Contents and Enrichment Coefficients of Heavy Metals in Sediment and Lotus Grown in Ponds at Downtown Wuyishan City
-
摘要: 采集武夷山市五夫镇白莲荷塘底泥和莲子、莲叶样品,检测Cu、Zn、Pb、Cr、Cd、As和Hg等7种重金属含量,并运用单项和内梅罗综合污染指数法评价生态风险及分析莲不同部位的富集系数。结果表明:底泥Cd和Hg超出《无公害农产品—种植业产地环境条件》标准限值;莲子和莲叶重金属分别符合《食品中污染物限量》、《绿色食品—茶叶》和《茶叶中铬、镉、汞、砷及氟化物限量》标准,两者富集系数存在显著差异,尤其莲叶对Hg强富集。不同生态型荷塘的底泥、莲子、莲叶中重金属综合污染指数均值排序一致,都为自然种植型荷塘 < 人为管理型荷塘 < 游览干预型荷塘。研究建议今后应加强荷塘底泥Cd和Hg污染源调查及选址评估,尽量降低农业、生活和交通污染影响。Abstract: Samples of sediment as well as seeds and leaves of the lotus grown in the pond at Wufu, downtown of Wuyishan city, were collected for this study. Contents of 7 heavy metals, including Cu, Zn, Pb, Cr, Cd, As and Hg, were determined. The ecological risk by the metals was evaluated based on the single pollution index, the comprehensive pollution index, and the enrichment coefficient of the lotus parts. The results showed that the Cd and Hg contents in the sediment exceeded the national standard limits set forth by the Environmental Conditions for Non-Pollution Agricultural Products Production Area. The heavy metals in the lotus seeds and leaves were within the Maximum Allowable Levels of Pollutants in Food, Green Food-Tea, and the Maximum Allowable Levels of Cr, Cd, Hg, As, and F in Tea.Significant differences existed in the enrichment coefficients on the two metals, especially Hg, in the lotus leaves. The average comprehensive pollution indices of the sediment, lotus seeds and leaves from ponds of different types exhibited a similar trend, that is, in an increasing order of:natural growing pond < managed pond < tourism-oriented pond. Thus, reinforced pollutant monitoring and control on pond sediment to mitigate the potential harms to the environment and consumer health by Cd and Hg at the locations was strongly recommended.
-
Keywords:
- heavy metals /
- lotus seed /
- lotus leaf /
- sediment /
- enrichment coefficient
-
近年来,随着工业化和城镇化的发展,我国耕地土壤污染严重。其中,农用地土壤重金属污染不仅威胁食品安全、人体健康和生态环境安全,还进一步加剧了我国人地矛盾[1-2]。国内外针对土壤重金属污染对植物的影响已有广泛的研究[3-4],但多集中在工业区、采矿区及实验室内展开,属于极端或者典型环境下的重金属累积特征,与一般的污染环境有很大差别[3, 5],且研究植物种类多是陆生和水生漂浮植物,对水生草本植物的研究报道较为欠缺[5-6]。
莲Nelumbo nucifera,又称荷、荷花、莲花、芙蕖等,为多年生高挺水草本植物,多分布在北美、中亚、西亚等亚热带和温带地区[6]。莲是我国最具特色、栽培面积最大、品种资源最丰富的水生经济作物,也是我国十大名花之一[7]。其不仅营养价值高,还在保健品、药材和化妆品等方面显示出潜在的应用价值[5-8]。目前,国内外对莲的有关报道多针对其不同部位的成分组成测试[8-10]、生理生化特征[5, 7]、营养价值和药用价值[6, 8, 11]等方面。对荷塘底泥环境中重金属含量对莲不同部位的重金属元素累积影响的相关报道罕见[12-13]。
为此,本研究以福建武夷山市五夫镇白莲荷塘的底泥、莲子和莲叶为研究对象,检测底泥、莲子、莲叶中重金属元素(Cu、Zn、Pb、Cr、Cd、As和Hg)含量的整体分布,并按不同生态类型荷塘进行环境风险评价,对莲子、莲叶对底泥元素的富集情况进行分析,以期为底泥与莲不同部位的重金属累积影响研究提供理论依据,并对促进荷塘底泥生态环境的维护、莲产业的健康发展、莲品质提高等具有重要意义。
1. 材料与方法
1.1 研究区概况
五夫镇位于福建省武夷山市东南部,地处浦城、建阳、武夷山三县(市)交接地带,总面积175.75 km2。五夫镇被称为“白莲之乡”。自南唐至清朝末年,五夫白莲一直作为皇室贡品,现已成功通过国家工商总局地理标志商标认证。目前,白莲种植面积稳定在666.67 hm2以上,年产值达7 000多万元,全镇成立的白莲合作社已达20多家,并积极引进新品种、改良种植和加工技术、发展规模种植,使白莲已成为五夫镇的一大特色支柱产业。
1.2 样品采集
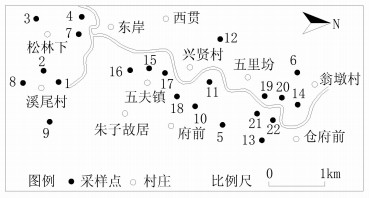
2016年9月上旬,通过武夷山五夫镇白莲基地的实地考察和资料收集,于不同生态条件选取22个有代表性的荷塘,包括自然种植型荷塘(6个样品,编号1~6)、人为管理型荷塘(8个样品,编号7~14)和游览干预型荷塘[主要为五夫镇游览区荷塘和下阳村(仓府前)的万亩荷塘基地,8个样品,编号15~22](图 1)。其中,自然种植型荷塘为未经施肥管理,年产干莲子为20~30 kg;人为管理型荷塘,年施肥量为:每667 m2荷塘尿素约25 kg,复合肥约150 kg,干莲子产量为60~80 kg。游览干预性荷塘为游客量相对密集,受外来游客干预影响的类型,为了增加景观生态效果,一般荷塘兼养鱼,每667 m2荷塘尿素约20 kg,复合肥约120 kg,干莲子产量为60~70 kg。
对选取的荷塘采用梅花布点法采集底泥样品。每个底泥样品以中间点为中心在10~20 m按照梅花形取5个小样组合而成,在各点处取0~20 cm的底泥,把取得的底泥充分混合之后按照四分法取约500 g入袋并编号。同时采集各底泥样品对应种植的莲子、莲叶样品,鲜重各约500 g。共计30个样品。
1.3 样品处理与测试
底泥样品在实验室内自然风干,去除底泥中植物残根、枯枝落叶、砾石等杂物,碾磨过20目尼龙筛,按四分法进一步混匀、缩分、采用玛瑙制备机将样品粉碎至100目并装袋备用。莲子、莲叶样品用自来水冲洗除去黏附的杂物、尘土等,再用去离子水清洗3遍,于60℃烘干至恒重,粉碎过80目筛,备用。底泥样品pH值的测定采用酸度计(土:水=1:2.5);有机碳(TOC)采用重铬酸钾容量法测定;总氮(TN)采用凯氏消煮法;总磷(TP)采用钼锑抗比色法;重金属Cu、Zn、Pb、Cr和Cd元素按盐酸-硝酸-高氯酸-氢氟酸消解法消解,再采用IRIS Advantage等离子体发射光谱仪(ICP-OES)测定;As和Hg则采用盐酸-硝酸消解法,以XGY1011型原子荧光光谱仪(AFS)测定。莲子、莲叶重金属元素以硝酸-高氯酸法消解,消解液的测定仪器与方法同底泥样品。测试分析工作由安徽省地质实验研究所实验测试中心承担,以上测试的样品加标回收率控制在90%~110%,每个样品各指标平行3次测试,取平均值作为统计数据。
1.4 评价方法与标准
1.4.1 重金属含量的评价方法
采用单项污染指数法和内梅罗综合污染指数法对荷塘底泥及莲子、莲叶中重金属污染现状进行评价。具体公式如下:
Pi=Ci/Si (1) P综={[(Ci/Si)max (2) 其中,Pi:i污染物指数值(当Pi≤1为非污染;1<Pi≤2为轻度污染;2<Pi≤3为中度污染;Pi>3为重度污染,Pi越大受到的污染越严重);Ci:i污染物实测值;Si:i污染物评价标准;(Ci/Si)max:土壤重金属单项污染指数最大值;(Ci/Si)ave:土壤中各重金属单项污染指数平均值;P综:采样点综合污染指数(P综≤0.7为安全;0.7 < P综≤1.0应警戒;1.0 < P综≤2.0是轻度污染;2.0 < P综≤3.0是中度污染;3.0 < P综为重度污染)。
1.4.2 重金属含量标准
底泥执行《无公害农产品——种植业产地环境条件》(NY/T 5010-2016)[14]中有关土壤环境质量二级标准(pH < 6.5)的水田规定限值为参照;莲子质量评价参照《食品安全国家标准——食品中污染物限量》(GB 2762-2017)[15]中谷物及其制品对应元素限值,莲叶质量评价参照茶叶相关标准:《绿色食品——茶叶》(NY/T 288-2012)[16]和《茶叶中铬、镉、汞、砷及氟化物限量》(NY 659-2003)[17]。涉及各类参照标准汇总见表 1。
表 1 不同参照标准中重金属含量Table 1. Reference standardson heavy metal contents1.4.3 富集系数
富集系数定义为作物中元素含量与土壤中对应元素含量的比值,运用富集系数可以反映作物对土壤(底泥)中重金属元素的富集能力[3, 12]。
2. 结果与分析
2.1 荷塘底泥重金属含量与评价
2.1.1 荷塘底泥基本理化性质的描述性统计
由表 2可知,五夫镇白莲荷塘底泥pH值整体范围为5.34~6.39,呈弱酸性,与南方酸性土壤特征相符;营养元素中有机碳、总氮、总磷的平均值分别为18.60、1.27和0.62 g·kg-1,肥力较高[19],有利于白莲生长。重金属元素Cu、Zn、Pb、Cr、Cd、As和Hg的最大值分别为48.81、186.76、126.08、62.79、0.46、4.50和0.58 mg·kg-1,除了Cd和Hg元素外,其余元素符合《无公害农产品——种植业产地环境条件》(NY/T 5010-2016)[14]标准限值;且元素Cr和As含量远低于《绿色食品——产地环境质量标准》[18]的限值要求,Cu、Zn低于但较接近其限值。
表 2 五夫荷塘底泥基本理化指标Table 2. Basic physicochemical properties of pond sediments at Wufu项目 pH TOC/
(g·kg-1)TN/
(g·kg-1)TP/
(g·kg-1)Cu/
(mg·kg-1)Zn/
(mg·kg-1)Pb/
(mg·kg-1)Cr/
(mg·kg-1)Cd/
(mg·kg-1)As/
(mg·kg-1)Hg/
(mg·kg-1)最小值 5.34 10.03 1.01 0.35 15.73 137.80 86.58 49.41 0.20 3.10 0.13 最大值 6.39 27.09 1.55 0.79 48.81 186.76 126.08 62.79 0.46 4.50 0.58 平均值 6.05 18.60 1.27 0.62 27.85 162.33 101.94 55.85 0.32 3.74 0.27 CV/% 23.45 23.17 8.47 18.92 31.43 10.38 13.41 7.89 29.73 12.98 60.47 2.1.2 荷塘底泥重金属污染风险评价
为了直观对比不同生态型荷塘重金属的污染状况,表 3显示了以《无公害农产品——种植业产地环境条件》(NY/T 5010-2016)[14]标准对底泥重金属进行单项污染和内梅罗综合污染的定量评价结果。由表 3可见,22个荷塘中6个荷塘的Cd元素和4个荷塘的Hg元素的单项污染指数超过1,为轻度污染;其余元素单因子评价结果为非污染。综合污染指数结果表明,13个荷塘满足安全范围,4个荷塘已达到警戒线,还有5个荷塘为轻度污染。其中,自然种植型荷塘底泥的各重金属元素为非污染,综合污染指数最小且都满足安全范围;人为管理型荷塘中编号9~11的荷塘处于警戒或轻污染,其他为非污染,整体综合污染平均值为警戒水平;而游览干预型荷塘18、19的荷塘底泥为非污染,其他4个荷塘为警戒或轻污染,整体平均也达到警戒水平。不同生态荷塘的重金属评价结果发现,各重金属单项污染指数和综合污染指数均值大小排序为:自然种植型荷塘<人为管理型荷塘<游览干预型荷塘。
表 3 五夫荷塘底泥单项污染和内梅罗污染指数评价Table 3. Individual and Nemerow pollution indiceson sediments from lotus ponds at Wufu荷塘类型 编号 单因子污染指数 P综合 污染程度 Cu Zn Pb Cr Cd As Hg 自然种植 1 0.31 0.38 0.21 0.13 0.51 0.10 0.57 0.46 安全 2 0.36 0.47 0.26 0.13 0.61 0.09 0.53 0.50 安全 3 0.35 0.42 0.24 0.14 0.57 0.11 0.63 0.51 安全 4 0.37 0.47 0.28 0.16 0.61 0.12 0.53 0.50 安全 5 0.38 0.48 0.30 0.19 0.60 0.15 0.53 0.51 安全 6 0.31 0.38 0.20 0.10 0.53 0.07 0.60 0.47 安全 平均值 0.34 0.42 0.24 0.13 0.56 0.10 0.55 0.48 安全 人为管理 7 0.58 0.67 0.28 0.18 0.77 0.12 0.60 0.63 安全 8 0.67 0.58 0.36 0.18 0.73 0.12 0.85 0.70 安全 9 0.66 0.56 0.35 0.17 0.70 0.12 1.13 0.88 警戒 10 0.54 0.78 0.39 0.21 1.03 0.13 0.57 0.82 警戒 11 0.73 0.84 0.46 0.22 1.15 0.13 1.31 1.04 轻污染 12 0.61 0.77 0.32 0.21 0.71 0.12 0.63 0.65 安全 13 0.66 0.58 0.36 0.18 0.72 0.13 0.84 0.69 安全 14 0.46 0.54 0.27 0.11 0.76 0.04 0.86 0.68 安全 平均值 0.63 0.70 0.36 0.20 0.85 0.12 0.85 0.79 警戒 游览干预 15 0.98 0.69 0.46 0.22 0.85 0.15 1.70 1.31 轻污染 16 0.91 0.92 0.50 0.24 1.52 0.11 1.94 1.51 轻污染 17 0.65 0.88 0.35 0.25 0.66 0.11 0.66 0.72 警戒 18 0.53 0.72 0.35 0.20 0.75 0.13 0.55 0.62 安全 19 0.55 0.77 0.41 0.20 0.78 0.15 0.67 0.65 安全 20 0.62 0.93 0.45 0.24 1.34 0.13 0.77 1.05 轻污染 21 0.54 0.79 0.36 0.22 1.28 0.11 0.47 0.98 警戒 22 0.51 0.79 0.38 0.21 1.34 0.10 0.44 1.02 轻污染 平均值 0.66 0.81 0.41 0.22 1.07 0.12 0.90 0.98 警戒 2.2 莲不同部位对重金属的积累特性
2.2.1 莲不同部位的重金属含量
由表 4可知,重金属元素Cu、Zn、Pb、Cr、Cd、As和Hg在莲子中的含量范围分别为:10.404~22.695、28.010~47.626、0.067~0.182、0.106~0.196、0.064~0.168、0.014~0.085和0.005~0.018 mg·kg-1;在莲叶中的含量范围分别为:3.752~6.410、13.265~25.088、0.560~1.712、0.292~0.450、0.034~0.100、0.135~0.214和0.005~0.046 mg·kg-1。整体而言,莲子重金属含量均值大小顺序为Zn>Cu>Cr>Pb>Cd >As>Hg;莲叶重金属含量均值大小顺序为Zn>Cu>Pb>Cr>As>Cd>Hg。
表 4 莲不同部位重金属含量Table 4. Heavy metal contents in lotus parts[单位/(mg·kg-1)] 莲不同部位 项目 Cu Zn Pb Cr Cd As Hg 莲子 最小值 10.404 28.010 0.067 0.106 0.064 0.014 0.005 最大值 22.695 47.626 0.182 0.196 0.168 0.085 0.018 平均值 15.547 40.819 0.113 0.154 0.111 0.027 0.008 CV(%) 20.50 10.56 28.80 11.77 24.70 53.82 35.37 莲叶 最小值 3.752 13.265 0.560 0.292 0.034 0.135 0.005 最大值 6.410 25.088 1.712 0.450 0.100 0.214 0.046 平均值 5.052 19.848 0.960 0.378 0.048 0.175 0.030 CV(%) 12.28 12.76 23.52 11.25 30.81 12.72 36.26 2.2.2 莲不同部位的重金属含量评价
莲子、莲叶重金属含量参考有关标准[15-17]评价的结果分别见表 5和表 6。由表 5和6可知,莲子中各重金属单项污染指数都小于1,属于非污染范围,满足各对应标准(表 1)安全限值规定。内梅罗污染指数评价结果得知,游览干预型荷塘中样点16荷塘对应的莲子中重金属Pb的单因子污染指数最大(0.91),综合污染指数略大于0.7,超出安全范围,应加以警戒,其余样点满足安全范围。此外,研究区莲叶中各重金属单项污染指数和综合污染指数全都满足安全范围。
表 5 莲子重金属单项和内梅罗污染指数评价Table 5. Individual heavy metal and Nemerow pollution indices on lotus seeds荷塘类型 编号 单因子污染指数 P综合 污染程度 Pb Cr Cd As Hg 自然种植 1 0.34 0.13 0.36 0.03 0.26 0.30 安全 2 0.63 0.14 0.55 0.03 0.29 0.51 安全 3 0.37 0.15 0.40 0.04 0.29 0.33 安全 4 0.63 0.17 0.56 0.06 0.30 0.51 安全 5 0.63 0.20 0.56 0.10 0.32 0.52 安全 6 0.38 0.16 0.41 0.05 0.30 0.34 安全 平均值 0.48 0.14 0.46 0.03 0.28 0.40 安全 人为管理 7 0.61 0.17 0.61 0.05 0.43 0.50 安全 8 0.59 0.16 0.55 0.05 0.39 0.48 安全 9 0.51 0.16 0.50 0.05 0.39 0.43 安全 10 0.38 0.14 0.52 0.03 0.33 0.42 安全 11 0.66 0.14 0.42 0.05 0.48 0.53 安全 12 0.67 0.17 0.65 0.06 0.55 0.56 安全 13 0.59 0.17 0.55 0.06 0.39 0.48 安全 14 0.46 0.11 0.30 0.04 0.34 0.37 安全 平均值 0.57 0.15 0.54 0.05 0.43 0.49 安全 游览干预 15 0.55 0.17 0.55 0.06 0.50 0.47 安全 16 0.91 0.16 0.49 0.05 0.56 0.71 警戒 17 0.74 0.17 0.69 0.07 0.66 0.62 安全 18 0.61 0.17 0.61 0.05 0.43 0.50 安全 19 0.40 0.13 0.35 0.04 0.40 0.34 安全 20 0.41 0.15 0.53 0.05 0.25 0.43 安全 21 0.36 0.14 0.69 0.03 0.27 0.53 安全 22 0.50 0.15 0.82 0.03 0.36 0.63 安全 平均值 0.56 0.15 0.59 0.05 0.43 0.53 安全 表 6 莲叶重金属单项和内梅罗污染指数评价Table 6. Individual and Nemerow pollution indices on lotus leavess荷塘类型 编号 单因子污染指数 P综合 污染程度 cu pb Cr Cd As Hg 自然种植 1 0.14 0.17 0.08 0.04 0.08 0.10 0.14 安全 2 0.18 0.17 0.06 0.03 0.08 0.11 0.15 安全 3 0.16 0.19 0.09 0.04 0.09 0.11 0.15 安全 4 0.20 0.19 0.09 0.06 0.11 0.13 0.17 安全 5 0.23 0.22 0.12 0.10 0.14 0.16 0.20 安全 6 0.17 0.20 0.10 0.05 0.10 0.12 0.16 安全 平均值 0.16 0.17 0.07 0.03 0.08 0.10 0.14 安全 人为管理 7 0.17 0.18 0.08 0.04 0.09 0.10 0.15 安全 8 0.18 0.17 0.07 0.04 0.08 0.12 0.15 安全 9 0.18 0.17 0.07 0.04 0.08 0.12 0.15 安全 10 0.17 0.15 0.08 0.04 0.09 0.14 0.15 安全 11 0.17 0.20 0.07 0.04 0.08 0.13 0.17 安全 12 0.19 0.18 0.08 0.05 0.10 0.11 0.16 安全 13 0.19 0.18 0.08 0.05 0.09 0.13 0.16 安全 14 0.13 0.15 0.05 0.03 0.06 0.10 0.12 安全 平均值 0.18 0.18 0.07 0.04 0.08 0.12 0.153 安全 游览干预 15 0.19 0.18 0.07 0.04 0.07 0.13 0.16 安全 16 0.16 0.23 0.06 0.04 0.07 0.11 0.18 安全 17 0.21 0.18 0.08 0.05 0.10 0.11 0.17 安全 18 0.18 0.16 0.08 0.04 0.08 0.10 0.15 安全 19 0.19 0.18 0.08 0.03 0.09 0.15 0.16 安全 20 0.15 0.34 0.09 0.04 0.11 0.14 0.26 安全 21 0.16 0.11 0.08 0.05 0.08 0.14 0.13 安全 22 0.21 0.15 0.08 0.07 0.08 0.11 0.17 安全 平均值 0.18 0.19 0.08 0.05 0.09 0.12 0.17 安全 相比不同生态型荷塘莲子的重金属评价结果发现,自然种植型荷塘莲子、莲叶的各重金属元素单项和综合污染指数最小;而人为管理型荷塘中和游览干预型荷塘莲的不同部位(莲子、莲叶)的重金属单项污染指数值差异不显著,综合评价结果后者数值更大,更靠近警戒线或已达到警戒线。综合评价指数均值排序为:自然种植型荷塘<人为管理型荷塘<游览干预型荷塘。
2.2.3 莲不同部位重金属的富集特征
由表 7可知,莲子对各元素的富集系数均值大小顺序如下:Cu>Cd>Zn>Hg>As>Cr>Pb;莲叶的富集系数均值顺序为:Cd>Cu>Zn>Hg>As>Pb>Cr。整体而言,Cu、Zn和Cd在莲叶中的富集系数值要明显低于其在莲子中的富集系数值,但Pb、Cr、As和Hg却明显高于莲子中的富集系数值。
表 7 莲不同部位重金属富集系数Table 7. Enrichment coefficients on heavy metals in lotus parts莲不同部位 Cu Zn Pb Cr Cd As Hg 莲子 0.588 0.336 0.001 0.003 0.473 0.008 0.039 莲叶 0.199 0.166 0.012 0.009 0.205 0.052 0.146 3. 讨论与结论
五夫白莲荷塘底泥为弱酸性,且肥力较高,有利于白莲生长。重金属元素Cu、Zn、Pb、Cr和As符合《无公害农产品——种植业产地环境条件》(NY/T 5010-2016)[14]标准限值;且元素Cr和As含量远低于《绿色食品——产地环境质量标准》[18]的限值要求。为促进研究区白莲产业的发展和升级,必须对荷塘底泥Cu、Zn、Pb、Cd和Hg元素含量加以严控,尤其应对已经超标的Cd和Hg元素的污染来源进一步调查与研究。
现行的重金属污染评价方法有很多,其中单项污染指数法和内梅罗综合污染指数法是目前国内外最为通用的评价方法之一[20]。以《无公害农产品——种植业产地环境条件》(NY/T 5010-2016)[14]标准对底泥重金属进行评价的结果表明,各荷塘底泥重金属单项和综合污染指数存在显著差异。除部分荷塘底泥Cd、Hg元素的单项污染指数超过1,为轻度污染;其余各元素评价结果为非污染。再次反映了研究区荷塘底泥针对性控制Cd、Hg元素对其底泥环境质量提高的重要性和紧迫性。不同生态荷塘底泥中重金属评价结果发现,各重金属单项污染指数和综合污染指数均值大小排序为:自然种植型荷塘<人为管理型荷塘<游览干预型荷塘。由此可见,后两种荷塘因为肥料施加和游览开发都明显增加了底泥的重金属含量。此外,荷塘样点16的综合污染指数最大,属于轻度污染,这很可能与其位于游客饮食服务中心区域范围有关,四周的餐饮业废物排放和旅游交通污染物排放造成了该处重金属含量整体值最高。这与居民垃圾(含餐饮业垃圾)排放和旅游交通污染物排放为旅游城市重要的重金属来源[3]的研究结论相一致。
莲子重金属含量均值大小顺序为Zn>Cu>Cr>Pb>Cd>As>Hg;莲叶重金属含量均值大小顺序为Zn>Cu>Pb>Cr>As>Cd>Hg。可见,莲的同一生长部位的不同元素含量分布存在差异,且莲的不同生长部位对同一生长环境的同种重金属富集效应也不同。莲子和莲叶中各重金属单项污染指数都小于1,属于非污染范围,满足各对应标准[15-17]安全限值规定。内梅罗污染指数评价结果得知,荷塘样点16对应的莲子重金属综合污染指数略超0.7,超过安全范围,应加以警戒,这与样点16的Pb元素单因子污染指数值较大有关;其余样点的莲子重金属综合污染指数满足安全范围。研究表明,Pb元素通常作为交通运输主要的标志性污染物,且交通排放的Pb影响最远达到道路两侧320 m以内的范围[21]。因此,样点16受近距离的汽车尾气的排放和生活污染来源都可能造成该处莲子Pb含量的增加[3, 21],这与上文样点16底泥中重金属Pb污染最为严重相一致。此外,研究区莲叶重金属综合污染指数全部满足安全范围,故将研究区莲叶作为茶饮品符合重金属方面的安全标准[16-17]要求,建议适当开发、推广荷叶销售,增加当地莲产业效益。
莲子、莲叶对各元素的富集系数存在显著差异。相比而言,莲子中Cu、Zn和Cd为强富集元素,Hg为中等富集元素,As、Cr和Pb为弱富集元素;而莲叶对Hg的富集性显著增强,均值达到0.146,高于莲子Hg的富集系数(均值为0.039),也明显高于莲藕中Hg的富集系数(范围为0.0242~0.0720)[12]。已有研究表明,作物中Hg的来源不仅有土壤、灌溉水还有空气等,其中空气中Hg的迁移影响不可忽视[22]。由于莲叶大面积接触空气,受大气中Hg的污染影响更大。这也与受大气污染影响下的蔬菜中Hg的含量分布为叶>果实>根的研究结果相符[23]。可见,莲的不同生长部位的生理生化特征是影响其对重金属元素富集差异的重要原因,其重金属不仅来源于土壤母质、生活源、交通运输排放和大气沉降等,此外各荷塘的农业管理方式和肥料施用量等不同也会对莲的重金属含量产生差异影响。
总体而言,不同生态型荷塘的底泥、莲子、莲叶中重金属综合污染指数均值排序一致,都为自然种植型荷塘<人为管理型荷塘<游览干预型荷塘。为了进一步提升莲子、莲叶品质,今后应加强荷塘底泥重金属含量控制,尤其要对Cd、Hg元素的污染源进行调查,同时对荷塘选址做适当评估,严格控制旅游开发带来的负面生态环境效益,加强游览区域的环境卫生管理,尽量降低农业(主要为肥料施加)、生活(含旅游餐饮)和交通污染源的影响。
-
表 1 不同参照标准中重金属含量
Table 1 Reference standardson heavy metal contents
表 2 五夫荷塘底泥基本理化指标
Table 2 Basic physicochemical properties of pond sediments at Wufu
项目 pH TOC/
(g·kg-1)TN/
(g·kg-1)TP/
(g·kg-1)Cu/
(mg·kg-1)Zn/
(mg·kg-1)Pb/
(mg·kg-1)Cr/
(mg·kg-1)Cd/
(mg·kg-1)As/
(mg·kg-1)Hg/
(mg·kg-1)最小值 5.34 10.03 1.01 0.35 15.73 137.80 86.58 49.41 0.20 3.10 0.13 最大值 6.39 27.09 1.55 0.79 48.81 186.76 126.08 62.79 0.46 4.50 0.58 平均值 6.05 18.60 1.27 0.62 27.85 162.33 101.94 55.85 0.32 3.74 0.27 CV/% 23.45 23.17 8.47 18.92 31.43 10.38 13.41 7.89 29.73 12.98 60.47 表 3 五夫荷塘底泥单项污染和内梅罗污染指数评价
Table 3 Individual and Nemerow pollution indiceson sediments from lotus ponds at Wufu
荷塘类型 编号 单因子污染指数 P综合 污染程度 Cu Zn Pb Cr Cd As Hg 自然种植 1 0.31 0.38 0.21 0.13 0.51 0.10 0.57 0.46 安全 2 0.36 0.47 0.26 0.13 0.61 0.09 0.53 0.50 安全 3 0.35 0.42 0.24 0.14 0.57 0.11 0.63 0.51 安全 4 0.37 0.47 0.28 0.16 0.61 0.12 0.53 0.50 安全 5 0.38 0.48 0.30 0.19 0.60 0.15 0.53 0.51 安全 6 0.31 0.38 0.20 0.10 0.53 0.07 0.60 0.47 安全 平均值 0.34 0.42 0.24 0.13 0.56 0.10 0.55 0.48 安全 人为管理 7 0.58 0.67 0.28 0.18 0.77 0.12 0.60 0.63 安全 8 0.67 0.58 0.36 0.18 0.73 0.12 0.85 0.70 安全 9 0.66 0.56 0.35 0.17 0.70 0.12 1.13 0.88 警戒 10 0.54 0.78 0.39 0.21 1.03 0.13 0.57 0.82 警戒 11 0.73 0.84 0.46 0.22 1.15 0.13 1.31 1.04 轻污染 12 0.61 0.77 0.32 0.21 0.71 0.12 0.63 0.65 安全 13 0.66 0.58 0.36 0.18 0.72 0.13 0.84 0.69 安全 14 0.46 0.54 0.27 0.11 0.76 0.04 0.86 0.68 安全 平均值 0.63 0.70 0.36 0.20 0.85 0.12 0.85 0.79 警戒 游览干预 15 0.98 0.69 0.46 0.22 0.85 0.15 1.70 1.31 轻污染 16 0.91 0.92 0.50 0.24 1.52 0.11 1.94 1.51 轻污染 17 0.65 0.88 0.35 0.25 0.66 0.11 0.66 0.72 警戒 18 0.53 0.72 0.35 0.20 0.75 0.13 0.55 0.62 安全 19 0.55 0.77 0.41 0.20 0.78 0.15 0.67 0.65 安全 20 0.62 0.93 0.45 0.24 1.34 0.13 0.77 1.05 轻污染 21 0.54 0.79 0.36 0.22 1.28 0.11 0.47 0.98 警戒 22 0.51 0.79 0.38 0.21 1.34 0.10 0.44 1.02 轻污染 平均值 0.66 0.81 0.41 0.22 1.07 0.12 0.90 0.98 警戒 表 4 莲不同部位重金属含量
Table 4 Heavy metal contents in lotus parts
[单位/(mg·kg-1)] 莲不同部位 项目 Cu Zn Pb Cr Cd As Hg 莲子 最小值 10.404 28.010 0.067 0.106 0.064 0.014 0.005 最大值 22.695 47.626 0.182 0.196 0.168 0.085 0.018 平均值 15.547 40.819 0.113 0.154 0.111 0.027 0.008 CV(%) 20.50 10.56 28.80 11.77 24.70 53.82 35.37 莲叶 最小值 3.752 13.265 0.560 0.292 0.034 0.135 0.005 最大值 6.410 25.088 1.712 0.450 0.100 0.214 0.046 平均值 5.052 19.848 0.960 0.378 0.048 0.175 0.030 CV(%) 12.28 12.76 23.52 11.25 30.81 12.72 36.26 表 5 莲子重金属单项和内梅罗污染指数评价
Table 5 Individual heavy metal and Nemerow pollution indices on lotus seeds
荷塘类型 编号 单因子污染指数 P综合 污染程度 Pb Cr Cd As Hg 自然种植 1 0.34 0.13 0.36 0.03 0.26 0.30 安全 2 0.63 0.14 0.55 0.03 0.29 0.51 安全 3 0.37 0.15 0.40 0.04 0.29 0.33 安全 4 0.63 0.17 0.56 0.06 0.30 0.51 安全 5 0.63 0.20 0.56 0.10 0.32 0.52 安全 6 0.38 0.16 0.41 0.05 0.30 0.34 安全 平均值 0.48 0.14 0.46 0.03 0.28 0.40 安全 人为管理 7 0.61 0.17 0.61 0.05 0.43 0.50 安全 8 0.59 0.16 0.55 0.05 0.39 0.48 安全 9 0.51 0.16 0.50 0.05 0.39 0.43 安全 10 0.38 0.14 0.52 0.03 0.33 0.42 安全 11 0.66 0.14 0.42 0.05 0.48 0.53 安全 12 0.67 0.17 0.65 0.06 0.55 0.56 安全 13 0.59 0.17 0.55 0.06 0.39 0.48 安全 14 0.46 0.11 0.30 0.04 0.34 0.37 安全 平均值 0.57 0.15 0.54 0.05 0.43 0.49 安全 游览干预 15 0.55 0.17 0.55 0.06 0.50 0.47 安全 16 0.91 0.16 0.49 0.05 0.56 0.71 警戒 17 0.74 0.17 0.69 0.07 0.66 0.62 安全 18 0.61 0.17 0.61 0.05 0.43 0.50 安全 19 0.40 0.13 0.35 0.04 0.40 0.34 安全 20 0.41 0.15 0.53 0.05 0.25 0.43 安全 21 0.36 0.14 0.69 0.03 0.27 0.53 安全 22 0.50 0.15 0.82 0.03 0.36 0.63 安全 平均值 0.56 0.15 0.59 0.05 0.43 0.53 安全 表 6 莲叶重金属单项和内梅罗污染指数评价
Table 6 Individual and Nemerow pollution indices on lotus leavess
荷塘类型 编号 单因子污染指数 P综合 污染程度 cu pb Cr Cd As Hg 自然种植 1 0.14 0.17 0.08 0.04 0.08 0.10 0.14 安全 2 0.18 0.17 0.06 0.03 0.08 0.11 0.15 安全 3 0.16 0.19 0.09 0.04 0.09 0.11 0.15 安全 4 0.20 0.19 0.09 0.06 0.11 0.13 0.17 安全 5 0.23 0.22 0.12 0.10 0.14 0.16 0.20 安全 6 0.17 0.20 0.10 0.05 0.10 0.12 0.16 安全 平均值 0.16 0.17 0.07 0.03 0.08 0.10 0.14 安全 人为管理 7 0.17 0.18 0.08 0.04 0.09 0.10 0.15 安全 8 0.18 0.17 0.07 0.04 0.08 0.12 0.15 安全 9 0.18 0.17 0.07 0.04 0.08 0.12 0.15 安全 10 0.17 0.15 0.08 0.04 0.09 0.14 0.15 安全 11 0.17 0.20 0.07 0.04 0.08 0.13 0.17 安全 12 0.19 0.18 0.08 0.05 0.10 0.11 0.16 安全 13 0.19 0.18 0.08 0.05 0.09 0.13 0.16 安全 14 0.13 0.15 0.05 0.03 0.06 0.10 0.12 安全 平均值 0.18 0.18 0.07 0.04 0.08 0.12 0.153 安全 游览干预 15 0.19 0.18 0.07 0.04 0.07 0.13 0.16 安全 16 0.16 0.23 0.06 0.04 0.07 0.11 0.18 安全 17 0.21 0.18 0.08 0.05 0.10 0.11 0.17 安全 18 0.18 0.16 0.08 0.04 0.08 0.10 0.15 安全 19 0.19 0.18 0.08 0.03 0.09 0.15 0.16 安全 20 0.15 0.34 0.09 0.04 0.11 0.14 0.26 安全 21 0.16 0.11 0.08 0.05 0.08 0.14 0.13 安全 22 0.21 0.15 0.08 0.07 0.08 0.11 0.17 安全 平均值 0.18 0.19 0.08 0.05 0.09 0.12 0.17 安全 表 7 莲不同部位重金属富集系数
Table 7 Enrichment coefficients on heavy metals in lotus parts
莲不同部位 Cu Zn Pb Cr Cd As Hg 莲子 0.588 0.336 0.001 0.003 0.473 0.008 0.039 莲叶 0.199 0.166 0.012 0.009 0.205 0.052 0.146 -
[1] ZHAO F J, Ma Y B, ZHU Y G, et al. Soil contamination in China:Current status and mitigation strategies[J]. Environmental Science & Technology, 2014, 49(2):750-759. http://cn.bing.com/academic/profile?id=aaa7e832b2ac797f78b581a73a603959&encoded=0&v=paper_preview&mkt=zh-cn
[2] 王玉军, 刘存, 周东美, 等.客观看待我国耕地土壤环境质量的现状-关于《全国土壤污染状况调查公报》中有关问题的讨论和建议[J].农业环境科学学报, 2014, 33(8):1465-1473. DOI: 10.11654/jaes.2014.08.001 [3] 叶宏萌, 李国平, 袁旭音, 等.武夷山市区土壤重金属积累及5种阔叶树富集特征[J].热带作物学报, 2016, 37(3):466-469. http://www.cqvip.com/QK/95551X/201603/668571647.html [4] LU K, YANG X, GIELEN G, et al. Effect of bamboo and rice straw biochars on the mobility and redistribution of heavy metals (Cd, Cu, Pb and Zn) in contaminated soil[J]. Journal of environmental management, 2017, 186(2):285-292. http://cn.bing.com/academic/profile?id=715723597f7c495114ef008b16f67053&encoded=0&v=paper_preview&mkt=zh-cn
[5] 孔德政, 裴康康, 李永华, 等.铅、镉和锌胁迫对荷花生理生化的影响[J].河南农业大学学报, 2010, 44(4):402-407. http://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-NNXB201004009.htm [6] ZHANG Y, LU X, ZENG S, et al. Nutritional composition, physiological functions and processing of lotus (Nelumbo nucifera Gaertn.) seeds:a review[J]. Phytochemistry Reviews, 2015, 14(3):321-334. DOI: 10.1007/s11101-015-9401-9
[7] 曾绍校, 陈秉彦, 郭泽镔, 等.莲子生理活性的研究进展[J].热带作物学报, 2012, 33(11):2110-2114. DOI: 10.3969/j.issn.1000-2561.2012.11.036 [8] ZHENG C, ZHANG Y, WANG G, et al. Determination of Major and Trace Elements in Lotus Seed by Inductively Coupled Plasma-Mass Spectrometry[J]. Asian Journal of Chemistry, 2013, 25(3):1759. http://cn.bing.com/academic/profile?id=bccfa25b3368e86a1cc1a8677eaa0ff8&encoded=0&v=paper_preview&mkt=zh-cn
[9] 陈在敏, 邹义栩, 王传之. ICP-MS法测定莲子中重金属元素含量[J].海峡药学.2013, 25(9):83-84. http://www.doc88.com/p-7846956309388.html [10] 张霖霖, 张涵, 黄坚铎. ICP-AES法测定莲子中微量元素[J].南昌大学学报:理科版, 1994, 18(4):410-418. http://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTotal-SDHG201106031.htm [11] BHAT R, SRIDHAR K R. Nutritional quality evaluation of electron beam-irradiated lotus (Nelumbo nucifera) seeds[J]. Food Chemistry, 2008, 107(1):174-184. DOI: 10.1016/j.foodchem.2007.08.002
[12] XIONG C, ZHANG Y, XU X, et al. Lotus roots accumulate heavy metals independently from soil in main production regions of China[J]. Scientia Horticulturae, 2013, 164(9):295-302. http://cn.bing.com/academic/profile?id=a6b23887af58938c87ddd5d91b448b86&encoded=0&v=paper_preview&mkt=zh-cn
[13] CAI D J.. Contents of heavy metals in lotus seed from REEs mining area[J]. Journal of Saudi Chemical Society, 2012, 16(2):175-176. http://cn.bing.com/academic/profile?id=4dcdb4b936f5916374fa7842f86bae92&encoded=0&v=paper_preview&mkt=zh-cn
[14] 中华人民共和国农业部. NY/T 5010-2016, 无公害农产品——种植业产地环境条件[S]. 北京: 中国标准出版社, 2016. [15] 中华人民共和国卫生部. GB2762-2017, 食品安全国家标准——食品中污染物限量[S]. 北京: 中国标准出版社, 2017. [16] 中华人民共和国农业部. NY/T 288-2012, 绿色食品——茶叶[S]. 北京: 中国标准出版社, 2012. [17] 中国农业部农业环境质量监督检验测试中心. NY 659-2003, 茶叶中铬、镉、汞、砷及氟化物限量[S]. 北京: 中国标准出版社, 2003. [18] 中华人民共和国农业部. NY/T 391-2013, 绿色食品——产地环境质量[S]. 北京: 中国标准出版社, 2013. [19] 全国土壤普查办公室.中国土壤[M].北京:中国农业出版社, 1998. [20] 叶宏萌, 李国平, 郑茂钟, 等.茶园土壤重金属空间分异及风险评价[J].森林与环境学报, 2016, 36(2):209-215. http://www.wanfangdata.com.cn/details/detail.do?_type=perio&id=fjlxyxb201602013 [21] VIARD B, PIHAN F, PROMEYRAT S, et al. Integrated assessment of heavy metal (Pb, Zn, Cd) highway pollution:bioaccumulation in soil, Graminaceae and land snails[J]. Chemosphere. 2004, 55(10):1349-1359. DOI: 10.1016/j.chemosphere.2004.01.003
[22] 叶宏萌, 郑茂钟, 李国平, 等.武夷岩茶主产区土壤及茶叶微量元素分布特征[J].森林与环境学报, 2016, 36(4):423-428. http://mall.cnki.net/magazine/Article/FJLB201604007.htm [23] SHARMA R K, AGRAWAL M, MARSHALL F M. Heavy metals in vegetables collected from production and market sites of a tropical urban area of India[J]. Food and chemical toxicology, 2009, 47(3):583-591. DOI: 10.1016/j.fct.2008.12.016
-
期刊类型引用(5)
1. 戴慧,赵文玉,王建辉,贺湘怡,龙潇. 湘莲不同器官中常见重金属含量检测及富集特征分析. 食品与机械. 2024(03): 60-67 .  百度学术
百度学术
2. 曹姗姗,韩昀,安民,孔繁涛,孙伟. 基于土壤重金属镉污染评价的“湘莲+”种植区划. 特产研究. 2022(05): 33-37+42 .  百度学术
百度学术
3. 张印,陈慧娜,吕广动,王忍,黄璜,陈灿. “莲+小龙虾”模式的技术流程与综合效益分析——以浏阳市“湘莲+”种植基地为例. 作物研究. 2020(03): 274-278 .  百度学术
百度学术
4. 叶宏萌,李国平,郑茂钟,袁旭音,徐晓敏,李少华. 武夷岩茶土壤铬、锌、镍元素的生物有效性及其影响因素. 福建农业学报. 2019(06): 711-718 .  本站查看
本站查看
5. 李静,唐青枫,张灵杰,陆春海. 重金属污染底泥的电动力学修复技术研究进展. 山东化工. 2019(17): 91-93 .  百度学术
百度学术
其他类型引用(0)




 下载:
下载:
