose 0.855** 0.535* −0.108 0.840** 0.705** 0.730** 0.754** 葡萄糖 Glucose 0.825** 0.456 −0.153 0.783** 0.703** 0.775** 0.782** 蔗糖 Sucrose 0.457 0.001 −0.054 0.386 −0.353 −0.081 −0.169 淀粉 Starch −0.842** −0.510 0.247 −0.715** −0.756** −0.750** −0.842** 如表2所示,蔗糖含量在K1处理中与SS合成方向活性之间呈极显著正相关,而在其他水平下没有明显相关性;与SPS之间在CK和K1条件下呈正相关,而在K2和K3处理中呈负相关,相关性均不明显。这说明SPS在蔗糖积累中的作用并不明显,少量施钾(K1)可以提高SS合成方向酶对无花果果实中蔗糖积累的作用。
如表2所示,淀粉含量在K2和K3处理中与α-淀粉酶与β-淀粉酶活性之间存在极显著负相关性,在K1处理中与α-淀粉酶之间存在极显著负相关性,而在CK中与α-淀粉酶与β-淀粉酶活性之间的相关性并不明显。这说明增施钾肥增强了α-淀粉酶与β-淀粉酶对淀粉降解的影响。
3. 讨论
3.1 不同施钾水平对无花果糖积累的影响
钾是植物的基本矿质元素之一,对果实的生长发育和果实品质的形成起着至关重要的作用。前人大量的研究发现,适量施钾可以有效地提高果实品质和可溶性糖含量[20-22]。本研究中,增施钾肥显著提高了果实发育中后期果糖、蔗糖和葡萄糖的含量和果实发育前期淀粉含量,显著降低了果实发育中后期淀粉的含量,促进了果实发育中淀粉向可溶性糖的转化,这与前人在苹果[11]、草莓[12]、番茄[13]、葡萄[23]上的研究一致。果糖和葡萄糖是无花果果实中主要的可溶性糖,其含量在果实发育前期增加缓慢,后期迅速增加。蔗糖含量呈先升高再降低又升高的趋势,这与Ersoy N等[24]的研究一致。淀粉含量呈先升高后迅速降低的趋势,这与李春丽[14]的研究略有出入,可能是因为不同的品种之间淀粉的积累规律不同。
3.2 糖代谢相关酶在糖积累中的作用
蔗糖代谢是无花果果实中糖积累的一个重要途径。AI、NI、SS分解方向的等关键酶在无花果果实中起分解蔗糖,生成果糖和葡萄糖或尿苷二磷酸葡萄糖,促进蔗糖卸载的作用。在本研究中,3种酶在大多施钾水平下,都与果糖和葡萄糖含量显著或极显著相关性,在无花果发育中果糖和葡萄糖的积累中起到了重要的作用。在果实发育中期,NI和SS分解方向活性略有降低,而AI活性一直保持在较高水平,且呈上升的趋势,这说明AI在这一时期对果实中果糖和葡萄糖的积累具有更重要的影响。在果实发育末期,AI活性、SS分解方向活性略微降低,而NI活性在这一时期迅速升高,维持了无花果在成熟期果实中葡萄糖和果糖的积累。蔗糖含量与SS合成方向、SPS在大多施钾水平下都呈正相关,其中与SS合成方向的相关系数更为显著,这与在梨[25]、甘蔗[26]和桃[27]等果实上的研究一致,SS合成方向对蔗糖积累的贡献更大。相对于转化酶和SS分解方向,SS合成方向、SPS的活性一直保持较低水平,且虽然蔗糖含量与SS合成方向、SPS在大多施钾水平下都呈正相关,但显著性并不明显。这可能与蔗糖在果实发育过程中卸载途径的变化有关[28]。α-淀粉酶和β-淀粉酶活性在增施钾肥的条件下,均呈逐渐上升的趋势,且与葡萄糖、果糖含量均呈显著或极显著正相关,与淀粉含量呈显著或极显著负相关。这说明淀粉酶在无花果果实发育过程中,对淀粉的分解起着重要的作用,促进了淀粉向可溶性糖的转化。这与前人在龙眼[29]、苹果[30]和猕猴桃[31]上的研究结果一致。
3.3 不同施钾水平对糖代谢相关酶活性的影响
不同水平的钾显著提高了无花果果实发育早期和末期AI和SS分解方向的活性,对NI影响较小,但极显著地提高了NI在果实发育成熟期的活性。这与张弦[11]在苹果中的研究结果一致。在甘薯[32]中,适量施钾提高了SS与Ivr(转化酶)的活性,有利于甘薯中蔗糖与淀粉的积累。在果实成熟期,CK、K1和K3处理组的AI和SS(分解方向)活性均有降低趋势,而K2处理组的AI和SS(分解方向)活性继续上升。这说明适量施钾显著提高了无花果果实成熟期AI和SS(分解方向)活性,对果实成熟期还原糖的积累有着重要的作用。果糖和葡萄糖与AI在K1和K3处理中呈显著正相关,在K2中呈极显著正相关,而在CK处理中没有表现出明显的相关性,这说明,适量施钾对提高AI在无花果果实发育过程中果糖和葡萄糖的积累中的作用有明显促进作用。对照组的α-淀粉酶和β-淀粉酶活性在整个发育过程中,整体变化不明显或者略有下降的趋势。而施钾处理组使α-淀粉酶和β-淀粉酶活性逐渐上升,且一直保持在较高水平。果糖和葡萄糖在CK中与α-淀粉酶与β-淀粉酶活性之间的相关性并不明显,在K1中与α-淀粉酶与β-淀粉酶活性之间存在显著或极显著正相关性,在K2和K3施钾水平下与α-淀粉酶与β-淀粉酶活性之间存在极显著正相关性。这些结果均表明了,适量施钾对淀粉酶在果实中还原糖积累作用的增益。在甘薯中,适量供钾既能提高块根中淀粉水解酶的活性还能提高SS的活性,是提高块根中可溶性糖的主要原因,这与本研究的结果一致[32]。增施钾肥对SPS活性的影响体现在无花果果实发育的各个时期,施钾水平与SPS活性在无花果发育的各个时期均呈显著或极显著正相关,而对SS合成方向则无显著影响。这与温志静[30]的研究结果一致。Kaack[33]研究表明,钾可以促进乙烯代谢相关酶活性,促进蛋白质的合成而调节乙烯的合成,钾含量与乙烯含量呈正相关。而Choudhur[34]研究表明乙烯对SPS基因起正向调控的作用,为本试验的结果提供了理论支撑。在番茄中[12],喷施磷酸二氢钾和土施钾肥处理均可以提高AI、NI、SS及SPS活性,且促进了光合产物合成和运输,提高了果实中葡萄糖、果糖和蔗糖的含量,这与本研究的结果一致。
4. 结论
本试验通过增施4个水平的K2SO4,研究不同施钾水平对无花果果实糖代谢的内在调控机制,结论如下:
(1)适量施钾可以提高无花果果实中的葡萄糖、果糖和蔗糖含量,加速淀粉的合成和降解速率,促进淀粉向可溶性糖的转化。到果实成熟期,适量施钾(K2)的果糖、葡萄糖和蔗糖含量分别比对照组提高了25.5%、32.0%、28.6%。
(2)无花果果实发育过程中,AI、NI、SS(分解方向)这3种酶均起到分解蔗糖生成还原糖的作用,α-淀粉酶和β-淀粉酶起到分解淀粉,生成还原糖的作用,促进了果实中果糖、葡萄糖的积累。SS(合成方向)相对于SPS对蔗糖积累的贡献更大。
(3)增施钾肥显著提高无花果果实发育早期和末期AI和SS(分解方向)的活性,极显著地提高NI在果实发育成熟期的活性,促进果实中果糖和葡萄糖含量的积累;提高α-淀粉酶和β-淀粉酶活性,且使其一直保持在较高水平,促进淀粉向可溶性糖的转化;提高无花果各个发育时期的SPS活性,对SS(合成方向)的影响较小,促进了果实中蔗糖的积累。
-
图 1 不同浓度PEG6000处理航2号植株情况
注:每幅图从左到右营养液中PEG6000的质量体积比分别为0%(CK)、18%、20%、22%、24%、26%;处理时间A: 0 h,B: 3 h,C: 24 h,D: 48 h,E: 72 h,F: 96 h,G: 7 d,H:恢复生长8 d。
Figure 1. Hang 2 plants treated by varying concentrations of PEG6000
Note: PEG600 concentrations in photos from left to right are 0% (CK), 18%, 20%, 22%, 24% and 26%; treatment time A=0 h, B=3 h, C=24 h, D=48 h, E=72 h, F=96 h, G=7 d, H=recovery after 8 d.
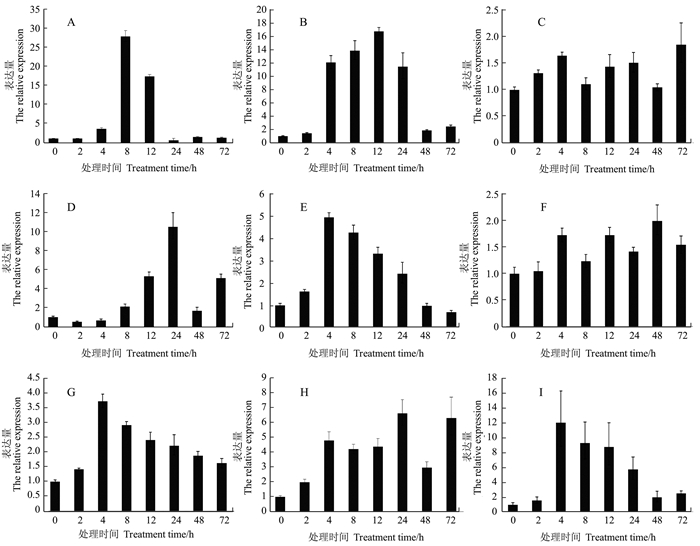
图 5 qRT-PCR分析抗氧化酶基因的表达情况
注:A为过氧化氢酶A基因表达量,B为过氧化氢酶B基因表达量,C为过氧化氢酶C基因表达量,D为过氧化物酶5基因表达量,E为过氧化物酶1基因表达量,F为质体铜/锌超氧化物歧化酶基因表达量,G为细胞质铜/锌超氧化物歧化酶基因表达量,H为抗坏血酸过氧化物酶基因的表达量,I为谷胱甘肽还原酶基因的表达量。
Figure 5. Expression analysis on antioxidant enzyme genes by qRT-PCR
Note:A:The relative expression of CATA, B:The relative expression of CATB, C:The relative expression of CATC, D:The relative expression of POX 5.1, E:The relative expression of POX 1, F:The relative expression of plastidic Cu/Zn-SOD, G:The relative expression of cytosolic Cu/Zn-SOD, H:The relative expression of APX, I:The relative expression of GR.
表 1 抗氧化酶基因引物序列
Table 1 Primers of antioxidant enzyme genes
基因名称
Gene names上游引物F/下游引物R(5′-3′)
Upstream primer F/Downstream primer R产物大小
Product/bp过氧化氢酶A基因CATA F:GAGGAGGCAGAAGGCGACGATA
R:CCCCCAACGACTCATCACACTG194 过氧化氢酶B基因CATB F:GACGGATGGTCCTGAACAAAAACA
R:CAAGACGGTGCCTTTGGGTATCA159 过氧化氢酶C基因CATC F:CTTCCCCGTCTTCTTCATCCGC
R:TCGTCGAAGAGGAAGGTGAACAT159 过氧化物酶5基因POX5.1 F:ACTTGGTTGCTCTCTCAGGTGCG
R:GGTGGGCGTCGTCGTGTC182 过氧化物酶1基因POX1 F:ACTCGTGCCCCAAGGCGAAGGA
R:GCTGTTGTCCAGGAGCACAGACG149 质体铜/锌超氧化物歧化酶基因plastidic Cu/Zn-SOD F:CCACCTCCACGAGTTTGGCGAT
R:CTCAGCTACACCTTCAGCATTGGC154 细胞质铜/锌超氧化物歧化酶基因cytosolic Cu/Zn-SOD F:GGAAATGTCACCGCTGGAGAAG
R:AACGACGGCTCTGCCAATGATT102 抗坏血酸过氧化物酶基因APX F:CTGCCGTCCCCTTCCACCCA
R:CCGCCAGAGAGGGCAACAAT154 谷胱甘肽还原酶基因GR F:TTCCTCCAAAGCCTGCTGTTCACT
R:GCCAGCCAACTAAACCTGATTACA101 内参基因,真核起始因子eIf4a F:TTGTGCTGGATGAAGCTGATG
R:GGAAGGAGCTGGAAGATATCATAGA76 内参基因,肌动蛋白基因Actin150 F:AGTGTCTGGATTGGAGGAT
R:TCTTGGCTTAGCATTCTTG150 表 2 不同质量体积比的PEG6000处理后植株存活率
Table 2 Plant survival rates after PEG6000 treatments in different mass and volume ratios
PEG质量体积比
Mass and volume
ratio of PEG/%植株数量
Plant
number存活的
植株数量
Survival plant存活率
Survival
rate/%0 25 25 100 18 25 25 100 20 25 25 100 22 25 3 12 24 25 0 0 26 25 0 0 -
[1] 匡勇, 夏石头.干旱对水稻生长发育的影响及提高水稻抗旱性的途径[J].北京农业, 2007(36):8-14. DOI: 10.3969/j.issn.1000-6966.2007.36.003 KUANG Y, XIA S T. Effects of drought on growth and development and approachs to promoting droughtresistance of rice[J].Beijing Agriculture, 2007(36):8-14.(in Chinese) DOI: 10.3969/j.issn.1000-6966.2007.36.003
[2] SALEHI S P, IZADPANAH M, FALAH H L, et al.Comparison of the effects of drought stress on pigments, peroxidase, osmotic adjustment and antioxidant enzymes in different accessions of anthemistinctoria and tripleurospermum servanes of natural resources gene bank of iran[J].En Journals, 2015:126-139.
[3] 蒋明义, 郭绍川.水分亏缺诱导的氧化胁迫和植物的抗氧化作用[J].植物生理学通讯, 1996, 32(2):144-150. http://d.old.wanfangdata.com.cn/Periodical/wjsjxx201808024 JIANG M Y, GUO S C. Oxidative stress and antioxidation induced by water deficiency in plants[J].Plant Physiology Communications, 1996, 32(2):144-150.(in Chinese) http://d.old.wanfangdata.com.cn/Periodical/wjsjxx201808024
[4] BOWLER C, MONTAGU M V, INZE D. Superoxide dismutase and stress tolerance[J]. Annual Review of Plant Physiology and Plant Molecular Biology, 1992, 43(1):83-116. DOI: 10.1146/annurev.pp.43.060192.000503
[5] APEL K, HIRT H. Reactive oxygen species:metabolism, oxidative stress, and signal transduction[J]. Annual Review of Plant Biology, 2004, 55(1):373-399. DOI: 10.1146/annurev.arplant.55.031903.141701
[6] NOCTOR G, FOYER C H. Ascorbate and glutathione:keeping active oxygen under control[J].Annual Review of Plant Physiology and Plant Molecular Biology, 1998, 49(1):249-279. DOI: 10.1146/annurev.arplant.49.1.249
[7] AMUDHA J, BALASUBRAMANI G. Recent molecular advances to combat abiotic stresstolerance in crop plants[J]. Biotechnol Mol Biol Rev, 2011(6):31-58.
[8] MORITA S, TASAKA M, FUJISAWA H, et al. A cDNA clone encoding a rice catalase isozyme[J]. Plant Physiol, 1994, 105(3):1015-1016. http://d.old.wanfangdata.com.cn/OAPaper/oai_pubmedcentral.nih.gov_160753
[9] HIGO K, HIGO H. Cloning and characterization of the rice CatA catalase gene, a homologue of the maize Cat3 gene[J]. Plant Molecular Biology, 1996, 30(3):505-521. DOI: 10.1007/BF00049328
[10] AGRAWAL G K, RAKWAL R, JWA N S. Stress signaling molecules involved in defense and protein phosphatase 2A inhibitorsmodulate OsCATC expression in rice (Oryza sativa) seedlings[J].Journal of Plant Physiology, 2001, 158(10):1349-1355. DOI: 10.1078/0176-1617-00607
[11] KIM S H, CHOI H S, CHO Y C, et al. Cold-Responsive Regulation of a Flower-Preferential Class Ⅲ Peroxidase Gene, OsPOX1, in Rice (Oryzasativa L.)[J]. Journal of Plant Biology, 2012, 55(2):123-131. DOI: 10.1007/s12374-011-9194-3
[12] SASAKI K, IWAI T, HIRAGA S, et al. Ten rice peroxidases redundantly respond to multiple stresses including infection with rice blast fungus[J]. Plant & Cell Physiology, 2004, 45(10):1442-52. http://www.wanfangdata.com.cn/details/detail.do?_type=perio&id=HighWire000002825548
[13] ALSCHER R G, ERTURK N, HEATH L S. Role of superoxide dismutases (SODs) in controlling oxidative stress in plants[J]. Journal of Experimental Botany, 2002, 53(372):1331-1341. DOI: 10.1093/jexbot/53.372.1331
[14] PRAKASH S R, SAMANT A, PRASHAR V, et al.Biochemical and functional characterization of OsCSD3, a novel CuZn superoxidedismutase from rice[J].Biochemical Journal, 2018, 475(19):3105-3121. DOI: 10.1042/BCJ20180516
[15] TEIXEIRA F K, MENEZES-BENAVENTE L, GALVÃO V C, et al.Rice ascorbate peroxidase gene family encodes functionally diverse isoforms localized in different subcellular compartments[J].Planta, 2006, 224(2):300-314. DOI: 10.1007/s00425-005-0214-8
[16] NOCTOR G, FOYER C H. Ascorbate and glutathione:keepingactive oxygen under control[J]. Annual Review of Plant Physiology & Plant Molecular Biology, 1998, 49(1):249-279. http://d.old.wanfangdata.com.cn/NSTLQK/NSTL_QKJJ0210504163/
[17] BASHIR K, NAGASAKA S, ITAI R N, et al. Expression and enzyme activity of glutathione reductase is upregulated by Fe-deficiency in graminaceous plants[J]. Plant Molecular Biology, 2007, 65(3):277-284. DOI: 10.1007/s11103-007-9216-1
[18] ROUHIER N I, COUTURIER J, JACQUOT J P. Genome-wide analysis of plant glutaredoxin systems[J]. Journal of Experimental Botany, 2006, 57(8):1685-1696. DOI: 10.1093/jxb/erl001
[19] 杨春杰, 张学昆, 邹崇顺, 等.PEG-6000模拟干旱胁迫对不同甘蓝型油菜品种萌发和幼苗生长的影响[J].中国油料作物学报, 2007, 29(4):425-430. DOI: 10.3321/j.issn:1007-9084.2007.04.013 YANG C J, ZHANG X K, ZOU C S, et al. Effects of drought simulated by PEG-6000 on germination and seedling growth of rapeseed(Brassica napus L.)[J].Chinese Journal of Oil Crop Sciences, 2007, 29(4):425-430.(in Chinese) DOI: 10.3321/j.issn:1007-9084.2007.04.013
[20] 李雪妹, 刘畅, 刘倩雯, 等.PEG预处理对水分胁迫下水稻叶片抗氧化酶同工酶及其表达的影响[J].作物杂志, 2016(6):107-111. http://d.old.wanfangdata.com.cn/Periodical/zwzz201606018 LI X M, LIU C, LIU Q W, et al. The effect of PEG pretreatment on expression of antioxidant isozymes of rice leaves under water stress[J]. Crops, 2016(6):107-111.(in Chinese) http://d.old.wanfangdata.com.cn/Periodical/zwzz201606018
[21] 陈美静, 刘倚雯, 张宝龙, 等.不同预处理对P EG胁迫下水稻幼苗抗氧化系统的影响[J], 江苏农业科学, 2015, 43(8):76-78. http://d.wanfangdata.com.cn/Periodical/jsnykx201508025 CHEN M J, LIU Y W, ZHANG B L, et al. The effect of different pretreatment on rice antioxidant system under PEG stress[J]. Jiangsu Agricultural Sciences, 2015, 43(8):76-78.(in Chinese) http://d.wanfangdata.com.cn/Periodical/jsnykx201508025
[22] 戴高兴, 彭克勤, 萧浪涛, 等.聚乙二醇模拟干旱对耐低钾水稻幼苗丙二醛、脯氨酸含量和超氧化物歧化酶活性的影响[J].中国水稻科学, 2006, 20(5):557-559. DOI: 10.3321/j.issn:1001-7216.2006.05.018 DAI G X, PENG K Q, XIAO L T, et al. Effect of drought stress simulated by peg on m alonaldehyde, proline contents andsuperoxide dismutase activity in low potassium tolerant rice seedlings[J]. Chinese J Rice Sci, 2006, 20(5):557-559.(in Chinese) DOI: 10.3321/j.issn:1001-7216.2006.05.018
[23] 张小娟, 宋涛, 甄晓辉, 等.模拟干旱胁迫对转C4双基因水稻幼苗光合功能及部分抗氧化酶活性的影响[J].江苏农业学报, 2014, 30(4):709-715. http://d.old.wanfangdata.com.cn/Periodical/jsnyxb201404003 ZHANG X J, SONG T, ZHEN X H, et al. Impact of simulated drought stress on photosynthesis and activities of someantioxidant enzymes of transgenic rice seedlings harboring maize PEPCand PPDK genes[J]. Jiangsu Journal of Agricultural Sciences, 2014, 30(40):709-715.(in Chinese) http://d.old.wanfangdata.com.cn/Periodical/jsnyxb201404003
-
期刊类型引用(12)
1. 陈梦瑶,翟芮瑾,林敏娟,马全会,王振磊. 多效唑对‘波姬红’无花果植株生长及果实品质的影响. 干旱地区农业研究. 2025(01): 117-124 .  百度学术
百度学术
2. 刘鹏莉,陈英乡,遇艳萍,于学娟,李钢,邹晓宇. 无花果营养成分及生物活性研究进展. 食品工业科技. 2023(06): 424-431 .  百度学术
百度学术
3. 周敏,杨国顺. 钾对刺葡萄果实品质及糖分代谢相关酶活性的影响. 中国南方果树. 2023(02): 124-129+134 .  百度学术
百度学术
4. 田钰君,许云飞,郭延平. 叶面喷施钾肥对无花果光合生理和叶绿素荧光特性的影响. 西北农林科技大学学报(自然科学版). 2023(07): 126-132 .  百度学术
百度学术
5. 应学兵,姜淑芳,高源,李璐瑶,姚凌燕,臧运祥. 高钾型水溶肥配施生物刺激素对茄子生长及品质的影响. 北方园艺. 2023(14): 1-7 .  百度学术
百度学术
6. 张树航,郭燕,张馨方,李颖,刘欢,王广鹏. 土壤主要矿质元素与板栗总糖和淀粉含量的关联性研究. 云南农业大学学报(自然科学). 2023(05): 816-822 .  百度学术
百度学术
7. 莫璋红,谢金兰,林丽,李长宁,覃宁,潘红春,黄应设,陈荣发,莫善平. 减量施氮间作豆科绿肥压青对甘蔗农艺性状及产质量的影响. 现代农业科技. 2023(20): 38-42+46 .  百度学术
百度学术
8. 陈琪,董静,周伟伟,庞忠俊,杨加仪,梁斌. 腐植酸钾和氨基酸肥料对砂培番茄生长与果实品质的影响. 华北农学报. 2023(S1): 300-306 .  百度学术
百度学术
9. 颜雨思,陆珺,宋科,李冰,杨静慧,张超. 不同施钾水平对‘玫瑰香’葡萄品质的影响. 天津农学院学报. 2022(03): 14-18 .  百度学术
百度学术
10. 杜佳铭,郭晓宏,刘倩婷,刘琳文,方瑜,穆文刚,寇莉萍. 1-MCP与PE保鲜膜处理对无花果贮藏特性的影响研究. 食品研究与开发. 2022(19): 10-18 .  百度学术
百度学术
11. 王小龙,张正文,邵学东,钟晓敏,王福成,史祥宾,张艺灿,王海波. 气象因子和施肥对赤霞珠植株矿质元素和果实品质的影响. 果树学报. 2022(11): 2074-2087 .  百度学术
百度学术
12. 王小龙,邵学东,张正文,钟晓敏,王福成,史祥宾,王宝亮,王海波. 梅乐葡萄叶片和果实矿质元素变化规律及相关性分析. 华北农学报. 2021(S1): 155-164 .  百度学术
百度学术
其他类型引用(18)





 下载:
下载: