Double Antibody Sandwich ELISA for Detection of Porcine Epidemic Diarrhea Virus
-
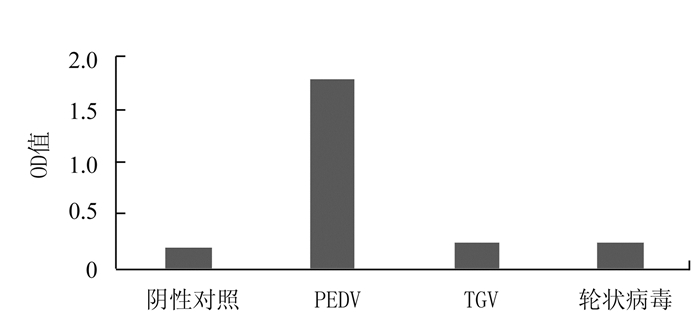
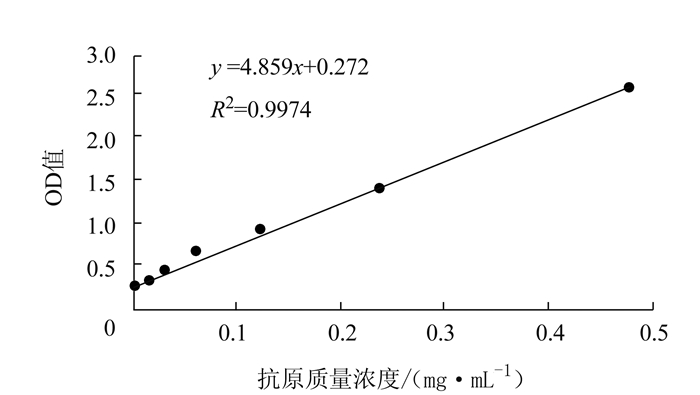
摘要: 采用特异性好的鼠源抗猪流行性腹泻病毒(PEDV)单克隆抗体为捕获抗体,兔源多克隆抗体为检测抗体,建立PEDV双抗体夹心ELISA检测方法。结果显示,该方法的最佳反应条件为:抗PEDV单克隆抗体E1包被质量浓度4.40 μg·mL-1,37℃包被2 h,采用5% BSA封闭液封闭1 h,兔抗PEDV抗体工作质量浓度为5.91 μg·mL-1,酶标二抗稀释度为1:2000,以OD450nm ≥ 0.381作为阳性判定标准。该ELISA方法对猪轮状病毒和猪传染性胃肠炎病毒无交叉反应。敏感度可达30 μg·mL-1(5×103.12);重复性变异系数小于10%。采用该方法和RT-PCR方法同时检测临床样品42份,阳性样品符合率为92.30%,表明建立的PEDV双抗体夹心ELISA检测方法具有特异性好、敏感性高和方便快捷等优点,可用于PEDV快速检测。
-
关键词:
- 猪流行性腹泻病毒 /
- 单克隆抗体 /
- 双抗体夹心ELISA
Abstract: A double antibody sandwich ELISA (DAS-ELISA) was developed using the high specificity, mouse-derived monoclonal antibody (Mab) as the capture antibody and the rabbit-derived polyclonal antibody against porcine epidemic diarrhea virus (PEDV) as the detecting antibody. The optimal reaction conditions for DAS-ELISA was determined to include a coating concentration of 4.40 g·mL-1 for PEDV MAb E1 with 1 h incubation at 37℃, the use of 5% BSA solution for blocking for 1 h, an application of 5.91 μg·mL-1 in concentration of rabbit polyclonal antibodies against PEDV, a 2 000×dilution of HRP, and the positive OD equal or greater than 0.381 at 450 nm wave length on the spectrophotometer measurement. The developed method showed no cross-reaction between porcine rotavirus and transmissible gastroenteritis virus. The detection sensitivity of the method was 30 g·mL-1(5×103.12); and, the coefficient variation of repetition, less than 10%. Furthermore, a total of 42 clinical samples were positively detected by the method in conjunction with RT-PCR at a rate of 92.30%. Consequently, it was concluded that the newly developed DAS-ELISA methodology was highly specific, sensitive, rapid, and hence, applicable for PEDV detection. -
0. 引言
【研究意义】土壤是农业可持续发展的重要自然资源,其中耕地的土壤环境质量是保障粮食安全的关键,是生态环境保护的重要对象。但随着工矿业与农业的迅速发展,土壤重金属污染日益严重[1],根据《全国土壤污染状况调查公报》显示,耕地土壤的点位超标率达到了19.4%,其中 Pb、Cd 和Cr的点位超标率分别为1.5%、7.0%和1.1%[2]。福建省农田重金属污染主要是采矿和冶炼过程中废水、废渣的不规范处理造成的,与此同时,土壤酸化严重也加剧了土壤重金属的污染风险[3]。土壤重金属污染具有积累性、隐蔽性和长期性的特点[4],容易被农作物吸收,通过食物链途径进入人体,严重危害健康。因此,重金属污染农田的修复与治理已成为亟待解决的问题。【前人研究进展】目前土壤重金属修复主要有物理、化学、生物和生态修复等技术[5],其中原位化学钝化修复技术由于其见效快、成本低、易操作等优点,广泛应用于修复大面积中轻度重金属污染农田[6]。多项研究表明,石灰可显著降低土壤有效态Cd含量以及稻米Cd含量[7,8]。Baltrenaite等[9]研究发现,利用木质生物炭可去除水中的Pb2+,银杏树生物炭和樟子松生物炭对Pb2+的吸附量分别是1.29~3.77 、2.37~4.49 μg·g−1,有较强的吸附效果。周颖等[10]研究发现,施用海泡石钝化处理过的猪粪,油菜的铜、锌吸收率分别降低5.94%~12.13%和4.21%~11.68%。夏鹏等[11]研究表明,生物质炭的施入能促进金属离子从可交换态向残渣态和可还原态转变,对土壤中Cr的钝化效果最佳。赵明柳等[12]研究发现,硅酸钠降低了土壤Pb、Zn的有效性。其中,降低Pb从根到茎(分蘖期)、从茎和叶到糙米(成熟期)的转移及Zn从根到茎(分蘖期)、从根到茎成熟期和从叶到糙米(成熟期)的转移。高瑞丽等[13]利用不同比例蒙脱石处理污染土壤后发现,5%的蒙脱石达到最佳效果,对Cu,Pb,Zn,Cd的弱酸提取态含量分别降低27.6%,19.2%,25.6%,19.2%。【本研究切入点】目前,对土壤钝化剂的研究主要集中在天然单一钝化剂材料以及短期的盆栽试验,实际运用容易受土壤性质、污染类型及程度等因素的影响,存在很强的局限性,缺少针对福建省酸性土壤的商品化钝化剂的田间效果对比试验。【拟解决的关键问题】本试验筛选了8种商品化钝化剂,以上海青和夏阳白作为试验作物,选取了屏南县某Cd、Pb和Cr复合污染的农田进行钝化剂比对试验。通过比较分析不同钝化剂对土壤pH值、重金属DTPA提取态、上海青和夏阳白的产量以及重金属含量的影响,挑选出效果最好的钝化剂产品,为福建省土壤安全利用提供技术支持。
1. 材料与方法
1.1 试验地点
于2019年5月,福建省屏南县岭下乡某矿区附近的农田(北纬27°07′48.84″,东经118°58′16.33″,海拔927 m)进行钝化剂对比试验。农田土壤的基本理化性质见表1。根据《土壤环境质量农用地土壤污染风险管控标准(试行)》(GB 15618—2018),试验田土壤的Pb和Cd重金属总量超过了农用地土壤污染风险筛选值,其中Cd总量超过标准的4.3倍,属于复合镉-铅污染的土壤。
表 1 试验农田土壤的基本理化性质Table 1. Basic physiochemical properties of soil at tested farm项目 Item pH OM/(g·kg−1) CEC/(cmol·kg−1) 土壤重金属总量Total amount of heavy metals in soil/(mg·kg−1) Cd Pb Cr As Ni 土壤 Soil 5.23 18.2 15.3 1.3 102.0 20.8 23.6 10.7 筛选值* filter value* 5.5 — — 0.3 70 150 40 60 注:*《土壤环境质量农用地土壤污染风险管控标准(试行)》(GB 15618—2018)
Note:*Soil Environmental Quality Standard for Soil Pollution Risk Control of Agricultural Land(Trial)(GB 15618—2018)1.2 试验材料
供试钝化剂:特贝钙土壤调理剂(A)、环保桥土壤调理剂(B)、Yonker土壤调理剂(C)、康源土壤调理剂(D)、海状元土壤调理剂(E)、万亩田有机肥(F)、土壤调理剂(G)和石灰(I)8种市面上常见的酸性土壤的钝化剂。钝化剂主要成分和组成原料以及施用量如表2所示,其中各钝化剂用量根据厂家指导用量添加。所有钝化剂重金属含量都低于《肥料中砷、镉、铅、铬、汞生态指标》(GB/T 23349—2009)中的限定标准。
表 2 钝化剂的基本信息Table 2. Basic information on applied soil passivating agents钝化剂
passivator主要成分
Main ingredients主要原料
main material每667 m2用量
Consumption per 667 m2
/kg特贝钙土壤调理剂(A)
Soil conditioner for Calcium Tebbe(A)CaO>45% 钙、磷、铁、锌微量元素
Calcium, phosphorus, iron, zinc trace elements牡蛎壳 Oyster shell 150 环保桥土壤调理剂(B)
Green Bridge Soil Conditioner(B)CaO>34%、SiO2>5.5% 生石灰、石灰石 海泡石、沸石
Quick lime, limestone, sepiolite, zeolite200 Yonker土壤调理剂(C)
Yonker Soil Conditioner(C)CaO>40%、MgO>20%、SiO2>15% 重质碳酸钙、生石灰、硅酸钙、海泡石
Heavy calcium carbonate, calcium oxide, calcium silicate, sepiolite200 康源土壤调理剂(D)
Kangyuan Soil conditioner(D)CaO>40%、MgO>5%、SiO2>7%、OM>10% 石灰石、硅酸钙
Limestone, calcium silicate60 海状元土壤调理剂(E)
Sea crown Soil Conditioner(E)CaO>45%、OM>20% 牡蛎壳、浒苔
Oyster shells, enteromorpha150 万亩田有机肥(F)
Ten thousand mu organic fertilizer(F)OM>35%、N+P2O5+K2O>5% — 300 土壤调理剂(G)
Soil conditioner(G)CaO>33%、MgO>5%、SiO2>28% 白云石、钾长石、石灰石
Dolomite, potassium feldspar, limestone200 OSA土壤重金属钝化剂(H)
OSA soil heavy metal passivator(H)CaO>46%、MgCO3>5%、SiO2>20%、OM>10% 麦饭石、菱镁矿、钾长石、腐殖酸
Medical stone, magnesite, potassium feldspar, humic acid300 石灰粉(I)
Lime(I)CaO>85% 生石灰
quicklime300 不施用钝化剂(CK)
No passivator(CK)— — 0 供试作物:上海青(第一季)、夏阳白(第二季)。
1.3 试验设计
试验于2019年6~12月进行,试验田面积330 m2(22 m×15 m),共布设30个小区,每个小区面积6 m2(6 m×1 m),小区间沟宽0.3 m,2排之间宽0.5 m,避免种植过程水肥混施。设置10种不同处理,每个处理3个重复,随机分布。钝化剂施加均根据厂家规定的添加量(表2),蔬菜种植密度保持一致,其他田间管理方式(如浇水、施肥、除草等)完全相同。第一季试验蔬菜为小青菜,于2019年7月移栽,2019年9月收获;第二季试验蔬菜为夏阳白,于2019年9月移栽,2019年10月收获。采集每个小区土壤样品和蔬菜地上部组织,测定蔬菜鲜产量。每个小区采集3个点0~20 cm土壤,混合为1个土壤样品,去除石头和杂质后自然风干后磨碎,通过2 mm和0.149 mm 尼龙筛,保存。蔬菜样用去离子水清洗,105 ℃杀青30 min,然后60 ℃烘干至恒重,粉碎,过100目尼龙筛,装入封口袋保存。
1.4 试验方法
土壤pH值用电位法,去土壤与离子水的比例为1:2.5(m/v)用pH计(GB/T 11165梅特勒-托利多仪器(上海) 有限公司)测定。土壤机械组成采用激光粒度仪测定。有机物含量(OM)用K2Cr2O7氧化法测定。阳离子交换容量(CEC)用醋酸铵(1 mol·L−1 NH4OAc,pH = 7.0)方法测定。土壤重金属全量用HCl-HF-HNO3-HClO4法消解,通过电感耦合等离子体质谱法(ICP-Mass,Nexion 300,Perkin Elmer,NY)测定Pb、Cd和Cr的含量。土壤中的Pb、Cd和Cr有效态含量用1 mol·L−1 HCl和DTPA溶液(二亚乙基三胺五乙酸,0.005 mol·L−1;CaCl2,0.01 mol·L−1;三乙醇胺[TEA],0.1 mol·L−1;pH = 7.3)提取,用ICP-MS测定。植物样用HNO3和H2O2消解法,使用微波消解系统(MARS6; CEM,NC,USA)消解后用ICP-MS测定。样品分析过程中以国家标准物质土壤(GBW07407)样品以及国家生物标准物质标准值(GBW10020GSB-11)作为参考,同时做空白对照组。
1.5 数据处理
使用Excel 2015进行数据的预处理,用SPSS 17.0进行方差分析(ANOVA)、Duncan多重比较、显著性差异(LSD)和Pearson相关性分析,进行统计分析。作图由Origin9.0软件绘制。
2. 结果与分析
2.1 不同钝化剂处理对上海青和夏阳白产量的影响
第一季上海青试验结果(图1)表明,上海青的产量均不同程度增加。与CK相比,所有处理组的上海青的产量都显著增加(P<0.05),增幅为37.8%~84.2%。其中,OSA土壤重金属钝化剂(H)处理后,上海青的产量最高,产量大小依次为:H>I>F>G>A>C>B>E>D>CK。对比石灰处理(I),只有OSA土壤重金属钝化剂(H)对上海青增产效果比石灰处理好,其余钝化剂处理均弱于石灰。
第二季夏阳白试验结果(图1)表明,对比第一季上海青产量增幅,钝化剂处理对夏阳白产量增幅有不同程度的降低。与CK相比,仅特贝钙土壤调理剂(A),石灰(I)处理组的夏阳白的产量存在显著性增加(P<0.05),增幅分别是65.4%,32.8%,其余处理对夏阳白处理无显著性影响。
2.2 不同钝化剂对土壤pH值的影响
图2显示,第一季上海青未施加钝化剂的土壤pH值为3.81,为酸性土壤。施加钝化剂后,土壤pH值均有不同程度的升高。其中,钝化剂C、H、B、I、G、F、A处理后的土壤pH值增加了0.59~1.44个单位,与CK处理相比均达到显著性差异(P<0.05)。Yonker土壤调理剂(C)和OSA土壤重金属钝化剂(H)对土壤pH值提升非常显著,分别达到 5.25和5.18,效果要优于石灰(I)处理。
第二季夏阳白试验土壤pH也表现出相似的趋势。钝化剂H、G、I、A处理组的土壤pH值增加了1.24~1.42个单位,与CK处理相比均达到显著性差异(P<0.05)。其中,OSA土壤重金属钝化剂(H)处理的土壤pH值最大,达到4.76,高于石灰(I)处理。
2.3 不同钝化剂对土壤重金属有效态含量的影响
重金属有效态提取剂有弱碱、弱酸、缓冲溶液、中性盐溶液和螯合剂,如HCl、EDTA、DTPA、CaCl2等[14-15]。本试验采用DTPA浸提的方法对不同钝化剂处理后的土壤重金属有效性进行分析,土壤中DTPA提取态Pb、Cd和Cr的含量见表3。
表 3 不同钝化剂对土壤中DTPA提取态Pb、Cd和Cr的含量的影响Table 3. Effects of soil treatments on contents of DTPA-extracted Pb, Cd, and Cr in soil(单位:mg·kg−1) 钝化剂 Passivator 第一季(上海青) the first season(Pakchoi) 第二季(夏阳白) the second season(Chinese cabbage) DTPA-Pb DTPA-Cd DTPA-Cr DTPA-Pb DTPA-Cd DTPA-Cr A 16.7±3.18 a 0.43±0.04 a 0.21±0.00 a 17.4±3.11 a 0.40±0.04 ab 0.20±0.00 c B 15.7±2.21 a 0.35±0.01 abc 0.20±0.01 a 17.0±1.56 a 0.41±0.02 ab 0.22±0.01 bc C 14.6±0.56 a 0.31±0.08 bcd 0.21±0.03 a 15.3±0.50 a 0.46±0.01 a 0.24±0.01 abc D 16.7±3.21 a 0.40±0.01 ab 0.20±0.02 a 16.9±4.24 a 0.40±0.03 ab 0.20±0.02 c E 15.2±0.86 a 0.24±0.06 d 0.22±0.01 a 14.1±0.35 a 0.34±0.07 b 0.21±0.02 c F 14.9±0.50 a 0.32±0.02 bcd 0.18±0.01 a 15.7±0.35 a 0.35±0.00 b 0.23±0.01 abc G 17.5±2.05 a 0.37±0.03 abc 0.21±0.02 a 15.6±1.60 a 0.37±0.03 b 0.27±0.05 ab H 17.7±0.85 a 0.28±0.08 cd 0.17±0.02 a 16.1±1.16 a 0.40±0.03 ab 0.22±0.00 bc I 16.6±2.12 a 0.36±0.02 abc 0.19±0.02 a 16.2±2.86 a 0.37±0.03 b 0.24±0.01 abc CK 15.7±1.49 a 0.35±0.03 abc 0.19±0.05 a 15.8±2.96 a 0.45±0.01 a 0.28±0.01 a 第一季上海青试验,钝化剂C、F、E和B降低了土壤DTPA提取态Pb含量,其中Yonker土壤调理剂(C)处理组降低最多,降幅为5.1%,与CK相比,不存在显著性差异( P > 0.05)。钝化剂E、H、C和F降低了土壤DTPA提取态Cd含量,降幅为8.9%~31.0%。海状元土壤调理剂(E)处理的土壤DTPA提取态Cd含量显著性降低(P<0.05),降幅为31.0%,效果最好。钝化剂H、F和I降低了土壤DTPA提取态Cr含量,其中OSA土壤重金属钝化剂(H)降低最多,降幅为9.4%,与CK相比,不存在显著性差异( P > 0.05)。
第二季夏阳白试验,钝化剂E、C、G和F降低了土壤DTPA提取态Pb含量,其中海状元土壤调理剂(E)降低最多,降幅为10.8%,与CK相比,不存在显著性差异( P > 0.05)。与CK处理相比,钝化剂E、F、I和G处理显著降低了土壤DTPA提取态Cd含量(P<0.05),降幅为19.2%~25.4%。海状元土壤调理剂(E)的土壤DTPA提取态Cd含量降幅最大,达到25.4%,效果最好。钝化剂D、A、E、H和B显著地降低了土壤DTPA提取态Cr含量(P<0.05),分别减少了28.6%、27.1%、23.9%、19.7%和19.7%。
2.4 不同钝化剂对上海青和夏阳白中重金属含量的影响
图3显示,第一季上海青试验,施加不同钝化剂后,上海青中Pb、Cd和Cr的含量均有不同程度降低。钝化剂H、I、A、F、C和D处理显著降低了上海青中Pb含量(P<0.05),降幅为31.7%~41.5%。其中,OSA土壤重金属钝化剂(H)处理的上海青中Pb含量降幅最大,达到41.5%,效果最好。除了钝化剂D,其余钝化剂处理显著降低了上海青中Cd含量(P<0.05),降幅为32.0%~46.0%。其中,同样是OSA土壤重金属钝化剂(H)处理的上海青中Cd含量降幅最大,达到46.0%,效果最好。与CK处理相比,钝化剂F、B、H和A处理组中的上海青中Cr含量存在显著性降低(P<0.05),分别降低了73.2%、69.6%、61.6%和52.7%。
第二季夏阳白试验,施加不同钝化剂后,夏阳白地上部组织中Pb、Cd和Cr的含量均有不同程度降低。与CK处理相比,OSA土壤重金属钝化剂(H)和特贝钙土壤调理剂(A)处理的夏阳白中Pb含量显著性降低(P<0.05),分别降低了53.7%和52.2%。钝化剂C、A、B、I、H、G和F处理显著降低了夏阳白中Cd含量(P<0.05),降幅为20.5%~34.6%。其中,Yonker土壤调理剂(C)处理的夏阳白中Cd含量降幅最大,达到34.6%,效果最好。钝化剂C、F、I、D、E、A和G处理显著降低夏阳白中Cr含量(P<0.05),降幅为43.7%~60.6%。其中,同样是Yonker土壤调理剂(C)处理的夏阳白中Cd含量降幅最大,达到60.6%,效果最好。
对比两季结果表明,第一季中OSA土壤重金属钝化剂(H)对降低上海青中重金属Pb和Cd含量的效果最好。第二季中Yonker土壤调理剂(C)对降低夏阳白中重金属Cd和Cr含量的效果最好。根据国家标准《食品中污染物限量》(B2762-2017),叶菜类蔬菜重金属的限量标准:Pb<0.3 mg·kg−1、Cd<0.2 mg·kg−1、Cr<0.5 mg·kg−1。第一季上海青试验,康源土壤调理剂(D)和空白(CK)处理组中上海青中的重金属Cd含量分别是0.247 mg·kg−1和0.272 mg·kg−1,分别超过国家标准的23.5%和36.0%。OSA土壤重金属钝化剂(H)、石灰粉(I)、特贝钙土壤调理剂(A)和Yonker土壤调理剂(C)处理后,上海青中的Cd含量分别为0.146 mg·kg−1、0.147 mg·kg−1、0.165 mg·kg−1和0.176 mg·kg−1,从超标下降至国家食品污染物限量标准以内。
2.5 相关性分析
将土壤中DTPA提取态Pb、Cd和Cr的含量、上海青和夏阳白中的Pb、Cd和Cr的含量和土壤pH值进行相关性统计分析(表4和表5)。
表 4 上海青中重金属含量和土壤Ph、土壤DTPA提取态含量的相关系数Table 4. Correlation between heavy metal contents in Pakchoi and pH or DTPA-extractable in soil指标 index pH DTPA-Pb DTPA-Cd DTPA-Cr Pb Cd Cr pH 1 DTPA-Pb −0.419* 1 DTPA-Cd −0.750** 0.248 1 DTPA-Cr −0.840** 0.380* 0.271 1 Pb −0.243 0.524** 0.252 0.316 1 Cd −0.578** 0.325 0.676** 0.203 −0.120 1 Cr −0.501** 0.178 0.461* 0.602** −0.034 0.207 1 注:* 表示显著相关(P<0.05);** 表示极显著相关(P<0.01);Pb、Cd和Cr为上海青中的含量。
Note:* indicates significant correlation(P<0.05), ** indicates a significant correlation(P<0.01); Pb, Cd and Cr are the contents of Pakchoi表 5 夏阳白中重金属含量和土壤Ph、土壤DTPA提取态含量的相关系数Table 5. Correlation between heavy metal contents in Chinese cabbages and pH or DTPA-extractable in soil指标 index pH DTPA-Pb DTPA-Cd DTPA-Cr Pb Cd Cr PH 1 DTPA-Pb −0.447* 1 DTPA-Cd −0.684** 0.279 1 DTPA-Cr −0.738** 0.220 0.357 1 Pb −0.330 0.419* 0.154 0.394* Cd −0.410* 0.315 0.511** 0.351 0.251 1 Cr −0.605** 0.138 0.453* 0.748** 0.035 0.254 1 注:* 表示显著相关(P<0.05);** 表示极显著相关(P<0.01);Pb、Cd和Cr为夏阳白地上部中的含量。
Note:* indicates significant correlation(P<0.05), ** indicates a significant correlation(P<0.01); Pb Cd and Cr are the contents of Chinese cabbage结果表明,第一季上海青试验,土壤中DTPA提取态Cd和Cr的含量、上海青中的Cd和Cr的含量与土壤pH呈极显著性负相关(P<0.01)。土壤中DTPA提取态Pb的含量与土壤pH呈显著性负相关(P<0.05)。土壤pH与土壤中DTPA提取态Pb、Cd和Cr的含量的相关系数分别是−0.419、−0.750 和−0.840。土壤pH与上海青中的Pb、Cd和Cr的含量的相关系数分别是−0.243、−0.578 和−0.501。
第二季夏阳白试验,土壤中DTPA提取态Cd和Cr的含量、夏阳白中的Cd和Cr的含量与土壤pH呈极显著性负相关(P<0.01)。土壤中DTPA提取态Pb的含量与土壤pH呈显著性负相关(P<0.05)。土壤pH与土壤中DTPA提取态Pb、Cd和Cr的含量的相关系数分别是−0.447、−0.684 和−0.738。土壤pH与夏阳白中的Pb、Cd和Cr的含量的相关系数分别是−0.330、−0.410 和−0.605。说明了土壤pH升高首先会引起土壤中DTPA提取态Pb、Cd和Cr的含量降低,从而抑制上海青和夏阳白对Pb、Cd和Cr的吸收和转运。
上海青中Pb含量与DTPA提取态Pb含量的相关系数是0.524,上海青中Cd含量与DTPA提取态Cd含量的相关系数是0.676,上海青中Cr含量与DTPA提取态Cr含量的相关系数是0.602,分别各自呈极显著正相关(P<0.01)。同上海青一样,夏阳白中Pb、Cd和Cr含量与土壤中DTPA提取态Pb、Cd和Cr含量分别各自呈极显著正相关(P<0.01)。
3. 讨论
化学钝化修复技术由于其钝化成本低、效率高、种类丰富,具有良好的前景。化学钝化剂种类繁多,前人对单一成分的钝化剂的研究较多,而对于复合型钝化剂的研究比较空缺,所以本研究将市面上常见的8种复合钝化剂进行对比试验,筛选出适合福建省酸性重金属污染土壤的钝化剂。
研究发现,特贝钙土壤调理剂(A)、OSA土壤重金属钝化剂(H)对上海青和夏阳白增产效果显著,可能是由于它们中含有丰富有机质以及钙、镁、磷等必需营养元素能促进蔬菜生长,这一研究结果与前人一致[16]。同时,pH的升高,负电荷对重金属离子的吸附,降低了其有效性,从而降低了重金属毒害作用,对产量有一定的促进作用[17]。施用OSA土壤重金属钝化剂(H)、Yonker土壤调理剂(C)和石灰(I)显著提高土壤pH,这是因为它们的主要成分是氧化钙和氧化镁,水解释放氢氧化物离子而增加土壤pH值,与以往研究结果相一致[18,19]。同时,对比两季,钝化剂对土壤pH的影响随时间的延长而减弱,可能是因为土壤的缓冲作用和降雨、灌溉条件下,钝化剂中碱性基团向下迁移,淋出根层[20]。
两季试验表明,海状元土壤调理剂(E)、OSA土壤重金属钝化剂(H)和Yonker土壤调理剂(C)对土壤中DTPA提取态Pb、Cd和Cr的含量降低效果比较突出,强于石灰(I)处理。这可能是由于它们是氧化钙、氧化镁和大量的有机质组成,一方面,它们通过提高土壤pH值,使土壤颗粒表面负电荷增加,促使土壤中Pb、Cd和Cr元素形成氢氧化物或碳酸盐结合态盐类沉淀[21],另一方面,有机质有丰富的活性功能基团,是效的络合剂,通过形成不溶性金属-有机复合物、降低土壤中重金属的水溶态及可交换态组分[22,23]。
比较前后两季的土壤DTPA提取态Pb、Cd和Cr的含量,结果表明,钝化剂对DTPA提取态含量的影响依次是Cd>Cr>Pb。同一钝化剂对不同重金属有效性的降低效果存在差异且第一季效果强于第二季与之前研究结果一致[24]。同时,相关性系数表明,上海青一样和夏阳白中Pb、Cd和Cr含量与土壤中DTPA提取态Pb、Cd和Cr含量分别各自呈极显著正相关(P<0.01)。因此,通过降低土壤中有效态Pb、Cd和Cr含量,减少土壤中的重金属向上转运,降低上海青和夏阳白中的重金属的含量,这与陈丹艳等[25]的研究结果一致。根据国家标准《食品中污染物限量》(B2762-2017),叶菜类蔬菜重金属的限量标准,钝化剂OSA土壤重金属钝化剂(H)、石灰粉(I)、特贝钙土壤调理剂(A)和Yonker土壤调理剂(C)将上海青中的Cd含量从超标降低至国家食品污染物限量标准内。
4. 结论
OSA土壤重金属钝化剂(H)处理上海青的产量最高,较对照增产84.2%。特贝钙土壤调理剂(A)对夏阳白的产量最高,较对照增产65.4%,效果都好于石灰(I)处理。
第一季中,Yonker土壤调理剂(C)和OSA土壤重金属钝化剂(H)显著提高土壤的pH值,第二季中OSA土壤重金属钝化剂(H)处理的土壤pH值最大,它们的效果都优于石灰(I)处理。
钝化剂对土壤中DTPA提取态Cd和Cr的含量降低比较明显。其中,海状元土壤调理剂(E)、OSA土壤重金属钝化剂(H)和Yonker土壤调理剂(C)对土壤中DTPA提取态Pb、Cd和Cr的含量降低效果比较突出,强于石灰(I)处理。
在两季试验中,土壤中DTPA提取态Pb、Cd和Cr的含量、上海青和夏阳白中的Cd和Cr的含量与土壤pH值呈极显著性负相关(P<0.01)。上海青和夏阳白中Pb、Cd和Cr含量与土壤中DTPA提取态Pb、Cd和Cr含量分别各自呈极显著正相关(P<0.01)。
OSA土壤重金属钝化剂(H)对降低上海青和夏阳白中Pb含量效果最好。OSA土壤重金属钝化剂(H)和Yonker土壤调理剂(C)对降低上海青和夏阳白中Cd含量效果最好。万亩田有机肥(F)和Yonker土壤调理剂(C)对降低上海青和夏阳白中Cr含量效果最好。其中,OSA土壤重金属钝化剂(H)、石灰粉(I)、特贝钙土壤调理剂(A)和Yonker土壤调理剂(C),将上海青中的Cd含量从超标降低至国家标准《食品中污染物限量》(B2762-2017)安全标准以内。其余所有处理组中的上海青和夏阳白中Pb和Cr均符合国家食品污染物限量标准。
综合考虑,OSA土壤重金属钝化剂(H)和Yonker土壤调理剂(C)对酸性土壤Pb、Cd和Cr复合污染钝化修复效果最佳。研究结果对福建省农用地土壤的安全利用具有重要的借鉴意义。
-
表 1 批内和批间重复试验结果(n=5)
Table 1 Intra-and inter-batch reproducibility test results on DAS-ELISA
样品 批内重复试验 批间重复试验 平均数 方差 变异系数
/%平均数 方差 变异系数
/%1 1.050 0.021 2.003 0.778 0.023 2.998 2 0.655 0.020 3.128 0.897 0.036 4.056 3 0.774 0.031 4.007 0.920 0.033 3.588 4 0.589 0.018 3.122 0.691 0.020 2.975 5 1.255 0.058 4.589 1.320 0.049 3.745 -
[1] MARTELLⅡ P, LAVAZZA A, NIGRELLI A D, et al. Epidemic of diarrhea caused by porcine epidemic diarrhea virus in Italy[J]. Vet Rec, 2008, 162:307-310. DOI: 10.1136/vr.162.10.307
[2] LUO Y, ZHANG J, DENG X, et al. Complete genome sequence of a highly prevalent isolate of porcine epidemic diarrhea virus in South China[J]. J Virol, 2012, 86(17):9551. DOI: 10.1128/JVI.01455-12
[3] VLASOVA A N, MARTHALER D, WANG Q, et al. Distinct characteristics and complex evolution of PEDV strains, North America, May 2013 February 2014[J]. Emerg Infect, 2014, 20(10):1620-1628. http://pubmedcentralcanada.ca/pmcc/articles/PMC4193278/
[4] 王隆柏, 林裕胜, 车勇良, 等.猪流行性腹泻病毒S、N和ORF3基因的遗传变异分析[J].畜牧兽医学报, 2014, 45(11):1830-1836. http://kns.cnki.net/KCMS/detail/detail.aspx?filename=xmsy201411013&dbname=CJFD&dbcode=CJFQ [5] 王隆柏, 王晨燕, 林裕胜, 等.猪流行性腹泻病毒E和M基因的克隆及变异分析[J].福建农业学报, 2015, 30(6):533-538. http://www.fjnyxb.cn/CN/abstract/abstract2697.shtml [6] 毛雅元, 张桂红, 葛俊伟, 等.猪流行性腹泻病毒地方株LJB/03分离及培养特性[J].病毒学报, 2010, 26(6):483-489. http://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-BDXB201006010.htm [7] 孙秀萍, 宋晗星, 苏高莉, 等.水泡性口炎病毒双抗体夹心ELISA检测方法的建立[J].中国预防兽医学报, 2012, 34(8):637-641. http://cdmd.cnki.com.cn/Article/CDMD-10183-1017156743.htm [8] CHANG S H, BAE J L, KANG T J, et al. Identification of the epitope region capable of inducing neutralizing antibodies against the porcine epidemic diarrhea virus[J]. Cells, 2002, 14:295-299. http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/12442904
[9] 吴玉璐, 朱建平, 杨莘, 等.猪流行性腹泻病毒N基因的表达及抗原性分析[J].动物预防学报, 2013, 35(4):299-303. http://kns.cnki.net/KCMS/detail/detail.aspx?filename=zgxq201304013&dbname=CJFD&dbcode=CJFQ [10] HUTCHINGS G H, FERRIS N P. Indirect sandwich ELISA for antigen detection of African swine fever virus:comparison of polyclonal and monoclonal antibodies[J]. J Virol Methods, 2006, 131(2):213-217. DOI: 10.1016/j.jviromet.2005.08.009
[11] PANADERO R, VAZQUEZ L, COLWELL D D, et al. Evaluation of an antigen capture ELISA for the early diagnosis of Hypoderma lineatum in cattle under field conditions[J]. Vet Parasitol, 2007, 147(3-4):297-302. DOI: 10.1016/j.vetpar.2007.04.004
[12] 张小兵, 邸祿芹, 吴萌, 等.单克隆抗体与多克隆抗体配对ELISA方法比较[J].生物技术通报, 2009, (11):125-129. http://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-SWJT200911031.htm [13] 李一经, 刘博, 姜艳平, 等.双抗体夹心ELISA检测排泄物PEDV[J].东北农业大学学报, 2015, 46(2):1-10. http://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-DBDN201502001.htm [14] 张清真, 陶洁, 殷秀辰, 等.猪流行性腹泻病毒双抗体夹心ELISA方法的建立[J].上海农业学报, 2017, 33(1):134-137. http://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-SHLB201701024.htm -
期刊类型引用(4)
1. 杜彩艳,孙秀梅,鲁海燕,毛妍婷,孙曦,马桂梅,普继雄,熊艳竹. 不同钝化剂对大白菜产量和吸收Cu、As、Cd、Pb的影响. 西南农业学报. 2023(02): 257-263 .  百度学术
百度学术
2. 黄淼杰,赵首萍,张棋,肖文丹,陈德,黄晓磊,叶雪珠. 常用钝化剂对叶菜类蔬菜重金属镉、汞、铅和铬积累的影响研究. 农产品质量与安全. 2022(02): 56-61 .  百度学术
百度学术
3. 刘静,秦樊鑫,罗谦,呼艳姣. 钝化剂对污染土壤汞钝化效果及辣椒吸收汞的影响. 土壤通报. 2022(06): 1461-1470 .  百度学术
百度学术
4. 聂娟娟,陶荣浩,王宗亚,丁文清,胡兆云,李丁,马友华. 调理剂对镉轻度污染农田蔬菜安全利用效果研究. 安徽科技学院学报. 2022(06): 33-40 .  百度学术
百度学术
其他类型引用(2)




 下载:
下载: